Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances and Health Outcomes in Children: A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Neurodevelopment and Attention
3.2. Cardiometabolic
3.3. Immunity, Allergic Response, Infection, and Asthma
3.4. Pubertal Onset Indicators
3.5. Thyroid Function
3.6. Renal Function
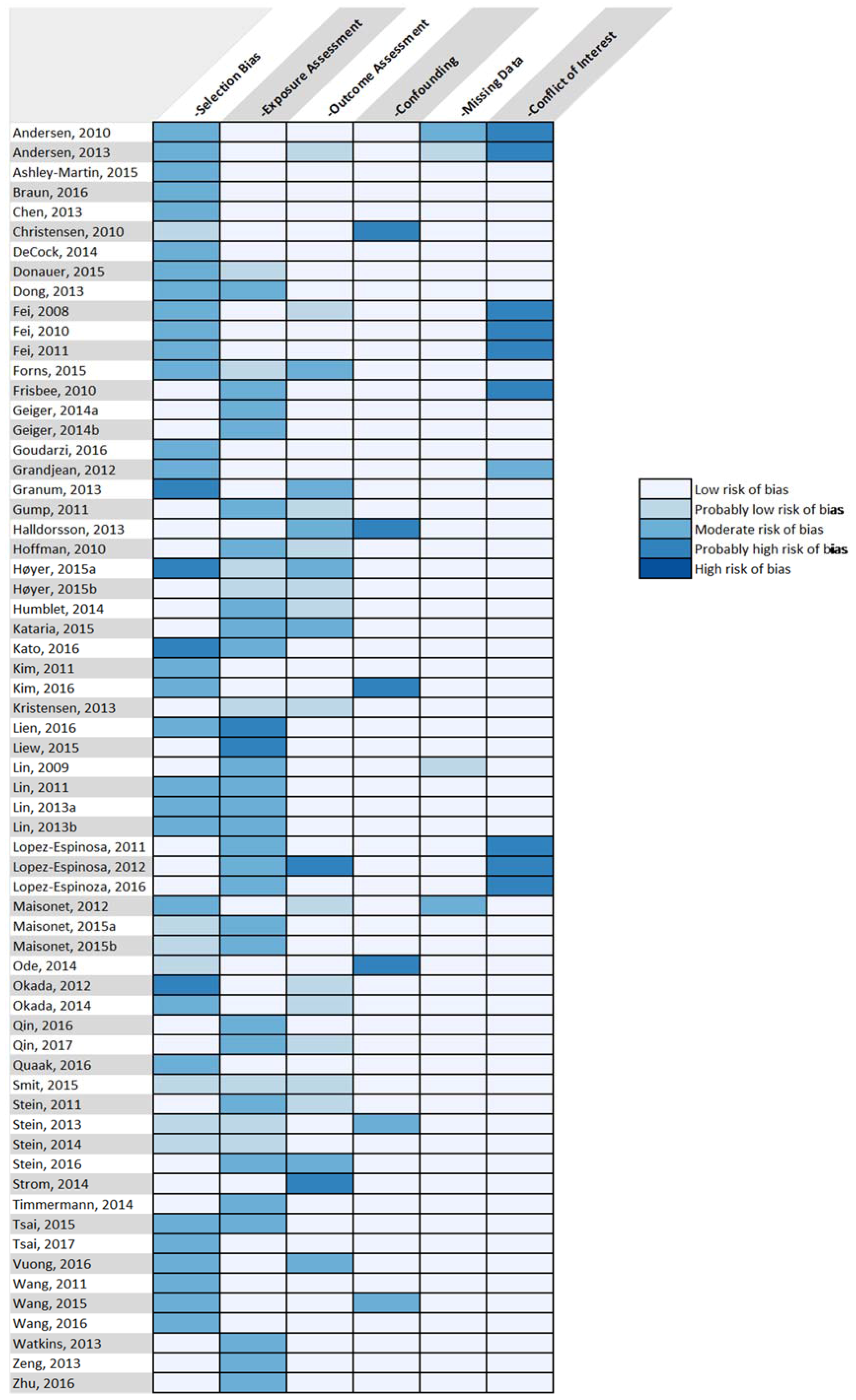
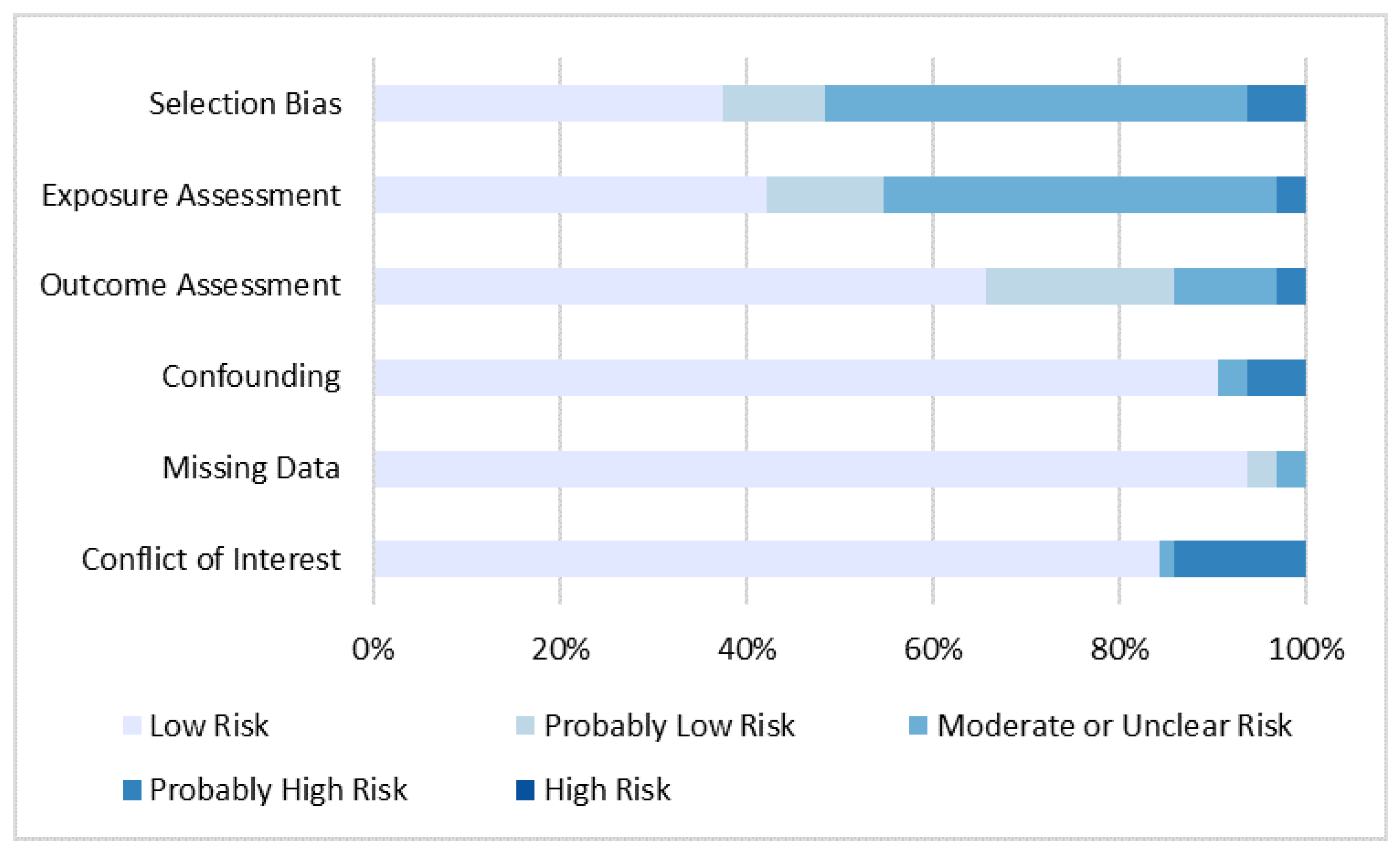
3.7. Risk of Bias Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Kato, K.; Wong, L.Y.; Jia, L.T.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Calafat, A.M. Trends in exposure to polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the U.S. Population: 1999–2008. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8037–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, L.S.; Huber, S.; Becher, G.; Thomsen, C. Characterisation of human exposure pathways to perfluorinated compounds—Comparing exposure estimates with biomarkers of exposure. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, D.; Lopez-Espinosa, M.J.; Armstrong, B.; Stein, C.R.; Fletcher, T. Relationships of Perfluorooctanoate and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Serum Concentrations between Mother-Child Pairs in a Population with Perfluorooctanoate Exposure from Drinking Water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.M.; Bennett, D.H.; Calafat, A.M.; Kato, K.; Strynar, M.; Andersen, E.; Moran, R.E.; Tancredi, D.J.; Tulve, N.S.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Serum concentrations of perfluorinated compounds (PFC) among selected populations of children and adults in California. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M. Early-life exposure to EDCs: Role in childhood obesity and neurodevelopment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calkins, K.; Devaskar, S.U. Fetal origins of adult disease. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2011, 41, 158–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corkins, M.R.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Golden, N.H.; Kim, J.H.; Magge, S.N.; Schwarzenberg, S.J. Nutrition in Children and Adolescents. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 100, 1217–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascon, M.; Vrijheid, M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. The Built Environment and Child Health: An Overview of Current Evidence. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.D.C.; Quackenboss, J.J.; Tulve, N.S. Contributions of a child’s built, natural, and social environments to their general cognitive ability: A systematic scoping review. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.N.; Hsu, M.H.; Griffin, K.J.; Raucy, J.L.; Johnson, E.F. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-alpha expression in human liver. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Xie, X.; Xie, Y.; Luo, D.; Zhang, D.; Yu, X.; et al. Maternal exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid inhibits luteal function via oxidative stress and apoptosis in pregnant mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 69, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashayekhi, V.; Tehrani, K.H.M.E.; Hashemzaei, M.; Tabrizian, K.; Shahraki, J.; Hosseini, M. Mechanistic approach for the toxic effects of perfluorooctanoic acid on isolated rat liver and brain mitochondria. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, S.; Araki, A.; Mitsui, T.; Miyashita, C.; Goudarzi, H.; Sasaki, S.; Cho, K.; Nakazawa, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Shinohara, N.; et al. Association of perfluoroalkyl substances exposure in utero with reproductive hormone levels in cord blood in the Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Tan, Y.S.; Strynar, M.J.; Perez, G.; Haslam, S.Z.; Yang, C. Perfluorooctanoic acid effects on ovaries mediate its inhibition of peripubertal mammary gland development in Balb/c and C57Bl/6 mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, L.W.; Qian, Z.M.; Chang, J.J.; King, C.; Paul, G.; Lin, S.; Chen, P.C.; Lee, Y.L.; Dong, G.H. Association of perfluoroalkyl substances exposure with reproductive hormone levels in adolescents: By sex status. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upham, B.L.; Park, J.S.; Babica, P.; Sovadinova, I.; Rummel, A.M.; Trosko, J.E.; Hirose, A.; Hasegawa, R.; Kanno, J.; Sai, K. Structure-activity-dependent regulation of cell communication by perfluorinated fatty acids using in vivo and in vitro model systems. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Espinosa, M.J.; Mondal, D.; Armstrong, B.; Bloom, M.S.; Fletcher, T. Thyroid function and perfluoroalkyl acids in children living near a chemical plant. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, C.C.; Bech, B.H.; Brix, N.; Nohr, E.A.; Bonde, J.P.E.; Henriksen, T.B. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and human fetal growth: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2015, 45, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.I.; Sutton, P.; Atchley, D.S.; Koustas, E.; Lam, J.; Sen, S.; Robinson, K.A.; Axelrad, D.A.; Woodruff, T.J. The Navigation Guide-Evidence-Based Medicine Meets Environmental Health: Systematic Review of Human Evidence for PFOA Effects on Fetal Growth. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Perfluoroalkyl chemicals and human fetal development: An epidemiologic review with clinical and toxicological perspectives. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 27, 212–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.I.; Sutton, P.; Atchley, D.; Koustas, E.; Lam, J.; Sen, S.; Robinson, K.; Axelrad, D.; Woodruff, T.J. The Navigation Guide Systematic Review Methodology Proof of Concept: PFOA and Fetal Growth. Birth Defects Res. A 2014, 100, 395. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Version 5.1.0; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, M.; Ansari, M.T.; Berkman, N.D.; Chang, S.; Hartling, L.; McPheeters, M.; Santaguida, P.L.; Shamliyan, T.; Singh, K.; Tsertsvadze, A. Assessing the risk of bias of individual studies in systematic reviews of health care interventions. In Methods Guide for Effectiveness and Comparative Effectiveness Reviews; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, J.; Melbye, M.; Olsen, S.F.; Sorensen, T.I.; Aaby, P.; Andersen, A.M.; Taxbol, D.; Hansen, K.D.; Juhl, M.; Schow, T.B.; et al. The Danish National Birth Cohort—Its background, structure and aim. Scand. J. Public Health 2001, 29, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisbee, S.J.; Brooks, A.P., Jr.; Maher, A.; Flensborg, P.; Arnold, S.; Fletcher, T.; Steenland, K.; Shankar, A.; Knox, S.S.; Pollard, C.; et al. The C8 health project: Design, methods, and participants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, J.Y.; Smith, S.J. Neural activity and the dynamics of central nervous system development. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiles, J.; Jernigan, T.L. The basics of brain development. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2010, 20, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, C.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Lipworth, L.; Olsen, J. Prenatal exposure to perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and maternally reported developmental milestones in infancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, C.; Olsen, J. Prenatal exposure to perfluorinated chemicals and behavioral or coordination problems at age 7 years. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donauer, S.; Chen, A.; Xu, Y.; Calafat, A.M.; Sjodin, A.; Yolton, K. Prenatal exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polyfluoroalkyl chemicals and infant neurobehavior. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.H.; Ha, E.H.; Liao, H.F.; Jeng, S.F.; Su, Y.N.; Wen, T.W.; Lien, G.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsieh, W.S.; Chen, P.C. Perfluorinated compound levels in cord blood and neurodevelopment at 2 years of age. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forns, J.; Iszatt, N.; White, R.A.; Mandal, S.; Sabaredzovic, A.; Lamoree, M.; Thomsen, C.; Haug, L.S.; Stigum, H.; Eggesbo, M. Perfluoroalkyl substances measured in breast milk and child neuropsychological development in a Norwegian birth cohort study. Environ. Int. 2015, 83, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, H.; Nakajima, S.; Ikeno, T.; Sasaki, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Miyashita, C.; Ito, S.; Araki, A.; Nakazawa, H.; Kishi, R. Prenatal exposure to perfluorinated chemicals and neurodevelopment in early infancy: The Hokkaido Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.R.; Savitz, D.A.; Bellinger, D.C. Perfluorooctanoate and neuropsychological outcomes in children. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Rogan, W.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Su, P.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, S.L. Prenatal exposure to perfluroalkyl substances and children’s IQ: The Taiwan maternal and infant cohort study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2015, 218, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.R.; Savitz, D.A. Serum perfluorinated compound concentration and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children 5–18 years of age. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, A.M.; Yolton, K.; Webster, G.M.; Sjodin, A.; Calafat, A.M.; Braun, J.M.; Dietrich, K.N.; Lanphear, B.P.; Chen, A. Prenatal polybrominated diphenyl ether and perfluoroalkyl substance exposures and executive function in school-age children. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strom, M.; Hansen, S.; Olsen, S.F.; Haug, L.S.; Rantakokko, P.; Kiviranta, H.; Halldorsson, T.I. Persistent organic pollutants measured in maternal serum and offspring neurodevelopmental outcomes—A prospective study with long-term follow-up. Environ. Int. 2014, 68, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gump, B.B.; Wu, Q.; Dumas, A.K.; Kannan, K. Perfluorochemical (PFC) exposure in children: Associations with impaired response inhibition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8151–8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, K.; Webster, T.F.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Weinberg, J.; Vieira, V.M. Exposure to polyfluoroalkyl chemicals and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in U.S. children 12–15 years of age. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyer, B.B.; Ramlau-Hansen, C.H.; Obel, C.; Pedersen, H.S.; Hernik, A.; Ogniev, V.; Jonsson, B.A.; Lindh, C.H.; Rylander, L.; Rignell-Hydbom, A.; et al. Pregnancy serum concentrations of perfluorinated alkyl substances and offspring behaviour and motor development at age 5–9 years—A prospective study. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, Z.; Ritz, B.; von Ehrenstein, O.S.; Bech, B.H.; Nohr, E.A.; Fei, C.; Bossi, R.; Henriksen, T.B.; Bonefeld-Jorgensen, E.C.; Olsen, J. Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and childhood autism in association with prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances: A nested case-control study in the Danish National Birth Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, G.W.; Huang, C.C.; Shiu, J.S.; Chen, M.H.; Hsieh, W.S.; Guo, Y.L.; Chen, P.C. Perfluoroalkyl substances in cord blood and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in seven-year-old children. Chemosphere 2016, 156, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaak, I.; de Cock, M.; de Boer, M.; Lamoree, M.; Leonards, P.; van de Bor, M. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Behavioral Development in Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ode, A.; Kallen, K.; Gustafsson, P.; Rylander, L.; Jonsson, B.A.; Olofsson, P.; Ivarsson, S.A.; Lindh, C.H.; Rignell-Hydbom, A. Fetal exposure to perfluorinated compounds and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in childhood. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.R.; Savitz, D.A.; Bellinger, D.C. Perfluorooctanoate exposure in a highly exposed community and parent and teacher reports of behaviour in 6–12-year-old children. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2014, 28, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellinger, D.C. Prenatal Exposures to Environmental Chemicals and Children’s Neurodevelopment: An Update. Saf. Health Work 2013, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, N.; Wilks, M.F. Neurodevelopmental and neurobehavioural effects of polybrominated and perfluorinated chemicals: A systematic review of the epidemiological literature using a quality assessment scheme. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 230, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, N.; Fredriksson, A.; Eriksson, P. Neonatal exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) causes neurobehavioural defects in adult mice. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spulber, S.; Kilian, P.; Wan Ibrahim, W.N.; Onishchenko, N.; Ulhaq, M.; Norrgren, L.; Negri, S.; Di Tuccio, M.; Ceccatelli, S. PFOS induces behavioral alterations, including spontaneous hyperactivity that is corrected by dexamfetamine in zebrafish larvae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Das, S.R.; La Du, J.; Corvi, M.M.; Bai, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, G.; Tanguay, R.L.; Dong, Q.; et al. Chronic PFOS exposures induce life stage-specific behavioral deficits in adult zebrafish and produce malformation and behavioral deficits in F1 offspring. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2013, 32, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, S.D.; Xiao, J.; Shankar, A. No association between perfluoroalkyl chemicals and hypertension in children. Integr. Blood Press. Control 2014, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.S.; Fei, C.; Gamborg, M.; Nohr, E.A.; Sorensen, T.I.; Olsen, J. Prenatal exposures to perfluorinated chemicals and anthropometric measures in infancy. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 172, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.S.; Fei, C.; Gamborg, M.; Nohr, E.A.; Sorensen, T.I.; Olsen, J. Prenatal exposures to perfluorinated chemicals and anthropometry at 7 years of age. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M.; Chen, A.; Romano, M.E.; Calafat, A.M.; Webster, G.M.; Yolton, K.; Lanphear, B.P. Prenatal perfluoroalkyl substance exposure and child adiposity at 8 years of age: The HOME study. Obesity 2016, 24, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonet, M.; Terrell, M.L.; McGeehin, M.A.; Christensen, K.Y.; Holmes, A.; Calafat, A.M.; Marcus, M. Maternal concentrations of polyfluoroalkyl compounds during pregnancy and fetal and postnatal growth in British girls. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halldorsson, T.I.; Rytter, D.; Haug, L.S.; Bech, B.H.; Danielsen, I.; Becher, G.; Henriksen, T.B.; Olsen, S.F. Prenatal exposure to perfluorooctanoate and risk of overweight at 20 years of age: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyer, B.B.; Ramlau-Hansen, C.H.; Vrijheid, M.; Valvi, D.; Pedersen, H.S.; Zviezdai, V.; Jonsson, B.A.; Lindh, C.H.; Bonde, J.P.; Toft, G. Anthropometry in 5- to 9-Year-Old Greenlandic and Ukrainian Children in Relation to Prenatal Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Adgent, M.; Su, P.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Hsiung, C.A.; Wang, S.L. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluorocarboxylic Acids (PFCAs) and Fetal and Postnatal Growth in the Taiwan Maternal and Infant Cohort Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1794–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermann, C.A.; Rossing, L.I.; Grontved, A.; Ried-Larsen, M.; Dalgard, C.; Andersen, L.B.; Grandjean, P.; Nielsen, F.; Svendsen, K.D.; Scheike, T.; et al. Adiposity and glycemic control in children exposed to perfluorinated compounds. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E608–E614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Ramlau-Hansen, C.H.; Ernst, E.; Olsen, S.F.; Bonde, J.P.; Vested, A.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Becher, G.; Haug, L.S.; Toft, G. Long-term effects of prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances on female reproduction. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, S.D.; Xiao, J.; Ducatman, A.; Frisbee, S.; Innes, K.; Shankar, A. The association between PFOA, PFOS and serum lipid levels in adolescents. Chemosphere 2014, 98, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, L.Y. Association among serum perfluoroalkyl chemicals, glucose homeostasis, and metabolic syndrome in adolescents and adults. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisbee, S.J.; Shankar, A.; Knox, S.S.; Steenland, K.; Savitz, D.A.; Fletcher, T.; Ducatman, A.M. Perfluorooctanoic acid, perfluorooctanesulfonate, and serum lipids in children and adolescents: Results from the C8 Health Project. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2010, 164, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.W.; Qian, Z.; Emo, B.; Vaughn, M.; Bao, J.; Qin, X.D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Lee, Y.L.; Dong, G.H. Association of polyfluoroalkyl chemical exposure with serum lipids in children. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonet, M.; Nayha, S.; Lawlor, D.A.; Marcus, M. Prenatal exposures to perfluoroalkyl acids and serum lipids at ages 7 and 15 in females. Environ. Int. 2015, 82, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wen, L.L.; Lin, L.Y.; Wen, T.W.; Lien, G.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, S.H.; Chien, K.L.; Sung, F.C.; Chen, P.C.; et al. Associations between levels of serum perfluorinated chemicals and adiponectin in a young hypertension cohort in Taiwan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10691–10698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Lin, L.Y.; Wen, T.W.; Lien, G.W.; Chien, K.L.; Hsu, S.H.; Liao, C.C.; Sung, F.C.; Chen, P.C.; Su, T.C. Association between levels of serum perfluorooctane sulfate and carotid artery intima-media thickness in adolescents and young adults. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3309–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, T.; Galloway, T.S.; Melzer, D.; Holcroft, P.; Cipelli, R.; Pilling, L.C.; Mondal, D.; Luster, M.; Harries, L.W. Associations between PFOA, PFOS and changes in the expression of genes involved in cholesterol metabolism in humans. Environ. Int. 2013, 57–58, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.T.; Zhao, Y.G.; Leung, P.Y.; Wong, C.K.C. Perinatal Exposure to Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Affects Glucose Metabolism in Adult Offspring. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, E.P.; White, S.S.; Stanko, J.P.; Gibbs-Flournoy, E.A.; Lau, C.; Fenton, S.E. Phenotypic dichotomy following developmental exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in female CD-1 mice: Low doses induce elevated serum leptin and insulin, and overweight in mid-life. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tittlemier, S.A.; Pepper, K.; Seymour, C.; Moisey, J.; Bronson, R.; Cao, X.-L.; Dabeka, R.W. Dietary exposure of Canadians to perfluorinated carboxylates and perfluorooctane sulfonate via consumption of meat, fish, fast foods, and food items prepared in their packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3203–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, S.L.; Plotkin, S.A.; Plotkin, S.A.; Orenstein, W. A short history of vaccination. Vaccines 2004, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mina, M.J.; Metcalf, C.J.; de Swart, R.L.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Grenfell, B.T. Long-term measles-induced immunomodulation increases overall childhood infectious disease mortality. Science 2015, 348, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, P.; Andersen, E.W.; Budtz-Jorgensen, E.; Nielsen, F.; Molbak, K.; Weihe, P.; Heilmann, C. Serum vaccine antibody concentrations in children exposed to perfluorinated compounds. JAMA 2012, 307, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangstrom, B.; Hovander, L.; Bignert, A.; Athanassiadis, I.; Linderholm, L.; Grandjean, P.; Weihe, P.; Bergman, A. Concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, polychlonnated biphenyls, and polychlorobiphenylols in serum from pregnant Faroese women and their children 7 years later. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9457–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granum, B.; Haug, L.S.; Namork, E.; Stolevik, S.B.; Thomsen, C.; Aaberge, I.S.; van Loveren, H.; Lovik, M.; Nygaard, U.C. Pre-natal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances may be associated with altered vaccine antibody levels and immune-related health outcomes in early childhood. J. Immunotoxicol. 2013, 10, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.R.; McGovern, K.J.; Pajak, A.M.; Maglione, P.J.; Wolff, M.S. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and indicators of immune function in children aged 12–19 years: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.H.; Tung, K.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Liu, M.M.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.; Jin, Y.H.; Hsieh, W.S.; Lee, Y.L.; Chen, P.C. Serum polyfluoroalkyl concentrations, asthma outcomes, and immunological markers in a case-control study of Taiwanese children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.D.; Qian, Z.M.; Dharmage, S.C.; Perret, J.; Geiger, S.D.; Rigdon, S.E.; Howard, S.; Zeng, X.W.; Hu, L.W.; Yang, B.Y.; et al. Association of perfluoroalkyl substances exposure with impaired lung function in children. Environ. Res. 2017, 155, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humblet, O.; Diaz-Ramirez, L.G.; Balmes, J.R.; Pinney, S.M.; Hiatt, R.A. Perfluoroalkyl chemicals and asthma among children 12–19 years of age: NHANES (1999–2008). Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Qin, X.D.; Zeng, X.W.; Paul, G.; Morawska, L.; Su, M.W.; Tsai, C.H.; Wang, S.Q.; Lee, Y.L.; Dong, G.H. Associations of serum perfluoroalkyl acid levels with T-helper cell-specific cytokines in children: By gender and asthma status. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, L.A.; Lenters, V.; Høyer, B.B.; Lindh, C.H.; Pedersen, H.S.; Liermontova, I.; Jönsson, B.A.; Piersma, A.H.; Bonde, J.P.; Toft, G. Prenatal exposure to environmental chemical contaminants and asthma and eczema in school-age children. Allergy 2015, 70, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, E.; Sasaki, S.; Kashino, I.; Matsuura, H.; Miyashita, C.; Kobayashi, S.; Itoh, K.; Ikeno, T.; Tamakoshi, A.; Kishi, R. Prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl acids and allergic diseases in early childhood. Environ. Int. 2014, 65, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, E.; Sasaki, S.; Saijo, Y.; Washino, N.; Miyashita, C.; Kobayashi, S.; Konishi, K.; Ito, Y.M.; Ito, R.; Nakata, A.; et al. Prenatal exposure to perfluorinated chemicals and relationship with allergies and infectious diseases in infants. Environ. Res. 2012, 112, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, I.-J.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Chen, C.-Y.; Fletcher, T.; Lien, G.-W.; Chiang, H.-L.; Chiang, C.-F.; Wu, T.-N.; Chen, P.-C. The effect of prenatal perfluorinated chemicals exposures on pediatric atopy. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley-Martin, J.; Dodds, L.; Levy, A.R.; Platt, R.W.; Marshall, J.S.; Arbuckle, T.E. Prenatal exposure to phthalates, bisphenol A and perfluoroalkyl substances and cord blood levels of IgE, TSLP and IL-33. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, C.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Lipworth, L.; Olsen, J. Prenatal exposure to PFOA and PFOS and risk of hospitalization for infectious diseases in early childhood. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWitt, J.C.; Peden-Adams, M.M.; Keller, J.M.; Germolec, D.R. Immunotoxicity of perfluorinated compounds: Recent developments. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos-Ryan, N.; Parent, S.; Vitaro, F.; Tremblay, R.E.; Seguin, J.R. Pubertal development, personality, and substance use: A 10-year longitudinal study from childhood to adolescence. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2013, 122, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, F.R.; Elks, C.E.; Murray, A.; Ong, K.K.; Perry, J.R. Puberty timing associated with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and also diverse health outcomes in men and women: The UK Biobank study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapanou, O.; Papadimitriou, A. Determinants of menarche. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2010, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, T.A.; Kalkwarf, H.J.; Zemel, B.S.; Lappe, J.M.; Oberfield, S.; Shepherd, J.A.; Winer, K.K.; Gilsanz, V. Bone Mineral Density in Childhood Study, G. Longitudinal tracking of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry bone measures over 6 years in children and adolescents: Persistence of low bone mass to maturity. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, K.Y.; Maisonet, M.; Rubin, C.; Holmes, A.; Calafat, A.M.; Kato, K.; Flanders, W.D.; Heron, J.; McGeehin, M.A.; Marcus, M. Exposure to polyfluoroalkyl chemicals during pregnancy is not associated with offspring age at menarche in a contemporary British cohort. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Espinosa, M.J.; Fletcher, T.; Armstrong, B.; Genser, B.; Dhatariya, K.; Mondal, D.; Ducatman, A.; Leonardi, G. Association of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) with age of puberty among children living near a chemical plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8160–8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonet, M.; Calafat, A.M.; Marcus, M.; Jaakkola, J.J.; Lashen, H. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Acids and Serum Testosterone Concentrations at 15 Years of Age in Female ALSPAC Study Participants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Espinosa, M.J.; Mondal, D.; Armstrong, B.G.; Eskenazi, B.; Fletcher, T. Perfluoroalkyl Substances, Sex Hormones, and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 at 6–9 Years of Age: A Cross-Sectional Analysis within the C8 Health Project. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.S.; Lin, C.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, M.H.; Hsu, S.H.; Chien, K.L.; Sung, F.C.; Chen, P.C.; Su, T.C. Association between perfluoroalkyl substances and reproductive hormones in adolescents and young adults. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2015, 218, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.S.; Stanko, J.P.; Kato, K.; Calafat, A.M.; Hines, E.P.; Fenton, S.E. Gestational and chronic low-dose PFOA exposures and mammary gland growth and differentiation in three generations of CD-1 mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Tan, Y.S.; Harkema, J.R.; Haslam, S.Z. Differential effects of peripubertal exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid on mammary gland development in C57Bl/6 and Balb/c mouse strains. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 27, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wen, L.L.; Lin, L.Y.; Wen, T.W.; Lien, G.W.; Hsu, S.H.; Chien, K.L.; Liao, C.C.; Sung, F.C.; Chen, P.C.; et al. The associations between serum perfluorinated chemicals and thyroid function in adolescents and young adults. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cock, M.; de Boer, M.R.; Lamoree, M.; Legler, J.; van de Bor, M. Prenatal exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals in relation to thyroid hormone levels in infants—A Dutch prospective cohort study. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.S.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, M.H.; Hsieh, W.S.; Chen, P.C. Perfluoroalkyl substances and thyroid hormones in cord blood. Environm. Pollut. 2017, 222, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Choi, K.; Ji, K.; Seo, J.; Kho, Y.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Hwang, I.; Jeon, J.; et al. Trans-placental transfer of thirteen perfluorinated compounds and relations with fetal thyroid hormones. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7465–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Itoh, S.; Yuasa, M.; Baba, T.; Miyashita, C.; Sasaki, S.; Nakajima, S.; Uno, A.; Nakazawa, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; et al. Association of perfluorinated chemical exposure in utero with maternal and infant thyroid hormone levels in the Sapporo cohort of Hokkaido Study on the Environment and Children’s Health. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, U.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, S.D.; Oh, J.E. Perfluoroalkyl substances in serum from South Korean infants with congenital hypothyroidism and healthy infants—Its relationship with thyroid hormones. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, D.; Rice, N.; Depledge, M.H.; Henley, W.E.; Galloway, T.S. Association between serum perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and thyroid disease in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, D.J.; Josson, J.; Elston, B.; Bartell, S.M.; Shin, H.M.; Vieira, V.M.; Savitz, D.A.; Fletcher, T.; Wellenius, G.A. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl acids and markers of kidney function among children and adolescents living near a chemical plant. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataria, A.; Trachtman, H.; Malaga-Dieguez, L.; Trasande, L. Association between perfluoroalkyl acids and kidney function in a cross-sectional study of adolescents. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.D.; Qian, Z.; Vaughn, M.G.; Huang, J.; Ward, P.; Zeng, X.W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, P.; Li, M.; et al. Positive associations of serum perfluoroalkyl substances with uric acid and hyperuricemia in children from Taiwan. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Ehresman, D.J.; Froehlich, J.W.; Seacat, A.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IOM (Institute of Medicine). Roundtable on Environmental Health Sciences, Research and Medicine. In Environmental Health Sciences Decision Making: Risk Management, Evidence, and Ethics-Workshop Summary; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gutzkow, K.B.; Haug, L.S.; Thomsen, C.; Sabaredzovic, A.; Becher, G.; Brunborg, G. Placental transfer of perfluorinated compounds is selective—A Norwegian Mother and Child sub-cohort study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-Ending Story of per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)? ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rappazzo, K.M.; Coffman, E.; Hines, E.P. Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances and Health Outcomes in Children: A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070691
Rappazzo KM, Coffman E, Hines EP. Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances and Health Outcomes in Children: A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(7):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070691
Chicago/Turabian StyleRappazzo, Kristen M., Evan Coffman, and Erin P. Hines. 2017. "Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances and Health Outcomes in Children: A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 7: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070691
APA StyleRappazzo, K. M., Coffman, E., & Hines, E. P. (2017). Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances and Health Outcomes in Children: A Systematic Review of the Epidemiologic Literature. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(7), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070691





