Identification, Expression Profiling, Microbial Binding, and Agglutination Analyses of Two Cathepsin B Genes in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of S. schlegelii CTSB
2.2. Characteristics of S. schlegelii CTSB Genes
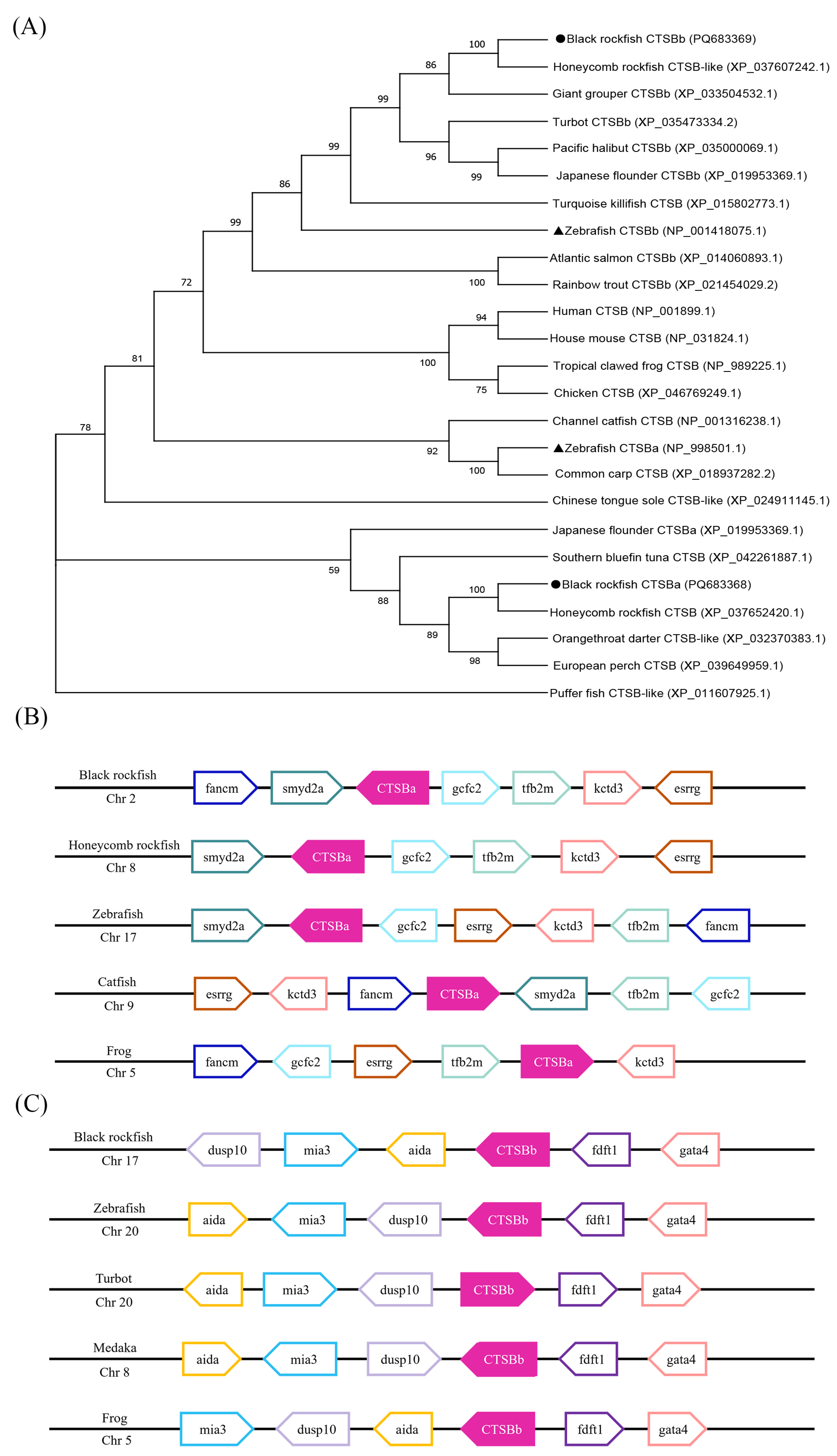
2.3. Phylogeny and Synteny Analyses
2.4. Basal Tissue Distribution
2.5. Expression Profiles of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb Following A. salmonicida
2.6. Binding Abilities of rSsCTSBa and rSsCTSBb to Microbial Ligands and Bacteria
2.7. Agglutination Assay with Bacteria
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Identification
4.2. Sequence Analyses
4.3. Subcellular Localization
4.4. Phylogeny and Synteny Analyses
4.5. Sample Collection of Healthy Black Rockfish
4.6. Bacterial Challenge and Sample Collection
4.7. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR Analyses
4.8. Purification of Recombinant SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb Protein (rSsCTSBa and rSsCTSBb)
4.9. Binding Abilities of rSsCTSBa and rSsCTSBb with Microbial Ligands and Bacteria
4.10. Agglutination of FITC-Labeled rSsCTSBa and rSsCTSBb with Bacteria
4.11. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cygler, M.; Sivaraman, J.; Grochulski, P.; Coulombe, R.; Storer, A.C.; Mort, J.S. Structure of rat procathepsin B: Model for inhibition of cysteine protease activity by the proregion. Structure 1996, 4, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chwieralski, C.E.; Welte, T.; Bühling, F. Cathepsin-regulated apoptosis. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2006, 11, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conus, S.; Simon, H.U. Cathepsins and their involvement in immune responses. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2010, 140, w13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. Families of serine peptidases. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 244, 19–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrer, K.M.; Peiffer, S.L.; E DiTomas, M. Two distinct gene subfamilies within the family of cysteine protease genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3063–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Deveraux, Q.; Turk, B.; Sali, A. Comprehensive search for cysteine cathepsins in the human genome. Biol. Chem. 2004, 385, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takio, K.; Towatari, T.; Katunuma, N.; Teller, D.C.; Titani, K. Homology of amino acid sequences of rat liver cathepsins B and H with that of papain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; Hu, G.; Li, T.; Chen, X.; Ao, J. Identification of cathepsin B from large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) and its role in the processing of MHC class II-associated invariant chain. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 45, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, L.C.; Rudensky, A.Y. The lysosomal cysteine proteases in MHC class II antigen presentation. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 207, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Wang, L.; Han, L.; Qian, L.; Tian, K.; Yuan, H.; Lou, H. Targeting the lysosome by an aminomethylated Riccardin D triggers DNA damage through cathepsin B-mediated degradation of BRCA1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 23, 1798–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Katar, M.; Linebaugh, B.; Sloane, B.; Berk, R. Expression of cathepsins B, D and L in mouse corneas infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 6408–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peri, P.; Nuutila, K.; Vuorinen, T.; Saukko, P.; Hukkanen, V. Cathepsins are involved in virus-induced cell death in ICP4 and Us3 deletion mutant herpes simplex virus type 1-infected monocytic cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, V.; Funkelstein, L.; Wegrzyn, J.; Bark, S.; Kindy, M.; Hook, G. Cysteine Cathepsins in the secretory vesicle produce active peptides: Cathepsin L generates peptide neurotransmitters and cathepsin B produces beta-amyloid of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Cai, J.; Yan, Y.; Guo, C.; Qin, Q. Characterization of cathepsin B gene from orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides involved in SGIV infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, I.S.; Kwon, J.; Mun, J.Y.; Park, S.B.; Jang, H.B.; Nho, S.W.; del Castillo, C.S.; Hikima, J.; Aoki, T.; Jung, T.S. Cathepsins in the kidney of olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, and their responses to bacterial infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, L. Cathepsin B of Cynoglossus semilaevis: Identification, expression, and activity analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 161, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.; Wang, R.; Xu, T. Comparative genomic of the teleost cathepsin B and H and involvement in bacterial induced immunity of miiuy croaker. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Song, L.; Tan, F.; Su, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.; Peatman, E. Identification and mucosal expression analysis of cathepsin B in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) following bacterial challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Bak, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.A.; Kim, N.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Sung, J.H.; Jeon, S.J.; Chung, J.K.; Lee, H.H. Olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) cystatin B: Cloning, tissue distribution, expression and inhibitory profile of piscine cystatin B. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 165, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.T.; Zhang, Y.B.; Chen, Y.D.; Zhu, R.; Dong, C.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Gui, J.F. Expressional induction of Paralichthys olivaceus cathepsin B gene in response to virus, poly I:C and lipopolysaccharide. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Cao, Z.; Qin, Q.; Liu, C.; Guo, W. Functional characterization of cathepsin B and its role in the antimicrobial immune responses in golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 123, 104128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, C.S.; Jung, S.J.; Oh, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Atypical Aeromonas salmonicida infection in the black rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli Hilgendorf, in Korea. J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, J.H.; Findlay, W.A.; Luebbert, C.C.; Mykytczuk, O.L.; Foote, S.J.; Taboada, E.N.; Carrillo, C.D.; Boyd, J.M.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Reith, M.E.; et al. Comparative genomics profiling of clinical isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida using DNA microarrays. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gustafson, C.E.; Thomas, C.J.; Trust, T.J. Detection of Aeromonas salmonicida from fish by using polymerase chain reaction amplification of the virulence surface array protein gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3816–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, D.; Tao, X.; Cao, M.; Li, C.; Fu, Q. Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary Analysis, and Expression Patterns of Cathepsin Superfamily in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) following Aeromonas salmonicida Infection. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janina, S.; Erik, G.; Reik, L.; Jürgen, B.; Ulrike, B.; Michael, G. Cathepsin B: Active site mapping with peptidic substrates and inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 27, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaket, T.P.; Kwon, T.K.; Kang, S.C. Cathepsins: Potent regulators in carcinogenesis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 198, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halangk, W.; Lerch, M.M.; Brandt-Nedelev, B.; Roth, W.; Ruthenbuerger, M.; Reinheckel, T.; Domschke, W.; Lippert, H.; Peters, C.; Deussing, J. Role of cathepsin B in intracellular trypsinogen activation and the onset of acute pancreatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose Cazzulo, J.; Stoka, V.; Turk, V. The major cysteine proteinase of Trypanosoma cruzi: A valid target for chemotherapy of Chagas disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2001, 7, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotte, P.; Van Criekinge, W.; Van de Craen, M.; Van Loo, G.; Desmedt, M.; Grooten, J.; Cornelissen, M.; De Ridder, L.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Fiers, W.; et al. Cathepsin B-mediated activation of the proinflammatory caspase-11. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancompernolle, K.; Van Herreweghe, F.; Pynaert, G.; Van de Craen, M.; De Vos, K.; Totty, N.; Sterling, A.; Fiers, W.; Vandenabeele, P.; Grooten, J. Atractyloside-induced release of cathepsin B, a protease with caspase-processing activity. FEBS Lett. 1998, 438, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canu, N.; Tufi, R.; Serafino, A.L.; Amadoro, G.; Ciotti, M.T.; Calissano, P. Role of the autophagic-lysosomal system on low potassium-induced apoptosis in cultured cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurochem. 2005, 92, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eykelbosh, A.J.; Van Der Kraak, G. A role for the lysosomal protease cathepsin B in zebrafish follicular apoptosis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 156, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lv, M.; Lv, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Duan, X.; Jin, C. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of cathepsin B from the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lv, M.; Lv, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Duan, X.; Jin, C.; Xiong, J.; Xu, F.; et al. Divergent roles of three cytochrome c in CTSB-modulating coelomocyte apoptosis in Apostichopus japonicus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 76, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, A.R.; Seo, J.S.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.K.; Chung, J.K.; Lee, H.H. Cloning, expression analysis and enzymatic characterization of cathepsin S from olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 157, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.G.; Chi, H. Cathepsin S of Sciaenops ocellatus: Identification, transcriptional expression and enzymatic activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; He, S.W.; Du, X.; Xie, B.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.H. Characterization, expression, enzymatic activity, and functional identification of cathepsin S from black rockfish Sebastes schlegelii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.-H.; Sun, B.-G. Expression characterization and activity analysis of a cathepsin B from Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, D.F.; Gnad, F.; Schropp, K.; Wiśniewski, J.R.; Mann, M. Mapping N-glycosylation sites across seven evolutionarily distant species reveals a divergent substrate proteome despite a common core machinery. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.R.; He, H.S.; Zhang, C.W.; Xu, X.M.; Zeng, Z.P.; Yuan, J.P.; Hong, Y.H.; Wang, J.H. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of cathepsin B from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellergaard, M.; Skovbakke, S.L.; Schneider, C.L.; Lauridsen, F.; Andresen, L.; Jensen, H.; Skov, S. N-glycosylation of asparagine 8 regulates surface expression of major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related protein A (MICA) alleles dependent on threonine 24. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20078–20091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Zeng, Q.; Zhou, T.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; et al. The chemokinome superfamily: II. The 64 CC chemokines in channel catfish and their involvement in disease and hypoxia responses. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 73, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Adelson, D.; Yilmaz, A.; Sze, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, J.J. Genomic organization, annotation, and ligand-receptor inferences of chicken chemokines and chemokine receptor genes based on comparative genomics. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, U.; Frantz, S. Role of T-cells in myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, P.A.; Furuta, K. The ins and outs of MHC class II-mediated antigen processing and presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unanue, E.R.; Turk, V.; Neefjes, J. Variations in MHC Class II Antigen Processing and Presentation in Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 34, 265–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, B. The multifaceted roles of the invariant chain CD74–More than just a chaperone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Homaei, A.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Akhtar, N. Cathepsins: Proteases that are vital for survival but can also be fatal. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolter, T.; Sandhoff, K. Principles of lysosomal membrane digestion: Stimulation of sphingolipid degradation by sphingolipid activator proteins and anionic lysosomal lipids. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatti, M.; Motta, M.; Di Bartolomeo, S.; Scarpa, S.; Cianfanelli, V.; Cecconi, F.; Salvioli, R. Reduced cathepsins B and D cause impaired autophagic degradation that can be almost completely restored by overexpression of these two proteases in Sap C-deficient fibroblasts. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 5159–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaya-Candela, A.P.; Ravagnani, F.G.; Dietrich, N.; Sousa, R.; Baptista, M.S. Specific photodamage on HT-29 cancer cells leads to endolysosomal failure and autophagy blockage by cathepsin depletion. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2024, 255, 112919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Nagai, A.; Sheikh, A.M.; Onoda, K.; Terashima, M.; Shiota, Y.; Araki, A.; Yamaguchi, S. Co-localization of cystatin C and prosaposin in cultured neurons and in anterior horn neurons with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 384, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröker, L.E.; Huisman, C.; Span, S.W.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Kruyt, F.A.; Giaccone, G. Cathepsin B mediates caspase-independent cell death induced by microtubule stabilizing agents in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, S.; Luo, J.-L. The multifaceted roles of cathepsins in immune and inflammatory responses: Implications for cancer therapy, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases. Biomark. Res. 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.J.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.W.; Xu, D.D.; Mo, Z.Q.; Li, J.Z.; Dan, X.M.; Luo, X.C. Role of major histocompatibility complex II antigen-presentation pathway genes in orange-spotted grouper infected with Cryptocaryon irritans. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, A.; Rojo, L.; Araujo-Bernal, S.; Garcia-Carreño, F.; Muhlia-Almazan, A. Cathepsin B from the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei: cDNA sequence analysis, tissues-specific expression and biological activity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 161, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Hu, X.; Hu, B.; Wen, C.; Li, Z. Identification and expression of cathepsin B from the freshwater mussel Cristaria plicata. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 225, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonović, M.; Turk, B. Cysteine cathepsins and extracellular matrix degradation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 2560–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevali, O.; Carletta, R.; Cambi, A.; Vita, A.; Bromage, N. Yolk formation and degradation during oocyte maturation in seabream Sparus aurata: Involvement of two lysosomal proteinases. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raldúa, D.; Fabra, M.; Bozzo, M.G.; Weber, E.; Cerdà, J. Cathepsin B-mediated yolk protein degradation during killifish oocyte maturation is blocked by an H+-ATPase inhibitor: Effects on the hydration mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, R456–R466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cattaneo, A.; Gobert, F.X.; Müller, M.; Toscano, F.; Flores, M.; Lescure, A.; Del Nery, E.; Benaroch, P. Cleavage of Toll-like receptor 3 by cathepsins B and H is essential for signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9053–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Yang, B.; Yu, W.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Q. Cathepsin B links oxidative stress to the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 362, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossowska-Nowicka, M.; Mielcarska, M.B.; Romaniewicz, M.; Kaczmarek, M.M.; Gregorczyk-Zboroch, K.P.; Struzik, J.; Grodzik, M.; Gieryńska, M.M.; Toka, F.N.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L. Ectromelia virus suppresses expression of cathepsins and cystatins in conventional dendritic cells to efficiently execute the replication process. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, E.P.; Riteau, N.; Moayeri, M.; Maier, N.; Mayer-Barber, K.D.; Pereira, R.M.; Lage, S.L.; Kubler, A.; Bishai, W.R.; D’Império-Lima, M.R.; et al. Lysosomal Cathepsin Release Is Required for NLRP3-Inflammasome Activation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Infected Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.W.; Du, X.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, J.J.; Xie, B.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhang, M.; Gu, H.J. Identification and characterization of a cathepsin K homologue that interacts with pathogen bacteria in black rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pišlar, A.; Nedeljković, B.B.; Perić, M.; Jakoš, T.; Zidar, N.; Kos, J. Cysteine Peptidase Cathepsin X as a Therapeutic Target for Simultaneous TLR3/4-mediated Microglia Activation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 2258–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisui, C.; Tsujinaka, T.; Morimoto, T.; Kan, K.; Iijima, S.; Yano, M.; Kominami, E.; Tanaka, K.; Monden, M. Interleukin-6 induces proteolysis by activating intracellular proteases (cathepsins B and L, proteasome) in C2C12 myotubes. Clin. Sci. (1979) 1995, 89, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Gao, C.; Song, H.; Yang, N.; Fu, Q.; Tan, F.; Li, C. Characterization, expression profiling and functional characterization of cathepsin Z (CTSZ) in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, N.; Fu, Q.; Su, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Yan, X.; Thongda, W.; Li, C. Full length transcriptome profiling reveals novel immune-related genes in black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, M.; Xiu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Yang, N.; Su, B.; Li, C. Identification of Antimicrobial Peptide Genes in Black Rockfish Sebastes schlegelii and Their Responsive Mechanisms to Edwardsiella tarda Infection. Biology 2021, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.E.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-L.; Li, D.-F.; Zhang, G.-S.; Wang, J.-W.; Niu, N. The Prediction of Rice Gene by Fgenesh. Agric. Sci. China 2008, 7, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muffato, M.; Louis, A.; Poisnel, C.E.; Roest Crollius, H. Genomicus: A database and a browser to study gene synteny in modern and ancestral genomes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1119–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative expression software tool (REST©) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 Helices labeled H1, H2, … and strands by their sheets A, B, …; motifs:
Helices labeled H1, H2, … and strands by their sheets A, B, …; motifs: 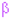 beta turn
beta turn 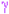 gamma turn
gamma turn  beta hairpin; disulphides:
beta hairpin; disulphides:  disulphide bond. (E,F) The 3D structures of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb were predicted using Phyre2 server. (G) Subcellular localization of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb in HEK293T cells was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. HEK293T cells were transfected with either GFP-empty and GFP-SsCTSBa or GFP-SsCTSBb. After 48 h, the cells were fixed and the nuclei stained with DAPI. Green fluorescence and blue fluorescence were visualized in the same field (Merge). Scale bars equal 20 μm. (H,I) Protein–protein interaction analysis of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb was predicted by STRING 12.0 with the setting of interaction evidence as network edges.
disulphide bond. (E,F) The 3D structures of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb were predicted using Phyre2 server. (G) Subcellular localization of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb in HEK293T cells was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. HEK293T cells were transfected with either GFP-empty and GFP-SsCTSBa or GFP-SsCTSBb. After 48 h, the cells were fixed and the nuclei stained with DAPI. Green fluorescence and blue fluorescence were visualized in the same field (Merge). Scale bars equal 20 μm. (H,I) Protein–protein interaction analysis of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb was predicted by STRING 12.0 with the setting of interaction evidence as network edges.
 Helices labeled H1, H2, … and strands by their sheets A, B, …; motifs:
Helices labeled H1, H2, … and strands by their sheets A, B, …; motifs: 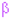 beta turn
beta turn 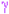 gamma turn
gamma turn  beta hairpin; disulphides:
beta hairpin; disulphides:  disulphide bond. (E,F) The 3D structures of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb were predicted using Phyre2 server. (G) Subcellular localization of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb in HEK293T cells was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. HEK293T cells were transfected with either GFP-empty and GFP-SsCTSBa or GFP-SsCTSBb. After 48 h, the cells were fixed and the nuclei stained with DAPI. Green fluorescence and blue fluorescence were visualized in the same field (Merge). Scale bars equal 20 μm. (H,I) Protein–protein interaction analysis of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb was predicted by STRING 12.0 with the setting of interaction evidence as network edges.
disulphide bond. (E,F) The 3D structures of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb were predicted using Phyre2 server. (G) Subcellular localization of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb in HEK293T cells was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. HEK293T cells were transfected with either GFP-empty and GFP-SsCTSBa or GFP-SsCTSBb. After 48 h, the cells were fixed and the nuclei stained with DAPI. Green fluorescence and blue fluorescence were visualized in the same field (Merge). Scale bars equal 20 μm. (H,I) Protein–protein interaction analysis of SsCTSBa and SsCTSBb was predicted by STRING 12.0 with the setting of interaction evidence as network edges.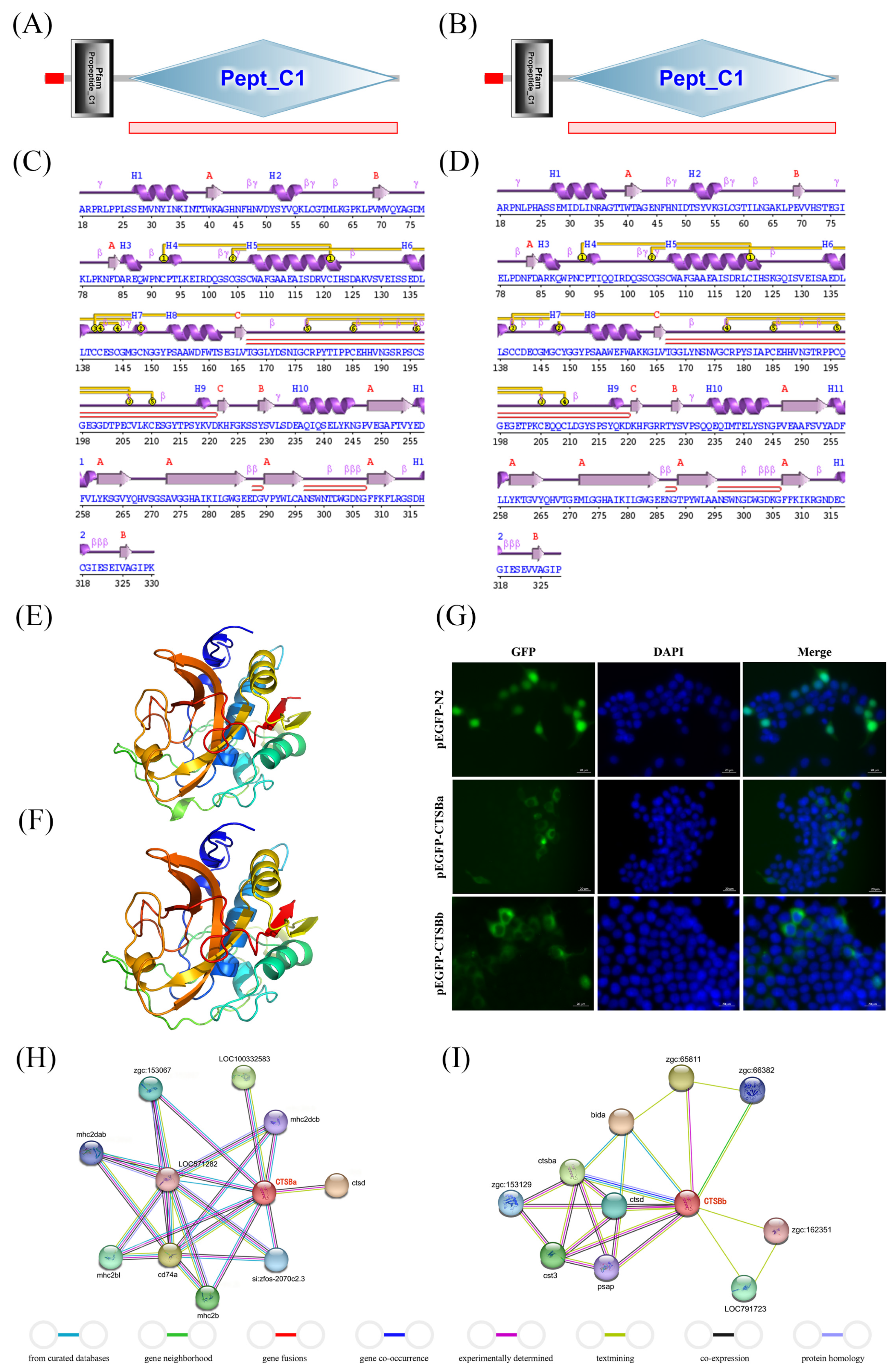



| Analyses | CTSBa | CTSBb |
|---|---|---|
| mRNA | 993 bp | 993 bp |
| No. of amino acids | 330 aa | 330 aa |
| Molecular weight | 36.06 kDa | 36.06 kDa |
| Theoretical pI | 5.38 | 5.20 |
| Formula | C1599H2412N424O486S22 | C1590H2411N433O487S21 |
| Instability index | 32.27 | 31.46 |
| Aliphatic index | 69.42 | 70.94 |
| Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) | −0.260 | −0.309 |
| Cysteine proteases active site | 3 | 3 |
| Protein kinase C phosphorylation site | 4 | 4 |
| Casein kinase II phosphorylation site | 4 | 2 |
| N-glycosylation site | 2 | 1 |
| Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu) | 37 | 37 |
| Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys) | 27 | 24 |
| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| CDS clone | |
| SsCTSBa-ORF F | CAGTCATTCTCTGTTCTCTGATTCC |
| SsCTSBa-ORF R | ACACTCGGCAGGAAATCGTATAAAT |
| SsCTSBb-ORF F | ATTTTGACCAGGACAGACACGAT |
| SsCTSBb-ORF R | GCAGATGTAAGATTTATGTGGCAAG |
| qPCR | |
| SsCTSBa F | CACTCCCAGCTACAAAGTAGAC |
| SsCTSBa R | CTACTGGGCCGTTCTTGTATAG |
| SsCTSBb F | TGGGCTGTTATGGTGGTTATC |
| SsCTSBb R | AGCCGACATTGGAGTTATACAG |
| β-actin F | GTGCGTGACATCAAGGAGAAGC |
| β-actin R | TGTTGTAGGTGGTCTCGTGGA |
| Subcellular localization | |
| EGFP-SsCTSBa F | CGTCAGATCCGCTAGCATGTGGCGTGCAGCTTTCCT |
| EGFP-SsCTSBa R | ACGGCCGGTGGATCCGTTTGGGAATCCCCGCC |
| EGFP-SsCTSBb F | CGTCAGATCCGCTAGCATGCATCCTCTGGCTCTCGTTT |
| EGFP-SsCTSBb R | ACGGCCGGTGGATCCGGTTGAGTGGGATTCCTGCC |
| Prokaryotic expression | |
| SsCTSBa-Pr F | GGTAAAATCGAAGAAGGATCCAGACCCCGCCTCCCACCACTGT |
| SsCTSBa-Pr R | AGAACCGTTACCAGAGGTACCTTTGGGAATCCCCGCCACAATC |
| SsCTSBb-Pr F | GGTAAAATCGAAGAAGGATCCCGGCCTAACCTCCCTCATGCCT |
| SsCTSBb-Pr R | AGAACCGTTACCAGAGGTACCGTTGAGTGGGATTCCTGCCACC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, X.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Lin, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, C.; et al. Identification, Expression Profiling, Microbial Binding, and Agglutination Analyses of Two Cathepsin B Genes in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050213
Zhuang X, Li X, Li W, Xu X, Lin F, Liu Y, Chen C, Zhang X, Zhang P, Li C, et al. Identification, Expression Profiling, Microbial Binding, and Agglutination Analyses of Two Cathepsin B Genes in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(5):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050213
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Xinghua, Xingchun Li, Wenpeng Li, Xuan Xu, Fengjun Lin, Yiying Liu, Chonghui Chen, Xiaoxu Zhang, Pei Zhang, Chao Li, and et al. 2025. "Identification, Expression Profiling, Microbial Binding, and Agglutination Analyses of Two Cathepsin B Genes in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii)" Marine Drugs 23, no. 5: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050213
APA StyleZhuang, X., Li, X., Li, W., Xu, X., Lin, F., Liu, Y., Chen, C., Zhang, X., Zhang, P., Li, C., & Fu, Q. (2025). Identification, Expression Profiling, Microbial Binding, and Agglutination Analyses of Two Cathepsin B Genes in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Marine Drugs, 23(5), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050213






