Postbiotics of Marine Origin and Their Therapeutic Application
Abstract
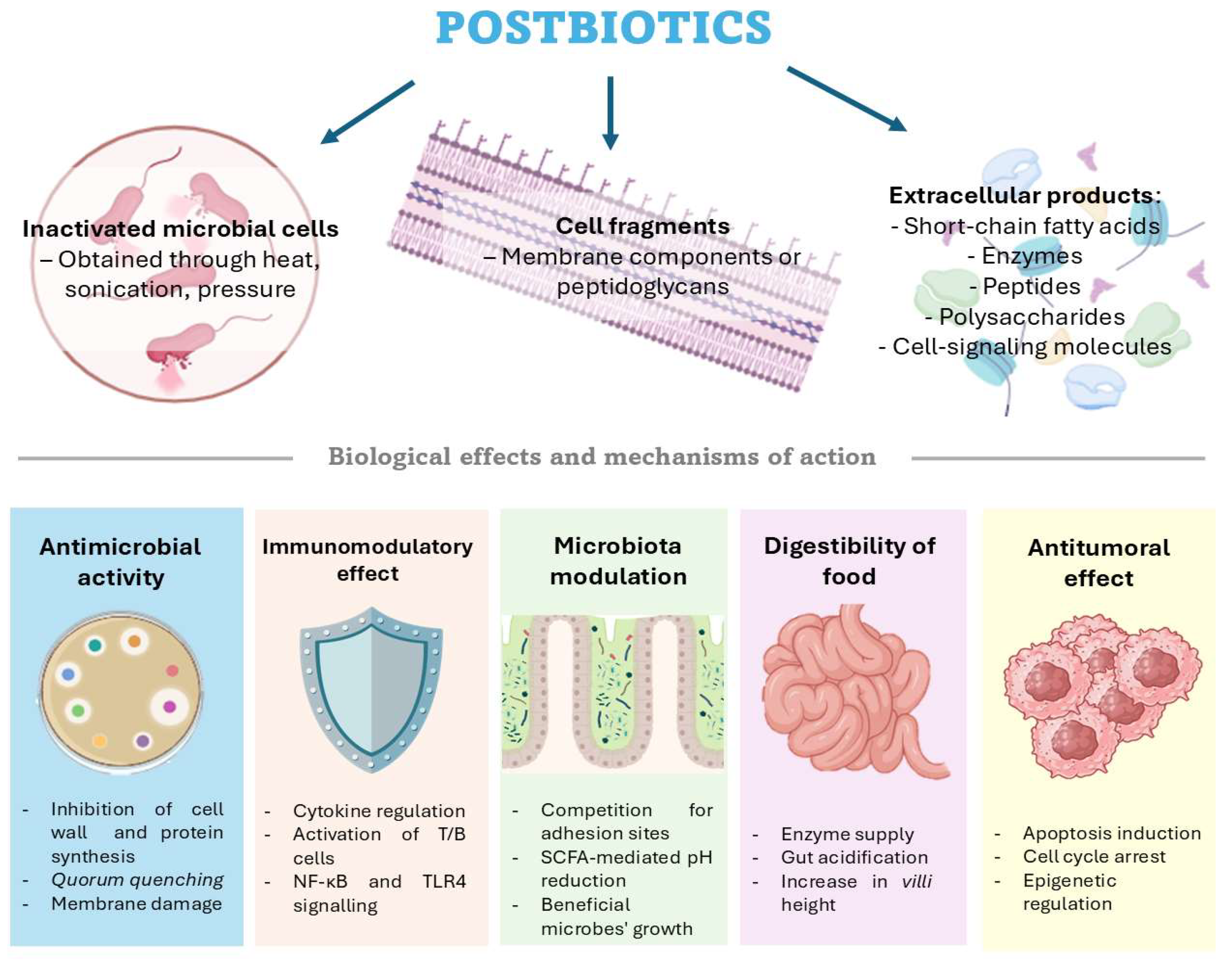
1. Introduction
2. The Use of Probiotics and Their Limitations
3. Use of Postbiotics for Health Management
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity
3.2. Immunomodulatory Effect
3.3. Microbiota Modulation
3.4. Digestibility of Food
3.5. Antitumoral Effects
4. The Marine Environment as a Source of Postbiotics
5. Postbiotics Isolated from the Aquatic Environment
| Strain | Postbiotic | Extraction Method | Biological Activities | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||||
| Bacillus amyloliquefaciens COFCAU_P1 | ECPs | Centrifugation and filtration | Growth, biofilm, and motility inhibition of A. hydrophyla, Vibrio spp., and S. galactiae | [128] |
| B. amyloliquefaciens MK135790 | ECPs | Centrifugation and ethyl acetate extraction | Inhibition of E. coli, B. cereus, B. subtilis, L. monocytogenes, S. aureus, and S. enterica typhimurium | [130] |
| Bacillus pumilus strain H2 | ECPs | Cell lysis and sonication | Inhibition of 29 different Vibrio strains | [131] |
| Bacillus pumilus UMA169 | ECPs | Centrifugation and filtration | Growth inhibition of P. damselae subsp. piscicida | [105] |
| Bacillus pumilus UMA216 | ECPs | Centrifugation and filtration | Growth inhibition of P. damselae subsp. piscicida and T. maritimum | [105] |
| Bacillus subtilis COFCAU_BSP3 | ECPs | Centrifugation and filtration | Growth, biofilm, and motility inhibition of A. hydrophyla, Vibrio spp., and S. galactiae | [128] |
| Bacillus subtilis | ECPs | Centrifugation and ethyl acetate extraction | Inhibition of S. aureus, E. coli, Klebsiella sp., Proteus sp., and S. typhi | [134] |
| Bacillus velezensis Z01 | Serine metalloprotease enzyme | Centrifugation, filtration, and circular dichroism analyzer | Thrombolytic activity, antiplatelet effects, and ability to improve blood coagulation | [135,136,163] |
| Halobacillus salinus C42 | N-(2′-phenylethyl)-isobutyramide 2,3-methyl-N-(2′-phenylethyl)-butyramide | Centrifugation and organic solvent extraction | Inhibit quorum sensing (QS) in C. violaceum CV026, Vibrio harveyi BB120, and Escherichia coli JB525 | [137] |
| Streptomyces vinaceusdrappus AMG31 | EPS | Centrifugation and alcohol precipitation | Anti-inflammatory effects, anti-Alzheimer’s activity, anti-obesity potential, and antidiabetic properties. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity against a broad spectrum of pathogenic bacteria | [138] |
| Weissella cibaria CECT 30731 | Heat-inactivated cells | Heat inactivation | Increased survival against pathogens of Y. ruckeri and A. salmonicida | [139] |
| Weissella cibaria CECT 30732 | Heat-inactivated cells | Heat inactivation | Increased survival against pathogens of Y. ruckeri | [139] |
| Weissella cibaria W.c.17MD | Heat-inactivated cells | Heat and centrifugation | Growth inhibition of A. salmonicida | [140] |
| Weissella cibaria W.c.13ID | Heat-inactivated cells | Heat and centrifugation | Antimicrobial activity of A. salmonicida and Y. ruckeri | [140] |
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||||
| Aeromonas salmonicida A3-47 and A. sobria A3-51 | OMPs | Centrifugation and sonication | Cross-reacted with antibodies obtained against V. harvey | [141] |
| Alcaligenes faecalis MK135791 as CAB38 | ECPs | Centrifugation and ethyl acetate extraction | Inhibition of B. subtilis, E. coli, and S. entrica typhimurium | [130] |
| Halomonas meridian KKU-MS11 | L-glutaminase enzyme | Supernatant purification | Inhibits tumor cell growth and promotes cancer cell death | [142,143] |
| Mameliella sp. M20D2D8 | ECPs | Organic solvent and centrifugation | Antiviral effect against Influenza A and B | [144] |
| Pseudoalteromonas flavipulchra | ECPs | Centrifugation and alcohol precipitation | Inhibition of Vibrio pathogens | [145,146] |
| Pseudoalteromonas piscicida S2040 | Siderophore (Pseudochelin A) | Organic solvent extraction | Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [146] |
| Pseudoalteromonas sp. IBRL PD4.8 | Fatty acids derived from ECPs | Organic solvent extraction | Produces antibacterial compounds and inhibits the biofilm of V. alginolyticus FB3 | [147] |
| Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 | ECPS | Centrifugation and filtration | Inhibited biofilm formation by S. epidermidis | [148,149] |
| Ruegeria pomeroyi DSS-3 | Proteins derived from ECPs | Centrifugation and filtration | Identification of the RTX-like protein with possible functions in interaction, nutrient uptake, toxicity, or defense | [47] |
| Shewanella putrefaciens Pdp11 | ECPs | Centrifugation and filtration | Growth, biofilm, and motility inhibition of Vibrio harveyi, Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida, and Vibrio anguillarum | [49,157] |
| Vibrio proteolyticus DCF12.2 | ECPs | Centrifugation, filtration, and ethanol inactivation | Modulate the expression of genes and improve growth performance and nutritional characteristics | [159,161,162] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGP | Antimicrobial growth promoter |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| CLPs | Pumilacidin-like cyclic lipopeptides |
| CFUs | Colony-forming units |
| ECPs | Extracellular products |
| EPSs | Exopolysaccharides |
| LPSs | Lipopolysaccharides |
| QS | Quorum sensing |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Baker, R.E.; Mahmud, A.S.; Miller, I.F.; Rajeev, M.; Rasambainarivo, F.; Rice, B.L.; Takahashi, S.; Tatem, A.J.; Wagner, C.E.; Wang, L.F.; et al. Infectious disease in an era of global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, D.E.; Kuhn, M.; Prettner, K. Modern infectious diseases: Macroeconomic impacts and policy responses. J. Econ. Lit. 2022, 60, 85–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaruaba, R.; Okoye, C.O.; Akan, O.D.; Mwaliko, C.; Ebido, C.C.; Ayoola, A.; Ayeni, E.A.; Odoh, C.K.; Abi, M.E.; Adebanjo, O.; et al. Socio-economic impacts of emerging infectious diseases in Africa. Infect. Dis. 2022, 54, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, J.F.; Grace, D.; Strand, T. The Consequences of human actions on risks for infectious diseases: A review. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 30048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klous, G.; Huss, A.; Heederik, D.J.J.; Coutinho, R.A. Human-livestock contacts and their relationship to transmission of zoonotic pathogens, a systematic review of literature. One Health 2016, 2, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Sobur, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Ievy, S.; Hossain, M.J.; Zowalaty, M.E.E.; Rahman, A.M.M.T.; Ashour, H.M. Zoonotic diseases: Etiology, impact, and control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, R.; Tago, D.; Treich, N. Infectious diseases and meat production. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2020, 76, 1019–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducrot, C.; Gautret, M.; Pineau, T.; Jestin, A. Scientific literature on infectious diseases affecting livestock animals, longitudinal worldwide bibliometric analysis. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, H.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A.; Thomas, J. Viral infections in cultured fish and shrimps: Current status and treatment methods. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 227–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, K.D.; Harvell, C.D.; Conrad, J.M.; Friedman, C.S.; Kent, M.L.; Kuris, A.M.; Powell, E.N.; Rondeau, D.; Saksida, S.M. infectious diseases affect marine fisheries and aquaculture economics. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, S. Emerging Diseases, Livestock expansion and biodiversity loss are positively related at global scale. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 248, 108707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.; Kamel, M. Climatic changes and their role in emergence and re-emergence of diseases. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22336–22352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, J.M.; Begon, M.; Ward, M.J.; Fèvre, E.M. Urbanization and disease emergence: Dynamics at the wildlife–livestock–human interface. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Pollock, E.; de Jong, M.C.M.; Keeling, M.J.; Klinkenberg, D.; Wood, J.L.N. Eight challenges in modelling infectious livestock diseases. Epidemics 2015, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinemerem Nwobodo, D.; Ugwu, M.C.; Oliseloke Anie, C.; Al-Ouqaili, M.T.S.; Chinedu Ikem, J.; Victor Chigozie, U.; Saki, M. Antibiotic Resistance: The challenges and some emerging strategies for tackling a global menace. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Alam, M. Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators (2022). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Evid. Based Nurs. 2024, 27, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, M.; Ranucci, E.; Romagnoli, P.; Giaccone, V. Antimicrobial resistance: A global emerging threat to public health systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority List, 2024 Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Rokana, N.; Chandra, M.; Singh, B.P.; Gulhane, R.D.; Gill, J.P.S.; Ray, P.; Puniya, A.K.; Panwar, H. Antimicrobial resistance: Its surveillance, impact, and alternative management strategies in dairy animals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 4, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.; Ward, M.; Van Bunnik, B.; Farrar, J. Antimicrobial resistance in humans, livestock and the wider environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.; Uwiera, R.R.E.; Kalmokoff, M.L.; Brooks, S.P.J.; Inglis, G.D. Antimicrobial growth promoter use in livestock: A requirement to understand their modes of action to develop effective alternatives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adisasmito, W.B.; Almuhairi, S.; Behravesh, C.B.; Bilivogui, P.; Bukachi, S.A.; Casas, N.; Becerra, N.C.; Charron, D.F.; Chaudhary, A.; Ciacci Zanella, J.R.; et al. One Health: A new definition for a sustainable and healthy future. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Khurshid, M.; Arshad, M.I.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.; Yasmeen, N.; Shah, T.; Chaudhry, T.H.; Rasool, M.H.; Shahid, A.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: One health one world outlook. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 771510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Coque, T.M.; Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L. Defining and combating antibiotic resistance from one health and global health perspectives. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuru, P.; Valeria D’Auria, M.; Muller, C.D.; Tammela, P.; Vuorela, H.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J. Exploring marine resources for bioactive compounds. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucko, J.; Starcevic, A.; Diminic, J.; Oros, D.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Putnik, P. Probiotic—Friend or Foe? Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, D.; Patel, S.; Kim, S.K. Probiotic Supplements Might Not Be Universally-Effective and Safe: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenster, K.; Freeburg, B.; Hollard, C.; Wong, C.; Laursen, R.R.; Ouwehand, A.C. The Production and delivery of probiotics: A review of a practical approach. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Nieuwboer, M.; Brummer, R.J.; Guarner, F.; Morelli, L.; Cabana, M.; Claassen, E. The administration of probiotics and synbiotics in immune compromised adults: Is it safe? Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Kang, D.K.; Paik, H.D.; Park, Y.S. Beyond Probiotics: A narrative review on an era of revolution. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katkowska, M.; Garbacz, K.; Kusiak, A. Probiotics: Should all patients take them? Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, M.; Baldi, A. Regulatory categories of probiotics across the globe: A review representing existing and recommended categorization. Indian. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 33, S2–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Velumani, D.; Lin, Y.C.; Haye, A. A comprehensive review of probiotic claims regulations: Updates from Asia-Pacific, United States, and Europe. PharmaNutrition 2024, 30, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdichon, F.; Budde-Niekiel, A.; Dubois, A.; Fritz, D.; Hatte, J.L.; Laulund, S.; McAuliffe, O.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Yao, S.; Zgoda, A.; et al. Inventory of Microbial Food Cultures with safety demonstration in fermented food products update of the bulletin of the IDF N°377-2002, N°455-2012 and N°495-2018. In Proceedings of the Bulletin of the International Dairy Federation, Brussels, Belgium, 12 September 2022; Volume 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Szajewska Hania and Vinderola, G. Current Regulatory Issues for the Use of Probiotics. In Probiotics and Child Gastrointestinal Health: Advances in Microbiology, Infectious Diseases and Public Health Volume 19; Stefano, G., Indrio, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 187–193. ISBN 978-3-031-58572-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, N.; Jan, S.Y.; Dar, A.H.; Dash, K.K.; Sarkar, A.; Shams, R.; Pandey, V.K.; Khan, S.A.; Amin, Q.A.; Hussain, S.Z. Promising bioactivities of postbiotics: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Hasannezhad, P.; Abbasi, A.; Khani, N. Antibacterial, Antiviral, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities of Postbiotics: A Review of mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 2629–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-González, P.F.; Liceaga, A.M.; Aguilar-Toalá, J.E. Postbiotics and paraprobiotics: From concepts to applications. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scauro, A.; Rocchetti, M.T.; Soccio, M.; la Gatta, B.; Liberatore, M.T.; De Simone, N.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D.; Russo, P. Postbiotic potential of newly isolated riboflavin-overproducing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strains. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 2025, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, S.M.A.; Behfar, A.; Saadat, A.; Ameri, A.; Yazdi, S.S.A.; Siahpoosh, A. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of natural postbiotics derived from five lactic acid bacteria. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2023, 18, e130785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, F.; Jafari, P.; Nomanpour, B.; Varmira, K.; Raissi, F. Inhibitory effects of postbiotic consisting sonication-killed Bifidobacterium bifidum on experimental triple negative breast neoplasm in mice: A preliminary study. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2022, 14, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Mishra, A.K.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Yadavalli, R.; Agrawal, D.C.; Reddy, H.P.; Gorrepati, R.; Reddy, C.N.; Mandal, S.K.; Shamim, M.Z.; et al. Postbiotics: The new horizons of microbial functional bioactive compounds in food preservation and security. Food Prod. Process Nutr. 2024, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie-Oleza, J.A.; Armengaud, J. In-Depth analysis of exoproteomes from marine bacteria by shotgun liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: The Ruegeria pomeroyi DSS-3 Case-Study. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2223–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gómez, O.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; García-Márquez, J.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T. Metabolite-Driven modulation of biofilm formation in shewanella: Insights from Shewanella sp. Pdp11 extracellular products. Microb. Ecol. 2025, 88, e70046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Pérez-Gómez, O.; García-Márquez, J.; Espinosa-Ruíz, C.; Cuesta, A.; Esteban, M.Á.; Alarcón-López, F.J.; Cárdenas, C.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Balebona, M.C.; et al. Microalgae and cyanobacteria as microbial substrate and their influence on the potential postbiotic capability of a bacterial probiotic. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e70046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englerová, K.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Nemcová, R.; Király, J.; Mad’ar, M.; Hajdučková, V.; Styková, E.; Mucha, R.; Reiffová, K. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens—Derived lipopeptide biosurfactants inhibit biofilm formation and expression of biofilm-related genes of Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, P.; Liu, R.; Zhang, D.; Suna, C. Pumilacidin-like Lipopeptides Derived from marine Bacterium bacillus sp. strain 176 suppress the motility of Vibrio alginolyticus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00450-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, G.; Zhou, S.; Sha, Z.; Sun, C. Characterization of antifungal lipopeptide biosurfactants produced by marine Bacterium bacillus sp. CS30. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Sen, R. Antimicrobial potential of a lipopeptide biosurfactant derived from a marine Bacillus circulans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almada, C.N.; Almada, C.N.; Martinez, R.C.R.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Paraprobiotics: Evidences on their ability to modify biological responses, inactivation methods and perspectives on their application in foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, B.; Delgado, S.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Lourenço, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Margolles, A. Probiotics, gut microbiota, and their influence on host health and disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tu, H.; Chen, T. Postbiotics in human health: A narrative review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Habsi, N.; Al-Khalili, M.; Haque, S.A.; Elias, M.; Al Olqi, N.; Al Uraimi, T. Health benefits of prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Jiang, W.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Chen, T.; Ma, J.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, W.; et al. Unlocking the power of postbiotics: A revolutionary approach to nutrition for humans and animals. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 725–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, K.; Singh, B.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, A.K.; Jindal, R.; Kumar, R. Potential of probiotics and postbiotics in aquaculture: Connecting current research gaps and future perspectives. Microbe 2025, 8, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, N.; Patel, J.; Singh, S.; Yadav, V.K.; Joshi, C.; Patani, A.; Prajapati, D.; Sahoo, D.K.; Patel, A. Postbiotic production: Harnessing the power of microbial metabolites for health applications. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1306192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.-T.; Lu, H.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.-W.; Shan, X.-F. The application and potential of postbiotics as sustainable feed additives in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2024, 592, 741237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, J.; Thangam, T.; Jahankir, M.J.B.; Parthasarathy, K. Bacteriocin Postbiotics for Tuberculosis Drug Development; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luenglusontigit, P.; Sathapondecha, P.; Saengsuwan, P.; Surachat, K.; Boonserm, P.; Singkhamanan, K. Effects of postbiotic from bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance producing Enterococcus faecalis on Toxigenic Clostridioides difficile. J. Health Sci. Med. Res. 2023, 41, 2023918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, C.; Draper, L.A.; Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. A comparison of the activities of lacticin 3147 and nisin against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus Species. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, D.; Hill, C.; Field, D.; Begley, M. Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes by the Staphylococcus capitis—Derived Bacteriocin Capidermicin. Food Microbiol. 2021, 94, 103661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, S.; Zirah, S.; Ben Taher, M.; Theolier, J.; Fernandez, B.; Rebuffat, S.F.; Fliss, I. Microcin J25 exhibits inhibitory activity against Salmonella newport in continuous fermentation model mimicking swine colonic conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.D.; Guo, E.; Wyllie, R.M.; Jensen, P.; Dawid, S. The pneumococcal bacteriocin streptococcin b is produced as part of the early competence cascade and promotes intraspecies competition. mBio 2025, 16, e0299324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, K.; Manigundan, K.; Rajesh Kannan, V.; Annamalai, K.K.; Manikkam, R.; Venugopal, G.; Krishnan, S. Analysis and Identification of Short-Chain Fatty Acid Postbiotics by Gas Chromatography; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvigioni, M.; Bertolini, A.; Codini, S.; Mazzantini, D.; Panattoni, A.; Massimino, M.; Celandroni, F.; Zucchi, R.; Saba, A.; Ghelardi, E. HPLC-MS-MS quantification of short-chain fatty acids actively secreted by probiotic strains. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1124144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandaliya, D.K.; Patel, S.; Seshadri, S. Postbiotic potential of SCFAs on metaflammation and gut microbiota alteration in diabetes. J. Biosci. 2025, 50, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaladejo-Riad, N.; El Qendouci, M.; Cuesta, A.; Esteban, M.Á. Ability of short-chain fatty acids to reduce inflammation and attract leucocytes to the inflamed skin of Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, M. Effects of dietary sodium acetate on growth, intestinal microbiota composition, and ammonia tolerance of juvenile Yellow Catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Aquaculture 2024, 581, 740480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontinha, F.; Martins, N.; Campos, G.; Peres, H.; Oliva-Teles, A. The effects of short-chain fatty acids in gut immune and oxidative responses of european sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax): An Ex Vivo Approach. Animals 2024, 14, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholan, P.M.; Han, A.; Woodie, B.R.; Watchon, M.; Kurz, A.R.M.; Laird, A.S.; Britton, W.J.; Ye, L.; Holmes, Z.C.; McCann, J.R.; et al. Conserved anti-inflammatory effects and sensing of butyrate in zebrafish. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1824563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Heng, X.; Guo, L.; Lessing, D.J.; Chu, W. SCFAs improve disease resistance via modulate gut microbiota, enhance immune response and increase antioxidative capacity in the host. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 120, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Shao, J.H.; Liao, Y.T.; Wang, L.N.; Jia, Y.; Dong, P.J.; Liu, Z.Z.; He, D.D.; Li, C.; Zhang, X. Regulation of short-chain fatty acids in the immune system. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1186892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.K.; Macia, L.; Mackay, C.R. Dietary Fiber and SCFAs in the Regulation of Mucosal Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilderink, R.; Verseijden, C.; Seppen, J.; Muncan, V.; van den Brink, G.R.; Lambers, T.T.; van Tol, E.A.; de Jonge, W.J. The SCFA butyrate stimulates the epithelial production of retinoic acid via inhibition of epithelial hdac. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G1138–G1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisevius, B.; Duscha, A.; Poschmann, G.; Stühler, K.; Motte, J.; Fisse, A.L.; Augustyniak, S.; Rehm, A.; Renk, P.; Böse, C.; et al. Propionic acid promotes neurite recovery in damaged multiple sclerosis neurons. Brain Commun 2024, 6, fcae182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilyurt, N.; Yılmaz, B.; Ağagündüz, D.; Capasso, R. Involvement of probiotics and postbiotics in the immune system modulation. Biologics 2021, 1, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Dharumadurai, D. Dietary Supplementation and Immunomodulatory Activity of Postbiotics in Fish; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhana, A.; Khan, Y.S. Biochemistry, Lipopolysaccharide; StatPearls: Petersburg, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.J.; Adin, D.M.; Stabb, E.V.; McFall-Ngai, M.J.; Apicella, M.A.; Gibson, B.W. The lipid a from Vibrio fischeri lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21203–21219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, F. The Lipopolysaccharide Lipid A Structure from the marine sponge-associated bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. 2A. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 110, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasikova, I.N.; Kapustina, N.V.; Isakov, V.V.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Solov’eva, T.F. Detailed Structure of Lipid A isolated from lipopolysaccharide from the Marine Proteobacterium marinomonas vaga ATCC 27119T. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M. Structural modifications of bacterial lipopolysaccharide that facilitate gram-negative bacteria evasion of host innate immunity. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Lipopolysaccharide delivery systems in innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2024, 45, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, B. Endotoxin, Toll-like Receptor 4, and the afferent limb of innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golwankar, A.; Pawar, R.; Tibile, R.; Sawant, S. In Silico characterization, homology modelling and structure-based functional annotation of Labeo rohita TLR4 Protein. Int. J. Adv. Biochem. Res. 2024, 8, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loes, A.N.; Hinman, M.N.; Farnsworth, D.R.; Miller, A.C.; Guillemin, K.; Harms, M.J. Identification and Characterization of Zebrafish Tlr4 Coreceptor Md-2. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Dong, F.; Jang, S.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Isolation and Analysis of a Novel Grass Carp Toll-like Receptor 4 (Tlr4) Gene Cluster Involved in the Response to Grass Carp Reovirus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Cai, S.Y.; Shao, J.Z.; Chen, J. Toll-Like Receptors, associated biological roles, and signaling networks in non-mammals. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulcre, M.P.; Alcaraz-Pérez, F.; López-Muñoz, A.; Roca, F.J.; Meseguer, J.; Cayuela, M.L.; Mulero, V. Evolution of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) recognition and signaling: Fish TLR4 does not recognize LPS and negatively regulates NF-ΚB activation. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.J.; Ning, Y.J.; Liu, H.; Nie, L.; Chen, J. A Novel lipopolysaccharide recognition mechanism mediated by internalization in teleost macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-López, A.; Tyrkalska, S.D.; Alcaraz-Pérez, F.; Cabas, I.; Candel, S.; Martínez Morcillo, F.J.; Sepulcre, M.P.; García-Moreno, D.; Cayuela, M.L.; Mulero, V. Evolution of LPS recognition and signaling: The bony fish perspective. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 145, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera-Rosales, L.B.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.E.; Ramírez-Moreno, E.; Quintero-Lira, A.; Contreras-López, E.; Jaimez-Ordaz, J.; Castañeda-Ovando, A.; Añorve-Morga, J.; Calderón-Ramos, Z.G.; Arias-Rico, J.; et al. Impact of the gut microbiota balance on the health-disease relationship: The importance of consuming probiotics and prebiotics. Foods 2021, 10, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panitsidis, I.; Barbe, F.; Chevaux, E.; Giannenas, I.; Demey, V. Probiotics, Prebiotics, Paraprobiotics, Postbiotics. In Sustainable Use of Feed Additives in Livestock: Novel Ways for Animal Production; Georgios, A., Giannenas, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 173–227. ISBN 978-3-031-42855-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danladi, Y.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Akit, H.; Tamrin, N.A.M.; Naeem, A.M. Impact of feeding postbiotics and paraprobiotics produced from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on colon mucosa microbiota in broiler chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 859284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Kyoung, H.; Park, K.I.; Oh, S.; Song, M.; Kim, Y. Postbiotic heat-killed Lactobacilli modulates on body weight associated with gut microbiota in a pig model. AMB Express 2022, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, A.; Huang, S.; Kuo, S.; Shu, M.; Tapia, C.P.; Yu, J.; Two, A.; Zhang, H.; Gallo, R.L.; et al. Propionic Acid and Its Esterified Derivative Suppress the Growth of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300. Benef. Microbes 2014, 5, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, M.; Karch, A.; Pieper, D.H. Colonic Butyrate-Producing Communities in Humans: An Overview Using Omics Data. mSystems 2017, 2, e00130-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.; De Paepe, K.; Van de Wiele, T. Postbiotics and their health modulatory biomolecules. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, J.D.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Wolfenden, R.E.; Vicente, J.L.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Menconi, A.; Bielke, L.R.; Hargis, B.M.; Tellez, G. Evaluation and selection of Bacillus species based on enzyme production, antimicrobial activity, and biofilm synthesis as direct-fed microbial candidates for poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.S.; Kim, I.H. Effect of Bacillus subtilis C-3102 spores as a probiotic feed supplement on growth performance, noxious gas emission, and intestinal microflora in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 3097–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Márquez, J.; Díaz, A.G.; Molina-Roque, L.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; de las Heras, V.; Simó-Mirabet, P.; Vizcaíno, A.J.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Alarcón-López, F.J.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; et al. Microalgal and cyanobacterial biomasses modified the activity of extracellular products from Bacillus pumilus: An in vitro and in vivo assessment. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakovich, L.J.; Balskus, E.P. Metabolic functions of the human gut microbiota: The role of metalloenzymes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 593–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, T.C.; Thanh, N.T.; Foo, H.L.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Azhar, B.K. feeding of different levels of metabolite combinations produced by Lactobacillus plantarum on growth performance, fecal microflora, volatile fatty acids and villi height in broilers. Anim. Sci. J. 2010, 81, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, F.; Campo-Celada, M.; Menéndez-Miranda, M.; García-Rodríguez, J.; Martínez-Fernández, A. Effect of postbiotic supplementation on nutrient digestibility and milk yield during the transition period in dairy cows. Animals 2024, 14, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuddin, W.I.; Loh, T.C.; Samsudin, A.A.; Foo, H.L.; Humam, A.M.; Shazali, N. Effects of postbiotic supplementation on growth performance, ruminal fermentation and microbial profile, blood metabolite and GHR, IGF-1 and MCT-1 gene expression in post-weaning lambs. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Duarte, M.E. Saccharomyces yeast postbiotics supplemented in feeds for sows and growing pigs for its impact on growth performance of Offspring and Growing Pigs in commercial farm environments. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danladi, Y.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Akit, H.; Tamrin, N.A.M.; Azizi, M.N. Effects of postbiotics and paraprobiotics as replacements for antibiotics on growth performance, carcass characteristics, small intestine histomorphology, immune status and hepatic growth gene expression in broiler chickens. Animals 2022, 12, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Afzal, Z.; Afzal, F.; Khan, R.U.; Elnesr, S.S.; Alagawany, M.; Chen, H. Use of postbiotic as growth promoter in poultry industry: A review of current knowledge and future prospects. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2023, 43, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvakova, M.; Kamlarova, A.; Stofilova, J.; Benetinova, V.; Bertkova, I. Probiotics and postbiotics in colorectal cancer: Prevention and complementary therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 3370–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, L.O.; Foo, H.L.; Loh, T.C.; Mohammed Alitheen, N.B.; Yeap, S.K.; Abdul Mutalib, N.E.; Abdul Rahim, R.; Yusoff, K. Postbiotic metabolites produced by Lactobacillus plantarum strains exert selective cytotoxicity effects on cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.; Patel, M.; Chandrasekaran, S. Metabolism, HDACs, and HDAC Inhibitors: A systems biology perspective. Metabolites 2021, 11, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asoudeh-Fard, A.; Beygi, M.Y.; Parsaei, A.; Mohkam, M.; Asoudeh-Fard, M.; Gholami, A. Postbiotic metabolites derived from Lactobacillus fermentum as potent antiproliferative bioresources on HeLa Cells with promising biocompatibility. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banday, A.H.; Azha, N.U.; Farooq, R.; Sheikh, S.A.; Ganie, M.A.; Parray, M.N.; Mushtaq, H.; Hameed, I.; Lone, M.A. Exploring the potential of marine natural products in drug development: A comprehensive review. Phytochem. Lett. 2024, 59, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; Coppola, D. Biodiversity, adaptation strategies, and opportunities in extreme marine environments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.B.; Su, Z.M.; Hu, D.H.; Bao, Y.L.; Meng, X.Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.X. Studies on molecular structure of hypericin and its interactions with HIV-1 protease by molecular modeling. Gaodeng Xuexiao Huaxue Xuebao Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2009, 30, 1402. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.K.; Yoon, S.J.; Song, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.J.; Suk, K.T. A Scheme to underpin key mediator(s) in salinosporamide(s) against pan-tumor via systems biology concept. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwang, S.A.; Sethi, G.; Chao, T.H.; Neuteboom, S.T.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Palladino, M.A.; Younes, A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Salinosporamide a (NPI-0052) potentiates apoptosis, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and inhibits invasion through down-modulation of NF-ΚB-Regulated gene products. Blood 2007, 110, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, R.K. Marine Biodiversity: Challenges, Trends, and a New Treaty. Environ. Law 2023, 53, 343–381. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Seukep, A.J.; Guo, M. Recent Advances in Molecular Docking for the Research and Discovery of Potential Marine Drugs. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Velasco, X.; Lucena, T.; Belda, A.; Gasol, J.M.; Sánchez, O.; Arahal, D.R.; Pujalte, M.J. Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization of 26 Novel Marine Bacterial Strains with Relevant Biogeochemical Roles and Widespread Presence across the Global Ocean. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1407904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hablützel, P.I.; Liu, Z.; Van Acker, E.; Janssen, C.R.; Asselman, J.; De Rijcke, M. Seasonal Dynamics of Bacterial Community Structure and Function in the Surf Zone Seawater of a Recreational Beach in Ostend, Belgium. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e70031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner-Lamia, J.; Huerta-Cepas, J. Exploring the Sediment-Associated Microbiota of the Mar Menor Coastal Lagoon. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1319961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanika, N.H.; Liaqat, N.; Chen, H.; Ke, J.; Lu, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. Fish gut microbiome and its application in aquaculture and biological conservation. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1521048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Devi, W.M.; Choudhury, T.G.; Kamilya, D.; Monsang, S.J.; Irungbam, S.; Saha, R.K. Unraveling the bioactivities and immunomodulatory potential of postbiotics derived from Bacillus subtilis and B. amyloliquefaciens for aquaculture. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 2025, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.R.; Kamilya, D.; Choudhury, T.G.; Rathore, G. Dietary administration of a host-gut derived probiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens COFCAU_P1 modulates immune-biochemical response, immune-related gene expression, and resistance of Labeo rohita to Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawhney, S.; Mishra, J.K. bioactive potential of bacterial endosymbionts isolated from Lamellodysidea herbacea, marine sponge from the coast of south Andaman, India, against human bacterial pathogens. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, L.L.; Li, E.W.; Hou, T.T.; Liu, Z.P. Mechanism of anti-vibrio activity of marine probiotic strain Bacillus pumilus H2, and characterization of the active substance. AMB Express 2017, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Márquez, J.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Torres, M.; Cerezo, I.M.; Ramos, E.; Alarcón, F.J.; Mancera, J.M.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Balebona, M.C. Potential Effects of microalgae-supplemented diets on the growth, blood parameters, and the activity of the intestinal microbiota in Sparus aurata and Mugil cephalus. Fishes 2023, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.R.; Choudhury, T.G.; Kamilya, D.; Monsang, S.J.; Parhi, J. Characterization of Bacillus spp. isolated from intestine of Labeo rohita—Towards identifying novel probiotics for aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, P.; Naik, C. Potential antimicrobial activity of Bacillus Subtilis isolated from marine environment of Bhatkal. World J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-García, C.; Béjar, V.; Martínez-Checa, F.; Llamas, I.; Quesada, E. Bacillus velezensis sp. Nov., a surfactant-producing bacterium isolated from the river Vélez in Málaga, Southern Spain. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, B.; Chen, G.; Liang, Z. purification and characterization of a fibrinolytic enzyme from marine Bacillus velezensis Z01 and assessment of its therapeutic efficacy in vivo. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, M.E.; Liu, J.; Wallace, J.; Akhlaghi, F.; Rowley, D.C. Secondary metabolites produced by the marine bacterium Halobacillus salinus that inhibit quorum sensing-controlled phenotypes in gram-negative bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareeb, A.; Fouda, A.; Kishk, R.M.; El Kazzaz, W.M. Unlocking the therapeutic potential of bioactive exopolysaccharide produced by marine actinobacterium Streptomyces vinaceusdrappus AMG31: A novel approach to drug development. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla-Pineda, M.; Ibañez, F.C.; Garrote-Achou, C.; Marzo, F. A Novel postbiotic product based on Weissella cibaria for enhancing disease resistance in rainbow trout: Aquaculture application. Animals 2024, 14, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla-Pineda, M.; Achou, C.G.; Díaz, J.; Gutiérrez-Falcon, A.; Bravo, M.; Herrera-Muñoz, J.I.; Peña-Navarro, N.; Alvarado, C.; Ibañez, F.C.; Marzo, F. In vitro evaluation of postbiotics produced from bacterial isolates obtained from rainbow trout and nile tilapia against the pathogens Yersinia ruckeri and Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. Salmonicida. Foods 2023, 12, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arijo, S.; Brunt, J.; Chabrillón, M.; Díaz-Rosales, P.; Austin, B. Subcellular Components of Vibrio harveyi and probiotics induce immune responses in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), against V. harveyi. J. Fish. Dis. 2008, 31, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, Y.S.; Alamri, S.A.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Alrumman, S.A.; Elbehairi, S.E.I.; Taha, T.H.; Hashem, M. L-Glutaminase synthesis by marine Halomonas meridiana isolated from the red sea and its efficiency against colorectal cancer cell lines. Molecules 2021, 26, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deberardinis, R.J.; Cheng, T. Q’s next: The diverse functions of glutamine in metabolism, cell biology and cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, J.G.; Moon, K.S.; Bin Jung, S.; Kwon, Y.M.; Kang, N.S.; Kim, J.H.; Nam, S.J.; Choi, G.; Baek, Y.B.; et al. Identification and characterization of a marine bacterium extract from Mameliella sp. M20D2D8 with antiviral effects against Influenza A and B viruses. Arch. Virol. 2024, 169, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.N.; Xu, Y.J.; Shao, M.M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Cao, J.Y.; Xu, J.L. Pseudoalteromonas flavipulchra as a dual-functional probiotic for aquaculture: Enhancing microalgae growth and antagonizing Vibrio pathogens. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1492142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, E.C.; Stierhof, M.; Goralczyk, S.; Vabre, F.M.; Pellissier, L.; Hanssen, K.Ø.; de la Cruz, M.; Díaz, C.; de Witte, P.; Copmans, D.; et al. Pseudochelin A, a Siderophore of Pseudoalteromonas piscicida S2040. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 2633–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supardy, N.A.; Ibrahim, D.; Nor, S.R.M.; Noordin, W.N.M. Bioactive Compounds of Pseudoalteromonas sp. IBRL PD4.8 inhibit growth of fouling bacteria and attenuate biofilms of Vibrio alginolyticus FB3. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusano, A.; Parrilli, E.; Marino, G.; Tutino, M.L. A novel genetic system for recombinant protein secretion in the antarctic Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Microb. Cell Fact. 2006, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillo, A.; Papa, R.; Ricciardelli, A.; Sannino, F.; Ziaco, M.; Tilotta, M.; Selan, L.; Marino, G.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Anti-biofilm activity of a long-chain fatty aldehyde from antarctic Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 against Staphylococcus Epidermidis Biofilm. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, J.L.; Ruiz-Jarabo, I.; Vargas-Chacoff, L.; Arijo, S.; León-Rubio, J.M.; García-Millán, I.; Martín del Río, M.P.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Mancera, J.M. Dietary administration of probiotic pdp11 promotes growth and improves stress tolerance to high stocking density in Gilthead Seabream Sparus auratus. Aquaculture 2010, 309, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, J.; Villasanta-González, A.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Balebona, M.C.; García de la Banda, I.; Moríñigo, M.Á.; Prieto-Álamo, M.J. Dietary administration of the probiotic shewanella putrefaciens pdp11 promotes transcriptional changes of genes involved in growth and immunity in Solea senegalensis Larvae. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 77, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, S.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Moriñigo, J.M.; Lobo, C.; García de la Banda, I.; Balebona, M.d.C.; Moriñigo, M.Á. Effects on Intestinal Microbiota and Immune Genes of Solea senegalensis after Suspension of the Administration of Shewanella putrefaciens Pdp11. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 58, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García de La Banda, I.; Lobo, C.; León-Rubio, J.M.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Moreno-Ventas, X.; Lucas, L.M.; Linares, F.; Arce, F.; et al. Influence of two closely related probiotics on juvenile Senegalese Sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup 1858) Performance and Protection against Photobacterium damselae subsp. Piscicida. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Vidal, S.; Lobo, C.; García de la Banda, I.; Esteban, M.A.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.A. Dietary administration of the probiotic SpPdp11: Effects on the intestinal microbiota and immune-related gene expression of farmed Solea senegalensis treated with oxytetracycline. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2015, 46, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerezo, I.M.; Pérez-Gómez, O.; Bautista, R.; Seoane, P.; Esteban, M.Á.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T. SpPdp11 administration in diet modified the transcriptomic response and its microbiota associated in mechanically induced wound Sparus aurata Skin. Animals 2023, 13, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, P.; Álvarez-Torres, D.; Balebona, M.C.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Béjar, J.; Alonso, M.C.; García-Rosado, E. Inhibition of Nervous Necrosis Virus Replication by Shewanella putrefaciens Pdp11 Extract. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; García-Márquez, J.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; González-Fernández, C.; Cuesta, A.; Espinosa-Ruíz, C.; Esteban, M.Á.; Alarcón, F.J.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.Á. Evaluation of the differential postbiotic potential of Shewanella putrefaciens Pdp11 cultured in several growing conditions. Mar. Biotechnol. 2024, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Cerezo, I.M.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; De La Banda, I.G.; Moreno-Ventas, X.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Balebona, M.C. A Tentative study of the effects of heat-inactivation of the probiotic strain Shewanella putrefaciens Ppd11 on Senegalese Sole (Solea senegalensis) intestinal microbiota and immune response. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, A.; García-Márquez, J.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Arijo, S. Effect of the potential probiotic Vibrio proteolyticus DCF12.2 on the Immune System of Solea senegalensis and Protection against Photobacterium damselae Subsp. Piscicida and Vibrio harveyi. Fishes 2023, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Márquez, J.; Vizcaíno, A.J.; Barany, A.; Galafat, A.; Acién, G.; Figueroa, F.L.; Alarcón, F.J.; Mancera, J.M.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Arijo, S.; et al. Evaluation of the Combined Administration of Chlorella fusca and Vibrio proteolyticus in Diets for Chelon labrosus: Effects on growth, metabolism, and digestive functionality. Animals 2023, 13, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Márquez, J.; Álvarez-Torres, D.; Cerezo, I.M.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Figueroa, F.L.; Alarcón, F.J.; Acién, G.; Martínez-Manzanares, E.; Abdala-Díaz, R.T.; Béjar, J.; et al. Combined Dietary Administration of Chlorella fusca and Ethanol-Inactivated Vibrio proteolyticus Modulates Intestinal Microbiota and Gene Expression in Chelon labrosus. Animals 2023, 13, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Gómez, O.; Rohra-Benítez, S.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; Cerezo, I.M.; Galafat, A.; Martínez-Manzanares, E.; Mancera, J.M.; Alarcón-López, F.J.; García-Márquez, J.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; et al. Dietary Administration of Postbiotics from Vibrio proteolyticus DCF12.2 enhanced intestinal integrity, microbiota, and immune response in juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Animals 2025, 15, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, N.T.; Vu, T.H.N.; Nguyen, N.A.; Nguyen, V.T.; Bui, T.L.; Ky, S.C.; Le, T.L.; Hoang, H.; Ngo, C.C.; Le, T.T.M.; et al. Phenotypic features and analysis of genes supporting probiotic action unravel underlying perspectives of Bacillus velezensis VTX9 as a Potential Feed Additive for Swine. Ann. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerezo, I.M.; Pérez-Gómez, O.; Rohra-Benítez, S.; Domínguez-Maqueda, M.; García-Márquez, J.; Arijo, S. Postbiotics of Marine Origin and Their Therapeutic Application. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090335
Cerezo IM, Pérez-Gómez O, Rohra-Benítez S, Domínguez-Maqueda M, García-Márquez J, Arijo S. Postbiotics of Marine Origin and Their Therapeutic Application. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(9):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090335
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerezo, Isabel M., Olivia Pérez-Gómez, Sonia Rohra-Benítez, Marta Domínguez-Maqueda, Jorge García-Márquez, and Salvador Arijo. 2025. "Postbiotics of Marine Origin and Their Therapeutic Application" Marine Drugs 23, no. 9: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090335
APA StyleCerezo, I. M., Pérez-Gómez, O., Rohra-Benítez, S., Domínguez-Maqueda, M., García-Márquez, J., & Arijo, S. (2025). Postbiotics of Marine Origin and Their Therapeutic Application. Marine Drugs, 23(9), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23090335






