Polystyrene Microplastics Can Aggravate the Damage of the Intestinal Microenvironment Caused by Okadaic Acid: A Prevalent Algal Toxin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of MPs and OA on the Viability of Caco-2 Cells
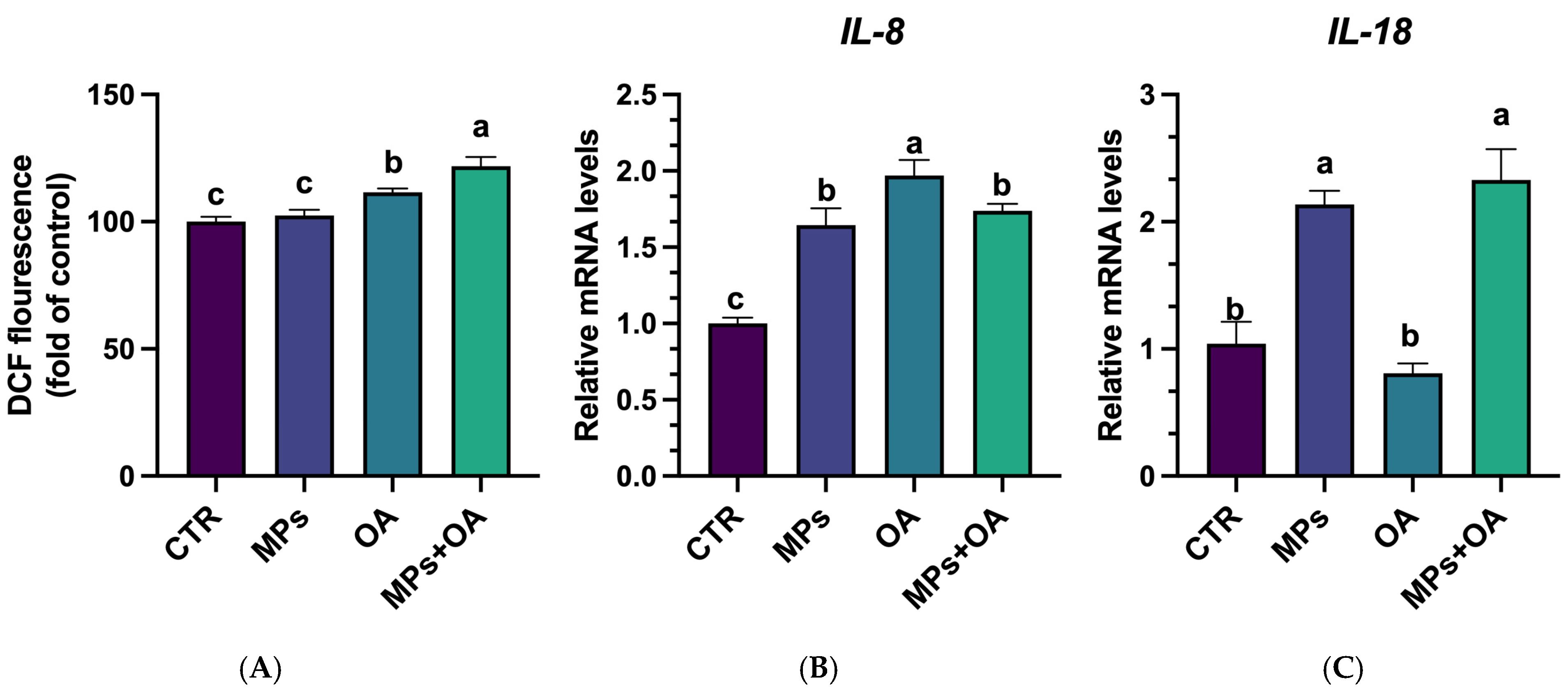
2.2. Co-Exposure of MPs- and OA-Enhanced ROS Production and Triggered Inflammatory Responses
2.3. MPs Promoted the Intracellular Accumulation of OA in Caco-2 Cells
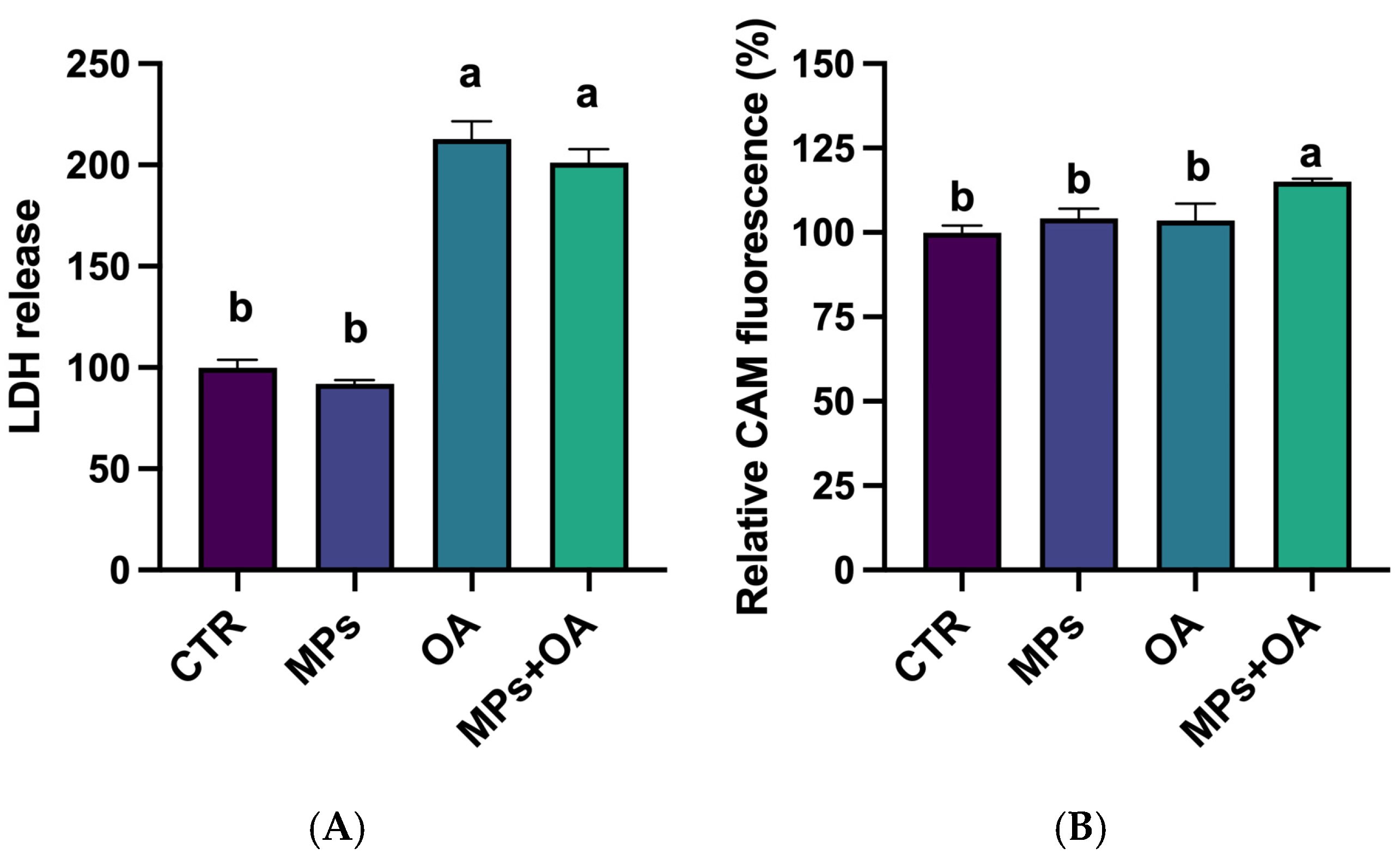
2.4. Changes in the LDH Release and ABC Transporter Activity
2.5. Effects of the MPs and OA Exposure on the Expression of Genes Related to the Intestinal Barrier
2.6. The Effect of MPs and OA Exposure on Gut Microbiota
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. MPs and OA
4.2. Cell Treatment Protocol
4.3. Cell Vitality Assays
4.4. Quantitative Determination of OA
4.5. Measurement of Intracellular ROS
4.6. Evaluation of Lactate Dehydrogenase Release
4.7. Determination of the Transmembrane ABC Transporter Activity
4.8. RT-qPCR Analysis
4.9. Feces Collection and Fermentation Culture
4.10. 16S rRNA Analysis of Fermentation Microbiota
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilcox, C.; Van Sebille, E.; Hardesty, B.D. Threat of plastic pollution to seabirds is global, pervasive, and increasing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 112, 11899–11904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.; Monteiro, C.E.; Sayed, A.E.D.H. Investigation of the impact caused by different sizes of polyethylene plastics (nano, micro, and macro) in common carp juveniles, Cyprinus carpio L., using multi-biomarkers. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, W.; Buriro, R.S.; Gandahi, J.A.; Chen, Y.; ul Aabdin, Z.; Bhutto, S.; Sun, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zou, H. A critical review on male-female reproductive and developmental toxicity induced by micro-plastics and nano-plastics through different signaling pathways. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 394, 110976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.S.; Cole, M.; Lewis, C. Interactions of microplastic debris throughout the marine ecosystem. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.Q.Y.; Valiyaveettil, S.; Tang, B.L. Toxicity of microplastics and nanoplastics in mammalian systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Lin, S.; Chen, M.; Hong, J.; Liu, C. Prevalence of phycotoxin contamination in shellfish from the Northern Bering Sea and the Chukchi Sea. Toxicon 2019, 167, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Li, D.W.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, W.D. Polystyrene microplastics exacerbated the toxicity of okadaic acid to the small intestine in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 281, 116628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.W.; Peng, X.C.; Li, H.Y.; Huang, L.; Li, D.W.; Liu, J.S.; Yang, W.D. Changes in colonic microbiotas in rat after long-term exposure to low dose of okadaic acid. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Cai, Q.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Yang, W. In vitro Interactions between okadaic acid and rat gut microbiome. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, R. Is Protein Phosphatase Inhibition Responsible for the Toxic Effects of Okadaic Acid in Animals? Toxins 2013, 5, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; Holmes, C.F.; Tsukitani, Y. Okadaic acid: A new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1990, 15, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creppy, E.E.; Traoré, A.; Baudrimont, I.; Cascante, M.; Carratú, M.-R. Recent Advances in the Study of Epigenetic Effects Induced by the Phycotoxin Okadaic Acid. Toxicology 2002, 181–182, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordier, S.; Monfort, C.; Miossec, L.; Richardson, S.; Belin, C. Ecological Analysis of Digestive Cancer Mortality Related to Contamination by Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins along the Coasts of France. Environ. Res. 2000, 84, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Rodas, V.; Maneiro, E.; Martínez, J.; Navarro, M.; Costas, E. Harmful algal blooms, red tides and human health: Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning and colorectal cancer. Anal. Real Acad. Farm 2006, 72, 391–408. [Google Scholar]
- Manerio, E.; Rodas, V.L.; Costas, E.; Hernandez, J.M. Sehllfish consumption: A major risk factor for colorectal cancer. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, I.d.P.; Menegotto, A.; Lana, P.d.C.; Mafra Junior, L.L. A new look at the potential role of marine plastic debris as a global vector of toxic benthic algae. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yu, R.; Fan, M.; Yang, Z.; Liao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xie, C.; Xuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Physiological and transcriptome analysis of Mytilus coruscus in response to Prorocentrum lima and microplastics. Front. Mar. 2022, 9, 1087667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, X.; He, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, C.; Qian, Z.J.; Hong, P.; Liang, Y.Q.; et al. Do polystyrene nanoplastics aggravate the toxicity of single contaminants (okadaic acid)? Using AGS cells as a biological model. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 3186–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yu, Z.; Lin, P.; Qiu, S.; He, L.; Wu, Z.; Ma, L.; Gu, Y.; He, L.; Dai, Z.; et al. Polystyrene nanoplastics promote the apoptosis in Caco-2 cells induced by okadaic acid more than microplastics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Weng, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y. Microplastic: A potential threat to human and animal health by interfering with the intestinal barrier function and changing the intestinal microenvironment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Kirby, J.; Reilly, C.M.; Luo, X.M. Leaky gut as a danger signal for autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalioto, R.M.; A Maggi, C.; Giuliani, S. Intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in disease and possible therapeutical interventions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 398–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burcelin, R.; Garidou, L.; Pomie, C. Immuno-microbiota cross and talk: The new paradigm of metabolic diseases. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chang, R.; Zhou, X.; Xu, C. Intestinal barrier function–non-alcoholic fatty liver disease interactions and possible role of gut microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2754–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barbara, G.; Buurman, W.; Ockhuizen, T.; Schulzke, J.D.; Serino, M.; Tilg, H.; Watson, A.; Wells, J.M. Intestinal permeability–a new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, L.; Tu, W.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z. Impacts of polystyrene microplastic on the gut barrier, microbiota and metabolism of mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, C.; Elson, C.; Hatton, R.; Weaver, C. Reciprocal interactions of the intestinal microbiota and immune system. Nature 2012, 489, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Kitai, T.; Hazen, S. Gut microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, B. Role of the gut microbiota in human nutrition and metabolism. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hong, X.L.; Sun, T.T.; Huang, X.W.; Wang, J.L.; Xiong, H. Fusobacterium nucleatum exacerbates colitis by damaging epithelial barriers and inducing aberrant inflammation. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Wu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Fu, Z. Effects of environmental pollutants on gut microbiota. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambuy, Y.; De Angelis, I.; Ranaldi, G.; Scarino, M.; Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. The Caco-2 cell line as a model of the intestinal barrier: Influence of cell and culture-related factors on Caco-2 cell functional characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Bao, Z.; Jin, C.; Miao, W.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Toxic effects and mechanisms of three commonly used fungicides on the human colon adenocarcinoma cell line Caco-2. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Size-Dependent Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Cytotoxicity and Efflux Pump Inhibition in Human Caco-2 Cells. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, C.; Ying, J.; Hua, B.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, W.; Ye, D.; Sun, X.; Mao, Y.; et al. Air pollutants, genetic susceptibility, and the risk of incident gastrointestinal diseases: A large prospective cohort study. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaes, N.; Idris, M.; Boesmans, W.; Alves, M.M.; Melotte, V. Nerves in gastrointestinal cancer: From mechanism to modulations. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 768–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara-Lemarroy, C.R.; Metz, L.; Meddings, J.B.; Sharkey, K.A.; Wee Yong, V. The intestinal barrier in multiple sclerosis: Implications for pathophysiology and therapeutics. Brain 2018, 141, 1900–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, J. Exposing to cadmium stress cause profound toxic effect on microbiota of the mice intestinal tract. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriello, M.C.; Hoffman, J.B.; Vsevolozhskaya, O.; Morris, A.J.; Hennig, B. Dioxin-like PCB 126 increases intestinal inflammation and disrupts gut microbiota and metabolic homeostasis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Li, T.; Yu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Feng, S.; Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Effects of subchronic oral toxic metal exposure on the intestinal microbiota of mice. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced reproductive toxicities induced by phthalates contaminated microplastics in male mice (Mus musculus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Guo, Y.; He, L.; Liao, X.; Chen, X.; He, L.; Lu, Z.; Qian, Z.J.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; et al. Nanoplastics aggravate the toxicity of arsenic to AGS cells by disrupting ABC transporter and cytoskeleton. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Yan, S.; Meng, Z.; Tian, S.; Jia, M.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Diao, J.; Zhu, W. Combined ingestion of polystyrene microplastics and epoxiconazole increases health risk to mice: Based on their synergistic bioaccumulation in vivo. Environ. Int. 2022, 166, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Yin, H.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z. Influence of the co-exposure of microplastics and tetrabromobisphenol A on human gut: Simulation in vitro with human cell Caco-2 and gut microbiota. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, M.; Niu, S.; Shang, M.; Chang, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, R.; Shen, X.; Xue, Y. ROS and DRP1 interactions accelerate the mitochondrial injury induced by polystyrene nanoplastics in human liver HepG2 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 379, 110502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Tian, Y.; Gan, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. In situ growth of nano-antioxidants on cellular vesicles for efficient reactive oxygen species elimination in acute inflammatory diseases. Nano Today 2021, 40, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epel, D.; Luckenbach, T.; Stevenson, C.; Macmanus-Spencer, L.; Hamdoun, A.; Smital, T. Efflux transporters: Newly appreciated roles in protection against pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3914–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shen, Z.; Wu, B.; Yu, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhang, X.; Ren, H. Cytotoxicity and efflux pump inhibition induced by molybdenum disulfide and boron nitride nanomaterials with sheetlike structure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10834–10842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, B.; Shen, Z.; Cherr, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, M. Comparison of cytotoxicity and inhibition of membrane ABC transporters induced by MWCNTs with different length and functional groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3985–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, R.; Chen, Y. Effects of ZnO nanoparticles on wastewater biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2826–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Ren, F.; Pang, G.; Li, Y. Imidacloprid increases intestinal permeability by disrupting tight junctions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Rodríguez, A.; Vila, L.; Cortés, C.; Hernández, A.; Marcos, R. Effects of differently shaped TiO2NPs (nanospheres, nanorods and nanowires) on the in vitro model (Caco-2/HT29) of the intestinal barrier. Part. Fibre. Toxicol. 2018, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, D.; Huo, H.; Zhang, W.; Adiliaghdam, F.; Morrison, S.; Ramirez, J.; Gul, S.; Hamarneh, S.; Hodin, R. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase regulates tight junction protein levels. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2016, 222, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, L.; García-Rodríguez, A.; Cortés, C.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Assessing the effects of silver nanoparticles on monolayers of differentiated Caco-2 cells, as a model of intestinal barrier. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 116, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, A.F.; Parrón, T.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Requena, M.; Alarcón, R.; López-Guarnido, O. Toxic effects of pesticide mixtures at a molecular level: Their relevance to human health. Toxicology 2013, 307, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Toxicological effects of microplastics and heavy metals on the Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.; Patterson, A. The gut microbiome: An orchestrator of xenobiotic metabolism. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, G.; Kremer, M.; Hines, I.N. Contribution of Gut Bacteria to Liver Pathobiology. Gastroent. Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 453563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, T.; Kong, J.; Stothard, P.; Willing, B. Defining the role of Parasutterella, a previously uncharacterized member of the core gut microbiota. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L. Structural Resilience of the Gut Microbiota in Adult Mice under High-Fat Dietary Perturbations. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, W.-L.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.-X.; Qian, M.; Bai, W.-D.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Rao, P.-F.; Ni, L.; Lv, X.-C. Grifola frondosa polysaccharides ameliorate lipid metabolic disorders and gut microbiota dysbiosis in high-fat diet fed rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorkildsen, L.; Nwosu, F.; Avershina, E.; Ricanek, P.; Perminow, G.; Brackmann, S.; Vatn, M.; Rudi, K. Dominant Fecal Microbiota in Newly Diagnosed Untreated Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 636785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, G.; Wang, Y.; Feng, B.; Hu, Y.; Mu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H. Escherichia Coli O101-Induced Diarrhea Develops Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in Rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zeng, K.; Song, C.; Chen, T.; Zou, Y. Translational selenium nanotherapeutics counter-acts multiple risk factors to improve surgery-induced cognitive impairment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 441, 135984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.-J.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.-W.; Wang, X.; Feng, N.-X.; Li, H.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Yang, W.-D. Polystyrene Microplastics Can Aggravate the Damage of the Intestinal Microenvironment Caused by Okadaic Acid: A Prevalent Algal Toxin. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030129
Huang H-J, Liu Y, Li D-W, Wang X, Feng N-X, Li H-Y, Mo C-H, Yang W-D. Polystyrene Microplastics Can Aggravate the Damage of the Intestinal Microenvironment Caused by Okadaic Acid: A Prevalent Algal Toxin. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(3):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030129
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Hong-Jia, Yang Liu, Da-Wei Li, Xiang Wang, Nai-Xian Feng, Hong-Ye Li, Ce-Hui Mo, and Wei-Dong Yang. 2025. "Polystyrene Microplastics Can Aggravate the Damage of the Intestinal Microenvironment Caused by Okadaic Acid: A Prevalent Algal Toxin" Marine Drugs 23, no. 3: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030129
APA StyleHuang, H.-J., Liu, Y., Li, D.-W., Wang, X., Feng, N.-X., Li, H.-Y., Mo, C.-H., & Yang, W.-D. (2025). Polystyrene Microplastics Can Aggravate the Damage of the Intestinal Microenvironment Caused by Okadaic Acid: A Prevalent Algal Toxin. Marine Drugs, 23(3), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030129






