Biomedical Exploitation of Chitin and Chitosan via Mechano-Chemical Disassembly, Electrospinning, Dissolution in Imidazolium Ionic Liquids, and Supercritical Drying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Chitin and Chitosan Nanofibrils
2.1. Mechanical Disassembly of Chitin Nanofibrils
2.2. Mechanical Disassembly of Chitosan Nanofibrils
2.3. Nanochitosan Obtained from Partially Deacetylated Chitin, or from Deacetylated Nanochitin
2.4. Applications
3. Electrospun Nanofibers
3.1. Chitosan + Nylon Electrospun Nanofibers
3.2. Applications in Cardiology
3.3. Other Preparations of Biomedical Interest
4. Ionic Liquids: New Reaction Media
5. Supercritical Drying
6. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Muzzarelli, RAA. Chitosan composites with inorganics, morphogenetic proteins and stem cells, for bone regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 83, 1433–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, RAA. Chitins and chitosans for the repair of wounded skin, nerve, cartilage and bone. Carbohydr. Polym 2009, 76, 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar, R; Chennazhi, KP; Srinivasan, S; Nair, SV; Furuike, T; Tamura, H. Chitin scaffolds in tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2011, 12, 1876–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C; Li, FF; Griffith, M; Ruel, M; Suuronen, EJ. Application of chitosan-based biomaterials for blood vessel regeneration. Polym. Org. Chem 2010, 297, 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Park, BK; Kim, MM. Applications of chitin and its derivatives in biological medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2010, 11, 5153–5165. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, TL. Chitin-based materials in tissue engineering: Applications in soft tissue and epithelial organ. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2011, 12, 1936–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, RAA; Boudrant, J; Meyer, D; Manno, N; DeMarchis, M; Paoletti, MG. Current views on fungal chitin/chitosan, human chitinases, food preservation, glucans, pectins and inulin: A tribute to Henri Braconnot, precursor of the carbohydrate polymers science, on the chitin bicentennial. Carbohydr Polym 2011, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, GA; Kok, MS; Harding, SE; Adams, GG. Polysaccharide drug delivery systems based on pectin and chitosan. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev 2010, 27, 257–283. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, RAA. Chitosans: New Vectors for Gene Therapy. In Handbook of Carbohydrate Polymers: Development, Properties and Applications; Ito, R, Matsuo, Y, Eds.; NOVA Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 583–604. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhury, A; Das, S. Recent advancement of chitosan-based nanoparticles for oral controlled delivery of insulin and other therapeutic agents. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Petkar, KC; Chavhan, SS; Agatonovik-Kustrin, S; Sawant, KK. Nanostructured materials in drug and gene delivery: A review of the state of the art. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst 2011, 28, 101–164. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, MP; Patel, RR; Patel, JK. Chitosan mediated targeted drug delivery system: A review. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci 2010, 13, 536–557. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B; Agarwal, R; Alam, MS. Textile-based smart wound dressings. Indian J. Fibre Textile Res 2010, 35, 174–187. [Google Scholar]
- Laurienzo, P. Marine polysaccharides in pharmaceutical applications: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2435–2465. [Google Scholar]
- Kean, T; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and safety of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, RAA. Chitin Nanostructures in Living Organisms. In Chitin Formation and Diagenesis; Gupta, SN, Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, RAA. Genipin-chitosan hydrogels as biomedical and pharmaceutical aids. Carbohydr. Polym 2009, 77, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y; Shi, XW; Kim, E; Robinson, LM; Nye, CK; Ghodssi, R; Rubloff, GW; Bentley, WE; Payne, GF. Chitosan to electroaddress biological components in lab-on-a-chip devices. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 84, 704–708. [Google Scholar]
- Ngah, WSW; Teong, LC; Hanafiah, MAKM. Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 83, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Quignard, F; Di Renzo, F; Guibal, E. From natural polysaccharides to materials for catalysis, adsorption, and remediation. Top. Curr. Chem 2010, 294, 165–197. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, C; Belleville, P; Popall, M; Nicole, L. Applications of advanced hybrid organic-inorganic nanomaterials: from laboratory to market. Chem. Soc. Rev 2011, 40, 696–753. [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar, R; Prabaharan, M; Nair, SV; Tamura, H. Novel chitin and chitosan nanofibers in biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Adv 2010, 28, 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, ZH; Zhang, ZY; Zhou, CR; Jiao, YP. Hydrophobic modifications of cationic polymers for gene delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci 2010, 35, 1144–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, RAA. Nanochitins and Nanochitosans, Paving the Way to Eco-Friendly and Energy-Saving Exploitation of Marine Resources. In Comprehensive Polymer Science, 2nd ed; Hoefer, R, Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2011; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, JL; Xia, WS; Liu, P; Cheng, QY; Tahirou, T; Gu, WX; Li, B. Chitosan modification and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1962–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, A; Yadav, SK; Yadav, SC. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, RAA. Chitins and chitosans as immunoadjuvants and non-allergenic drug carriers. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 292–312. [Google Scholar]
- Baldrick, P. The safety of chitosan as a pharmaceutical excipient. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol 2010, 56, 290–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kose, R; Kondo, T. Favorable 3D-network formation of chitin nanofibers dispersed in water prepared using aqueous counter collision. Fiber 2011, 67, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ifuku, S; Nogi, M; Abe, K; Yoshioka, M; Morimoto, M; Saimoto, H; Yano, H. Preparation of chitin nanofibers with a uniform width as alpha-chitin from crab shells. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Ifuku, S; Nogi, M; Yoshioka, M; Morimoto, M; Yano, H; Saimoto, H. Fibrillation of dried chitin into 10–20 nm nanofibers by a simple grinding method under acidic conditions. Carbohydr. Polym 2010, 81, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Shams, MI; Ifuku, S; Nogi, M; Oku, T; Yano, H. Fabrication of optically transparent chitin nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 102, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ifuku, S; Morooka, S; Nakagaito, AN; Morimoto, M; Saimoto, H. Preparation and characterization of optically transparent chitin nanofiber/(meth)acrylic resin composites. Green Chem 2011, 13, 1708–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Ifuku, S; Morooka, S; Morimoto, M; Saimoto, H. Acetylation of chitin nanofibers and their transparent nanocomposite films. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, YM; Saito, T; Isogai, A. Preparation of chitin nanofibers from squid pen beta-chitin by simple mechanical treatment under acid conditions. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, DG; Wu, QL; Chang, PR; Gao, GZ. Self-assembled liquid crystal film from mechanically defibrillated chitosan nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 84, 686–689. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, DG; Chang, PR; Chen, MD; Wu, QL. Chitosan colloidal suspension composed of mechanically disassembled nanofibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci 2010, 354, 637–643. [Google Scholar]
- Watthanaphanit, A; Supaphol, P; Tamura, H; Tokura, S; Rujiravanit, R. Wet-spun alginate/chitosan whiskers nanocomposite fibers: Preparation, characterization and release characteristic of the whiskers. Carbohydr. Polym 2010, 79, 738–746. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, YM; Saito, T; Isogai, A. Individual chitin nano-whiskers prepared from partially deacetylated alpha-chitin by fibril surface cationization. Carbohydr. Polym 2010, 79, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Ifuku, S; Nomura, R; Morimoto, M; Saimoto, H. Preparation of chitin nanofibers from mushrooms. Materials 2011, 4, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, RAA; Morganti, P; Morganti, G; Palombo, P; Palombo, M; Biagini, G; Mattioli-Belmonte, M; Giantomassi, F; Orlandi, F; Muzzarelli, C. Chitin nanofibrils with chitosan glycolate composites as wound medicaments. Carbohydr. Polym 2007, 70, 274–284. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B; Shi, XL; Xiao, JQ; Zhang, Y; Chu, XH; Gu, JY; Tan, JJ; Gu, ZZ; Ding, YT. Influence of chitosan nanofiber scaffold on porcine endogenous retroviral expression and infectivity in pig hepatocytes. World J. Gastroenterol 2011, 17, 2774–2780. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, HY; Burger, C; Hsiao, BS; Chu, B. Ultrafine polysaccharide nanofibrous membranes for water purification. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 970–976. [Google Scholar]
- Tzoumaki, MV; Moschakis, T; Kiosseoglou, V; Biliaderis, CG. Oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by chitin nanocrystal particles. Food Hydrocoll 2011, 25, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C; Chen, R; Ke, QF; Morsi, Y; Zhang, KH; Mo, XM. Electrospun collagen-chitosan-polyurethane nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineered tubular grafts. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 82, 307–315. [Google Scholar]
- Hariraksapitak, P; Supaphol, P. Preparation and properties of alpha-chitin-whisker-reinforced hyaluronan-gelatin nanocomposite scaffolds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 2010, 117, 3406–3418. [Google Scholar]
- Yerlikaya, F; Aktas, Y; Capan, Y. LC-UV determination of melatonin from chitosan nanoparticles. Chromatographia 2010, 71, 967–970. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, A; Lovric, J; Voinovich, D; Filipovic-Grcic, J. Melatonin-loaded lecithin/chitosan nanoparticles: Physicochemical characterisation and permeability through Caco-2 cell monolayers. Int. J. Pharm 2009, 381, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Kofuji, K; Nakamura, M; Isobe, T; Murata, Y; Kawashima, S. Stabilization of alpha-lipoic acid by complex formation with chitosan. Food Chem 2008, 109, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, PR; Jian, RJ; Yu, JG; Ma, XF. Starch-based composites reinforced with novel chitin nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym 2010, 80, 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Azeredo, HMC; Mattoso, LHC; Avena-Bustillos, RJ; Ceotto, G; Munford, ML; Wood, D; McHugh, TH. Nanocellulose reinforced chitosan composite films as affected by nanofiller loading and plasticizer content. J. Food Sci 2010, 75, N1–N7. [Google Scholar]
- Junkasem, J; Rujiravanit, R; Supaphol, P. Fabrication of alpha-chitin whisker-reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite nanofibres by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4519–4528. [Google Scholar]
- Li, XX; Li, XY; Ke, BL; Shi, XW; Du, YM. Cooperative performance of chitin whisker and rectorite fillers on chitosan films. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 85, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Ezhova, ZA; Koval, EM; Zakharov, NA; Kalinnikov, VT. Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of nanocrystalline chitosan-containing calcium carbonate apatites. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem 2011, 56, 841–846. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, R; Cochrane, B; Naguib, H; Lee, PC. Fabrication and characterization of melt-blended polylactide-chitin composites and their foams. J. Cell. Plast 2011, 47, 282–299. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmala, R; Il, BW; Navamathavan, R; El-Newehy, MH; Kim, HY. Preparation and characterizations of anisotropic chitosan nanofibers via electrospinning. Macromol. Res 2011, 19, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, A; Bhattarai, N; Kievit, FM; Rossol, M; Zhang, MQ. Electrospinning of chitosan derivative nanofibers with structural stability in an aqueous environment. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys 2011, 13, 9969–9972. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, V; Patanaik, A; Anandjiwala, RD; Maaza, M. Optimization of Electrospinning Parameters for Chitosan Nanofibres. Curr. Nanosci 2011, 7, 396–401. [Google Scholar]
- Muzzarelli, RAA. Potential of chitin/chitosan-bearing materials for uranium recovery: An interdisciplinary review. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 84, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmala, R; Navamathavan, R; Kang, HS; El-Newehy, MH; Kim, HY. Preparation of polyamide-6/chitosan composite nanofibers by a single solvent system via electrospinning for biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 83, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmala, R; Navamathavan, R; El-Newehy, MH; Kim, HY. Preparation and electrical characterization of polyamide-6/chitosan composite nanofibers via electrospinning. Mater. Lett 2011, 65, 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, HT; Han, J; Xue, Y; Nie, HL; Zhu, LM; Branford-White, CJ. Surface Modification of Electrospun Nylon Nanofiber Based Dye Affinity Membrane and Its Application to Papain Adsorption. Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Beijing, China, 11–13 June 2009; 1, pp. 955–958.
- Hussain, A; Collins, G; Cho, CH. Electrospun Chitosan-Based Nanofiber Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Engineering Applications. Proceedings of 2010 IEEE 36th Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference, New York, NY, USA, 26–28 March 2010; pp. 62–63.
- Cynthia, W; Shital, P; Rui, C; Owida, A; Morsi, Y. Biomimetic electrospun gelatin-chitosan polyurethane for heart valve leaflets. J. Mech. Med. Biol 2010, 10, 563–576. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, DM; Huang, HM; Blackwood, K; MacNeil, S. A novel route for the production of chitosan/polylactide-co-glycolide) graft copolymers for electrospinning. Biomed. Mater 2011, 5, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Skotak, M; Leonov, AP; Larsen, G; Noriega, S; Subramanian, A. Biocompatible and biodegradable ultrafine fibrillar scaffold materials for tissue engineering by facile grafting of l-lactide onto chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar]
- Klossner, RR; Queen, HA; Coughlin, AJ; Krause, WE. Correlation of chitosan’s rheological properties and its ability to electrospin. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar]
- Ziani, K; Henrist, C; Jerome, C; Aqil, A; Mate, JI; Cloots, R. Effect of nonionic surfactant and acidity on chitosan nanofibers with different molecular weights. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 83, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, HL; Huang, J; Yu, JH; Liu, SY; Gu, P. Electrospun chitosan-graft-poly (epsilon-caprolactone)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) cationic nanofibrous mats as potential scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2011, 48, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shalumon, KT; Anulekha, KH; Chennazhi, KP; Tamura, H; Nair, SV; Jayakumar, R. Fabrication of chitosan/poly(caprolactone) nanofibrous scaffold for bone and skin tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2011, 48, 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, ZQ; Leach, MK; Chu, XH; Wang, YC; Tian, TA; Shi, XL; Ding, YT; Gu, ZZ. Electrospun chitosan nanofibers for hepatocyte culture. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol 2010, 6, 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, ZX; Zheng, W; Li, L; Zheng, YF. Fabrication, characterization and in vitro drug release behavior of electrospun PLGA/chitosan nanofibrous scaffold. Mater. Chem. Phys 2011, 125, 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, YF; Zhang, KH; Chen, F; Ke, QF; Mo, XM. Cross-linking of gelatin and chitosan complex nanofibers for tissue-engineering scaffolds. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed 2011, 22, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, KH; Qian, YF; Wang, HS; Fan, LP; Huang, C; Mo, XM. Electrospun silk fibroin-hydroxybutyl chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds to biomimic extracellular matrix. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed 2011, 22, 1069–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Almodovar, J; Kipper, MJ. Coating electrospun chitosan nanofibers with polyelectrolyte multilayers using the polysaccharides heparin and N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan. Macromol. Biosci 2010, 11, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, DZ; Yu, K; Ai, YF; Zhen, HP; Nie, J; Kennedy, JF. The mineralization of electrospun chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membranes. Carbohydr. Polym 2010, 84, 990–996. [Google Scholar]
- Espindola-Gonzalez, A; Martinez-Hernandez, AL; Fernandez-Escobar, F; Castano, VM; Brostow, W; Datashvili, T; Velasco-Santos, C. Natural-synthetic hybrid polymers developed via electrospinning: the effect of PET in chitosan/starch system. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2010, 12, 1908–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, MY; Lee, J. Chitosan fibrous 3D networks prepared by freeze drying. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 84, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, H; Matsumoto, H; Hara, S; Minagawa, M; Tanioka, A; Yako, H; Yamagata, Y; Inoue, K. Preparation of polysaccharide nanofiber fabrics by electrospray deposition: Additive effects of polyethylene oxide. Polym. J 2005, 37, 391–398. [Google Scholar]
- Horzum, N; Boyaci, E; Eroglu, AE; Shahwan, T; Demir, MM. Sorption efficiency of chitosan nanofibers toward metal ions at low concentrations. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, XP; Li, Z; Kang, WM; Cheng, BW. Electrospun antibacterial chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles. New Mater Adv Mater 2011, 152–153, 1333–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Su, P; Wang, CJ; Yang, XY; Chen, XY; Gao, CY; Feng, XX; Chen, JY; Ye, JA; Gou, ZR. Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: The favorable effect of metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 84, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Uygun, A; Kiristi, M; Oksuz, L; Manolache, S; Ulusoy, S. Hydrazine plasma modification of chitosan for antibacterial activity and nanofiber applications. Carbohydr. Res 2011, 346, 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, CC; Lou, CW; Lu, CT; Huang, SH; Chao, CY; Lin, JH. Evaluation of the Preparation and Biocompatibility of Poly(vinyl alcohol)(PVA)/chitosan Composite Electrospun Membranes. Adv Mater Res 2010, 123–125, 975–978. [Google Scholar]
- Swatloski, RP; Spear, SK; Holbrey, JD; Rogers, RD. The dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, HB; Zhang, SB; Li, SH. Chitin and chitosan dissolved in ionic liquids as reversible sorbents of CO2. Green Chem 2006, 8, 630–633. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, S; Takegawa, A; Kaneko, Y; Kadokawa, J; Yamagata, M; Ishikawa, M. Performance of electric double-layer capacitor with acidic cellulose-chitin hybrid gel electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc 2010, 157, A203–A208. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, K; Murakami, M; Kaneko, Y; Takada, A; Nakamura, Y; Kadokawa, J. Weak gel of chitin with ionic liquid, 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2009, 45, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Park, TJ; Jung, YJ; Choi, SW; Park, H; Kim, H; Kim, E; Lee, SH; Kim, JH. Native chitosan/cellulose composite fibers from an ionic liquid via electrospinning. Macromol. Res 2011, 19, 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Takegawa, A; Murakami, M; Kaneko, Y; Kadokawa, J. Preparation of chitin/cellulose composite gels and films with ionic liquids. Carbohydr. Polym 2010, 79, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y; Sasaki, T; Irie, S; Sakurai, K. A novel biomass-ionic liquid platform for the utilization of native chitin. Polymer 2008, 49, 2321–2327. [Google Scholar]
- Kadokawa, J; Takegawa, A; Mine, S; Prasad, K. Preparation of chitin nanowhiskers using an ionic liquid and their composite materials with polyvinyl alcohol. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 84, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, WT; Zhu, J; Wang, XL; Huang, Y; Wang, YZ. Dissolution behavior of chitin in ionic liquids. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2010, 49, 528–541. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y; Lu, XM; Sun, N; Rogers, RD. Dissolution or extraction of crustacean shells using ionic liquids to obtain high molecular weight purified chitin and direct production of chitin films and fibers. Green Chem 2010, 12, 968–971. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, CJ; Wu, QL. A novel polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogel reinforced with natural chitosan nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 84, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, DB; Jiang, JL; Kuang, LJ; Jiang, J; Zheng, W; Liang, HJ. Smart chitosan-based stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for the controlled delivery of hydrophobic pharmaceuticals. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1298–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, AN; Luo, ZP; Akbulut, M. Ionic liquid mediated auto-templating assembly of CaCO3-chitosan hybrid nanoboxes and nanoframes. Chem. Commun 2011, 47, 2312–2314. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, JH; He, CY; Pang, XJ; Hu, KC. Amperometric immunosensor for prostate specific antigen based on gold nanoparticles/ionic liquid/chitosan hybrid film. Anal. Lett 2011, 44, 908–921. [Google Scholar]
- Safavi, A; Farjami, F. Electrodeposition of gold-platinum alloy nanoparticles on ionic liquid-chitosan composite film and its application in fabricating an amperometric cholesterol biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron 2011, 26, 2547–2552. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, SS; Duarte, ARC; Carvalho, AP; Mano, JF; Reis, RL. Green processing of porous chitin structures for biomedical applications combining ionic liquids and supercritical fluid technology. Acta Biomater 2011, 7, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Moribe, K; Tozuka, Y; Yamamoto, K. Supercritical carbon dioxide processing of active pharmaceutical ingredients for polymorphic control and for complex formation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 2008, 60, 328–338. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovic, N; Bouchard, A; Hofland, GW; Witkamp, GJ; Crommelin, DJA; Jiskoot, W. Stabilization of proteins in dry powder formulations using supercritical fluid technology. Pharm. Res 2004, 21, 1955–1969. [Google Scholar]
- Diez-Municio, M; Montilla, A; Herrero, M; Olano, A; Ibanez, E. Supercritical CO2 impregnation of lactulose on chitosan: A comparison between scaffolds and microspheres form. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 57, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Casettari, L; Castagnino, E; Stolnik, S; Lewis, A; Howdle, SM; Illum, L. Surface Characterisation of Bioadhesive PLGA/Chitosan Microparticles Produced by Supercritical Fluid Technology. Pharm. Res 2011, 28, 1668–1682. [Google Scholar]
- Cardea, S; Pisanti, P; Reverchon, E. Generation of chitosan nanoporous structures for tissue engineering applications using a supercritical fluid assisted process. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2010, 54, 290–295. [Google Scholar]
- Robitzer, M; Tourrette, A; Horga, R; Valentin, R; Boissiere, M; Devoisselle, JM; Di Renzo, F; Quignard, F. Nitrogen sorption as a tool for the characterisation of polysaccharide aerogels. Carbohydr. Polym 2011, 85, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- El Kadib, A; Molvinger, K; Cacciaguerra, T; Bousmina, M; Brunel, D. Chitosan templated synthesis of porous metal oxide microspheres with filamentary nanostructures. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 2011, 142, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, MR; Hunt, AJ. Synthesis and properties of chitosan-silica hybrid aerogels. J. Non-Cryst Solids 2001, 285, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Rinki, K; Dutta, PK; Hunt, AJ; Clark, JH; Macquarrie, DJ. Preparation of chitosan based scaffolds using supercritical carbon dioxide. Macromol. Symp 2009, 277, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Rinki, K; Dutta, PK. Physicochemical and biological activity study of genipin-crosslinked chitosan scaffolds prepared by using supercritical carbon dioxide for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2010, 46, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas-Hernandez, R; Ruiz-Trevino, FA; Ortiz-Estrada, CH; Luna-Barcenas, G; Prokhorov, Y; Alvarado, JFJ; Sanchez, IC. Chitin microstructure formation by rapid expansion techniques with supercritical carbon dioxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 2009, 48, 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, R; Cochrane, B; Naguib, H; Lee, PC. Fabrication and characterization of melt-blended polylactide-chitin composites and their foams. J. Cell. Plast 2011, 47, 282–299. [Google Scholar]
- Correlo, VM; Costa-Pinto, AR; Sol, P; Covas, JA; Bhattacharya, M; Neves, NM; Reis, RL. Melt processing of chitosan-based fibers and fiber-mesh scaffolds for the engineering of connective tissues. Macromol. Biosci 2010, 10, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Jeung, S; Mishra, MK. Hot melt reactive extrusion of chitosan and poly(acrylic acid). Int. J. Polym. Mater 2011, 60, 102–113. [Google Scholar]
- Thuaksuban, N; Nuntanaranont, T; Pattanachot, W; Suttapreyasri, S; Cheung, LK. Biodegradable polycaprolactone-chitosan three-dimensional scaffolds fabricated by melt stretching and multilayer deposition for bone tissue engineering: Assessment of the physical properties and cellular response. Biomed. Mater 2011, 6, 100–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, CD; Annabi, N; Khademhosseini, A; Dehghani, F. Fabrication of porous chitosan scaffolds for soft tissue engineering using dense gas CO2. Acta Biomater 2011, 7, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Gozke, G; Posten, C. Electrofiltration of biopolymers. Food Eng. Rev 2010, 2, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Beckham, GT; Crowley, MF. Examination of the α-chitin structure and decrystallization thermodynamics at the nanoscale. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, RH; Huang, JR; Tsai, ML; Tseng, LZ; Hsu, CH. Differences in degradation kinetics for sonolysis, microfluidization and shearing treatments of chitosan. Polym. Int 2011, 60, 897–902. [Google Scholar]
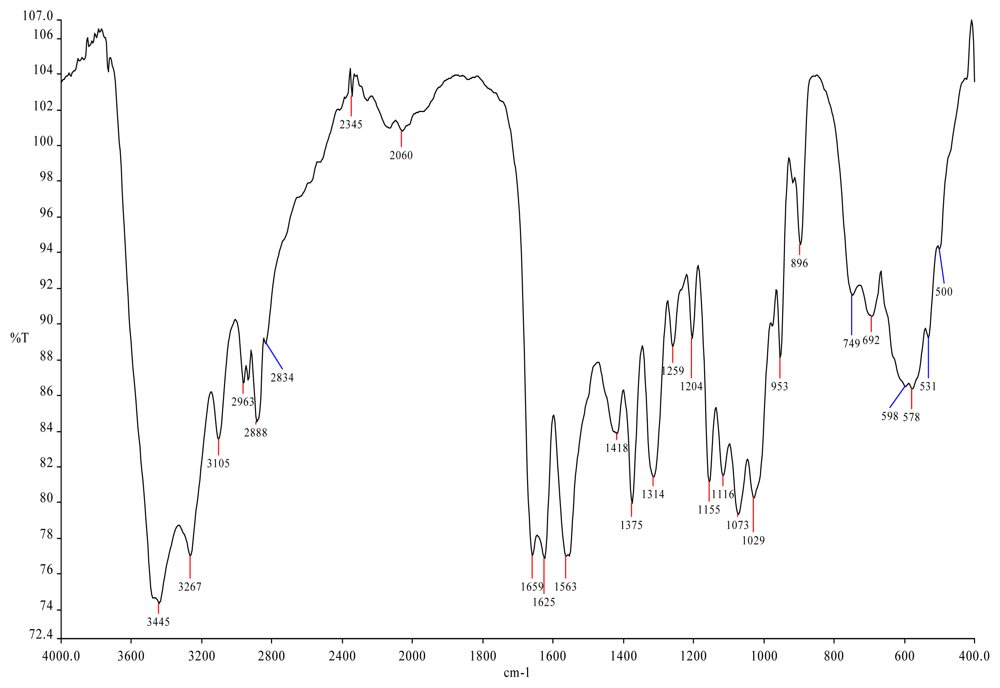
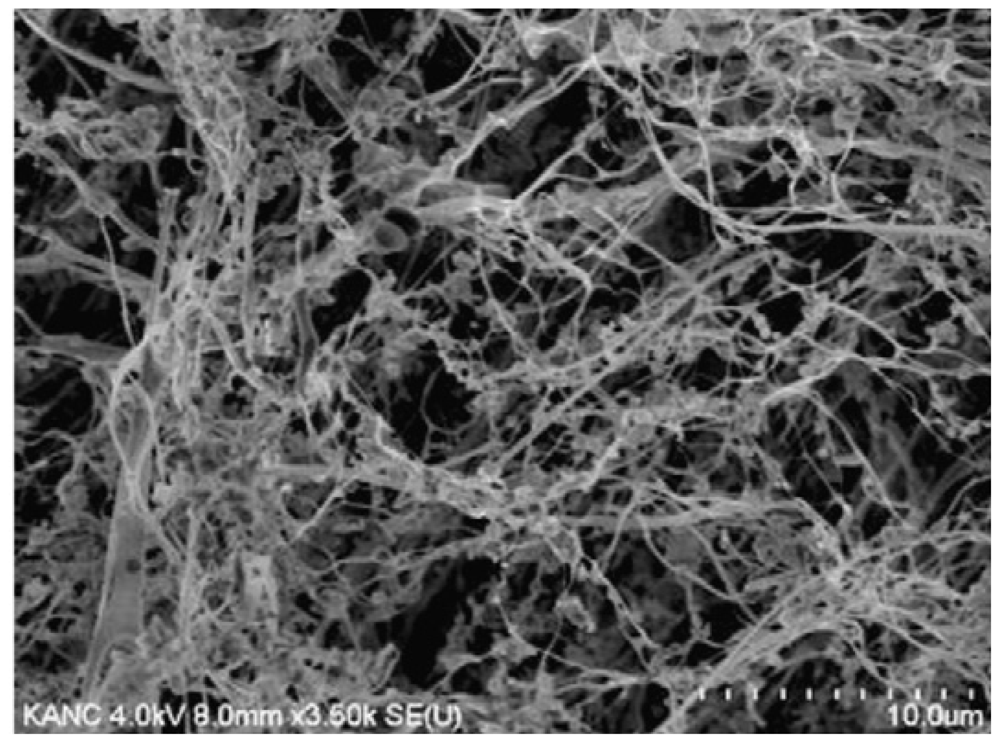
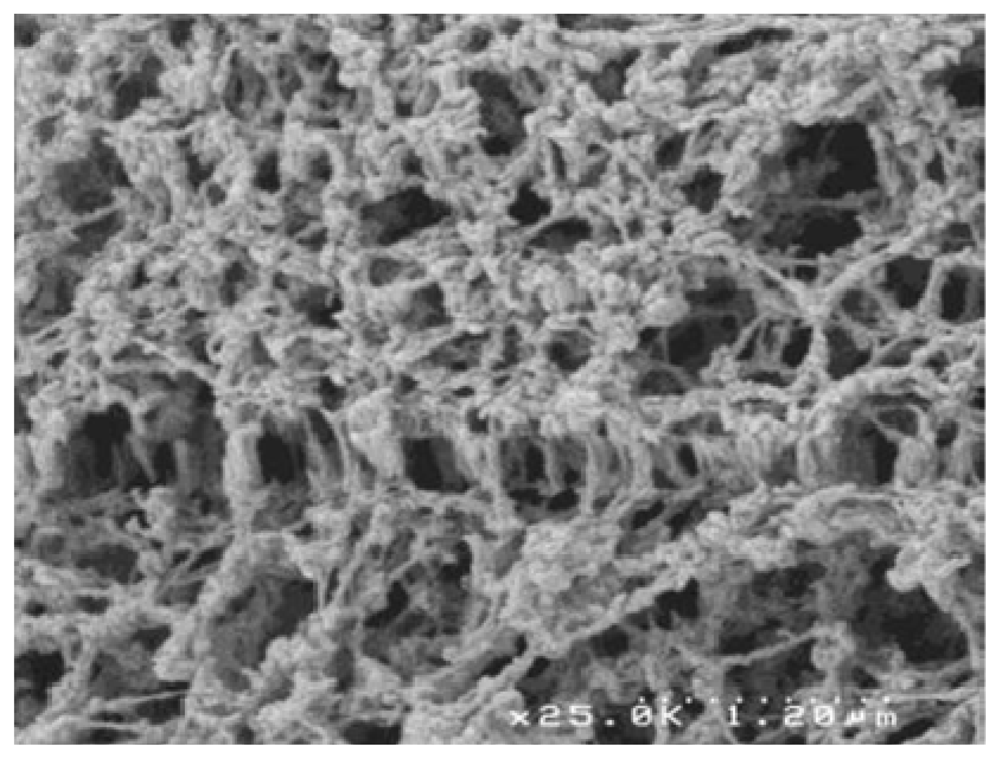
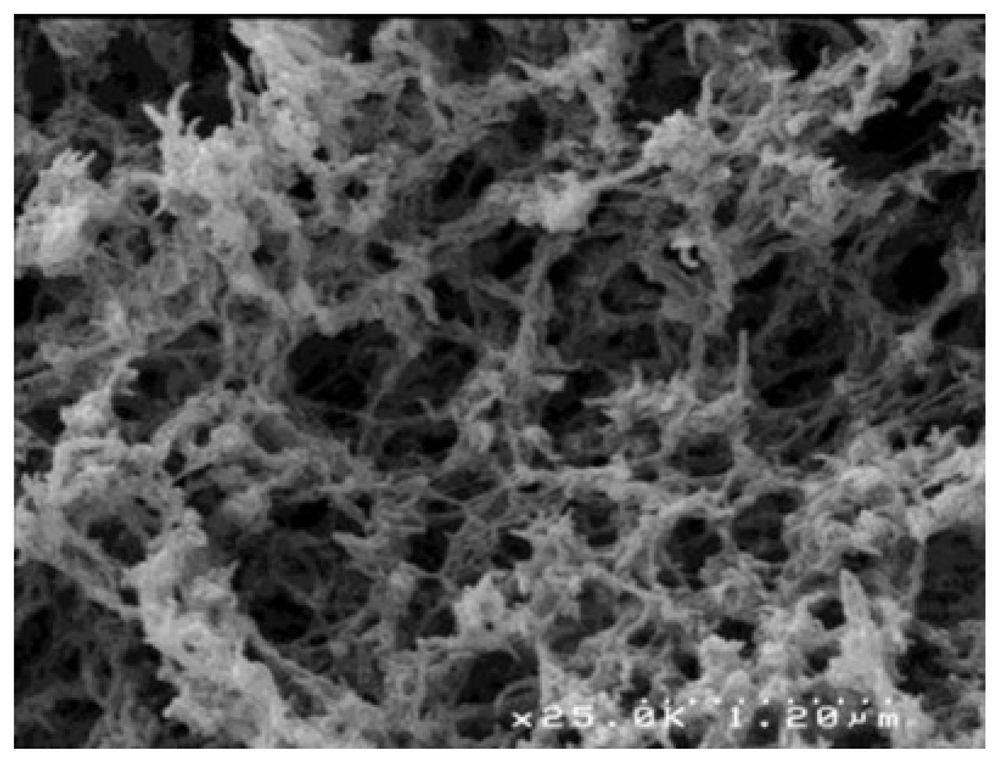
| Polymer | Origin and viscosity | Solubility (w/w%) at 110 °C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AmiCl | AmiBr | BmiAc | BmiCl | ||
| α-Chitin | Crab | n.a. | Soluble, 9.1 | n.a | n.a. |
| α-Chitin | Crab, η 35 cp | Insoluble | n.a. | Soluble, 6 | Partly soluble |
| β-Chitin | Squid pen, η 15 cp | Insoluble | n.a. | Soluble, 7 | Partly soluble |
| β-Chitin | Squid pen, η 278 cp | Insoluble | n.a. | Soluble, 3 | Insoluble |
| Chitosan | Crab, Mv 97 kDa | Soluble, 8 | n.a. | Soluble, 12 | Soluble, 10 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Muzzarelli, R.A.A. Biomedical Exploitation of Chitin and Chitosan via Mechano-Chemical Disassembly, Electrospinning, Dissolution in Imidazolium Ionic Liquids, and Supercritical Drying. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1510-1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9091510
Muzzarelli RAA. Biomedical Exploitation of Chitin and Chitosan via Mechano-Chemical Disassembly, Electrospinning, Dissolution in Imidazolium Ionic Liquids, and Supercritical Drying. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(9):1510-1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9091510
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuzzarelli, Riccardo A. A. 2011. "Biomedical Exploitation of Chitin and Chitosan via Mechano-Chemical Disassembly, Electrospinning, Dissolution in Imidazolium Ionic Liquids, and Supercritical Drying" Marine Drugs 9, no. 9: 1510-1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9091510
APA StyleMuzzarelli, R. A. A. (2011). Biomedical Exploitation of Chitin and Chitosan via Mechano-Chemical Disassembly, Electrospinning, Dissolution in Imidazolium Ionic Liquids, and Supercritical Drying. Marine Drugs, 9(9), 1510-1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9091510




