Marine-Derived Antioxidants: A Comprehensive Review of Their Therapeutic Potential in Oxidative Stress-Associated Diseases
Abstract
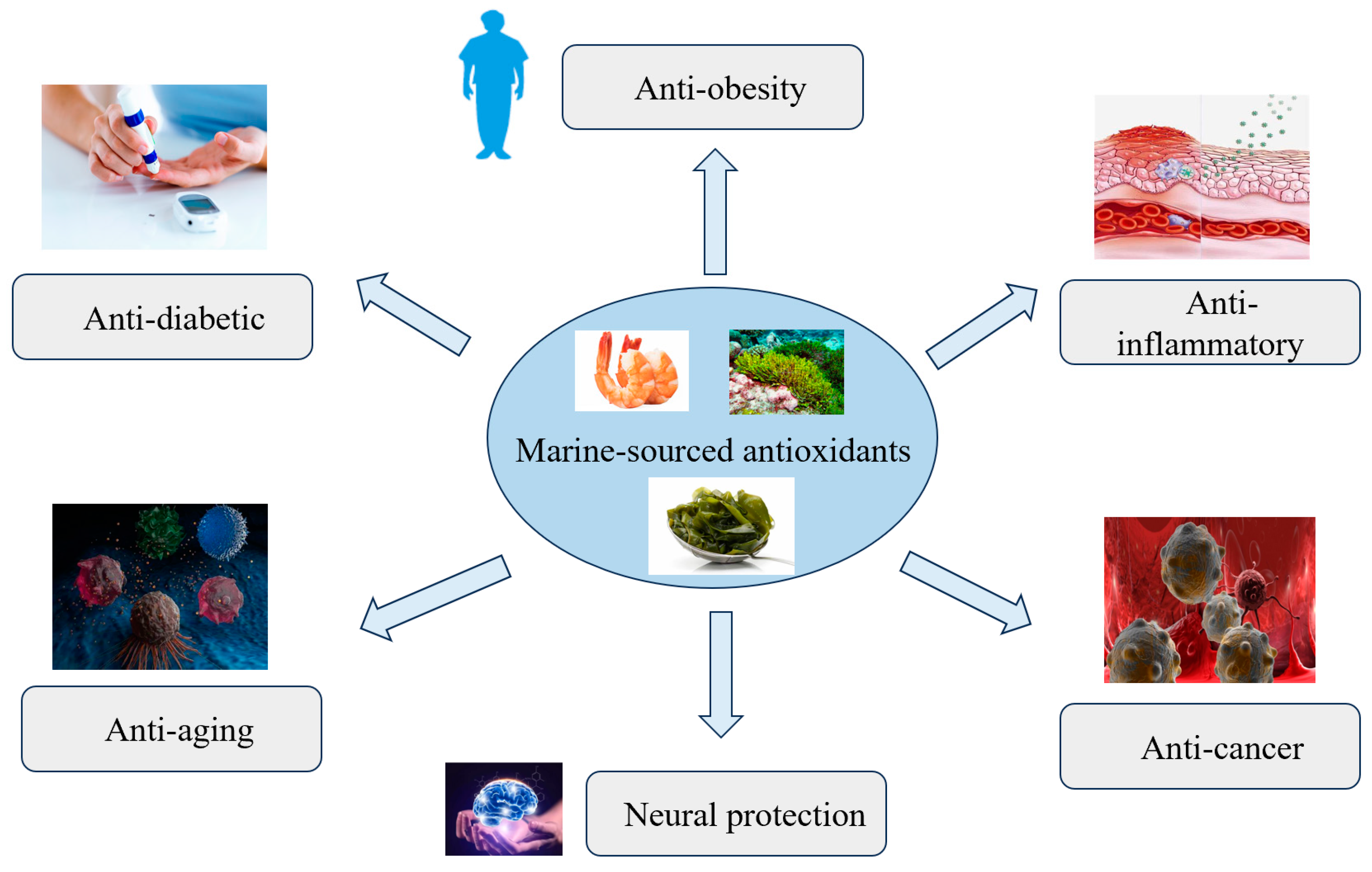
1. Introduction
2. Sources of Marine-Derived Antioxidants
2.1. Polysaccharides from Algae
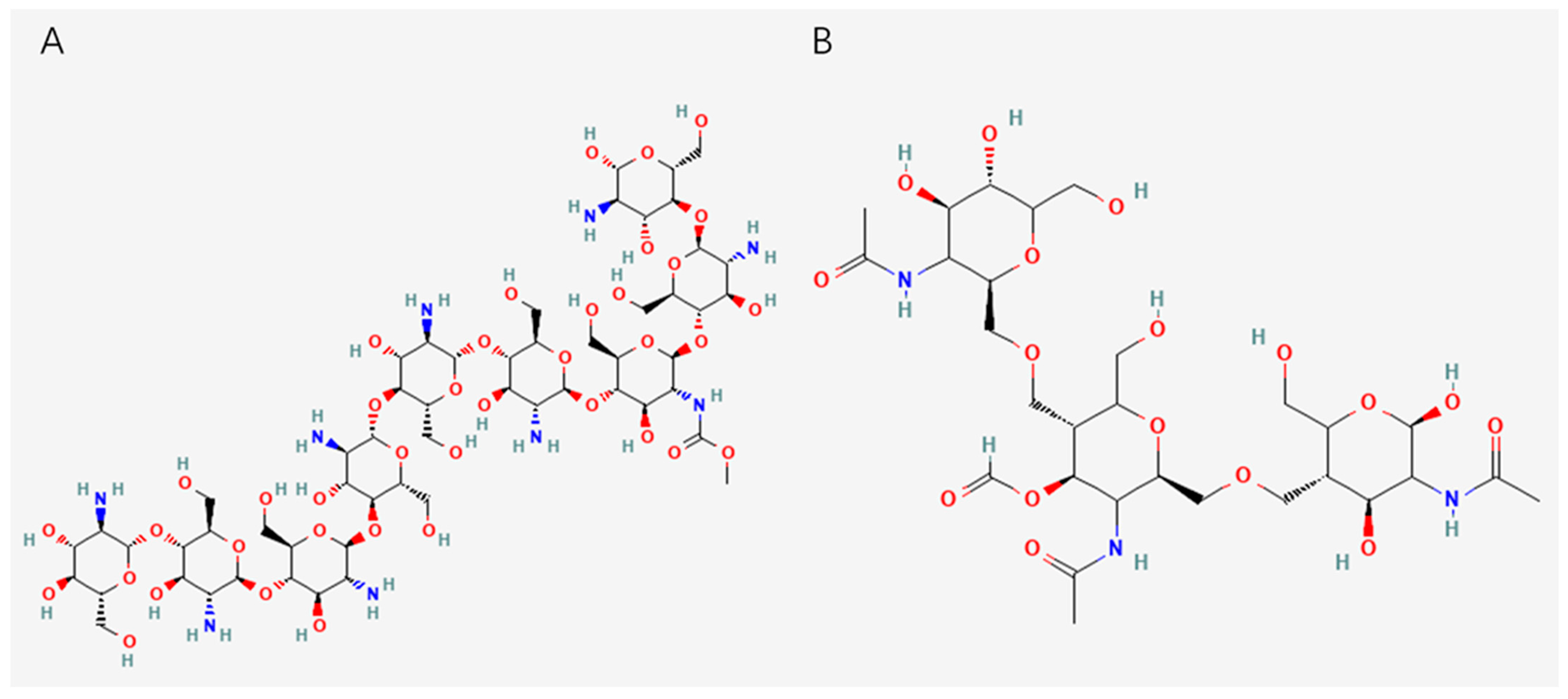
2.2. Polysaccharides from Animals
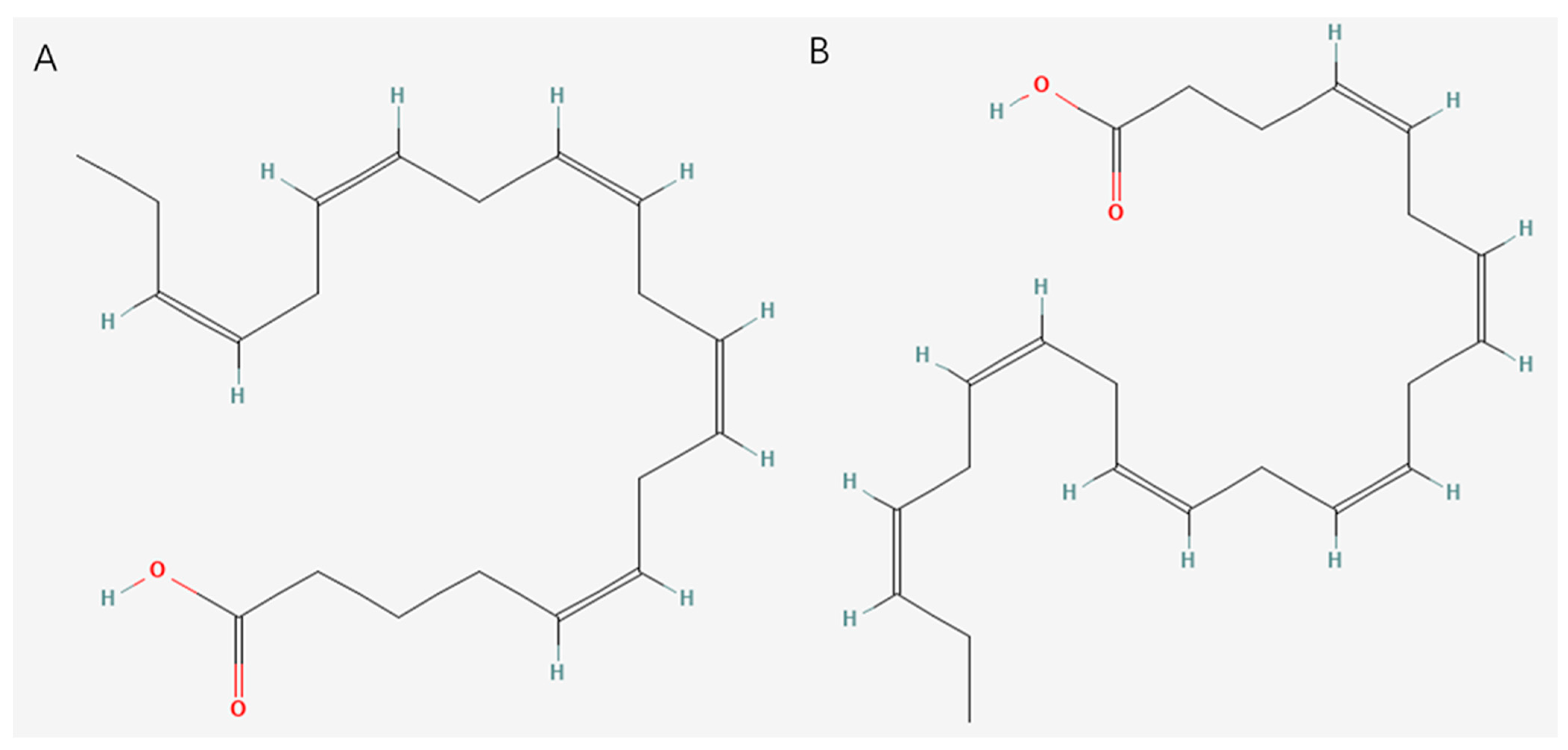
2.3. Unsaturated Fatty Acids
2.4. Superoxide Dismutase of Marine Organisms
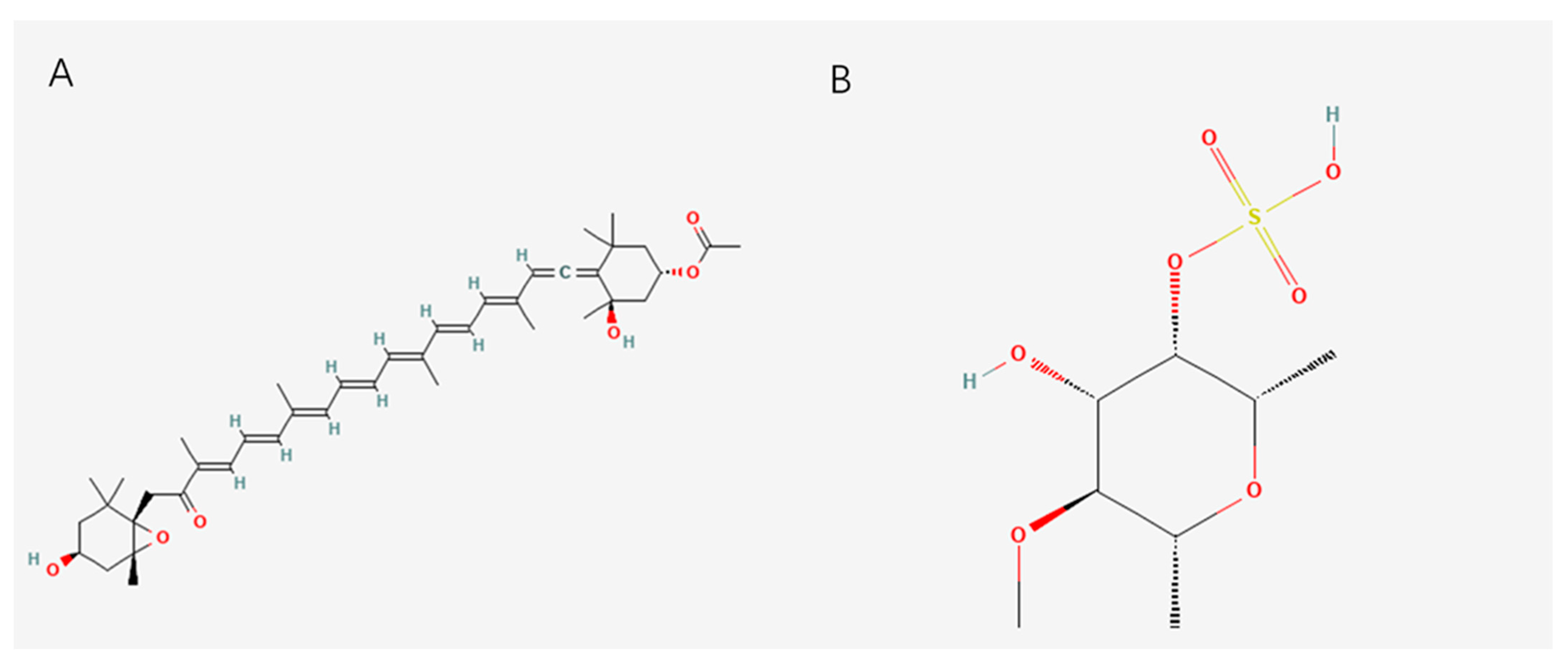
2.5. Vitamins
3. Antioxidant Mechanism and Potential of Disease Treatment
4. Advantages and Challenges
4.1. Advantages
4.2. Challenges
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romano, G.; Costantini, M.; Sansone, C.; Lauritano, C.; Ruocco, N.; Ianora, A. Marine microorganisms as a promising and sustainable source of bioactive molecules. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, A.; Joseph, A.; Nair, B.G. Promising bioactive compounds from the marine environment and their potential effects on various diseases. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odeleye, T.; White, W.L.; Lu, J. Extraction techniques and potential health benefits of bioactive compounds from marine molluscs: A review. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, J.O.; Cotas, J.; Valado, A.; Pereira, L. Algae Food Products as a Healthcare Solution. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Rezaei, M.; McClements, D.J. Bioactive functional ingredients from aquatic origin: A review of recent progress in marine-derived nutraceuticals. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1242–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simat, V.; Elabed, N.; Kulawik, P.; Ceylan, Z.; Jamroz, E.; Yazgan, H.; Cagalj, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ozogul, F. Recent Advances in Marine-Based Nutraceuticals and Their Health Benefits. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zheng, Q.; Gao, W.; Xiao, Y.; Shi, L.; Lin, F.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L.; et al. Synergistic microglial modulation by laminarin-based platinum nanozymes for potential intracerebral hemorrhage therapy. Biomaterials 2025, 319, 123212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Hernandez, G.; Ramos-Silva, J.A.; Perez-Soto, E.; Figueroa, M.; Flores-Berrios, E.P.; Sanchez-Chapul, L.; Andrade-Cabrera, J.L.; Luna-Angulo, A.; Landa-Solis, C.; Aviles-Arnaut, H. Anticancer Activity of Plant Tocotrienols, Fucoxanthin, Fucoidan, and Polyphenols in Dietary Supplements. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadar, E.; Pesterau, A.M.; Prasacu, I.; Ionescu, A.M.; Pascale, C.; Dragan, A.L.; Sirbu, R.; Tomescu, C.L. Marine Antioxidants from Marine Collagen and Collagen Peptides with Nutraceuticals Applications: A Review. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repici, A.; Hasan, A.; Capra, A.P.; Scuderi, S.A.; Paterniti, I.; Campolo, M.; Ardizzone, A.; Esposito, E. Marine Algae and Deriving Biomolecules for the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Potential Clinical Therapeutics to Decrease Gut Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers? Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, W.; Baj, J.; Maciejewski, R. Antioxidants: Classification, Natural Sources, Activity/Capacity Measurements, and Usefulness for the Synthesis of Nanoparticles. Materials 2021, 14, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadinejad, F.; Geir Moller, S.; Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori, M.; Bidkhori, G.; Jami, M.S. Molecular Mechanisms behind Free Radical Scavengers Function against Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tziveleka, L.A.; Tammam, M.A.; Tzakou, O.; Roussis, V.; Ioannou, E. Metabolites with Antioxidant Activity from Marine Macroalgae. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Wei, B.; Wang, S.; Ke, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. The Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides Derived from Marine Organisms: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Xia, Q.; Li, P.; Sun, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, S. Protective Effect of Marine Peptide from Netunea arthritica cumingii Against Gentamicin-Induced Hair Cell Damage in Zebrafish. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Qi, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C. Degradation of chondroitin sulfate: Mechanism of degradation, influence factors, structure-bioactivity relationship and application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 301, 120361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lan, W.; Xie, J. Chemical modifications in the structure of marine polysaccharide as serviceable food processing and preservation assistant: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 223, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Abu Bakar Saddique, M.; Liang, Y.; Guan, G.; Su, H.; Hu, B.; Yang, S.; Luo, X.; Ren, M. Microalgae: A good carrier for biological selenium enrichment. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 416, 131768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Kim, M.J.; Seo, J.; Moon, K.M.; Lee, B. The Beneficial Roles of Seaweed in Atopic Dermatitis. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Kasai, K.; Nozaka, H.; Nakamura, T. Chondroitin sulfate is not digested at all in the mouse small intestine but may suppress interleukin 6 expression induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 642, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.D.; Cheng, J.H.; Sun, D.W. Structure-activity relationships and activity enhancement techniques of marine bioactive peptides (MBPs). Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 15, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhiravel, S.; Dave, D.; Shahidi, F. Bioactives from marine resources as natural health products: A review. Pharmacol. Rev. 2025, 77, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, T.; Lang, S.; Ulber, R.; Muffler, K. Novel procedures for the extraction of fucoidan from brown algae. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Huang, X.; Cheong, K.L. Recent Advances in Marine Algae Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structure, and Activities. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangguan, F.; Ma, N.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, T.; An, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, H. Fucoxanthin suppresses pancreatic cancer progression by inducing bioenergetics metabolism crisis and promoting SLC31A1-mediated sensitivity to DDP. Int. J. Oncol. 2025, 66, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.I.; Imran, H.; Akram, F.; Khalid, T.; Shehzadi, S. Marine Carotenoids: Unlocking Advanced Antioxidant Mechanisms and Therapeutic Applications for Oxidative Stress. Mol. Biotechnol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, D.; Fard, M.V.; Mohammadhasani, K.; Barati, M.; Nattagh-Eshtivani, E. Carotenoids Improve Obesity and Fatty Liver Disease via Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ye, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Fucoxanthin Ameliorates Kidney Injury by CCl(4)-Induced via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress, Suppressing Ferroptosis, and Modulating Gut Microbiota. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 7407–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagowska, K.; Jurgonski, A.; Mori, M.; Yamori, Y.; Murakami, S.; Ito, T.; Toda, T.; Pieczynska-Zajac, J.M.; Bajerska, J. Effects of dietary seaweed on obesity-related metabolic status: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2025, 83, e116–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.D.; Ma, D.Y.; Shi, S.R.; Song, S.L.; Li, W.L.; Qi, X.H.; Guo, S.D. Preparation and bioactivities of low-molecular weight fucoidans and fuco-oligosaccharides: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 356, 123377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrincic, A.; Balbino, S.; Zoric, Z.; Pedisic, S.; Bursac Kovacevic, D.; Elez Garofulic, I.; Dragovic-Uzelac, V. Advanced Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Brown Algal Polysaccharides. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahan, M.S.; Hasan, A.; Rahman, M.H.; Meem, K.N.; Moni, A.; Hannan, M.A.; Uddin, M.J. Protective effects of fucoidan against kidney diseases: Pharmacological insights and future perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Fauziee, N.A.; Chang, L.S.; Wan Mustapha, W.A.; Nor, A.R.M.; Lim, S.J. Functional polysaccharides of fucoidan, laminaran and alginate from Malaysian brown seaweeds (Sargassum polycystum, Turbinaria ornata and Padina boryana). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Usoltseva, R.V.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Surits, V.V.; Imbs, T.I.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Besednova, N.N.; Ivanushko, L.A.; Ermakova, S.P. Structural diversity of fucoidans and their radioprotective effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.Q.; Zhao, S.; Li, S.D.; Song, C. Application of Chitosan, Chitooligosaccharide, and Their Derivatives in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Chavarria, I.; Roa, F.J.; Sandoval, F.; Munoz-Flores, C.; Kappes, T.; Acosta, J.; Bertinat, R.; Altamirano, C.; Valenzuela, A.; Sanchez, O.; et al. Chitosan Microparticles Enhance the Intestinal Release and Immune Response of an Immune Stimulant Peptide in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, K.; Raorane, C.J.; Ramkumar, V.; Ulagesan, S.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Raj, V.; Krishnakumar, G.S.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.C. Update on Chitosan-Based Hydrogels: Preparation, Characterization, and Its Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Applications. Gels 2022, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budai, L.; Budai, M.; Fulopne Papay, Z.E.; Vilimi, Z.; Antal, I. Rheological Considerations of Pharmaceutical Formulations: Focus on Viscoelasticity. Gels 2023, 9, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, E.; Lukova, P.; Baldzhieva, A.; Katsarov, P.; Nikolova, M.; Iliev, I.; Peychev, L.; Trica, B.; Oancea, F.; Delattre, C.; et al. Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fucoidan: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramod Kumar, P.; Harish Prashanth, K.V. Diet with Low Molecular Weight Chitosan exerts neuromodulation in Rotenone induced Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 146, 111860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ojha, B.; Morris, C.; Jiang, M.; Wojcikiewicz, E.P.; Rao, P.P.; Du, D. Positively Charged Chitosan and N-Trimethyl Chitosan Inhibit Abeta40 Fibrillogenesis. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin Shamsabadi, A.; Zhang, Z.; Rumi, S.S.; Chabi, S.; Lucia, L.A.; Abidi, N. High-pressure CO(2) treatment of cellulose, chitin and chitosan: A mini review and perspective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, H.; Lestre, G.M.; Solstad, R.G.; Cabral, A.E.; Botelho, A.; Helbig, C.; Coppola, D.; de Pascale, D.; Robbens, J.; Raes, K.; et al. Current and Expected Trends for the Marine Chitin/Chitosan and Collagen Value Chains. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekarska, K.; Sikora, M.; Owczarek, M.; Jozwik-Pruska, J.; Wisniewska-Wrona, M. Chitin and Chitosan as Polymers of the Future-Obtaining, Modification, Life Cycle Assessment and Main Directions of Application. Polymers 2023, 15, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffrey, C.; Leamy, A.; O’Sullivan, E.; Zabetakis, I.; Lordan, R.; Nasopoulou, C. Cardiovascular Diseases and Marine Oils: A Focus on Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Polar Lipids. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kones, R.; Howell, S.; Rumana, U. n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease: Principles, Practices, Pitfalls, and Promises—A Contemporary Review. Med. Princ. Pract. 2017, 26, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Chugh, V.; Gupta, A.K. Essential fatty acids as functional components of foods—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2289–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Kong, F.; Liu, B.F.; Song, X.; Ren, N.Q.; Ren, H.Y. Ozone oxidation of actual waste leachate coupled with culture of microalgae for efficient lipid production under different temperatures. Water Res. 2025, 277, 123305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocksedge, S.P.; Mantecon, L.; Castano, E.; Infante, C.; Bailey, S.J. The Potential of Superoxide Dismutase-Rich Tetraselmis chuii as a Promoter of Cellular Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, C.A.A.; Grougnet, R.; Nicolau, E.; Picot, L.; de Oliveira Junior, R.G. Carotenoids from Marine Microalgae as Antimelanoma Agents. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Tian, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xue, G.; Cui, J.; Yan, C.; Yuan, J. Prophylactic vitamin C supplementation regulates DNA demethylation to protect against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 695, 149463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Ishimaru, M.; Hatate, H.; Sugiura, Y.; Matsushita, T. Relationship between 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal contents and commercial grade by organoleptic judgement in Japanese dried laver Porphyra spp. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, E.; Oh, S. Effects of water activity on the lipid oxidation and antioxidants of dried laver (porphyra) during storage in the dark. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C1144–C1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoupras, A.; Brummell, C.; Kealy, C.; Vitkaitis, K.; Redfern, S.; Zabetakis, I. Cardio-Protective Properties and Health Benefits of Fish Lipid Bioactives; The Effects of Thermal Processing. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohym, H.H.; Hemeda, M.S.; Elsayed, A.M.; Farrag, M.S.; Elsayed, H.A.; Ezzat, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Makloph, M. Interleukin-10 levels in azithromycin-induced cardiac damage and the protective role of combined selenium and vitamin E treatment. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Liao, M.; Li, Y.; She, F.; Zhang, P. Association between dietary vitamin E intake and incident cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular, and all-cause mortality: A prospective cohort study using NHANES 2003-2018 data. Int. J. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Risk Prev. 2025, 24, 200340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, T.; Yagi, K.; Ishikawa, C.; Atarashi, M.; Watanabe, A.; Kato, Y. Continuous renal replacement therapy with vitamin E-coated polysulfone hemofilter reduces inflammatory responses in a porcine lipopolysaccharide-treated model. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2025, 29, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Zheng, C.; Wu, W.; Yu, G.; Wang, P. Exopolysaccharides from Marine Microbes: Source, Structure and Application. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasukumar, B.; Prabakaran, G.; Gunalan, B.; Moovendhan, M. Chemical composition, structural features, surface morphology and bioactivities of chitosan derivatives from lobster (Thenus unimaculatus) shells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, K.; Bai, F.; Ge, P.; Tan, M. Algal protein: Structural functionality, advanced extraction technologies, and challenges for applications in food nutrition security. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veena, C.K.; Josephine, A.; Preetha, S.P.; Varalakshmi, P.; Sundarapandiyan, R. Renal peroxidative changes mediated by oxalate: The protective role of fucoidan. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liang, S.; Yao, X.R.; Jin, Y.X.; Shen, X.H.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, J.B.; Kim, N.H. Laminarin improves developmental competence of porcine early stage embryos by inhibiting oxidative stress. Theriogenology 2018, 115, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajauria, G.; Ravindran, R.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Rai, D.K.; Sweeney, T.; O’Doherty, J. Molecular characteristics and antioxidant activity of laminarin extracted from the seaweed species Laminaria hyperborea, using hydrothermal-assisted extraction and a multi-step purification procedure. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, M.; Bell, T.; Denes, A.; Falshaw, R.; Itzhaki, R. Anti-HSV1 activity of brown algal polysaccharides and possible relevance to the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anraku, M.; Fujii, T.; Kondo, Y.; Kojima, E.; Hata, T.; Tabuchi, N.; Tsuchiya, D.; Goromaru, T.; Tsutsumi, H.; Kadowaki, D.; et al. Antioxidant properties of high molecular weight dietary chitosan in vitro and in vivo. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelishomi, Z.H.; Goliaei, B.; Mahdavi, H.; Nikoofar, A.; Rahimi, M.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Mamashli, F.; Bigdeli, B. Antioxidant activity of low molecular weight alginate produced by thermal treatment. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Stanger, L.; Freedman, J.C.; Prieur, A.; Thav, R.; Tena, J.; Holman, T.R.; Holinstat, M. Supplementation with omega-3 or omega-6 fatty acids attenuates platelet reactivity in postmenopausal women. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2022, 15, 2378–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adili, R.; Hawley, M.; Holinstat, M. Regulation of platelet function and thrombosis by omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018, 139, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevigato, T.; Masci, M.; Caproni, R. Quality of Fish-Oil-Based Dietary Supplements Available on the Italian Market: A Preliminary Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Malik, R.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, T.P.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singroha, G.; Vij, S.; Kumar, N. Nisin and Class IIa Bacteriocin Resistance Among Listeria and Other Foodborne Pathogens and Spoilage Bacteria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2011, 17, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duda, M.K.; O’Shea, K.M.; Tintinu, A.; Xu, W.; Khairallah, R.J.; Barrows, B.R.; Chess, D.J.; Azimzadeh, A.M.; Harris, W.S.; Sharov, V.G.; et al. Fish oil, but not flaxseed oil, decreases inflammation and prevents pressure overload-induced cardiac dysfunction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 81, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenjancevic, I.; Pitha, J. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids-Vascular and Cardiac Effects on the Cellular and Molecular Level (Narrative Review). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N.; Van Dyke, T.E. Resolving inflammation: Dual anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution lipid mediators. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N. Novel lipid mediators and resolution mechanisms in acute inflammation: To resolve or not? Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1576–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; Redfern, S.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease: Are marine phospholipids the answer? Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2861–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Xiong, Q.; Yin, Y.; Ling, Z.; Chen, S. The Effects of Fish Oil on Cardiovascular Diseases: Systematical Evaluation and Recent Advance. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 802306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuMweis, S.; Jew, S.; Tayyem, R.; Agraib, L. Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid containing supplements modulate risk factors for cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomised placebo-control human clinical trials. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 31, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J.K.; Calder, P.C. The Differential Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikan, M.Z.; Lambuk, L.; Reshidan, N.; Ahmad Hairi, H.; Abd Ghapor, A.A.; Mohamud, R.; Abdul Nasir, N.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Vitamin E in Ocular Neurodegenerative Disorders: An Update on the Emerging Evidence and Therapeutic Implications. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 41, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierczak-Baranska, J.; Boguszewska, K.; Adamus-Grabicka, A.; Karwowski, B.T. Two Faces of Vitamin C-Antioxidative and Pro-Oxidative Agent. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, D.Q.; Ngo, T.C.; Thong, N.M.; Nam, P.C. Is Vitamin A an Antioxidant or a Pro-oxidant? J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 9348–9357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, A.S.; Viitanen, A.K.; Kanerva, T.; Saamanen, A.; Aguerre-Chariol, O.; Fable, S.; Dermigny, A.; Karoski, N.; Fraboulet, I.; Koponen, I.K.; et al. Occupational Exposure and Environmental Release: The Case Study of Pouring TiO(2) and Filler Materials for Paint Production. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, M.G.; Atkinson, J. Vitamin E, antioxidant and nothing more. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitto, E.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J.; Karbownik, M.; Manchester, L.C.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Fulia, F.; Barberi, I. Individual and synergistic antioxidative actions of melatonin: Studies with vitamin E, vitamin C, glutathione and desferrrioxamine (desferoxamine) in rat liver homogenates. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Niki, E.; Shimasaki, H. Free radical-mediated chain oxidation of low density lipoprotein and its synergistic inhibition by vitamin E and vitamin C. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 279, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Rho, N.K.; Park, K.Y. Skin aging from mechanisms to interventions: Focusing on dermal aging. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1195272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y. Biomarkers, oxidative stress and autophagy in skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 59, 101036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaccio, F.; D’Arino, A.; Caputo, S.; Bellei, B. Focus on the Contribution of Oxidative Stress in Skin Aging. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Rimm, E.B. Fish intake, contaminants, and human health: Evaluating the risks and the benefits. JAMA 2006, 296, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Qindeel, M.; Nunes, L.V.; Duarte, M.T.S.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Soriano, R.N.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Marine-Derived Biologically Active Compounds for the Potential Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.S.; Haq, M.; Park, S.W.; Han, J.M.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, S.M.; Park, J.S.; Chun, M.S.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Recent advances in recovering bioactive compounds from macroalgae and microalgae using subcritical water extraction: Prospective compounds and biological activities. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Lee, J.; Kwon, H.K.; Kim, M.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.; Son, H.; Park, C.; Yoo, H.Y. Efficient Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Molecules from Brown Macroalga Sargassum horneri: Optimal Extraction, Antioxidant and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Gao, S.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Han, Z.; Li, Q.; He, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Polymer-Encapsulated Catalase for Targeted Redox Regulation in Acute Liver Injury. Small 2025, e2412349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranov, S.V.; Toichkin, A.M.; Belous, O.S.; Gureeva, E.V.; Barinova, S.S.; Ryabushko, V.I. Heavy metals and arsenic in macrophytes, sediments and seawater from the coastal area of Northern and Central Vietnam. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 213, 117672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Lek, S.; Xiao, J. Species-specific bioaccumulation and health risk assessment of heavy metal in seaweeds in tropic coasts of South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassarma, B.; Mahapatra, S.K.; Nandi, D.K.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Samanta, S. Protective role of butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and hydroxytoluene (BHT) against oxidative stress-induced inflammatory response in carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatorenal toxicity. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Compound Category | Antioxidant Mechanism | Typical Disease Application | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown algae | Polysaccharides | Clear ROS and activate nrf2/are pathway | AD [41], kidney injury [63] | Low molecular weight improves bioavailability |
| Deep-sea fish | ω-3 PUFAs | Inhibit lipid peroxidation and regulate inflammatory mediators | Cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome [60,91] | Improvement of water solubility by nano-emulsion |
| Microorganisms | Enzymes | Catalytically decompose O2− to H2O2 | Oxidative stress-related inflammation and aging [89] | Genetic engineering to improve thermal stability |
| Microalgae | Vitamins | Direct free radical scavenging and vitamin E regeneration | Kidney injury, skin aging [90] | Microencapsulation to prevent oxidative degradation |
| Group | Antioxidants of Marine Origin | Synthetic Antioxidants |
| Source | Marine organisms (such as algae, animals, microorganisms) | Chemical synthesis |
| Main ingredients | Polysaccharides; unsaturated fatty acids; vitamins | Butyl hydroxytoluene; butyl hydroxyanisole |
| Bioavailability | Relatively good, such as small molecular polysaccharides and unsaturated fatty acids, which are easily absorbed | Relatively low; some synthetic antioxidants have limited absorption in vivo |
| Toxicity risk | Relatively low, natural source, good biocompatibility | Relatively high and may be toxic after long-term use |
| Cost | High extraction and purification costs | Relatively low chemical synthesis cost |
| Application area | Food, medicine, health products, cosmetics, and other fields | Food, plastics, rubber, and other fields as antioxidants |
| Clinical research stage | Some of them are in preclinical or early stages, and the research continues to deepen | The research is mature, and they are widely used |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Ren, Y.; Ren, T.; Yu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, X. Marine-Derived Antioxidants: A Comprehensive Review of Their Therapeutic Potential in Oxidative Stress-Associated Diseases. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060223
Zhang R, Ren Y, Ren T, Yu Y, Li B, Zhou X. Marine-Derived Antioxidants: A Comprehensive Review of Their Therapeutic Potential in Oxidative Stress-Associated Diseases. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(6):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060223
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ruiqiu, Yuke Ren, Tianqi Ren, Yue Yu, Bo Li, and Xiaobing Zhou. 2025. "Marine-Derived Antioxidants: A Comprehensive Review of Their Therapeutic Potential in Oxidative Stress-Associated Diseases" Marine Drugs 23, no. 6: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060223
APA StyleZhang, R., Ren, Y., Ren, T., Yu, Y., Li, B., & Zhou, X. (2025). Marine-Derived Antioxidants: A Comprehensive Review of Their Therapeutic Potential in Oxidative Stress-Associated Diseases. Marine Drugs, 23(6), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23060223




