The Structural Diversity of Carbohydrate Antigens of Selected Gram-Negative Marine Bacteria
Abstract
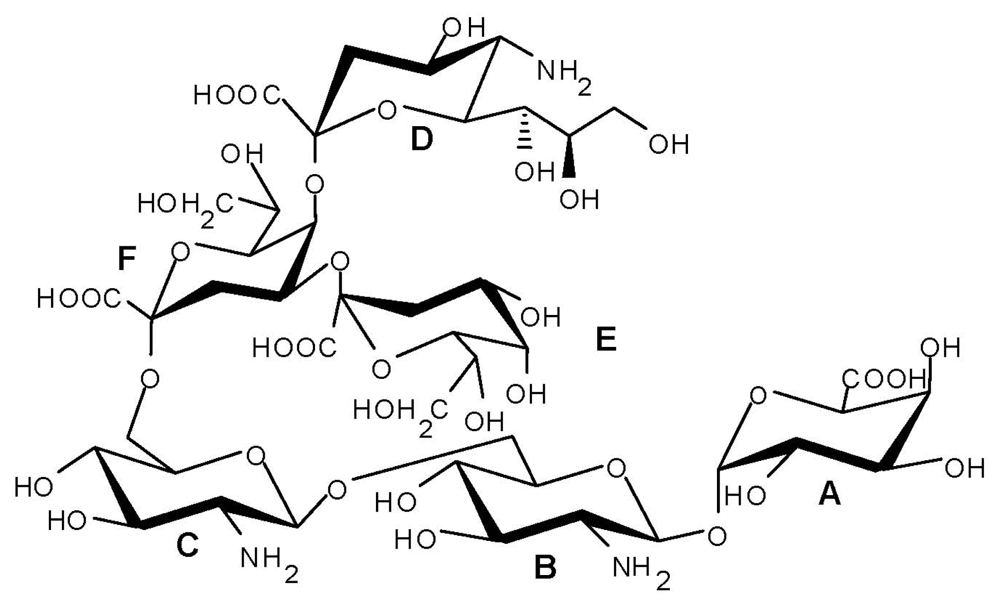
:1. Introduction
2. Structure of Carbohydrate Antigens of Gammaproteobacteria
2.1. Genus Alteromonas
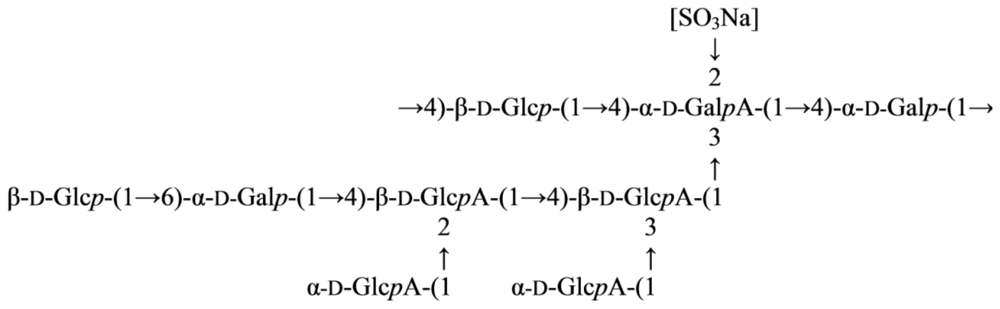
2.2. Genus Microbulbifer
2.3. Genus Pseudoalteromonas
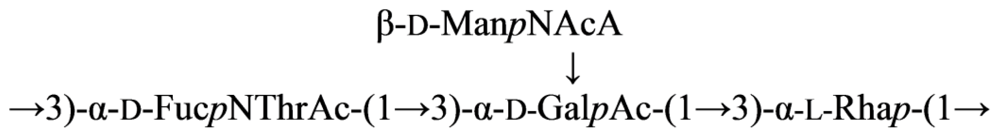
2.4. Genus Plesiomonas
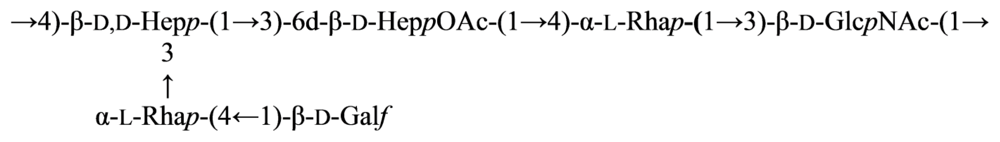
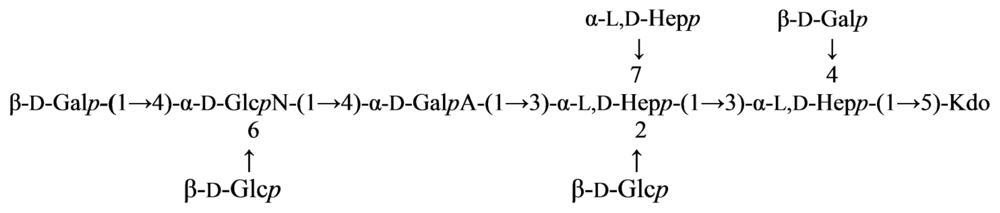
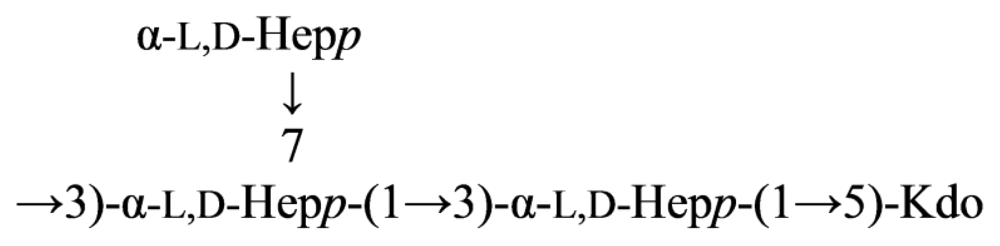
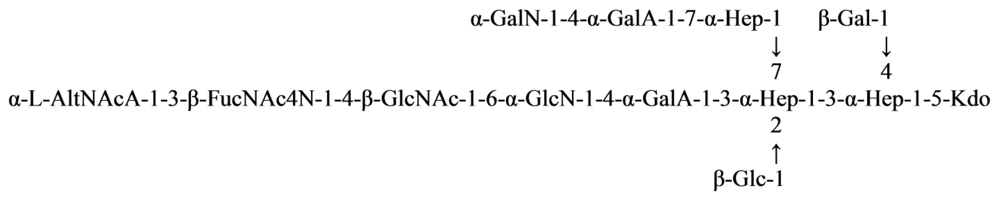

2.5. Genus Shewanella

2.6. Genus Aeromonas
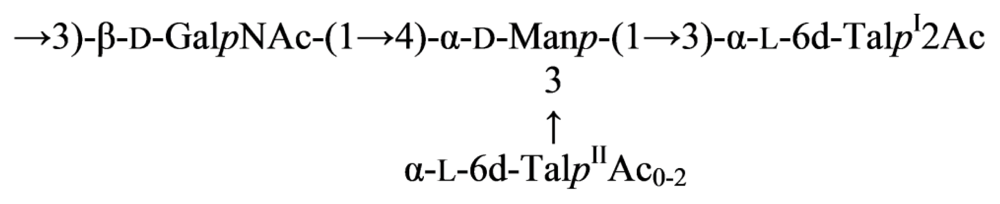
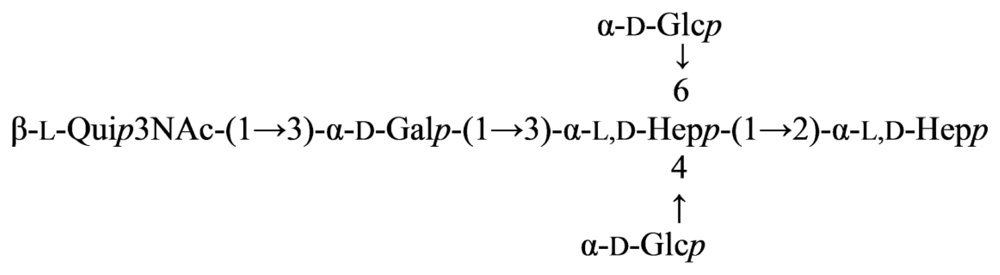

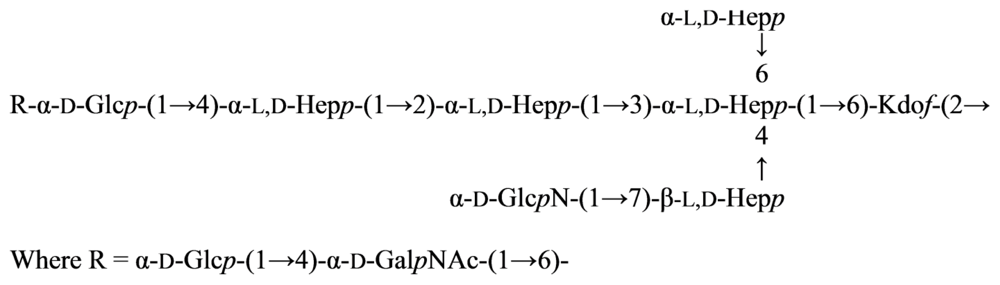
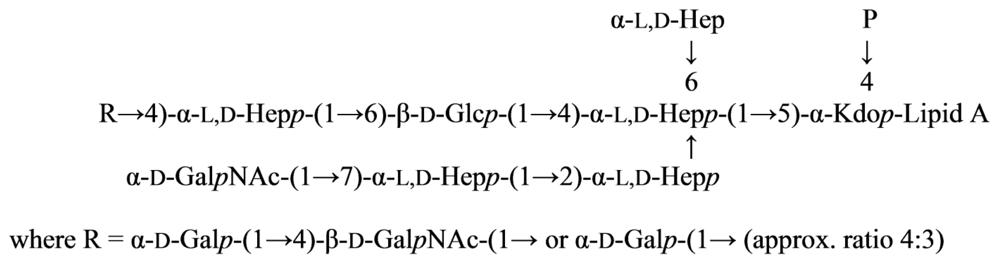



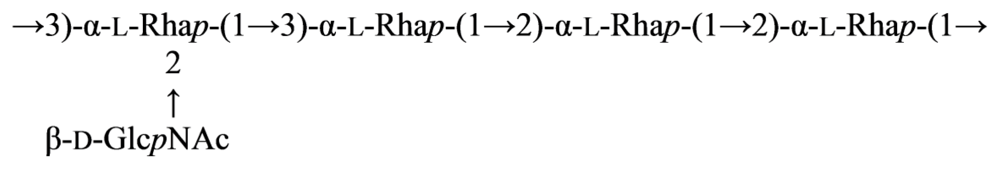
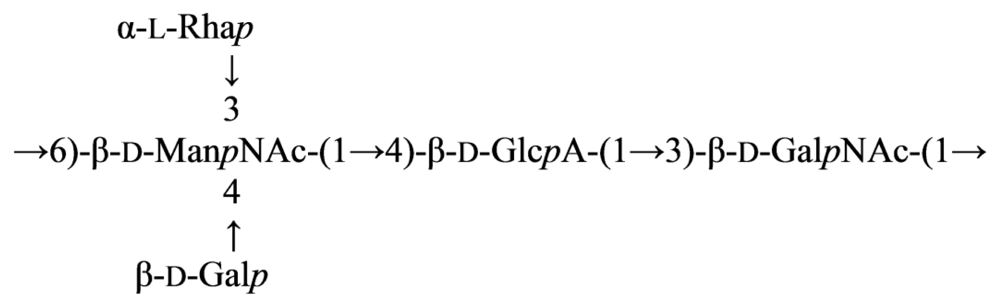
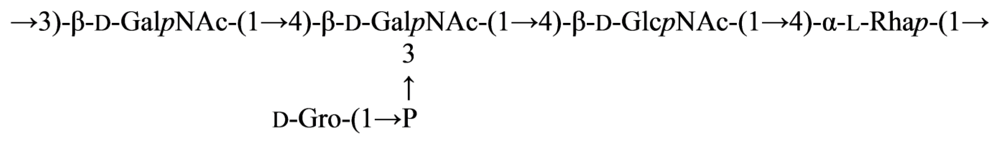
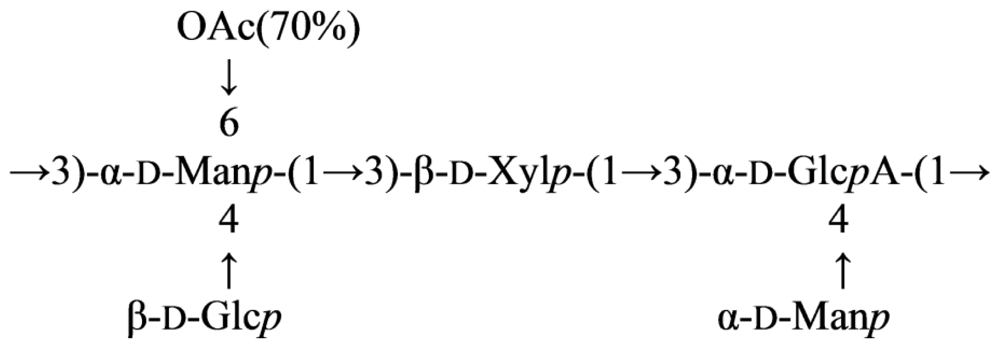
2.7. Genus Idiomarina
3. Structure of Carbohydrate Antigens of Cytophaga-Flavobacterium-Flexibacter Phylum
3.1. Genus Flexibacter
3.2. Genus Flavobacterium
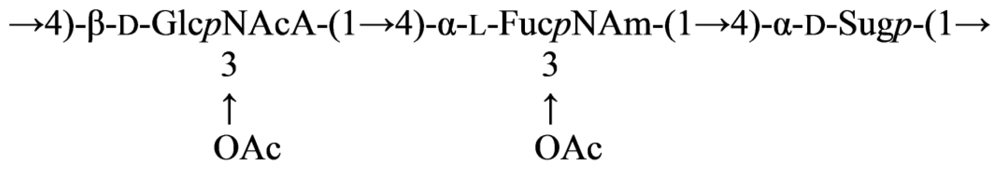
3.3. Genus Cellulophaga
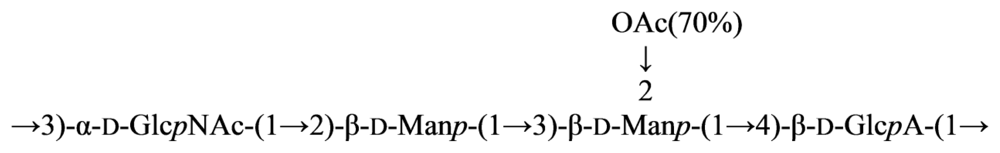
4. Structure of Carbohydrate Antigens of Alphaproteobacteria
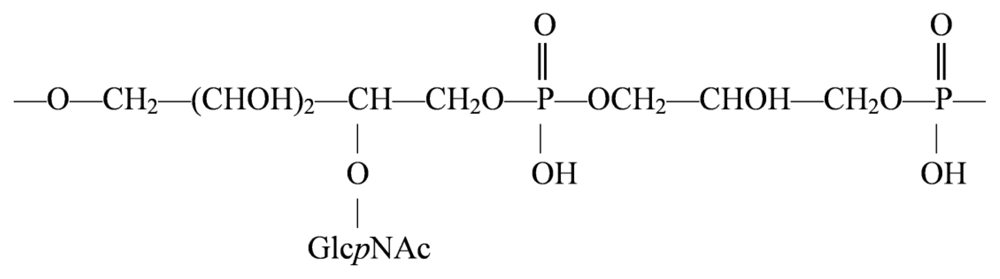
4.1. Genus Sulfitobacter
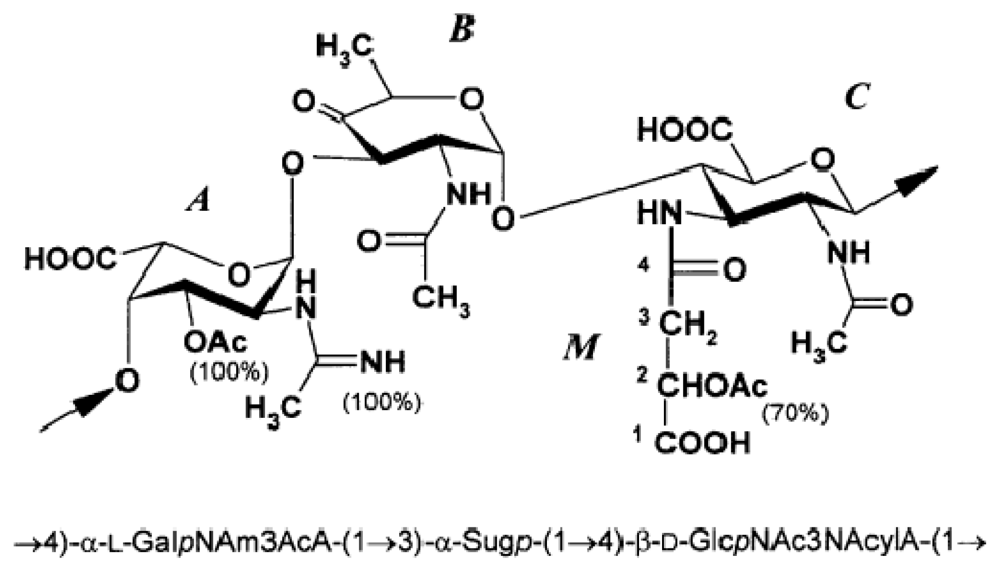
4.2. Genus Loktanella
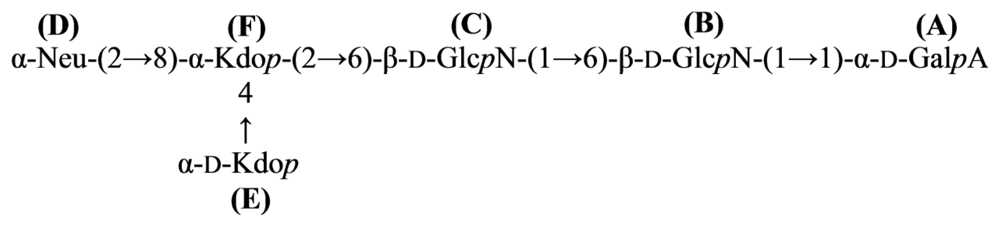
5. Conclusions
Subject Index
Acknowledgments
References
- Head, IM; Jones, DM; Röling, WFM. Marine microorganisms make a meal of oil. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2006, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Hau, HH; Gralnick, JA. Ecology and biotechnology of the genus Shewanella. Ann. Rev. Microbiol 2007, 61, 237–258. [Google Scholar]
- Caroff, M; Karibian, D. Structure of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res 2003, 338, 2431–2447. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, SG. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides—Themes and variations. Prog. Lipid Res 1996, 35, 283–343. [Google Scholar]
- Raetz, CRH; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar]
- Kenne, L; Lindberg, B. Bacterial Polysaccharides. In The Polysaccharides; Aspinall, O, Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 287–363. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, YA; Kochetkov, NK. The structure of lipopolysaccharides of Gram-negative bacteria. III. The structure of O-antigens: A review. Biochemistry (Mosc. ) 1994, 59, 1325–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, P-E. The Chemistry of the Polysaccharide Chains in Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides. In Endotoxin in Health and Disease; Brade, H, Opal, SM, Vogel, S, Morrison, DC, Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 155–178. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, YA. O-specific polysaccharides of Gram-negative bacteria. In Microbial Glycobiology: Structures, Relevance and Applications; Moran, A, Holst, O, Brennan, P, von Itzstein, M, Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2010; pp. 57–73. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarenko, EL; Komandrova, NA; Gorshkova, RP; Tomshich, SV; Zubrov, VA; Kilcoyne, M; Savage, AV. Structures of polysaccharides and oligosaccharides of some Gram-negative marine Proteobacteria. Carbohydr. Res 2003, 338, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarenko, EL. Structure of Carbohydrate Antigens of Some Gram-negative Marine Proteobacteria. In Nanoscale Structure and Properties of Microbial Cell Surfaces; Ivanova, EP, Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 111–144. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, S; Silipo, A; Nazarenko, EL; Lanzetta, R; Parrilli, M; Molinaro, A. Molecular structure of endotoxins from gram-negative marine bacteria: An update. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 85–112. [Google Scholar]
- Holst, O. Chemical structure of the core region of lipopolysaccharides. In Endotoxin in Health and Disease; Brade, H, Morrison, DC, Opal, S, Vogel, S, Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 115–154. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, E; Korenevsky, A; Beveridge, TJ. The structure of the rough-type lipopolysaccharide from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, containing 8-amino-8-deoxy-Kdo and an open-chain form of 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-d-galactose. Carbohydr. Res 2003, 338, 1991–1997. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, E; Korenevsky, A; Beveridge, TJ. The structure of the core region of the lipopolysaccharide from Shewanella algae BrY, containing 8-amino-3,8-dideoxy-d-manno-oct- 2-ulosonic acid. Carbohydr. Res 2004, 339, 737–740. [Google Scholar]
- Silipo, A; Leone, S; Molinaro, A; Sturiale, L; Garozzo, D; Nazarenko, EL; Gorshkova, RP; Ivanova, EP; Lanzetta, R; Parrilli, M. Complete structural elucidation of a novel lipooligosaccharide from the outer membrane of the marine bacterium Shewanella pacifica. Eur. J. Org. Chem 2005, 2005, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar]
- Silipo, A; Molinaro, A; Nazarenko, EL; Sturiale, L; Garozzo, D; Gorshkova, RP; Nedashkovskaya, OI; Lanzetta, R; Parrilli, M. Structural characterization of the carbohydrate backbone of the lipooligosaccharide of the marine bacterium Arenibacter certesii strain KMM 3941T. Carbohydr. Res 2005, 340, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, S; Molinaro, A; Sturiale, L; Garozzo, D; Nazarenko, EL; Gorshkova, RP; Ivanova, EP; Shevchenko, LS; Lanzetta, R; Parrilli, M. The outer membrane of the marine Gram-negative bacterium Alteromonas addita is composed of a very short-chain lipopolysaccharide with a high negative charge density. Eur. J. Org. Chem 2007, 2007, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Taxonomy Browser. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi accesed on 26 September 2011.
- Ivanova, EP; Flavier, S; Christen, R. Phylogenetic relationships among marine Alteromonas-like proteobacteria: Emended description of the family Alteromonadaceae and proposal of Pseudoalteromonadaceae fam. nov., Colwelliaceae fam. nov., Shewanellaceae fam. nov., Moritellaceae fam. nov., Ferrimonadaceae fam. nov., Idiomarinaceae fam. nov. and Psychromonadaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 2004, 54, 1773–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, EP; Bowman, JP; Lysenko, AM; Zhukova, NV; Gorshkova, NM; Sergeev, AF; Mikhailov, VV. Alteromonas addita sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 2005, 55, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, EP; Gorshkova, NM; Mikhailov, VV; Sergeev, AF; Gladkikh, RV; Goryachev, VA; Dudarev, OV; Botsul, AI; Mozherovsky, AV; Slinko, EN; et al. Distribution of saprophytic bacteria in the atomic submarine accident zone in Chazhma Bay, Sea of Japan. Russ. J. Mar. Biol 2005, 31, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkova, RP; Isakov, VV; Denisenko, VA; Nazarenko, EL; Ivanova, EP; Shevchenko, LS. Structure of the repeating unit of the Alteromonas addita type strain KMM 3600T O-specific polysaccharide. Chem. Nat. Compd. (Russ. ) 2008, 44, 549–551. [Google Scholar]
- Raguenes, GH; Peres, A; Ruimy, R; Pignet, P; Christen, R; Loaec, M; Rougeaux, H; Barbier, G; Guezennec, JG. Alteromonas infernus sp. nov., a new polysaccharide-producing bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. J. Appl. Microbiol 1997, 82, 422–430. [Google Scholar]
- Roger, O; Kervarec, N; Ratiskol, J; Colliec-Jouault, S; Chevolot, L. Structural studies of the main exopolysaccharide produced by the deep-sea bacterium Alteromonas infernus. Carbohydr. Res 2004, 339, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar]
- González, JM; Mayer, F; Moran, MA; Hodson, RE; Whitman, WB. Microbulbifer hydrolyticus gen. nov., sp. nov., and Marinobacterium georgiense gen. nov., sp. nov., two marine bacteria from a lignin-rich pulp mill waste enrichment community. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol 1997, 47, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkova, RP; Isakov, VV; Nedashkovskaya, OI; Nazarenko, EL. Structure of carbohydrate antigens from Microbulbifer sp. KMM 6242. Chem. Nat. Compd. (Russ. ) 2011, 46, 837–840. [Google Scholar]
- Hanniffy, OM; Shashkov, AS; Senchenkova, SN; Tomshich, SV; Komandrova, NA; Romanenko, LA; Knirel, YA; Savage, AV. Structure of a highly acidic O-specific polysaccharide of lipopolysaccharide of Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis KMM 223 containing l-iduronic acid and -QuiNHb4NHb. Carbohydr. Res 1998, 307, 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Hanniffy, OM; Shashkov, AS; Senchenkova, SN; Tomshich, SV; Komandrova, NA; Romanenko, LA; Knirel, YA; Savage, AV. Structure of an acidic O-specific polysaccharide of Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis type strain ATCC 14393 containing 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-d and -l-galacturonic acids and 3-(N-acetyl-d-alanyl)amino-3,6-dideoxy-d-glucose. Carbohydr. Res 1999, 321, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon, J; Shashkov, AS; Senchenkova, SN; Tomshich, SV; Komandrova, NA; Romanenko, LA; Knirel, YA; Savage, AV. Structure of an acidic polysaccharide from a marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas distincta KMM 638 containing 5-acetamido-3,5,7,9- tetradeoxy-7-formamido-l-glycero-l-manno-nonulosonic acid. Carbohydr. Res 2001, 330, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zubkov, VA; Nazarenko, EL; Gorshkova, RP; Ivanova, EP; Shashkov, AS; Knirel, YA; Paramonov, NA; Ovodov, YS. Structure of the capsular polysaccharide from Alteromonas sp. CMM 155. Carbohydr. Res 1995, 275, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarenko, EL; Zubkov, VA; Shashkov, AS; Knirel, YA; Gorshkova, RP; Ivanova, EP; Ovodov, YS. Structure of the repeating unit of an acidic polysaccharide from Alteromonas macleodii 2MM6. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem 1993, 19, 740–751. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkova, RP; Nazarenko, EL; Zubkov, VA; Shashkov, AS; Knirel, YA; Paramonov, NA; Meshkov, SV; Ivanova, EP. Structure of the capsular polysaccharide from Alteromonas nigrifaciens IAM 13010T containing 2-acetamido-2,6-dideoxy-l-talose and 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid. Carbohydr. Res 1997, 299, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon, J; Perepelov, AV; Shashkov, AS; Nazarenko, EL; Zubkov, VA; Gorshkova, RP; Ivanova, EP; Gorshkova, NM; Knirel, YA; Savage, AV. Structure of an acidic polysaccharide from the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas flavipulchra NCIMB 2033T. Carbohydr. Res 2003, 338, 459–462. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg, B. Bacterial polysaccharides: Components. In Polysaccharides: Structural Diversity and Functional Versatility; Dumitriu, S, Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 237–273. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkova, RP; Nazarenko, EL; Zubkov, VA; Ivanova, EP; Ovodov, YS; Shashkov, AS; Knirel, YA. Structure of the repeating unit of an acidic polysaccharide from Alteromonas haloplanktis KMM 156. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem 1993, 19, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Komandrova, NA; Tomshich, SV; Isakov, VV; Romanenko, LA. Structure of the sulphated O-specific polysaccharide of the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas marinoglutinosa KMM 232. Biochemistry (Mosc. ) 1998, 63, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Rougeaux, H; Guezennec, J; Carlson, RW; Kervarec, N; Pichon, R; Talaga, P. Structural determination of the exopolysaccharide of Pseudoalteromonas strain HYD 721 isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Carbohydr. Res 1999, 315, 273–285. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkova, RP; Nazarenko, EL; Isakov, VV; Zubkov, VA; Gorshkova, NM; Romanenko, LA; Ivanova, EP. Structure of the glycerophosphate-containing O-specific polysaccharide from Pseudoalteromonas sp. KMM 639. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem 1998, 24, 839–841. [Google Scholar]
- Romanenko, LA; Zhukova, NV; Rhode, M; Lysenko, AM; Mikhailov, V; Stackebrandt, E. Pseudoalteromonas agarivorans sp. nov., a novel marine agarolytic bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 2003, 53, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Komandrova, NA; Isakov, VV; Tomshich, SV; Romanenko, LA; Perepelov, AV; Shashkov, AS. Structure of an acidic O-specific polysaccharide of the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas agarivorans KMM 232 (R-form). Biochemistry (Mosc. ) 2010, 75, 623–628. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, EP; Sawabe, T; Lysenko, AM; Gorshkova, NM; Hayashi, K; Zhukova, NV; Nicolau, DV; Christen, R; Mikhailov, VV. Pseudoalteromonas translucida sp. nov. and Pseudoalteromonas paragorgicola sp. nov., and emended description of the genus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Bacteriol 2002, 52, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Holmstrom, C; Kjelleberg, S. Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol 1999, 30, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier, MJ. Alteromonas rubra sp. nov., a new marine antibiotic-producing bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol 1976, 26, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier, MJ. Modification of bacterial respiration by a micromolecular polyanionic antibiotic produced by a marine Alteromonas. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 1976, 9, 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinovskaya, NI; Ivanova, EP; Alexeeva, YV; Gorshkova, NM; Kuznetsova, TA; Dmitrenok, AS; Nicolau, DV. Low-molecular-weight, biologically active compounds from marine Pseudoalteromonas species. Curr. Microbiol 2004, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, PR; Fenical, W. Strategies for the discovery of secondary metabolites from marinebacteria: ecological perspectives. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 1994, 48, 559–584. [Google Scholar]
- Kilcoyne, M; Shashkov, AS; Knirel, YA; Gorshkova, RP; Nazarenko, EL; Ivanova, EP; Gorshkova, NM; Senchenkova, SN; Savage, AV. The structure of the O-polysaccharide of the Pseudoalteromonas rubra ATCC 29570T lipopolysaccharide containing a keto sugar. Carbohydr. Res 2005, 340, 2369–2375. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, E; Korenevsky, A; Beveridge, TJ. The structure of the O-specific polysaccharide chain of the Shewanella algae BrY lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res 2003, 338, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, P-E; Lindberg, B; Lindquist, U. Structural studies of the capsular polysaccharide from Streptococcus pneumoniae type V. Carbohydr. Res 1985, 140, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Sadovskaya, I; Brisson, J-R; Kheu, NH; Mutharia, LM; Altman, E. Structural characterization of the lipopolysaccharide O-antigen and capsular polysaccharide of Vibrio ordalii serotype O:2. Eur. J. Biochem 1998, 253, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- MacLean, LL; Perry, MB; Crump, EM; Kay, WW. Structural characterization of the lipopolysaccharide O-polysaccharide antigen produced by Flavobacterium columnare ATCC 43622. Eur. J. Biochem 2003, 270, 3440–3446. [Google Scholar]
- Senchenkova, SN; Shashkov, AS; Knirel, YA; Esteve, C; Alcaide, E; Merino, S; Tomas, JM. Structure of a polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Vibrio vulnificus clinical isolate YJ016 containing 2-acetimidoylamino-2-deoxy-l-galacturonic acid. Carbohydr. Res 2009, 344, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Shashkov, AS; Senchenkova, SN; Chizhov, AO; Knirel, YA; Esteve, C; Alcaide, E; Merino, S; Tomas, JM. Structure of a polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharides of Vibrio vulnificus strains CECT 5198 and S3-I2-36, which is remarkably similar to the O-polysaccharide of Pseudoalteromonas rubra ATCC 29570. Carbohydr. Res 2009, 344, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Findlay, JA; Jaseja, M; Brisson, J-R. Forbeside C, a saponin from Asterias forbesi. Complete structure by nuclear magnetic resonance methods. Can. J. Chem 1987, 65, 2605–2611. [Google Scholar]
- Itakura, Y; Komori, T. Structure elucidation of two new oligoglycoside sulfates, versicoside B and versicoside C. Liebigs Ann. Chem 1986, 1986, 359–373. [Google Scholar]
- Okano, K; Nakamura, T; Kamiya, Y; Ikegami, S. Structure of ovarian asterosaponin-1 in the starfish Asterias amurensis. Agric. Biol. Chem 1981, 45, 805–807. [Google Scholar]
- Ruimy, R; Breittmayer, V; Elbaze, P; Lafay, B; Boussemart, O; Gauthier, M; Christen, R. Phylogenetic analysis and assessment of the genera Vibrio, Photobacterium, Aeromonas, and Plesiomonas deduced from small-subunit rRNA sequences. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol 1994, 44, 416–426. [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten, R; Farberman, D; Norton, J; Ellison, J; Kiehlbauch, J; Morris, T; Smith, P. Plesiomonas shigelloides and Salmonella serotype Hartford infections associated with a contaminated water supply-Livingston County, New York, 1996. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep 1998, 47, 394–396. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, DA; Bens, MS; Craun, GF; Calderon, RL; Herwaldt, BL. Surveillance for waterborne-disease outbreaks—United States 1995–1996. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep 1998, 47, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, S; Matsushita, S; Dejsirilert, S; Kudoh, Y. Incidence and clinical symptoms of Aeromonas-associated travellers’ diarrhoea in Tokyo. Epidemiol. Infect 1997, 119, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Rautelin, H; Sivonen, A; Kuikka, A; Renkonen, OV; Valtonen, V; Kosunen, TU. Enteric Plesiomonas shigelloides infections in Finnish patients. Scand. J. Infect. Dis 1995, 27, 495–498. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, AC; Yuen, KY; Ha, SY; Chiu, DC; Lau, YL. Plesiomonas shigelloides septicemia: Case report and literature review. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol 1996, 13, 265–269. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, K; Shirai, M; Ishioka, T; Kakuya, F. Neonatal Plesiomonas shigelloides septicemia and meningitis: A case and review. Acta Paediatr. Jpn 1994, 36, 450–452. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, L; Monte, R; Ramirez, M; Garcia, B; Urbaskova, P; Aldova, E. Characterization of Plesiomonas shigelloides from diarrheic children. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 1998, 6, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Korner, RJ; MacGowan, AP; Warner, B. The isolation of Plesiomonas shigelloides in polymicrobial septicemia originating from the biliary tree. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. Virol. Parasitol. Infect. Dis 1992, 277, 334–339. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, T; Sakazaki, R. On the serology of Plesiomonas shigelloides. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol 1978, 31, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, T; Arakawa, E; Itoh, K; Kosako, Y; Inoue, K; Zhengshi, Y; Aldova, E. New O and H antigens of Plesiomonas shigelloides and their O antigenic relationships to Shigella boydii. Curr. Microbiol 1994, 28, 351–354. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, MJ; Ansaruzzaman, M; Quadri, F; Hossain, A; Kibriya, AK; Haider, K; Faruque, SM; Alam, AN. Characterisation of Plesiomonas shigelloides strains that share type-specific antigen with Shigella flexneri 6 and common group 1 antigen with Shigella flexneri spp. ans Shigella dysenteriae 1. J. Med. Microbiol 1993, 39, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Linnerborg, M; Widmalm, G; Weintraub, A; Albert, MJ. Structural elucidation of the O-antigen lipopolysaccharide from two strains of Plesiomonas shigelloides that share a type specific antigen with Shigella flexneri 6, and the common group 1 antigen with Shigella flexneri spp and Shigella dysenteriae 1. Eur. J. Biochem 1995, 231, 839–844. [Google Scholar]
- Czaja, J; Jachymek, W; Niedziela, T; Lugowski1, C; Aldova, E; Kenne, L. Structural studies of the O-specific polysaccharide from Plesiomonas shigelloides strain CNCTC 113/92. Eur. J. Biochem 2000, 267, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Niedziela, T; Dag, S; Lukasiewicz, J; Dzieciatkowska, M; Jachymek, W; Lugowski, C; Kenne, L. Complete lipopolysaccharide of Plesiomonas shigelloides O74:H5 (strain CNCTC 144/92). 1. Structural analysis of the highly hydrophobic lipopolysaccharide, including the O-antigen, its biological repeating unit, the core oligosaccharide, and the linkage between them. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10422–10433. [Google Scholar]
- Pieretti, G; Corsaro, MM; Lanzetta, R; Parrilli, M; Canals, R; Merino, S; Tomas, JM. Structural studies of the O-chain polysaccharide from Plesiomonas shigelloides strain 302-73 (serotype O1). Eur. J. Org. Chem 2008, 2008, 3149–3155. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewska, A; Lukasiewicz, J; Niedziela, T; Szewczuk, Z; Lugowski, C. Structural analysis of the O-specific polysaccharide isolated from Plesiomonas shigelloides O51 lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res 2009, 344, 894–900. [Google Scholar]
- Goethals, K; Leyman, B; Van Den Eede, G; Van Montagu, M; Holsters, M. An Azorhizobium caulinodans ORS571 locus involved in lipopolysaccharide production and nodule formation on Sesbania rostrata stems and roots. J. Bacteriol 1994, 176, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, H; Knirel, YA; Helbig, JH; Zahringer, U. Identification of an alpha-d-Manp-(1→8)-Kdo disaccharide in the inner core region and the structure of the complete core region of the Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res 1997, 304, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Banoub, JH; Aneed, AEl; Cohen, AM; Joly, N. Structural investigation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides by mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev 2010, 29, 606–650. [Google Scholar]
- Niedziela, T; Lukasiewicz, J; Jachymek, W; Dzieciatkowska, M; Lugowski, C; Kenne, L. Core oligosaccharides of Plesiomonas shigelloides O54:H2 (strain CNCTC 113/92). J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 11653–11663. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, JJ, III; Arduino, MJ; Hickman-Brenner, FW. Balows, A, Trũper, HG, Dworkin, M, Wim, H, Schleifer, KH, Eds.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 3, pp. 3012–3043.
- Szu, SC; Robbins, JB; Schneerson, R; Pozsgay, V; Chu, C. Polysaccharide-based conjugate vaccines for enteric bacterial infections: typhoid fever, nontyphoid salmonellosis, shigellosis, cholera, and Esherichia coli 0157. In New Generation Vaccines; Levine, MM, Kaper, JB, Rappuoli, R, Liu, MA, Good, MF, Eds.; Informa Healthcare: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 934–939. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, JG; Wang, L; Reeves, PR. Comparison of O-antigen gene clusters of Escherichia coli (Shigella) sonnei and Plesiomonas shigelloides O17: Sonnei gained its current plasmid-borne O-antigen genes from P. shigelloides in a recent event. Infect. Immun 2000, 68, 6056–6061. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, DN; Trofa, AC; Sadoff, J; Chu, C; Bryla, D; Shiloach, J; Cohen, D; Ashkenazi, S; Lerman, Y; Egan, W. Synthesis, characterization, and clinical evaluation of conjugate vaccines composed of the O-specific polysaccharides of Shigella dysenteriae type 1, Shigella flexneri type 2a, and Shigella sonnei (Plesiomonas shigelloides) bound to bacterial toxoids. Infect. Immun 1993, 61, 3678–3687. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, H; Nakamura, A. Identification of Shigella sonnei form I plasmid genes necessary for cell invasion and their conservation among Shigella species and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun 1986, 53, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Sayeed, S; Sack, DA; Qadri, F. Protection from Shigella sonnei infection by immunisation of rabbits with Plesiomonas shigelloides (SVC O1). J. Med. Microbiol 1992, 37, 382–384. [Google Scholar]
- Kubler-Kielb, J; Schneerson, R; Mocca, C; Vinogradov, E. The elucidation of the structure of the core part of the LPS from Plesiomonas shigelloides serotype O17 expressing O-polysaccharide chain identical to the Shigella sonnei O-chain. Carbohydr. Res 2008, 343, 3123–3127. [Google Scholar]
- Pieretti, G; Corsaro, MM; Lanzetta, R; Parrilli, M; Vilches, S; Merino, S; Tomás, JM. Structure of the core region from the lipopolysaccharide of Plesiomonas shigelloides strain 302-73 (serotype O1). Eur. J. Org. Chem 2009, 2009, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Pieretti, G; Carillo, S; Lindner, B; Rosa Lanzetta, R; Parrilli, M; Natalia Jimenez, N; Regue, M; Tomas, JM; Corsaro, MM. The complete structure of the core of the LPS from Plesiomonas shigelloides 302-73 and the identification of its O-antigen biological repeating unit. Carbohydr. Res 2010, 345, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, EV; Lindner, B; Kocharova, NA; Senchenkova, SN; Shashkov, AS; Knirel, YA; Holst, O; Gremyakova, TA; Shaikhutdinova, RZ; Anisimov, AP. The core structure of the lipopolysaccharide from the causative agent of plague, Yersinia pestis. Carbohydr. Res 2002, 337, 775–777. [Google Scholar]
- Isshiki, Y; Kawahara, K; Zahringer, U. Isolation and characterisation of disodium (4-amino-4- deoxy-β-l-arabinopyranosyl)-(1→8)-d-glycero-α-d-talo-oct-2-ulopyranosylonate)-(2→4)-(methyl 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulopyranosid)onate from the lipopolysaccharide of Burkholderia cepacia. Carbohydr. Res 1998, 313, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara, K; Brade, H; Rietschel, ET; Zahringer, U. Studies on the chemical structure of the core-lipid A region of the lipopolysaccharide of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus NCTC 10305: Detection of a new 2-octulosonic acid interlinking the core oligosaccharide and lipid A component. Eur. J. Biochem 1987, 163, 489–495. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, EV; Lindner, B; Seltmann, G; Radziejewska-Lebrecht, J; Holst, O. Lipopolysaccharides from Serratia marcescens possess one or two 4-amino-4-deoxy-larabinopyranose 1-phosphate residues in the lipid A and d-glycero-d-talo-oct-2-ulopyranosonic acid in the inner core region. Chem. Eur. J 2006, 12, 6692–6700. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, AE; Lies, D; Li, G; Nealson, K; Zhou, J; Tiedje, JM. DNA/DNA hybridization to microarrays reveals gene-specific differences between closely related microbial genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9853–9858. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, E; Nossova, L; Korenevsky, A; Beveridge, TJ. The structure of the capsular polysaccharide of Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-4. Carbohydr. Res 2005, 340, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, E; Kubler-Kielb, J; Korenevsky, A. The structure of the carbohydrate backbone of the LPS from Shewanella spp. MR-4. Carbohydr. Res 2008, 343, 2701–2705. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarenko, EL; Perepelov, AV; Shevchenko, LS; Daeva, ED; Ivanova, EP; Shashkov, AS; Widmalm, G. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide from Shewanella japonica KMM 3601 containing 5,7-diacetamido-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-d-glycero-d-talo-non-2-ulosonic acid. Biochemistry (Mosc. ) 2011, 76, 791–796. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, YA; Senchenkova, SN; Kocharova, NA; Shashkov, AS; Helbig, JH; Zähringer, U. Identification of a homopolymer of 5-acetamidino-7-acetamido-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-d-glycero-dtalo- nonulosonic acid in the lipopolysaccharides of Legionella pneumophila non-1 serogroups. Biochemistry (Mosc. ) 2001, 66, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B; Adams, C. Fish Pathogens. In The Genus Aeromonas; Austin, B, Altwegg, M, Gosling, PJ, Joseph, S, Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1996; pp. 197–244. [Google Scholar]
- Figueras, MJ. Clinical relevance of Aeromonas. Rev. Med. Microbiol 2005, 16, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra, MJ; Guedes-Novais, S; Alves, A; Rema, P; Tacao, M; Correia, A; Martinez-Murcia, AJ. Resistance to β-lactam antibiotics in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Int. Microbiol 2004, 7, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra, MJ; Figueras, MJ; Martinez-Murcia, AJ. Updated phylogeny of the genus Aeromonas. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol 2006, 56, 2481–2487. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Murcia, AJ; Benlloch, S; Collins, MD. Phylogenetic interrelationships of members of the genera Aeromonas and Plesiomonas as determined by 16S ribosomal DNA sequencing: Lack of congruence with results of DNA-DNA hybridizations. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol 1992, 42, 412–421. [Google Scholar]
- Yanez, MA; Catalan, V; Apraiz, D; Figueras, MJ; Martinez-Murcia, AJ. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Aeromonas based on gyrB gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 2003, 53, 875–883. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, JM; Abbott, SL; Khashe, S; Kellogg, GH; Shimada, T. Further studies on biochemical characteristics and serologic properties of the genus Aeromonas. J. Clin. Microbiol 1996, 34, 1930–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, JM; Guthertz, LS; Kokka, RP; Shimada, T. Aeromonas species in septicemia: Laboratory characteristics and clinical observations. Clin. Infect. Dis 1994, 19, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, YA; Shashkov, AS; Senchenkova, SN; Merino, S; Tomas, JM. Structure of the O-polysaccharide of Aeromonas hydrophila O:34; a case of random O-acetylation of 6-deoxy-l-talose. Carbohydr. Res 2002, 337, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Banoub, JH; Shaw, DH. Structural investigations on the core oligosaccharide of Aeromonas hydrophila (chemotype III) lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res 1981, 98, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, YA; Vinogradov, E; Jimenez, N; Merino, S; Tomás, JM. Structural studies on the R-type lipopolysaccharide of Aeromonas hydrophila. Carbohydr. Res 2004, 339, 787–793. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z; Larocque, S; Vinogradov, E; Brisson, J-R; Dacanay, A; Greenwell, M; Brown, LL; Li, J; Altman, E. Structural studies of the capsular polysaccharide and lipopolysaccharide O-antigen of Aeromonas salmonicida strain 80204-1 produced under in vitro and in vivo growth conditions. Eur. J. Biochem 2004, 271, 4507–4516. [Google Scholar]
- Sadovskaya, I; Brisson, J-R; Mutharia, LM; Altman, E. Structural studies of the lipopolysaccharide O-antigen and capsular polysaccharide of Vibrio anguillarum serotype O:2. Carbohydr. Res 1996, 283, 111–127. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, DH; Hart, MJ; Lüderitz, O. Structure of the core oligosaccharide in the lipopolysaccharide isolated from Aeromonas salmonicida ssp. salmonicida. Carbohydr. Res 1992, 231, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z; Li, J; Vinogradov, E; Altman, E. Structural studies of the core region of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res 2006, 341, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, MJ. Vibrio cholerae O139 Bengal. J. Clin. Microbiol 1994, 32, 2345–2349. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, MJ; Ansaruzzaman, M; Shimada, T; Rahman, A; Bhuiyan, NA; Nahar, S; Qadri, E; Islam, MS. Character-ization of Aeromonus trota strains that cross-react with Vibrio cholerae O139 Bengal. J. Clin. Microbiol 1995, 33, 3119–3123. [Google Scholar]
- Waldor, MK; Mekalanos, JJ. Vibrio cholerae O139 specific gene sequences. Lancet 1994, 343, 1366. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, YA; Paredes, L; Jansson, P-E; Weintraub, A; Widmalm, G; Albert, MJ. Structure of the capsular polysaccharide of Vibrio cholerae O139 synonym Bengal containing d-galactose-4,6-cyclophosphate. Eur. J. Biochem 1995, 232, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, YA; Senchenkova, SN; Jansson, P-E; Weintraub, A; Ansaruzzaman, M; Albert, MJ. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of an Aerornonas trota strain cross-reactive with Vibrio cholerae O139 Bengal. Eur. J. Biochem 1996, 238, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M; Carlin, N; Leontein, K; Lindquist, U; Slettengren, K. Structural studies of the O-antigenic polysaccharide of Escherichia coli 086, which possesses blood-group B activity. Carbohydr. Res 1989, 185, 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, MB; MacLean, LL. Structure of the polysaccharide O-antigen of Salmonella riogrande O:40 (group R) related to blood group A activity. Carbohydr. Res 1992, 232, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kozinska, A; Figueras, MJ; Chacon, MR; Soler, L. Phenotypic characteristics and pathogenicity of Aeromonas genomospecies isolated from common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). J. Appl. Microbiol 2002, 93, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Kozinska, A; Guz, L. The effect of various Aeromonas bestiarum vaccines on non-specific immune parameters and protection of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 2004, 16, 437–445. [Google Scholar]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A; Kozinska, A; Russa, R; Holst, O. The structure of the O-specific polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Aeromonas bestiarum strain 207. Carbohydr. Res 2010, 345, 680–684. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z; Liu, X; Dacanay, A; Harrison, BA; Fast, M; Colquhoun, DJ; Lund, V; Brown, LL; Li, J; Altman, E. Carbohydrate analysis and serological classification of typical and atypical isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida: A rationale for the lipopolysaccharide-based classification of A. salmonicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2007, 23, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Linnenborg, M; Wildmalm, G; Rahman, MM; Jansson, P-E; Holme, T; Qadri, F; Albert, MJ. Structural studies of the O-antigenic polysaccharide from an Aeromonas caviae strain. Carbohydr. Res 1996, 291, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Barer, MR; Millership, SE; Tabaqchali, S. Relationship of toxin production to species in the genus Aeromonas. J. Med. Microbiol 1986, 22, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Bechet, M; Blondeau, R. Factors associated with the adherence and biofilm formation by Aeromonas caviae on glass surfaces. J. Appl. Microbiol 2003, 94, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Gryllos, I; Shaw, JG; Gavin, R; Merino, S; Tomas, JM. Role of flm locus in mesophilic Aeromonas species adherence. Infect. Immun 2001, 69, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z; Liu, X; Li, J; Altman, E. Structural characterization of the O-chain polysaccharide of Aeromonas caviae ATCC 15468 lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res 2008, 343, 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Kocharova, NA; Thomas-Oates, JE; Knirel, YA; Shashkov, AS; Dabrowski, U; Kochetkov, NK; Stanislavsky, ES; Klolodkova, EV. The structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Citrobacter O16 containing glycerol phosphate. Eur. J. Biochem 1994, 219, 653–661. [Google Scholar]
- Jachymek, W; Czaja, J; Neidziela, T; Lugowski, C; Kenne, L. Structural studies of the O-specific polysaccharide of Hafnia alvei strain PCM 1207 lipopolysaccharide. Eur. J. Biochem 1999, 266, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziejska, K; Perepelov, AV; Zablotni, A; Drzewiecka, D; Senchenkova, SN; Zych, K; Shashkov, AS; Knirel, YA; Sidorczyk, Z. Structure of the glycerol phosphate-containing O-polysaccharides and serological studies of the lipopolysaccharides of Proteus mirabilis CCUG 10704 (OE) and Proteus vulgaris TG 103 classified into a new Proteus serogroup, O54. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol 2006, 47, 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, M; Richards, JC; Perry, MB; Kniskern, PJ. Structural analysis of the specific capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 45 (American type 72). Biochemistry 1988, 27, 6820–6829. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, JM; Abbou, SLJ; Janda, M; Abbott, SL. Evolving concepts regarding the genus Aeromonas: An expanding panorama of species, disease presentations, and unanswered questions. Clin. Infect. Dis 1998, 27, 332–997. [Google Scholar]
- Crivelli, C; Demarta, A; Peduzzi, R. Intestinal secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) response to Aeromonas exoproteins in patients with naturally acquired Aeromonas diarrhea. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol 2001, 30, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Iager, F; Reicher, F; Ganter, JLMS. Structural and rheological properties of polysaccharides from mango (Mangifera indica L.) pulp. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2002, 31, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X; Ruan, D; Jin, Y; Shashkov, AS; Senchenkova, SN; Kilkoyne, M; Zhang, L. Chemical structure of aeromonas gum—Extracellular polysaccharide from Aeromonas nichidenii 5797. Carbohydr. Res 2004, 339, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Ochoa, F; Santos, VE; Casas, JA; Gomes, E. Xanthan gum: Production, recovery, and properties. Biotechnol. Adv 2000, 18, 549–579. [Google Scholar]
- Lattner, D; Flemming, H-C; Mayer, C. 13C-NMR study of the interaction of bacterial alginate with bivalent cations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2003, 18, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Gacesa, P. Alginates. Carbohydr. Polym 1988, 8, 161–182. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, IV. Microbial polysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria. Int. Dairy J 2001, 11, 663–674. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, EP; Romanenko, LA; Chun, J; Matte, MH; Matte, AR; Mikhailov, VV; Svetashev, VI; Huq, A; Maugel, T; Colwell, RR. Idiomarina gen. nov., comprising novel indigenous deep-sea bacteria from the Pacific Ocean, including descriptions of two species, Idiomarina abyssalis sp. nov. and Idiomarina zobellii sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 2000, 50, 901–907. [Google Scholar]
- Kilcoyne, M; Perepelov, AV; Tomshich, SV; Komandrova, NA; Shashkov, AS; Romanenko, LA; Knirel, YA; Savage, AV. Structure of the O-polysaccharide of Idiomarina zobellii KMM 231T containing two unusual amino sugars with the free amino group, 4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-d-glucose and 2-amino-2-deoxy-l-guluronic acid. Carbohydr. Res 2004, 339, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Torii, M; Sakakibara, K; Kuroda, K. Occurrence of 2-amino-2-deoxy-hexuronic acids as constituents of Vibrio parahaemolyticus K15 antigen. Eur. J. Biochem 1973, 37, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkova, RP; Nazarenko, EL; Zubkov, VA; Ivanova, EP; Gorshkova, NM; Isakov, VV. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide from Pseudoalteromonas nigrifaciens KMM 161. Biochemistry (Mosc. ) 2002, 67, 810–814. [Google Scholar]
- Reistad, R. 2-Amino-2-deoxyguluronic acid: A constituent of the cell wall of Halococcus sp., strain 24. Carbohydr. Res 1974, 36, 420–423. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, EV; Shashkov, AS; Knirel, YA; Kochetkov, NK; Tochtamysheva, NV; Averin, SP; Goncharova, OV; Khlebnikov, VS. Structure of the O-antigen of Francisella tularensis strain 15. Carbohydr. Res 1991, 214, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Leslie, MR; Parolis, H; Parolis, LAS. The structure of the O-antigen of Escherichia coli O116:K+:H10. Carbohydr. Res 1999, 321, 246–256. [Google Scholar]
- Parolis, H; Parolis, LAS; Olivieri, G. Structural studies on the Shigella-like Escherichia coli O121 O-specific polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res 1997, 303, 319–325. [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen, E; Romanowska, E; Kocharova, NA; Knirel, YA; Shashkov, AS; Kochetkov, NK. The structure of glycerol teichoic acid-like O-specific polysaccharide of Hafnia alvei 1205. Carbohydr. Res 1992, 231, 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, Y; Sakane, T; Suzuki, M; Hatano, K. Phylogenetic structure of the genera Flexibacter, Flexithrix, and Microscilla deduced from 16S rRNA sequence analysis. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol 2002, 48, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Bernadet, JF. Immunization with bacterial antigens: Flavobacterium and Flexibacterium infections. Dev. Biol. Stand 1997, 90, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Handlinger, J; Soltani, M; Percival, S. The pathology of Flexibacter maritimus in aquaculture species in Tasmania, Australia. J. Fish Dis 1997, 20, 159–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ostland, VE; LaTrace, C; Morrison, D; Ferguson, HW. Flexibacter maritimus associated with bacterial stomatitis in Atlantic salmon smolts reared in net-pens in, British Columbia. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1999, 11, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, E; MacLean, LL; Crump, EM; Perry, MB; Kay, WW. Structure of the polysaccharide chain of the lipopolysaccharide from Flexibacter maritimus. Eur. J. Biochem 2003, 270, 1810–1815. [Google Scholar]
- MacLean, LL; Vinogradov, E; Crump, EM; Perry, MB; Kay, WW. The structure of the lipopolysaccharide O-antigen produced by Flavobacterium psychrophilum (259-93). Eur. J. Biochem 2001, 268, 2710–2716. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardet, JF; Segers, P; Vancanneyt, M; Berthe, F; Kersters, K; Vandamme, P. Cutting a Gordian knot: Emended classification and description of the genus Flavobacterium, emended description of the family Flavobacteriaceae, and proposal of Flavobacterium hydatis nom. nov. (basonym, Cytophaga aquatilis Strohl and Tait 1978). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol 1996, 46, 128–148. [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi, RA; Nanetti, A; Ferri, M; Mastroianni, A; Coronado, OV; Chiodo, F. Flavobacterium spp. organisms as opportunistic pathogens during advanced HIV disease. J. Infect 1999, 39, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ostland, VE; McGrogan, DG; Ferguson, HW. Cephalic osteochondritis and necrotic sceritis in intensively reared salmonids associated with Flexibacter psychrophilus. J. Fish Dis 1997, 20, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard, I. Virulence mechanisms in Cytophaga psychrophilia and other Cytophaga-like bacteria pathogenic for fish. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis 1993, 3, 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Crump, EM; Perry, MB; Clouthier, SC; Kay, WW. Antigenic characterization of the fish pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2001, 67, 750–759. [Google Scholar]
- Hermansson, K; Perry, MB; Altman, E; Brisson, J-R; Garcia, MM. Structural studies of the O-antigenic polysaccharide of Fusobacterium necrophorum. Eur. J. Biochem 1993, 212, 801–809. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, YA; Zdorovenko, GM; Veremeychenko, SN; Lipkind, GM; Shashkov, AS; Zakharova, IY; Kochetkov, NK. The structure of the O-specific polysaccharide chain of Pseudomonas aurantiaca IMB31 lipopolysaccharide. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem 1988, 14, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, TA; Jansson, P-E; Lindberg, B; Lindberg, J. Structural studies of the Vibrio cholerae O:3 O-antigen polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res 1991, 215, 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- Hermasson, K; Jansson, P-E; Holme, T; Gustavsson, B. Structural studies of the Vibrio cholerae O:5 O-antigen polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res 1993, 248, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, YA; Vinogradov, EV; Shashkov, AS; Wilkinson, SG; Tahara, Y; Dmitriev, BA; Kochetkov, NK; Stanislasky, ES; Mashilova, GM. Somatic antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The structure of O-specific polysaccharide chains of the lipopolysaccharide from P. aeruginosa O1 (Lanyi), O3 (Habs), O13 and O14 (Wokatsch), and the serologically related strain NCTC 8505. Eur. J. Biochem 1986, 155, 659–669. [Google Scholar]
- Zehavi, U; Sharon, N. Structural studies of 4-acetamido-2-amino-2,4,6-trideoxy-d-glucose (N-Acetylbacillosamine), the N-acetyl-diamino sugar of Bacillus licheniformis. J. Biol. Chem 1973, 248, 432–435. [Google Scholar]
- Tschesche, R; Hoppe, H-J; Snatzke, G; Wulff, G; Fehlhaber, H-W. On parasorboside, the glycosidic precursor of parasorbic acid, from berries of Mountain Ash. Chem. Ber 1971, 104, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Ofek, I; Doyle, RJ. Bacterial Adhesion to Cells And Tissues; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1994; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tomshich, SV; Komandrova, NA; Widmalm, G; Nedashkovskaya, OI; Shashkov, AS; Perepelov, AV. Structure of an acidic O-specific polysaccharide from Cellulophaga baltica. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem 2007, 33, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov, AV; Shashkov, AS; Tomshich, SV; Komandrova, NA; Nedashkovskaya, OI. A pseudoaminic acid-containing O-specific polysaccharide from a marine bacterium Cellulophaga fucicola. Carbohydr. Res 2007, 342, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshkova, RP; Isakov, VV; Shevchenko, LS; Ivanova, EP; Denisenko, VA; Nazarenko, EL. Structure of teichoic acid from the marine proteobacterium Sulfitobacter brevis KMM 6006. Chem. Nat. Compd. (Russ. ) 2007, 43, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, EP; Zhukova, NV; Lysenko, AM; Gorshkova, NM; Sergeev, AF; Mikhailov, VV; Bowman, JP. Loktanella agnita sp. nov. and Loktanella rosea sp. nov., from the north-west Pacific Ocean. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol 2005, 55, 2203–2207. [Google Scholar]
- Ierano, T; Silipo, A; Nazarenko, EL; Gorshkova, RP; Ivanova, EP; Garozzo, D; Sturiale, L; Lanzetta, R; Parrilli, M; Molinaro1, A. Against the rules: A marine bacterium, Loktanella rosea, possesses a unique lipopolysaccharide. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 586–593. [Google Scholar]
- Raetz, CRH; Reynolds, CM; Trent, MS; Bishop, RE. Lipid A modification systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2007, 76, 295–329. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazarenko, E.L.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. The Structural Diversity of Carbohydrate Antigens of Selected Gram-Negative Marine Bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1914-1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9101914
Nazarenko EL, Crawford RJ, Ivanova EP. The Structural Diversity of Carbohydrate Antigens of Selected Gram-Negative Marine Bacteria. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(10):1914-1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9101914
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazarenko, Evgeny L., Russell J. Crawford, and Elena P. Ivanova. 2011. "The Structural Diversity of Carbohydrate Antigens of Selected Gram-Negative Marine Bacteria" Marine Drugs 9, no. 10: 1914-1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9101914
APA StyleNazarenko, E. L., Crawford, R. J., & Ivanova, E. P. (2011). The Structural Diversity of Carbohydrate Antigens of Selected Gram-Negative Marine Bacteria. Marine Drugs, 9(10), 1914-1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9101914




