Isolation and Purification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Prepared by Marine Bacillus velezensis Z-1 Protease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
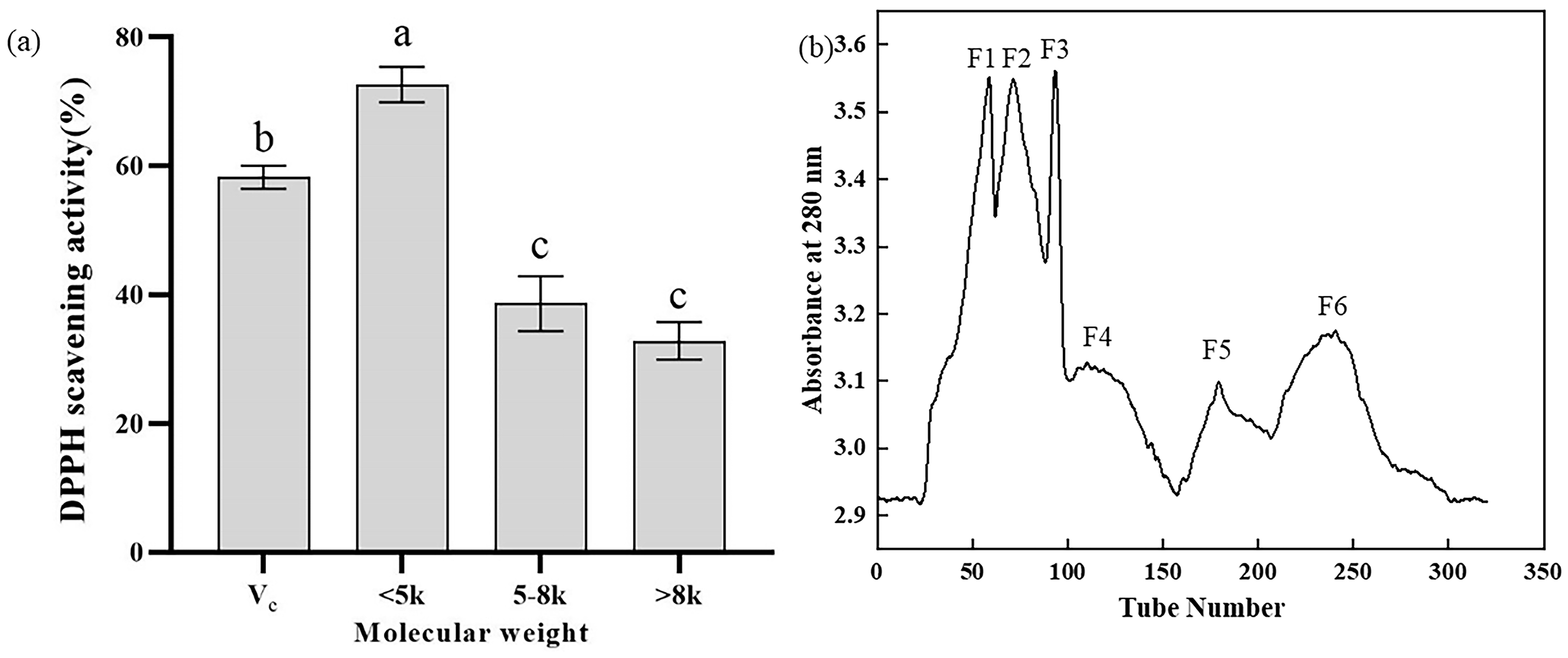
2.1. Separation, Purification, and Activity Determination of Y-1
2.2. Determination of In Vitro Activities
2.3. Identification of Peptide Sequences
2.4. Screening and Characterization of Bioactive Peptides
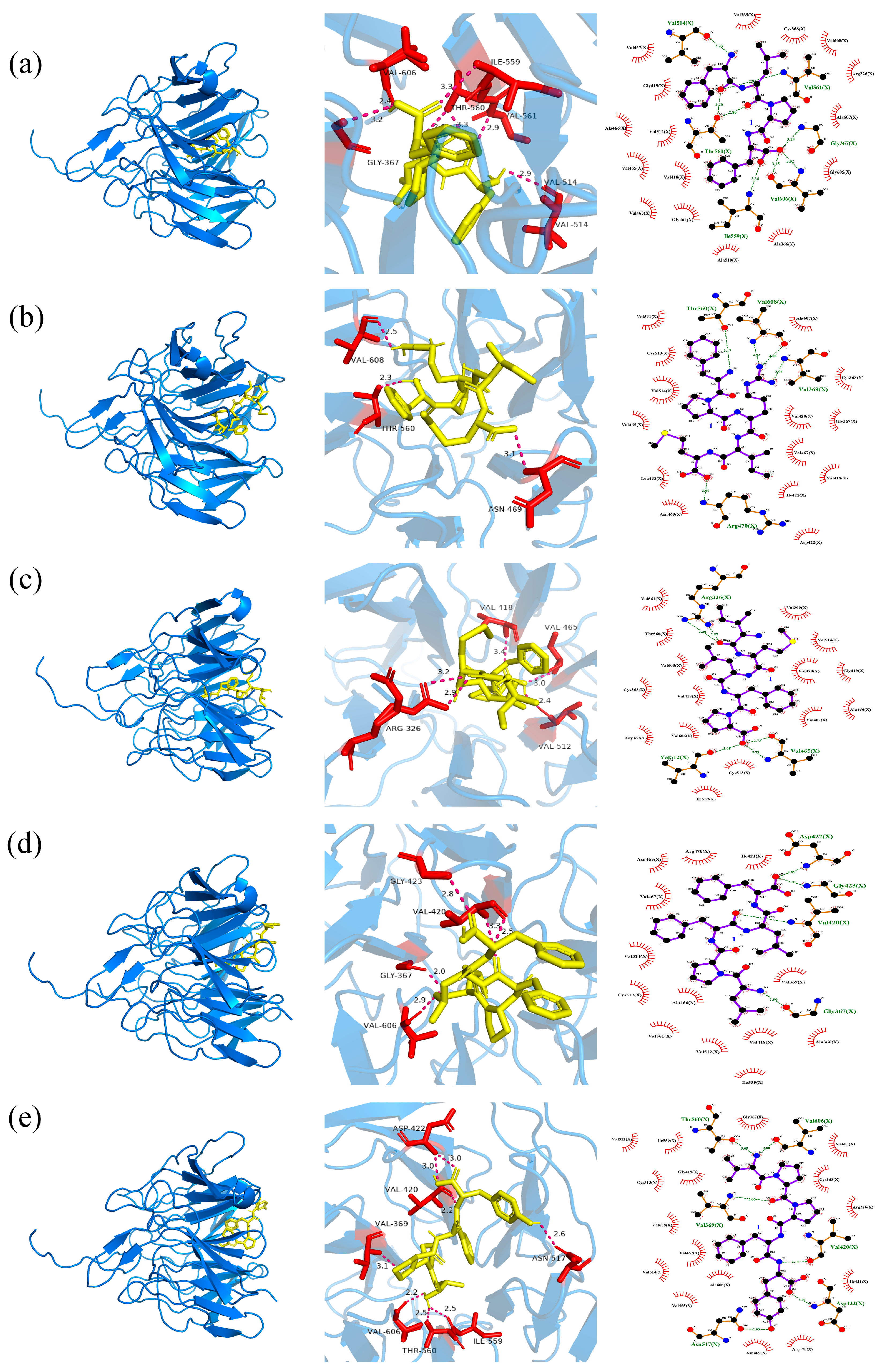
2.5. Molecular Docking
2.5.1. The Docking of Polypeptides with CD38
2.5.2. The Docking of Polypeptides with Keap1
2.6. Identification of the Antioxidant Activity of Peptides
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.1.1. Materials
4.1.2. Reagents
4.2. Preparation, Separation, and Purification of Mussel Bioactive Peptide
4.2.1. Bioactive Peptide Preparation
4.2.2. Ultrafiltration
4.2.3. Separation and Purification via Gel Filtration Chromatography
4.3. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
4.3.1. Determination of DPPH Scavenging Activity
4.3.2. Determination of Superoxide Anion Scavenging Activity
4.4. Determination of Lipid-Lowering Ability
4.4.1. Determination of Pancreatic Cholesterol Esterase Inhibitory Activity
4.4.2. Determination of Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity
4.5. Determination of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
4.6. Identification of Peptide Fractions
4.7. Screening of Bioactive Peptides
4.8. Peptide Synthesis
4.9. Verification of the Antioxidant Activity of Polypeptides
4.10. Data Analysis Method
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purohit, K.; Reddy, N.; Sunna, A. Exploring the Potential of Bioactive Peptides: From Natural Sources to Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen Christian, T.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Teufel, F.G.; Kjrulff, S.K.; Wang, Z.; Meng, G.; Jessen, C.; Heljo, P.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, X. Combining Mass Spectrometry and Machine Learning to Discover Bioactive Peptides. Nat. Commun. 2022, 11, 4033. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Liu, H.-S.; Yan, J.-X.; Shi, Q.; Yang, H.; Cao, S.-Q.; Qi, X.-Y. Identification and Molecular Mechanism of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Squid Skin Protein Hydrolysates: In Silico and in Vitro Analysis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 214, 117081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zh, T.; Li, X.; Sadiq, F.A.; Mao, K.; Gao, J.; Mi, S.; Liu, X.; Deng, W.; Chitrakar, B.; Sang, Y. Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysates of Scallop (Argopecten irradians) Mantle Using Enzymatic and Microbial Methods: Preparation, Purification, Identification and Characterization. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 164, 113636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, Z.; Rakariyatham, K.; Yu, C.; Shahidi, F.; Zhou, D. Antioxidant Activity and Functional Properties of Alcalase-Hydrolyzed Scallop Protein Hydrolysate and Its Role in the Inhibition of Cytotoxicity in Vitro. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant Peptides from the Protein Hydrolysate of Monkfish (Lophius litulon) Muscle: Purification, Identification, and Cytoprotective Function on HepG2 Cells Damage by H2O2. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Pan, C.; Cai, M.M.; Li, L.H.; Yang, X.Q.; Xiang, H.; Chen, S.J. Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Grateloupia livida Hydrolysates: Purification and Identification. Foods 2022, 11, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Nam, K.; Huang, X.; Ahn, D.U. Plant- and Animal-Based Antioxidants’ Structure, Efficacy, Mechanisms, and Applications: A Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Pan, R.; Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, B. Clam Peptides: Preparation, Flavor Properties, Health Benefits, and Safety Risks. Food Res. Int. 2025, 207, 116113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khasmakhi, N.E.; Rahimabadi, E.Z.; Sangatash, M.M. Purification and Characterization of Antioxidant Peptide Fractions from Protein Hydrolysate of Rainbow Trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss) Viscera. Food Res. Int. 2025, 206, 116027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hou, Z.; Liu, B.; Guo, X.; Zhu, B.; Hu, Y. Study on the Antioxidant and Antiosteoporotic Activities of the Oyster Peptides Prepared by Ultrasound-Assisted Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 112, 107211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Ren, G.Y.; Zhang, B.; Ma, F.L.; Fan, J.L.; Qiu, Z.J. Screening and Identification of a Novel Antidiabetic Peptide from Collagen Hydrolysates of Chinese Giant Salamander Skin: Network Pharmacology, Inhibition Kinetics and Protection of Ir-Hepg2 Cells. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 3329–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, L.; He, J.; Ming, L.; Jambal, T.; Mijiddorj, B.; Maizul, B.; Enkhtuul, T.; Ji, R.M.T. Identification and Molecular Docking of a Novel Antidiabetic Peptide from Protamex-Camel Milk Protein Hydrolysates against A-Amylase and Dpp-Iv. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 152, 105884. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.W.; Ma, R.L.; Cui, G.J.; Wen, Y.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.G. Rice Bran Peptide with A-Glucosidase Inhibition Activity: Preparation, Evaluation and Molecular Mechanism. J. Cereal Sci. 2024, 115, 103837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.J.; Xing, L.J.; Wang, Z.X.; Cai, J.M.; Toldrá, F.; Zhang, W.A. Study on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Porcine Bone Collagen Peptides Prepared by Ultrasound-Assisted Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 101, 106697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, M.; Kilari, B.P.; Mudgil, P.; Nirmal, N.P.; Ojha, S.; Ayoub, M.A.; Amin, A.; Maqsood, S. Bioactive peptides with potential anticancer properties from various food protein sources: Status of recent research, production technologies, and developments. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2025, 45, 1076–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Liu, F.J.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, G.H.; Cai, D.; Yu, J.H.; Yin, F.W.; Zhou, D.Y. Preparation and Hepatoprotective Activities of Peptides Derived from Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and Clams (Ruditapes philippinarum). Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, A.S.; Pintado, M.E. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Marine Sources: Biological and Functional Properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 348–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, R.; Cheng, Y.; Qin, J.H.; Yang, J.; Fang, Y.W.; Lyu, M.S.; Wang, S.J. Screening and Characteristics of Marine Bacillus velezensis Z-1 Protease and Its Application of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Mussels to Prepare Antioxidant Active Substances. Molecules 2022, 27, 6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang Han, L.H.; Hong, H.; Pan, J.; Liu, H.G.; Luo, Y.K. Purification and Identification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Silver Carp Muscle Hydrolysate after Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion and Transepithelial Transport. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; James, M.D.; Maes, E.; Kumar, L.; Serventi, L. Proximate Composition, Peptide Characterization and Bioactive Properties of Faba Bean Blanching Water. Food Res. Int. 2025, 200, 115426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.F.; Deng, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.T.; He, L.; Ma, G.Y.; Li, S.J.; Li, H.B. Bovine Liver Hydrolysates Based on Six Proteases: Physicochemical Properties, Emulsification Characteristics, Antioxidant Capacity Assessment, and Peptide Identification. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 208, 116718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimatu, B.M.; Zhao, L.Y.; Biao, Y.; Ma, G.X.; Yang, W.J.; Pei, F.; Hu, Q.H. Antioxidant Potential of Edible Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Protein Hydrolysates and Their Ultrafiltration Fractions. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaprasob, R.; Khongdetch, J.; Laohakunjit, N.; Selamassakul, O.; Kaisangsri, N. Isolation and Characterization, Antioxidant, and Antihypertensive Activity of Novel Bioactive Peptides Derived from Hydrolysis of King Boletus Mushroom. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 160, 113287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.B.; Lu, A.C.; Sun, Y.N.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Huang, P.T.; Yang, A.P.; Li, Z.W.; Cao, Y.; et al. Purification and Identification of Antioxidant and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Peptides from Guangdong Glutinous Rice Wine. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 169, 113953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Chi, C.-F.; Ma, J.-H.; Luo, H.-Y.; Xu, Y.-F. Purification and Characterisation of a Novel Antioxidant Peptide Derived from Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Protein Hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olagunju, A.I.; Omoba, O.S.; Enujiugha, V.N.; Alashi, A.M.; Aluko, R.E. Pigeon Pea Enzymatic Protein Hydrolysates and Ultrafiltration Peptide Fractions as Potential Sources of Antioxidant Peptides: An in Vitro Study. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 97, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Jiang, S.Q.; Li, Y.Z.; Xie, D.M.; Li, J.X. Residue Profiles of Peptides with Cholesterol Esterase and Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activities through Virtual Screening and Sequence Analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Wu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, D.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Ma, Q.; Jiang, W. Extraction, Identification, and Molecular Mechanisms of A-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Defatted Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) Powder Hydrolysates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Dai, S.X.; Cai, Z.X.; Shi, J.B.; Sun, P.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y.P. Theoretical Guiding with Molecular Docking for the Screening of High-Sensitive Aie Probes for Specific Protein Detection. Talanta 2025, 283, 127161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.L.; Tang, H.G.; Li, H.H.; Da, S.; Ciren, D.; Peng, X.Y.; Zhao, K. Identification, Characterization, and Insights into the Mechanism of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-Iv Inhibitory Peptides from Yak Hemoglobin by in Silico Exploration, Molecular Docking, and in Vitro Assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekun, L.; Zhang, W.; Abubaker, M.A.; Shu, Q.; Liu, Y. In Silico Identification and Experimental Validation of Two Types of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (Ace) and Xanthine Oxidase (Xo) Milk Inhibitory Peptides. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141864. [Google Scholar]
- Gayathiri, E.; Prakash, P.; Chaudhari, S.Y.; Sabarathinam, S.; Priyadharshini, S.D.; Al-Sadoon, M.K.; Panneerselvam, J.; Chang, S.W.; Ravindran, B.; Mani, R.R. Interaction of Molecular Mechanisms of Plant-Derived Metabolites in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Network Pharmacology, Docking and Molecular Dynamics Approach on Akt1 Kinase. Energy Nexus 2025, 17, 100351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summart, R.; Imsoonthornruksa, S.; Yongsawatdigul, J.; Ketudat-Cairns, M.; Udomsil, N. Characterization and Molecular Docking of Tetrapeptides with Cellular Antioxidant and Ace Inhibitory Properties from Cricket (Acheta domesticus) Protein Hydrolysate. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzain, M.; Ali, E.M.M.; Zamzami, M.; Qadri, I.; Choudhry, H.; Chaieb, K.; Kouidhi, B.; Altayb, H.N. Identification of Antimicrobial Bioactive Peptides from the Camel Milk Protein Lactoferrin: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation, and in Vitro Study. Food Humanit. 2024, 3, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Qu, L.P.; He, B.W. Preparation, Identification and Molecular Docking of Two Novel Anti-Aging Peptides from Perilla Seed. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.H.; Aidy, E.A.; Said, M.A.; Kebeish, R.; Al-Badwy, A.H. Biochemical and Molecular Docking-Based Assessment of Spirulina Platensis’s Bioactive Constituents for Their Potential Application as Natural Anticancer Drug. Algal Res.-Biomass Biofuels Bioprod. 2024, 82, 103624. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.N.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, S.Y.; Bu, Y.; Zhu, W.H.; Li, X.P. Identification and Molecular Mechanism of Novel Antioxidant Peptide from Fish Sauce: A Combined Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Simulation. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, B.J.; Wu, X.D.; Xia, Z.H.; Wu, G.H.; Guo, Q.Y.; Lyu, S.; Wang, S.J. Multiple Bioactivities of Peptides from Hydrolyzed Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. Molecules 2023, 28, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.F.; Dai, Q.F.; Zheng, K.W.; Ma, Q.B.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.Q.; Jiang, W.; Yan, X.J. Exploring the Inhibitory Potential of Kphs-Al-Derived Gllf Peptide on Pancreatic Lipase and Cholesterol Esterase Activities. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.F.; Lai, X.H.; Wu, X.D.; Wang, H.Y.; Weng, N.H.; Lu, J.; Lyu, M.S.; Wang, S.J. Isolation of a Novel Anti-Diabetic α-Glucosidase Oligo-Peptide Inhibitor from Fermented Rice Bran. Foods 2023, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Gómez, B.; Barba, F.J.; Mora, L.; Pérez-Santaescolástica, C.; Toldrá, F. Bioactive Peptides as Natural Antioxidants in Food Products—A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Jahandideh, F.; Wu, J. Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 608979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Name | A | Length | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLPF | 523.3 | 4 | 49.5 | 100 | 3.37 | −8.3 | −9.7 |
| IMLFP | 620.3 | 5 | 52.9 | 100 | 3.29 | −7.6 | −7.9 |
| LPFLF | 636.4 | 5 | 59.9 | 100 | 2.12 | −9.1 | −8.3 |
| FPRIM | 663.4 | 5 | 35.7 | 80 | 6.35 | −7.8 | −7.7 |
| VPPFY | 622.3 | 5 | 37.5 | 80 | 5.30 | −9.1 | −9.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Shi, P.; Cao, Y.; Shi, B.; Shen, H.; Zhao, S.; Gao, Y.; Chi, H.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y. Isolation and Purification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Prepared by Marine Bacillus velezensis Z-1 Protease. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080294
Lu J, Shi P, Cao Y, Shi B, Shen H, Zhao S, Gao Y, Chi H, Wang L, Shi Y. Isolation and Purification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Prepared by Marine Bacillus velezensis Z-1 Protease. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(8):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080294
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jing, Pujing Shi, Yutian Cao, Bingxin Shi, Huilin Shen, Shuai Zhao, Yuchen Gao, Huibing Chi, Lei Wang, and Yawei Shi. 2025. "Isolation and Purification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Prepared by Marine Bacillus velezensis Z-1 Protease" Marine Drugs 23, no. 8: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080294
APA StyleLu, J., Shi, P., Cao, Y., Shi, B., Shen, H., Zhao, S., Gao, Y., Chi, H., Wang, L., & Shi, Y. (2025). Isolation and Purification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Prepared by Marine Bacillus velezensis Z-1 Protease. Marine Drugs, 23(8), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23080294





