Identification of TRPV1-Inhibitory Peptides from Takifugu fasciatus Skin Hydrolysate and Their Skin-Soothing Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Virtual Screening Based on the TRPV1 Receptor
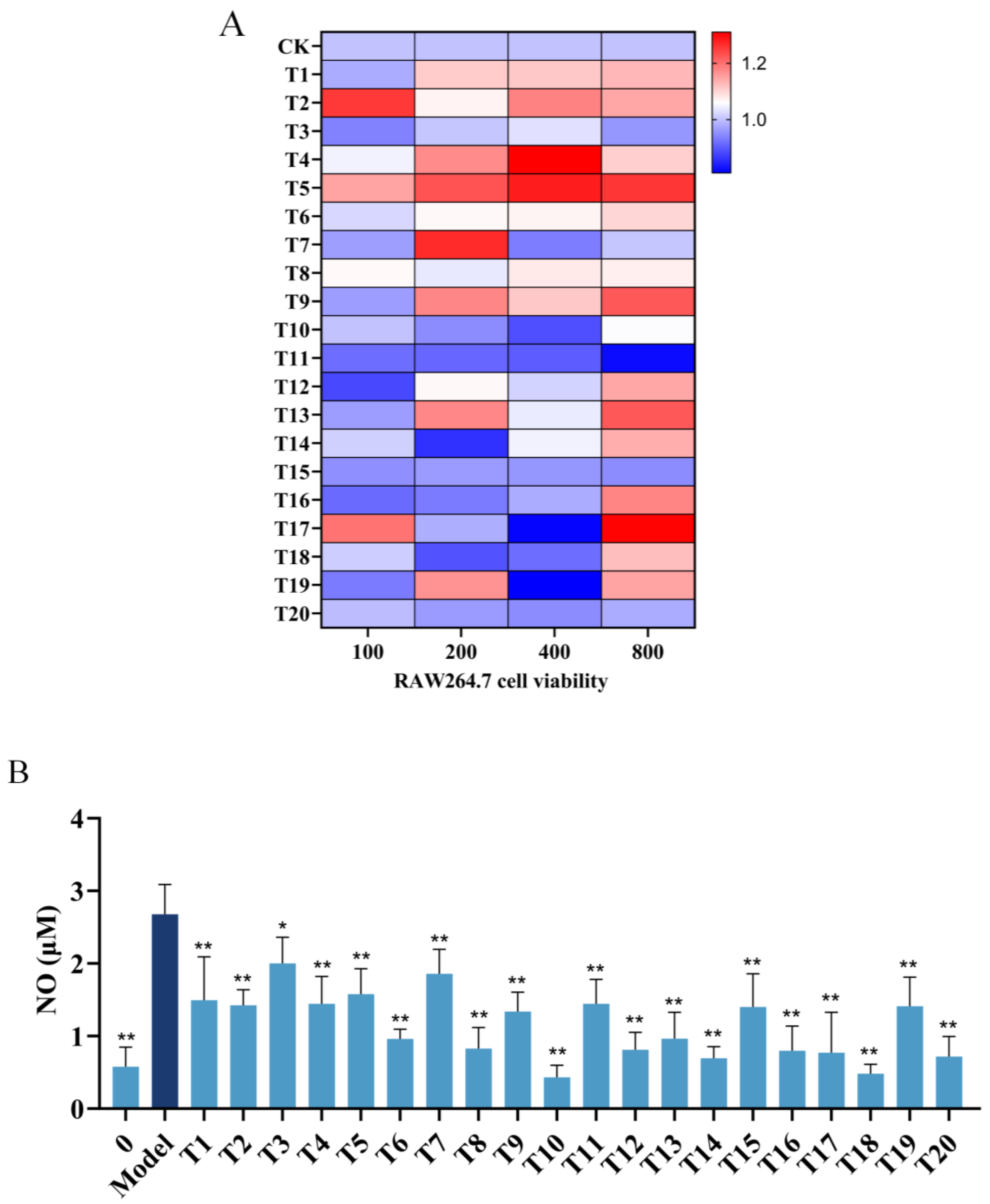
2.2. Inhibitory Effects of Hit Peptides on NO Production
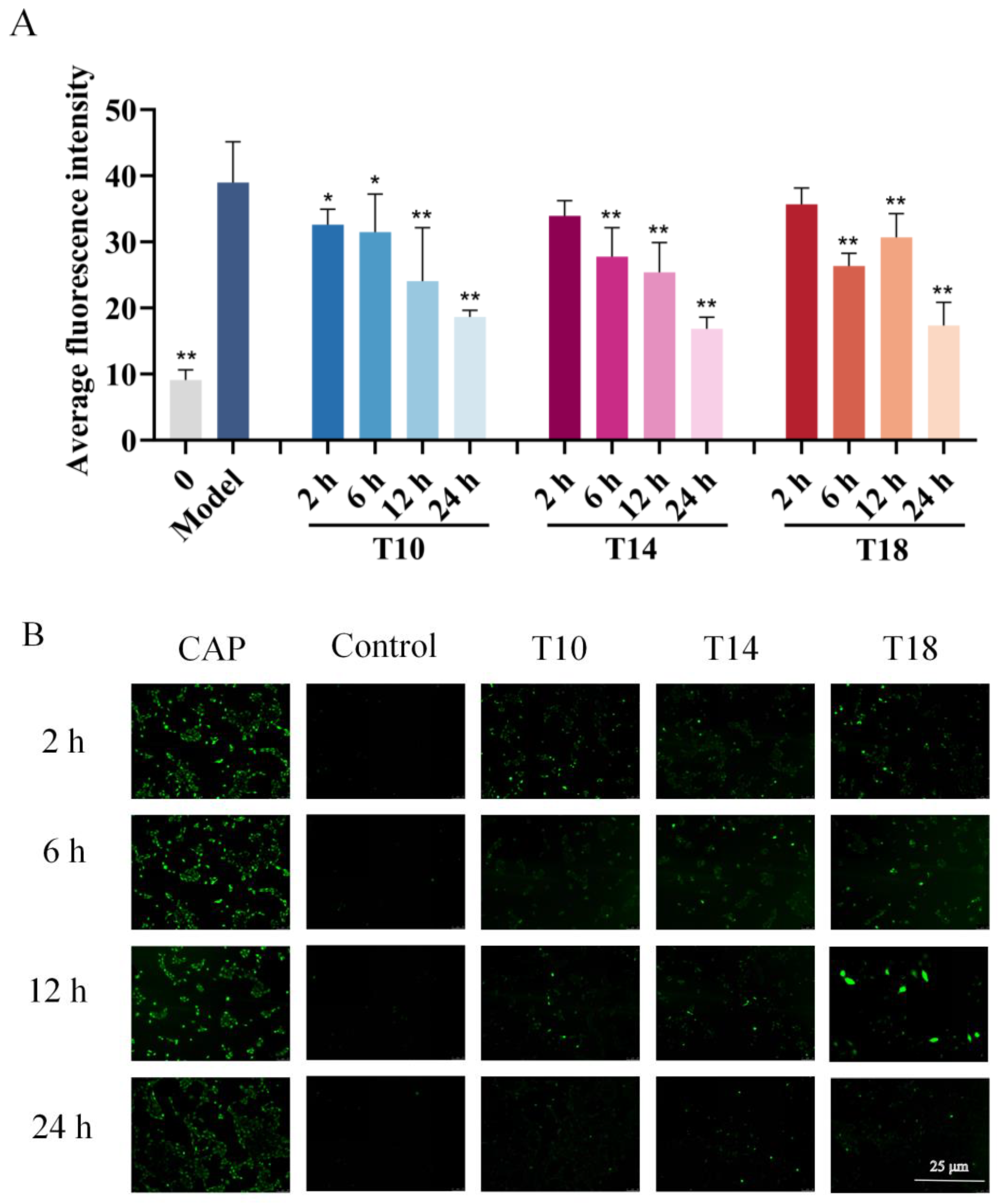
2.3. Inhibitory Effects of Hit Peptides on Capsaicin (CAP)-Induced Ca2+ Influx in HaCaT Cells
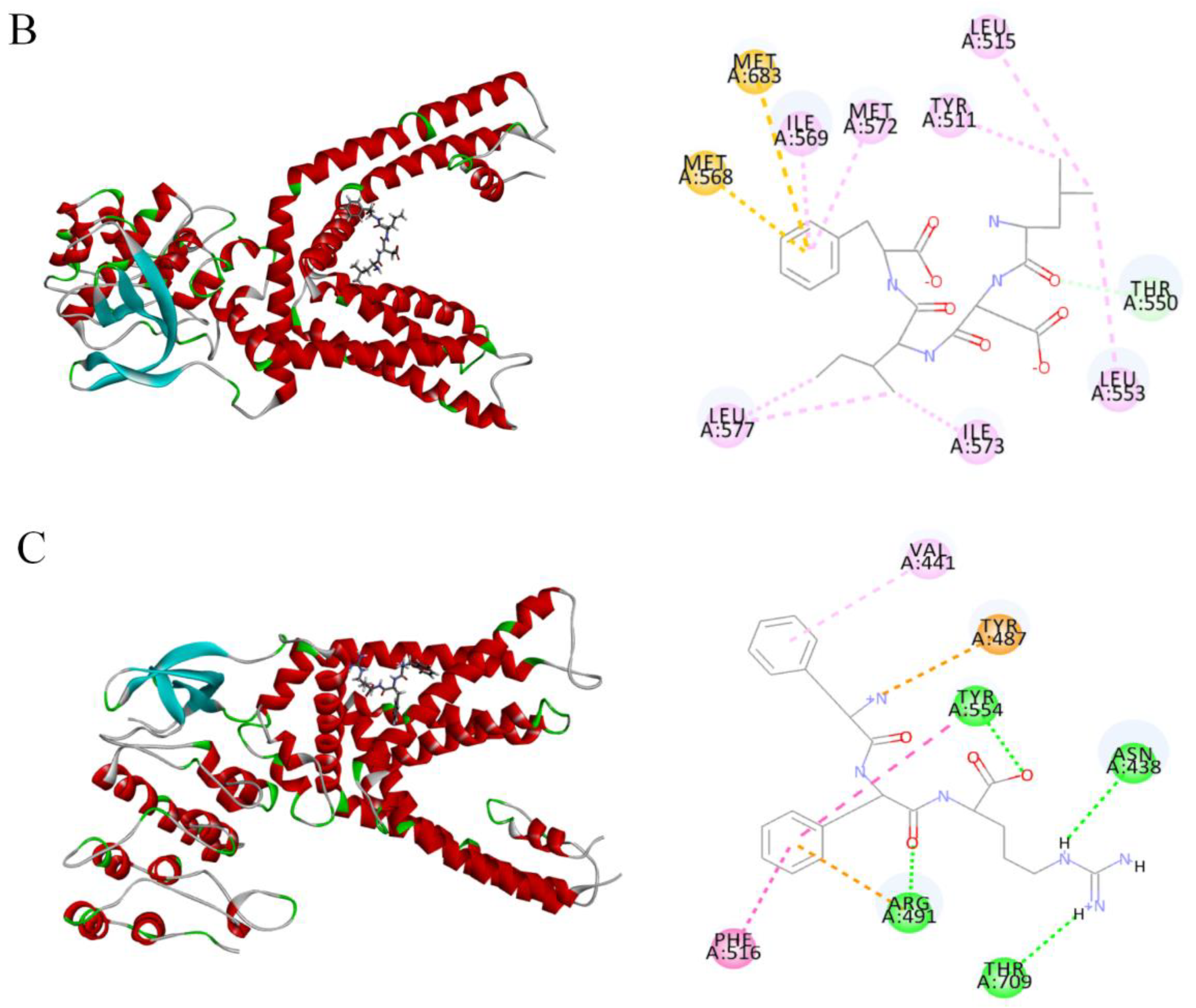
2.4. Molecular Docking of Candidate Polypeptides with TRPV1
2.5. Effects of T14 on Cytokine Expression Levels in RAW 264.7 Cells
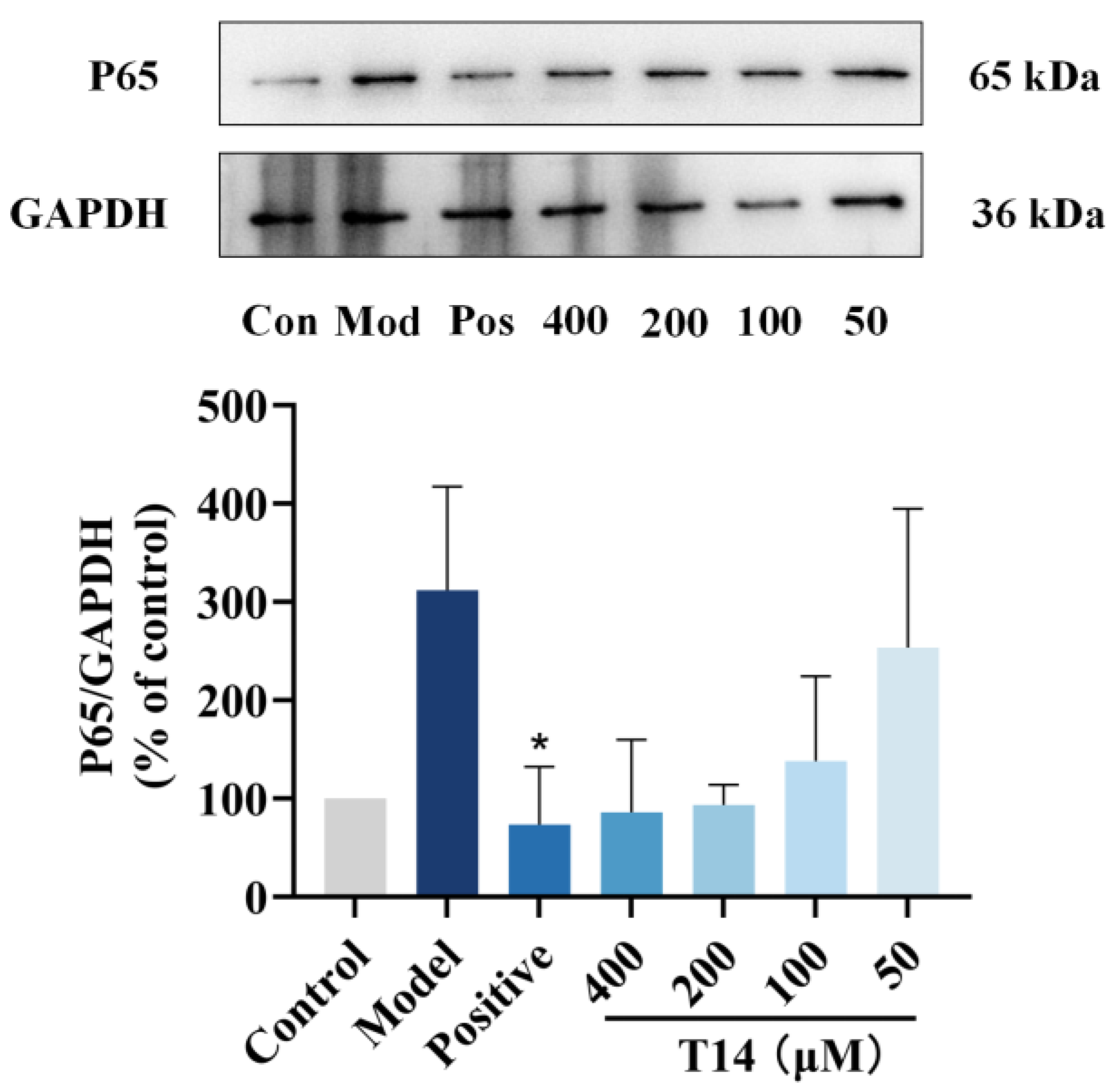
2.6. T14 Inhibits the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in CAP-Induced HaCaT Cells
2.7. T14 Reduces Inflammatory Responses in HUVECs
2.8. Network Pharmacological Analysis
2.8.1. Prediction of T14 Action Targets
2.8.2. PPI Network Construction
2.8.3. KEGG Pathway Enrichment and GO Enrichment Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Low-Molecular Weight T. fasciatus Skin Hydrolysate
4.2. Identification of Polypeptide Sequences by Nano-Scale High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
4.3. Virtual Screening of Hit Peptides
4.4. Cell Viability and NO Content Assays
4.5. Ca2+ Content Assay
4.6. Mouse Cytokine Array Analysis
4.7. Western Blot Analysis of NF-κB Pathway Protein Expression
4.8. HUVEC Cell Stimulatory Response
4.9. Network Pharmacology Analysis
4.9.1. Prediction of Potential Therapeutic Targets of T14 in SS
4.9.2. PPI Network Construction
4.9.3. KEGG Pathway Enrichment and GO Analysis
4.10. Data Processing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, L. Chinese Clinical Guidelines for Sensitive Skin (2024 edition). Chin. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdain, R.; de Lacharrière, O.; Bastien, P.; Maibach, H.I. Ethnic variations in self-perceived sensitive skin: Epidemiological survey. Contact Dermat. 2002, 46, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, C.M.; Shaw, S.; De Lacharrière, O.; Baverel, M.; Reiche, L.; Jourdain, R.; Bastien, P.; Wilkinson, J.D. Sensitive skin: An epidemiological study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2001, 145, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misery, L.; Morisset, S.; Seite, S.; Brenaut, E.; Ficheux, A.; Fluhr, J.W.; Delvigne, V.; Taieb, C. Relationship between sensitive skin and sleep disorders, fatigue, dust, sweating, food, tobacco consumption or female hormonal changes: Results from a worldwide survey of 10 743 individuals. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenaut, E.; Misery, L.; Taieb, C. Sensitive Skin in the Indian Population: An Epidemiological Approach. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.; Shimoda, L.M.N.; Kawakami, J.K.; Ang, L.; Bacani, A.J.; Baker, J.D.; Badowski, C.; Speck, M.; Stokes, A.J.; Small-Howard, A.L.; et al. Myrcene and terpene regulation of TRPV1. Channels 2019, 13, 344–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X. Study on Virtual Screening for Targeted TRPV1 Channel Modulators. Master’s Thesis, Academy of Military Science, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.G.; Du, H.Y.; Gerhard, S.; Imke, M.; Liu, W. Inhibition of TRPV1 prevented skin irritancy induced by phenoxyethanol. A preliminary in vitro and in vivo study. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.S. Research progress of TRPV1 channel in pathologic pain. Chin. J. Pain Med. 2021, 27, 841–844+850. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Wang, Y. Efficacy evaluation of cosmetics (V) Scientific support for soothing skin efficacy claims. China Surfactant Deterg. Cosmet. 2018, 48, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Kedzierski, R.M.; Yanagisawa, M. Endothelin system: The double-edged sword in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 851–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teder, P.; Noble, P.W. A Cytokine Reborn? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 23, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iosageanu, A.; Ilie, D.; Craciunescu, O.; Seciu-Grama, A.M.; Oancea, A.; Zarnescu, O.; Moraru, I.; Oancea, F. Effect of Fish Bone Bioactive Peptides on Oxidative, Inflammatory and Pigmentation Processes Triggered by UVB Irradiation in Skin Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Liang, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. The wound healing effects of the Tilapia collagen peptide mixture TY001 in streptozotocin diabetic mice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2848–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, Q.; Gao, R.C.; Cai, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.H. The protective effect of collagen peptides from bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) skin and bone to attenuate UVB-induced photoaging via MAPK and TGF-β signaling pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 93, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia Campos, P.; Franco, R.S.B.; Kakuda, L.; Cadioli, G.F.; Costa, G.D.; Bouvret, E. Oral Supplementation with Hydrolyzed Fish Cartilage Improves the Morphological and Structural Characteristics of the Skin: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, G.; Qiao, K.; Xu, M.; Cai, S.; Liao, D.; Liu, Z. Preparation of collagen peptide fromFugu bimaculatusskin and its efficacy and irritation evaluation in cosmetics. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2020, 32, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xue, K.; Tang, H.; Zhang, G.; Qiao, K.; Xu, M.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z. Photoprotective effect of collagen peptides from the skin of Takifugu Photoprotective effect of collagen peptides from the skin of Takifugu. J. Fish. Res. 2024, 46, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. Extaction of Collagen Peptides from fugu Bimacujatus Skin and Their Cosmeticefficacy. Master’s Thesis, Jimei University, Xiamen, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.N.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S.S. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2008, 15, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Nie, C.; Wang, Y.; Ai, L.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, F.; Wang, G. Rapid Screening and Verification of α-Lactalbumin-Derived ACE Inhibitory Peptides. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Pittayapruek, P.; Meephansan, J.; Prapapan, O.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Photoaging and Photocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol Sci. 2016, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, A.; Shao, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, Y. Advancements in research on immune cells and cytokines in the treatment of acute lung injury. Proceeding Clin. Med. 2024, 33, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y. Research progress on genetically engineered cytokines. Chin. J. Biol. 2023, 36, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, T.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Ulzii, D.; Miake, S.; Fujishima, K.; Sakai, S.; Chiba, T.; Tsuji, G.; Furue, M. Topical application of endothelin receptor a antagonist attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasiform skin inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Thakur, M.; Mishra, M.; Yadav, M.; Vibhuti, R.; Menon, A.M.; Nagda, G.; Dwivedi, V.P.; Dakal, T.C.; Yadav, V. Gene regulation of intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1): A molecule with multiple functions. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 240, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Peng, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y. Mechanism of Anti-depression Mechanism of Akebiae Fructus Basedon Network Pharmacology. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zheng, J. Understand spiciness: Mechanism of TRPV1 channel activation by capsaicin. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, B.; Tugues, S.; Greter, M. GM-CSF: From Growth Factor to Central Mediator of Tissue Inflammation. Immunity 2016, 45, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napetschnig, J.; Wu, H. Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, R.; Hoffmann, A.; Levchenko, A. Understanding NF-κB signaling via mathematical modeling. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Stebut, E. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 13, 455–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Xu, Y.; Guo, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xia, M.; Tan, B.; Liu, X.; Feng, H.; Chen, Y. CCL5/CCR5-mediated peripheral inflammation exacerbates blood–brain barrier disruption after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.E.; Saini, D.K. The ERK-p38MAPK-STAT3 Signalling Axis Regulates iNOS Expression and Salmonella Infection in Senescent Cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 744013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GONG, T.; Si, K.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Research advances in the role of MAPK cascade in regulation of cell growth, immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J. Cent. South Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2022, 47, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar]
- DeVore, S.B.; Schuetz, M.; Alvey, L.; Lujan, H.; Ochayon, D.E.; Williams, L.; Chang, W.; Filuta, A.; Ruff, B.; Kothari, A.; et al. Regulation of MYC by CARD14 in human epithelium is a determinant of epidermal homeostasis and disease. Cell Rep. 2024, 1247, 00918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 2005, 438, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizanova, O.; Penesova, A.; Sokol, J.; Hokynkova, A.; Samadian, A.; Babula, P. Signaling pathways in cutaneous wound healing. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1030851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodó, E.; Kovács, I.; Telek, A.; Varga, A.; Paus, R.; Kovács, L.; Bíró, T. Vanilloid receptor-1 (VR1) is widely expressed on various epithelial and mesenchymal cell types of human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbanzadeh, S.; Khojini, J.Y.; Abouali, R.; Alimardan, S.; Zahedi, M.; Tahershamsi, Z.; Tajbakhsh, A.; Gheibihayat, S.M. Clearing the Path: Exploring Apoptotic Cell Clearance in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disorders for Therapeutic Advancements. Mol. Biotechnol. 2024, 24, 01222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talagas, M.; Misery, L. Role of Keratinocytes in Sensitive Skin. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Gu, L.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, M.; Yuan, W. Endothelin-1 triggers human peritoneal mesothelial cells’ proliferation via ERK1/2-Ets-1 signaling pathway and contributes to endothelial cell angiogenesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Fan, J.; Cai, B.; Lv, Y.; Zeng, M.; Hao, Y.; Giancotti, F.G.; Fu, B.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor enhances cancer cell adhesion to microvascular endothelium in vivo. Exp. Physiol. 2009, 95, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, M. Pterostilbene and 4′-Methoxyresveratrol Inhibited Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Molecules 2018, 23, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.Q.; Ma, L.; Chen, T.; Zhang, W.X.; Chang, K.; Wang, J. Sophorolipid inhibits histamine-induced itch by decreasing PLC/IP3R signaling pathway activation and modulating TRPV1 activity. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, R.J.; Chen, Y.M.; Ye, X.; Chen, Q.X.; Shen, D.Y.; Wang, Q. Synthesis of caffeic acid ester morpholines and their activation effects on tyrosinase. Process Biochem. 2017, 62, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Ge, W.; Li, G.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, S. In Silico Analysis of Novel DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides Released from Camel Milk Lactoferrin and the Possible Pathways Involved in Diabetes Protection. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Han, L.; Ma, J.; Wu, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tong, X. Exploring the synergistic and complementary effects of berberine and paeoniflorin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus by network pharmacology. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 919, 174769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, M.; Pan, F.; Li, J.; Dou, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Cai, S. In silico analysis of novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides released from Macadamia integrifolia antimicrobial protein 2 (MiAMP2) and the possible pathways involved in diabetes protection. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Number | ID | Grid_Score |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | WTKIHF | −106.138 |
| T2 | FSWLA | −103.8745 |
| T3 | LFNW | −95.4542 |
| T4 | WSPW | −89.0253 |
| T5 | IFDL | −87.6124 |
| T6 | SLQFF | −87.3296 |
| T7 | WLGY | −86.9512 |
| T8 | MQGW | −86.6209 |
| T9 | LFIL | −85.6879 |
| T10 | QFF | −84.5399 |
| T11 | IFSL | −84.5094 |
| T12 | GFIF | −84.2106 |
| T13 | YDF | −83.7816 |
| T14 | LDIF | −83.5353 |
| T15 | LRF | −83.4104 |
| T16 | PAGGGDPI | −83.3656 |
| T17 | RWI | −83.2909 |
| T18 | FFR | −82.5188 |
| T19 | FID | −82.3704 |
| T20 | QMML | −82.144 |
| Peptides | RMSD (Å) | Residues with Hydrogen Bonds | Residues with Hydrophobic Interactions | Residues with Electrostatic Action | Sulfur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T10 | 3.27 | ASN438 (2.77 Å, 2.69 Å) ARG491 (2.73 Å, 2.82 Å) TYR555 (2.38 Å, 2.12 Å) | VAL441 (5.00 Å) PHE488 (4.71 Å) ARG491 (4.43 Å) | ARG491 (4.52 Å) GLU513 (3.51 Å) TYR554 (4.07 Å) | |
| T14 | 2.96 | THR550 (2.24 Å) | MET572 (4.26 Å) LEU553 (5.27 Å) TYR511 (4.59 Å) LEU515 (5.32 Å) LEU553 (5.27 Å) LEU577 (4.83 Å, 4.96 Å) ILE569 (4.78 Å) | MET568 (5.86 Å) MET683 (5.95 Å) | |
| T18 | 3.24 | TYR554 (1.95 Å) ASN438 (2.64 Å) ARG491 (4.87 Å) THR709 (2.52 Å) | PHE516 (4.04 Å) TYR554 (4.86 Å) VAL441 (5.28 Å) | ARG491 (4.93 Å) TYR487 (4.36 Å) |
| Number | Target | Degree |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | STAT3 | 24 |
| 2 | MAPK3 | 22 |
| 3 | SPHK1 | 18 |
| 4 | CTSB | 18 |
| 5 | HDAC1 | 16 |
| 6 | HDAC6 | 12 |
| 7 | PLAU | 12 |
| 8 | SERPINE1 | 12 |
| 9 | CTSG | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, D.; Wu, R.; Qiao, K.; Chen, K.; Su, Y.; Cai, S.; Xu, M.; Liu, S.; et al. Identification of TRPV1-Inhibitory Peptides from Takifugu fasciatus Skin Hydrolysate and Their Skin-Soothing Mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050196
Tang H, Chen B, Zhang D, Wu R, Qiao K, Chen K, Su Y, Cai S, Xu M, Liu S, et al. Identification of TRPV1-Inhibitory Peptides from Takifugu fasciatus Skin Hydrolysate and Their Skin-Soothing Mechanisms. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(5):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050196
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Haiyan, Bei Chen, Dong Zhang, Ruowen Wu, Kun Qiao, Kang Chen, Yongchang Su, Shuilin Cai, Min Xu, Shuji Liu, and et al. 2025. "Identification of TRPV1-Inhibitory Peptides from Takifugu fasciatus Skin Hydrolysate and Their Skin-Soothing Mechanisms" Marine Drugs 23, no. 5: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050196
APA StyleTang, H., Chen, B., Zhang, D., Wu, R., Qiao, K., Chen, K., Su, Y., Cai, S., Xu, M., Liu, S., & Liu, Z. (2025). Identification of TRPV1-Inhibitory Peptides from Takifugu fasciatus Skin Hydrolysate and Their Skin-Soothing Mechanisms. Marine Drugs, 23(5), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23050196






