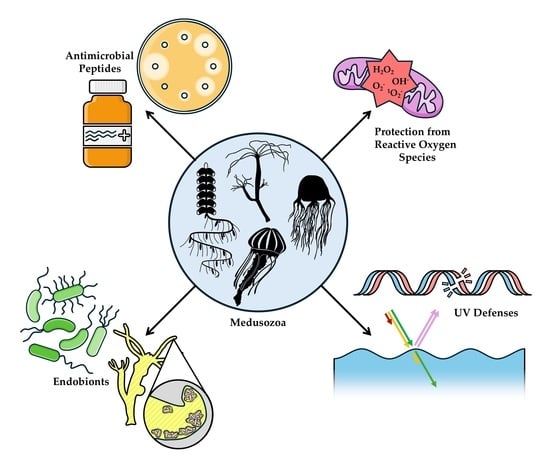
Chemical Defenses in Medusozoa
Abstract
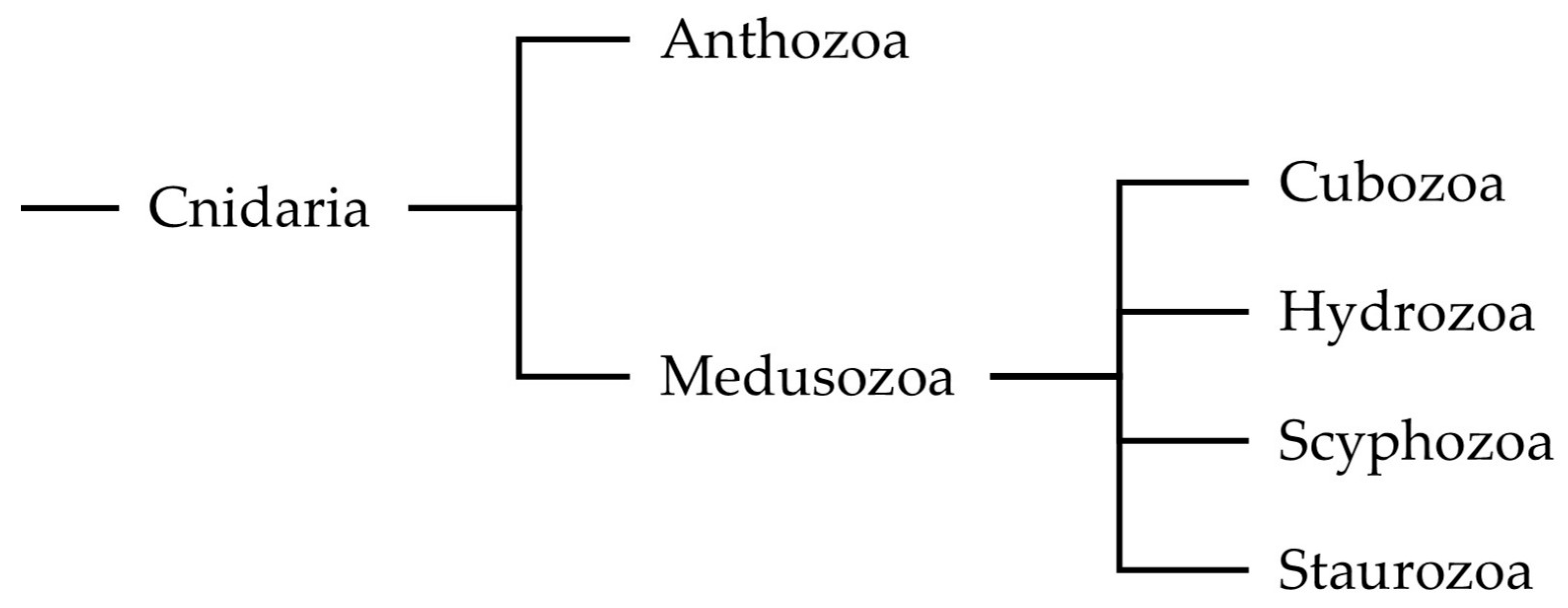
:1. Introduction
2. Ultra-Violet Light Protective Compounds
3. Defense Against Reactive Oxygen Species
3.1. Production of Reactive Oxygen Species
3.2. Examples of Oxidative Defense Compounds
3.3. Distribution of Oxidative Defense Compounds
4. Antimicrobial Peptides
4.1. Efficacy of AMPs
4.2. Spatial Distribution of AMPs
4.2.1. Hydrozoa
4.2.2. Scyphozoa
4.3. Temporal Variability in AMP Distribution
4.3.1. Hydra
4.3.2. Scyphozoa
5. Endobionts
5.1. Host Benefits of Endosymbionts
5.2. Spatial Distribution of Endobionts
5.2.1. Hydrozoa
5.2.2. Scyphozoa
5.3. Temporal Variability of Endobionts
5.3.1. Hydrozoa
5.3.2. Scyphozoa
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WoRMS. Cnidaria. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1267 (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Mariscal, R.N. Cnidaria: Cnidae. In Biology of the Integument: Invertebrates; Bereiter-Hahn, J., Matoltsy, A.G., Richards, K.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- D’Ambra, I.; Lauritano, C. A Review of Toxins from Cnidaria. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Patocka, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Oleksak, P.; Valis, M.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Marine Invertebrate Peptides: Antimicrobial Peptides. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 785085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Richa; Sinha, R.P.; Singh, S.P.; Häder, D.P. Photoprotective compounds from marine organisms. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 537–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, A.; Larkum, A.; Cox, G.; Kühl, M.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Fluorescent pigments in corals are photoprotective. Nature 2000, 408, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WoRMS. Medusozoa. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1740301 (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Savoca, S.; Di Fresco, D.; Alesci, A.; Capillo, G.; Spanò, N. Mucus secretions in Cnidarian, an ecological, adaptive and evolutive tool. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2022, 13, 11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, R.H.; Steinberg, D.K.; Bronk, D.A. Production of dissolved organic matter and inorganic nutrients by gelatinous zooplankton in the York River estuary, Chesapeake Bay. J. Plankton Res. 2009, 32, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, L.J.; Norrman, B. Release of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) by the scyphozoan jellyfish Aurelia aurita and its potential influence on the production of planktic bacteria. Mar. Biol. 1995, 121, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Mo, F.; Jiang, G.; Liang, H.; Ma, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, L.; Mariottini, G.L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Stress-Induced Mucus Secretion and Its Composition by a Combination of Proteomics and Metabolomics of the Jellyfish Aurelia coerulea. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niggl, W.; Naumann, M.S.; Struck, U.; Manasrah, R.; Wild, C. Organic matter release by the benthic upside-down jellyfish Cassiopea sp. fuels pelagic food webs in coral reefs. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 384, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramondenc, S.; Eveillard, D.; Guidi, L.; Lombard, F.; Delahaye, B. Probabilistic modeling to estimate jellyfish ecophysiological properties and size distributions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubot, N.; Giering, S.L.C.; Lucas, C.H. Similarities between the biochemical composition of jellyfish body and mucus. J. Plankton Res. 2022, 44, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinta, T.; Klun, K.; Herndl, G.J. The importance of jellyfish–microbe interactions for biogeochemical cycles in the ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 2011–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, R.H.; Steinberg, D.K.; del Giorgio, P.A.; Bouvier, T.C.; Bronk, D.A.; Graham, W.M.; Ducklow, H.W. Jellyfish blooms result in a major microbial respiratory sink of carbon in marine systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10225–10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, A.; Baba, T.; Dohmae, N.; Yamamura, M.; Wada, H.; Ushida, K. Mucin (Qniumucin), a Glycoprotein from Jellyfish, and Determination of Its Main Chain Structure. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwa, A.; Thiéry, A.; Lombard, F.; Lilley, M.K.S.; Boisset, C.; Bramard, J.-F.; Bottero, J.-Y.; Barthélémy, P. Accumulation of nanoparticles in “jellyfish” mucus: A bio-inspired route to decontamination of nano-waste. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.; Tellam, R.; Xu, B.; Zhao, Z.; Willcox, M.; Kongsuwan, K. Isolation, biochemical characterization and anti-adhesion property of mucin from the blue blubber jellyfish (Catostylus mosaicus). Biosci. Methods 2011, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengar, Ž.; Klun, K.; Dogsa, I.; Rotter, A.; Stopar, D. Sequestration of Polystyrene Microplastics by Jellyfish Mucus. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 690749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, E.A.; Habibi, M.; Haddad, E.; Sammar, M.; Angel, D.L.; Dror, H.; Lahovitski, H.; Booth, A.M.; Sabbah, I. Mechanism of nanoplastics capture by jellyfish mucin and its potential as a sustainable water treatment technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambra, I.; Merquiol, L. Jellyfish from Fisheries By-Catches as a Sustainable Source of High-Value Compounds with Biotechnological Applications. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffey, B.L. Sources and measurement of ultraviolet radiation. Methods 2002, 28, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljbour, S.M.; Alves, R.N.; Agustí, S. Aerobic respiration, biochemical composition, and glycolytic responses to ultraviolet radiation in jellyfish Cassiopea sp. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1031977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, T.J. Penetration of UV irradiance into the global ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedetti, M.; Sempéré, R. Penetration of Ultraviolet Radiation in the Marine Environment. A Review. Photochem. Photobiol. 2006, 82, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Richa; Kumar, A.; Tyagi, M.B.; Sinha, R.P. Molecular mechanisms of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage and repair. J. Nucleic Acids 2010, 2010, 592980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Wu, R.S.S. UV induces reactive oxygen species, damages sperm, and impairs fertilisation in the sea urchin Anthocidaris crassispina. Mar. Biol. 2005, 148, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moan, J. Visible light and UV radiation. In Radiation at Home, Outdoors and in the Workplace; Brune, D., Hellborg, R., Persson, B.R.R., Pääkkönen, R., Eds.; Scandinavian Science Publisher: Oslo, Norway, 2001; pp. 69–85. [Google Scholar]
- Buma, A.G.J.; Boelen, P.; Jeffrey, W.H.; Webb, A.R.; Neale, P.J.; Kieber, D.J.; Wetzel, R.G.; Blumthaler, M.; Hargreaves, B.R.; Zepp, R.G.; et al. UVR-induced DNA damage in aquatic organisms. In UV Effects in Aquatic Organisms and Ecosystems; Helbling, E.W., Zagarese, H., Helbling, E.W., Zagarese, H., Hader, D.-P., Jori, G., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 291–328. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.E.; Zepp, R.G.; Lucas, R.M.; Madronich, S.; Austin, A.T.; Ballaré, C.L.; Norval, M.; Sulzberger, B.; Bais, A.F.; McKenzie, R.L.; et al. Solar ultraviolet radiation in a changing climate. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, C.; D’Angelo, C.; Wiedenmann, J. Trade-Offs Associated with Photoprotective Green Fluorescent Protein Expression as Potential Drivers of Balancing Selection for Color Polymorphism in Reef Corals. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O. Discovery of Green Fluorescent Protein. In Green Fluorescent Protein; Wiley-Liss: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Di Camillo, C.; Puce, S.; Romagnoli, T.; Tazioli, S.; Totti, C.; Bavestrello, G. Relationships between benthic diatoms and hydrozoans (Cnidaria). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2005, 85, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahat, M. An Ecological Approach to Hydra-Cell Colonization by Algae–Algae/Hydra Symbioses. Oikos 1991, 62, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz, J.J.; Lindquist, N. Chemical defense among hydroids on pelagic Sargassum: Predator deterrence and absorption of solar UV radiation by secondary metabolites. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 155, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquet, R.S.; Phelan, M.A. An unusual blue mesogleal protein from the mangrove jellyfish Cassiopea xamachana. Mar. Biol. 1987, 94, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, M.A.; Matta, J.L.; Reyes, Y.M.; Fernando, R.; Boykins, R.A.; Blanquet, R.S. Associations between metals and the blue mesogleal protein of Cassiopea xamachana. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, D. Shallow-water hydroids of Bermuda. The Thecatae, exclusive of Plumularioidea. R. Ont. Mus. Life Sci. Contrib. 1991, 154, 1–140. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, B.S.; Dawson, M.N.; Crow, G.L.; Hofmann, D.K. Global phylogeography of Cassiopea (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae): Molecular evidence for cryptic species and multiple invasions of the Hawaiian Islands. Mar. Biol. 2004, 145, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.C.; Orr, M.C.; Ma, K.; Costello, M.J.; Waller, J.; Provoost, P.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Qiao, H. Sampling biases shape our view of the natural world. Ecography 2021, 44, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaartvedt, S.; Titelman, J.; Røstad, A.; Klevjer, T.A. Beyond the average: Diverse individual migration patterns in a population of mesopelagic jellyfish. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozman, A.; Titelman, J.; Kaartvedt, S.; Eiane, K.; Aksnes, D.L. Jellyfish distribute vertically according to irradiance. J. Plankton Res. 2017, 39, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, T.M.; Widder, E.A. The correlation of downwelling irradiance and staggered vertical migration patterns of zooplankton in Wilkinson Basin, Gulf of Maine. J. Plankton Res. 1997, 19, 1975–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, W.M.; Costello, J.H.; Colin, S.P.; Malej, A.; Lučić, D.; Onofri, V.; Benović, A. In Situ Manipulation of Vertically Migrating Gelatinous Zooplankton Using Nighttime Blue-Water Scuba in the South-Central Adriatic Sea. Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat. 2009, 19, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Pagés, F.; Gili, J.M. Vertical distribution of epipelagic siphonophores at the confluence between Benguela waters and the Angola Current over 48 hours. In Coelenterate Biology: Recent Research on Cnidaria and Ctenophora; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira Júnior, M.; Brandini, F.P.; Codina, J.C.U. Diel Vertical Dynamics of Gelatinous Zooplankton (Cnidaria, Ctenophora and Thaliacea) in a Subtropical Stratified Ecosystem (South Brazilian Bight). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearre, S. Eat and run? The hunger/satiation hypothesis in vertical migration: History, evidence and consequences. Biol. Rev. 2003, 78, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaartvedt, S.; Klevjer, T.A.; Torgersen, T.; Sørnes, T.A.; Røstad, A. Diel vertical migration of individual jellyfish (Periphylla periphylla). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.A.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotinat, P.; Fricano, C.; Toullec, G.; Röttinger, E.; Barnay-Verdier, S.; Furla, P. Intrinsically High Capacity of Animal Cells From a Symbiotic Cnidarian to Deal with Pro-Oxidative Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 819111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, H.; Halliwell, B. Damage to DNA by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: Role in inflammatory disease and progression to cancer. Biochem. J. 1996, 313, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berking, S.; Czech, N.; Gerharz, M.; Herrmann, K.; Hoffmann, U.; Raifer, H.; Sekul, G.; Siefker, B.; Sommerei, A.; Vedder, F. A newly discovered oxidant defence system and its involvement in the development of Aurelia aurita (Scyphozoa, Cnidaria): Reactive oxygen species and elemental iodine control medusa formation. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2005, 49, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Hedges, S.B. TimeTree: A Resource for Timelines, Timetrees, and Divergence Times. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 1812–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock, S.H.D.; Moline, M.A.; Case, J.F. Bioluminescence in the Sea. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 443–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock, S.H.; Rivers, T.J.; Robison, B.H. Can coelenterates make coelenterazine? Dietary requirement for luciferin in cnidarian bioluminescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11148–11151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringwood, A.H.; Lowder, M.; Provance, E.; O’Dea, J.; Gaspar, T.; Latijnhouwers, K.R.W.; Chamberland, V.F.; Vermeij, M.J.A. Cnidarian models for toxicology. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 281, 107265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, G.V.; Oktyabrsky, O.N. Glutathione in Bacteria. Biochemistry 2005, 70, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabili, L.; Rizzo, L.; Caprioli, R.; Leone, A.; Piraino, S. Jellyfish Bioprospecting in the Mediterranean Sea: Antioxidant and Lysozyme-Like Activities from Aurelia coerulea (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) Extracts. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Lecci, R.M.; Durante, M.; Meli, F.; Piraino, S. The Bright Side of Gelatinous Blooms: Nutraceutical Value and Antioxidant Properties of Three Mediterranean Jellyfish (Scyphozoa). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4654–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, A.; Lecci, R.M.; Milisenda, G.; Piraino, S. Mediterranean jellyfish as novel food: Effects of thermal processing on antioxidant, phenolic, and protein contents. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1611–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, L.; Enrique-Navarro, A.; Li Volsi, R.; Ortega, M.J. The Large Jellyfish Rhizostoma luteum as Sustainable a Resource for Antioxidant Properties, Nutraceutical Value and Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou-Abdallah, F.; Chasteen, N.D.; Lesser, M.P. Quenching of superoxide radicals by green fluorescent protein. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2006, 1760, 1690–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, J.-F.; Wergifosse, B.; Noiset, O.; Dubuisson, M.-N.; Janssens, B.; Thompson, E. The Origins of Marine Bioluminescence: Turning Oxygen Defence Mechanisms Into Deep-Sea Communication Tools. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccarotto, A.; Sollitto, M.; Leclère, L.; Panzella, L.; Gerdol, M.; Leone, S.; Castellano, I. Molecular evolution of ovothiol biosynthesis in animal life reveals diversity of the natural antioxidant ovothiols in Cnidaria. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 227, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habetha, M.; Bosch, T.C.G. Symbiotic Hydra express a plant-like peroxidase gene during oogenesis. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmeister-Ullerich, S.A.H.; Herrmann, D.; Kielholz, J.; Schweizer, M.; Schaller, H.C. Isolation of a putative peroxidase, a target for factors controlling foot-formation in the coelenterate Hydra. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 4597–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. First report of a peroxiredoxin homologue in jellyfish: Molecular cloning, expression and functional characterization of CcPrx4 from Cyanea capillata. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Qiu, L.; Zou, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase from jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Qing, Y.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Cui, J.; Li, P. Isolation, identification and characterization of a novel antioxidant protein from the nematocyst of the jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widder, E.A. Bioluminescence in the Ocean: Origins of Biological, Chemical, and Ecological Diversity. Science 2010, 328, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, M. Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP): Applications, Structure, and Related Photophysical Behavior. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 759–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridovich, I. Superoxide and the Superoxide Dismutases: An Introduction by Irwin Fridovich. In Redox-Active Therapeutics; Batinić-Haberle, I., Rebouças, J.S., Spasojević, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Greenbaum, L.; Rothmann, C.; Lavie, R.; Malik, Z. Green Fluorescent Protein Photobleaching: A Model for Protein Damage by Endogenous and Exogenous Singlet Oxygen. Biol. Chem. 2000, 381, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangenberg, D.B. Iodine induction of metamorphosis in Aurelia. J. Exp. Zool. 1967, 165, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Tan, J.; Bian, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, S. Metabolomics provide insights into the endogenous mechanism of strobilation in the scyphozoan jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dratman, M.B.; Martin, J.V. The many faces of thyroxine. AIMS Neurosci. 2020, 7, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, S.; Bosch, T.C.G. Foot differentiation and genomic plasticity in Hydra: Lessons from the PPOD gene family. Dev. Genes. Evol. 2006, 216, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qausain, S.; Basheeruddin, M. Unraveling the Peroxidase Activity in Peroxiredoxins: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanisms, Functions, and Biological Significance. Cureus 2024, 16, e66117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, A.; Lecci, R.M.; Durante, M.; Piraino, S. Extract from the Zooxanthellate Jellyfish Cotylorhiza tuberculata Modulates Gap Junction Intercellular Communication in Human Cell Cultures. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1728–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Maeda, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Ogawa, S.; Fukuda, K.; Nagatsuka, N.; Nagao, K.; Ueno, S. Antioxidant activity of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai measured by the oxygen radical absorbance capacity and hydroxyl radical averting capacity methods. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 4, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Geng, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. Jellyfish Peptide as an Alternative Source of Antioxidant. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Domenico, S.; De Rinaldis, G.; Paulmery, M.; Piraino, S.; Leone, A. Barrel Jellyfish (Rhizostoma pulmo) as Source of Antioxidant Peptides. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, C.; Li, P. In vitro determination of antioxidant activity of proteins from jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Li, P. Radical scavenging activity of protein from tentacles of jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, C.; Zhao, J.; Shi, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, J.; Fu, Y.; Jin, W.; Zhu, B. Separation and Characterization of Antioxidative and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptide from Jellyfish Gonad Hydrolysate. Molecules 2018, 23, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, E. Assessment of Antioxidant Capacity in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malej, A.; Kogovšek, T.; Ramšak, A.; Catenacci, L. Blooms and population dynamics of moon jellyfish in the northern Adriatic. CBM-Cah. Biol. Mar. 2012, 53, 337. [Google Scholar]
- Peggy Hsieh, Y.H.; Leong, F.M.; Rudloe, J. Jellyfish as food. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotz, L.; Pauly, D. Studying jellyfish fisheries: Toward accurate national catch reports and appropriate methods for stock assessments. In Jellyfish: Ecology, Distribution Patterns and Human Interactions; Marriotini, G.L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, UK, 2017; pp. 313–329. [Google Scholar]
- Brotz, L. Jellyfish fisheries:A global assessment. In Global Atlas of Marine Fisheries: A Critical Appraisal of Catches and Ecosystem Impacts; Pauly, D., Zeller, D., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 110–124. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.N.; Bristi, N.J.; Rafiquzzaman, M. Review on in vivo and in vitro methods evaluation of antioxidant activity. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rinaldis, G.; Leone, A.; De Domenico, S.; Bosch-Belmar, M.; Slizyte, R.; Milisenda, G.; Santucci, A.; Albano, C.; Piraino, S. Biochemical Characterization of Cassiopea andromeda (Forsskål, 1775), Another Red Sea Jellyfish in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Domenico, S.; De Rinaldis, G.; Mammone, M.; Bosch-Belmar, M.; Piraino, S.; Leone, A. The Zooxanthellate Jellyfish Holobiont Cassiopea andromeda, a Source of Soluble Bioactive Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, C.L.; Ciufo, S.; Domrachev, M.; Hotton, C.L.; Kannan, S.; Khovanskaya, R.; Leipe, D.; McVeigh, R.; O’Neill, K.; Robbertse, B.; et al. NCBI Taxonomy: A comprehensive update on curation, resources and tools. Database 2020, 2020, baaa062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, Z.B.; Pintão, A.M.; Costa, I.M.; Calejo, M.T.; Bandarra, N.M.; Abreu, P. Composition and In Vitro Antioxidant Effects of Jellyfish Catostylus tagi from Sado Estuary (SW Portugal). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2009, 18, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasol, J.M.; Kirchman, D.L. Microbial Ecology of the Oceans; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.J.; Hemmrich, G.; Ball, E.E.; Hayward, D.C.; Khalturin, K.; Funayama, N.; Agata, K.; Bosch, T.C. The innate immune repertoire in cnidaria—Ancestral complexity and stochastic gene loss. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmrich, G.; Miller, D.J.; Bosch, T.C.G. The evolution of immunity: A low-life perspective. Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, T.C.G.; Augustin, R.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Fraune, S.; Hemmrich, G.; Zill, H.; Rosenstiel, P.; Jacobs, G.; Schreiber, S.; Leippe, M.; et al. Uncovering the evolutionary history of innate immunity: The simple metazoan Hydra uses epithelial cells for host defence. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Kellogg, C.A.; Rohwer, F. Coral Microbiology. Oceanography 2007, 20, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Kushmaro, A. Microbial Diseases of Corals: Pathology and Ecology. In Coral Reefs: An Ecosystem in Transition; Dubinsky, Z., Stambler, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 451–464. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, Y.; Ohtsuka, S.; Hirabayashi, T.; Okada, S.; Ogawa, N.O.; Ohkouchi, N.; Shimazu, T.; Nishikawa, J. Seasonal changes in infection with trematode species utilizing jellyfish as hosts: Evidence of transmission to definitive host fish via medusivory. Parasite 2016, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delannoy, C.M.J.; Houghton, J.D.R.; Fleming, N.E.C.; Ferguson, H.W. Mauve Stingers (Pelagia noctiluca) as carriers of the bacterial fish pathogen Tenacibaculum maritimum. Aquaculture 2011, 311, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-j.; Gallo, R.L. Antimicrobial peptides. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R14–R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Grice, I.D. Antimicrobials from Cnidarians. A New Perspective for Anti-Infective Therapy? Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, R.; Bosch, T.C.G. Cnidarian Immunity: A Tale of Two Barriers. In Invertebrate Immunity; Söderhäll, K., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, T.C.G. Cnidarian-microbe interactions and the origin of innate immunity in metazoans. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Korać, P.; Želježić, D.; Sertić Perić, M.; Peharec Štefanić, P.; Sirovina, D.; Novosel, M.; Gottstein, S. Hydra for 21st Century—A Fine Model in Freshwater Research. Water 2024, 16, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, R.; Fraune, S.; Franzenburg, S.; Bosch, T.C.G. Where Simplicity Meets Complexity: Hydra, a Model for Host–Microbe Interactions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 710, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klimovich, A.; Bosch, T.C.G. Novel technologies uncover novel ‘anti’-microbial peptides in Hydra shaping the species-specific microbiome. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2024, 379, 20230058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantin, B.; Leggett, J.; Ebert, S.; Craig, W.A. Correlation between in vitro and in vivo activity of antimicrobial agents against gram-negative bacilli in a murine infection model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1991, 35, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locher, H.H.; Seiler, P.; Chen, X.; Schroeder, S.; Pfaff, P.; Enderlin, M.; Klenk, A.; Fournier, E.; Hubschwerlen, C.; Ritz, D.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Antibacterial Evaluation of Cadazolid, a New Antibiotic for Treatment of Clostridium difficile Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Dingley, A.J.; Augustin, R.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Stanisak, M.; Gelhaus, C.; Gutsmann, T.; Hammer, M.U.; Podschun, R.; Bonvin, A.M.; et al. Hydramacin-1, structure and antibacterial activity of a protein from the basal metazoan Hydra. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, R.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Jungnickel, S.; Hemmrich, G.; Spudy, B.; Podschun, R.; Bosch, T.C.G. Activity of the Novel Peptide Arminin against Multiresistant Human Pathogens Shows the Considerable Potential of Phylogenetically Ancient Organisms as Drug Sources. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5245–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, R.; Fraune, S.; Bosch, T.C.G. How Hydra senses and destroys microbes. Semin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Balandin, S.V.; Aleshina, G.M.; Tagaev, A.A.; Leonova, Y.F.; Krasnodembsky, E.D.; Men’shenin, A.V.; Kokryakov, V.N. Aurelin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from jellyfish Aurelia aurita with structural features of defensins and channel-blocking toxins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 348, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T. Defensins: Antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, R.; Schröder, K.; Murillo Rincón, A.P.; Fraune, S.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Herbst, E.-M.; Wittlieb, J.; Schwentner, M.; Grötzinger, J.; Wassenaar, T.M.; et al. A secreted antibacterial neuropeptide shapes the microbiome of Hydra. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, K.; Bosch, T.C.G. The Origin of Mucosal Immunity: Lessons from the Holobiont Hydra. mBio 2016, 7, e01184-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraune, S.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Augustin, R.; Franzenburg, S.; Knop, M.; Schröder, K.; Willoweit-Ohl, D.; Bosch, T.C.G. Bacteria–bacteria interactions within the microbiota of the ancestral metazoan Hydra contribute to fungal resistance. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, T.C.G. Understanding complex host-microbe interactions in Hydra. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, R.; Siebert, S.; Bosch, T.C.G. Identification of a kazal-type serine protease inhibitor with potent anti-staphylococcal activity as part of Hydra’s innate immune system. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, E.; Múnera, M.; Suescún-Bolívar, L.P. In silico characterization of Cnidarian’s antimicrobial peptides. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1065717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkendorff, K.; Davis, A.R.; Bremner, J.B. Chemical Defense in the Egg Masses of Benthic Invertebrates: An Assessment of Antibacterial Activity in 39 Mollusks and 4 Polychaetes. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2001, 78, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoot, S.C.; Plante, C.J.; Podolsky, R.D. Anti-bacterial activity in egg masses of Melanochlamys diomedea across habitats differing in sediment properties and bacterial load. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 524, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, H.; Muramoto, K.; Ogata, K. Antibacterial activity in the egg mass of a sea hare. Experientia 1984, 40, 947–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraune, S.; Augustin, R.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Wittlieb, J.; Gelhaus, C.; Klimovich, V.B.; Samoilovich, M.P.; Bosch, T.C.G. In an early branching metazoan, bacterial colonization of the embryo is controlled by maternal antimicrobial peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18067–18072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.J.; Littlefield, C.L.; Archer, W.E.; Bode, H.R. Embryogenesis in Hydra. Biol. Bull. 1997, 192, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabili, L.; Rizzo, L.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Angilè, F.; Del Coco, L.; Girelli, C.R.; Lomartire, S.; Piraino, S.; Basso, L. The Jellyfish Rhizostoma pulmo (Cnidaria): Biochemical Composition of Ovaries and Antibacterial Lysozyme-like Activity of the Oocyte Lysate. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Parker, G.; D’Elia, C.F.; Cook, C.B. Interactions Between Corals and Their Symbiotic Algae. In Coral Reefs in the Anthropocene; Birkeland, C., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 99–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ollerton, J.; McCollin, D.; Fautin, D.G.; Allen, G.R. Finding NEMO: Nestedness engendered by mutualistic organization in anemonefish and their hosts. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, L.; Rizzo, L.; Marzano, M.; Intranuovo, M.; Fosso, B.; Pesole, G.; Piraino, S.; Stabili, L. Jellyfish summer outbreaks as bacterial vectors and potential hazards for marine animals and humans health? The case of Rhizostoma pulmo (Scyphozoa, Cnidaria). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinta, T.; Kogovšek, T.; Klun, K.; Malej, A.; Herndl, G.J.; Turk, V. Jellyfish-Associated Microbiome in the Marine Environment: Exploring Its Biotechnological Potential. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, M.C.; Urban-Rich, J.; Moisander, P.H. Bacterial associations with the hydromedusa Nemopsis bachei and scyphomedusa Aurelia aurita from the North Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Biol. Res. 2016, 12, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Becking, L.E.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Freitas, R.M.; Gomes, N.C.M. Jellyfish-associated bacterial communities and bacterioplankton in Indonesian Marine lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppong-Danquah, E.; Miranda, M.; Blümel, M.; Tasdemir, D. Bioactivity Profiling and Untargeted Metabolomics of Microbiota Associated with Mesopelagic Jellyfish Periphylla periphylla. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland-Bräuer, N.; Neulinger, S.C.; Pinnow, N.; Künzel, S.; Baines, J.F.; Schmitz, R.A. Composition of Bacterial Communities Associated with Aurelia aurita Changes with Compartment, Life Stage, and Population. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6038–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Sun, T.; Peng, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z. Bacterial communities associated with hydromedusa Gonionemus vertens in different regions in Chinese coastal waters. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuett, C.; Doepke, H. Endobiotic bacteria and their pathogenic potential in cnidarian tentacles. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2010, 64, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olio, L.R.; Beran, A.; Flander-Putrle, V.; Malej, A.; Ramšak, A. Diversity of Dinoflagellate Symbionts in Scyphozoan Hosts From Shallow Environments: The Mediterranean Sea and Cabo Frio (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 867554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeghri, N.; Pondaven, P.; Stibor, H.; Dawson, M.N. Review of the diversity, traits, and ecology of zooxanthellate jellyfishes. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland-Bräuer, N.; Pinnow, N.; Langfeldt, D.; Roik, A.; Güllert, S.; Chibani, C.M.; Reusch, T.B.H.; Schmitz, R.A. The Native Microbiome is Crucial for Offspring Generation and Fitness of Aurelia aurita. mBio 2020, 11, e02336-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ye, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Sun, T.; Wang, L.; Hao, W.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z. Microbiota regulates life-cycle transition and nematocyte dynamics in jellyfish. iScience 2023, 26, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, N.; Weiland-Bräuer, N.; Joel, S.; Chibani, C.M.; Schmitz, R.A. The Life Cycle of Aurelia aurita Depends on the Presence of a Microbiome in Polyps Prior to Onset of Strobilation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00262-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahat, M.; Dimentman, C. Cultivation of Bacteria-Free Hydra viridis: Missing Budding Factor in Nonsymbiotic Hydra. Science 1982, 216, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, F.; Kim, E.L.; Li, J.L.; Hong, J.; Bae, K.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, J.H. Antibacterial Polyketides from the Jellyfish-Derived Fungus Paecilomyces variotii. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraune, S.; Bosch, T.C.G. Long-term maintenance of species-specific bacterial microbiota in the basal metazoan Hydra. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13146–13151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. Exploring the Antibacterial and Antifungal Potential of Jellyfish-Associated Marine Fungi by Cultivation-Dependent Approaches. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.M.; Degen, D.; Jang, K.H.; Ebright, R.H.; Fenical, W. Salinamide F, new depsipeptide antibiotic and inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase from a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, P.J. Systematic distribution of bioluminescence in living organisms. J. Biolumin. Chemilumin. 1987, 1, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; Haddock, S.H.D. Quantification of bioluminescence from the surface to the deep sea demonstrates its predominance as an ecological trait. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabili, L.; Gravili, C.; Piraino, S.; Boero, F.; Alifano, P. Vibrio harveyi Associated with Aglaophenia octodonta (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabili, L.; Gravili, C.; Tredici, S.M.; Piraino, S.; Talà, A.; Boero, F.; Alifano, P. Epibiotic Vibrio Luminous Bacteria Isolated from Some Hydrozoa and Bryozoa Species. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 56, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabili, L.; Gravili, C.; Tredici, S.M.; Boero, F.; Alifano, P. Association of a luminous Vibrio sp., taxonomically related to Vibrio harveyi, with Clytia linearis (Thornely, 1900) (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 396, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyholm, S.V.; McFall-Ngai, M.J. A lasting symbiosis: How the Hawaiian bobtail squid finds and keeps its bioluminescent bacterial partner. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doepke, H.; Herrmann, K.; Schuett, C. Endobacteria in the tentacles of selected cnidarian species and in the cerata of their nudibranch predators. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2012, 66, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikou, P.; Gokbulut, C.; Kosker, A.R.; Campàs, M.; Ozogul, F. An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos Kramar, M.; Tinta, T.; Lučić, D.; Malej, A.; Turk, V. Bacteria associated with moon jellyfish during bloom and post-bloom periods in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0198056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Gerdts, G.; Holst, S.; Wichels, A. Bacterial communities associated with scyphomedusae at Helgoland Roads. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viver, T.; Orellana, L.H.; Hatt, J.K.; Urdiain, M.; Díaz, S.; Richter, M.; Antón, J.; Avian, M.; Amann, R.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; et al. The low diverse gastric microbiome of the jellyfish Cotylorhiza tuberculata is dominated by four novel taxa. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 3039–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Lara, S.; Urdiain, M.; Mora-Ruiz, M.; Prieto, L.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Prokaryotic microbiota in the digestive cavity of the jellyfish Cotylorhiza tuberculata. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 38, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashyreva, D.; Votýpka, J.; Yabuki, A.; Horák, A.; Lukeš, J. Description of new diplonemids (Diplonemea, Euglenozoa) and their endosymbionts: Charting the morphological diversity of these poorly known heterotrophic flagellates. Protist 2025, 177, 126090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzenburg, S.; Fraune, S.; Altrock, P.M.; Künzel, S.; Baines, J.F.; Traulsen, A.; Bosch, T.C.G. Bacterial colonization of Hydra hatchlings follows a robust temporal pattern. ISME J. 2013, 7, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceh, J.; Gonzalez, J.; Pacheco, A.S.; Riascos, J.M. The elusive life cycle of scyphozoan jellyfish-metagenesis revisited. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mysara, M.; Vandamme, P.; Props, R.; Kerckhof, F.M.; Leys, N.; Boon, N.; Raes, J.; Monsieurs, P. Reconciliation between operational taxonomic units and species boundaries. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.D.; Kling, J.D.; Araya, R.; Ceh, J. Jellyfish Life Stages Shape Associated Microbial Communities, While a Core Microbiome Is Maintained Across All. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trischman, J.A.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Jensen, P.R.; Dwight, R.; Fenical, W.; McKee, T.C.; Ireland, C.M.; Stout, T.J.; Clardy, J. Salinamides A and B: Anti-inflammatory depsipeptides from a marine streptomycete. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimovich, A.; Giacomello, S.; Björklund, Å.; Faure, L.; Kaucka, M.; Giez, C.; Murillo-Rincon, A.P.; Matt, A.-S.; Willoweit-Ohl, D.; Crupi, G.; et al. Prototypical pacemaker neurons interact with the resident microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17854–17863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkarev, Z.O.; Panteleev, P.V.; Balandin, S.V.; Gizatullina, A.K.; Altukhov, D.A.; Finkina, E.I.; Kokryakov, V.N.; Arseniev, A.S.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Recombinant expression and solution structure of antimicrobial peptide aurelin from jellyfish Aurelia aurita. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 429, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
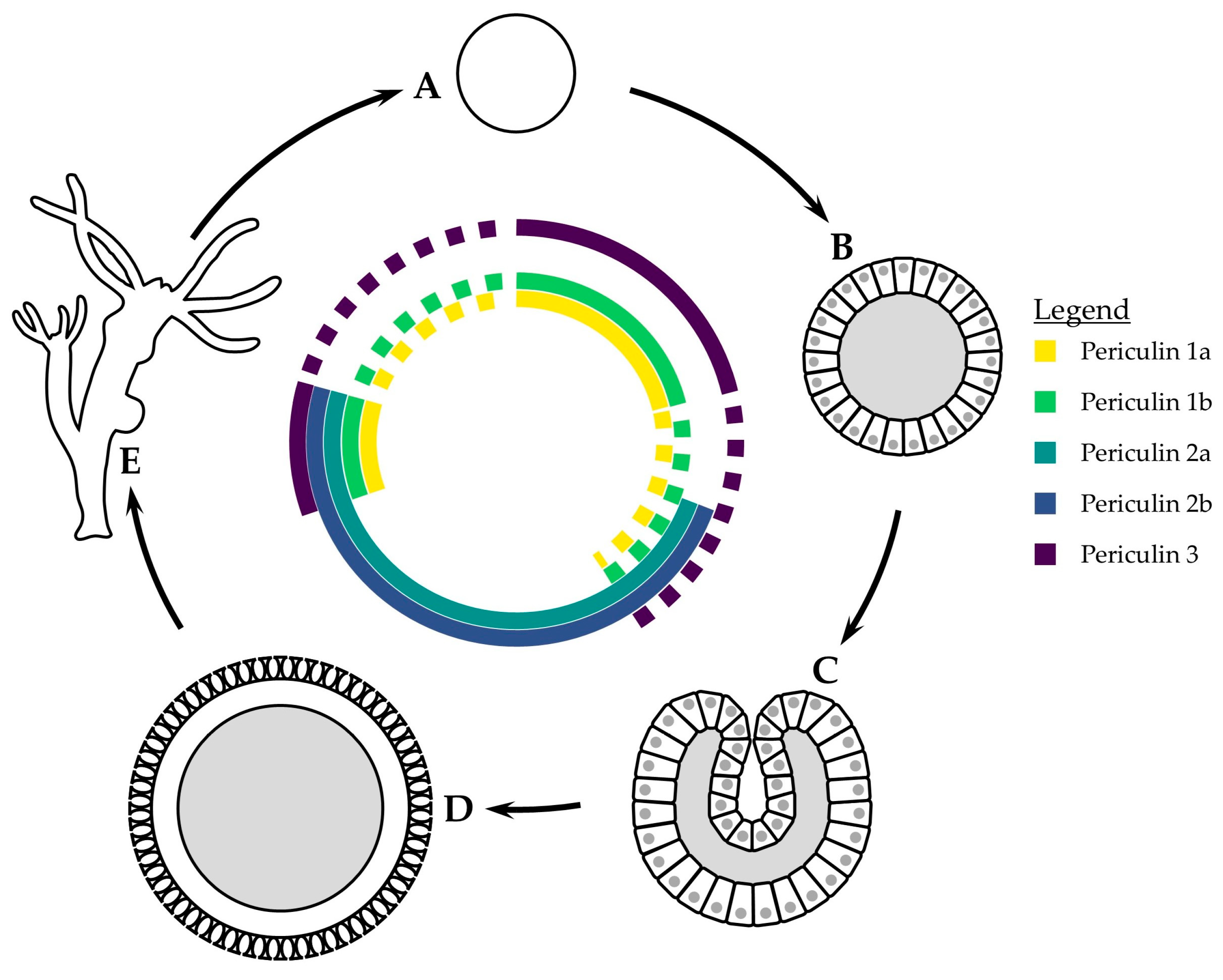
| Defense System | Quenched Radical | Species | Unique to Medusozoa | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFP | O2− | - | No | [63] |
| Coelenterazine | O2− and 1O2− | - | No | [64] |
| Glutathione | Various | - | No | [57] |
| Ovothiol | H2O2 | - | No | [65] |
| Iodide—Tyrosine | H2O2 | Aurelia aurita | Unknown | [53] |
| HvAPX1 | H2O2 | Hydra viridissima | Yes | [66] |
| ppod1 | H2O2 | Hydra vulgaris | Yes | [67] |
| ppod2 | H2O2 | H. vulgaris | Yes | [67] |
| CcPrx4 | H2O2 | Cyanea capillata | Yes | [68] |
| CcSOD1 | O2− | C. capillata | Yes | [69] |
| SmP90 | O2− | Stomolophus meleagris | Yes | [70] |
| Order | Species | Antioxidant Activity | Phenols | Proteins | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semaeostomeae | Aurelia coerulea | Higher | Higher | Higher | [59] |
| Higher | Higher | Higher | [61] | ||
| Rhizostomeae | Cotylorhiza tuberculata | Higher | Higher | Higher | [61] |
| Cassiopea andromeda | No Difference | Higher | Higher | [93] | |
| No Difference | Higher | Higher | [94] | ||
| Catostylus tagi | No Difference | – | Higher | [96] | |
| Rhizostoma pulmo | No Difference | No Difference | No Difference | [61] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lincoln, O.J.; Houghton, J.D.R.; Zakariya, M.; Lauritano, C.; D’Ambra, I. Chemical Defenses in Medusozoa. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060229
Lincoln OJ, Houghton JDR, Zakariya M, Lauritano C, D’Ambra I. Chemical Defenses in Medusozoa. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(6):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060229
Chicago/Turabian StyleLincoln, Oliver J., Jonathan D. R. Houghton, Muhammad Zakariya, Chiara Lauritano, and Isabella D’Ambra. 2025. "Chemical Defenses in Medusozoa" Marine Drugs 23, no. 6: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060229
APA StyleLincoln, O. J., Houghton, J. D. R., Zakariya, M., Lauritano, C., & D’Ambra, I. (2025). Chemical Defenses in Medusozoa. Marine Drugs, 23(6), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060229