Metabolomic Profiling and Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of Caulerpa lentillifera (Sea Grape) Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
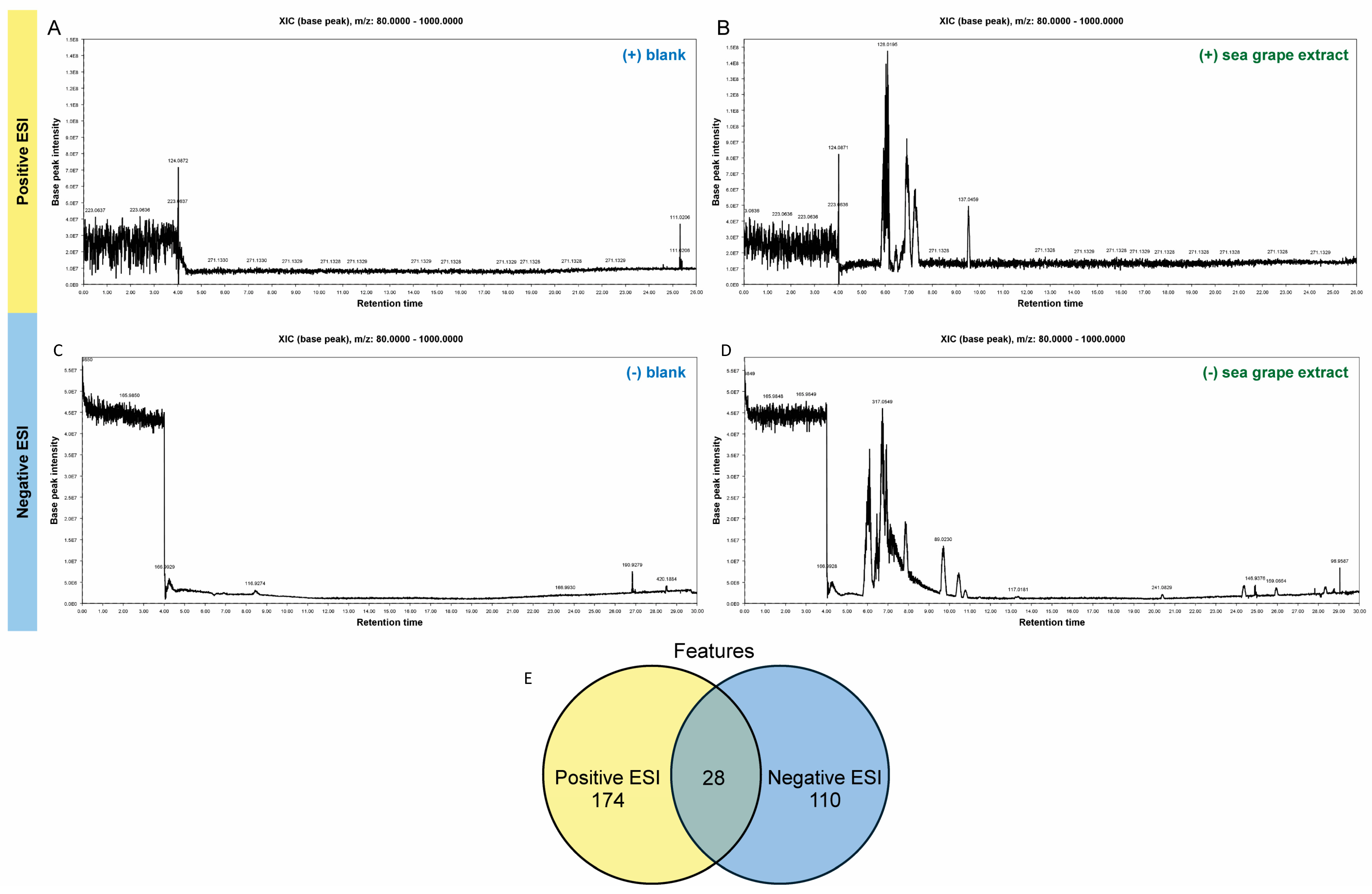
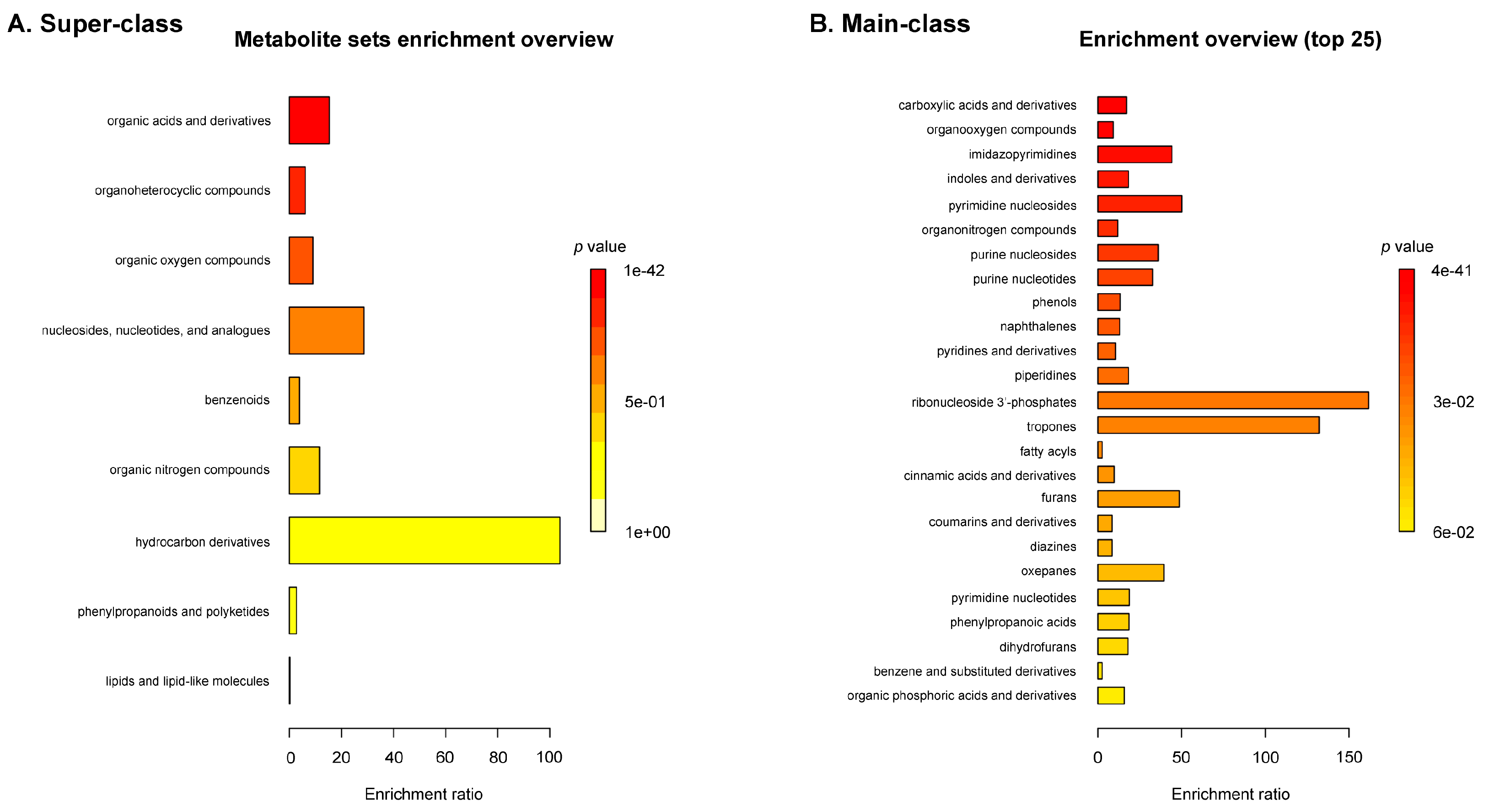
2.1. Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling of Sea Grape Extract Using LC-MS/MS
2.2. Sea Grape Extract Exhibits Selective Antibacterial Activity
2.3. Sea Grape Extracts Strongly Inhibit H. pylori Growth
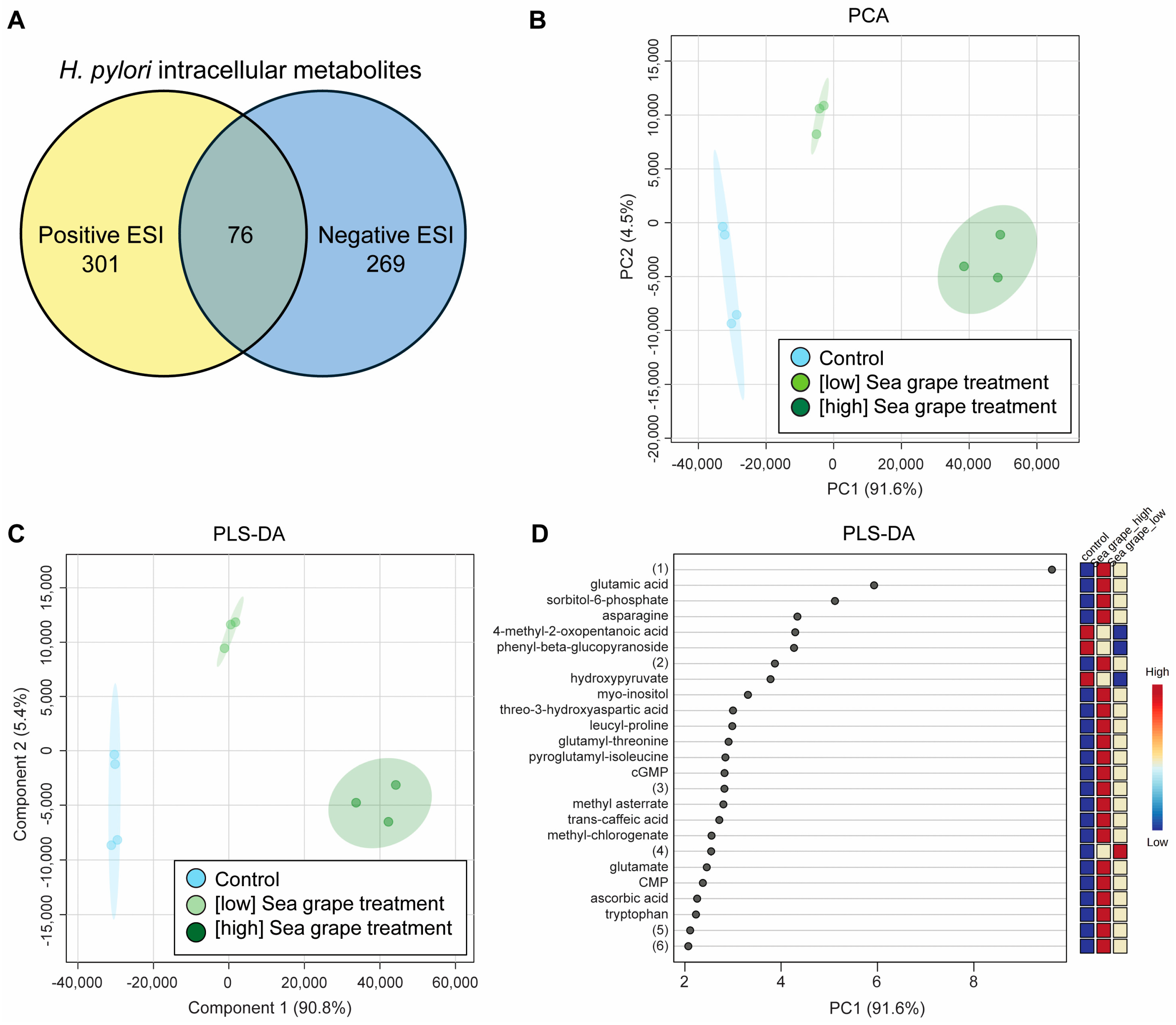
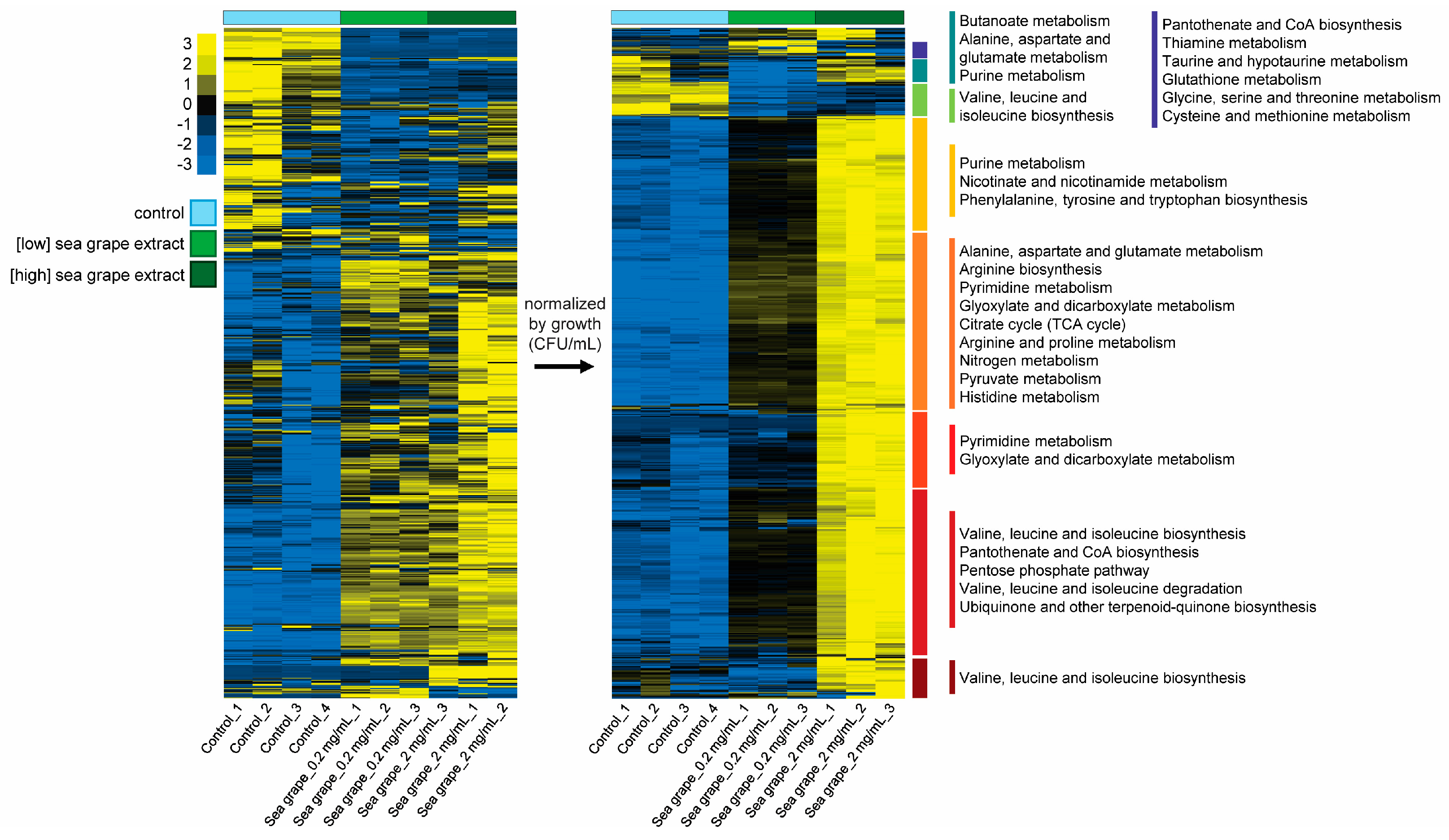
2.4. Sea Grape Extracts Led to Metabolic Changes in H. pylori
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Biomass and Extract Preparation
3.2. Strains and Media
3.3. Antibacterial Property Evaluation
3.4. Chemical Composition Analyses of Sea Grape Extract
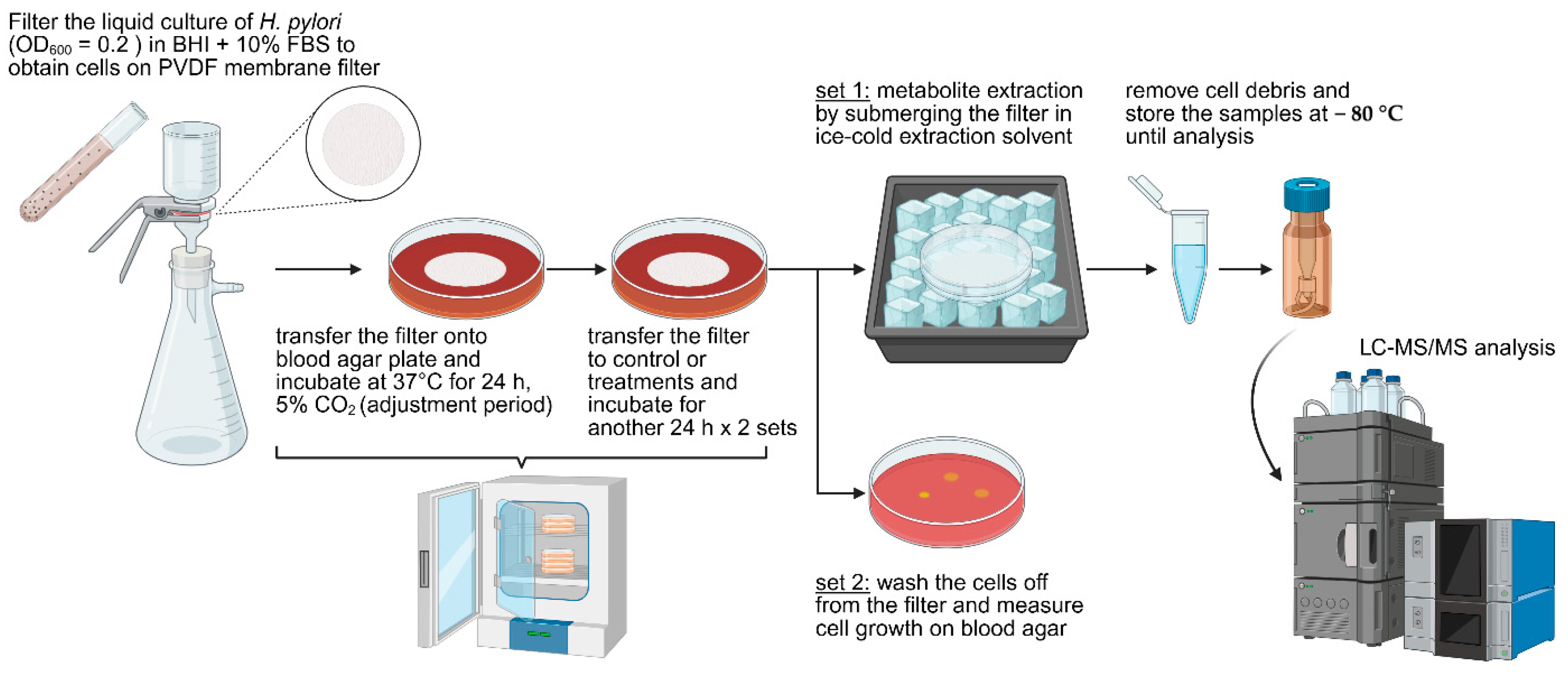
3.5. Examination of Metabolic Response of H. pylori Treated with Sea Grape Extract
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.-C.; Malfertheiner, P.; Yu, H.-T.; Kuo, C.-L.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Meng, F.-T.; Wu, Y.-X.; Hsiao, J.-L.; Chen, M.-J.; Lin, K.-P. Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and incidence of gastric cancer between 1980 and 2022. Gastroenterology 2024, 166, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboobi, R.; Fallah, F.; Yadegar, A.; Dara, N.; Aghdam, M.K.; Asgari, B.; Hakemi-Vala, M. Expression analysis of miRNA-155 level in Helicobacter pylori related inflammation and chronic gastritis. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2022, 14, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Mégraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—The Maastricht V/Florence consensus report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaidi, I.; Bounder, G.; Jouimyi, R.M.; Boura, H.; Elyounsi, I.; Kheir, F.-Z.; Benomar, H.; Badre, W.; Zerouali, K.; Maachi, F. Comparative study of Helicobacter pylori resistance to clarithromycin and metronidazole and its association with epidemiological factors in a moroccan population. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, P. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori reshapes gut microbiota and facilitates the evolution of antimicrobial resistance through gene transfer and genomic mutations in the gut. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, S.W.; Barnett, M.L.; MacFadden, D.R.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hernández-Díaz, S.; Lipsitch, M.; Grad, Y.H. The distribution of antibiotic use and its association with antibiotic resistance. eLife 2018, 7, e39435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syakilla, N.; George, R.; Chye, F.Y.; Pindi, W.; Mantihal, S.; Wahab, N.A.; Fadzwi, F.M.; Gu, P.H.; Matanjun, P. A review on nutrients, phytochemicals, and health benefits of green seaweed, Caulerpa lentillifera. Foods 2022, 11, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-N.; Sun, S.-S.; Liu, M.-Z.; Yan, M.-C.; Liu, Y.-F.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Natural bioactive compounds from marine fungi (2017–2020). J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 24, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.K.; Parida, S.; Behera, A.K.; Adhikary, S.P.; Lukatkin, A.A.; Lukatkin, A.S.; Jena, M. Seaweed in the diet as a source of bioactive metabolites and a potential natural immunity booster: A comprehensive review. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Li, P. Advances in cultivation, wastewater treatment application, bioactive components of Caulerpa lentillifera and their biotechnological applications. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Preez, R.; Majzoub, M.E.; Thomas, T.; Panchal, S.K.; Brown, L. Caulerpa lentillifera (sea grapes) improves cardiovascular and metabolic health of rats with diet-induced metabolic syndrome. Metabolites 2020, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amornlerdpison, D.; Yoojam, S.; Mengumphan, K.; Lailerd, N. Functional ingredients on creating value added in sea grape, Caulerpa lentillifera. J. Agric. Res. Ext. 2023, 40, 115671. [Google Scholar]
- Srinorasing, T.; Chirasuwan, N.; Bunnag, B.; Chaiklahan, R. Lipid extracts from Caulerpa lentillifera waste: An alternative product in a circular economy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ai, C.; Song, S.; Chen, X. Caulerpa lentillifera polysaccharides enhance the immunostimulatory activity in immunosuppressed mice in correlation with modulating gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4315–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, B.; Do, D.T.; Nguyen, H.M.; Do, B.H.; Le, H.T. Preparation, characterization, and anti-adhesive activity of Sulfate polysaccharide from Caulerpa lentillifera against Helicobacter pylori. Polymers 2022, 14, 4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koodkaew, I.; Pitakwongsaporn, S.; Jarussophon, N.; Wichachucherd, B. Chemical Profile, Antioxidant activity and α-glucosidase inhibition of sea grape Caulerpa lentillifera collected from different sites in Thailand. Trends Sci. 2024, 21, 7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rojas, A.; Nath, A.; El Shazely, B.; Santi, G.; Kim, J.J.; Weise, C.; Kuropka, B.; Rolff, J. Antimicrobial peptide induced-stress renders Staphylococcus aureus susceptible to toxic nucleoside analogs. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, K.; Jeon, Y.-J. Bio-functionalities of proteins derived from marine algae—A review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalile, B.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Vervliet, B.; Verbeke, K. The role of short-chain fatty acids in microbiota–gut–brain communication. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniyappan, S.; Sridhar, A.; Kari, Z.A.; Téllez-Isaías, G.; Ramasamy, T. Evaluation of phytochemical screening, pigment content, in vitro antioxidant, antibacterial potential and GC-MS metabolite profiling of green seaweed Caulerpa racemosa. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshibangu-Kabamba, E.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori infection and antibiotic resistance—From biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Agathokleous, E.; Kapoor, R.; Kozumbo, W.J.; Rattan, S.I. Re-analysis of herbal extracts data reveals that inflammatory processes are mediated by hormetic mechanisms. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2019, 314, 108844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, H.; Miyoshi, S.; Araho, D.; Kanamoto, T.; Terakubo, S.; Nakashima, H.; Tsuda, T.; Sunaga, K.; Amano, S.; Ohkoshi, E. Efficient utilization of licorice root by alkaline extraction. In Vivo 2014, 28, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Cui, L.; Natarajan, M.; Barone, P.W.; Wolfrum, J.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Rice, S.A.; Springs, S.L. The ratio of nicotinic acid to nicotinamide as a microbial biomarker for assessing cell therapy product sterility. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 25, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio, B.V.; dos Santos Ramos, M.A.; Da Silva, P.B.; Bauab, T.M. Antimicrobial activity of natural products against Helicobacter pylori: A review. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2014, 13, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, A.; Scortecci, K.C.; Boylan, F. A review on flavonoids as anti-Helicobacter pylori agents. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivyna de Araújo Rêgo, R.; Guedes Silvestre, G.F.; Ferreira de Melo, D.; Albino, S.L.; Pimentel, M.M.; Silva Costa Cruz, S.B.; Silva Wurzba, S.D.; Rodrigues, W.F.; Goulart de Lima Damasceno, B.P.; Cançado Castellano, L.R. Flavonoids-rich plant extracts against Helicobacter pylori infection as prevention to gastric cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 951125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, M.; Arif, M.; Hamouda, H.I.; Khan, S.; Abdalla, M.; Shabana, S.; Rozan, H.E.; Khan, T.U.; Chi, Z.; Liu, C. Preparation, urease inhibition mechanisms, and anti-Helicobacter pylori activities of hesperetin-7-rhamnoglucoside. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Song, K.; Jia, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Dong, R. Antimicrobial activity of syringic acid against Cronobacter sakazakii and its effect on cell membrane. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakoshi, M. Multilayered regulation of amino acid metabolism in Escherichia coli. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2024, 77, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Tian, S.-q.; Wang, S.-w.; Liu, Y.-l.; Li, H.; Peng, B. Pyruvate abundance confounds aminoglycoside killing of multidrug-resistant bacteria via glutathione metabolism. Research 2024, 7, 0554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibayama, K.; Wachino, J.i.; Arakawa, Y.; Saidijam, M.; Rutherford, N.G.; Henderson, P.J. Metabolism of glutamine and glutathione via γ-glutamyltranspeptidase and glutamate transport in Helicobacter pylori: Possible significance in the pathophysiology of the organism. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, A.; Sarkar, D.; Shetty, K. Elicitation of stress-induced phenolic metabolites for antimicrobial applications against foodborne human bacterial pathogens. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarewicz, M.; Drożdż, I.; Tarko, T.; Duda-Chodak, A. The interactions between polyphenols and microorganisms, especially gut microbiota. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva de Abreu, T.; Braga, M.A.; Trento, M.V.C.; Konig, I.F.M.; Machado, G.H.A.; Ferreira da Cunha, E.F.; Marcussi, S. Gallic and vanillic acids as promising succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors and antigenotoxic agents. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2021, 31, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrenovich, M.; Li, Y.; Tayahi, M.; Reddy, V.P. Polyphenols and small phenolic acids as cellular metabolic regulators. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 4152–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, N.S. Amino Acid Metabolism. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2021, 13, a040584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuvalov, O.; Petukhov, A.; Daks, A.; Fedorova, O.; Vasileva, E.; Barlev, N.A. One-carbon metabolism and nucleotide biosynthesis as attractive targets for anticancer therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23955–23977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.C.; Maddocks, O.D.K. One-carbon metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, N.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, R.; Wei, X.; Fan, M. Transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling uncovers response mechanisms of Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris DSM 3922T to acid stress. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00022–e00023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaniya, A.; Mehta, S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Fiehn, O. MassBank of North America: Using untargeted metabolomics and multistage fragmentation mass spectral libraries to annotate natural products in plants. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Plant Spectroscopy Conference, Berlin, Germany, 24–28 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Seitzer, P.; Bennett, B.; Melamud, E. MAVEN2: An updated open-source mass spectrometry exploration platform. Metabolites 2022, 12, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, B.D.; Yuan, J.; Kimball, E.H.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Absolute quantitation of intracellular metabolite concentrations by an isotope ratio-based approach. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisithkul, T.; Schroeder, J.W.; Trujillo, E.A.; Yeesin, P.; Stevenson, D.M.; Chaiamarit, T.; Coon, J.J.; Wang, J.D.; Amador-Noguez, D. Metabolic remodeling during biofilm development of Bacillus subtilis. mBio 2019, 10, e00623–e00719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thacharoen, C.; Inkaewwong, T.; Jumpathong, W.; Kaewsapsak, P.; Rattanapot, T.; Pisithkul, T. Metabolomic Profiling and Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of Caulerpa lentillifera (Sea Grape) Extract. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070282
Thacharoen C, Inkaewwong T, Jumpathong W, Kaewsapsak P, Rattanapot T, Pisithkul T. Metabolomic Profiling and Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of Caulerpa lentillifera (Sea Grape) Extract. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(7):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070282
Chicago/Turabian StyleThacharoen, Chananchida, Thisirak Inkaewwong, Watthanachai Jumpathong, Pornchai Kaewsapsak, Thiravat Rattanapot, and Tippapha Pisithkul. 2025. "Metabolomic Profiling and Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of Caulerpa lentillifera (Sea Grape) Extract" Marine Drugs 23, no. 7: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070282
APA StyleThacharoen, C., Inkaewwong, T., Jumpathong, W., Kaewsapsak, P., Rattanapot, T., & Pisithkul, T. (2025). Metabolomic Profiling and Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of Caulerpa lentillifera (Sea Grape) Extract. Marine Drugs, 23(7), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070282






