Analytical Approaches to the Rapid Characterisation of Marine Glycolipids in Bioproduct Discovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods for the Extraction and Concentration of Marine Glycolipids
2.1. Methods of Glycolipid Extraction
2.2. Methods of Glycolipid Purification
3. TLC-Based Detection Methods for Glycolipids
3.1. Qualitative TLC
3.2. Quantitative TLC-Coupled Detection Methods
3.2.1. TLC-Densitometry
3.2.2. TLC-FID
3.3. TLC-MS
4. LC-MS/MS Methods for the Analysis of Marine Glycolipids
4.1. HILIC-MS
4.2. RPLC-MS/MS
4.3. SFC-MS
4.4. 2D-LC-MS
4.5. ESI-MS/MS Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D-LC | Two-dimensional liquid chromatography |
| 9-AA | 9-amino acridine |
| BUME | Butanol:methanol |
| DEAE | Diethylaminoethyl |
| DESI | Desorption electrospray ionisation |
| DGDG | Digalactosyldiacylglycerol |
| DGMG | Digalactosylmonoacylglycerol |
| DHB | Dihydroxy benzoic acid |
| DME | Dimethyl ether |
| ESI | Electrospray ionisation |
| FID | Flame ionisation detection |
| galCer | Galactosylceramide |
| GD | Disialo ganglioside |
| GGL | Glycoglycerolipid |
| gluCer | Glucosylceramide |
| GM | Monosialo ganglioside |
| GQ | Tetrasialo ganglioside |
| GSL | Glycosphingolipid |
| GT | Trisialo ganglioside |
| HILIC | Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography |
| HIP | Hexane:isopropanol |
| IM-MS | Ion mobility mass spectrometry |
| KDN | 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nonulosonic acid |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| LCB | Long chain base |
| LESA | Liquid extraction surface analysis |
| MAG | Monoacylglycerol |
| MALDI | Matrix assisted laser desorption ionisation |
| MGDG | Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol |
| MGMG | Monogalactosylmonoacylglycerol |
| MRM | Multiple reaction monitoring |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| MTBE | Methyl-tert-butyl-ether |
| Neu5Ac | N-acetyl neuraminic acid |
| Neu5Gc | N-glycolyl neuraminic acid |
| NPLC | Normal-phase liquid chromatography |
| PLE | Pressurised liquid extraction |
| QQQ | Triple quadrupole |
| QTOF | Quadrupole time of flight |
| RPLC | Reverse-phase liquid chromatography |
| scCO2 | Supercritical carbon dioxide |
| SFC | Supercritical fluid chromatography |
| SFE | Supercritical fluid extraction |
| SLIM | Structures for lossless ion manipulations |
| SPE | Solid-phase extraction |
| SQDG | Sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol |
| SQMG | Sulfoquinovosylmonoacylglycerol |
| TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
| UAE | Ultrasonic-assisted extraction |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Tabandeh, M.; Goh, E.W.; Salman, A.A.; Heidelberg, T.; Duali Hussen, R.S. Functionalized glycolipids for potential bioconjugation of vesicles. Carbohydr. Res. 2018, 469, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusane, D.H.; Pawar, V.S.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Venugopalan, V.P.; Kumar, A.R.; Zinjarde, S.S. Anti-biofilm potential of a glycolipid surfactant produced by a tropical marine strain of Serratia marcescens. Biofouling 2011, 27, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anestopoulos, I.; Kiousi, D.-E.; Klavaris, A.; Maijo, M.; Serpico, A.; Suarez, A.; Sanchez, G.; Salek, K.; Chasapi, S.A.; Zompra, A.A.; et al. Marine-Derived Surface Active Agents: Health-Promoting Properties and Blue Biotechnology-Based Applications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourith, N.; Kanlayavattanakul, M. Natural surfactants used in cosmetics: Glycolipids. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng-Sánchez, I.; Sarabia, F. Chemistry and Biology of Bioactive Glycolipids of Marine Origin. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jala, R.C.R.; Vudhgiri, S.; Kumar, C.G. A comprehensive review on natural occurrence, synthesis and biological activities of glycolipids. Carbohydr. Res. 2022, 516, 108556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, E.; Leal, M.C.; Lillebø, A.I.; Domingues, P.; Domingues, M.R.; Calado, R. Bioprospecting of Marine Macrophytes Using MS-Based Lipidomics as a New Approach. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.; Melo, T.; Rey, F.; Costa, E.; Moreira, A.S.P.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, P.; Lillebø, A.I.; Calado, R.; Rosário Domingues, M. Insights of species-specific polar lipidome signatures of seaweeds fostering their valorization in the blue bioeconomy. Algal Res. 2021, 55, 102242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, F.; Melo, T.; Lopes, D.; Couto, D.; Marques, F.; Domingues, M.R. Applications of lipidomics in marine organisms: Progress, challenges and future perspectives. Mol. Omics 2022, 18, 357–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A. Marine Glycolipids. In Fortschritte der Chemie Organischer Naturstoffe/Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1997; pp. 215–301. [Google Scholar]
- Cepas, V.; Gutiérrez-Del-Río, I.; López, Y.; Redondo-Blanco, S.; Gabasa, Y.; Iglesias, M.J.; Soengas, R.; Fernández-Lorenzo, A.; López-Ibáñez, S.; Villar, C.J.; et al. Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Strains as Producers of Lipids with Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, I.; Yamakawa, T. Glycoglycerolipids. In New Comprehensive Biochemistry; Wiegandt, H., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 10, pp. 101–197. [Google Scholar]
- Plouguerné, E.; da Gama, B.A.; Pereira, R.C.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Glycolipids from seaweeds and their potential biotechnological applications. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Cong, P.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Comprehensive Lipidomic Analysis of Three Edible Brown Seaweeds Based on Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4138–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coniglio, D.; Bianco, M.; Ventura, G.; Calvano, C.D.; Losito, I.; Cataldi, T.R.I. Lipidomics of the Edible Brown Alga Wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Electrospray Ionization and Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2021, 26, 4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, T.; Figueiredo, A.R.P.; da Costa, E.; Couto, D.; Silva, J.; Domingues, M.R.; Domingues, P. Ethanol Extraction of Polar Lipids from Nannochloropsis oceanica for Food, Feed, and Biotechnology Applications Evaluated Using Lipidomic Approaches. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-S.; Wang, Z.-G. Glyceroglycolipids in marine algae: A review of their pharmacological activity. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1008797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Yu, G.; Guan, H. Total synthesis and structure-activity relationship of glycoglycerolipids from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3634–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, V.; Abedi, M.; Yegdaneh, A. Bioassay-guided isolation of glycolipids from the seaweed Gracilaria corticata. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnathan, G.; Couzinet-Mossion, A.; Wielgosz-Collin, G. Glycolipids from Marine Invertebrates. In Outstanding Marine Molecules: Chemistry, Biology, Analysis, 1st ed.; La Barre, S., Kornprobst, J.-M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; pp. 99–162. [Google Scholar]
- Careaga, V.P.; Maier, M.S. Cerebrosides from Marine Organisms. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Attaur, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 42, pp. 59–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, T.; Zaima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Sakai, S.; Noguchi, R.; Hirata, T. Isolation of Sphingoid Bases of Sea Cucumber Cerebrosides and Their Cytotoxicity against Human Colon Cancer Cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Zakharenko, V.M.; Kicha, A.A.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Popov, R.S.; Svetashev, V.I.; Ivanchina, N.V. New Ceramides and Cerebrosides from the Deep-Sea Far Eastern Starfish Ceramaster patagonicus. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Xue, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, Z.; Leng, K.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Sea cucumber cerebrosides and long-chain bases from Acaudina molpadioides protect against high fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3428–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Ishida, M.; Aida, K.; Tsuduki, T.; Zhang, J.; Manabe, Y.; Hirata, T.; Sugawara, T. Dietary Cerebroside from Sea Cucumber (Stichopus japonicus): Absorption and Effects on Skin Barrier and Cecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7014–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Kanie, Y.; Kanie, O.; Shimizu, Y. A unique structural distribution pattern discovered for the cerebrosides from starfish Asterias amurensis. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 473, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, E.A.; Sibille, E.; Martine, L.; Chaux-Picquet, F.; Bretillon, L.; Berdeaux, O. Apprehending ganglioside diversity: A comprehensive methodological approach. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Yanagisawa, M.; Ariga, T. Glycosphingolipid structures. In Introduction to Glycoscience; Synthesis of Carbohydrates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 73–122. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z. The Structural Diversity of Natural Glycosphingolipids (GSLs). J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2022, 41, 63–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Cong, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xue, C.; Xu, J. Characterizing gangliosides in six sea cucumber species by HILIC-ESI-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Cong, P.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Characterization of Gangliosides in Three Sea Urchin Species by HILIC–ESI-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7641–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Stonik, V.A.; Ivanchina, N.V. Sphingolipids of Asteroidea and Holothuroidea: Structures and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, D.; Compostella, F.; Ronchetti, F.; Scala, A.; Toma, L.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H. Glycoglycerolipid analogues active as anti-tumor-promoters: The influence of the anomeric configuration. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 35, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, I.M. Glycolipid Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, W.W.; Han, X. Chromatographic analysis of molecular species of intact phospholipids and glycolipids. In Lipid Analysis, 4th ed.; Christie, W.W., Han, X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Imbs, A.B.; Ermolenko, E.V.; Grigorchuk, V.P.; Sikorskaya, T.V.; Velansky, P.V. Current Progress in Lipidomics of Marine Invertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Comprehensive analysis of lipids in biological systems by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 61, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Prasad, P.; Shang, X.; Keum, Y.S. Advances in Lipid Extraction Methods-A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khot, M.; Raut, G.; Ghosh, D.; Alarcón-Vivero, M.; Contreras, D.; Ravikumar, A. Lipid recovery from oleaginous yeasts: Perspectives and challenges for industrial applications. Fuel 2020, 259, 116292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Carpena, M.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Echave, J.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Garcia-Perez, P.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Cao, H.; Nie, S.; Xiao, J.; et al. Seaweed polysaccharides: Emerging extraction technologies, chemical modifications and bioactive properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1901–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Wu, Z.-X.; Yin, F.-W.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, H.-K.; Zhang, J.-R.; Qin, L.; Shahidi, F. Extraction and detailed characterization of phospholipid-enriched oils from six species of edible clams. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, J.; Catchpole, O.; Moreno, T.; Lagutin, K.; MacKenzie, A.; Fenton, T.; Williams, A.M. Extraction of neutral lipids and phospholipids from marine biomasses using subcritical and supercritical fluids. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2024, 206, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Han, X. Accurate Quantification of Lipid Species by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry—Meets a Key Challenge in Lipidomics. Metabolites 2011, 1, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Separation of Glycolipids/Sphingolipids from Glycerophospholipids on TiO2 Coating in Aprotic Solvent for Rapid Comprehensive Lipidomic Analysis with Liquid Microjunction Surface Sampling-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11250–11259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, S.; Masson, E.; Sibille, E.; Cabaret, S.; Berdeaux, O. Rapid sample preparation for ganglioside analysis by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1137, 121956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.; Benedetti, B.; Cavaliere, C.; Cerrato, A.; La Barbera, G.; Montone, C.M.; Piovesana, S.; Laganà, A. Enrichment procedure based on graphitized carbon black and liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry for elucidating sulfolipids composition of microalgae. Talanta 2019, 205, 120162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Treblin, M.; Sitz, T.; Rohn, S. Development of a targeted HPLC-ESI-QqQ-MS/MS method for the quantification of sulfolipids from a cyanobacterium, selected leafy vegetables, and a microalgae species. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 1941–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesi, A.; Guella, G. A fast liquid chromatography-mass Spectrometry methodology for membrane lipid profiling through hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1384, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbu, M.; Zamfir, A.D. Modern separation techniques coupled to high performance mass spectrometry for glycolipid analysis. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 1155–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Lucy, C.A. Coupling normal phase liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: Strategies and applications. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6478–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustam, Y.H.; Reid, G.E. Analytical Challenges and Recent Advances in Mass Spectrometry Based Lipidomics. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 374–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, F.; Lopes, D.; Maciel, E.; Monteiro, J.; Skjermo, J.; Funderud, J.; Raposo, D.; Domingues, P.; Calado, R.; Domingues, M.R. Polar lipid profile of Saccharina latissima, a functional food from the sea. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, E.; Melo, T.; Reis, M.; Domingues, P.; Calado, R.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, M.R. Polar Lipids Composition, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Atlantic Red Seaweed Grateloupia turuturu. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Kamide, Y.; Hirai, M.Y.; Saito, K. Plant lipidomics based on hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled to ion trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Akiyama, H.; Tanaka, K.; Kohyama-Koganeya, A.; Greimel, P.; Hirabayashi, Y. Separation and analysis of mono-glucosylated lipids in brain and skin by hydrophilic interaction chromatography based on carbohydrate and lipid moiety. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1031, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hájek, R.; Jirásko, R.; Lísa, M.; Cífková, E.; Holčapek, M. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Characterization of Gangliosides in Biological Samples. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12425–12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Cong, P.; Wang, Y.; Sugawara, T.; Xue, C.; Xu, J. High Throughput Analysis of Cerebrosides from the Sea Cucumber Pearsonothria graeffei by Liquid Chromatography—Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, B.; Kazazić, S.P.; Cvitešić, A.; Penezić, A.; Frka, S. Improved separation and analysis of glycolipids by Iatroscan thin-layer chromatography–flame ionization detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1409, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striby, L.; Lafont, R.; Goutx, M. Improvement in the Iatroscan thin-layer chromatographic-flame ionisation detection analysis of marine lipids. Separation and quantitation of monoacylglycerols and diacylglycerols in standards and natural samples. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 849, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, C.C.; Bodennec, G.; Gentien, P. Determination of glycoglycerolipids by Chromarod thin-layer chromatography with Iatroscan flame ionization detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 741, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, K.M.; Schiller, J. Applications of thin-layer chromatography to the analysis of lipids. In Instrumental Thin-Layer Chromatography, 2nd ed.; Poole, C.F., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 437–472. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, K.M.; Schiller, J. The value of coupling thin-layer chromatography to mass spectrometry in lipid research—A review. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1185, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.-X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Du, M.; Zhu, B.-W.; Qin, L. Improving Lipidomic Coverage Using UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS for Marine Shellfish by Optimizing the Mobile Phase and Resuspension Solvents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8677–8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, T.; Alves, E.; Azevedo, V.; Martins, A.S.; Neves, B.; Domingues, P.; Calado, R.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, M.R. Lipidomics as a new approach for the bioprospecting of marine macroalgae—Unraveling the polar lipid and fatty acid composition of Chondrus crispus. Algal Res. 2015, 8, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, E.; Melo, T.; Moreira, A.S.P.; Alves, E.; Domingues, P.; Calado, R.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, M.R. Decoding bioactive polar lipid profile of the macroalgae Codium tomentosum from a sustainable IMTA system using a lipidomic approach. Algal Res. 2015, 12, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toribio, L.; Martín, M.T.; Bernal, J. Supercritical Fluid Chromatography in Bioanalysis–A Review. J. Sep. Sci. 2024, 47, e70003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolrab, D.; Peterka, O.; Chocholoušková, M.; Holčapek, M. Ultrahigh-performance supercritical fluid chromatography/mass spectrometry in the lipidomic analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 149, 116546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Jin, G.; Yan, J.; Shen, A.; Zhou, H.; Yang, F.; Liang, X. An offline two-dimensional supercritical fluid chromatography × reversed phase liquid chromatography tandem quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry system for comprehensive gangliosides profiling in swine brain extract. Talanta 2020, 208, 120366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, M.J.; Miller, K.E.; Jorgenson, J.W.; Kennedy, R.T. Two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for lipidomics using off-line coupling of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography with 50 cm long reversed phase capillary columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1687, 463707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampler, E.; Schoeny, H.; Mitic, B.M.; El Abiead, Y.; Schwaiger, M.; Koellensperger, G. Simultaneous non-polar and polar lipid analysis by on-line combination of HILIC, RP and high resolution MS. Analyst 2018, 143, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valmori, M.; Marie, V.; Fenaille, F.; Colsch, B.; Touboul, D. Recent methodological developments in data-dependent analysis and data-independent analysis workflows for exhaustive lipidome coverage. Front. Anal. Sci. 2023, 3, 1118742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Satoh, A.; Uchino, H.; Cajka, T.; Arita, M.; Arita, M. Mass Spectrometry Data Repository Enhances Novel Metabolite Discoveries with Advances in Computational Metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattos, B.B.; Romanos, M.T.V.; Souza, L.M.d.; Sassaki, G.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Glycolipids from macroalgae: Potential biomolecules for marine biotechnology? Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2011, 21, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rod-In, W.; Monmai, C.; Shin, I.S.; You, S.; Park, W.J. Neutral Lipids, Glycolipids, and Phospholipids, Isolated from Sandfish (Arctoscopus japonicus) Eggs, Exhibit Anti-Inflammatory Activity in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells through NF-κB and MAPKs Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Miyazawa, T.; Higuchi, O.; Takekoshi, H.; Miyazawa, T.; Kinoshita, M. Characterization of Glycolipids in the Strain Chlorella pyrenoidosa. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2022, 68, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennerholm, L.; Fredman, P. A procedure for the quantitative isolation of brain gangliosides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Lipids Lipid Metab. 1980, 617, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.J.; Zhang, G.L.; Schnaar, R.L. Ganglioside Extraction, Purification and Profiling. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 169, e62385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenders, R.G.; de Jong, J.G.; Wevers, R.A. Extraction and purification of gangliosides from plasma and fibroblasts before analysis by thin layer chromatography. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1995, 32 Pt 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Hakomori, S.-i. Quantitative isolation of total glycosphingolipids from animal cells. J. Lipid Res. 1971, 12, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, D.; Venkata Subhash, G.; Saxena, N.; Kargupta, W.; Sapre, A.; Dasgupta, S. Switchable green solvents for lipids extraction from microalgae. In Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science; Inamuddin, Boddula, R., Asiri, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 157–176. [Google Scholar]
- Archanaa, S.; Moise, S.; Suraishkumar, G.K. Chlorophyll interference in microalgal lipid quantification through the Bligh and Dyer method. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 46, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyash, V.; Liebisch, G.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Shevchenko, A.; Schwudke, D. Lipid extraction by methyl-tert-butyl ether for high-throughput lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfgren, L.; Forsberg, G.-B.; Ståhlman, M. The BUME method: A new rapid and simple chloroform-free method for total lipid extraction of animal tissue. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, A.; Radin, N.S. Lipid extraction of tissues with a low-toxicity solvent. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 90, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sostare, J.; Di Guida, R.; Kirwan, J.; Chalal, K.; Palmer, E.; Dunn, W.B.; Viant, M.R. Comparison of modified Matyash method to conventional solvent systems for polar metabolite and lipid extractions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1037, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgich, M.; Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Branco-Vieira, M.; Caetano, N.S. Comparison of different lipid extraction procedures applied to three microalgal species. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechev, J.T.; Edvinsen, G.K.; Eilertsen, K.E. Fatty Acid Composition of the Lipids from Atlantic Salmon-Comparison of Two Extraction Methods without Halogenated Solvents. Foods 2021, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutignano, A.; Luongo, E.; Nuzzo, G.; Pagano, D.; Manzo, E.; Sardo, A.; Fontana, A. Profiling of complex lipids in marine microalgae by UHPLC/tandem mass spectrometry. Algal Res. 2016, 17, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Blackburn, G.J.; Mohd Fauzi, N.; Pitt, A.R.; Spickett, C.M. A comparison of five lipid extraction solvent systems for lipidomic studies of human LDL. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckebosch, E.; Bruneel, C.; Termote-Verhalle, R.; Muylaert, K.; Foubert, I. Influence of extraction solvent system on extractability of lipid components from different microalgae species. Algal Res. 2014, 3, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servaes, K.; Maesen, M.; Prandi, B.; Sforza, S.; Elst, K. Polar Lipid Profile of Nannochloropsis oculata Determined Using a Variety of Lipid Extraction Procedures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3931–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, B.Y.; Ma, L.; Khor, G.L.; van der Does, Y.; Rowan, A.; McJarrow, P.; MacGibbon, A.K.H. Ganglioside Composition in Beef, Chicken, Pork, and Fish Determined Using Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6295–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lydic, T.A.; Busik, J.V.; Reid, G.E. A monophasic extraction strategy for the simultaneous lipidome analysis of polar and nonpolar retina lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Señoráns, M.; Castejón, N.; Señoráns, F.J. Advanced Extraction of Lipids with DHA from Isochrysis galbana with Enzymatic Pre-Treatment Combined with Pressurized Liquids and Ultrasound Assisted Extractions. Molecules 2020, 25, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elst, K.; Maesen, M.; Jacobs, G.; Bastiaens, L.; Voorspoels, S.; Servaes, K. Supercritical CO2 Extraction of Nannochloropsis sp.: A Lipidomic Study on the Influence of Pretreatment on Yield and Composition. Molecules 2018, 23, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pühringer, M.; Rampler, E.; Castejón, N. Unwrapping the (glyco-)lipidome in the microalgae Microchloropsis gaditana: Effects of eco-friendly extraction methods. Algal Res. 2024, 79, 103480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Sweeney, T.; O’Doherty, J.; Rajauria, G. Recent Advances in the Use of Greener Extraction Technologies for the Recovery of Valuable Bioactive Compounds from Algae. In Recent Advances in Micro and Macroalgal Processing; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 96–122. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Vazquez, A.; Carpena, M.; Barciela, P.; Cassani, L.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Prieto, M.A. Pressurized Liquid Extraction for the Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Seaweeds for Food Industry Application: A Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Vivas, D.; Ortega-Barbosa, J.P.; Parada-Alfonso, F.; Ferreira, S.R.S.; del Pilar Sánchez-Camargo, A. Supercritical fluid extraction of lipids, carotenoids, and other compounds from marine sources. In Innovative and Emerging Technologies in the Bio-Marine Food Sector; Garcia-Vaquero, M., Rajauria, G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 277–317. [Google Scholar]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Abert-Vian, M. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. Mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouahid, A.; Seengeon, K.; Martino, M.; Crampon, C.; Kramer, A.; Badens, E. Selective extraction of neutral lipids and pigments from Nannochloropsis salina and Nannochloropsis maritima using supercritical CO2 extraction: Effects of process parameters and pre-treatment. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2020, 165, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalluddin, N.A.; Ismail, N.; Mutalib, S.R.A.; Sikin, A.M. Sc-CO2 extraction of fish and fish by-products in the production of fish oil and enzyme. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getachew, A.T.; Jacobsen, C.; Sørensen, A.-D.M. Supercritical CO2 for efficient extraction of high-quality starfish (Asterias rubens) oil. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2024, 206, 106161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catchpole, O.; Moreno, T.; Montañes, F.; Tallon, S. Perspectives on processing of high value lipids using supercritical fluids. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 134, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, D.; Yuan, L.; Sun, Y.; Han, D.; Hu, Q. Solid Matrix-Supported Supercritical CO2 Enhances Extraction of γ-Linolenic Acid from the Cyanobacterium Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis and Bioactivity Evaluation of the Molecule in Zebrafish. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Qiao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, Y. Preparation of Ganglioside GM1 by Supercritical CO2 Extraction and Immobilized Sialidase. Molecules 2019, 24, 3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sugawara, T.; Zhang, T.; Koretaro, T. The Extraction, Separation Technology, and New Product Development of Functional Lipids from Sea Cucumber. In Advances in Sea Cucumber Processing Technology and Product Development; Xue, C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 259–292. [Google Scholar]
- Nekrasov, E.V.; Tallon, S.J.; Vyssotski, M.V.; Catchpole, O.J. Extraction of lipids from New Zealand fern fronds using near-critical dimethyl ether and dimethyl ether–water–ethanol mixtures. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2021, 170, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.C.; Kruse, A. The use of dimethyl ether as an organic extraction solvent for biomass applications in future biorefineries: A user-oriented review. Fuel 2019, 254, 115703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Watanabe, M. Advances in low-temperature extraction of natural resources using liquefied dimethyl ether. Resour. Chem. Mater. 2022, 1, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Kanda, H.; Wahyudiono; Machmudah, S. Extraction of carotenoids and lipids from algae by supercritical CO2 and subcritical dimethyl ether. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 96, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.C.; Konnerth, P.; Kruse, A. Extraction of common microalgae by liquefied dimethyl ether: Influence of species and pretreatment on oil yields and composition. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, L.; Mei, L.; Kanda, H. Extraction and Separation of Natural Products from Microalgae and Other Natural Sources Using Liquefied Dimethyl Ether, a Green Solvent: A Review. Foods 2024, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, C.; Valentão, P.; Ferreres, F.; Andrade, P.B. Alternative and Efficient Extraction Methods for Marine-Derived Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3182–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catchpole, O.; Ryan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Fenton, K.; Grey, J.; Vyssotski, M.; MacKenzie, A.; Nekrasov, E.; Mitchell, K. Extraction of lipids from fermentation biomass using near-critical dimethylether. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2010, 53, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Oshita, K.; Takaoka, M. Effective lipid extraction from undewatered microalgae liquid using subcritical dimethyl ether. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzelmann, S.M.; Bale, N.J.; Hopmans, E.C.; Damsté, J.S.S.; Schouten, S.; Meer, M.T.J.v.d. Critical Assessment of Glyco- and Phospholipid Separation by Using Silica Chromatography. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.; Moreira, A.S.P.; Rey, F.; da Costa, E.; Melo, T.; Maciel, E.; Rego, A.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, P.; Calado, R.; et al. Lipidomic signature of the green macroalgae Ulva rigida farmed in a sustainable integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, E.; Melo, T.; Moreira, A.S.; Bernardo, C.; Helguero, L.; Ferreira, I.; Cruz, M.T.; Rego, A.M.; Domingues, P.; Calado, R.; et al. Valorization of Lipids from Gracilaria sp. through Lipidomics and Decoding of Antiproliferative and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, F.; Costa, E.d.; Campos, A.M.; Cartaxana, P.; Maciel, E.; Domingues, P.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Calado, R.; Cruz, S. Kleptoplasty does not promote major shifts in the lipidome of macroalgal chloroplasts sequestered by the sacoglossan sea slug Elysia viridis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körber, T.T.; Sitz, T.; Abdalla, M.A.; Mühling, K.H.; Rohn, S. LC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis of Sulfolipids and Galactolipids in Green and Red Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) as Influenced by Sulfur Nutrition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellgren, L.I. Occurrence of bioactive sphingolipids in meat and fish products. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2001, 103, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Bisson, J.; Friesen, J.B.; Pauli, G.F.; Simmler, C. Selective Chlorophyll Removal Method to “Degreen” Botanical Extracts. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Echten-Deckert, G. Sphingolipid Extraction and Analysis by Thin-Layer Chromatography. In Methods in Enzymology; Merrill, A.H., Hannun, Y.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 312, pp. 64–79. [Google Scholar]
- Schnaar, R.L.; Sandhoff, R.; Tiemeyer, M.; Kinoshita, T. Glycosphingolipids. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Woodbury, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, W.W.; Han, X. Chromatographic analysis of sphingolipids. In Lipid Analysis, 4th ed.; Christie, W.W., Han, X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 125–142. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, A.; Kato, M.; Miyazaki, S.; Kyogashima, M. Separation of glycosphingolipids with titanium dioxide. Glycoconj. J. 2018, 35, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Kyogashima, M. Simple separation of glycosphingolipids in the lower phase of a Folch’s partition from crude lipid fractions using zirconium dioxide. Glycoconj. J. 2022, 39, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L.K. A liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometric approach for the determination of gangliosides GD3 and GM3 in bovine milk and infant formulae. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.F.; Prieto, P.A. Special Considerations for Glycolipids and Their Purification. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 1993, 22, 17.13.11–17.13.13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledeen, R.W.; Yu, R.K.; Eng, L.F. Gangliosides of human myelin: Sialosylgalactosylceramide (g7) as a major component. J. Neurochem. 1973, 21, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, G.D.; Wiegant, V.M.; Dunn, A.J. Interspecies Comparison of Brain Ganglioside Patterns Studied by Two-Dimensional Thin-Layer Chromatography. J. Neurochem. 1981, 37, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Shimizu, T.; Taguchi, R. Targeted analysis of ganglioside and sulfatide molecular species by LC/ESI-MS/MS with theoretically expanded multiple reaction monitoring. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 2678–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaar, R.L.; Needham, L.K. Thin-layer chromatography of glycosphingolipids. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; Volume 230, pp. 371–389. [Google Scholar]
- Smyth, T.J.P.; Rudden, M.; Tsaousi, K.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Protocols for the Detection and Chemical Characterisation of Microbial Glycolipids. In Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology Protocols: Biochemical Methods; McGenity, T.J., Timmis, K.N., Nogales, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Smyth, T.J.P.; Perfumo, A.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Isolation and Analysis of Low Molecular Weight Microbial Glycolipids. In Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology; Timmis, K.N., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 3705–3723. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, A.K.; Käppeli, O.; Fiechter, A.; Reiser, J. Hydrocarbon assimilation and biosurfactant production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 4212–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aveiro, S.S.; Melo, T.; Figueiredo, A.; Domingues, P.; Pereira, H.; Maia, I.B.; Silva, J.; Domingues, M.R.; Nunes, C.; Moreira, A.S.P. The Polar Lipidome of Cultured Emiliania huxleyi: A Source of Bioactive Lipids with Relevance for Biotechnological Applications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, B.M.; Daniels, D.G.H.; Fearn, T.; Stewart, B.A. Lipid compositions, baking qualities and other characteristics of wheat varieties grown in the U.K. J. Cereal Sci. 1987, 5, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B.; Süß, R.; Teuber, K.; Eibisch, M.; Schiller, J. Lipid analysis by thin-layer chromatography—A review of the current state. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2754–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, G.; Zullo, F. The use of iodine staining for the quantitative analysis of lipids separated by thin layer chromatography. Lipids 1987, 22, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, T.; Watarai, S.; Kushi, Y.; Kasama, T.; Kodama, H. Analysis of gangliosides from carp intestinal mucosa. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 16, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müthing, J.; Distler, U. Advances on the compositional analysis of glycosphingolipids combining thin-layer chromatography with mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2010, 29, 425–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshio, H.; Keiko, K.; Hideyoshi, H.; Yasuo, S.; Makoto, M.; Mamoru, S.; Tomoya, O. Sensitive enzyme-immunostaining and densitometric determination of ganglio-series gangliosides on thin-layer plate: Pmol detection of gangliosides in cerebrospinal fluid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Lipids Lipid Metab. 1986, 876, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljetić, B.; Labak, I.; Blažetić, S.; Stambuk, A.; Heffer, M. Distribution of mono-, di- and trisialo gangliosides in the brain of Actinopterygian fishes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kates, M. Glycolipids of Higher Plants, Algae, Yeasts, and Fungi. In Glycolipids, Phosphoglycolipids, and Sulfoglycolipids; Kates, M., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 235–320. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Goto-Inoue, N.; Yoshida-Noro, C.; Suzuki, A. Structural Characterization of Neutral Glycosphingolipids by Thin-Layer Chromatography Coupled to Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Quadrupole Ion Trap Time-of-Flight MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5736–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müthing, J. High-resolution thin-layer chromatography of gangliosides. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 720, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harth, S.; Dreyfus, H.; Urban, P.F.; Mandel, P. Direct thin-layer chromatography of gangliosides of a total lipid extract. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenberger, W.; Araki, S.; Müller, D.G. Betaine lipids and phospholipids in brown algae. Phytochemistry 1993, 34, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembitsky, V.M.; Pechenkina-Shubina, E.E.; Rozentsvet, O.A. Glycolipids and fatty acids of some seaweeds and marine grasses from the black sea. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2279–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neskovic, N.; Sarlieve, L.; Nussbaum, J.-L.; Kostic, D.; Mandel, P. Quantitative thin-layer chromatography of glycolipids in animal tissues. Clin. Chim. Acta 1972, 38, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.E.; Henderson, R.J. The rapid analysis of neutral and polar marine lipids using double-development HPTLC and scanning densitometry. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1989, 129, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrova, N.F.; Ghidoni, R.; Karpova, O.B.; Nalivayeva, N.N.; Malesci, A.; Tettamanti, G. Systematic position of fish species and ganglioside composition and content. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1986, 83, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandroglio, F.; Loberto, N.; Valsecchi, M.; Chigorno, V.; Prinetti, A.; Sonnino, S. Thin layer chromatography of gangliosides. Glycoconj. J. 2009, 26, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Wöhrmann, A.P.A.; Rahmann, H. Brain gangliosides and cold-adaptation in high-antarctic fish. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1995, 23, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, L.; Sonnino, S. Alkali-labile gangliosides. Glycoconj. J. 2023, 40, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.F. High-performance precoated stationary phases. In Instrumental Thin-Layer Chromatography, 2nd ed.; Poole, C.F., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Fine, J.B.; Sprecher, H. Unidimensional thin-layer chromatography of phospholipids on boric acid-impregnated plates. J. Lipid Res. 1982, 23, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deranieh, R.M.; Joshi, A.S.; Greenberg, M.L. Thin-Layer Chromatography of Phospholipids. In Membrane Biogenesis: Methods and Protocols; Rapaport, D., Herrmann, J.M., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Pinault, M.; Guimaraes, C.; Dumas, J.-F.; Servais, S.; Chevalier, S.; Besson, P.; Goupille, C. A 1D High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Method Validated to Quantify Phospholipids Including Cardiolipin and Monolysocardiolipin from Biological Samples. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 1900240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobańska, A.W. Impregnated silica-based layers in thin layer chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2020, 43, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodennec, J.; Pelled, D.; Futerman, A.H. Aminopropyl solid phase extraction and 2 D TLC of neutral glycosphingolipids and neutral lysoglycosphingolipids. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitman, J.; Wood, D.L. Quantitative Densitometry in Situ of Lipids Separated by thin Layer Chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1981, 4, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macala, L.; Yu, R.; Ando, S. Analysis of brain lipids by high performance thin-layer chromatography and densitometry. J. Lipid Res. 1983, 24, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meullemiestre, A.; Breil, C.; Abert-Vian, M.; Chemat, F. Analytical Methodology for Lipid Extraction and Quantification from Oleaginous Microorganisms. In Modern Techniques and Solvents for the Extraction of Microbial Oils; Meullemiestre, A., Breil, C., Abert-Vian, M., Chemat, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cebolla, V.L.; Jarne, C.; Vela, J.; Garriga, R.; Membrado, L.; Galbán, J. Scanning densitometry and mass spectrometry for HPTLC analysis of lipids: The last 10 years. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2021, 44, 148–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Mizuta, M. Fluorometric detection of glycosphingolipids on thin-layer chromatographic plates. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, W.W.; Han, X. Chromatographic analysis of lipids: General principles. In Lipid Analysis, 4th ed.; Christie, W.W., Han, X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 21–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cebolla, V.L.; Mateos, E.; Garriga, R.; Jarne, C.; Membrado, L.; Cossío, F.P.; Gálvez, E.M.; Matt, M.; Delgado-Camón, A. Changes in Fluorescent Emission Due to Non-covalent Interactions as a General Detection Procedure for Thin-Layer Chromatography. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Miyazaki, M.; Matsuda, J.; Yoneshige, A. High-performance thin-layer chromatography/mass spectrometry for the analysis of neutral glycosphingolipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2011, 1811, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Jarne, C.; Cebolla, V.L.; Galbán, J.; Savirón, M.; Orduna, J.; Membrado, L.; Lapieza, M.-P.; Romero, E.; Sanz Vicente, I.; et al. A Hyphenated Technique based on High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography for Determining Neutral Sphingolipids: A Proof of Concept. Chromatography 2015, 2, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, M.; Zamfir, A.D. Modern techniques for separation, mass spectrometric detection, and characterization of glycolipids. In Carbohydrate Analysis by Modern Liquid Phase Separation Techniques, 2nd ed.; El Rassi, Z., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 485–527. [Google Scholar]
- Niimura, Y.; Tomori, M.; Tadano-Aritomi, K.; Toida, T.; Ishizuka, I. The major acidic glycolipids from the kidney of the Pacific salmon (Oncorhynchus keta): Characterization of a novel ganglioside, fucosyl-N-acetylgalactosaminyl-GM1. J. Biochem. 1999, 126, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadano-Aritomi, K.; Ishizuka, I. Determination of peracetylated sulfoglycolipids using the azure A method. J. Lipid Res. 1983, 24, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethke, U.; Müthing, J.; Schauder, B.; Conradt, P.; Mühlradt, P.F. An improved semi-quantitative enzyme immunostaining procedure for glycosphingolipid antigens on high performance thin layer chromatograms. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 89, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyakudo, F.; Adams, E.; Van Schepdael, A. Thin-Layer Chromatography–Flame Ionization Detection. Chromatographia 2020, 83, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, A.; Baker, A.L.; Nichols, D.S.; Bowman, J.P.; Britz, M.L. Application of Thin-Layer Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detection (TLC-FID) to Total Lipid Quantitation in Mycolic-Acid Synthesizing Rhodococcus and Williamsia Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinanoglou, V.J.; Strati, I.F.; Bratakos, S.M.; Proestos, C.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Miniadis-Meimaroglou, S. On the combined application of Iatroscan TLC-FID and GC-FID to identify total, neutral, and polar lipids and their fatty acids extracted from foods. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 859024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, C.C. Separation of Aquatic Lipid Classes by Chromarod Thin-Layer Chromatography with Measurement by latroscan Flame Ionization Detection. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1987, 44, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, C.C.; Ackman, R.G. Chromarod separations for the analysis of marine lipid classes by iatroscan chromatography-flame ionization detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1983, 262, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeebullah, S.F.K.; Alagarsamy, S.; Haddad, S.A.; Yamani, F.A. Composition, In vitro Antioxidant and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Effects of Lipids Isolated from Fifteen Species of Seaweeds. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Zhou, Y.; Costello, C.E. Direct analysis of sialylated or sulfated glycosphingolipids and other polar and neutral lipids using TLC-MS interfaces. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, K.M.; Prabutzki, P.; Leopold, J.; Nimptsch, A.; Lemmnitzer, K.; Vos, D.R.N.; Hopf, C.; Schiller, J. A new update of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in lipid research. Prog. Lipid Res. 2022, 86, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, G.; Ifa, D.R.; Wu, C.; Corso, G.; Cooks, R.G. Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Lipids after Two-Dimensional High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Partial Separation. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1744–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlin, L.S.; Ferreira, C.R.; Dill, A.L.; Ifa, D.R.; Cooks, R.G. Desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for lipid characterization and biological tissue imaging. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1811, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Chen, H. Direct analysis of liquid samples by desorption electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (DESI-MS). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelsbach, M.; Varesio, E.; Hopfgartner, G. Liquid extraction surface analysis (LESA) of hydrophobic TLC plates coupled to chip-based nanoelectrospray high-resolution mass spectrometry. Chimia 2014, 68, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B. Analysis of phospolipids and glycolipids by thin-layer chromatography–matrix-assisted laser desorption and ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1259, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, J.; Prabutzki, P.; Engel, K.M.; Schiller, J. A Five-Year Update on Matrix Compounds for MALDI-MS Analysis of Lipids. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskolla, T.W.; Karas, M. Compelling Evidence for Lucky Survivor and Gas Phase Protonation: The Unified MALDI Analyte Protonation Mechanism. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B.; Schiller, J.; Süß, R.; Nimptsch, A.; Schürenberg, M.; Suckau, D. Capabilities and disadvantages of combined matrix-assisted laser-desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) and high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC): Analysis of egg yolk lipids. JPC-J. Planar Chromatogr.-Mod. TLC 2009, 22, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillen, J.C.; Fincher, J.A.; Klein, D.R.; Spraggins, J.M.; Caprioli, R.M. Effect of MALDI matrices on lipid analyses of biological tissues using MALDI-2 postionization mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 55, e4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhasz, P.; Costello, C.E. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of underivatized and permethylated gangliosides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1992, 3, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Kwon, S.; Kim, Y.K. Graphene Oxide Derivatives and Their Nanohybrid Structures for Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Small Molecules. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Qin, P.; Wu, X.; Cai, Z. Nanomaterials as Assisted Matrix of Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry for the Analysis of Small Molecules. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.; Yeung, E.S. Colloidal Graphite-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry and MSn of Small Molecules. 1. Imaging of Cerebrosides Directly from Rat Brain Tissue. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 2373–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, P.-Y.; Manikandan, M.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, H.-F. Graphene nanoflakes as an efficient ionizing matrix for MALDI-MS based lipidomics of cancer cells and cancer stem cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7334–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H. Improved MALDI imaging MS analysis of phospholipids using graphene oxide as new matrix. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertesz, V.; Van Berkel, G.J. Fully automated liquid extraction-based surface sampling and ionization using a chip-based robotic nanoelectrospray platform. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dill, A.L.; Ifa, D.R.; Manicke, N.E.; Ouyang, Z.; Cooks, R.G. Mass spectrometric imaging of lipids using desorption electrospray ionization. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 2883–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takáts, Z.; Wiseman, J.M.; Gologan, B.; Cooks, R.G. Mass spectrometry sampling under ambient conditions with desorption electrospray ionization. Science 2004, 306, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifa, D.R.; Wu, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Cooks, R.G. Desorption electrospray ionization and other ambient ionization methods: Current progress and preview. Analyst 2010, 135, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Bhatia, R. Liquid extraction surface analysis-mass spectrometry: An advanced and environment-friendly analytical tool in modern analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 2746–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.H.; Huxtable, L.H.; Willcox, M.D.; Blanksby, S.J.; Mitchell, T.W. Automated surface sampling of lipids from worn contact lenses coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Analyst 2013, 138, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarne, C.; Membrado, L.; Saviron, M.; Vela, J.; Orduna, J.; Garriga, R.; Galban, J.; Cebolla, V.L. Globotriaosylceramide-related biomarkers of fabry disease identified in plasma by high-performance thin-layer chromatography—Densitometry—Mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1638, 461895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopold, J.; Popkova, Y.; Engel, K.M.; Schiller, J. Recent Developments of Useful MALDI Matrices for the Mass Spectrometric Characterization of Lipids. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, A.J.; Tocher, D.R.; Sargent, J.R. Thin-layer chromatography—Flame ionization detection and the quantitation of marine neutral lipids and phospholipids. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 88, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackman, R.G. Flame ionization detection applied to thin-layer chromatography on coated quartz rods. Methods Enzymol. 1981, 72, 205–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Noga, S. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)—A powerful separation technique. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, A.J. Hydrophilic-interaction chromatography for the separation of peptides, nucleic acids and other polar compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 1990, 499, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauve, B.; Guillarme, D.; Cléon, P.; Veuthey, J.L. Evaluation of various HILIC materials for the fast separation of polar compounds. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalbe-Herrmann, M.; Willmann, J.; Leibfritz, D. Separation of phospholipid classes by hydrophilic interaction chromatography detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5179–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandera, P.; Janás, P. Recent advances in stationary phases and understanding of retention in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 967, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, G.; Yan, J.; He, X.; Li, X.; Liang, X. Recent advances in hydrophilic interaction liquid interaction chromatography materials for glycopeptide enrichment and glycan separation. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandera, P. Stationary and mobile phases in hydrophilic interaction chromatography: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 692, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyler, A.R.; Armstrong, B.L.; Cha, J.Y.; Zhou, M.X.; Yang, Q.; Robinson, R.I.; Dunphy, R.; Burinsky, D.J. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography on amino-silica phases complements reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis for peptide analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 724, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosova, Z.; Gonzalez, S.V.; Voigt, A.; Bruheim, P. High Throughput Semiquantitative UHPSFC–MS/MS Lipid Profiling and Lipid Class Determination. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2021, 59, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmel, J.P.; Cochran, J.A.; Ulmer, C.Z.; Levy, A.J.; Patterson, R.E.; Olsen, B.C.; Yost, R.A.; Bowden, J.A.; Garrett, T.J. Software tool for internal standard based normalization of lipids, and effect of data-processing strategies on resulting values. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Song, J.; Yang, T.; Liao, Y.; Gong, G.; Huang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z. High-sensitivity qualitative and quantitative analysis of human, bovine and goat milk glycosphingolipids using HILIC-MS/MS with internal standards. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 312, 120795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Han, X. Selection of internal standards for accurate quantification of complex lipid species in biological extracts by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry—What, how and why? Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2017, 36, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Fedorova, M. Evaluation of lipid quantification accuracy using HILIC and RPLC MS on the example of NIST® SRM® 1950 metabolites in human plasma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, B.; Norris, C.; Lowe, E.; McJarrow, P. Liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry for quantitative analysis of gangliosides. Lipids 2009, 44, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Kitajima, K. KDN (deaminated neuraminic acid): Dreamful past and exciting future of the newest member of the sialic acid family. Glycoconj. J. 2006, 23, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaar, R.L.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; Hildebrandt, H. Sialic acids in the brain: Gangliosides and polysialic acid in nervous system development, stability, disease, and regeneration. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 461–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Cong, P.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Comparative lipid profile of four edible shellfishes by UPLC-Triple TOF-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cong, P.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Meng, N.; Fan, X.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Comprehensive Lipid Profile of Eight Echinoderm Species by RPLC–Triple TOF-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8230–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Cong, P.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Comparative Lipid Profile Analysis of Four Fish Species by Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9423–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windarsih, A.; Irnawati; Suratno; Warmiko, H.D.; Alam, L.P.M.; Utami, I.D.; Rohman, A.; Indrianingsih, A.W. Lipidomics Analysis of Different Marine Fish Oils Using Untargeted Liquid Chromatography–Orbitrap High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Chemometrics. Chromatographia 2024, 87, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, E.; Domingues, P.; Melo, T.; Coelho, E.; Pereira, R.; Calado, R.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, M.R. Lipidomic Signatures Reveal Seasonal Shifts on the Relative Abundance of High-Valued Lipids from the Brown Algae Fucus vesiculosus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.S.P.; da Costa, E.; Melo, T.; Sulpice, R.; Cardoso, S.M.; Pitarma, B.; Pereira, R.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, P.; Calado, R.; et al. Seasonal plasticity of the polar lipidome of Ulva rigida cultivated in a sustainable integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. Algal Res. 2020, 49, 101958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popendorf, K.J.; Fredricks, H.F.; Van Mooy, B.A. Molecular ion-independent quantification of polar glycerolipid classes in marine plankton using triple quadrupole MS. Lipids 2013, 48, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Duan, J.; Xue, C.; Feng, T.; Dong, P.; Sugawara, T.; Hirata, T. Analysis and comparison of glucocerebroside species from three edible sea cucumbers using liquid chromatography-ion trap-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12246–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, P.X.; Gao, R.C.; Xue, C.H.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, H.W.; Khan, M.N.; Xue, Y.; Sugawara, T.; Xu, J. Molecular species analysis of monosialogangliosides from sea urchin Strongylocentrotus nudus by RPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, R.J.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Avrainvilloside, a 6-Deoxy-6-aminoglucoglycerolipid from the Green Alga Avrainvillea nigricans. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1428–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.M.; Sayed, A.M.; Abdelwahab, M.F.; Albohy, A.; Abdulrazik, B.S.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Bringmann, G.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Identifying the specific-targeted marine cerebrosides against SARS-CoV-2: An integrated computational approach. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36042–36059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cífková, E.; Hájek, R.; Lísa, M.; Holčapek, M. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry of (lyso)phosphatidic acids, (lyso)phosphatidylserines and other lipid classes. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1439, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaner, R.L.; Allegood, J.C.; Park, H.; Wang, E.; Kelly, S.; Haynes, C.A.; Sullards, M.C.; Merrill, A.H. Quantitative analysis of sphingolipids for lipidomics using triple quadrupole and quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometers[S]. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1692–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignol, N.; Chang, K.; Hamler, R.; Schilling, A.E.; Khanna, R.; Lockhart, D.J.; Clark, S.W.; Benjamin, E.R. Glucosylceramide Quantitation in Normal and Glucocerebrosidase-Deficient Mouse Brain and Human Cell Lines. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 105, S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Dane, A.; Spijksma, G.; Wang, M.; van der Greef, J.; Luo, G.; Hankemeier, T.; Vreeken, R.J. An efficient hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography separation of 7 phospholipid classes based on a diol column. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1220, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, W.; Rasmussen, H.T. Orthogonal method development using hydrophilic interaction chromatography and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of pharmaceuticals and impurities. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1083, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santalova, E.A.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Structural Analysis of the Minor Cerebrosides from a Glass Sponge Aulosaccus sp. Lipids 2015, 50, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Mitsutake, S.; Ishikawa, J.; Takagi, Y.; Akiyama, M.; Shimizu, H.; Tomiyama, T.; Igarashi, Y. Dietary glucosylceramide improves skin barrier function in hairless mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2006, 44, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanishi, K.; Shiono, N.; Shirai, H.; Dombo, M.; Kimata, H. Reduction of transepidermal water loss by oral intake of glucosylceramides in patients with atopic eczema. Allergy 2005, 60, 1454–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillou, S.; Ghabri, S.; Jannot, C.; Gaillard, E.; Lamour, I.; Boisnic, S. The moisturizing effect of a wheat extract food supplement on women’s skin: A randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, S.; Wada, S.; Sato, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Aoi, W.; Higashi, A. Effect of Torula Yeast (Candida utilis)-Derived Glucosylceramide on Skin Dryness and Other Skin Conditions in Winter. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2018, 64, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, T. Sphingolipids as Functional Food Components: Benefits in Skin Improvement and Disease Prevention. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9597–9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zábranská, M.; Vrkoslav, V.; Sobotníková, J.; Cvačka, J. Analysis of plant galactolipids by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with accurate mass measurement. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2012, 165, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Schütz, A.-L.; Galano, J.-M.; Herrfurth, C.; Feussner, K.; Durand, T.; Brodhun, F.; Feussner, I. The Alphabet of Galactolipids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2011, 2, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, A.; Carbone, V.; Saggese, P.; Takagaki, K.; Pizza, C. Novel Galactolipids from the Leaves of Ipomoea batatas L.: Characterization by Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Electrospray Ionization–Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10289–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggli, T.; Bühr, C.; Schürch, S. Challenges in the Analysis of Gangliosides by LC-MS. Chimia 2022, 76, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobburi, A.L.P.; Kipruto, E.W.; Inman, D.M.; Anderson, D.J. A new LC-MS/MS technique for separation of gangliosides using a phenyl-hexyl column: Systematic separation according to sialic acid class and ceramide subclass. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2021, 44, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, R.C.; Zhang, Q. Isobaric Labeling of Intact Gangliosides toward Multiplexed LC–MS/MS-Based Quantitative Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2578–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; German, J.B.; Kjelden, R.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Barile, D. Quantitative Analysis of Gangliosides in Bovine Milk and Colostrum-Based Dairy Products by Ultrahigh Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9689–9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordillo, R. Supercritical fluid chromatography hyphenated to mass spectrometry for metabolomics applications. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Dean, B.; Liang, X. A technical overview of supercritical fluid chromatography-mass spectrometry (SFC-MS) and its recent applications in pharmaceutical research and development. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2021, 40, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si-Hung, L.; Bamba, T. Current state and future perspectives of supercritical fluid chromatography. Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 149, 116550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, J.; Ye, F.; Zhou, T.; Gongke, L. Advances of supercritical fluid chromatography in lipid profiling. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, P.; Inferrera, V.; Sciarrone, D.; Mondello, L. Supercritical fluid chromatography for lipid analysis in foodstuffs. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolrab, D.; Chocholoušková, M.; Jirásko, R.; Peterka, O.; Holčapek, M. Validation of lipidomic analysis of human plasma and serum by supercritical fluid chromatography–mass spectrometry and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2375–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Fukusaki, E.; Bamba, T. Simultaneous analysis for water- and fat-soluble vitamins by a novel single chromatography technique unifying supercritical fluid chromatography and liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1362, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desfontaine, V.; Losacco, G.L.; Gagnebin, Y.; Pezzatti, J.; Farrell, W.P.; González-Ruiz, V.; Rudaz, S.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Guillarme, D. Applicability of supercritical fluid chromatography—Mass spectrometry to metabolomics. I—Optimization of separation conditions for the simultaneous analysis of hydrophilic and lipophilic substances. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1562, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losacco, G.L.; Bennett, R.; Ahmad, I.A.H.; Barrientos, R.C.; DaSilva, J.O.; Dong, Y.; Schuppe, A.W.; Wang, Z.; Aiken, S.; Mangion, I.; et al. Dual-Gradient Unified Chromatography: A New Paradigm for Versatility in Simultaneous Multicomponent Analysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamba, T.; Shimonishi, N.; Matsubara, A.; Hirata, K.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kobayashi, A.; Fukusaki, E. High throughput and exhaustive analysis of diverse lipids by using supercritical fluid chromatography-mass spectrometry for metabolomics. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 105, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lísa, M.; Jiránková, T. Highly repeatable and selective ultrahigh-performance supercritical fluid chromatography—Mass spectrometry interclass separation in lipidomic studies. Microchem. J. 2022, 178, 107376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchikata, T.; Matsubara, A.; Nishiumi, S.; Yoshida, M.; Fukusaki, E.; Bamba, T. Development of oxidized phosphatidylcholine isomer profiling method using supercritical fluid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1250, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Uchikata, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Yokoi, Y.; Nishiumi, S.; Yoshida, M.; Fukusaki, E.; Bamba, T. Supercritical fluid chromatography/Orbitrap mass spectrometry based lipidomics platform coupled with automated lipid identification software for accurate lipid profiling. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1301, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lísa, M.; Holčapek, M. High-Throughput and Comprehensive Lipidomic Analysis Using Ultrahigh-Performance Supercritical Fluid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 7187–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaiger, M.; Schoeny, H.; El Abiead, Y.; Hermann, G.; Rampler, E.; Koellensperger, G. Merging metabolomics and lipidomics into one analytical run. Analyst 2019, 144, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.S.; Liang, H.J.; Lin, M.H.; Tang, C.H.; Wu, K.Y.; Kuo, M.L.; Lin, C.Y. Two-dimensional LC-MS/MS to enhance ceramide and phosphatidylcholine species profiling in mouse liver. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lísa, M.; Cífková, E.; Holčapek, M. Lipidomic profiling of biological tissues using off-line two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5146–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Liu, R.; Yang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Guan, Y.; Qian, D.; Wang, T.; Liu, H. Lipid profiling of rat peritoneal surface layers by online normal- and reversed-phase 2D LC QToF-MS[S]. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2833–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, D.Y.; Moon, M.H. On-line two-dimensional capillary strong anion exchange/reversed phase liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for comprehensive lipid analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1310, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narváez-Rivas, M.; Vu, N.; Chen, G.Y.; Zhang, Q. Off-line mixed-mode liquid chromatography coupled with reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry to improve coverage in lipidomics analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 954, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- François, I.; Sandra, P. Comprehensive supercritical fluid chromatography×reversed phase liquid chromatography for the analysis of the fatty acids in fish oil. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4005–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holčapek, M.; Ovčačíková, M.; Lísa, M.; Cífková, E.; Hájek, T. Continuous comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of complex lipidomic samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5033–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Zaeem, M.; Fillier, T.A.; Nadeem, M.; Vidal, N.P.; Manful, C.; Cheema, S.; Cheema, M.; Thomas, R.H. Targeting Modified Lipids during Routine Lipidomics Analysis using HILIC and C30 Reverse Phase Liquid Chromatography coupled to Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Wei, D.; Chen, F.; Yang, S.-T. Lipidomic profiling and discovery of lipid biomarkers in snow alga Chlamydomonas nivalis under salt stress. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2012, 114, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Qin, L.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhou, D.Y.; Xu, X.B.; Du, M.; Zhu, B.W.; Thornton, M. Evaluation of lipid profile in different tissues of Japanese abalone Haliotis discus hannai Ino with UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS-based lipidomic study. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ye, M.; Xu, J.; Guo, C.; Zheng, H.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yan, X. Lipid Profile in Different Parts of Edible Jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8283–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.M.; Iacomini, M.; Gorin, P.A.J.; Sari, R.S.; Haddad, M.A.; Sassaki, G.L. Glyco- and sphingophosphonolipids from the medusa Phyllorhiza punctata: NMR and ESI-MS/MS fingerprints. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2007, 145, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.G.; Joo, M.; Park, J.M.; Kim, M.A.; Mok, J.; Cho, S.H.; Sohn, Y.C.; Lee, H. Lipid Profiling of Pacific Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai) at Different Developmental Stages Using Ultrahigh Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2022, 2022, 5822562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Liu, K.-H.; Lee, D.Y.; DeFelice, B.; Meissen, J.K.; Fiehn, O. LipidBlast in silico tandem mass spectrometry database for lipid identification. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Ikeda, K.; Takahashi, M.; Satoh, A.; Mori, Y.; Uchino, H.; Okahashi, N.; Yamada, Y.; Tada, I.; Bonini, P.; et al. A lipidome atlas in MS-DIAL 4. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K.; et al. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmel, J.P.; Kroeger, N.M.; Ulmer, C.Z.; Bowden, J.A.; Patterson, R.E.; Cochran, J.A.; Beecher, C.W.W.; Garrett, T.J.; Yost, R.A. LipidMatch: An automated workflow for rule-based lipid identification using untargeted high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmel, J.P.; Li, X.; Stow, S.M.; Sartain, M.J.; Murali, A.; Kemperman, R.; Tsugawa, H.; Takahashi, M.; Vasiliou, V.; Bowden, J.A.; et al. Lipid Annotator: Towards Accurate Annotation in Non-Targeted Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS/MS) Lipidomics Using A Rapid and User-Friendly Software. Metabolites 2020, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Gerichten, J.; Saunders, K.; Bailey, M.J.; Gethings, L.A.; Onoja, A.; Geifman, N.; Spick, M. Challenges in Lipidomics Biomarker Identification: Avoiding the Pitfalls and Improving Reproducibility. Metabolites 2024, 14, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köfeler, H.C.; Eichmann, T.O.; Ahrends, R.; Bowden, J.A.; Danne-Rasche, N.; Dennis, E.A.; Fedorova, M.; Griffiths, W.J.; Han, X.; Hartler, J.; et al. Quality control requirements for the correct annotation of lipidomics data. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Riano, C.; León-Espinosa, G.; Regalado-Reyes, M.; García, A.; DeFelipe, J.; Barbas, C. Advanced lipidomics using UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS reveals novel lipids in hibernating syrian hamsters. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1743, 465692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiang, T.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Huang, X.; Mao, R.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, C.; Zhao, S.; et al. LipidIN: A comprehensive repository for flash platform-independent annotation and reverse lipidomics. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, M.; Ishihara, M.; Tiemeyer, M.; Aoki, K.; Ranzinger, R. DANGO: An MS data annotation tool for glycolipidomics. BBA Adv. 2025, 7, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weatherly, D.B.; Arpinar, F.S.; Porterfield, M.; Tiemeyer, M.; York, W.S.; Ranzinger, R. GRITS Toolbox—A freely available software for processing, annotating and archiving glycomics mass spectrometry data. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, N.; Mayer, G.; Has, C.; Kopczynski, D.; Al Machot, F.; Schwudke, D.; Ahrends, R.; Marcus, K.; Eisenacher, M.; Turewicz, M. A Current Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics Tools, Data Formats and Resources for Mass Spectrometry Lipidomics. Metabolites 2022, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Züllig, T.; Köfeler, H.C. High Resolution Mass Spectrometry in Lipidomics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2021, 40, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, G.; Smith, A.J.; Astarita, G. Ion mobility mass spectrometry in the omics era: Challenges and opportunities for metabolomics and lipidomics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2022, 41, 722–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.A.; Leaptrot, K.L.; May, J.C.; McLean, J.A. New frontiers in lipidomics analyses using structurally selective ion mobility-mass spectrometry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, G.; Angel, P.; Williams, J.P.; Richardson, K.; Olivos, H.J.; Thompson, J.W.; Menikarachchi, L.; Lai, S.; Walsh, C.; Moseley, A.; et al. Ion mobility-derived collision cross section as an additional measure for lipid fingerprinting and identification. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camunas-Alberca, S.M.; Moran-Garrido, M.; Sáiz, J.; Gil-de-la-Fuente, A.; Barbas, C.; Gradillas, A. Integrating the potential of ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry in the separation and structural characterisation of lipid isomers. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1112521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, C.N.; Nagy, G. Recent advances in high-resolution traveling wave-based ion mobility separations coupled to mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2025, 44, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, R.; Webb, I.K.; Deng, L.; Garimella, S.V.B.; Prost, S.A.; Ibrahim, Y.M.; Baker, E.S.; Smith, R.D. Lipid and Glycolipid Isomer Analyses Using Ultra-High Resolution Ion Mobility Spectrometry Separations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormwood Moser, K.L.; Van Aken, G.; DeBord, D.; Hatcher, N.G.; Maxon, L.; Sherman, M.; Yao, L.; Ekroos, K. High-defined quantitative snapshots of the ganglioside lipidome using high resolution ion mobility SLIM assisted shotgun lipidomics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1146, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, C.N.; Nagy, G. Permethylation and Metal Adduction: A Toolbox for the Improved Characterization of Glycolipids with Cyclic Ion Mobility Separations Coupled to Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 13725–13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poad, B.L.J.; Zheng, X.; Mitchell, T.W.; Smith, R.D.; Baker, E.S.; Blanksby, S.J. Online Ozonolysis Combined with Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry Provides a New Platform for Lipid Isomer Analyses. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
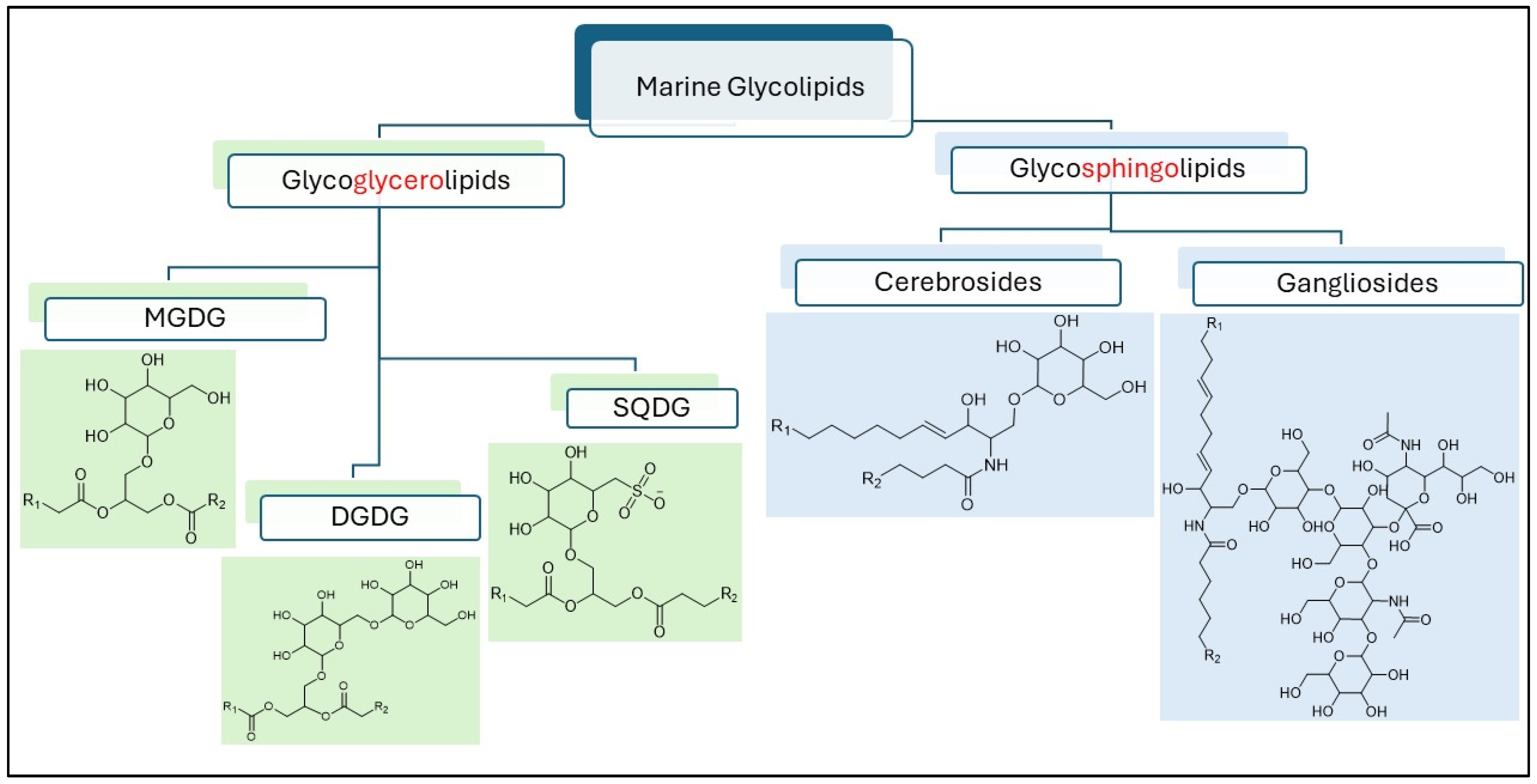
| Biphasic Solvent Systems | Frequency of Application in Glycolipids Analysis | Advantages | Disadvantages | Application Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroform:methanol based Bligh and Dyer and Folch methods [80,81] | Frequent use | Wide coverage of total lipidome in organic phase. | Solvent toxicity and laborious steps involved in phase partitioning. Less selective for glycolipids; co-extraction of pigments from marine samples. Potential losses of glycolipids in interface emulsion layer. Aqueous phase needs to be recovered for gangliosides. | Method may require modifications based on sample composition for effective phase separation. Further purifications are often essential. |
| Butanol:methanol based BUME method [85] | Limited use | Rapid extraction in upper organic phase. Lipids recovery similar to chloroform:methanol. | Lack of in-depth studies targeting marine glycolipids. | Good enrichment of polar lipids in non-marine samples. More investigations are essential. |
| Methyl-tert-butyl-ether:methanol based Matyash method [84] | Limited use | Rapid extraction in upper organic phase. Lipid recovery similar to chloroform:methanol. | Limited information on glycolipids enrichment. | More studies are essential, given the lower polarity of the solvent system. |
| Advanced Lipid Extraction Methods | Sample Types | Targeted Glycolipid Type/Subclass | Enrichment Levels Compared to Conventional Methods | Analytical Approach | Application Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressurised fluid extraction (PLE) using hexane:isopropanol | Marine microalgae | Total glycolipids | Higher | NPLC-ELSD-based quantitation [96] | More investigations targeting other subclasses of glycolipids from a range of marine biomasses other than microalgae are essential |
| Ultrasonic assisted extraction (UAE) using hexane:isopropanol | Marine microalgae | Total glycolipids | Higher | NPLC-ELSD-based quantitation [96] | |
| UAE using ethanol | Total lipids, including GGLs (MGDG, DGDG) | Higher | LC-MS/MS peak area analysis using class-specific internal standards [98] | ||
| UAE using ethanol | Polar lipids, including DGDG and SQDG | Comparable profile | Molecular diversity and relative abundance analysis using LC-MS/MS [16] | ||
| Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) (scCo2 + ethanol as co-solvent) | Marine microalgae | Polar lipids, including total glycolipids | Lower | Gravimetry of fractions, as well as quantitation based on LC-MS peak area/mass of extract [93] | SFE and DME, including sequential extraction steps, can be examined to recover glycolipids from residual biomass |
| Dimethyl ether extraction (DME) | Non-marine biomass | Total fatty acids associated with neutral and polar lipids, including GGLs (MGDG, DGDG, SQDG) and cerebrosides | Lower | Analysis of fatty acids from neutral lipids and polar lipids/glycolipids, along with qualitative TLC tests on biomass residues [110] |
| Samples | Glycolipid Subclasses Resolved | TLC Approach | TLC Solvent Systems | Detection Method/Staining | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purified glycolipid fractions | MGDG, DGDG, and SQDG | Single development TLC | Chloroform:methanol:water | Orcinol-sulfuric acid | [60,73,75,148] |
| Neutral GSLs (cerebroside subclasses) | [128,136,145,149] | ||||
| Acidic GSLs (Ganglioside subclasses) | Chloroform:methanol:water with added salt (e.g., 0.2% CaCl2) | Resorcinol–hydrochloric acid | [27,128,142,145,150] | ||
| Gangliosides, including minor subclasses such as O-acetylated and lactonized gangliosides | 2D-TLC | [134,151,156,157] | |||
| Crude lipids | MGDG, DGDG, and SQDG | Multiple/sequential development TLC | Multiple solvent systems of different polarity | TLC coupled with partial-scan FID | [58,60] |
| TLC Coupled Techniques for Glycolipids Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| TLC-Densitometry | TLC-FID | TLC-MS | |
| Glycolipids identification level | Class/subclass level; requires staining reagent/standards. | Class/subclass level; requires standards. | Subclass and molecular species level. |
| Quantification | Time-consuming due to the requirement of derivatization. | Rapid and robust; allows for direct quantification without derivatization. | Allows for relative quantitation, but prone to ionisation sensitivity (require standards). |
| Advantages | Low-cost, widely used and well-established classical method. Wide range of TLC stationary phases available for better retention and selectivity. | Rapid analysis and low-cost instrumentation. | Higher sensitivity to low-abundance glycolipid species. |
| Disadvantages | Requires staining/derivatization. Limited application due to a lack of marine specific standards for glycolipids. | Resolving power can be lower due to the limited choice of chromarod stationary phases (silica and alumina). | Expensive instrumentation for developing a robust TLC-MS interface. |
| Application notes | Resolving power can be improved by automated gradient development, 2D-TLC, and use of modified-phase TLC plates. | Special approaches like multiple-sequential-development TLC and partial-scan-FID can improve resolution for glycolipids. | Advanced elution-based interfaces allow for the direct structural characterisation of glycolipids with enhanced resolution and sensitivity. |
| References | [142,160,166,169] | [58,60,179,210,211] | [61,185] |
| Sample Source | Extraction and Enrichment Method | LC-MS/MS Method | Types and Number of Glycolipid Molecular Species Detected | Quantification Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown alga wakame (U. pinnatifida) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method. Sulfolipids enrichment by normal-phase SPE, eluted with acetonitrile:water (80:20, v/v) and 0.1% formic acid. | LC coupled with Q-Exactive Quadrupole-Orbitrap-MS. Bare silica HILIC for total lipids analysis. C18 RPLC for sulfolipids analysis. | 16 SQDG, 6 SQMG, 12 DGDG, and 5 DGMG among >200 polar lipid species. | Determination of relative abundance of molecular species without quantification. | [15] |
| Three brown seaweeds (L. japonica, U. pinnatifida, and S. natans) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method. | C18 RPLC coupled with QTOF-MS. | 30–66 MGDG, 20–45 DGDG, 13–48 SQDG, 3–4 MGMG, 19–121 acylated MGDG, 2–4 DGMG, 6–35 acylated DGDG, 1 SQMG, and 1–9 hexosylceramides among 675 lipid molecules across three samples. | Lipid class-specific semi-quantification using an external standard method. | [14] |
| Four shellfish species (R. philippinarum, O. gigas, C. farreri and M. edulis) | Modified Folch method. | C18 RPLC coupled with Triple TOF-MS. | 4–16 hexosylceramides among >600 molecules across four samples. | Lipid class-specific semi-quantification using an internal standard method. | [228] |
| Eight echinoderm species (A. japonicus, A. molpadioides, C. frondosa, P. californicus, T. ananas, A. amurensis, G. crenularis, and S. nudus) | Modified Folch method. | C18 RPLC coupled with Triple TOF-MS. | 4–8 SQDG and 39–73 hexosylceramides among 961 lipid molecules across eight samples. | Lipid class specific semi-quantification using an internal standard method. | [229] |
| Four fish species (S. niphonius, S. maximus, O. keta and C. idellus) | Modified Folch method. | C18 RPLC coupled with QTOF-MS. | Six hexosylceramides detected in S. maximus among >700 lipid molecular species across four samples. | Class specific semi-quantification using an external standard method. | [230] |
| Five marine fish species (L. campechanus, E. lanceolatus, S. canaliculatus, L. calcarifer and K. pelamis) | n-Hexane. | C18 RPLC coupled with Orbitrap-MS. | 1–14 hexosylceramides 0–1 MGDG and 0–1 SQDG among >1000 lipid molecules across five samples (detected in positive ESI mode). 3–13 MGDG among 100–300 lipid species (detected in negative ESI mode). | Lipidomic assessment without quantification. | [231] |
| Marine microalgae (N. oceanica) | Monophasic solvent extractions followed by phase partition using the Folch method. | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 15 MGDG, 5 MGMG, 14 DGDG, 2 DGMG, 10 SQDG, and 1 SQMG among 128 lipid species. | Comparison of extraction efficiency based on relative abundance without quantification. | [16] |
| Marine plankton (E. huxleyi) | Modified Folch method. | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 17 MGDG, 8 MGMG, 7 DGDG, 1 DGMG, 24 SQDG, 3 SQMG, and 2 sialylated GSLs composed of KDN among 134 lipid species. | Estimation of total glycolipids in crude extracts using the orcinol colorimetric method. Relative abundance of molecular species without quantification. | [140] |
| Brown alga (F. vesiculosus) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method. | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 26 MGDG, 4 MGMG 27 DGDG, 5 DGMG, 13 SQDG, and 6 SQMG among 187 lipid species. | Relative abundance of molecular species without quantification. | [232] |
| Six seaweeds samples Chlorophyta (U. rigida, C. tomentosum) Rhodophyta (P. palmata, G. gracilis, P. dioica), and Ochrophyta (F. vesiculosus) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method. | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 6–24 MGDG, 8–12 MGMG, 10–22 DGDG, 3–7 DGMG, 17–26 SQDG, and 1–5 SQMG among 144–275 lipid species across six samples. | Relative abundance of molecular species without quantification. | [8] |
| Atlantic red seaweed (G. turuturu) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method. | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 16 MGDG, 13 DGDG, 13 MGMG, 4 DGMG, 20 SQDG, and 8 SQMG. | Relative percentage of molecular species based on the normalised peak area of each extracted ion chromatogram. | [53] |
| Green seaweed (U. rigida) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method. | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 9 MGDG, 13 DGDG, 20 SQDG, 6 MGMG, 6 DGMG, and 5 SQMG among 150 lipid species. | Relative quantification at subclass level by the integration of molecular peak areas. Relative abundance measurement based on the normalised peak area of each extracted ion chromatogram relative to the internal standard for the same class. | [233] |
| Green macroalga (U. rigida) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method followed by normal-phase SPE for polar lipids fraction. Glycolipids eluted with acetone:methanol (9:1, v/v). | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 27 MGDG, 13 MGMG, 13 DGDG, 9 DGMG 20 SQDG, and 5 SQMG among 202 polar lipid species. | Polar lipid profiling without quantification. | [120] |
| Sugar kelp (S. latissimi) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method followed by normal-phase SPE for polar lipids fraction. Glycolipids eluted with acetone:methanol (9:1, v/v). | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 14 MGDG, 15 DGDG, 25 SQDG, and 3 SQMG among 197 lipid molecules. | Polar lipid profiling without quantification. | [52] |
| Sacoglossan sea slug (E. viridis), and Green alga (C. tomentosum) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method followed by normal-phase SPE for polar lipids fraction. Glycolipids eluted with acetone:methanol (9:1, v/v). | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 2 MGDG, 6 DGDG, and 12 SQDG among 62 molecular species from E. viridis. 2 MGDG, 6 DGDG, and 16 SQDG among 76 molecular species C. tomentosum. | Polar lipid profiling without quantification. | [122] |
| Red seaweed (C. crispus) | MTBE method. | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Linear Ion Trap-MS. | 30 SQDG, 19 DGDG, and 4 galactosylceramides. | Polar lipid profiling without quantification. | [64] |
| Green seaweed (C. tomentosum) | Methanol extraction followed using TLC, and re-extraction of polar lipids using chloroform:methanol (2:1, v/v). | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Linear Ion Trap-MS. | 7 SQDG, 4 SQMG, 13 DGDG, and 10 MGDG. | Polar lipid profiling without quantification. | [65] |
| Red alga (Gracilaria spp.) | Modified Bligh and Dyer method followed by normal-phase SPE for polar lipids fraction. Glycolipids eluted with acetone:methanol (9:1, v/v). | Bare silica HILIC coupled with Linear Ion Trap-MS for total lipids analysis. Direct infusion ESI-QTOF-MS/MS for fractions analysis. | 9 MGDG, 10 DGDG, 12 SQDG, and 3 SQMG among 147 lipid molecular species. | Polar lipid profiling without quantification. | [121] |
| Marine plankton | Modified Bligh and Dyer method. | NPLC coupled with QQQ-MS. | MGDG, DGDG, and SQDG among 9 polar lipid subclasses. | Sum quantification of molecular species of each subclass based on characteristic neutral loss scan for each subclass. | [234] |
| Microalgae species (C. cryptica, N. salina, T. weissflogii, A. minutum and A. tamutum) | MTBE method followed by silica gel column chromatography. Glycolipids eluted with acetone:methanol (9:1, v/v). Additional purification of GGLs (MGDG, DGDG, and SQDG) using Sephadex LH-20. | Biphenyl RPLC coupled with Q-Exactive-Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap-MS. | At least 21 MGDG, 14 DGDG, 7 SQDG among >350 lipid species across five samples. | Molecular diversity and relative abundance of lipid molecular species. Absolute quantification of lipid species using five standards representing the lipid classes, including MGDG and SQDG. | [90] |
| Sea cucumber species (A. molpadioides, C. frondosa, and A. japonicus) | Sequential extractions using chloroform:methanol (2:1, v/v), followed by re-extraction with ethyl acetate:n-butanol (2:1, v/v), and precipitation of residue with acetone. Glucocerebroside enrichment by normal phase silica gel column chromatography, eluted with chloroform:methanol (25:1 to 10:1, v/v). | C18 RPLC coupled with Ion Trap-MS. | 12, 26, and 52 glucocerebroside molecular species across three samples. Characteristic glucocerebrosides consisting of C17/C18 sphingoid bases (d17:1 and d18:2) and C18-C25 saturated/monounsaturated and hydroxy/non-hydroxy fatty acid groups. | Structural characterisation without quantification. | [235] |
| Starfish (A. amurensis) | Bligh and Dyer method. Glucocerebroside enrichment using normal-phase silica gel column chromatography, eluted with chloroform:methanol:water (90:10:0.1, v/v/v). | C18 RPLC coupled with Ion Trap-TOF-MS. | >23 molecular peaks of cerebrosides including several structural isomers. Three groups of cerebrosides: one consisting of C22 LCBs and <C16 fatty acyl group, and the other two consisting of C18 LCBs and either >C23 or <C18 fatty acyl groups with various number and position of unsaturation(s). Key structures consisting of trihydroxy and branched triene sphingoid bases. | Structural characterisation without quantification. | [26] |
| Sea cucumber (P. graeffei) | Chloroform:methanol (2:1, v/v) followed by mild saponification (potassium hydroxide in methanol), phase partition and recovery of chloroform phase. Glucocerebrosides enrichment by normal-phase SPE, eluted with chloroform:methanol (100:0 to 90:10, v/v). | C18 RPLC coupled with QTOF-MS. | 89 cerebroside molecular species. Unique structures possessing d17:1 and branched sphingoid bases and those with hydroxy fatty acids. | Structural characterisation without quantitation. | [57] |
| Sea cucumber (B. marmorata, I. fuscus, H. polli, H. mexicana, C. frondosa and P. califormicus) | Svennerholm and Fredman method. Gangliosides purified by SPE using C8 cartridges. | Amino HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS. | 17 subclasses of GM, GD, GT, GQ, and GP gangliosides, consisting of different substituents in sialic head (sulphate, fucose and inositolphosphate). | Semi-quantitative analysis using GD3 isolated from bovine milk as an external standard. | [30] |
| Sea urchin (S. nudus, H. pulcherrimus, and G. crenularis) | Svennerholm and Fredman method. Gangliosides purified by SPE using C8 cartridges. | Amino HILIC coupled with Q-Exactive-Orbitrap-MS. | 14 subclasses of gangliosides with three distinct sialic acid features (Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN), along with sulphated sialic acids. | Semi-quantitative analysis using GM1, GD1 and GT1 as external standards. | [31] |
| Sea urchin (S. nudus) | Svennerholm and Fredman method. Gangliosides purified by C8 column, followed by anion exchange chromatography using DEAE-Sephadex A25. | C8 RPLC coupled with QQQ-MS. | >50 molecules of GM gangliosides. Structures composed of two distinct sialic acid types, Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc, and their sulphated forms. | Ganglioside profiling based on MS/MS- and MRM-based relative quantification. | [236] |
| Fish fillets (C. nudipinnis, R. faughni, O. tshawytscha, C. auratus) along with other non-marine food samples | Modified Svennerholm and Fredman method. Gangliosides enriched by SPE using C18 cartridges. | Amino-propyl HILIC coupled with Orbitrap-MS. | Five subclasses of gangliosides, including GM3, GD3, GD1a, GD1b, GT1b, and GM2. | Subclass levels quantification of gangliosides using both ab external standard and standard addition technique. | [94] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhakal, S.; Nalder, T.D.; Marshall, S.N.; Barrow, C.J. Analytical Approaches to the Rapid Characterisation of Marine Glycolipids in Bioproduct Discovery. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090352
Dhakal S, Nalder TD, Marshall SN, Barrow CJ. Analytical Approaches to the Rapid Characterisation of Marine Glycolipids in Bioproduct Discovery. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(9):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090352
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhakal, Sudarshan, Tim D. Nalder, Susan N. Marshall, and Colin J. Barrow. 2025. "Analytical Approaches to the Rapid Characterisation of Marine Glycolipids in Bioproduct Discovery" Marine Drugs 23, no. 9: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090352
APA StyleDhakal, S., Nalder, T. D., Marshall, S. N., & Barrow, C. J. (2025). Analytical Approaches to the Rapid Characterisation of Marine Glycolipids in Bioproduct Discovery. Marine Drugs, 23(9), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090352






