Bioactive Polyketides from Amphidinium spp.: An In-Depth Review of Biosynthesis, Applications, and Current Research Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
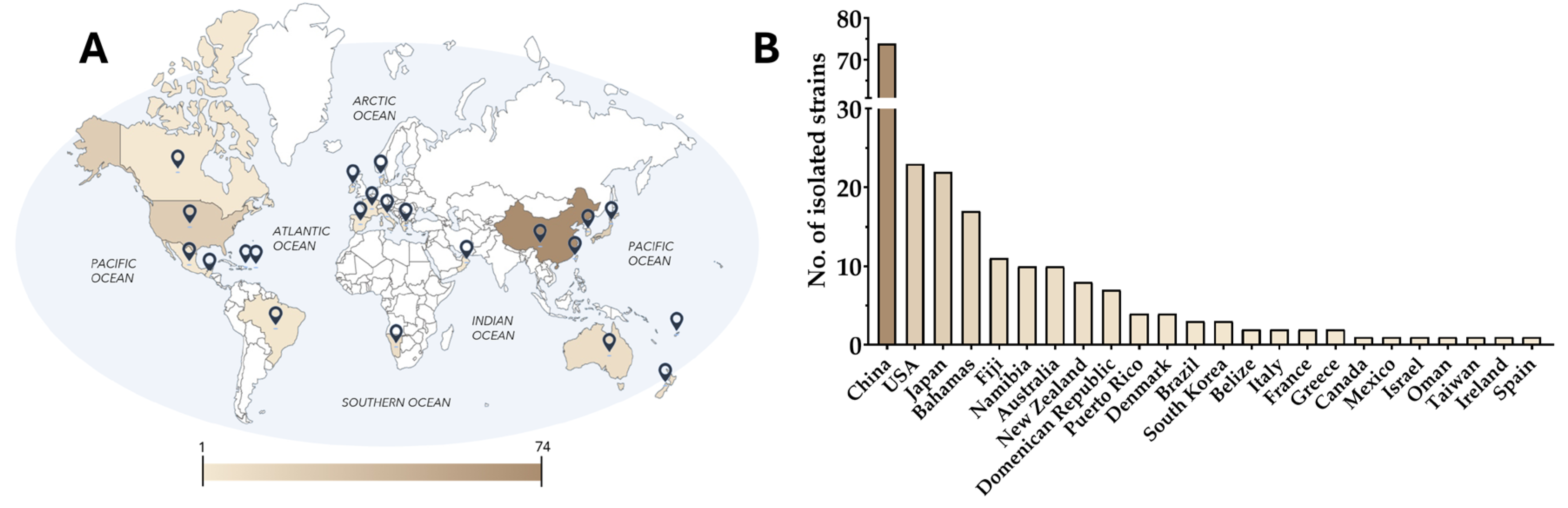
2. An Overview of Dinoflagellate Polyketides
3. Amphidinium Polyketides: Chemical Structures and Biological Activities
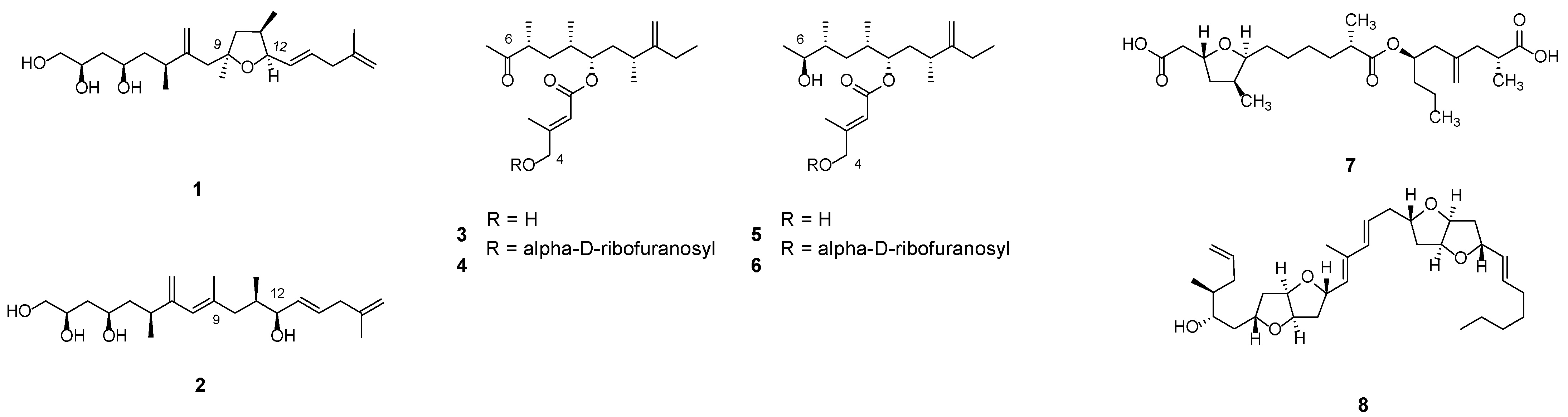
3.1. Linear Polyketides
3.2. Macrolides
4. Amphidium Polyketides Biosynthesis
4.1. Amphidinium PKS Genes Discovery
4.2. Labelling Experiments in Amphidinium Polyketides Biosynthetic Studies
4.2.1. Labelling Patterns of Amphidinolides
4.2.2. Labelling Studies of Amphidinols and Other Linear Polyketides
5. Research Gaps in Biotechnological Applications of APKs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Assunção, J.; Catarina Guedes, A.; Xavier Malcata, F. Biotechnological and Pharmacological Applications of Biotoxins and Other Bioactive Molecules from Dinoflagellates. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, C.; Ferrante, M.I.; Rogato, A. Marine Natural Products from Microalgae: An -Omics Overview. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, C.; Barra, G.; Saponaro, M.; Manzo, E.; Fioretto, L.; Ziaco, M.; Nuzzo, G.; d’Ippolito, G.; De Palma, R.; Fontana, A. A New Bioassay Platform Design for the Discovery of Small Molecules with Anticancer Immunotherapeutic Activity. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MarinLit Dedicated to Marine Natural Products Research. Available online: https://pubs.rsc.org/marinlit (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Abdel-Razek, A.S.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Allam, A.; Morsy, O.M.; Othman, S.I. Microbial Natural Products in Drug Discovery. Processes 2020, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Future Markets Insights. Available online: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Mayer, A.; Mayer, V.; Swanson-Mungerson, M.; Pierce, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Nakamura, F.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Marine Pharmacology in 2019–2021: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and Other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, D.; Lee, J. Recent Advances in Marine-Derived Compounds as Potent Antibacterial and Antifungal Agents: A Comprehensive Review. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretto, L.; Ziaco, M.; Gallo, C.; Nuzzo, G.; d’Ippolito, G.; Lupetti, P.; Paccagnini, E.; Gentile, M.; DellaGreca, M.; Appavou, M.-S.; et al. Direct Evidence of the Impact of Aqueous Self-Assembly on Biological Behavior of Amphiphilic Molecules: The Case Study of Molecular Immunomodulators Sulfavants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 611, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaco, M.; Fioretto, L.; Nuzzo, G.; Fontana, A.; Manzo, E. Short Gram-Scale Synthesis of Sulfavant A. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2020, 24, 2728–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Ramírez, M.d.C.; Hernández-Melgar, A.G.; Cembella, A.D.; Maskrey, B.H.; Díaz-Rubio, L.J.; Córdova-Guerrero, I.; Bernáldez-Sarabia, J.; González-Maya, L.; Esquivel-Rodríguez, B.; Bustos-Brito, C.; et al. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis and Cytotoxicity of Extracts of the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium eilatiense Against Human Cancer Cell Lines. Toxins 2025, 17, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine Pharmacology. Available online: www.marinepharmacology.org (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Hertweck, C. The Biosynthetic Logic of Polyketide Diversity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4688–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bian, Z.; Hu, S.; Dickinson, C.F.; Benjamin, M.M.; Jia, J.; Tian, Y.; Place, A.; Hanna, G.S.; Luesch, H.; et al. The Chemistry of Phytoplankton. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 13099–13177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feling, R.H.; Buchanan, G.O.; Mincer, T.J.; Kauffman, C.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Salinosporamide A: A Highly Cytotoxic Proteasome Inhibitor from a Novel Microbial Source, a Marine Bacterium of the New Genus Salinospora. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, F. A Quantitative Review of the Lifestyle, Habitat and Trophic Diversity of Dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata, Alveolata). Syst. Biodivers. 2012, 10, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellmann, R.; Stüken, A.; Orr, R.J.S.; Svendsen, H.M.; Jakobsen, K.S. Biosynthesis and Molecular Genetics of Polyketides in Marine Dinoflagellates. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1011–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, F.J.R.; Hoppenrath, M.; Saldarriaga, J.F. Dinoflagellate Diversity and Distribution. In Protist Diversity and Geographical Distribution; Foissner, W., Hawksworth, D.L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 8, pp. 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, F. Diversity and Classification of Dinoflagellates. In Dinoflagellates; Rao, D.V.S., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–10. ISBN 9781536178883. [Google Scholar]
- Orefice, I.; Balzano, S.; Romano, G.; Sardo, A. Amphidinium spp. as a Source of Antimicrobial, Antifungal, and Anticancer Compounds. Life 2023, 13, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-S.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Yu, Y.; Wu, J.; Shen, L. A Polyol-Polyol Super-Carbon-Chain Compound Containing Thirty-Six Carbon Stereocenters from the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium gibbosum: Absolute Configuration and Multi-Segment Modification. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. Genomic Understanding of Dinoflagellates. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.A.; Suggett, D.J.; Doblin, M.A.; Kohli, G.S.; Seymour, J.R.; Fabris, M.; Ralph, P.J. Unravelling the Functional Genetics of Dinoflagellates: A Review of Approaches and Opportunities. Perspect. Phycol. 2016, 3, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Hackett, J.D.; Van Dolah, F.M.; Nosenko, T.; Lidie, K.L.; Bhattacharya, D. Tertiary Endosymbiosis Driven Genome Evolution in Dinoflagellate Algae. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, R.F.; Patron, N.J.; Keeling, P.J. Phylogenetic History of Plastid-Targeted Proteins in the Peridinin-Containing Dinoflagellate Heterocapsa triquetra. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, D.-Z. Neurotoxins from Marine Dinoflagellates: A Brief Review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; González-Armas, R.; Verdugo-Díaz, G.; Okolodkov, Y.B.; Pérez-Cruz, B.; Díaz-Ortíz, J.A. Seasonality of the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Cf. Carterae (Dinophyceae: Amphidiniales) in Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Riveroll, L.M.; Juárez, O.E.; Okolodkov, Y.B.; Mejía-Camacho, A.L.; Ramírez-Corona, F.; Casanova-Gracia, D.; Osorio-Ramírez, M.d.C.; Cervantes-Urieta, V.A.; Cembella, A.D. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of the Benthic Dinoflagellate Amphidinium from Coastal Waters of Mexico. Phycology 2023, 3, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karafas, S.; Teng, S.T.; Leaw, C.P.; Alves-de-Souza, C. An Evaluation of the Genus Amphidinium (Dinophyceae) Combining Evidence from Morphology, Phylogenetics, and Toxin Production, with the Introduction of Six Novel Species. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 128–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calado, A.J.; Moestrup, Ø. On the Freshwater Dinoflagellates Presently Included in the Genus Amphidinium, with a Description of Prosoaulax Gen. Nov. Phycologia 2005, 44, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolapsakis, N.; Economou-Amilli, A. A New Marine Species of Amphidinium (Dinophyceae) from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Acta Protozool. 2009, 48, 153–170. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, S.; Flø Jørgensen, M.; Daugbjerg, N.; Rhodes, L. Amphidinium Revisited. II. Resolving Species Boundaries in the Amphidinium operculatum Species Complex (Dinophyceae), Including the Descriptions of Amphidinium trulla sp. Nov. and Amphidinium gibbosum. Comb. Nov. 1. J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Riveroll, L.M.; Weber, J.; Krock, B. First Identification of Amphidinols from Mexican Strains and New Analogs. Toxins 2023, 15, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousseau, A.; Siano, R.; Probert, I.; Bach, S.; Mehiri, M. Marine Dinoflagellates as a Source of New Bioactive Structures. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 65, pp. 125–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Iwai, T.; Sakai, K.; Gonoi, T.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinins C–F, Amphidinolide Q Analogues from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5624–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ishibashi, M. Amphidinin A, a Novel Amphidinolide-Related Metabolite from the Cultured Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 7049–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Endo, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinin B, a New Polyketide Metabolite from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, K.; Minamida, M.; Akakabe, M.; Tsuda, M.; Konishi, Y.; Tominaga, A.; Tsuda, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J. Amphirionin-2, a Novel Linear Polyketide with Potent Cytotoxic Activity from a Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamida, M.; Kumagai, K.; Ulanova, D.; Akakabe, M.; Konishi, Y.; Tominaga, A.; Tanaka, H.; Tsuda, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; et al. Amphirionin-4 with Potent Proliferation-Promoting Activity on Bone Marrow Stromal Cells from a Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 4858–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akakabe, M.; Kumagai, K.; Tsuda, M.; Konishi, Y.; Tominaga, A.; Tsuda, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J. Amphirionin-5, a Novel Linear Polyketide from a Cultured Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species with a Potent Cell Proliferation-Promoting Activity. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Makihara, R.; Minamida, M.; Tsuda, M.; Akakabe, M.; Kumagai, K.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Suzuki, T. Amphirionins-3 and -6, New Polyketides from the Cultured Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species. Heterocycles 2020, 100, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Fujita, T.; Naoki, H. Amphidinol, a Polyhydroxy-Polyene Antifungal Agent with an Unprecedented Structure, from a Marine Dinoflagellate, Amphidinium klebsii. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 9859–9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echigoya, R.; Rhodes, L.; Oshima, Y.; Satake, M. The Structures of Five New Antifungal and Hemolytic Amphidinol Analogs from Amphidinium carterae Collected in New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.K.; Matsumori, N.; Murata, M.; Tachibana, K. Isolation and Chemical Structure of Amphidinol 2, a Potent Hemolytic Compound from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium klebsii. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 6279–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutignano, A.; Nuzzo, G.; Sardo, A.; Fontana, A. The Missing Piece in Biosynthesis of Amphidinols: First Evidence of Glycolate as a Starter Unit in New Polyketides from Amphidinium carterae. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; Barone, M.E.; Campanile, F.; Touzet, N.; Thomas, O.P. Amphidinol C, a Major Polyketide from an Irish Strain of the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae. Phytochem. Lett. 2022, 51, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, N.; Houdai, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Matsumori, N.; Adachi, S.; Oishi, T.; Murata, M.; Iwashita, T.; Fujita, T. Structures of New Amphidinols with Truncated Polyhydroxyl Chain and Their Membrane-Permeabilizing Activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 6548–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Van Wagoner, R.M.; Misner, I.; Tomas, C.; Wright, J.L.C. Structure and Biosynthesis of Amphidinol 17, a Hemolytic Compound from Amphidinium carterae. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, G.; Cutignano, A.; Sardo, A.; Fontana, A. Antifungal Amphidinol 18 and Its 7-Sulfate Derivative from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1524–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Cornelio, K.; Hanashima, S.; Malabed, R.; Murata, M.; Matsumori, N.; Zhang, H.; Hayashi, F.; Mori, S.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Structures of the Largest Amphidinol Homologues from the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae and Structure—Activity Relationships. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2883–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Ishibashi, M.; Nakamichi, H.; Kosaka, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kobayashi, J. Luteophanol A, a New Polyhydroxyl Compound from Symbiotic Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 3820–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Tsuda, M.; Doi, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Nakamichi, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Kobayashi, J. Luteophanols B and C, New Polyhydroxyl Compounds from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 14455–14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Takahashi, A.; Tsuda, M.; Kobayashi, J. Luteophanol D, New Polyhydroxyl Metabolite from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Mar. Drugs 2005, 3, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdai, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Morsy, N.; Matsumori, N.; Satake, M.; Murata, M. Hairpin Conformation of Amphidinols Possibly Accounting for Potent Membrane Permeabilizing Activities. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-C.; Zhao, D.; Guo, Y.-W.; Wu, H.-M.; Trivellone, E.; Cimino, G. Lingshuiols A and B, Two New Polyhydroxy Compounds from the Chinese Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 5501–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.-M.; Yu, B.; Huang, X.-C.; Guo, Y.-W.; Zhai, Q.; Jin, R. The Cytotoxicity of Lingshuiol: A Comparative Study with Amphidinol 2 on Membrane Permeabilizing Activities. Toxicon 2007, 50, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Kubota, T.; Takahashi, M.; Ishibashi, M.; Tsuda, M.; Naoki, H. Colopsinol A, a Novel Polyhydroxyl Metabolite from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 1478–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Tsuda, M.; Takahashi, M.; Ishibashi, M.; Oka, S.; Kobayashi, J. Colopsinols D and E, New Polyhydroxyl Linear Carbon Chain Compounds from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Tsuda, M.; Takahashi, M.; Ishibashi, M.; Naoki, H.; Kobayashi, J. Colopsinols B and C, New Long Chain Polyhydroxy Compounds from Cultured Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin 1 1999, 23, 3483–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Shimbo, K.; Kubota, T.; Tsuda, M. Bioactive Macrolides and Polyketides from Marine Dinoflagellates. Pure Appl. Chem. 2003, 75, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inuzuka, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamada, K.; Uemura, D. Amdigenol A, a Long Carbon-Backbone Polyol Compound, Produced by the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inuzuka, T.; Yamada, K.; Uemura, D. Amdigenols E and G, Long Carbon-Chain Polyol Compounds, Isolated from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 6319–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Kubota, Y.; Funabiki, K.; Uemura, D.; Inuzuka, T. Amdigenol D, a Long Carbon-Chain Polyol, Isolated from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 152376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Sakuma, Y.; Shimbo, K.; Tsuda, M.; Nakano, M.; Uozumi, Y.; Kobayashi, J. Amphezonol A, a Novel Polyhydroxyl Metabolite from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 4369–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-J.; Kuo, C.-M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-M.; Lu, C.-K. Carteraol E, a Potent Polyhydroxyl Ichthyotoxin from the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 2512–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washida, K.; Koyama, T.; Yamada, K.; Kita, M.; Uemura, D. Karatungiols A and B, Two Novel Antimicrobial Polyol Compounds, from the Symbiotic Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 2521–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Ishibashi, M.; Nakamura, H.; Ohizumi, Y.; Yamasu, T.; Sasaki, T.; Hirata, Y. Amphidinolide-A, a Novel Antineoplastic Macrolide from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 5755–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolides O and P, Novel 15-Membered Macrolides from the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp.: Analysis of the Relative Stereochemistry and Stable Solution Conformation. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 6062–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Cheng, J.-F.; Kikuchi, Y.; Ishibashi, M.; Yamamura, S.; Ohizumi, Y.; Ohta, T.; Nozoe, S.; Koba-Yashi, J.; Sasaki, T. Amphidinolides G and H: New Potent Cytotoxic Macrolides from the Cultured Symbiotic Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Sp. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1991, 56, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Takahashi, M.; Ishibashi, M. Amphidinolide Q, a Novel 12-Membered Macrolide from the Cultured Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 1449–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hamashima, M.; Nakamura, H.; Hirata, Y.; Sasakic, T.; Kobayashi, J.I. Amphidinolide-B, a Novel Macrolide with Potent Antineoplastic Activity from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidhiurn sp. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1987, 1, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.I.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ishibashi, M. Amphidinolide M, a Novel 29-Membered Macrolide from the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Magn. Reson. 1994, 59, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi, M.; Yamaguchi, N.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide N, a Novel 26-Membered Macrolide with Remarkably Potent Cytotoxicity from the Cultured Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 12, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Ishibashi, M.; Walchli, M.R.; Nakamura, H.; Hirata, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Ohizumi, Y. Amphidinolide C: The First Twenty-Five Membered Macrocyclic Lactone with Potent Antineoplastic Activity from the Cultured Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, J. Studies on the Macrolides from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Sp.: Structures of Amphidinolides R and S and a Succinate Feeding Experiment. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 7827–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Kubota, T.; Endo, T.; Tsuda, M. Amphidinolides T2, T3, and T4, New 19-Membered Macrolides from the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. and the Biosynthesis of Amphidinolide T1. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide L, a New Cytotoxic 27-Membered Macrolide from the Cultured Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 3734–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Ishiyama, H.; Kobayashi, J. Absolute Stereochemistry of Amphidinolide B. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 8241–8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Berríos, R.R.; Ríos-Delgado, A.M.; Perdomo-Lizardo, A.P.; Cardona-Rivera, A.E.; Vidal-Rosado, Á.G.; Narváez-Lozano, G.A.; Nieves-Quiñones, I.A.; Rodríguez-Vargas, J.A.; Álamo-Diverse, K.Y.; Lebrón-Acosta, N.; et al. Extraction, Isolation, Characterization, and Bioactivity of Polypropionates and Related Polyketide Metabolites from the Caribbean Region. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, T.; Endo, T.; Tsuda, M.; Shiro, M.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide T5, a New 19-Membered Macrolide from a Dinoflagellate and X-Ray Structure of Amphidinolide T1. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 6175–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Endo, T.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide U, Novel 20-Membered Macrolide from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 14565–14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimbo, K.; Tsuda, M.; Izui, N.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide W, a New 12-Membered Macrolide from Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Izui, N.; Shimbo, K.; Sato, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Katsumata, K.; Horiguchi, T.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide X, a Novel 16-Membered Macrodiolide from Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 5339–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Izui, N.; Shimbo, K.; Sato, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide Y, a Novel 17-Membered Macrolide from Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp.: Plausible Biogenetic Precursor of Amphidinolide X. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 9109–9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, I.; Maranda, L.; Young, K.A.; Shimizu, Y.; Fairchild, C.; Cornell, L.; MacBeth, J.; Huang, S. Isolation and Structure of Caribenolide I, a Highly Potent Antitumor Macrolide from a Cultured Free-Swimming Caribbean Dinoflagellate, Amphidinium sp. S1-36-5. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 1084–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Kubota, T. Amphidinolactone A, a New 13-Membered Macrolide from Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Heterocycles 2007, 72, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Oguchi, K.; Iwamoto, R.; Okamoto, Y.; Kobayashi, J.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Ozawa, T.; Masuda, A.; Kitaya, Y.; et al. Iriomoteolide-1a, a Potent Cytotoxic 20-Membered Macrolide from a Benthic Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 4469–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, M.; Kumagai, K.; Masuda, A.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J. Iriomoteolide-2a, a Cytotoxic 23-Membered Macrolide from Marine Benthic Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species. Heterocycles 2015, 91, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguchi, K.; Tsuda, M.; Iwamoto, R.; Okamoto, Y.; Kobayashi, J.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Ozawa, T.; Masuda, A.; Kitaya, Y.; et al. Iriomoteolide-3a, a Cytotoxic 15-Membered Macrolide from a Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 1567–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unzue, A.; Cribiú, R.; Hoffman, M.M.; Knehans, T.; Lafleur, K.; Caflisch, A.; Nevado, C. Iriomoteolides: Novel Chemical Tools to Study Actin Dynamics. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 3793–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, K.; Tsuda, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Masuda, A.; Tsuda, M. Iriomoteolides-9a and 11a: Two New Odd-Numbered Macrolides from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akakabe, M.; Kumagai, K.; Tsuda, M.; Konishi, Y.; Tominaga, A.; Tsuda, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J. Iriomoteolide-13a, a Cytotoxic 22-Membered Macrolide from a Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 2962–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Makihara, R.; Tsuda, M.; Suzuki, T. Iriomoteolides-14a and 14b, New Cytotoxic 15-Membered Macrolides from Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium Species. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.K.R.; Bailey, C.B. Crosstalk between Primary and Secondary Metabolism: Interconnected Fatty Acid and Polyketide Biosynthesis in Prokaryotes. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 91, 129377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.L.; Du, F.; Nong, F.T.; Li, J.; Huang, P.W.; Ma, W.; Gu, Y.; Sun, X.M. Function of the Polyketide Synthase Domains of Schizochytrium sp. on Fatty Acid Synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, D.A.; Huitt-Roehl, C.R.; Jakob, R.P.; Kravetz, J.M.; Storm, P.A.; Alley, J.R.; Townsend, C.A.; Maier, T. The Structural Organization of Substrate Loading in Iterative Polyketide Synthases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, F.T.; Sørensen, J.L.; Giese, H.; Sondergaard, T.E.; Frandsen, R.J.N. Quick Guide to Polyketide Synthase and Nonribosomal Synthetase Genes in Fusarium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 155, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Whicher, J.R.; Hansen, D.A.; Hale, W.A.; Chemler, J.A.; Congdon, G.R.; Narayan, A.R.H.; Håkansson, K.; Sherman, D.H.; Smith, J.L.; et al. Structure of a Modular Polyketide Synthase. Nature 2014, 510, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Tao, W.; Qi, Z.; Wei, J.; Shi, T.; Kang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, L. Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Chain Release of the Polyene PKS Thioesterase Domain. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 762–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, Z. Structural Enzymology of Iterative Type I Polyketide Synthases: Various Routes to Catalytic Programming. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 1498–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivina, A.; Yuet, K.P.; Hsu, J.; Khosla, C. Evolution and Diversity of Assembly-Line Polyketide Synthases. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 12524–12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Du, L. Iterative Polyketide Biosynthesis by Modular Polyketide Synthases in Bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Li, C. Application of Synthetic Biology to the Biosynthesis of Polyketides. Synth. Biol. Eng. 2024, 2, 10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenke-Kodama, H.; Sandmann, A.; Müller, R.; Dittmann, E. Evolutionary Implications of Bacterial Polyketide Synthases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhang, L. Type II Polyketide Synthases: A Bioinformatics-Driven Approach. ChemBioChem 2023, 24, e202200775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Ogata, H.; Goto, S. Type III Polyketide Synthases: Functional Classification and Phylogenomics. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.J. Engineering Polyketide Synthases and Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, T.R.; Shende, V.V.; Wierzbicki, I.H.; Pendleton, A.L.; Watervoot, N.F.; Auber, R.P.; Gonzalez, D.J.; Wisecaver, J.H.; Moore, B.S. Giant Polyketide Synthase Enzymes in the Biosynthesis of Giant Marine Polyether Toxins. Science (1979) 2024, 385, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, S.; Oyler, B.L.; Williams, E.; Khan, M.M.; Goodlett, D.R.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A.R. Investigating A Multi-Domain Polyketide Synthase in Amphidinium carterae. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Barua, A.; Ruvindy, R.; Savela, H.; Ajani, P.A.; Murray, S.A. The Genetic Basis of Toxin Biosynthesis in Dinoflagellates. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Satake, M.; Wright, J.L.C. Polyketide Biosynthesis in Dinoflagellates: What Makes It Different? Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1101–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, K.S.; Snyder, R.V. The Biosynthesis of Polyketide Metabolites by Dinoflagellates. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 93–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Qin, G.; Nakanishi, K.; Zagorski, M.G. Biosynthetic Studies of Brevetoxins, Potent Neurotoxins Produced by the Dinoflagellate Gymnodinium breve. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6234–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.N.; Shimizu, Y. Biosynthesis of Brevetoxins. Evidence for the Mixed Origin of the Backbone Carbon Chain and Possible Involvement of Dicarboxylic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 2184–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzis, J.A.; Chau, R.; Kohli, G.S.; Murray, S.A.; Neilan, B.A. Biosynthesis of Toxic Naturally-Occurring Seafood Contaminants. Toxicon 2010, 56, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, M.; Tachibana, K.; Satake, M. Complete 13C-Labeling Pattern of Yessotoxin a Marine Ladder-Frame Polyether. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolides and Its Related Macrolides from Marine Dinoflagellates. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKinnon, S.L.; Cembella, A.D.; Burton, I.W.; Lewis, N.; LeBlanc, P.; Walter, J.A. Biosynthesis of 13-Desmethyl Spirolide C by the Dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 8724–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Okita, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Okino, T.; Yamaguchi, K. From the Dinoflagellate Alexandrium hiranoi. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, G.R.; Burton, I.W.; LeBlanc, P.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Studies of the Biosynthesis of DTX-5a and DTX-5b by the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum maculosum : Regiospecificity of the Putative Baeyer—Villigerase and Insertion of a Single Amino Acid in a Polyketide Chain. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.L.C.; Hu, T.; McLachlan, J.L.; Needham, J.; Walter, J.A. Biosynthesis of DTX-4: Confirmation of a Polyketide Pathway, Proof of a Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation Step, and Evidence for an Unusual Carbon Deletion Process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8757–8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Yao, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H. Research Progress in the Biosynthetic Mechanisms of Marine Polyether Toxins. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cane, D.E.; Deng, Z. The Enzymology of Polyether Biosynthesis. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 459, 187–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, R.V.; Gibbs, P.D.L.; Palacios, A.; Abiy, L.; Dickey, R.; Lopez, J.V.; Rein, K.S. Polyketide Synthase Genes from Marine Dinoflagellates. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Iinuma, Y.; Kobayashi, J. Cloning of Polyketide Synthase Genes from Amphidinolide-Producing Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachvaroff, T.R.; Place, A.R. From Stop to Start: Tandem Gene Arrangement, Copy Number and Trans-Splicing Sites in the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.P.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Place, A.R. A Global Approach to Estimating the Abundance and Duplication of Polyketide Synthase Domains in Dinoflagellates. Evol. Bioinform. 2021, 17, 11769343211031871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachvaroff, T.R.; Williams, E.P.; Jagus, R.; Place, A.R. A Cryptic Noncanonical Multi-Module PKS/NRPS Found in Dinoflagellates. In Proceedings of the 16 International Conference on Harmful Algae, Wellington, New Zealand, 27–31 October 2015; pp. 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, E.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A. Dinoflagellate Phosphopantetheinyl Transferase (PPTase) and Thiolation Domain Interactions Characterized Using a Modified Indigoidine Synthesizing Reporter. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A. A Comparison of Dinoflagellate Thiolation Domain Binding Proteins Using In Vitro and Molecular Methods. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Kohli, G.S.; Morey, J.S.; Murray, S.A. Both Modular and Single-domain Type I Polyketide Synthases Are Expressed in the Brevetoxin-producing Dinoflagellate, Karenia brevis (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2017, 53, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.; Takahashi, M.; Ishibashi, M. Biosynthetic Studies of Amphidinolide J: Explanation of the Generation of the Unusual Odd-Numbered Macrocyclic Lactone. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 16, 1639–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Shimbo, K.; Tsuda, M.; Kobayashi, J. Biosynthetic Studies of Amphidinolides G and H: Unusual Labeling Patterns in Feeding Experiments with 13C-Labeled Acetates. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Izui, N.; Sato, M.; Kobayashi, J. Biosynthetic Study of Amphidinolide W. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 976–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tsuda, M.; Kubota, T.; Sakuma, Y.; Kobayashi, J. Biosynthetic Study of Amphidinolide B. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1366–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Tsuda, M.; Kobayashi, J. Biosynthetic Study of Amphidinolide C. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 5975–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Sato, H.; Iwai, T.; Kobayashi, J. Biosynthetic Study of Amphidinin A and Amphidinolide P. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdai, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Murata, M.; Satake, M.; Ota, S.; Oshima, Y.; Rhodes, L.L. Acetate Labeling Patterns of Dinoflagellate Polyketides, Amphidinols 2, 3 and 4. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 5551–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Amador, A.; Molina-Miras, A.; López-Rosales, L.; Sánchez-Mirón, A.; García-Camacho, F.; Souto, M.L.; Fernández, J.J. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of New Amphidinol Analogues from Amphidinium carterae Cultivated in a Pilot-Scale Photobioreactor. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.D.Y.; Terry, D.B.; Smith, L.H. In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment of ADME and PK Properties During Lead Selection and Lead Optimization—Guidelines, Benchmarks and Rules of Thumb; Sarine, M., Abigail, G., Hannah, B., Eds.; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Pedrielli, G. From Discovery to Production: Challenges and Novel Methodologies for Next Generation Biomanufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2022 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 11–14 December 2022; pp. 238–252. [Google Scholar]
- Molina-Miras, A.; Morales-Amador, A.; de Vera, C.R.; López-Rosales, L.; Sánchez-Mirón, A.; Souto, M.L.; Fernández, J.J.; Norte, M.; García-Camacho, F.; Molina-Grima, E. A Pilot-Scale Bioprocess to Produce Amphidinols from the Marine Microalga Amphidinium carterae: Isolation of a Novel Analogue. Algal Res. 2018, 31, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Muñoz, D.; Praptiwi, R.A.; Lawton, L.A.; Edwards, C. High Value Phycotoxins from the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 638739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Kubota, T. Bioactive Macrolides and Polyketides from Marine Dinoflagellates of the Genus Amphidinium. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Miras, A.; Bueso-Sánchez, A.; Cerón-García, M.D.C.; Sánchez-Mirón, A.; Contreras-Gómez, A.; García-Camacho, F. Effect of Nitrogen, Phosphorous, and Light Colimitation on Amphidinol Production and Growth in the Marine Dinoflagellate Microalga Amphidinium carterae. Toxins 2022, 14, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.E.; Murphy, E.; Fierli, D.; Campanile, F.; Fleming, G.T.A.; Thomas, O.P.; Touzet, N. Bioactivity of Amphidinol-Containing Extracts of Amphidinium carterae Grown Under Varying Cultivation Conditions. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Camacho, F.; Gallardo-Rodríguez, J.J.; Sánchez-Mirón, A.; Chisti, Y.; Molina-Grima, E. Genetic Algorithm-Based Medium Optimization for a Toxic Dinoflagellate Microalga. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Grünewald, C.; Bayliss, C.; Fonlut, F.; Chapuli, E. Long-Term Dinoflagellate Culture Performance in a Commercial Photobioreactor: Amphidinium carterae Case. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Tsuda, M. Amphidinolides, Bioactive Macrolides from Symbiotic Marine Dinoflagellates. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, K.W.; Ko, J.-Y.; Shah, M.M.R.; Lee, J.-H.; Kang, M.-C.; Kwon, O.-N.; Lee, J.-B.; Jeon, Y.-J. In Vitro Studies of Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Activities of Organic Solvent Extracts from Cultured Marine Microalgae. Algae 2013, 28, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.M.R.; Samarakoon, K.W.; An, S.-J.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-B. Growth Characteristics of Three Benthic Dinoflagellates in Mass Culture and Their Antioxidant Properties. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 11, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-de la Rosa, A.; López-Rosales, L.; Contreras-Gómez, A.; Sánchez-Mirón, A.; García-Camacho, F.; Cerón-García, M.d.C. Salinity as an Abiotic Stressor for Eliciting Bioactive Compounds in Marine Microalgae. Toxins 2024, 16, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichouh-Aiadi, S.; Gallardo-Rodríguez, J.J.; López-Rosales, L.; Cerón-García, M.C.; García-Camacho, F.; Sánchez-Mirón, A. Exploring Quorum Sensing for Inducing Bioactives Overproduction in the Dinoflagellate Microalga Amphidinium carterae. Algal Res. 2024, 83, 103719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Qu, R.; Wu, W.; Jiang, C.; Shao, D.; Shi, J. Applications of Microbial Co-cultures in Polyketides Production. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; De Luca, D.; Ferrarini, A.; Avanzato, C.; Minio, A.; Esposito, F.; Ianora, A. De Novo Transcriptome of the Cosmopolitan Dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae to Identify Enzymes with Biotechnological Potential. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beedessee, G.; Kubota, T.; Arimoto, A.; Nishitsuji, K.; Waller, R.F.; Hisata, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Satoh, N.; Kobayashi, J.; Shoguchi, E. Integrated Omics Unveil the Secondary Metabolic Landscape of a Basal Dinoflagellate. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Yao, G.; Wang, K.; Bao, S.; Han, P.; Wang, F.; Song, T.; Jiang, H. Transcriptomic Analysis of Polyketide Synthesis in Dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum lima. Harmful Algae 2023, 123, 102391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A.C.; Molina-Miras, A.; Aguilera-Sáez, L.M.; López-Rosales, L.; Cerón-García, M.D.C.; Sánchez-Mirón, A.; Olmo-García, L.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; García-Camacho, F.; Molina-Grima, E.; et al. Production of Amphidinols and Other Bioproducts of Interest by the Marine Microalga Amphidinium carterae Unraveled by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Metabolomics Approach Coupled to Multivariate Data Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9667–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, S.; Durnford, D.G. Photoacclimation Strategies of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in Response to High-Light Stress in Stationary Phase. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2025, 262, 113082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Flores, A.; Galindo-Sánchez, C.E.; Sánchez-Saavedra, M.d.P. Effects of the Salinity on the Growth, Hemolytic Activity, Fatty Acid Content, and Expression of Polyketide Synthase and Fatty Acid Synthase Genes of Amphidinium carterae (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2025, 142, 102788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kichouh-Aiadi, S.; López-Rosales, L.; Gallardo-Rodríguez, J.J.; Cerón-García, M.C.; Sánchez-Mirón, A.; García-Camacho, F. Effects of Hormones on the Growth and Metabolite Production of Amphidinium carterae under Carbon Sufficient and Carbon Limited Conditions. Algal Res. 2025, 85, 103810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichouh-Aiadi, S.; Gallardo-Rodríguez, J.J.; Cerón-García, M.C.; López-Rosales, L.; García-Camacho, F.; Sánchez-Mirón, A. Exploring the Potential of Epigenetic Chemicals to Increase Metabolite Production in the Dinoflagellate Microalga Amphidinium carterae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacellar Mendes, L.; Vermelho, A. Allelopathy as a Potential Strategy to Improve Microalgae Cultivation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Eun, H.; Prabowo, C.P.S. Metabolic Engineering and Synthetic Biology Approaches for the Heterologous Production of Aromatic Polyketides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Shi, X.; Lin, S. Heterologous Expression and Cell Membrane Localization of Dinoflagellate Opsins (Rhodopsin Proteins) in Mammalian Cells. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te, M.R.; Lohuis; Miller, D.J. Genetic Transformation of Dinoflagellates (Amphidinium and Symbiodinium): Expression of GUS in Microalgae Using Heterologous Promoter Constructs. Plant J. 1998, 13, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.P.; Haerizadeh, F.; Hildebrand, M. Molecular Genetic Manipulation of Microalgae: Principles and Applications. In Handbook of Microalgal Culture; Richmond, A., Emeritus, Hu, Q., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 146–167. [Google Scholar]
- Rae, P.M.M.; Steele, R.E. Modified Bases in the DNAs of Unicellular Eukaryotes: An Examination of Distributions and Possible Roles, with Emphasis on Hydroxymethyluracil in Dinoflagellates. Biosystems 1978, 10, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olano, C.; Lombó, F.; Méndez, C.; Salas, J.A. Improving Production of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites in Actinomycetes by Metabolic Engineering. Metab. Eng. 2008, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Bacha, N.; Ahmad, B.; Lutfullah, G.; Farooq, U.; Cox, R.J. Fungi as Chemical Industries and Genetic Engineering for the Production of Biologically Active Secondary Metabolites. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Bañares, R. Transgenic Microalgae as Green Cell-Factories. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmo, I.C.; Barbrook, A.C.; Lassadi, I.; Chen, J.E.; Geisler, K.; Smith, A.G.; Aranda, M.; Purton, S.; Waller, R.F.; Nisbet, R.E.R.; et al. Genetic Transformation of the Dinoflagellate Chloroplast. eLife 2019, 8, e45292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeckisch, N.; Yang, I.; Wohlrab, S.; Glöckner, G.; Kroymann, J.; Vogel, H.; Cembella, A.; John, U. Comparative Genomic and Transcriptomic Characterization of the Toxigenic Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.E.; Bachvaroff, R.T.; Place, R.A. The Phosphopantetheinyl Transferases in Dinoflagellates. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fürstner, A. From Total Synthesis to Diverted Total Synthesis: Case Studies in the Amphidinolide Series. Isr. J. Chem. 2011, 51, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamiya, Y.; Ebine, M.; Matsumori, N.; Oishi, T. Total Synthesis of Amphidinol 3: A General Strategy for Synthesizing Amphidinol Analogues and Structure-Activity Relationship Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3472–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciss, I.; Seck, M.; Figadère, B.; Ferrié, L. Advances Toward Amphidinolides C, F and U: Isolations, Synthetic Studies and Total Syntheses. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202400471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
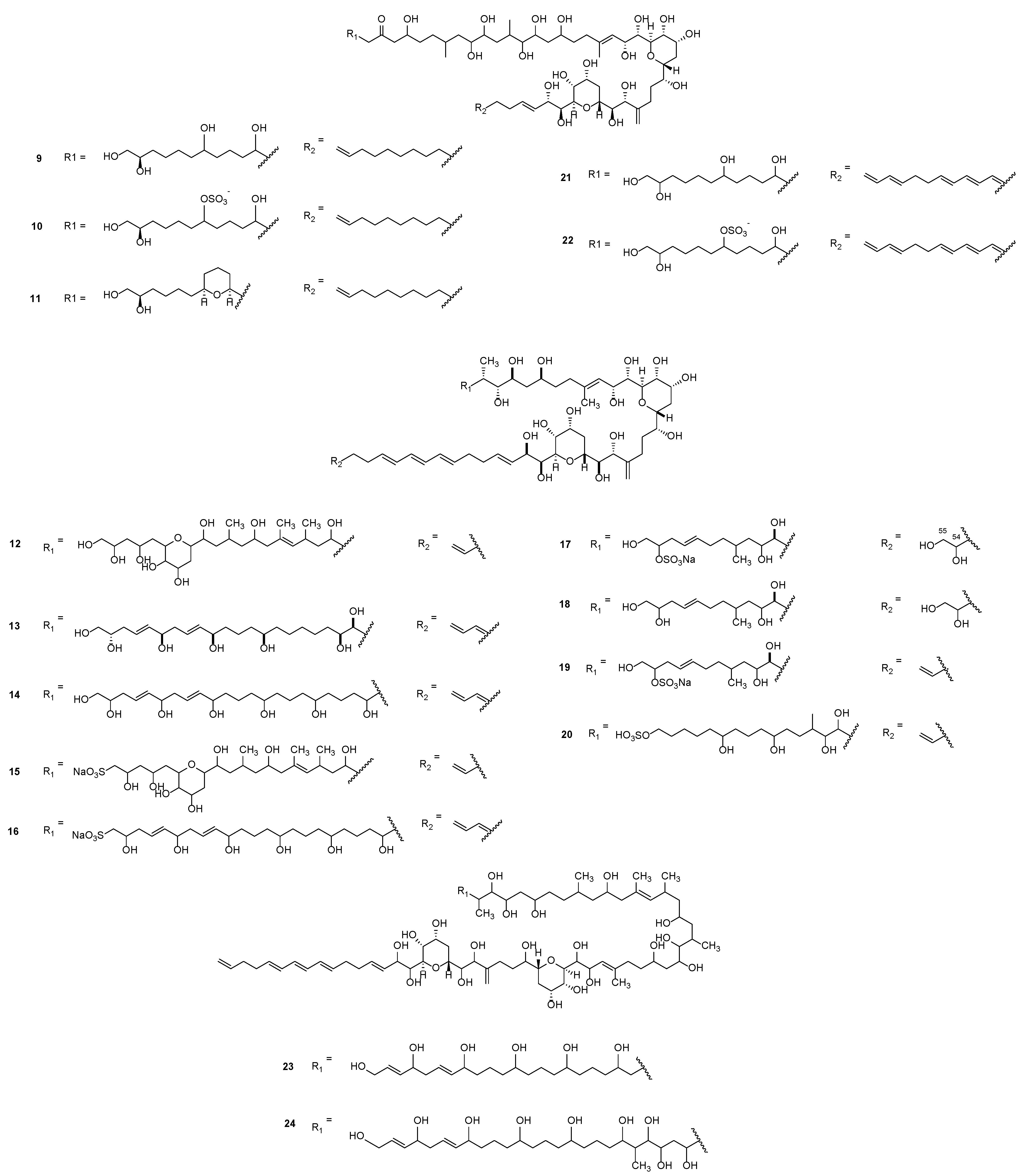
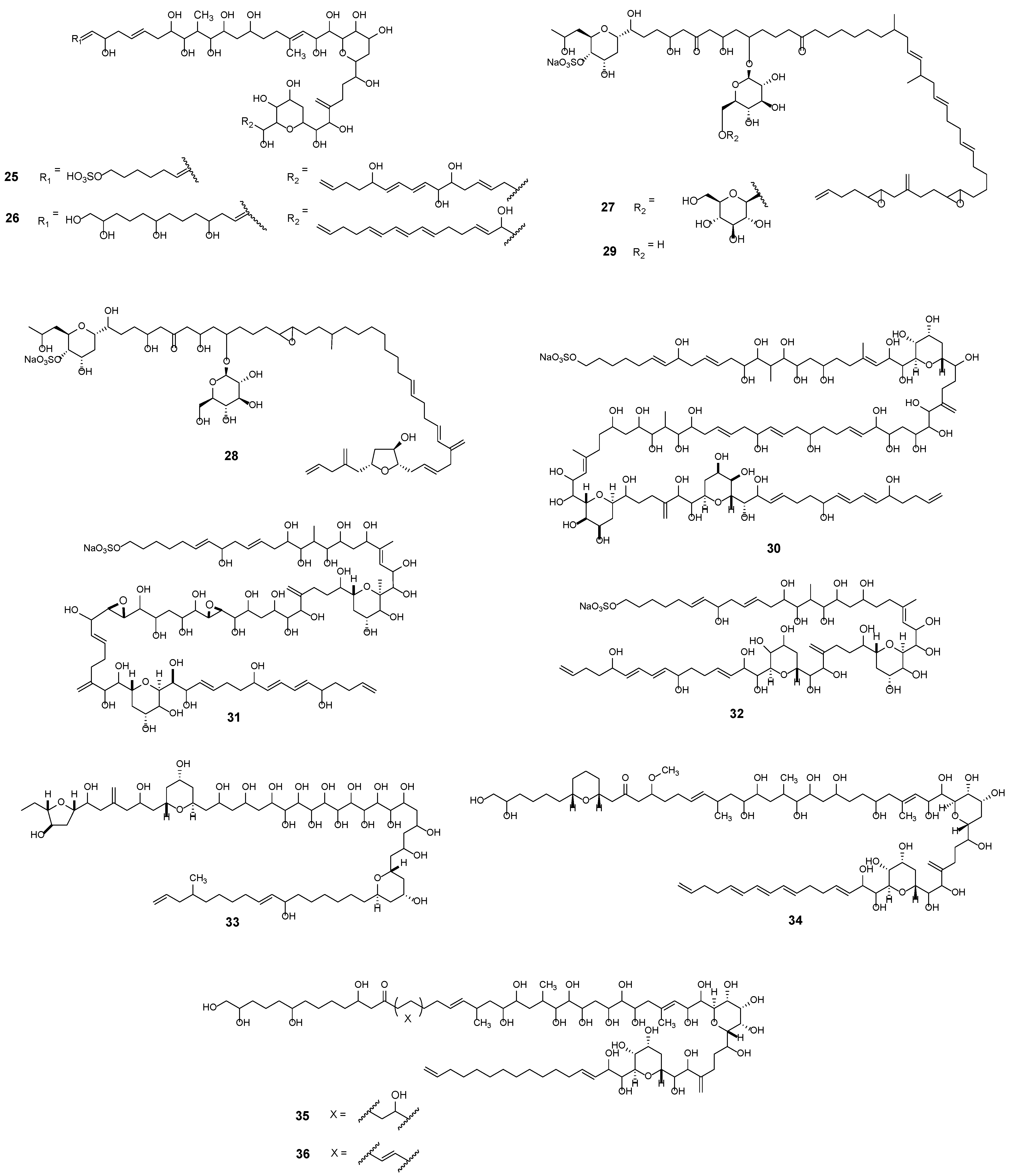





| Organism | Condition | Dosage | Approach | Molecules | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. gibbosum | Phosphorous starvation | 22 µM | Transcriptomic | - | [156] |
| A. carterae BMCC33 (Dn241EHU) | L/D cycle 24:0 | - | Metabolomic | Amphidinol A and B | [158] |
| Light intensity | 573 µE m−2 s−1 | Haemolytic Activity | Amphidinols * | [145] | |
| Hyposalinity | 5 PSU | Haemolytic Activity | Amphidinols * | [152] | |
| 2-naphthoxyacetic acid (BNOA) | 14.84 µM | Haemolytic Activity | Amphidinols * | [161] | |
| 2-chlorobenzoic acid (CA) | 19.23 µM 192.32 µM | Haemolytic Activity | Amphidinols * | [161] | |
| Jasmonic acid (JA) | 2.38 µM 142.67 µM | Haemolytic activity | Amphidinols * | [161] | |
| Culture supernatant of Heterosigma akashiwo | - | Haemolytic Activity | Amphidinols * | [153] | |
| Culture supernatant of Pavlova sp. | - | Haemolytic Activity | Amphidinols * | [153] | |
| A. carterae CCAP 1102/8 (LACW11) | LED blue light | 100 μmol/m2/s | Metabolomic | Amphidinols A, B, C, 22 | [146] |
| NaHCO3 | 2.5 mM | Metabolomic | Amphidinols A, B, C, 22 | [146] | |
| Hypersalinity | 0.8 g/L | Metabolomic | Amphidinols A, B, C, 22 | [146] | |
| H202 | 0.5 mM | Metabolomic | Amphidinols A, B, C, 22 | [146] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, N.; Quaini, G.; Ziaco, M.; Castiglia, D.; Ruggiero, A.; D’Amelia, V.; Di Napoli, C.; Esposito, S.; Fontana, A.; Nuzzo, G.; et al. Bioactive Polyketides from Amphidinium spp.: An In-Depth Review of Biosynthesis, Applications, and Current Research Trends. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060255
Russo N, Quaini G, Ziaco M, Castiglia D, Ruggiero A, D’Amelia V, Di Napoli C, Esposito S, Fontana A, Nuzzo G, et al. Bioactive Polyketides from Amphidinium spp.: An In-Depth Review of Biosynthesis, Applications, and Current Research Trends. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(6):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060255
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Noemi, Giulia Quaini, Marcello Ziaco, Daniela Castiglia, Alessandra Ruggiero, Vincenzo D’Amelia, Concetta Di Napoli, Sergio Esposito, Angelo Fontana, Genoveffa Nuzzo, and et al. 2025. "Bioactive Polyketides from Amphidinium spp.: An In-Depth Review of Biosynthesis, Applications, and Current Research Trends" Marine Drugs 23, no. 6: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060255
APA StyleRusso, N., Quaini, G., Ziaco, M., Castiglia, D., Ruggiero, A., D’Amelia, V., Di Napoli, C., Esposito, S., Fontana, A., Nuzzo, G., & Landi, S. (2025). Bioactive Polyketides from Amphidinium spp.: An In-Depth Review of Biosynthesis, Applications, and Current Research Trends. Marine Drugs, 23(6), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060255












