Marine Benthic Diatoms Contain Compounds Able to Induce Leukemia Cell Death and Modulate Blood Platelet Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
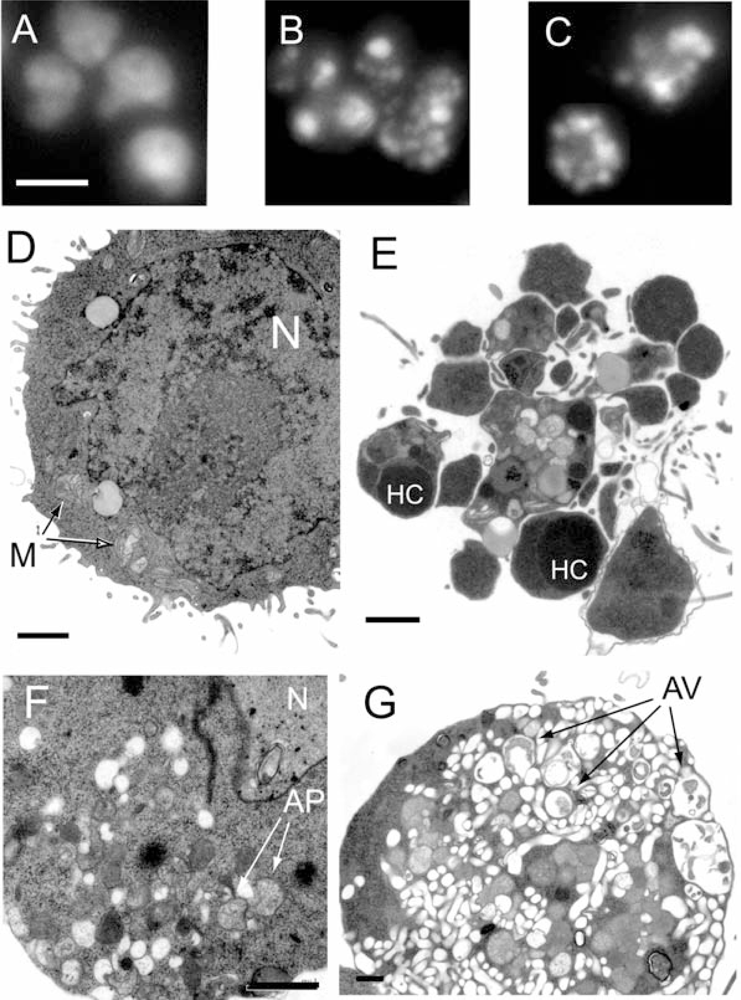
2.1. Marine benthic diatoms are a rich source of leukemia cell death inducing activity
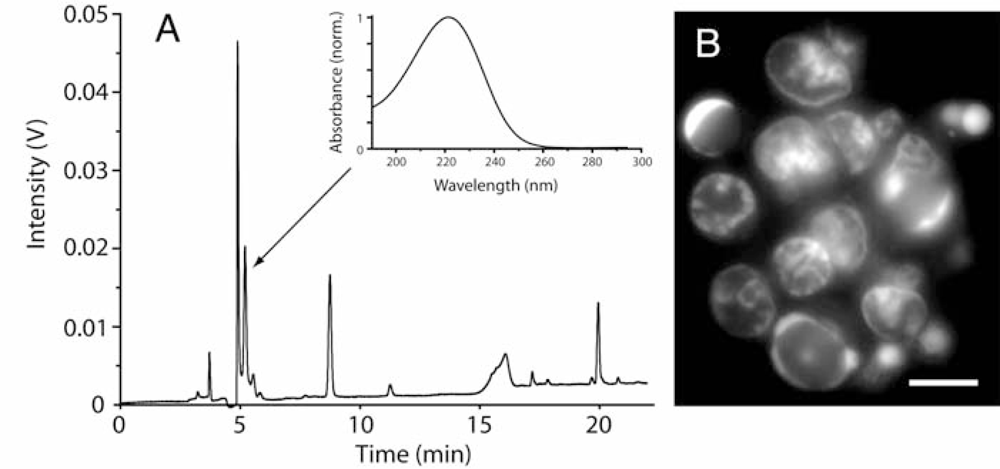
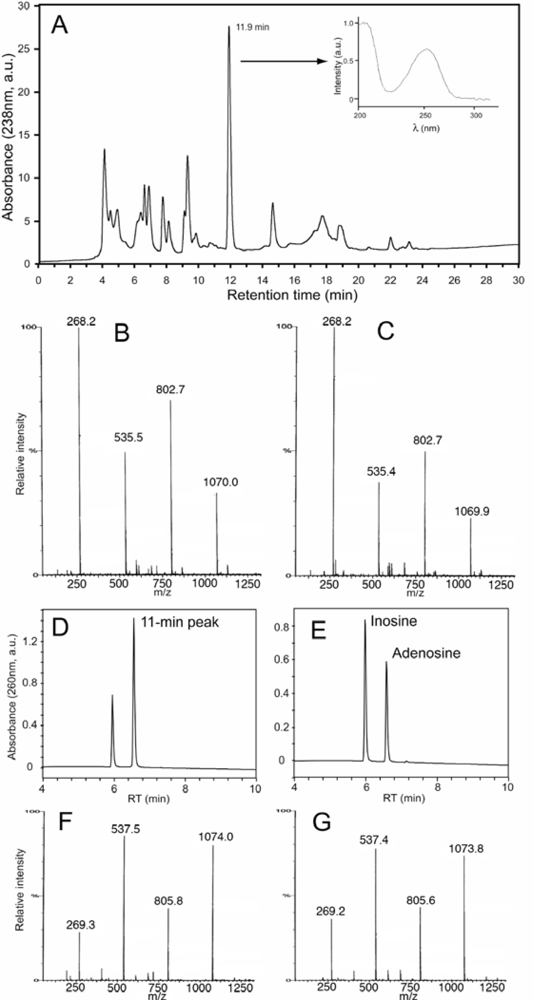
2.2. Diatoms may contain unusually high level of adenosine and other adenosine deaminase-sensitive compounds
2.3. Screen for platelet activation modulating activity in diatom extracts
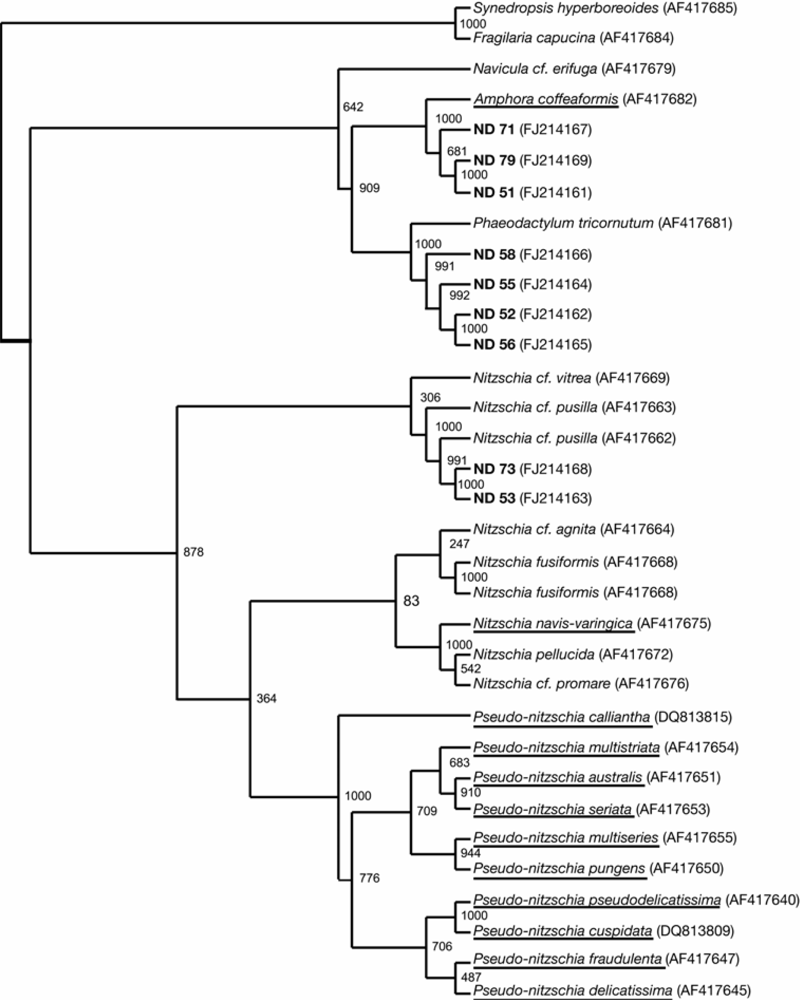
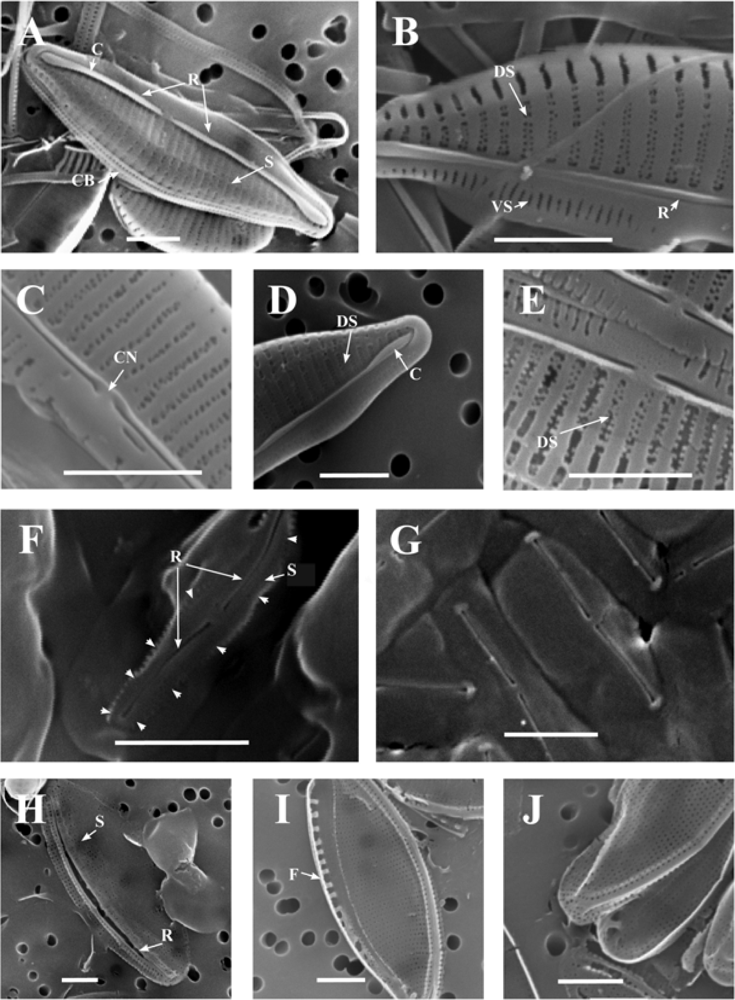
2.4. Taxonomy of the diatom isolates
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Diatom isolation and cultivation
4.2. Preparation of diatom crude extracts
4.3. Cell handling, experimental conditions and assessment of cell viability
4.4. Preparation of human blood platelets and experimental conditions
4.5. Extraction and isolation of bioactive material
4.6. Q-TOF Ultima Global/Mass Spectrometry conditions
4.7. Quantification of adenosine content in aqueous diatom extracts
4.8. DNA accession numbers of diatom isolates
5. Supplementary data
5.1. Mass cultivation of the diatom isolate ND58
5.2. Taxonomy and phylogeny of diatom isolates
5.2.1. Light microscopy
5.2.2. Scanning electron microscopy
5.2.3. DNA extraction and amplification of parts of LSU rDNA
5.2.4. Alignment and analyses of sequences
Acknowledgments
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References
- Norton, TA; Melkonian, M; Andersen, RA. Algal biodiversity. Phycologia 1996, 35, 308–326. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, DG; Droop, SJM. Biodiversity, biogeography and conservation of diatoms. Hydrobiologia 1996, 336, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, AE; Vardi, A; Bowler, C. An ecological and evolutionary context for integrated nitrogen metabolism and related signaling pathways in marine diatoms. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2006, 9, 264–273. [Google Scholar]
- Perl, TM; Bédard, L; Kosatsky, T; Hockin, JC; Todd, ECD; Remis, RS. An outbreak of toxic encephalopathy caused by eating mussels contaminated with domoic acid. New Engl J Med 1990, 322, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Miralto, A; Barone, G; Romano, G; Poulet, SA; Ianora, A; Russo, GL; Buttino, I; Mazzarella, G; Laabir, M; Cabrini, M; Giacobbe, MG. The insidious effect of diatoms on copepod reproduction. Nature 1999, 402, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Pohnert, G. Diatom/copepod interactions in plankton: The indirect chemical defense of unicellular algae. Chembiochem 2005, 6, 946–959. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, JB; Hayashi, K; Hirata, M; Kuroda, E; Suzuki, E; Kubo, Y; Hayashi, T. Antiviral sulfated polysaccharide from Navicula directa, a diatom collected from deep-sea water in Toyama Bay. Biol Pharm Bull 2006, 29, 2135–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Selheim, F; Herfindal, L; Martins, R; Vasconcelos, V; Døskeland, SO. Neuro-apoptogenic and blood platelet targeting toxins in benthic marine cyanobacteria from the Portuguese coast. Aquat Toxicol 2005, 74, 294–306. [Google Scholar]
- Herfindal, L; Oftedal, L; Selheim, F; Wahlsten, M; Sivonen, K; Døskeland, SO. A high proportion of Baltic Sea benthic cyanobacterial isolates contain apoptogens able to induce rapid death of isolated rat hepatocytes. Toxicon 2005, 46, 252–260. [Google Scholar]
- Seite, P; Ruchaud, S; Hillion, J; Gendron, MC; Bruland, O; Segal-Bendirdjian, E; Døskeland, SO; Lillehaug, JR; Lanotte, M. Ectopic expression of Bcl-2 switches over nuclear signalling for cAMP- induced apoptosis to granulocytic differentiation. Cell Death Differ 2000, 7, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Tronstad, KJ; Gjertsen, BT; Krakstad, C; Berge, K; Brustugun, OT; Døskeland, SO; Berge, RK. Mitochondrial-targeted fatty acid analog induces apoptosis with selective loss of mitochondrial glutathione in promyelocytic leukemia cells. Chem Biol 2003, 10, 609–618. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, CF; Maynes, JT; Perreault, KR; Dawson, JF; James, MN. Molecular enzymology underlying regulation of protein phosphatase-1 by natural toxins. Curr Med Chem 2002, 9, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sandal, T; Aumo, L; Hedin, L; Gjertsen, BT; Døskeland, SO. Irod/Ian5: an inhibitor of gamma-radiation- and okadaic acid-induced apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 2003, 14, 3292–3304. [Google Scholar]
- Serres, MH; Fladmark, KE; Døskeland, SO. An ultrasensitive competitive binding assay for the detection of toxins affecting protein phosphatases. Toxicon 2000, 38, 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Bøe, R; Gjertsen, BT; Døskeland, SO; Vintermyr, OK. 8-Chloro-cAMP induces apoptotic cell death in a human mammary carcinoma cell (MCF-7) line. Br J Cancer 1995, 72, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Houge, G; Robaye, B; Eikhom, TS; Golstein, J; Mellgren, G; Gjertsen, BT; Lanotte, M; Døskeland, SO. Fine mapping of 28S rRNA sites specifically cleaved in cells undergoing apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 1995, 15, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Lebeau, T; Robert, JM. Diatom cultivation and biotechnologically relevant products. Part II: current and putative products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2003, 60, 624–632. [Google Scholar]
- Walne, PR. Large scale culture of larvae of Ostrea edulis. L Minist Agric Fish Invest (London) 1966, 25, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Seglen, PO. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol 1976, 13, 29–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mellgren, G; Vintermyr, OK; Døskeland, SO. Okadaic acid, cAMP, and selected nutrients inhibit hepatocyte proliferation at different stages in G1: Modulation of the cAMP effect by phosphatase inhibitors and nutrients. J Cell Physiol 1995, 163, 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Lacaze, N; Gombaud-Saintonge, G; Lanotte, M. Conditions controlling long-term proliferation of Brown Norway rat promyelocytic leukemia in vitro: primary growth stimulation by microenvironment and establishment of an autonomous Brown Norway ‘leukemic stem cell line’. Leuk Res 1983, 7, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Krakstad, C; Herfindal, L; Gjertsen, BT; Bøe, R; Vintermyr, OK; Fladmark, KE; Døskeland, SO. CaM-kinaseII dependent commitment to microcystin-induced apoptosis is coupled to cell budding, but not to shrinkage or chromatin hypercondensation. Cell Death Differ 2006, 13, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Tysnes, OB; Aarbakke, GM; Verhoeven, AJ; Holmsen, H. Thin-layer chromatography of polyphosphoinositides from platelet extracts: interference by an unknown phospholipid. Thromb Res 1985, 40, 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Selheim, F; Holmsen, H; Vassbotn, FS. Platelet-derived growth factor inhibits platelet activation in heparinized whole blood. Thromb Res 1999, 95, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Hasle, GR. Some specific preparations; diatoms. In Phytoplankton Manual; Sournia, A, Ed.; Unesco: Paris, France, 1978; pp. 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, DG. Nitzschia Subgenus Nitzschia. 8th diatom symposium 1984; notes for a monograph of the Bacillariaceae 1984, 2, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, R; Cox, EJ; Karayeva, NI; Mann, DG; Paddock, TBB; Simonsen, R; Sims, PA. An amended terminology fro the siliceous components of the diatom cell. Nova Hedwig Beih 1979, 64, 513–533. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, RM. Taxonomy and Classification of Diatom Genus Melosira Ca Agardh .3. Melosira-Lineata (Dillw) C a Ag and Melosira-Varians C a Ag. Phycologia 1978, 17, 237–250. [Google Scholar]
- Sabater, S; Tomas, X; Cambra, J; Langebertalot, H. Diatom Flora of the Cape of Creus Peninsula, Catalonia, Ne of Spain. Nova Hedwigia 1990, 51, 165–195. [Google Scholar]
- Lewin, JC. The taxonomic position of Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Gen Microbiol 1958, 18, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Borowitzka, MA; Volcani, BE. Polymorphic diatom Phaeodactylum-tricornutum-Ultrastructure of its morphotypes. J Phycol 1978, 14, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Bertalot, H; Bonik, K. Mass development of up to date rare or unknown diatoms indicating zones of progressive saprobity in European rivers. Arch Hydrobiol 1976, (suppl.49), 303–332. [Google Scholar]
- Lundholm, N; Daugbjerg, N; Moestrup, O. Phylogeny of the Bacillariaceae with emphasis on the genus Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) based on partial LSU rDNA. Eur J Phycol 2002, 37, 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Scholin, CA; Herzog, M; Sogin, M; Anderson, DM. Identification of group-specific and strain-specific genetic-markers for globally distributed Alexandrium (Dinophyceae). 2. Sequence-analysis of a fragment of the LSU ribosomal-RNA gene. J Phycol 1994, 30, 999–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Nunn, GB; Theisen, BF; Christensen, B; Arctander, P. Simplicity-correlated size growth of the nuclear 28S ribosomal RNA D3 expansion segment in the crustacean order Isopoda. J Mol Evol 1996, 42, 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, TA. BioEdit: a user friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z; Schwartz, S; Wagner, L; Miller, W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol 2000, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, JD; Higgins, DG; Gibson, TJ. Clustal-W-Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanmougin, F; Thompson, JD; Gouy, M; Higgins, DG; Gibson, TJ. Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal x. Trends Biochem Sci 1998, 23, 403–405. [Google Scholar]
- Page, RDM. TreeView: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 1996, 12, 357–358. [Google Scholar]

| Isolate no. | Geographical origin of isolates | Toxicity | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatocytes | IPC-81wt | IPC-Bcl-2 | ||||||||
| A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | ||
| ND50 | Odda | − | − | − | ++ | + | − | − | − | − |
| ND51 | Masfjord | − | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| ND52 | Puddefjorden | − | − | − | ++ | + | − | ++ | − | − |
| ND53 | Utne | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| ND55 | Masfjord | − | − | − | ++ | + | − | + | − | − |
| ND56 | Odda | − | − | − | ++ | − | − | + | − | − |
| ND58 | Puddefjorden | + | − | − | ++ | − | − | + | − | − |
| ND71 | Puddefjorden | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| ND73 | Tromøy | + | − | − | ++ | + | − | + | − | − |
| ND79 | Puddefjorden | − | + | − | ++ | + | − | − | − | − |
| Isolate no. | Taxonomy of isolates | Adenosine content, μg ado/mg DW | Modulation of TRAP-induced platelet activation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenosine deaminase | ||||
| Without | With | |||
| ND50 | Melosira sp. | 0.21 | --- | --- |
| ND51 | Amphora cf. margalefii Tomás sp. nov. | 0.07 | --- | -- |
| ND52 | Phaeodactylum tricornutum | 0.16 | -- | --- |
| ND53 | Nitzschia cf. pusilla | <0.05 | + | + |
| ND55 | Phaeodactylum tricornutum | 0.18 | --- | --- |
| ND56 | Phaeodactylum tricornutum | 0.19 | --- | --- |
| ND58 | Phaeodactylum tricornutum | 0.17 | --- | --- |
| ND71 | Amphora cf. delicatissima or new Amphora sp. | <0.05 | -- | - |
| ND73 | Nitzschia cf. pusilla | 0.31 | --- | ○ |
| ND79 | Amphora cf. delicatissima or new Amphora sp. | 0.15 | --- | ○ |
| P. tricornutum, CCAP | 0.11 | |||
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Prestegard, S.K.; Oftedal, L.; Coyne, R.T.; Nygaard, G.; Skjærven, K.H.; Knutsen, G.; Døskeland, S.O.; Herfindal, L. Marine Benthic Diatoms Contain Compounds Able to Induce Leukemia Cell Death and Modulate Blood Platelet Activity. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 605-623. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7040605
Prestegard SK, Oftedal L, Coyne RT, Nygaard G, Skjærven KH, Knutsen G, Døskeland SO, Herfindal L. Marine Benthic Diatoms Contain Compounds Able to Induce Leukemia Cell Death and Modulate Blood Platelet Activity. Marine Drugs. 2009; 7(4):605-623. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7040605
Chicago/Turabian StylePrestegard, Siv Kristin, Linn Oftedal, Rosie Theresa Coyne, Gyrid Nygaard, Kaja Helvik Skjærven, Gjert Knutsen, Stein Ove Døskeland, and Lars Herfindal. 2009. "Marine Benthic Diatoms Contain Compounds Able to Induce Leukemia Cell Death and Modulate Blood Platelet Activity" Marine Drugs 7, no. 4: 605-623. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7040605
APA StylePrestegard, S. K., Oftedal, L., Coyne, R. T., Nygaard, G., Skjærven, K. H., Knutsen, G., Døskeland, S. O., & Herfindal, L. (2009). Marine Benthic Diatoms Contain Compounds Able to Induce Leukemia Cell Death and Modulate Blood Platelet Activity. Marine Drugs, 7(4), 605-623. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7040605




