Microwave Pretreatment-Induced Significant Nutrient and Metabolite Changes in Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
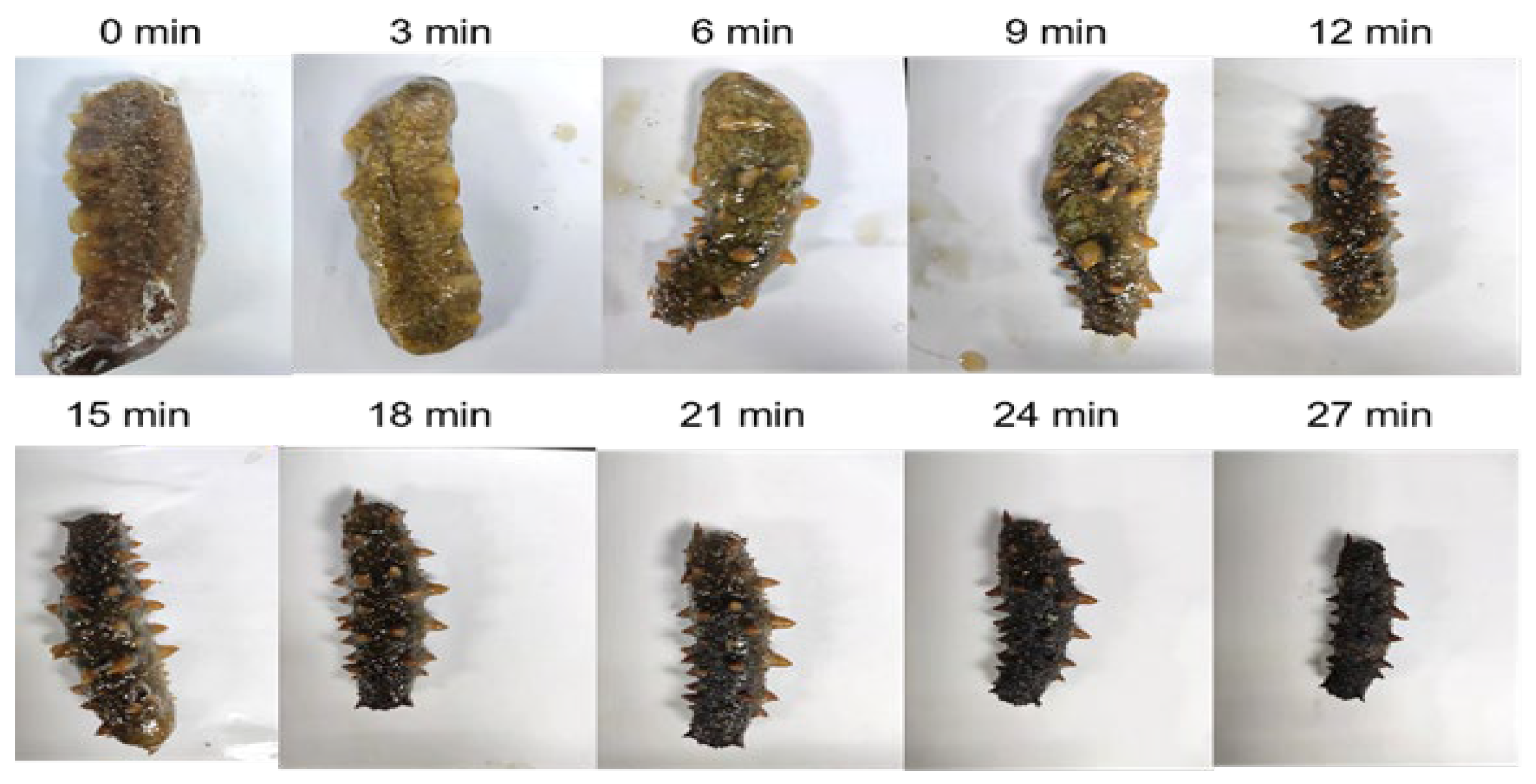
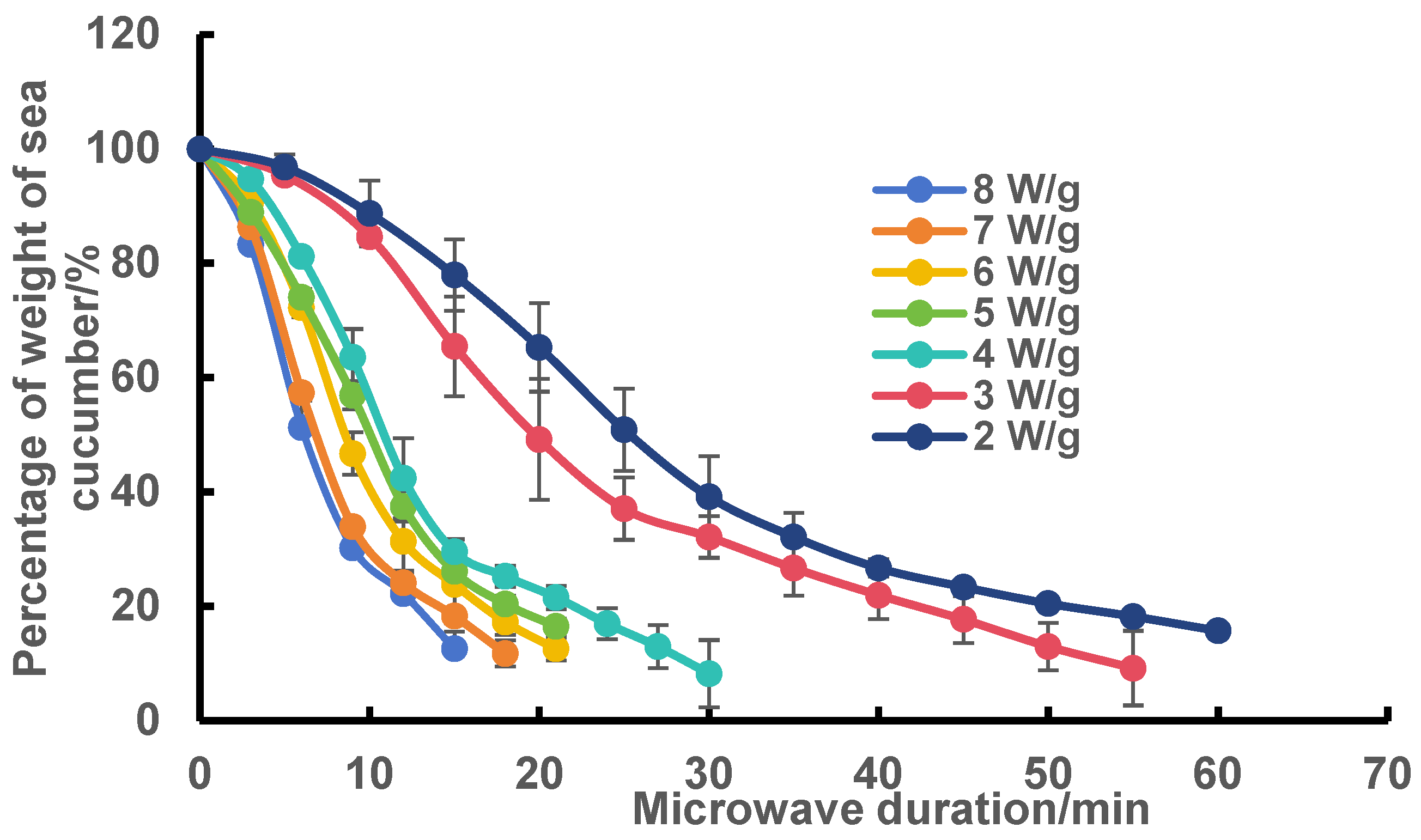
2.1. Effect of Microwave Power and Microwave Time on the Dehydration of Frozen Sea Cucumber Body Wall
2.2. Effect of Microwave Pretreatment on Endogenous Protease Activities in Frozen Sea Cucumber Body Wall
2.3. Comparison of Nutrient Contents in Sea Cucumber Body Walls with Different Pretreatments
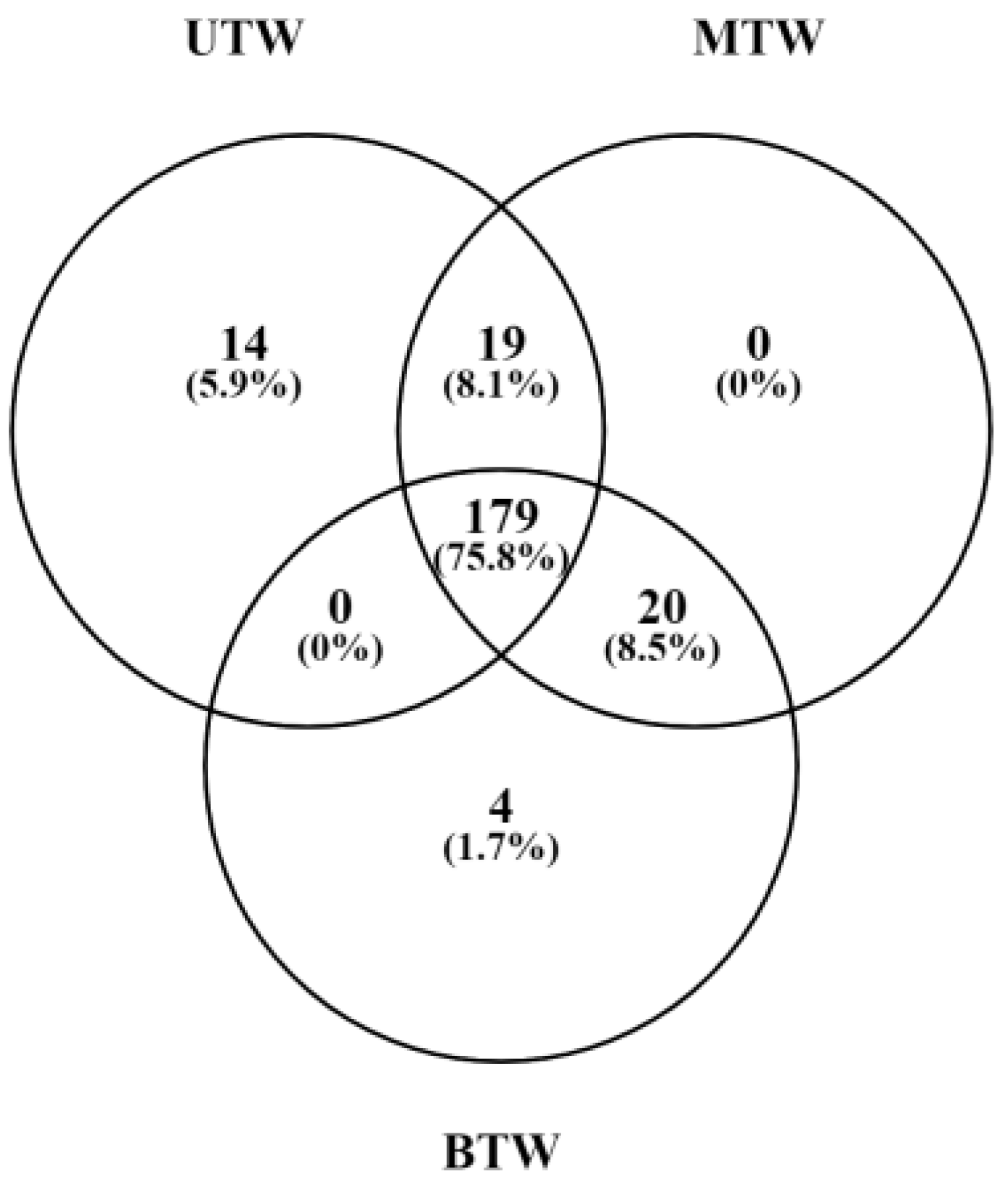
2.4. Differences in Metabolites Between MTW, BTW, and UTW Based on GC-MS Analysis
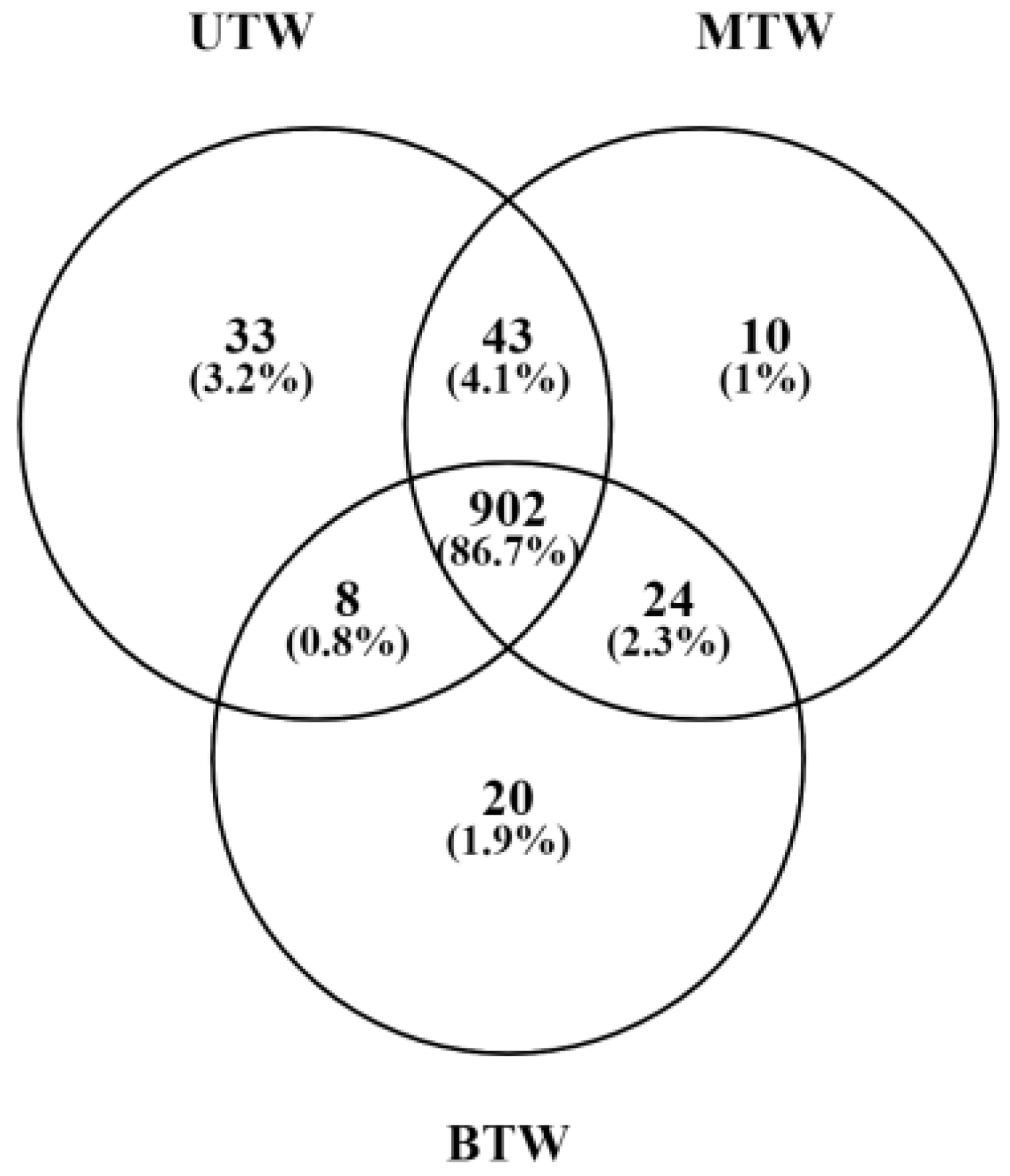
2.5. Differences in Metabolites Between MTW, BTW, and UTW Based on LC-MS Analysis
2.6. Significant Differences of the Metabolites in Sea Cucumber Body Walls with Different Pretreatment by GC-MS Analysis
2.7. Significant Differences of the Metabolites in Sea Cucumber Body Walls with Different Pretreatment by LC-MS Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Sea Cucumber Materials
3.3. Plotting of Microwave Dehydration Curves
3.4. Effect of Microwave Pretreatment on Endogenous Protease Activities in Sea Cucumber Body Wall
3.5. Sample Preparation for Compositional Analysis and Metabolomics Analysis
3.6. Determination of Proximate Composition
3.7. Determination of Total Saponin Content
3.8. Proteinase Activity and the Residual Enzyme Activity
3.9. GC-MS Analysis of UTW, BTW, and MTW
3.9.1. Sample Preparation for GC-MS Analysis
3.9.2. GC-MS Analysis
3.9.3. Metabolites Identification
3.10. LC−MS Analysis of UTW, BTW, and MTW
3.10.1. Sample Preparation for LC-MS Analysis
3.10.2. LC-MS Analysis
3.10.3. Metabolite Identification
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mondol, M.A.M.; Shin, H.J.; Rahman, M.A.; Islam, M.T. Sea cucumber glycosides: Chemical structures, producing species and important biological properties. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Kunisaki, N.; Urano, N.; Kimura, S. Collagen as the major edible component of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus). J. Food Sci. 2006, 67, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, G.W.; Ko, S.C.; Lee, D.H.; Heo, S.J.; Jung, W.K. Biological activities and biomedical potential of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus): A review. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Comparative metabolomic analysis of the body wall from four varieties of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Lin, C.; Yang, H. Microplastic ingestion by the farmed sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senadheera, T.R.L.; Dave, D.; Shahidi, F. Sea cucumber derived type I collagen: A comprehensive review. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhou, D.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Dong, X.P.; Li, D.M.; Shahidi, F. The role of matrix metalloprotease (MMP) to the autolysis of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5752–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Wang, M.; Jing, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, C.; Ying, W.G. Quality changes of Apostichopus japonicus under different pre-cooking processes. Sci. Ecnology Food Ind. 2016, 37, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, P.; Jia, A.; Heimann, K.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C. Hot water pretreatment-induced significant metabolite changes in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xi, Y.S. Drying characteristics and drying quality of carrot using a two-stage microwave process. J. Food Eng. 2005, 68, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalou, S.; Ordoudi, S.A.; Mantzouridou, F.T. On the effect of microwave heating on quality characteristics and functional properties of persimmon juice and its residue. Foods 2021, 10, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipcak, A.S.; Ismail, O. Microwave drying of fish, chicken and beef samples. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, C.; Azadi, P. Carbohydrate structure analysis: Methods and applications. SLAS Technol. 2020, 25, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lin, R.; Cheng, S.; Wang, S.; Yuan, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Tan, M. Effects of microwave vacuum drying on the moisture migration, microstructure, and rehydration of sea cucumber. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, M.; Huang, F.; Zheng, C.; Deng, Q. Effect of pretreatment with dehulling and microwaving on the flavor characteristics of cold-pressed rapeseed oil by GC-MS-PCA and electronic nose discrimination. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C961–C970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaki, S.; Aono, S.; Hayakawa, K.; Fu, B.X.; Otobe, C. Changes in protein non-covalent bonds and aggregate size during dough formation. Foods 2020, 9, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, F.; Eisenberg, T.; Pietrocola, F.; Kroemer, G. Spermidine in health and disease. Science 2018, 359, eaan2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.-K. Tagatose: Properties, applications, and biotechnological processes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.C.; Cordingley, D.M.; Cornish, S.M.; Gualano, B.; Roschel, H.; Ostojic, S.M.; Rawson, E.S.; Roy, B.D.; Prokopidis, K.; Giannos, P.; et al. Effects of creatine supplementation on brain function and health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibaut, S.; Coeffic, T.; Boutoille, D.; Lemenand, O.; Birgand, G.; Caillon, J. Résistance aux antibiotiques des Entérobactéries urinaires isolées chez les patients vivant en établissements d’hébergement pour personnes âgées dépendantes (Ehpad). Méd. Mal. Infect. 2020, 50, S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, G.P.; Rubin, M.A.; Mello, C.F. Modulation of learning and memory by natural polyamines. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 112, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liang, N.; Lang, D.; Zhou, D.; Dong, X.; Peng, J.; Liu, L.; Pan, B.; Xing, B. Heating methods generate different amounts of persistent free radicals from unsaturated fatty acids. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallot, C.; Mazzocco, J.; Meillon, C.; Semama, D.S.; Chantegret, C.; Ternoy, N.; Martin, D.; Donier, A.; Gregoire, S.; Creuzot-Garcher, C.P.; et al. Alteration of erythrocyte membrane polyunsaturated fatty acids in preterm newborns with retinopathy of prematurity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, J.M.; Martínez-Chanta, M.L.; Lu, S.C. S-adenosylmethionine metabolism and liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, B.; Park, B.Y.; Oh, C.J.; Kim, M.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Lee, I.K.; Park, O.; Baek, S.; et al. CycloZ improves hyperglycemia and lipid metabolism by modulating lysine acetylation in KK-Ay mice. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostojic, S.M. Diagnostic and pharmacological potency of creatine in post-viral fatigue syndrome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Levin, G.V.; Donner, T.W. Tagatose, a new antidiabetic and obesity control drug. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, Z.Z.; Xiao, J.X.; Zong, A.Z.; Qiu, B.; Jia, M.; Liu, L.N.; Xu, T.C. Research on the mechanism of microwave-toughened starch on glucolipid metabolism in mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9789–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaus, T.M.; Greenberg, K.; Suri, P.; Geddes, C.D. Elucidation of a non-thermal mechanism for DNA/RNA fragmentation and protein degradation when using Lyse-It. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeWitt, P.A. Levodopa therapy for parkinson’s disease: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhawat, P.S.; Srinivas, S.R.; Matern, D.; Bennett, M.J.; Boriack, R.; George, V.; Xu, H.; Prasad, P.D.; Roon, P.; Ganapathy, V. Spontaneous development of intestinal and colonic atrophy and inflammation in the carnitine-deficient jvs (OCTN2(−/−)) mice. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2007, 92, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Montanes, J.; Gandara, E.; Moreno-Galarraga, L.; Hershey, M.S.; Lopez-Gil, J.F.; Kales, S.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Fernandez-Montero, A. ACE-Vitamin index and risk of glaucoma: The SUN project. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.K.; Jacobson, E.L. Vitamin B3 in health and disease: Toward the second century of discovery. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1813, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claustrat, B.; Leston, J. Melatonin: Physiological effects in humans. Neurochirurgie 2015, 61, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroyraya, M.; Hanna, P.J.; Siangcham, T.; Tinikul, R.; Jattujan, P.; Poomtong, T.; Sobhon, P. Nutritional components of the sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2017, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.R.; Tschinkel, W.R. Ant fat extraction with a soxhlet extractor. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2009, 2009, pdb-prot5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuko, T.; Minami, A.; Iwasaki, N.; Majima, T.; Nishimura, S.; Lee, Y.C. Carbohydrate analysis by a phenol-sulfuric acid method in microplate format. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 339, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Xin, L.; Da-Yong, Z.; Dong-Dong, M.; Zi-Qiang, L.; Yan-Fei, L.; Liang, S.; Xiu-Ping, D.; Dong-Mei, L.; Bei-Wei, Z.; Kunihiko, K.; et al. Effects of endogenous cysteine proteinases on structures of collagen fibres from dermis of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus). Food Chem. 2017, 232, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Smith, C.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Uritboonthai, W.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Siuzdak, G. Solvent-dependent metabolite distribution, clustering, and protein extraction for serum profiling with mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifertova, M.; Cechova, E.; Llansola, M.; Felipo, V.; Vykoukalova, M.; Kocan, A. Determination of selected neurotoxic insecticides in small amounts of animal tissue utilizing a newly constructed mini-extractor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6015–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelock, A.M.; Wheelock, C.E. Trials and tribulations of ‘omics data analysis: Assessing quality of SIMCA-based multivariate models using examples from pulmonary medicine. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Poulos, R.C.; Liu, J.; Zhong, Q. Machine learning for multi-omics data integration in cancer. iScience 2022, 25, 103798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Compounds (Dry Weight) | UTW (4.16 ± 0.34 g) | MTW (3.14 ± 0.18 g) | BTW (1.98 ± 0.42 g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | |||
| mg/g (DW) | 551.7 ± 16.6 a | 707.0 ± 14.0 b | 739.0 ± 13.0 c |
| Total protein (mg) | 2295.1 ± 187.6 b | 2220.0 ± 127.3 b | 1463.0 ± 310.4 a |
| Compared with the untreated group (%) | -- | 96.73 | 63.75 |
| Fat | |||
| mg/g (DW) | 37.62 ± 7.52 a | 46.00 ± 2.51 b | 31.84 ± 7.50 a |
| Total fat (mg) | 156.50 ± 31.28 b | 144.44 ± 7.88 b | 63.04 ± 14.85 a |
| Compared with the untreated group (%) | -- | 92.29 | 40.26 |
| Ash | |||
| mg/g (DW) | 37.22 ± 0.27 c | 17.49 ± 0.17 a | 26.28 ± 0.35 b |
| Total ash (mg) | 154.84 ± 1.12 b | 54.91 ± 0.53 a | 52.03 ± 0.69 a |
| Compared with the untreated group (%) | -- | 35.46 | 33.60 |
| Total sugar | |||
| mg/g (DW) | 106.16 ± 0.0211 c | 77.42 ± 0.0106 b | 67.58 ± 0.0023 a |
| Total sugar (mg) | 441.60 ± 0.0878 c | 243.10 ± 0.0616 b | 133.80 ± 0.0046 a |
| Compared with the untreated group (%) | -- | 55.05 | 30.30 |
| Total saponin | |||
| mg/g (DW) | 0.4595 ± 0.0132 c | 0.2445 ± 0.0327 a | 0.3533 ± 0.0251 b |
| Total saponin (mg) | 1.912 ± 0.0549 c | 0.7677 ± 0.1027 b | 0.6995 ± 0.0497 a |
| Compared with the untreated group (%) | 40.15 | 36.58 |
| Metabolites | Quant. Mass | RT (min) | VIP | p Value | Relative Ratio (MTW/UTW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| amino acids | |||||
| aspartic acid | 133 | 13.75 | 1.12 | 0.0126 | 0.46 |
| leucine | 131 | 10.52 | 1.17 | 0.0254 | 0.34 |
| oxyproline | 129 | 13.81 | 1.52 | 0.0013 | 0.32 |
| threonine | 119 | 12.02 | 1.47 | 0.0007 | 0.31 |
| glutamic acid | 147 | 14.95 | 1.55 | 0.0003 | 0.29 |
| methionine | 149 | 13.76 | 1.68 | 0.0104 | 0.29 |
| glycine | 75 | 10.99 | 1.92 | 0.0007 | 0.24 |
| lysine | 146 | 18.22 | 1.73 | 0.0015 | 0.21 |
| vitamins | |||||
| pantothenic acid | 219 | 18.91 | 1.17 | 0.0113 | 0.43 |
| sugar | |||||
| tagatose | 180 | 17.42 | 1.53 | 0.0370 | 0.47 |
| erythrulose | 120 | 12.71 | 2.58 | 0.0022 | 0.14 |
| organic acids | |||||
| succinate | 118 | 11.09 | 1.03 | 0.001 | 0.44 |
| creatine | 131 | 14.18 | 1.48 | 0.0003 | 0.31 |
| fatty acids | |||||
| linoleate | 280 | 21.00 | 1.37 | 0.0034 | 3.06 |
| arachidonic acid | 304 | 22.37 | 1.01 | 0.0006 | 2.13 |
| Metabolites | Quant. Mass | RT (min) | VIP | p Value | Relative Ratio (MTW/BTW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| amino acids | |||||
| methionine | 149 | 13.76 | 2.91 | 0.0003 | 12.47 |
| lysine | 146 | 18.22 | 2.83 | 0 | 10.28 |
| tyrosine | 181 | 18.4 | 2.45 | 0 | 8.06 |
| valine | 117 | 9.73 | 1.78 | 0 | 4.61 |
| aspartic acid | 133 | 13.75 | 1.65 | 0.0011 | 4.53 |
| phenylalanine | 165 | 15.06 | 1.72 | 0.0001 | 4.50 |
| proline | 115 | 10.89 | 1.62 | 0.0015 | 4.13 |
| isoleucine | 131 | 10.8 | 1.68 | 0 | 4.02 |
| glutamic acid | 147 | 14.95 | 1.52 | 0.0001 | 3.78 |
| threonine | 119 | 12.02 | 1.37 | 0.0009 | 3.47 |
| alanine | 89 | 8.13 | 1.06 | 0.0001 | 2.48 |
| nucleic acids and their derivatives | |||||
| n-alpha-Acetyl-L-guanine | 174 | 15.91 | 1.31 | 0.0002 | 3.08 |
| organic acids | |||||
| guanidineacetic acid | 117 | 14.53 | 2.43 | 0.0005 | 9.36 |
| creatine | 131 | 14.18 | 1.37 | 0.0007 | 3.43 |
| sugar | |||||
| fructose | 180 | 17.75 | 2.70 | 0.0004 | 11.20 |
| sorbets | 180 | 17.66 | 2.37 | 0.0012 | 10.03 |
| tagatose | 180 | 17.42 | 1.61 | 0.03 | 5.68 |
| isomaltose | 342 | 26.08 | 1.58 | 0.0015 | 4.31 |
| maltose | 360 | 25.31 | 1.08 | 0.0026 | 2.27 |
| Metabolites | Quant. Mass | RT (min) | Ion Mode | VIP | p Value | Relative Ratio (MTW/UTW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| glycerophospholipids | ||||||
| LPI 20:5 | 618 | 8.34 | neg | 2.09 | 0.0005 | 4.39 |
| LPI 20:4 | 620 | 8.98 | neg | 2.29 | 0.0002 | 3.50 |
| LPA 18:0 | 438 | 10.43 | neg | 1.7 | 0.0011 | 3.47 |
| LPE 14:0 | 425 | 7.97 | neg | 1.53 | 0.0107 | 3.07 |
| PC 0-20:2 | 547 | 9.68 | pos | 1.66 | 0.0081 | 2.42 |
| LPE 18:3 | 475 | 8.38 | neg | 1.46 | 0.0076 | 2.38 |
| PC 0-16:0-20:5 | 812 | 9.83 | neg | 1.69 | 0.004 | 2.36 |
| LPA 20:5 | 456 | 8.37 | neg | 1.6 | 0.0016 | 2.34 |
| LPA 20:4 | 458 | 8.89 | neg | 1.77 | 0.0038 | 2.33 |
| LPC 0-18:3 | 503 | 9.68 | pos | 1.34 | 0.0026 | 2.21 |
| LPE 18:2 | 477 | 8.84 | pos | 1.66 | 0.0069 | 2.20 |
| LPE 16:2 | 449 | 8.04 | neg | 1.33 | 0.0486 | 2.12 |
| LPE 18:2 | 477 | 8.83 | neg | 1.73 | 0.001 | 2.11 |
| LPC 16:2 | 537 | 8.17 | neg | 1.28 | 0.0372 | 2.08 |
| LPC 18:3 | 563 | 8.53 | neg | 1.38 | 0.0104 | 2.03 |
| LPE 16:1 | 451 | 8.53 | neg | 1.48 | 0.0135 | 2.00 |
| LPE 15:0 | 439 | 8.62 | neg | 1.57 | 0.0087 | 1.99 |
| PC 24:2 | 617 | 10.52 | pos | 1.05 | 0.0124 | 1.89 |
| LPC 20:2-SN1 | 547 | 9.95 | Pos | 1.43 | 0.0066 | 1.87 |
| LPC 18:0-SN1 | 523 | 10.09 | pos | 1.33 | 0.019 | 1.81 |
| LPA22:6 | 482 | 8.84 | neg | 1.27 | 0.037 | 1.8 |
| LPE 0-15:1 | 423 | 9.11 | neg | 1.11 | 0.0384 | 1.78 |
| LPC 15:0-SN1 | 481 | 8.81 | pos | 1.38 | 0.0193 | 1.78 |
| LPC 14:0 | 467 | 8.93 | neg | 1.43 | 0.035 | 1.77 |
| LPE 16:0 | 218 | 9.16 | pos | 1.37 | 0.0462 | 1.73 |
| LPC 20:5 | 587 | 8.43 | neg | 1.12 | 0.0197 | 1.67 |
| LPI 16:0 | 572 | 8.83 | neg | 1.31 | 0.0279 | 1.62 |
| PC 0-15:0 | 963 | 8.56 | pos | 1.2 | 0.0343 | 1.60 |
| LPC 16:0-SN1 | 495 | 9.42 | pos | 1.24 | 0.0462 | 1.54 |
| PC 44:11 | 902 | 11.25 | pos | 1.4 | 0.0187 | 0.44 |
| organic acids | ||||||
| succinate | 118 | 2.57 | neg | 1.32 | 0.0005 | 0.56 |
| amino acids | ||||||
| valine | 214 | 2.03 | pos | 1.13 | 0.0005 | 0.49 |
| proline | 228 | 2.08 | pos | 1.34 | 0.0012 | 0.46 |
| tyrosine | 252 | 5.18 | neg | 2.28 | 0 | 0.10 |
| nucleic acids and their derivatives | ||||||
| uracil nucleotide | 404 | 1.97 | neg | 1.51 | 0.0072 | 0.41 |
| deoxythymidine nucleotide | 322 | 5.27 | neg | 1.66 | 0.0084 | 0.39 |
| deoxycytosine | 307 | 3.44 | neg | 1.46 | 0.0099 | 0.35 |
| fatty acids | ||||||
| HFA 20:4/20:4 | 606 | 9.82 | neg | 1.48 | 0.0227 | 2.31 |
| HFA 22:6/20:3 | 632 | 9.70 | neg | 1.23 | 0.0083 | 2.22 |
| Linolenic (C18:2N6T) | 280 | 8.18 | pos | 1.53 | 0.0063 | 2.12 |
| vitamins | ||||||
| vitamin D3 | 384 | 8.55 | pos | 1.25 | 0.0258 | 1.91 |
| pantothenic acid | 219 | 5.03 | neg | 1.51 | 0.0025 | 0.43 |
| glycolipid | ||||||
| LPS 19:0 | 539 | 11.03 | neg | 1.71 | 0.002 | 4.23 |
| LPS 18:0 | 525 | 10.1 | neg | 1.15 | 0.0273 | 2.94 |
| LPS 19:1 | 537 | 10.13 | neg | 1.74 | 0.0016 | 2.76 |
| LPS 16:1 | 495 | 8.63 | neg | 1.44 | 0.0277 | 2.66 |
| LPS 20:1 | 551 | 10.77 | neg | 1.75 | 0.001 | 2.64 |
| LPS 20:4 | 545 | 8.89 | neg | 1.84 | 0.0027 | 2.56 |
| LPS 22:4 | 573 | 10.77 | neg | 1.68 | 0.0009 | 2.53 |
| LPS 18:1 | 523 | 9.6 | neg | 1.57 | 0.0145 | 2.35 |
| LPS 21:1 | 565 | 11.33 | neg | 1.49 | 0.0055 | 2.28 |
| LPS 22:5 | 571 | 9.15 | neg | 1.25 | 0.0429 | 1.76 |
| others | ||||||
| levodopa | 197 | 5.98 | neg | 1.24 | 0.0072 | 2.75 |
| carnitine | 161 | 3.68 | pos | 1.74 | 0.0018 | 0.36 |
| spermidine | 145 | 1.07 | pos | 1.67 | 0.001 | 0.23 |
| Metabolites | Quant. Mass | RT (min) | Ion Mode | VIP | p Value | Relative Ratio (MTW/BTW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| glycerophospholipids | ||||||
| galactosylceramide0-17:1-2:0 | 554 | 7.23 | pos | 1.56 | 0.0214 | 4.91 |
| galactosylceramide0-15:1-2:0 | 504 | 6.7 | pos | 1.35 | 0.0278 | 3.03 |
| LPE 0-15:1 | 423 | 9.11 | neg | 1.78 | 0.002 | 2.82 |
| LPI 16:0 | 572 | 8.83 | neg | 1.85 | 0.0001 | 2.22 |
| LPI 20:4 | 620 | 8.98 | neg | 1.1 | 0.0014 | 1.99 |
| LPG 17:0 | 498 | 11.21 | neg | 1.01 | 0.0006 | 0.65 |
| LPC 0-22:6 | 553 | 9.28 | pos | 1.21 | 0.0488 | 0.64 |
| LPE 17:1 | 465 | 8.96 | pos | 1.12 | 0.047 | 0.63 |
| LPC 0-16:1 | 479 | 9.29 | pos | 1.28 | 0.0066 | 0.61 |
| LPC 20:3 | 591 | 9.36 | neg | 1.15 | 0.0039 | 0.59 |
| LPC 17:1 | 553 | 9.16 | neg | 1.16 | 0.0273 | 0.58 |
| LPC 20:0 | 582 | 9.52 | neg | 1.31 | 0.0204 | 0.58 |
| LPC 20:1 | 595 | 10.47 | neg | 1.49 | 0.0085 | 0.56 |
| LPC 22:6 | 613 | 8.86 | neg | 1.29 | 0.011 | 0.56 |
| LPI 18:1 | 598 | 10.35 | neg | 1.13 | 0.0053 | 0.56 |
| LPC 0-17:1 | 539 | 9.86 | neg | 1.66 | 0.0036 | 0.54 |
| LPC 22:5 | 615 | 9.16 | neg | 1.07 | 0.0446 | 0.54 |
| LPC 0-20:1 | 581 | 11.16 | neg | 1.18 | 0.0416 | 0.53 |
| LPG18:1 | 510 | 10.51 | neg | 1.37 | 0.0022 | 0.52 |
| LPC 21:1 | 609 | 10.93 | neg | 1.26 | 0.0199 | 0.51 |
| LPE 18:4 | 473 | 7.94 | neg | 1.01 | 0.0287 | 0.51 |
| LPC 0-20:5 | 573 | 8.91 | neg | 1.32 | 0.0172 | 0.49 |
| LPE 20:3 | 503 | 9.16 | neg | 1.12 | 0.01 | 0.49 |
| LPE 22:6 | 525 | 8.54 | pos | 1.47 | 0.0136 | 0.48 |
| LPC 0-18:2 | 551 | 9.69 | neg | 1.32 | 0.0342 | 0.47 |
| PG 20:5 | 530 | 8.67 | neg | 1.34 | 0.0105 | 0.47 |
| LPC 22:1 | 623 | 11.39 | neg | 1.23 | 0.0133 | 0.46 |
| LPC 0-19:2 | 565 | 10.08 | neg | 1.55 | 0.0084 | 0.41 |
| Lysops 22:6 | 569 | 8.59 | neg | 1.83 | 0.0002 | 0.40 |
| PC 0-22:6-2:0 | 641 | 9.48 | neg | 2 | 0.0001 | 0.39 |
| PG 16:0 | 484 | 10.08 | neg | 1.8 | 0.0014 | 0.39 |
| PL 0-18:5-3:0 | 513 | 8.63 | pos | 1.73 | 0.0017 | 0.36 |
| LPA 18:0 | 438 | 10.61 | neg | 1.44 | 0.0275 | 0.36 |
| LPC 0-20:4 | 575 | 9.42 | neg | 1.73 | 0.0046 | 0.34 |
| LPE 20:5 | 499 | 8.3 | neg | 1.76 | 0 | 0.33 |
| LPE 20:4 | 501 | 8.76 | neg | 1.95 | 0 | 0.30 |
| LPC 0-17:2 | 537 | 8.5 | neg | 1.49 | 0.0046 | 0.28 |
| PG 16:1 | 482 | 8.71 | neg | 1.34 | 0.0037 | 0.26 |
| PG 20:2 | 536 | 11.2 | neg | 1.86 | 0.0004 | 0.24 |
| LPE 22:5 | 527 | 8.98 | neg | 1.7 | 0.0003 | 0.22 |
| amino acids | ||||||
| phenylalanine | 165 | 4.93 | pos | 1.65 | 0 | 3.23 |
| L-Valyl proline | 117 | 1.77 | pos | 1.54 | 0.0002 | 2.60 |
| proline | 115 | 1.41 | pos | 1.34 | 0.0083 | 2.20 |
| nucleic acids and their derivatives | ||||||
| deoxyadenosine monophosphate | 331 | 2.01 | neg | 1.78 | 0.0002 | 3.23 |
| uracil nucleotide | 324 | 1.93 | neg | 1.35 | 0.0351 | 2.04 |
| Vitamins | ||||||
| vitamin A | 286 | 9.26 | pos | 1.77 | 0.0057 | 2.43 |
| nicotinic acid | 123 | 1.86 | pos | 1.39 | 0.0006 | 1.91 |
| fatty acids | ||||||
| ST 28:2; 0; s | 478 | 6.34 | neg | 1.32 | 0.0081 | 0.58 |
| ST 27:1; 0; S | 466 | 8.29 | neg | 1.08 | 0.0242 | 0.51 |
| ST 29:1; 0; s | 494 | 9.84 | neg | 1.08 | 0.0097 | 0.45 |
| ST 24:1; 03; G;S | 513 | 7.03 | neg | 1.62 | 0.0141 | 0.23 |
| FAHFA 20:4/3:0 | 376 | 9.87 | neg | 1.54 | 0 | 0.22 |
| FAHFA 22:6/3:0 | 400 | 9.77 | neg | 1.72 | 0.0012 | 0.21 |
| FAHFA 20:5/3:0 | 374 | 9.39 | neg | 1.42 | 0 | 0.19 |
| glycolipid | ||||||
| LPS 22:6 | 569 | 8.77 | neg | 1.70 | 0.0000 | 0.37 |
| LPS 22:1 | 579 | 6.95 | neg | 1.46 | 0.0328 | 0.18 |
| others | ||||||
| quercetin | 302 | 4.92 | neg | 1.94 | 0.0001 | 3.05 |
| melatonin | 232 | 5.35 | neg | 1.48 | 0.0001 | 2.79 |
| levodopa | 197 | 5.98 | neg | 1.06 | 0.012 | 0.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, D.; Liu, F.; Jia, A.; Liu, X.; Cui, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M. Microwave Pretreatment-Induced Significant Nutrient and Metabolite Changes in Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060249
Song D, Liu F, Jia A, Liu X, Cui T, Zhang H, Zhang M. Microwave Pretreatment-Induced Significant Nutrient and Metabolite Changes in Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(6):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060249
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Dairong, Fang Liu, Airong Jia, Xue Liu, Tingting Cui, Hui Zhang, and Miansong Zhang. 2025. "Microwave Pretreatment-Induced Significant Nutrient and Metabolite Changes in Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus" Marine Drugs 23, no. 6: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060249
APA StyleSong, D., Liu, F., Jia, A., Liu, X., Cui, T., Zhang, H., & Zhang, M. (2025). Microwave Pretreatment-Induced Significant Nutrient and Metabolite Changes in Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Marine Drugs, 23(6), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060249







