Reeler Domain-Containing Proteins Involved in the Antibacterial Immunity of Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
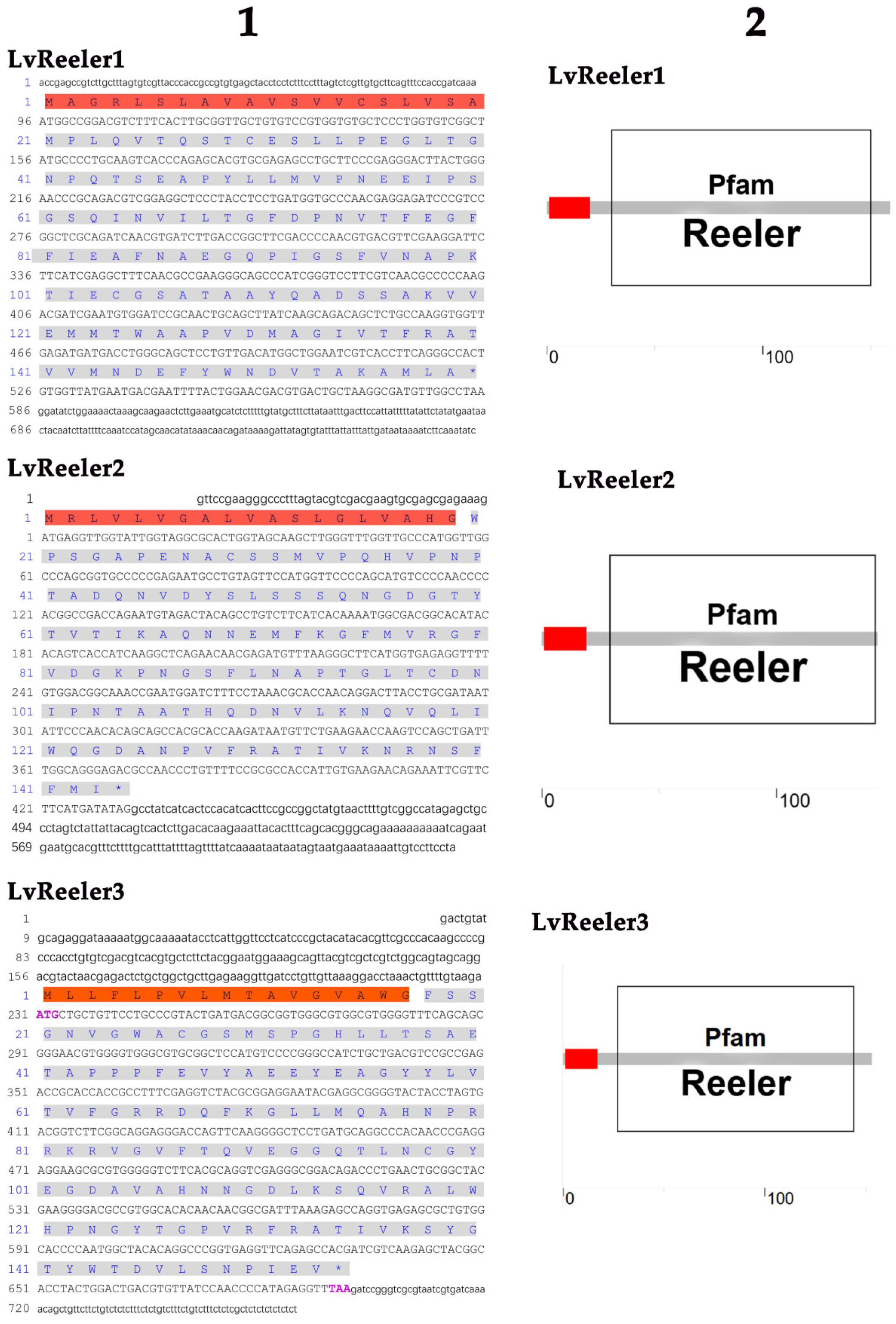
2.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of LvReeler
2.2. Multiple-Sequence Aligment and Phylogenetic Analysis
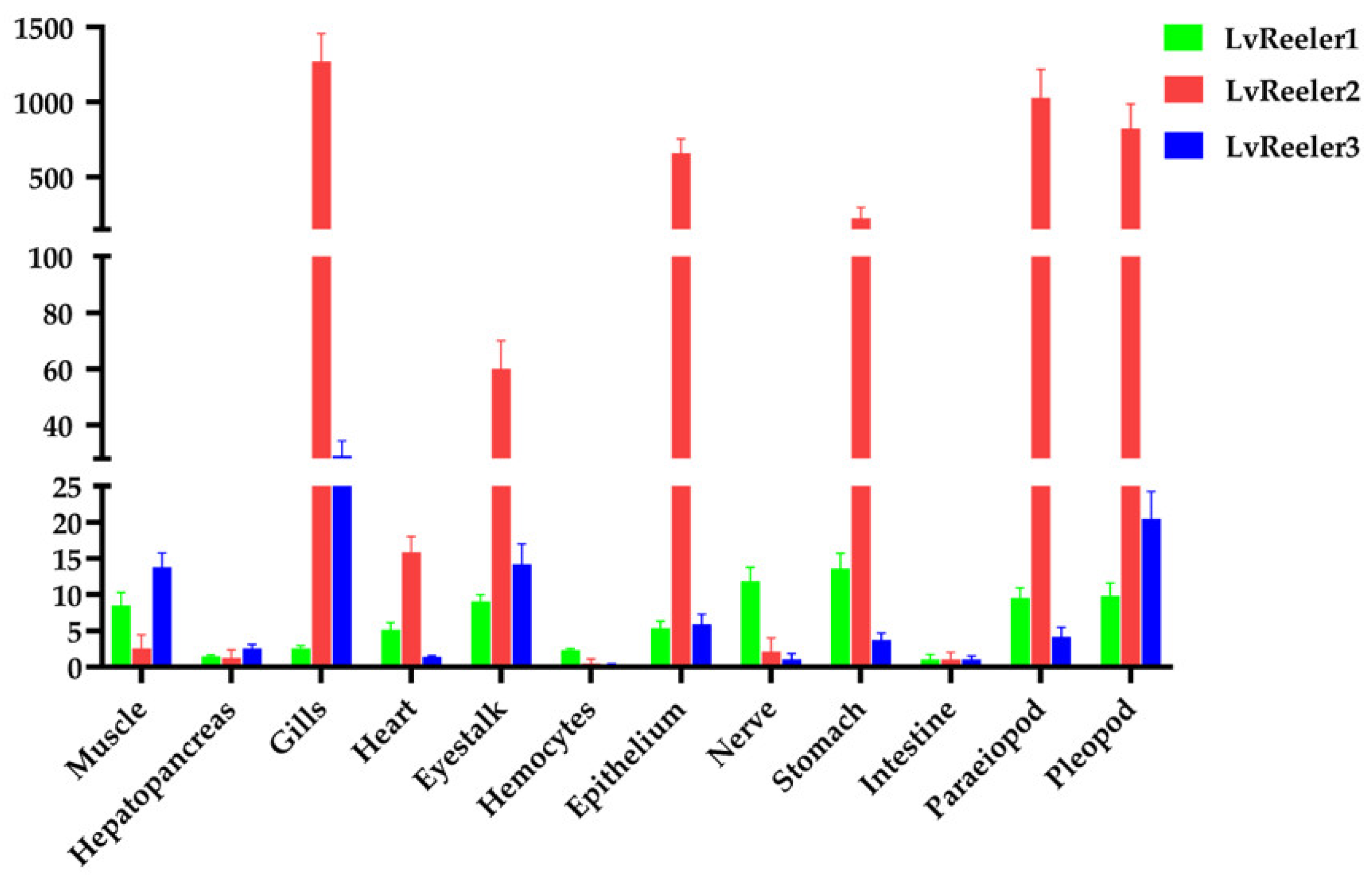
2.3. Tissue Distribution of LvReeler in Healthy L. vannamei
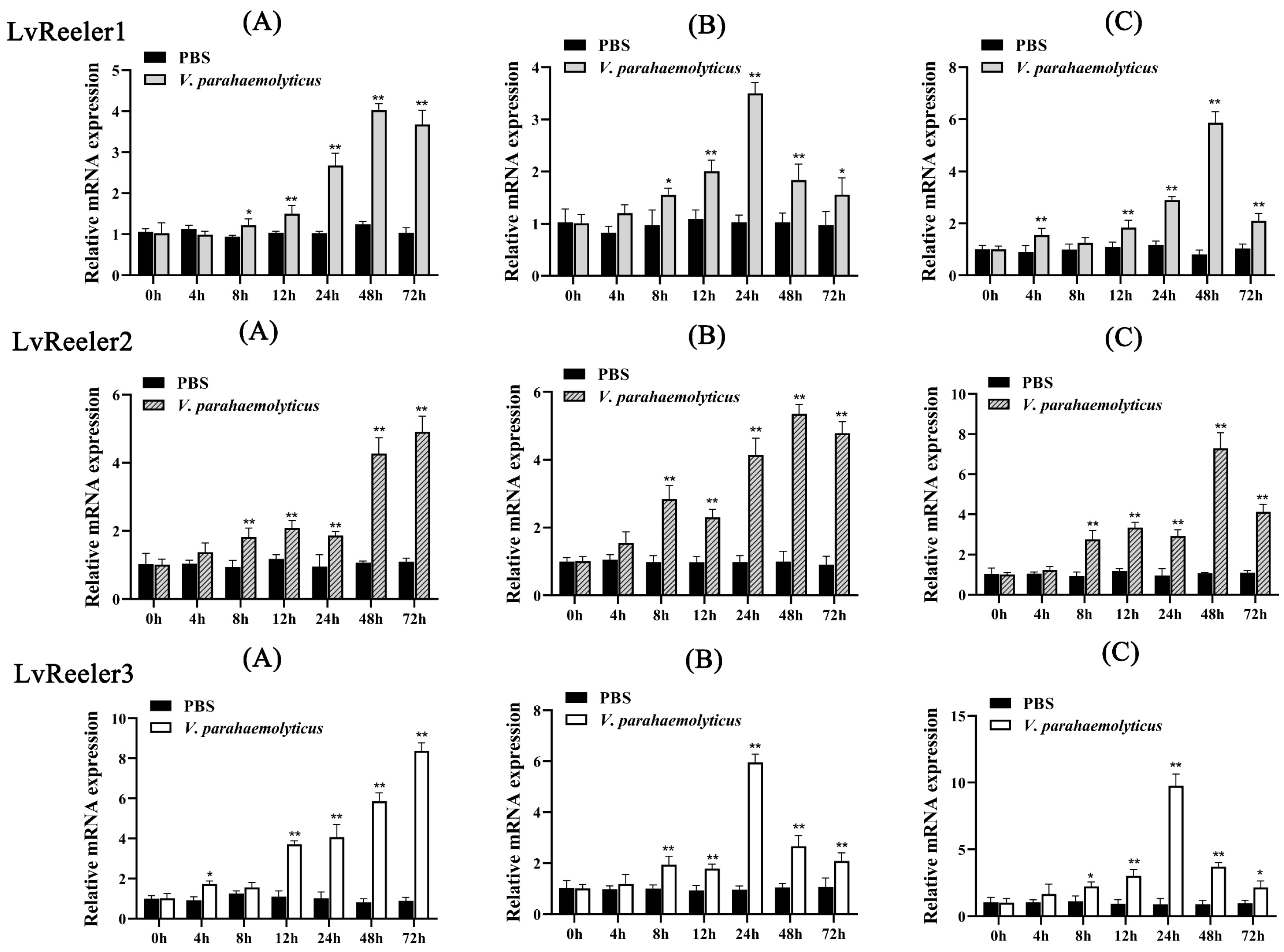
2.4. Expression Profiles of LvReeler in Response to V. parahaemolyticus Infection
2.5. Function of LvReelers in V. parahaemolyticus Infection
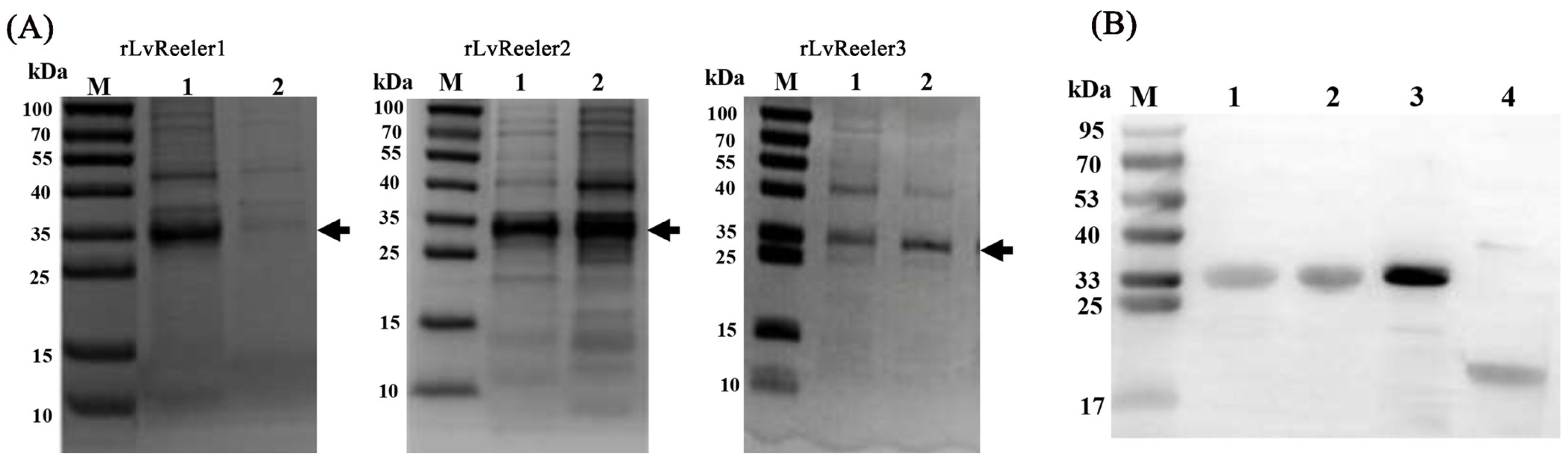
2.6. Recombinant Expression of LvReelers
2.7. Antibacterial Activity of rLvReelers In Vitro
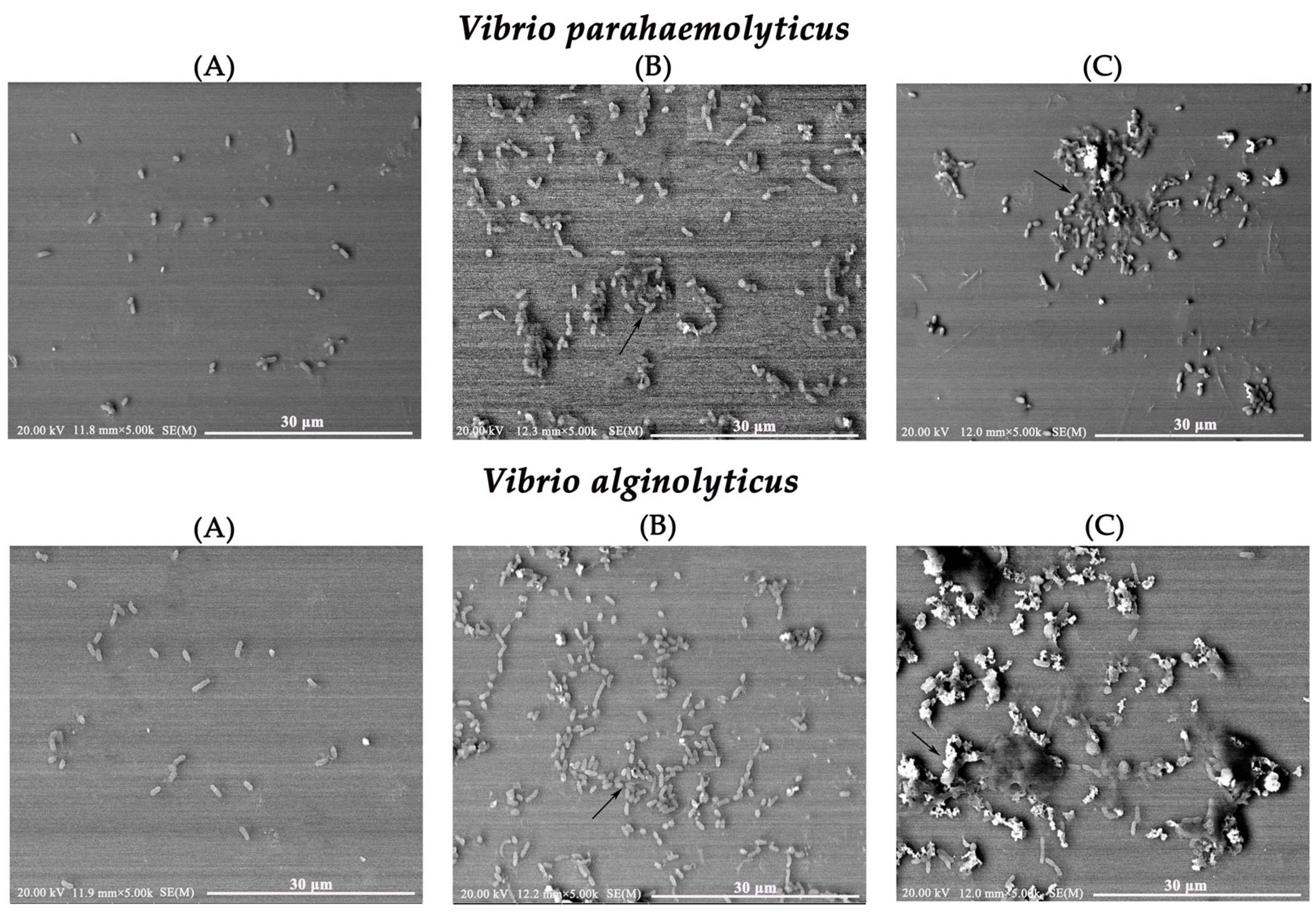
2.8. Morphological Changes in Vibrio Using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Microorganisms
4.2. Cloning of the ORFs of LvReelers
4.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.4. Tissue Distribution and V. parahaemolyticus Challenge Assays
4.5. RNA Interference and Survival Testing
4.6. Recombinant Expression and Purification of LvReelers
4.7. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.8. Antibacterial Assay for rLvReelers
4.9. SEM Observation
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Li, E.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L. Gut Microbiota and its modulation for healthy farming of pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, C.d.S.; Wan, A.H.L. Vibrio and major commercially important vibriosis diseases in decapod crustaceans. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 110, 107527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurhafizah, W.W.I.; Lee, K.L.; Laith, A.A.R.; Nadirah, M.; Danish-Daniel, M.; Zainathan, S.C.; Najiah, M. Virulence properties and pathogenicity of multidrug-resistant Vibrio harveyi associated with luminescent vibriosis in pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 186, 107594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; He, J.G. Effects of environmental stress on shrimp innate immunity and white spot syndrome virus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassanakajon, A.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Supungul, P.; Tang, S. Discovery of immune molecules and their crucial functions in shrimp immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 34, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsari, N.; Maskaew, S.; Obchoei, S.; Kwankaew, P.; Senghoi, W.; Utarabhand, P.; Runsaeng, P. Determination of the efficacy of using a serine protease gene as a DNA vaccine to protect against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in Litopenaeus vannamei. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 135, 104459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.S.; Nguyen, T.; Stanley-Samuelson, D.W. Eicosanoids mediate insect nodulation responses to bacterial infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 91, 12418–12422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcangelo, G.; Miao, G.G.; Chen, S.C.; Soares, H.D.; Morgan, J.I.; Curran, T. A protein related to extracellular matrix proteins deleted in the mouse mutant Reeler. Nature 1995, 374, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, H.H.; Herz, J. Reelin activates SRC family tyrosine kinases in neurons. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchi, C.C.; Wannenes, F.; Persico, A.M.; Ciafré, S.A.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Farace, M.G.; Keller, F. Reelin is a serine protease of the extracellular matrix. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.E.; Finsen, B.; Goffinet, A.M.; Issinger, O.G.; Boldyreff, B. A Reeler mutant mouse with a new, spontaneous mutation in the Reelin gene. Mol. Brain Res. 2002, 105, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissir, F.; Goffinet, A.M. Reelin and brain development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanost, M.R.; Bradfield, J.Y.; Cook, K.E.; Locke, J.; Wells, M.A.; Wyatt, G.R. Gene structure, cDNA sequence, and developmental regulation of a low molecular weight hemolymph protein from Locusta migratoria. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1988, 8, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhe, A.S.; John, S.H.; Nagaraju, J. Noduler, a novel immune up-regulated protein mediates nodulation response in insects. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 6943–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-W.; Park, S.-S.; Park, D.-S.; Kim, M.G.; Kim, S.C.; Brey, P.T.; Park, H.Y. Isolation and characterization of immune-related genes from the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea, using pcr-based differential display and subtractive cloning. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 28, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Johnson, T.J.; Myers, A.A.; Kanost, M.R. Identification by subtractive suppression hybridization of bacteria-induced genes expressed in Manduca sexta fat body. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 33, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, A.B.G.; Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Guimarães, J.A.; Francischetti, I.M.B. A catalog for the transcripts from the venomous structures of the caterpillar Lonomia obliqua: Identification of the proteins potentially involved in the coagulation disorder and hemorrhagic syndrome. Gene 2005, 355, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Y.; Xue, J.; Wu, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.X. An immune-induced Reeler Protein is involved in the Bombyx mori melanization cascade. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Zhou, K.M.; Wang, X.W. Identification and characterization of a Reeler domain containing protein in Procambarus clarkii provides new insights into antibacterial immunity in crustaceans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. Rep. 2023, 4, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Su, Z.; Wei, E.; Li, C.; Weng, S.; Xu, X.; He, J. A microRNA-mediated positive feedback regulatory loop of the NF-κB pathway in Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3842–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftherianos, I.; Heryanto, C.; Bassal, T.; Zhang, W.; Tettamanti, G.; Mohamed, A. Haemocyte-mediated immunity in insects: Cells, processes and associated components in the fight against pathogens and parasites. Immunology 2021, 164, 401–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubovskiy, I.M.; Kryukova, N.A.; Glupov, V.V.; Ratcliffe, N.A. Encapsulation and nodulation in insects. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2016, 13, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.S.; Stanley, D.W. Investigation of an immune response to bacterial infection. In Proceedings of the 21st Workshop/Conference of the Association for Biology Laboratory Education (ABLE), Lincoln, NE, USA, 1–5 June 1999; Karcher, S.J., Ed.; University of Nebraska: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2000; pp. 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Tang, S.; Otuka, H.; Ito, K.; Sato, R. Nodule formation in Bombyx mori larvae is regulated by BmToll10-3. J. Insect Physiol. 2022, 142, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocks, C.; Cho, J.H.; Nehme, N.; Ulvila, J.; Pearson, A.M.; Meister, M.; Strom, C.; Conto, S.L.; Hetru, C.; Stuart, L.M.; et al. Eater, a transmembrane protein mediating phagocytosis of bacterial pathogens in Drosophila. Cell 2005, 123, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokura, A.; Fu, G.S.; Sakamoto, M.; Endo, H.; Tanaka, S.; Kikuta, S.; Tabunoki, H.; Sato, R. Factors functioning in nodule melanization of insects and their mechanisms of accumulation in nodules. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 60, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavine, M.D.; Strand, M.R. Insect hemocytes and their role in immunity. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyavathi, V.V.; Minz, A.; Nagaraju, J. Nodulation: An unexplored cellular defense mechanism in insects. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.; Mang, D.; Fu, G.S.; Tanaka, S.; Endo, H.; Kikuta, S.; Sato, R. Mechanisms of nodule-specific melanization in the hemocoel of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 70, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyavathi, V.V.; Narra, D.; Nagaraju, J. Noduler, an immune protein augments infection-induced cell proliferation through cross-talking with p38 MAPK. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.A.; Subramanian, G.M.; Halpern, A.; Sutton, G.G.; Charlab, R.; Nusskern, D.R.; Wincker, P.; Clark, A.G.; Ribeiro, J.C.; Wides, R. The genome sequence of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Science 2002, 298, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nene, V.; Wortman, J.R.; Lawson, D.; Haas, B.; Kodira, C.; Tu, Z.J.; Loftus, B.; Xi, Z.; Megy, K.; Grabherr, M.; et al. Genome Sequence of Aedes aegypti, a Major Arbovirus Vector. Science 2007, 316, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, G.J.P.; Weihrauch, D. Exploring the versatility of the perfused crustacean gill as a model for transbranchial transport processes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 254, 110572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.C.; Liu, C. Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A concern of seafood safety. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Mega, K.; Yamano, Y.; Morishima, I. cDNA cloning and expression of bacteria-induced Hdd11 gene from eri-silkworm, Samia cynthia ricini. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 136, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.; Li, N.; Shi, X.; Olga, V.; Wang, X.; Diao, X.; Zhou, H.; Tang, X. Physiological and muscle tissue responses in Litopenaeus vannamei under hypoxic stress via iTRAQ. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 979472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.F.; Dai, T.M.; Zhong, S.Q.; Jin, M.; Sun, P.; Zhou, Q.C. Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection impairs intestinal barrier function and nutrient absorption in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Sun, C.; Chan, S.; Shi, L. Functional characterization of a protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) gene in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chan, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, S. Identification and characterization of a laccase from Litopenaeus vannamei Involved in Anti-Bacterial Host Defense. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hou, C.; Xiao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Li, C.; Shi, L. Identification and function of an Arasin-like peptide from Litopenaeus vannamei. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 125, 104174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.B.; Mao, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, L.S.; Su, Y.Q.; Li, Y. The antibacterial activity and mechanism analysis of piscidin 5 like from Larimichthys crocea. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 92, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tang, W.; Zhang, R.; Ding, S. Analysis of enzyme activity, antibacterial activity, antiparasitic activity and physico-chemical stability of skin mucus derived from Amphiprion clarkii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Microorganism (MIC, μM) | rLvReeler1 (MIC) | rLvReeler2 (MIC) | rLvReeler3 (MIC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | 60 | 40 | 30 |
| Vibrio alginolyticus | 50 | 60 | 30 |
| Vibrio harveyi | 60 | 50 | 50 |
| Primers | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| For ORF cloning | |
| LvReeler1-F | GCTTTAGTGTCGTTACCCACCG |
| LvReeler1-R | TTAGGCCAACATCGCCTTAGCA |
| LvReeler2-F | CGACGAAGTGCGAGCGAGAA |
| LvReeler2-R | GGCGGAAGTGATGTGGAGTGAT |
| LvReeler3-F | CTGTTTTGTAAGAATGCTGCTGT |
| LvReeler3-R | TCTTAAACCTCTATGGGGTTGGA |
| For qPCR | |
| qLvReeler1-F | TGCCAAGGTGGTTGAGATGA |
| qLvReeler1-R | CCAACATCGCCTTAGCAGTC |
| qLvReeler2-F | CAGTCACCATCAAGGCTCAGAACAA |
| qLvReeler2-R | CGTGGCTGCTGTGTTGGGAAT |
| qLvReeler3-F | GGCACACAACAACGGCGATTT |
| qLvReeler3-R | GGATAACACGTCAGTCCAGTAGGT |
| qVP16s-F | GGTGTAGCGGTGAAATGCGTAG |
| qVP16s-R | CCACAACCTCCAAGTAGACATCG |
| For dsRNA Synthesis | |
| GFP-T7-F | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGTCAGCGTGTCCGGCGAG |
| GFP-T7-R | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGTCTTCTGCTTGTCGGC |
| GFP-F | TCAGCGTGTCCGGCGAG |
| GFP-R | TCTTCTGCTTGTCGGCC |
| LvReeler1-T7-F | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTCTTTCACTTGCGGTTGCTG |
| LvReeler1-T7-R | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAAGGTGACGATTCCAGCCA |
| LvReeler1-F | GTCTTTCACTTGCGGTTGCTG |
| LvReeler1-R | GAAGGTGACGATTCCAGCCA |
| LvReeler2-T7-F | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGTGAGGTTGGTATTGGTAGGCG |
| LvReeler2-T7-R | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGAAAACAGGGTTGGCGTCT |
| LvReeler2-F | TGAGGTTGGTATTGGTAGGCG |
| LvReeler2-R | GGAAAACAGGGTTGGCGTCT |
| LvReeler3-T7-F | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGTGGGGTTTCAGCAGCGG |
| LvReeler3-T7-R | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTCAGTCCAGTAGGTGCCGTAG |
| LvReeler3-F | TGGGGTTTCAGCAGCGG |
| LvReeler3-R | GTCAGTCCAGTAGGTGCCGTAG |
| For Protein Expression | |
| pLvReeler1-KpnI-F | ggGGTACCATGCCCCTGCAAGTCACCCA |
| pLvReeler1-EcoRI-R | ggGAATTCTTAGGCCAACATCGCCTTAG |
| pLvReeler2-KpnI-F | ggGGTACCTGGCCCAGCGGTGCCCCC |
| pLvReeler2-EcoRI-R | ggGAATTCCCTATATCATGAAGAACGAA |
| pLvReeler3-KpnI-F | ggGGTACCTTCAGCAGCGGGAACGTGG |
| pLvReeler3-EcoRI-R | ggGAATTCTTAAACCTCTATGGGGTTGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, J.; Dai, G.; Xing, H.; Fu, Z.; Ke, S.; Shi, L. Reeler Domain-Containing Proteins Involved in the Antibacterial Immunity of Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050215
Qi J, Dai G, Xing H, Fu Z, Ke S, Shi L. Reeler Domain-Containing Proteins Involved in the Antibacterial Immunity of Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(5):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050215
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Jianying, Guoqing Dai, Huiling Xing, Zhibin Fu, Sheng Ke, and Lili Shi. 2025. "Reeler Domain-Containing Proteins Involved in the Antibacterial Immunity of Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei" Marine Drugs 23, no. 5: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050215
APA StyleQi, J., Dai, G., Xing, H., Fu, Z., Ke, S., & Shi, L. (2025). Reeler Domain-Containing Proteins Involved in the Antibacterial Immunity of Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Marine Drugs, 23(5), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050215






