Contrasting Eutrophication Risks and Countermeasures in Different Water Bodies: Assessments to Support Targeted Watershed Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
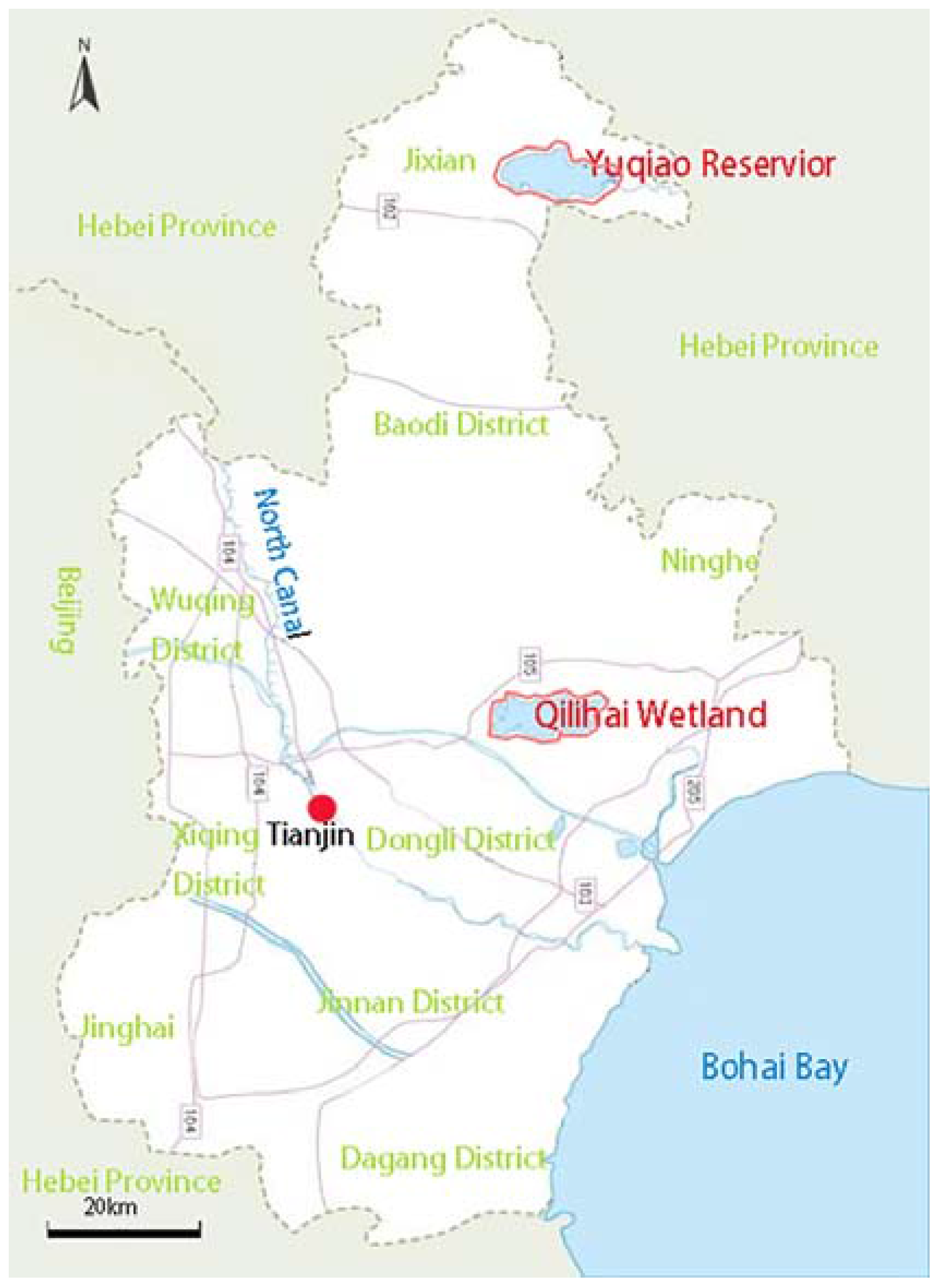
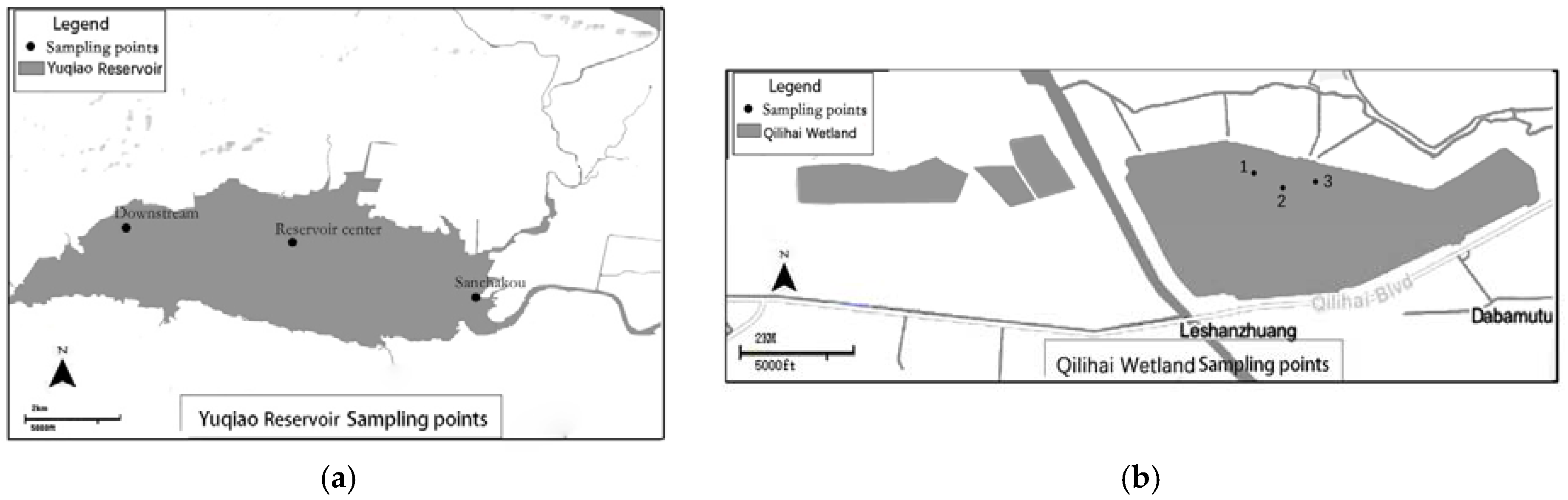
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Quality of the Two Reservoirs
2.3. Eutrophication Situation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Water Quality
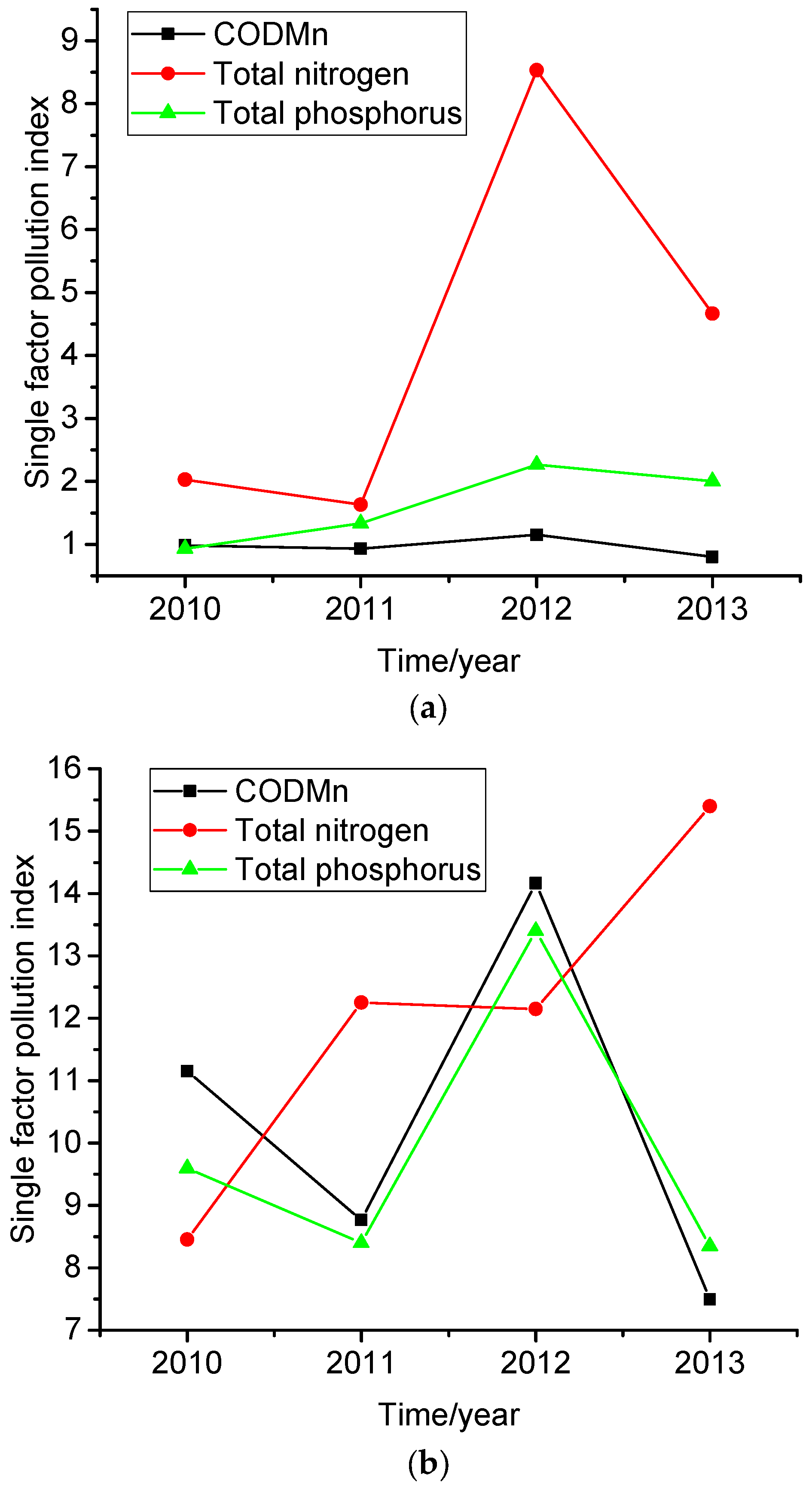
3.2. Ratio Changes of TN/TP
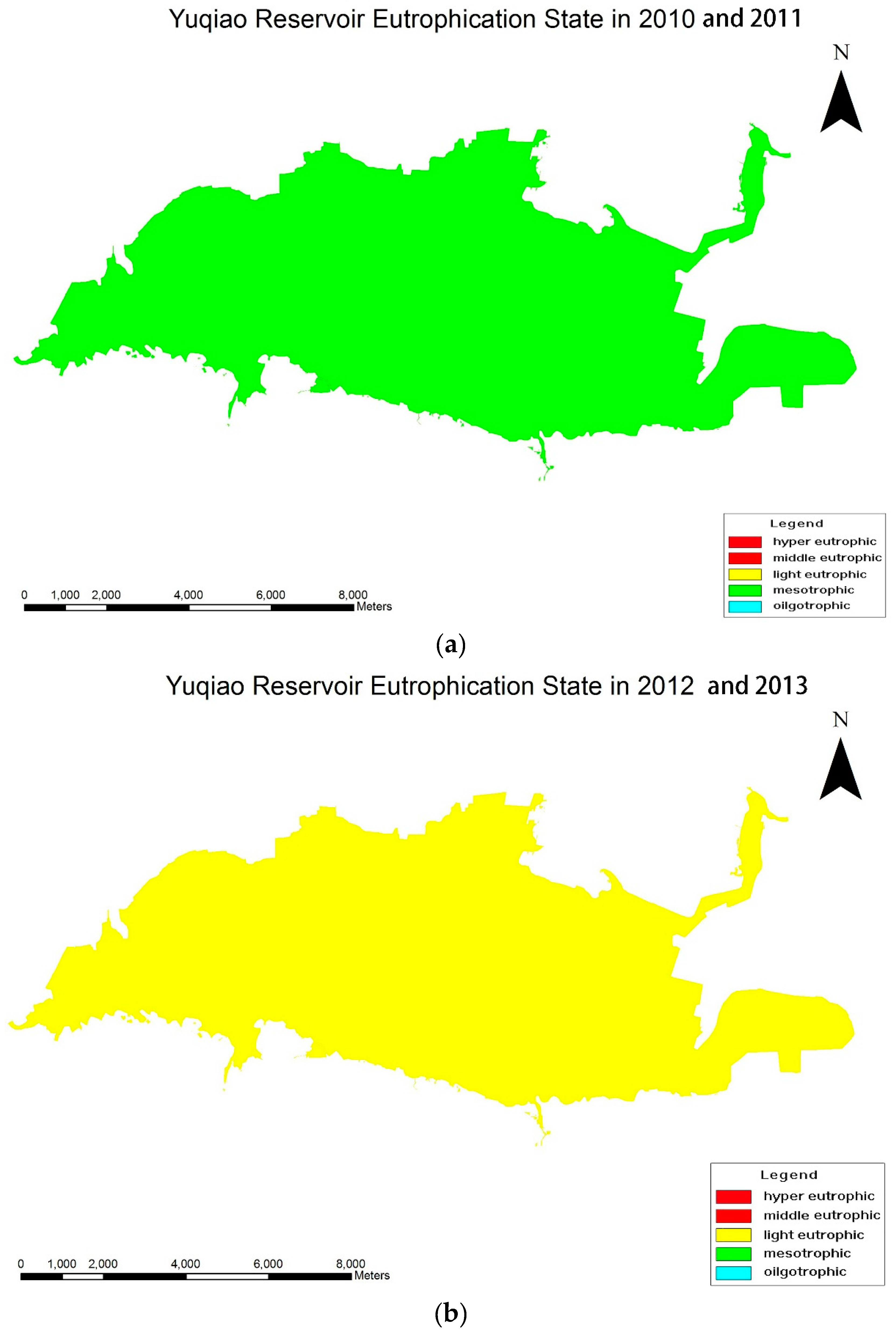
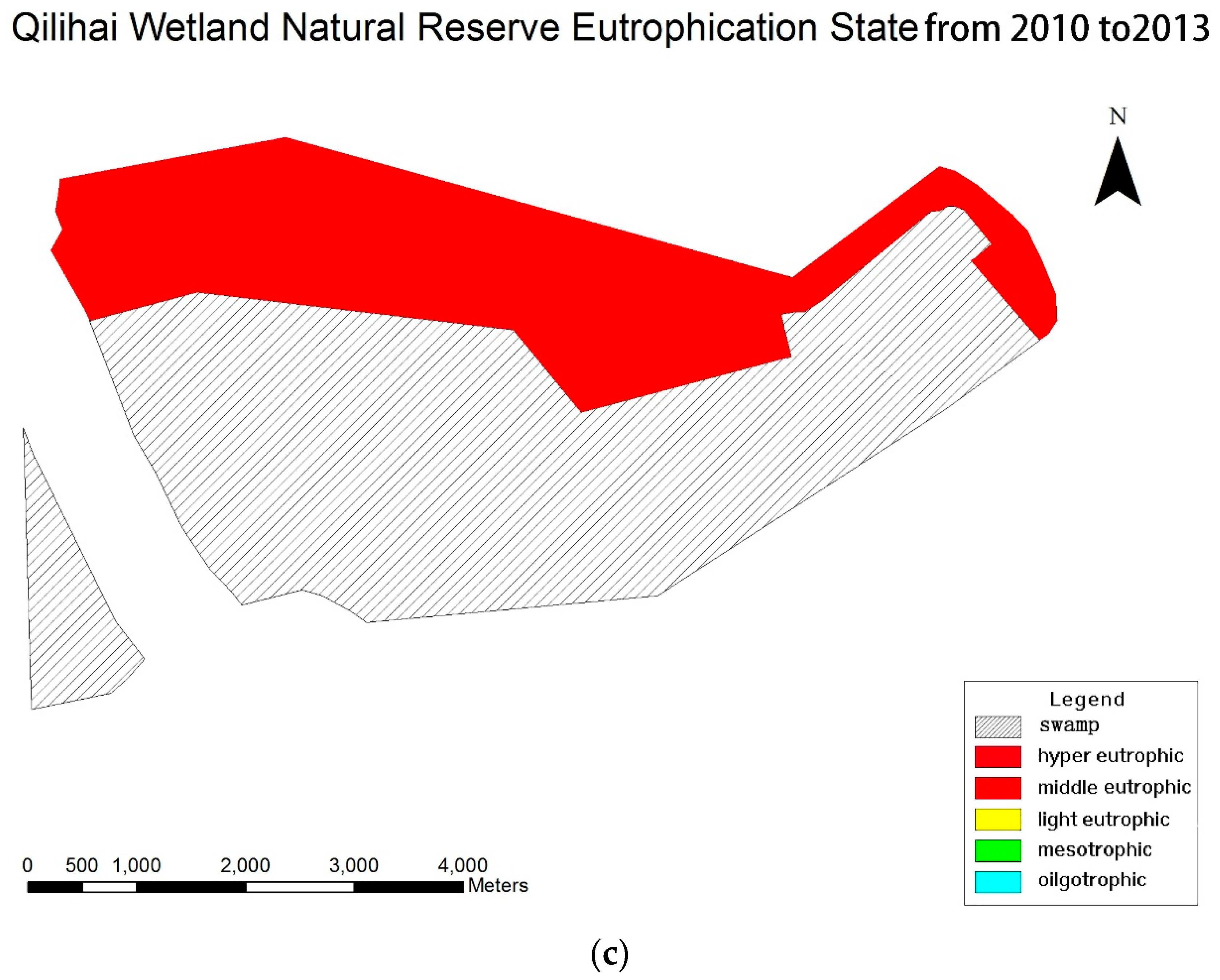
3.3. Eutrophication Evaluation
3.4. Analysis of Nutrient Sources
3.4.1. Internal Sources
3.4.2. External Sources
3.5. Management and Measures
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van, H.E.; Deluchat, V.; Chazal, P.M. Environmental impact of two successive chemical treatments in a small shallow eutrophied lake: Part II. Case of copper sulfate. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 3, 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, H. Control of Eutrophication in Inland Waters; Ellis Horwood Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Mental Protection. State of the Marine Environment; Reports and Studies no. 39; United Nations Environment Programmers: Nairobi, Kenya, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Priorities for Coastal Science; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.M. Submerged aquatic vegetation in relation to different nutrient regimes. Ophelia 1995, 41, 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avanzo, C.; Kremer, J.N.; Wainright, S.C. Ecosystem production and respiration in response to eutrophication in shallow temperate estuaries. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 1996, 141, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauxwell, J.; McClelland, J.; Behr, P.J.; Valiela, L. Relative importance of grazing and nutrient controls of macroalgal biomass in three temperate shallow estuaries. Estuaries 1998, 21, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveite, S. 0-Group Cod Investigations on the Norwegian Skagerrak Coast. In Proceedings of the Propagation of Cod Gadus morhua L.: An International Symposium, Arendal, Norway, 14–17 June 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Pohle, D.G.; Bricelj, V.M.; Garcia-Esquivel, Z. The eelgrass canopy: An above-bottom refuge from benthic predators for juvenile bay scallops Argopecten irradiants. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 74, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L.; Orth, R.J. Structural components of eelgrass (Zoster marina) meadows in the lower Chesapeake Bay-Fishes. Estuaries 1980, 3, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.R.; Canuel, E.A. A geochemical record of eutrophication and anoxia in Chesapeake Bay sediments: Anthropogenic influence on organic matter composition. Mar. Chem. 2000, 69, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkiss, I.J.; Ho, K.C. Are changes in N: Pratiosin coastal waters the key to increased red tide blooms? Hydrobiologia 1997, 352, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theissen, K.M.; Hobbs, W.O.; Hobbs, J.M.R.; Zimmer, K.D.; Domine, L.M.; Cotner, J.B.; Sugita, S. The altered ecology of Lake Christina: A record of regime shifts, land-use change, and management from a temperate shallow lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahere, T.S.; Mtsambiwa, M.Z.; Chifamba, P.C.; Nhiwatiwa, T. Climate change impact on the limnology of Lake Kariba, Zambia–Zimbabwe. Afr. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 39, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randsalu-Wendrup, L.; Conley, D.J.; Carstensen, J.; Hansson, L.-A.; Brönmark, C.; Fritz, S.C.; Choudhary, P.; Routh, J.; Hammarlund, D. Combining limnology and palaeolimnology to investigate recent regime shifts in a shallow, eutrophic lake. J. Paleolimnol. 2014, 51, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; van Nes, E.H. Shallow lakes theory revisited: Various alternative regimes driven by climate, nutrients, depth and lake size. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soerensen, A.L.; Schartup, A.T.; Gustafsson, E.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Undeman, E.; Björn, E. Eutrophication increases phytoplankton methyl mercury concentrations in a coastal sea—A baltic sea case study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11787–11796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Zhou, F.; Guo, H.C.; Sheng, H.; Liu, H.; Dao, X.; He, C.J. Analysis of spatial and temporal water pollution patterns in Lake Dianchi using multivariate statistical methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.J.; He, W.; Liu, W.X.; Qing, N.; Ouyang, H.L.; Wang, Q.M.; Kong, X.Z.; He, Q.S.; Yang, C.; Yang, B.; et al. The seasonal and spatial variations of phytoplankton community and their correlation with environmental factors in a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Z.; He, W.; Liu, W.X.; Yang, B.; Xu, F.L.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Mooij, W.M. Changes in food web structure and ecosystem functioning of a large shallow Chinese lake during the 1950, 1980 and 2000. Ecol. Modell. 2016, 319, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Deng, X.Z.; Ling, Y.Z. Influencing factors of lake eutrophication in China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 21, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.C.; Gao, J.F.; Zhang, Y.J. Modeling impacts of water transfers on alleviation of phytoplankton aggregation in Lake Taihu. J. Hydroinform. 2015, 17, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, G. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.W. The evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 1977, 195, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, D.L. The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Karl, E.; Lancelot, C.; Gene, E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Cho, K.H.; Park, J.; Cha, S.M.; Kim, J.H. Development of early-warming protocol for predicting chlorophyll—A concentration using machine learning models in freshwater and estuarine reservoirs, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N. Nitrogen in aquatic ecosystems. Ambio 2002, 31, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, R.; Zhang, X.L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, X.; He, B.; Guo, H.C. Uncertainty-based analysis on water quality response to water diversions for Lake Chenghai: A multiple-pattern inverse modeling approach. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Liu, H.X. Current situations and promoted suggestions on legislation of water function district management. China Water Conserv. 2012, 18, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Some thoughts on the management of water function areas. China Water Conserv. 2004, 4, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chuai, X.M. Study on the Basis and Control Standard of Eutrophication and Nutrients of Lakes in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B.H. Water Environmental Quality Benchmark, Standard and Total Water Pollution Control Strategy for River Basin. Environ. Sci. Res. 2006, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.M. Study on Agriculture Non-Point Source Pollution and Control Measures in Yuqiao Reservoir Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.K. Research on the Ecological Protection of Qilihai Wetland Reserve in Tianjin. Ph.D. Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Hebei, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.P. Analysis on Ecological Restoration of Nature Wetland Reserve and Its Green Exploration—Taking Qilihai National Nature Wetland Reserve as Example. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2009, 1, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Wei, Y.F. Strengthening the protection and restoration of the ecological environment of the Qilihai wetland. Seek Knowl. 2016, 1, 35–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.G.; Lee, H.; Lee, D.H. Wetland restoration to enhance biodiversity in urban areas: A comparative analysis. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 7, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, H.; Snow, J.A.; Stein, S.; Buda, S.; Zhai, J.Q.; Jiang, T.; Krysanova, V.; Kundazaewicz, Z.W. Predictors of precipitation for improved water resources management in the Tarim River basin: Creating a seasonal forecast model. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 125, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.S.; Xu, Z.X.; Wu, W.; Tang, F.F. Assessment and spatiotemporal variation analysis of water quality in the Zhangweinan River Basin, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1641–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.C.; Li, Z.J.; Ma, H.Y.; Wang, L.C.; Martin, J.D. Identification of the hydro geochemical processes and assessment of groundwater quality using classic integrated geochemical methods in the Southeastern part of Ordos basin, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, W. Water Quality Indices: A Survey of Indices Used in the United States; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Nasiri, F.; Maqsood, I.; Huang, G.; Fuller, N. Water quality index: A fuzzy river-pollution decision support expert system. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2007, 133, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; He, H.; Tan, X.H.; Gao, A.L.; Xue, S. Establishment and Application of Water Quality Assessment Model for Jiaozhou Bay Basin. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 518–523, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tia, Y.B.; Wang, J.Y. Influence factor analysis and assessment of water quality in national nature reserve in Ruoergai Wetland, Sichuan, China. Energ. Educ. Sci. Technol. Part A Energ. Sci. Res. 2012, 29, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Tian, S.Y.; Jia, R.; Liu, X. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of HCHs and DDTs in estuary wetland sediments from the Bohai Bay, North China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.Y.; Ma, J.J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W.C. Evaluation of ecosystem health for the coastal wetlands at the Yangtze Estuary, Shanghai. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 21, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.K.; Yuen, K.L.; Li, P.F.; Lau, W.H.; Chiu, C.M.; Yuen, S.W.; Baker, D.M. To swim or not to swim? A disagreement between microbial indicators on beach water quality assessment in Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwell, M.A.; Wuddivira, M.N.; Gobin, J.F. Abiotic water quality control on mangrove distribution in estuarine river channels assessed by a novel boat-mounted electromagnetic-induction technique. Water SA 2016, 42, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.Z.; Zou, R.; He, B.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.S.; Zhu, Y.G. A three-dimensional water quality modeling approach for exploring the eutrophication response to load reduction scenarios in Lake Yilong (China). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deus, R.; Brito, D.; Kenov, I.A.; Lima, M.; Costa, V.; Medeiros, A.; Neves, R.; Alves, C.N. Three-dimensional model for analysis of spatial and temporal patterns of phytoplankton in Tucuruí reservoir, Pará, Brazil. Ecol. Modell. 2013, 253, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouiten, H.; Díaz, C.Á.; Gómez, A.G.; Cortezón, J.A.R.; Alba, J.G. An advanced tool for eutrophication modeling in coastal lagoons: Application to the Victoria lagoon in the north of Spain. Ecol. Modell. 2013, 265, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Z.; Chen, F.D.; Zhou, Y.B. A novel eutrophication assessment model for aquaculture water area via Artificial neural networks. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2015, 12, 2909–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Yu, Z.M.; Song, X.X.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Cao, X.H.; Liang, Y.B. Application of an integrated Methodology for eutrophication assessment: A case study in the Bohai Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.L.; Ma, C.Z.; Xi, B.D.; Su, J.; Zai, F.Y.; Ji, D.F.; He, Z.S. Establishing eutrophication assessment standards for four lake regions, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Hu, S.; Dong, F.F.; Zou, R.; Zhao, L.; Guo, H.C.; Zhu, X.; He, B. Quantitative evaluation of lake eutrophication responses under alternative water diversion scenarios: A water quality modeling based statistical analysis approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.C. Chinese Lake Environment; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.Q.; Wu, M.; Dai, X.C.; Chai, P.H. Phosphorus storage dynamics and adsorption characteristics for sediment from a drinking water source reservoir and its relation with sediment compositions. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 64, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guildford, S.J.; Hecky, R.E. Total Nitrogen, Total Phosphorus, and Nutrient Limitation in Lakes and Oceans: Is There a Common Relationship? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 6, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Z.; Liu, K.F.; Qian, J.; Yang, J.W.; Zhang, P.P. Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Pollution and Eutrophication Evaluation of Typical Landscape Water in Hefei. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 1718–1726. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.Y.; Kang, K.; Zhu, L. Relationship between TN/TP and algal production cycle and production in water. J. Chongqing Universit. 2007, 1, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Laguna, A.; Ouattara, A.; Gonzalez, R.O.; Baron, O.; Fama, G.; El Mamouni, R.; Guiot, S.; Monroy, O.; Macarie, H. A single and low cost technique for determining the granulometry of up flow anaerobic sludge blanket sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.K.; Peng, S.; Zhao, X.H.; Li, X. Development of a two-dimensional eutrophication model in an urban lake (China) and the application of uncertainty analysis. Ecol. Modell. 2017, 345, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Y.; Hou, R.H. Eutrophication Trend and Causes of Yuqiao Reservoir. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2001, 9, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.M. Present Environmental Status about Yuqiao Reservoir and Research on Pollution Prevention Technique. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, B.; Ma, C.C.; Wang, Z.L. Distribution of Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Reed Marsh Sediment and Its Eco-Chemical Metrological Characteristics. Wetl. Sci. 2016, 6, 908–915. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.M.; Liu, J.L. Study on Water Resources Status and Ecological Water Requirement of Qilihai Wetland. Min. Explor. 2010, 6, 598–602. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.M.; Yin, C.Q.; Wang, X.H. Characteristics of Nitrogen Loss Concentration in Agricultural Small Watersheds around Yuqiao Reservoir. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 28, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.G.; Wei, X.T.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of the precursors of trihalomethanes and haloacetic acids in the Yuqiao Reservoir in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 17508–17517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Zhang, B.H.; Yao, H.M. Application of the grey relational analysis to the assessment of the environmental of surface water—Qilihai wetland as an example. Miner. Explor. 2010, 6, 603–607. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.B. Study on water resources restoration planning of the Qilihai wetlands in Tianjin. Sci. Technol. Vis. 2014, 08, 299. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.W.; Liu, M.D.; Li, Z.J.; Lu, S.S. Degeneration characteristics and rehabilitation of Qilihai Wetland environment ecological system. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 12, 244–248. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.L. Development and Research of Water Environment Quality Evaluation System of Tianjin Waters. J. Salt Chem. Ing. 2009, 1, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, S.S. Ecological Renew of Wetland in Qilihai Lake. Urban Environ. Urban Ecol. 2003, 16, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Bernal, B.; Hernandez, M.E. Ecosystem services of wetlands. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. 2015, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Indicators | CODMn | TN | TP | Chl-a | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade I | 2 | 0.2 | 0.02 | - | - |
| Grade II | 4 | 0.5 | 0.025 | - | - |
| Grade III | 6 | 1 | 0.05 | - | - |
| Parameter | Chla | TP | TN | SD | CODMn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rij | 1 | 0.84 | 0.82 | −0.83 | 0.83 |
| r2ij | 1 | 0.7056 | 0.6724 | 0.6889 | 0.6889 |
| Wj | 0.26626 | 0.18787 | 0.17903 | 0.18342 | 0.18342 |
| Grades | Values |
|---|---|
| Oligotrophic | TLI (∑) < 30 |
| Mesotrophic | 30 ≤ TLI (∑) ≤ 50 |
| light eutrophic | 50 < TLI (∑) ≤ 60 |
| middle eutrophic | 60 < TLI (∑) ≤ 70 |
| hyper eutrophic | TLI (op) > 70 |
| Test Items | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | Standard Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CODMn | 3.933333 | 3.733333 | 4.603333 | 3.2 | II ≤ 4 III ≤ 6 |
| TN | 1.013667 | 0.816667 | 4.266667 | 2.333333 | II ≤ 0.5 III ≤ 1 |
| TP | 0.023333 | 0.033333 | 0.056667 | 0.05 | II ≤ 0.025 III ≤ 0.05 |
| Chl-a | 13.53333 | 10.41 | 16.4 | 10.66667 | - |
| SD | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.83 | 0.9 | - |
| Test Items | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | Standard Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CODMn | 22.30 | 17.53 | 28.33 | 14.99 | I ≤ 2 V ≤ 15 |
| TN | 1.69 | 2.45 | 2.43 | 3.08 | I ≤ 0.2 1.5 < V ≤ 2.0 |
| TP | 0.192 | 0.168 | 0.268 | 0.167 | I ≤ 0.02 0.2 < IV ≤ 0.3 |
| Chl-a | 87.209 | 33.45 | 92.85 | 54.70 | — |
| SD | 0.38 | 0.18 | 1.23 | 0.27 | — |
| Year | TN | TP | CODMn | Chl-a | SD | TLI (∑) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 54.75995 | 33.33215 | 37.53206 | 53.29199 | 64.62706 | 48.99333 |
| 2011 | 51.09924 | 39.12455 | 36.14339 | 50.44245 | 55.50898 | 46.74031 |
| 2012 | 79.10711 | 47.74196 | 41.71763 | 55.37848 | 54.79479 | 55.57921 |
| 2013 | 68.88323 | 45.70931 | 32.04144 | 50.70696 | 53.22399 | 50.06019 |
| Year | TN | TP | CODMn | Chl-a | SD | TLI (∑) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 63.4189 | 67.55978 | 83.70305 | 73.52582 | 69.95113 | 70.80658 |
| 2011 | 69.70973 | 65.39123 | 77.29874 | 63.11916 | 84.44709 | 71.23871 |
| 2012 | 69.57088 | 72.97568 | 90.07175 | 74.2065 | 47.16393 | 71.09521 |
| 2013 | 73.58631 | 65.29427 | 77.23796 | 68.46024 | 76.58107 | 71.8827 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Chu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, M.; Wang, Y. Contrasting Eutrophication Risks and Countermeasures in Different Water Bodies: Assessments to Support Targeted Watershed Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070695
Li T, Chu C, Zhang Y, Ju M, Wang Y. Contrasting Eutrophication Risks and Countermeasures in Different Water Bodies: Assessments to Support Targeted Watershed Management. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(7):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070695
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tong, Chunli Chu, Yinan Zhang, Meiting Ju, and Yuqiu Wang. 2017. "Contrasting Eutrophication Risks and Countermeasures in Different Water Bodies: Assessments to Support Targeted Watershed Management" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 7: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070695
APA StyleLi, T., Chu, C., Zhang, Y., Ju, M., & Wang, Y. (2017). Contrasting Eutrophication Risks and Countermeasures in Different Water Bodies: Assessments to Support Targeted Watershed Management. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(7), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070695





