Biochemical Composition and Alkaline Extraction Optimization of Soluble Bioactive Compounds from the Green Algae Caulerpa cylindraceae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
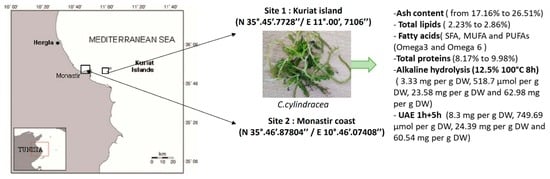
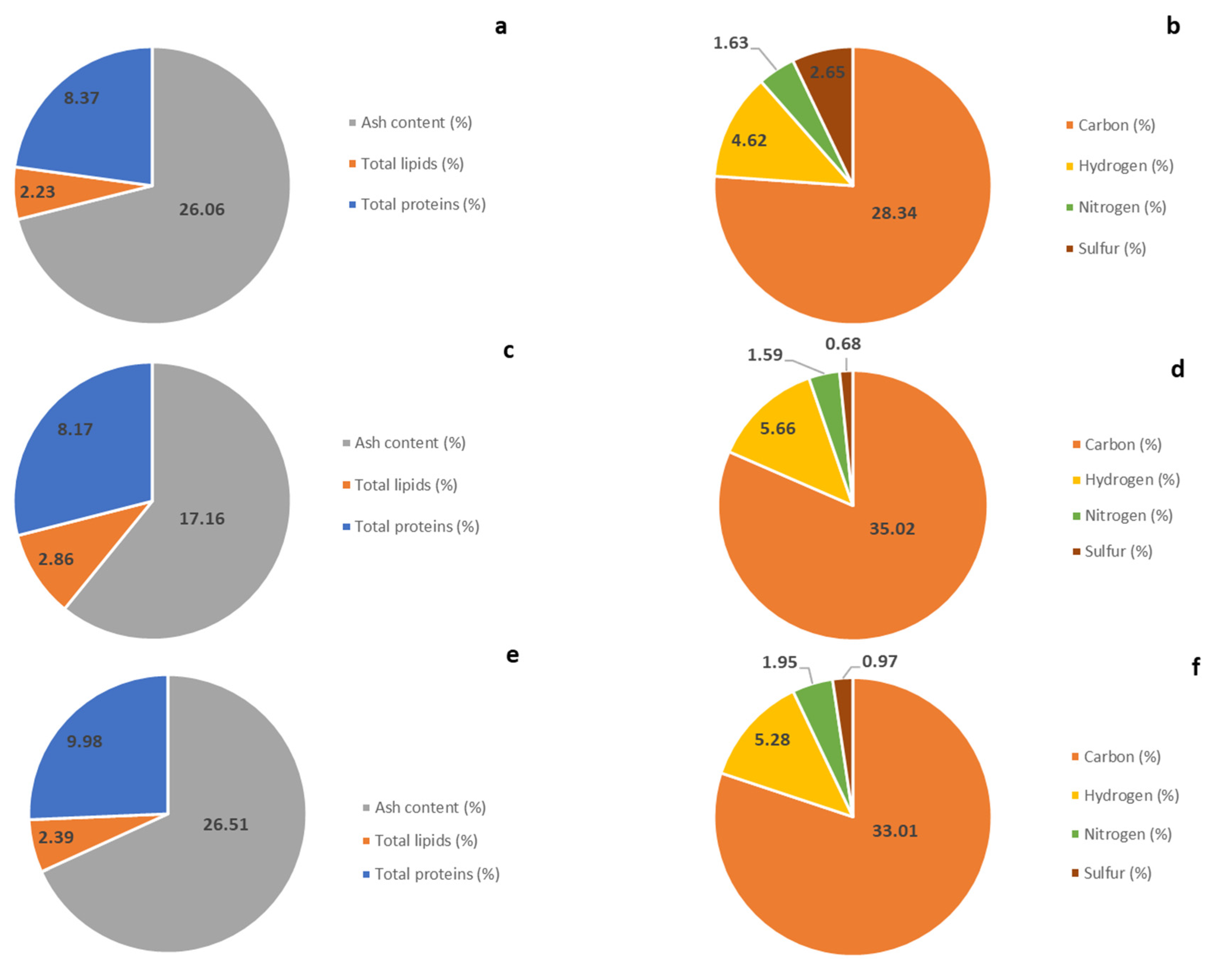
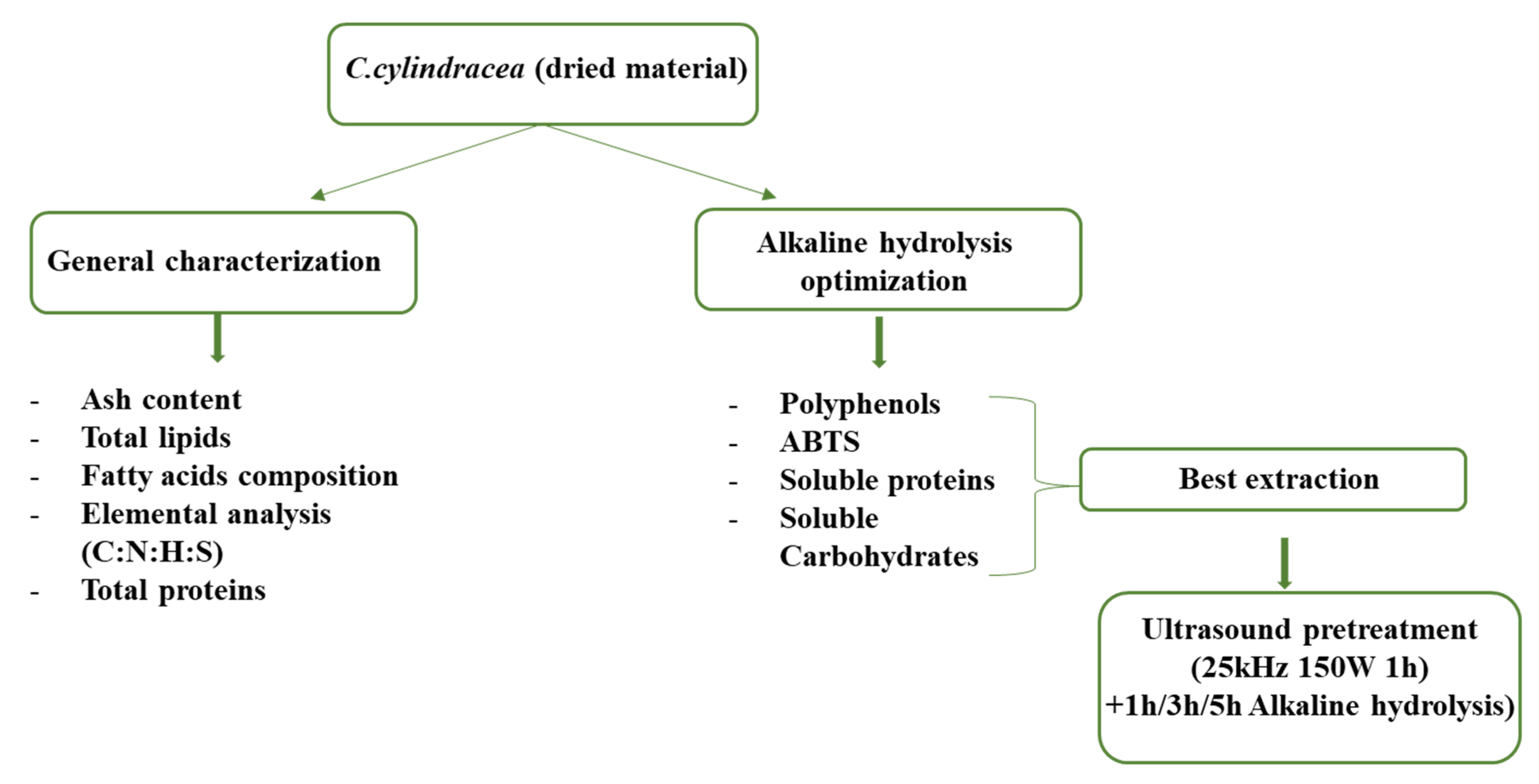
2.1. Caulerpa cylindracea Biochemical Composition
2.2. Algae Fatty Acid Composition
2.3. Conventional Method
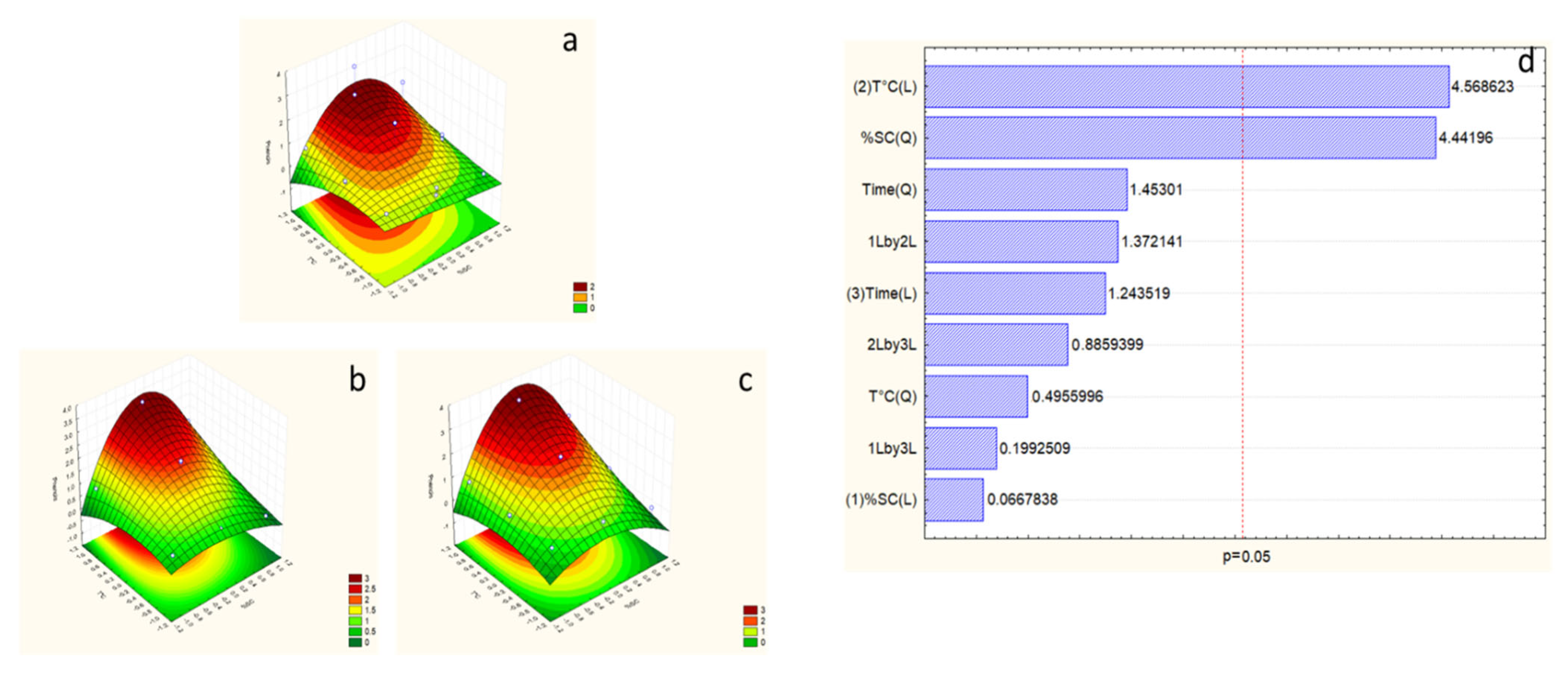
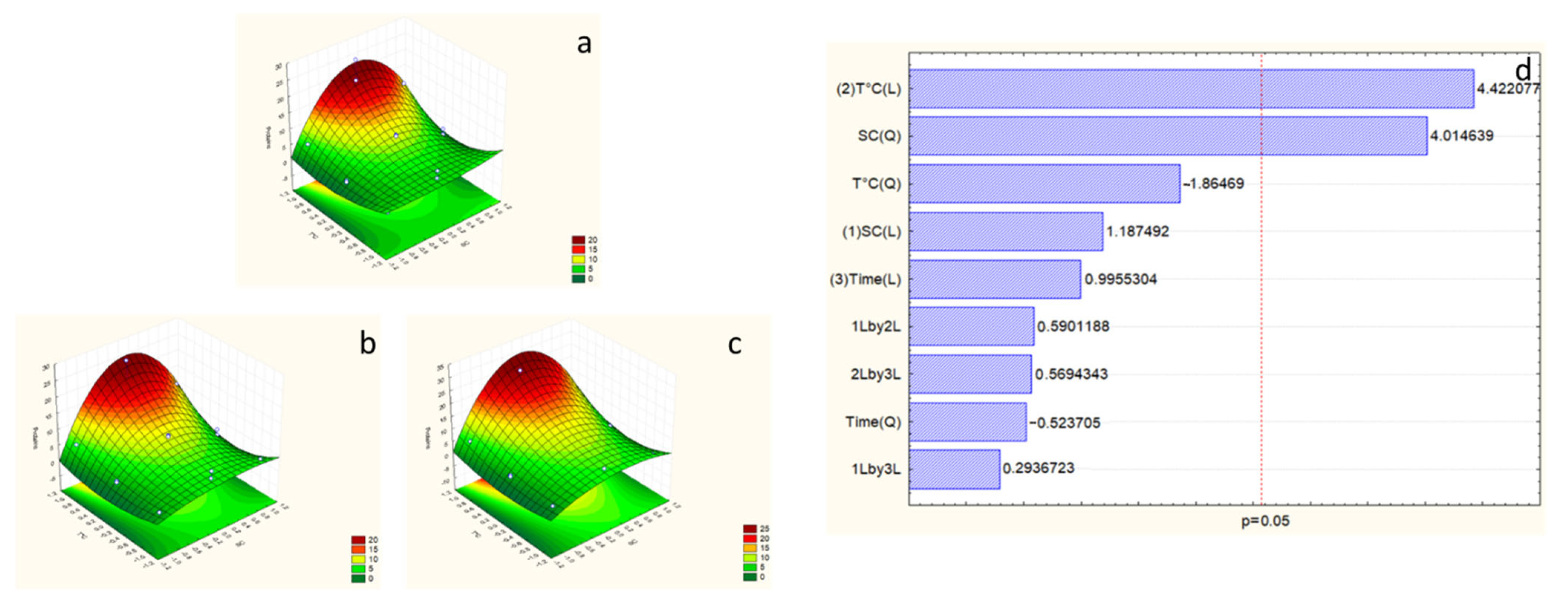
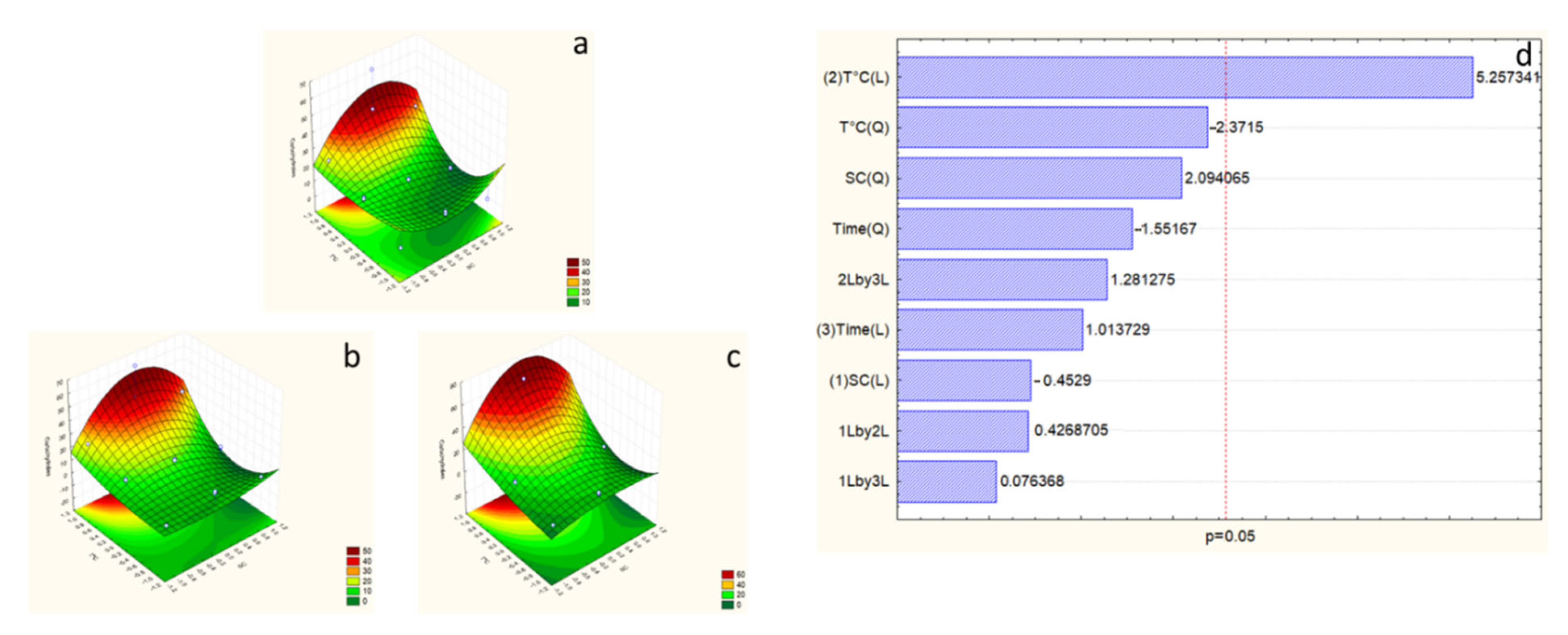
2.4. Response Surface Model for Alkaline Hydrolysis
2.5. Effects of Extraction Variables on Polyphenols
2.6. Effects of Extraction Variables on Antioxidant Activity
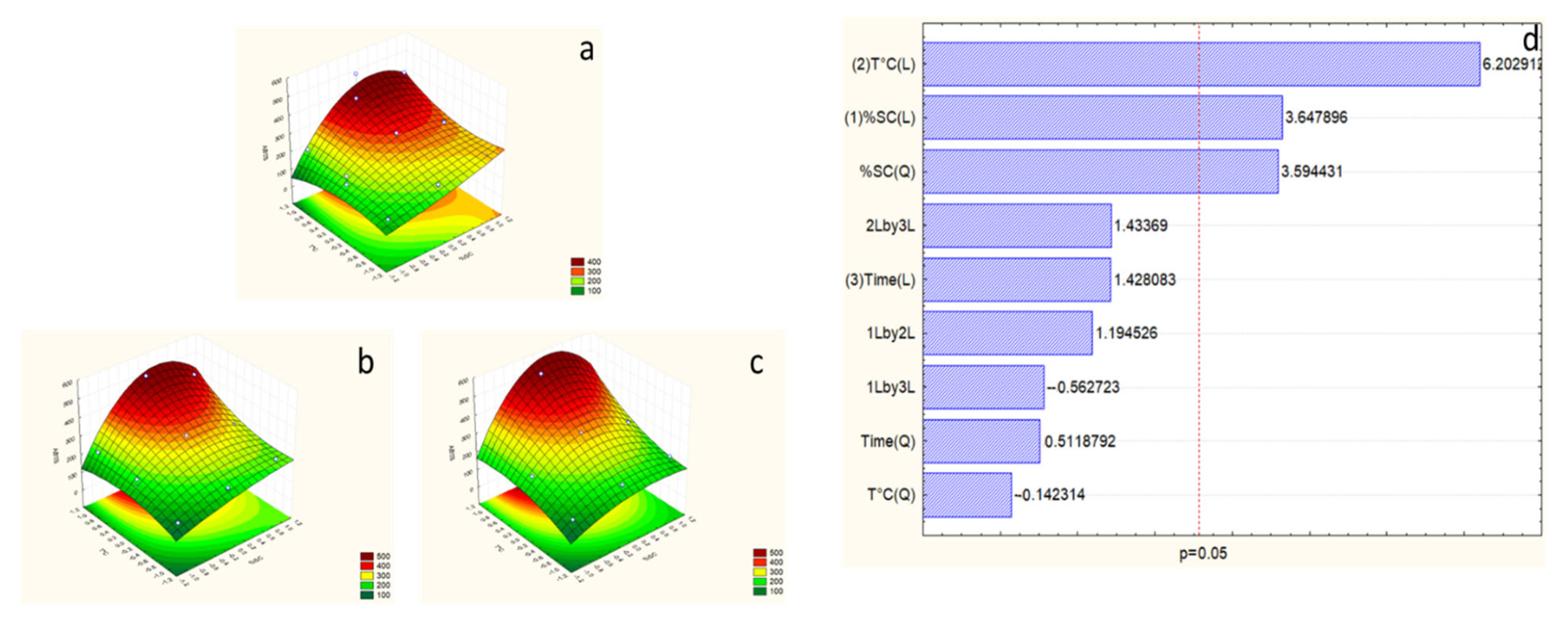
2.7. Effects of Extraction Variables on Proteins
2.8. Effects of Extraction Variables on Carbohydrates
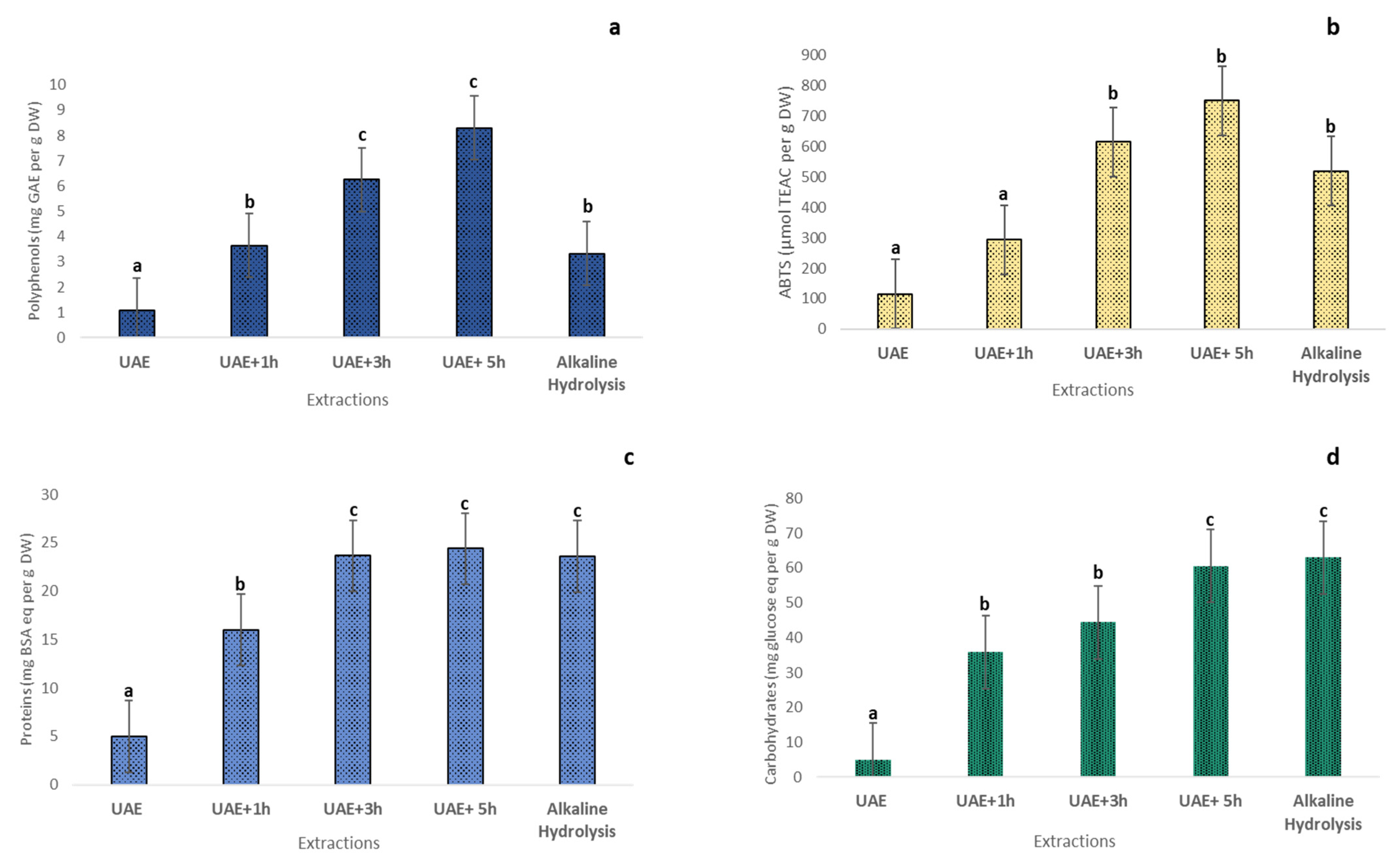
2.9. Effects of Ultrasound Pretreatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Material
4.2. General Characterization Prior to Alkaline Hydrolysis Optimization
4.2.1. Ash Content
4.2.2. Total Lipids
4.2.3. Gas Chromatography of Fatty Acids
4.2.4. Elemental Analysis
4.2.5. Proteins Content
4.3. Conventional Extraction
4.4. Alkaline Hydrolysis Extraction
Response Surface Model Design
4.5. Combination of Ultrasound Extraction (UAE) and Alkaline Hydrolysis
4.6. Quantification of Bioactive Compounds
4.6.1. Polyphenols
4.6.2. Antioxidant Capacity
4.6.3. Soluble Proteins
4.6.4. Soluble Carbohydrates
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raniello, R.; Mollo, E.; Lorenti, M.; Gavagnin, M.; Buia, M.C. Phytotoxic Activity of Caulerpenyne from the Mediterranean Invasive Variety of Caulerpa racemosa: A Potential Allelochemical. Biol. Invasions 2007, 9, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Carbone, M.; Castelluccio, F.; Pozone, F.; Roussis, V.; Templado, J.; Ghiselin, M.T.; Cimino, G. Factors Promoting Marine Invasions: A Chemoecological Approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4582–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, A.; Fraschetti, S.; Scopa, M.; Rizzo, L.; Danovaro, R. Meiofauna Communities, Nematode Diversity and C Degradation Rates in Seagrass (Posidonia oceanica L.) and Unvegetated Sediments Invaded by the Algae Caulerpa cylindracea (Sonder). Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 119, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlizzi, A.; Felline, S.; Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Perfetti, V.; Cutignano, A.; Mollo, E. Detrimental Physiological Effects of the Invasive Alga Caulerpa racemosa on the Mediterranean White Seabream Diplodus Sargus. Aquat. Biol. 2011, 12, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbi, S.; Giuliani, M.E.; Pittura, L.; d’Errico, G.; Terlizzi, A.; Felline, S.; Grauso, L.; Mollo, E.; Cutignano, A.; Regoli, F. Could Molecular Effects of Caulerpa racemosa Metabolites Modulate the Impact on Fish Populations of Diplodus sargus? Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 96, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felline, S.; Mollo, E.; Ferramosca, A.; Zara, V.; Regoli, F.; Gorbi, S.; Terlizzi, A. Can a Marine Pest Reduce the Nutritional Value of Mediterranean Fish Flesh? Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollo, E.; Cimino, G.; Ghiselin, M.T. Alien Biomolecules: A New Challenge for Natural Product Chemists. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, G.S.; van Reine, W.F.P.; Huisman, J.M.; Draisma, S.G.A.; D. Gurgel, C.F. Resolving Phenotypic Plasticity and Species Designation in the Morphologically Challenging Caulerpa racemosa–peltata Complex (Chlorophyta, Caulerpaceae). J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabili, L.; Fraschetti, S.; Acquaviva, M.I.; Cavallo, R.A.; De Pascali, S.A.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Gerardi, C.; Narracci, M.; Rizzo, L. The Potential Exploitation of the Mediterranean Invasive Alga Caulerpa cylindracea: Can the Invasion Be Transformed into a Gain? Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmawan, M.; Fajarningsih, N.D.; Sihono; Irianto, H.E. Caulerpa: Ecology, Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential. In Marine Niche: Applications in Pharmaceutical Sciences: Translational Research; Nathani, N.M., Mootapally, C., Gadhvi, I.R., Maitreya, B., Joshi, C.G., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus Raposo, M.F.; De Morais, A.M.B.; De Morais, R.M.S.C. Marine Polysaccharides from Algae with Potential Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2967–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdugo, R.P.; Terme, N.; Lang, M.; Pliego-Cortés, H.; Marty, C.; Hurtado, A.Q.; Bedoux, G.; Bourgougnon, N. An Analysis of the Nutritional and Health Values of Caulerpa racemosa (Forsskål) and Ulva fasciata (Delile)—Two Chlorophyta Collected from the Philippines. Molecules 2020, 25, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, W.-F.; Tay, V.; Tan, S.-H.; Yow, Y.-Y.; Chew, J. Decoding Antioxidant and Antibacterial Potentials of Malaysian Green Seaweeds: Caulerpa racemosa and Caulerpa lentillifera. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.-Y.; Huang, X.; Cheong, K.-L. Recent Advances in Marine Algae Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structure, and Activities. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, W.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Q. The Structure-Activity Relationship between Marine Algae Polysaccharides and Anti-Complement Activity. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Singh, A.; Akram, W.; Upadhyay, A.; Abrol, G.S. Algal Lipids: A Review on Current Status and Future Prospects in Food Processing. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e17618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, F.; Cartaxana, P.; Melo, T.; Calado, R.; Pereira, R.; Abreu, H.; Domingues, P.; Cruz, S.; Domingues, M.R. Domesticated Populations of Codium tomentosum Display Lipid Extracts with Lower Seasonal Shifts than Conspecifics from the Wild—Relevance for Biotechnological Applications of This Green Seaweed. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.; Rey, F.; Melo, T.; P. Moreira, A.S.; Marques, F.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, P.; Domingues, M.R. Mapping the Polar Lipidome of Macroalgae Using LC-MS-Based Approaches for Add-Value Applications. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2023, 125, 2300005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černá, M. Chapter 24-Seaweed Proteins and Amino Acids as Nutraceuticals. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Marine Medicinal Foods; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 64, pp. 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiviya, P.; Gamage, A.; Gama-Arachchige, N.S.; Merah, O.; Madhujith, T. Seaweeds as a Source of Functional Proteins. Phycology 2022, 2, 216–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echave, J.; Otero, P.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Prieto, M.A. Seaweed-Derived Proteins and Peptides: Promising Marine Bioactives. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotas, J.; Leandro, A.; Monteiro, P.; Pacheco, D.; Figueirinha, A.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; da Silva, G.J.; Pereira, L. Seaweed Phenolics: From Extraction to Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Cotas, J. Therapeutic Potential of Polyphenols and Other Micronutrients of Marine Origin. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liao, W.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, C. An Overview on the Nutritional and Bioactive Components of Green Seaweeds. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2023, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, A.; Klun, K.; Francé, J.; Mozetič, P.; Orlando-Bonaca, M. Non-Indigenous Species in the Mediterranean Sea: Turning From Pest to Source by Developing the 8Rs Model, a New Paradigm in Pollution Mitigation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira-Casais, A.; Otero, P.; Garcia-Perez, P.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Pereira, A.G.; Carpena, M.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Prieto, M.A. Benefits and Drawbacks of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction for the Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Marine Algae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelichi, S.; Sørensen, A.-D.M.; Hajfathalian, M.; Jacobsen, C. Effect of Post-Extraction Ultrasonication on Compositional Features and Antioxidant Activities of Enzymatic/Alkaline Extracts of Palmaria Palmata. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Y.; Yuan, W. Ultrasound for Microalgal Cell Disruption and Product Extraction: A Review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 87, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Yin, X.; Zeng, Q.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J. Isolation, Structure, and Surfactant Properties of Polysaccharides from Ulva lactuca L. from South China Sea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.J.; Xie, C.; Duan, X.; Ng, K.; Suleria, H.A.R. Optimization of Ultrasonic Extraction Parameters for the Recovery of Phenolic Compounds in Brown Seaweed: Comparison with Conventional Techniques. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssouf, L.; Lallemand, L.; Giraud, P.; Soulé, F.; Bhaw-Luximon, A.; Meilhac, O.; D’Hellencourt, C.L.; Jhurry, D.; Couprie, J. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Structural Characterization by NMR of Alginates and Carrageenans from Seaweeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 166, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, B.P. Ash Content Determination. In Nielsen’s Food Analysis Laboratory Manual; Ismail, B.P., Nielsen, S.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasmiati, K.; Syahrul, S.; Badraeni, B.; Rahmi, M.H. Proximate and Mineral Compositions of the Green Seaweeds Caulerpa lentilifera and Caulerpa racemosa from South Sulawesi Coast, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1119, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Gupta, V.; Kumari, P.; Reddy, C.R.K.; Jha, B. Assessment of Nutrient Composition and Antioxidant Potential of Caulerpaceae Seaweeds. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, M.R.; Calado, R. Lipids of Marine Algae—Biomolecules with High Nutritional Value and Important Bioactive Properties. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini, I. The Potential of Algae in the Nutricosmetic Sector. Molecules 2023, 28, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, D.; Rey, F.; Leal, M.C.; Lillebø, A.I.; Calado, R.; Domingues, M.R. Bioactivities of Lipid Extracts and Complex Lipids from Seaweeds: Current Knowledge and Future Prospects. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermid, K.J.; Stuercke, B. Nutritional Composition of Edible Hawaiian Seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2003, 15, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matanjun, P.; Mohamed, S.; Mustapha, N.M.; Muhammad, K. Nutrient Content of Tropical Edible Seaweeds, Eucheuma cottonii, Caulerpa lentillifera and Sargassum polycystum. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagappan, T.; Vairappan, C.S. Nutritional and Bioactive Properties of Three Edible Species of Green Algae, Genus Caulerpa (Caulerpaceae). J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuldin, W.H.; Shapawi, R.; Shaleh, S.R.M. Biochemical Composition of Enigmatic Green Macroalgae, Caulerpa macrodisca Decaisne (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P.; DiNicolantonio, J.J. The Importance of a Balanced ω-6 to ω-3 Ratio in the Prevention and Management of Obesity. Open Heart 2016, 3, e000385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailhaud, G.; Guesnet, P. Fatty Acid Composition of Fats Is an Early Determinant of Childhood Obesity: A Short Review and an Opinion. Obes. Rev. 2004, 5, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The Importance of the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio in Cardiovascular Disease and Other Chronic Diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordalina, M.; Pinheiro, H.M.; Mateus, M.; da Fonseca, M.M.R.; Cesário, M.T. Macroalgae as Protein Sources—A Review on Protein Bioactivity, Extraction, Purification and Characterization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, G.P.B.; Santiañez, W.J.E.; Trono, G.C.; Montaño, M.N.E.; Araki, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Hasegawa, T. Seaweed Biomass of the Philippines: Sustainable Feedstock for Biogas Production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratana-arporn, P.; Chirapart, A. Nutritional Evaluation of Tropical Green Seaweeds Caulerpa lentillifera and Ulva reticulata. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2006, 40, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Li, P. Advances in Cultivation, Wastewater Treatment Application, Bioactive Components of Caulerpa lentillifera and Their Biotechnological Applications. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaa, F.; Wijesinghe, U.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Althobaiti, N.A.; Albalawi, A.E.; Khan, B.A.; Menaa, B. Marine Algae-Derived Bioactive Compounds: A New Wave of Nanodrugs? Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Abdel-Raouf, N.; Alwutayd, K.; AbdElgawad, H.; Abdelhameed, M.S.; Hammouda, O.; Elsayed, K.N.M. Seasonal Changes in the Biochemical Composition of Dominant Macroalgal Species along the Egyptian Red Sea Shore. Biology 2023, 12, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, K.; Adhikari, U.; Lerouge, P.; Ray, B. Polysaccharides from Caulerpa racemosa: Purification and Structural Features. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancia, M.; Fernández, P.V.; Leliaert, F. Diversity of Sulfated Polysaccharides From Cell Walls of Coenocytic Green Algae and Their Structural Relationships in View of Green Algal Evolution. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 554585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagaki, T.; Maeda, M.; Kanazawa, K.; Ishizuka, Y.; Nakanishi, H. Structures of Caulerpa Cell Wall Microfibril Xylan with Detection of β-1,3-Xylooligosaccharides as Revealed by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization/Time of Flight/Mass Spectrometry. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, V.A.; Navarro, D.A.; Ponce, N.M.A.; Stortz, C.A. Seaweed Polysaccharides: Structure and Applications. In Industrial Applications of Renewable Biomass Products: Past, Present and Future; Goyanes, S.N., D’Accorso, N.B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 75–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, P.X.; Alberghina, J.; Confalonieri, V.; Errea, M.I.; Estevez, J.M.; Ciancia, M. Sulfated Polysaccharides in the Freshwater Green Macroalga Cladophora surera Not Linked to Salinity Adaptation. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavilala, S.L.; D’Souza, J.S. Algal Polysaccharides and Their Biological Applications. In Marine Algae Extracts; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 411–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. Algal Extracts: Technology and Advances. Eng. Life Sci. 2014, 14, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hosano, N.; Hosano, H. Recovering Microalgal Bioresources: A Review of Cell Disruption Methods and Extraction Technologies. Molecules 2022, 27, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Escobedo-Avellaneda, Z.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Welti-Chanes, J. State-of-the-Art Extraction Methodologies for Bioactive Compounds from Algal Biome to Meet Bio-Economy Challenges and Opportunities. Molecules 2018, 23, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.T.; García-García, P.; Korbee, N.; Vega, J.; Señoráns, F.J.; Figueroa, F.L. Optimizing the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Porphyra linearis (Rhodophyta): Evaluating Alkaline and Enzymatic Hydrolysis for Nutraceutical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Martín, E.; Forbes-Hernández, T.; Romero, A.; Cianciosi, D.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. Influence of the Extraction Method on the Recovery of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds from Food Industry By-Products. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 131918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaiogiannis, D.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Athanasiadis, V.; Bozinou, E.; Makris, D.P.; Lalas, S.I. Successive Solvent Extraction of Polyphenols and Flavonoids from Cistus creticus L. Leaves. Oxygen 2023, 3, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Robinson, N.A.; Warner, R.D.; Barrow, C.J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A.R. LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS Characterization of Seaweed Phenolics and Their Antioxidant Potential. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, Y.L.; Lim, Y.Y.; Omar, M.; Khoo, K.S. Antioxidant Activity of Three Edible Seaweeds from Two Areas in South East Asia. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, I.H.; Bandaranayake, U.; Keerthirathna, L.R.; Manawadu, C.; Silva, R.M.; Mohamed, B.; Ali, R.; Peiris, D.C. Integration of in Vitro and In-Silico Analysis of Caulerpa racemosa against Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Anticancer Activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, G. Preparation and Antioxidant Property of Extract and Semipurified Fractions of Caulerpa racemosa. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Ueng, J.-P.; Tsai, G.-J. Proximate Composition, Total Phenolic Content, and Antioxidant Activity of Seagrape (Caulerpa lentillifera). J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C950–C958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangestuti, R.; Haq, M.; Rahmadi, P.; Chun, B.-S. Nutritional Value and Biofunctionalities of Two Edible Green Seaweeds (Ulva lactuca and Caulerpa racemosa) from Indonesia by Subcritical Water Hydrolysis. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanna, B.; Choudhary, B.; Mishra, A. Metabolite Profiling, Antioxidant, Scavenging and Anti-Proliferative Activities of Selected Tropical Green Seaweeds Reveal the Nutraceutical Potential of Caulerpa spp. Algal Res. 2018, 36, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farasat, M.; Khavari-Nejad, R.-A.; Nabavi, S.M.B.; Namjooyan, F. Antioxidant Properties of Two Edible Green Seaweeds From Northern Coasts of the Persian Gulf. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2013, 8, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayak, R.C.; Sudha, S.A.; Chatterji, A. Bio-Screening of a Few Green Seaweeds from India for Their Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Potential. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2471–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushanth, V.; Rajashekhar, M. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities in the Four Species of Marine Microalgae Isolated from Arabian Sea of Karnataka Coast. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2015, 4, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, E.-S.; Thi, N.D. Effects of Extraction and Processing Methods on Antioxidant Compound Contents and Radical Scavenging Activities of Laver (Porphyra tenera). Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 19, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, J.; Baskaran, R.; Baskaran, V. Profiling of Bioactives and in Vitro Evaluation of Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Property of Polyphenols of Marine Algae Padina tetrastromatica. Algal Res. 2021, 55, 102250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caronni, S.; Addis, F.; Delaria, M.A.; Gentili, R.; Montagnani, C.; Navone, A.; Panzalis, P.; Citterio, S. Comparative Evaluation of Multiple Protein Extraction Procedures from Three Species of the Genus Caulerpa. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 2485–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qudus B Aroyehun, A.; Abdul Razak, S.; Palaniveloo, K.; Nagappan, T.; Suraiza Nabila Rahmah, N.; Wee Jin, G.; Chellappan, D.K.; Chellian, J.; Kunnath, A.P. Bioprospecting Cultivated Tropical Green Algae, Caulerpa racemosa (Forsskal) J. Agardh: A Perspective on Nutritional Properties, Antioxidative Capacity and Anti-Diabetic Potential. Foods 2020, 9, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honwichit, O.; Ruengsaengrob, P.; Buathongjan, C.; Charoensiddhi, S. Influence of Extraction Methods on the Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharide Extracts from Discarded Sea Grape (Caulerpa lentillifera). J. Fish. Environ. 2022, 46, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Peasura, N.; Laohakunjit, N.; Kerdchoechuen, O.; Wanlapa, S. Characteristics and Antioxidant of Ulva intestinalis Sulphated Polysaccharides Extracted with Different Solvents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebringerová, A.; Hromádková, Z. An Overview on the Application of Ultrasound in Extraction, Separation and Purification of Plant Polysaccharides. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2010, 8, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez-Fernández, N.; Domínguez, H.; Torres, M.D. A Green Approach for Alginate Extraction from Sargassum muticum Brown Seaweed Using Ultrasound-Assisted Technique. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummat, V.; Tiwari, B.K.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Condon, K.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; O’Doherty, J.; O’Donnell, C.; Rajauria, G. Optimisation of Ultrasound Frequency, Extraction Time and Solvent for the Recovery of Polyphenols, Phlorotannins and Associated Antioxidant Activity from Brown Seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, A.T.; Jacobsen, C.; Holdt, S.L. Emerging Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Phenolics: Opportunities and Challenges. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Tavanandi, H.A.; Mantri, V.A.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S. Ultrasound Assisted Methods for Enhanced Extraction of Phycobiliproteins from Marine Macro-Algae, Gelidium pusillum (Rhodophyta). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A Simple Method For The Isolation And Purification Of Total Lipides From Animal Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, S.; Barbarino, E.; De Paula, J.; Pereira, L.; Lanfer-Marquez, U. Amino Acid Composition, Protein Content and Calculation of Nitrogen-to-protein Conversion Factors for 19 Tropical Seaweeds. Phycol. Res. 2002, 50, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Brunton, N.P.; Patras, A.; Tiwari, B.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Martin-Diana, A.B.; Barry-Ryan, C. Optimization of Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Antioxidant Compounds from Marjoram (Origanum majorana L.) Using Response Surface Methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, T.G.; Goldberg, H.J.V. The Anthrone Method for the Determination of Carbohydrates in Foods and in Oral Rinsing. J. Dent. Res. 1956, 35, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fatty Acids | RT (min) | % Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSS1 | CWS1 | CSS2 | ||
| Saturated Fatty acids (SFA) | ||||
| C12:0 lauric | 21.47 | 0.47 | 0.39 | 0.47 |
| C14:0 myristic | 24.90 | 4.63 | 4.95 | 3.67 |
| C16:0 palmitic acid | 28.41 | 33.7 | 31.87 | 32.91 |
| C18:0 stearic acid | 31.80 | 1.77 | 1.50 | 1.54 |
| C21:0 heneicosanoic | 38.55 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.17 |
| C21:0 heneicosanoic acid | 37.99 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 0.60 |
| C22:0 behenate | 39.38 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.19 |
| Monounsaturated Fatty acids (MUFA) | ||||
| C16:1 palmitoleic acid | 29.69 | 2.71 | 3.31 | 2.65 |
| C18:1(ω 9) cis oleic acid | 32.92 | 10.51 | 8.50 | 10.19 |
| C22:1 erucate | 40.13 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 |
| Polyunsaturated Matty acids (PUFA) | ||||
| C18:2 (ω6) linoleic acid | 34.58 | 4.19 | 4.01 | 4.37 |
| C18:3 ω6 γ-linolenic acid | 35.86 | 0.48 | 0.65 | 0.37 |
| C18:3 ω3 α-linolenic acid | 36.54 | 6.06 | 6.62 | 4.37 |
| C20:3 ω6 eicosatrienoic acid | 40.39 | 1.95 | 1.71 | 1.80 |
| C21:4 arachidonic acid methyl ester | 42.40 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 0.79 |
| C22:2 cis13,16-docisadienoic | 43.08 | 1.43 | 1.30 | 1.14 |
| SFA | 41.55 | 39.39 | 39.64 | |
| MUFA | 13.38 | 11.81 | 12.84 | |
| PUFA | 10.73 | 11.28 | 9.11 | |
| PUFA ω6 | 6.62 | 6.37 | 6.54 | |
| PUFA ω3 | 6.06 | 6.62 | 4.37 | |
| Ratio ω6/ω3 | 1.09 | 0.96 | 1.49 | |
| Runs | X1 | X2 | X3 | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 30 | 4.5 | 0.61 ± 0.03 | 132.35 ± 0.11 | 2.69 ± 0.05 | 5.77 ± 0.08 |
| 2 | 12.5 | 30 | 1 | 0.30 ± 0.09 | 190.69 ± 0.55 | 2.90 ± 0.09 | 13.63 ± 0.20 |
| 3 | 12.5 | 30 | 8 | 0.62 ± 0.02 | 194.52 ± 0.128 | 5.41 ± 0.05 | 12.22 ± 0.16 |
| 4 | 25 | 30 | 4.5 | 0.15 ± 0.005 | 227.17 ± 0.21 | 3.26 ± 0.002 | 5.02 ± 0.19 |
| 5 | 0 | 65 | 1 | 0.67 ± 0.003 | 167.14 ± 0.20 | 2.61 ± 0.019 | 19.73 ± 0.24 |
| 6 | 0 | 65 | 8 | 0.68 ± 0.008 | 215.45 ± 0.76 | 3.15 ± 0.03 | 21.16 ± 0.23 |
| 7 | 12.5 | 65 | 4.5 | 2.09 ± 0.01 | 332.11 ± 0.91 | 7.16 ± 0.03 | 21.29 ± 0.12 |
| 8 | 12.5 | 65 | 4.5 | 2.08 ± 0.02 | 330.29 ± 1.25 | 7.18 ± 0.10 | 21.03 ± 0.25 |
| 9 | 12.5 | 65 | 4.5 | 2.11 ± 0.01 | 330.25 ± 0.18 | 7.27 ± 0.04 | 21.46 ± 0.24 |
| 10 | 25 | 65 | 1 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 277.83 ± 3.20 | 1.47 ± 0.09 | 13.99 ± 0.44 |
| 11 | 25 | 65 | 8 | 0.60 ± 0.016 | 275.05 ± 1.00 | 0.75 ± 0.05 | 10.62 ± 0.16 |
| 12 | 0 | 100 | 4.5 | 0.84 ± 0.003 | 217.26 ± 1.03 | 5.27 ± 0.06 | 27.83 ± 0.17 |
| 13 | 12.5 | 100 | 1 | 2.13 ± 0.07 | 384.70 ± 1.64 | 11.69 ± 0.14 | 21.71 ± 0.07 |
| 14 | 12.5 | 100 | 8 | 3.33 ± 0.05 | 518.70 ± 1.92 | 23.58 ± 0.21 | 62.98 ± 0.67 |
| 15 | 25 | 100 | 4.5 | 1.73 ± 0.03 | 420.53 ± 0.83 | 14.06 ± 0.18 | 25.51 ± 0.25 |
| Runs | X1 | X2 | X3 | Y1 | Y2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 30 | 3 | 1.47 ± 0.05 | 4.46 ± 0.08 |
| 2 | 7.5 | 30 | 1 | 4.61 ± 0.13 | 10.20 ± 0.02 |
| 3 | 7.5 | 30 | 5 | 6.94 ± 0.18 | 11.76 ± 0.26 |
| 4 | 15 | 30 | 3 | 3.59 ± 0.16 | 4.66 ± 0.07 |
| 5 | 0 | 65 | 1 | 2.32 ± 0.23 | 17.20 ± 0.25 |
| 6 | 0 | 65 | 5 | 1.94 ± 0.1 | 16.30 ± 0.23 |
| 7 | 7.5 | 65 | 3 | 9.70 ± 0.23 | 14.74 ± 0.31 |
| 8 | 7.5 | 65 | 3 | 9.55 ± 0.18 | 14.67 ± 0.17 |
| 9 | 7.5 | 65 | 3 | 9.30 ± 0.22 | 13.94 ± 0.43 |
| 10 | 15 | 65 | 5 | 3.05 ± 0.11 | 7.01 ± 0.22 |
| 11 | 15 | 65 | 5 | 4.77 ± 0.05 | 7.44 ± 0.23 |
| 12 | 0 | 100 | 3 | 5.34 ± 0.04 | 23.04 ± 0.34 |
| 13 | 7.5 | 100 | 1 | 18.94 ± 0.06 | 41.62 ± 0.12 |
| 14 | 7.5 | 100 | 5 | 25.33 ± 0.23 | 65.56 ± 0.23 |
| 15 | 15 | 100 | 3 | 11.67 ± 0.08 | 30.70 ± 0.32 |
| Responses | Optimization 1 | Optimization 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| F-test value F9,5-tab = 4.77 | Phenols | 5.12 | - |
| ABTS | 7.86 | - | |
| Proteins | 3.40 | 4.89 | |
| Carbohydrates | 4.72 | 10.01 | |
| R2 | Phenols | 0.90 | - |
| ABTS | 0.93 | - | |
| Proteins | 0.86 | 0.89 | |
| Carbohydrates | 0.89 | 0.90 | |
| Related Error of Best extraction | Phenols | 15.08 | - |
| ABTS | 8.06 | - | |
| Proteins | 14.92 | 14.03 | |
| Carbohydrates | 11.53 | 12.69 |
| Symbols | Independent Variables | Coded Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| X1 | Sodium Carbonate (%) | 0 | 12.5 | 25 |
| X2 | Temperature (C) | 30 | 65 | 100 |
| X3 | Time (h) | 1 | 4.5 | 8 |
| Symbols | Independent Variables | Coded Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| X1 | Sodium Carbonate (%) | 0 | 7.5 | 15 |
| X2 | Temperature (C) | 30 | 65 | 100 |
| X3 | Time (h) | 1 | 3 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tahar, A.; Zghida, H.; Pereira, D.T.; Korbee, N.; Treichel, H.; Figueroa, F.L.; Achour, L. Biochemical Composition and Alkaline Extraction Optimization of Soluble Bioactive Compounds from the Green Algae Caulerpa cylindraceae. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050208
Tahar A, Zghida H, Pereira DT, Korbee N, Treichel H, Figueroa FL, Achour L. Biochemical Composition and Alkaline Extraction Optimization of Soluble Bioactive Compounds from the Green Algae Caulerpa cylindraceae. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(5):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050208
Chicago/Turabian StyleTahar, Amani, Haïfa Zghida, Débora Tomazi Pereira, Nathalie Korbee, Helen Treichel, Félix L. Figueroa, and Lotfi Achour. 2025. "Biochemical Composition and Alkaline Extraction Optimization of Soluble Bioactive Compounds from the Green Algae Caulerpa cylindraceae" Marine Drugs 23, no. 5: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050208
APA StyleTahar, A., Zghida, H., Pereira, D. T., Korbee, N., Treichel, H., Figueroa, F. L., & Achour, L. (2025). Biochemical Composition and Alkaline Extraction Optimization of Soluble Bioactive Compounds from the Green Algae Caulerpa cylindraceae. Marine Drugs, 23(5), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050208