Mixotrophic Cultivation of Dunaliella tertiolecta in Cheese Whey Effluents to Enhance Biomass and Exopolysaccharides (EPS) Production: Biochemical and Functional Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Selection of Optimal CW Concentration
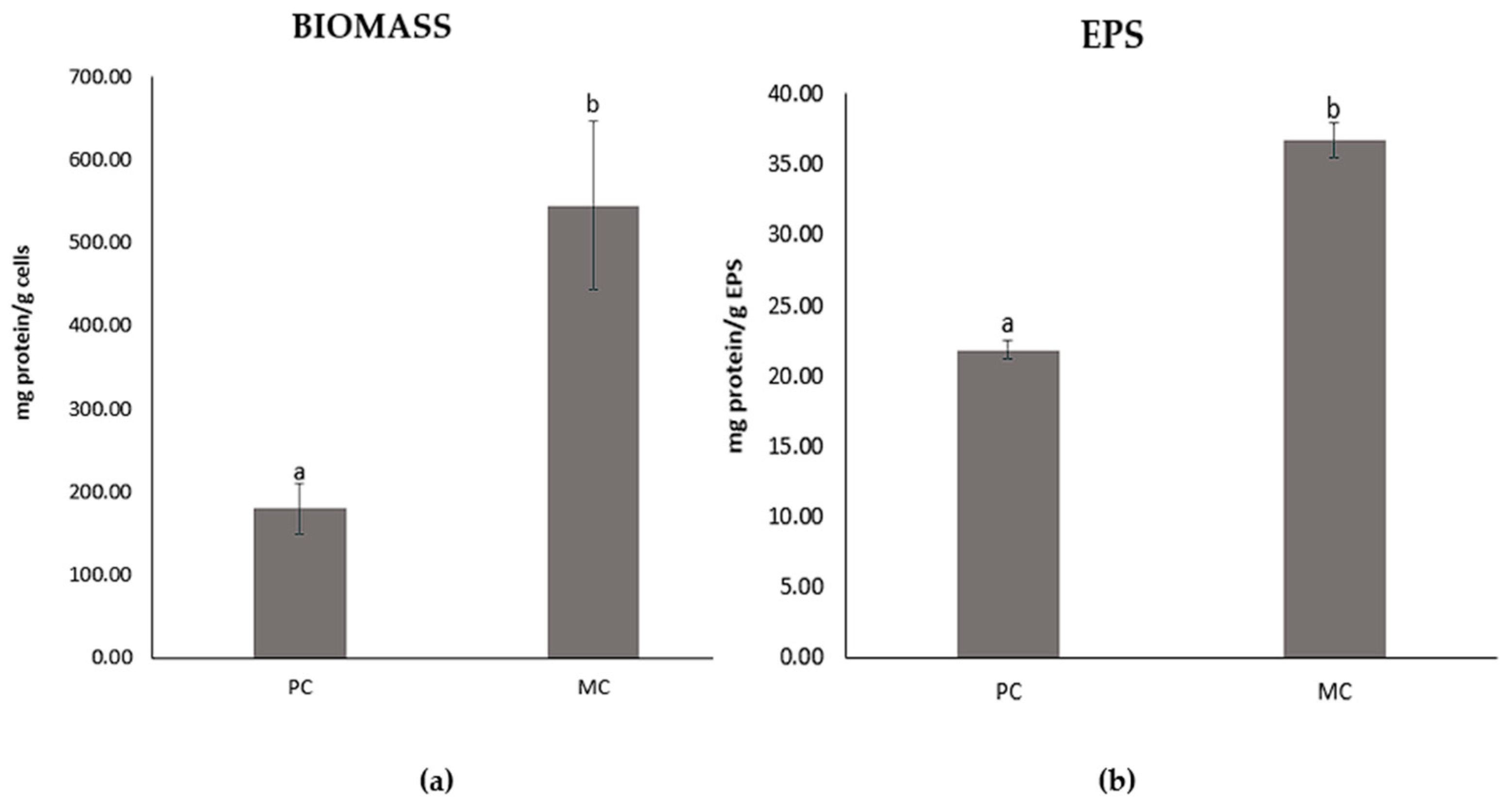
2.2. Growth Rate of D. tertiolecta Production of Biomass and Extracellular Polymeric Substances
2.3. Composition of the Cheese Whey
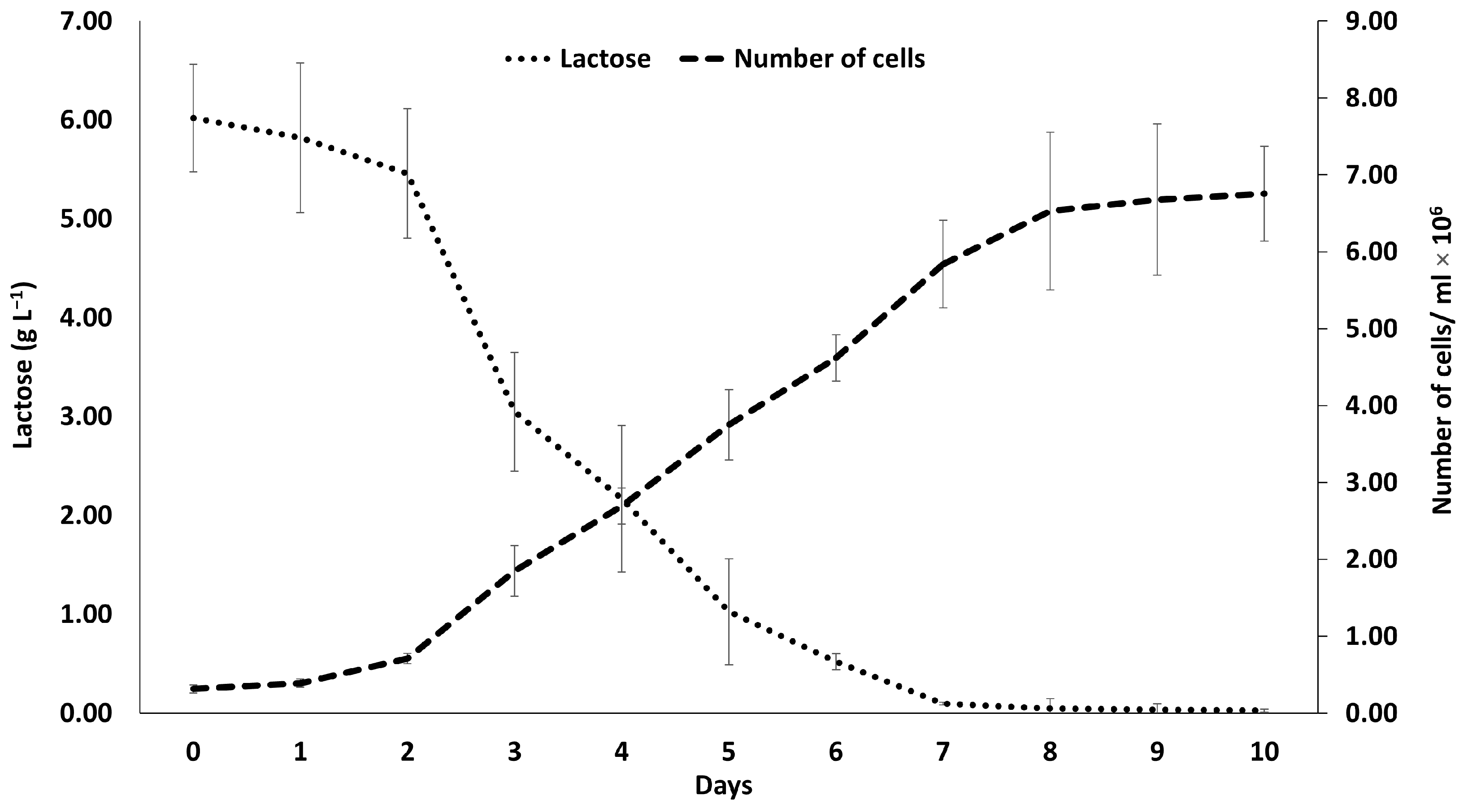
2.4. Determination of the Lactose Content Reduction
2.5. Characterization of the EPSs by FT-IR ATR
2.6. Total Protein Contents of the EPSs and Biomass
2.7. Total Sugar Content of EPS
2.8. Determination of Fatty Acids Profile of the Biomass
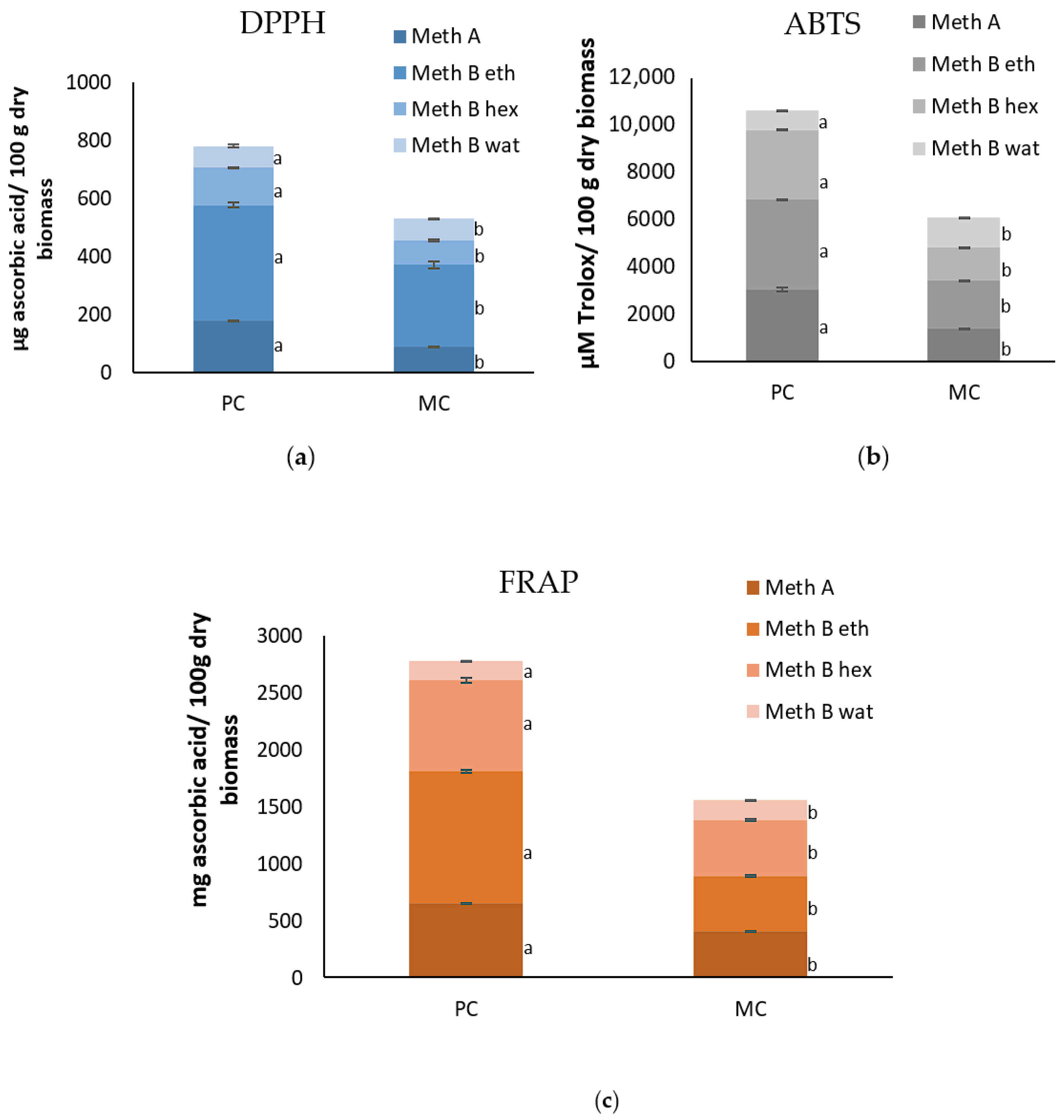
2.9. Antioxidant Capacity of the EPSs and Biomass
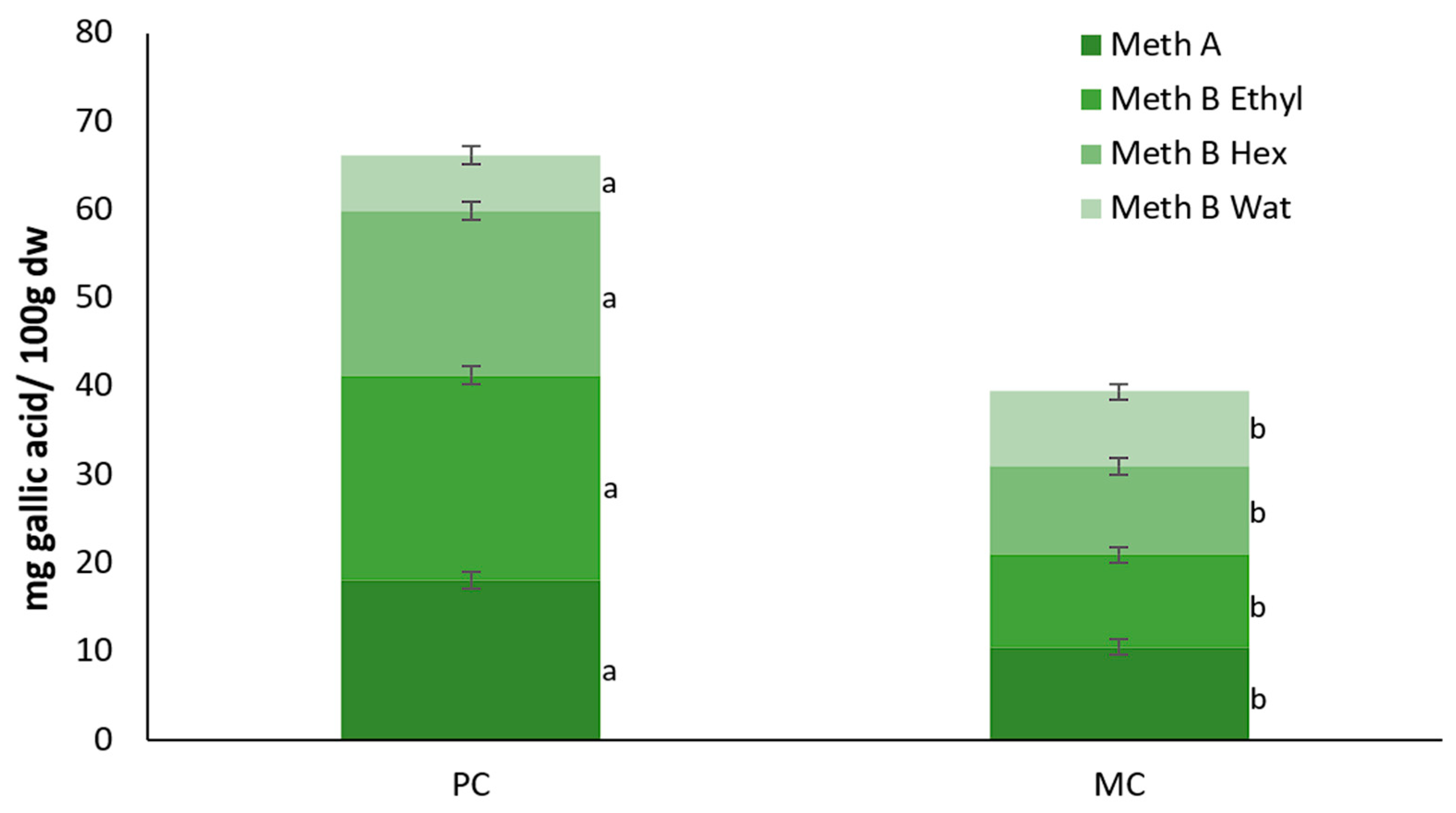
2.10. Total Polyphenol Contents of the EPSs and Biomass
2.11. Determination of Chlorophyll and Carotenoids Contents of the Biomass
2.12. Physicochemical Properties of the EPS
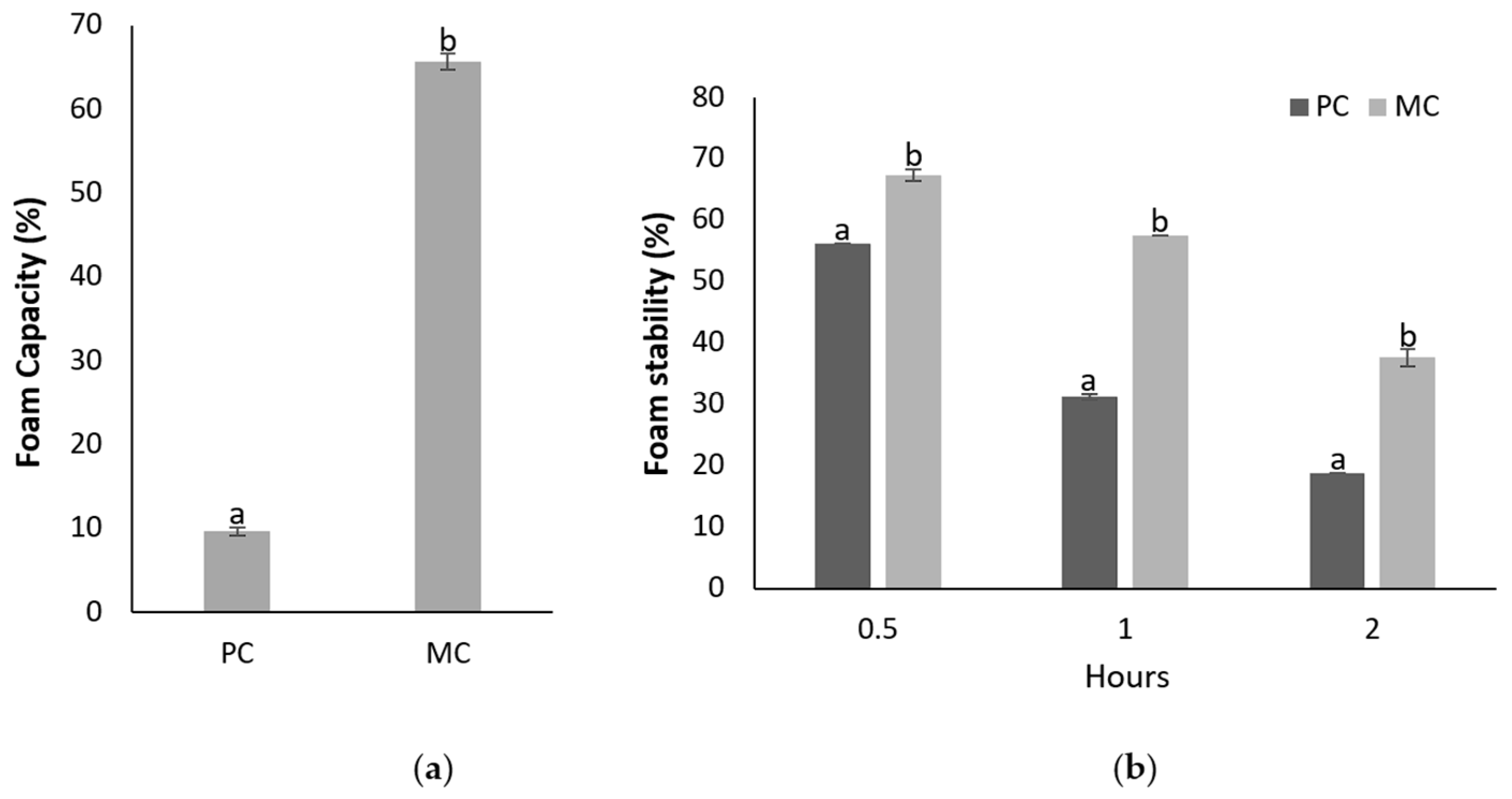
2.12.1. Foam Capacity and Foam Stability
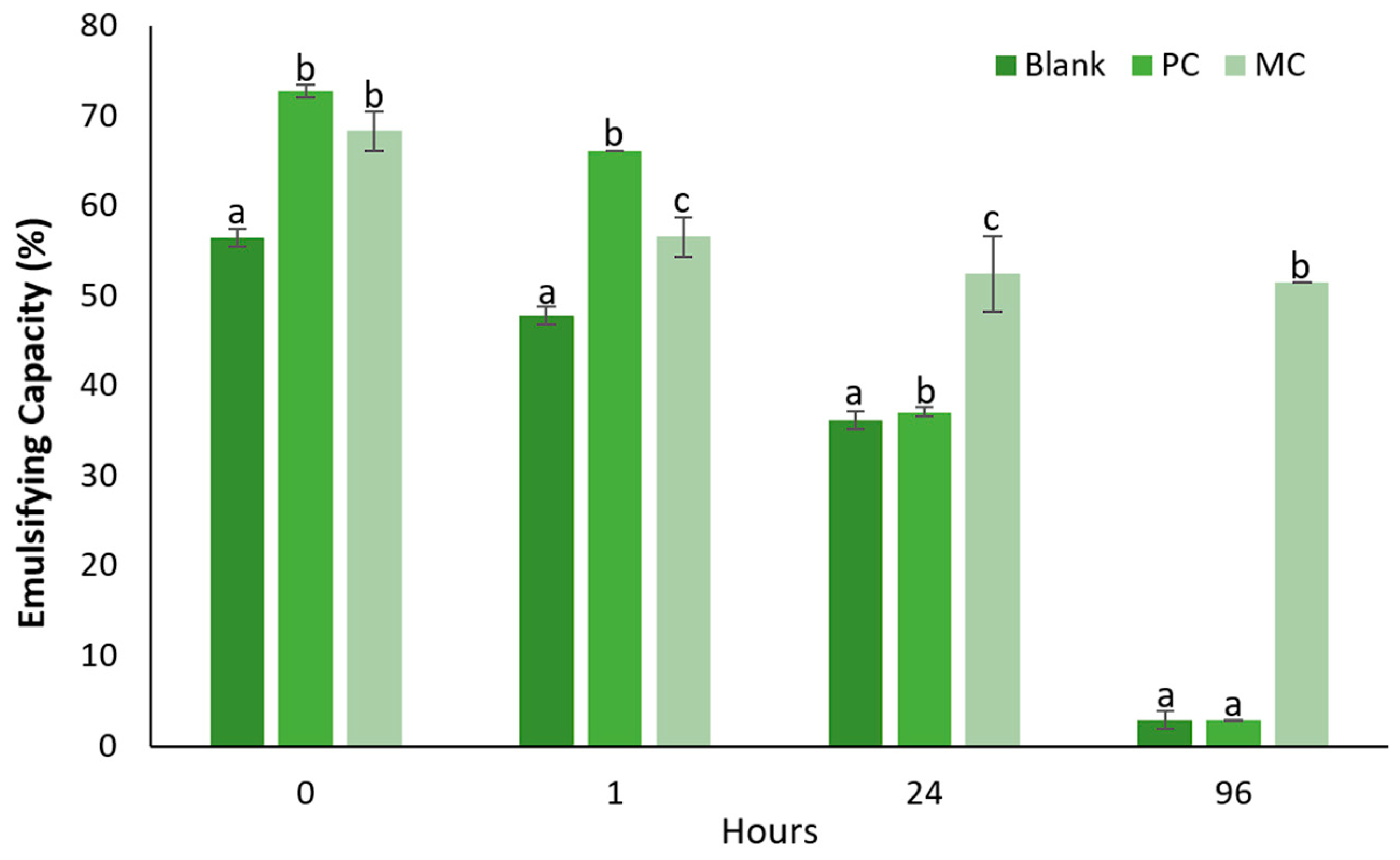
2.12.2. Emulsification Capacity
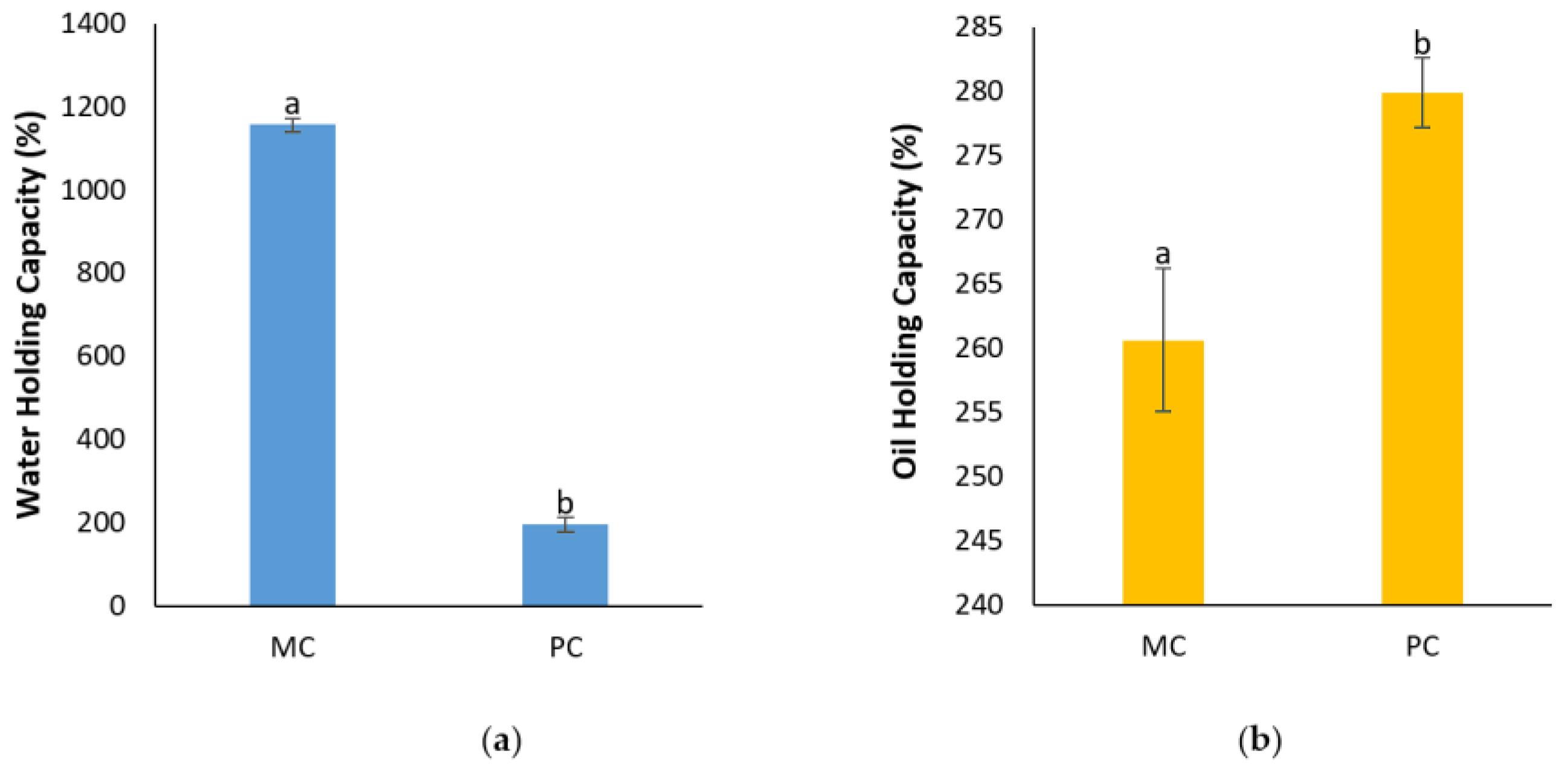
2.12.3. Determination of Water Holding Capacity (WHC) and Oil Holding Capacity (OHC)
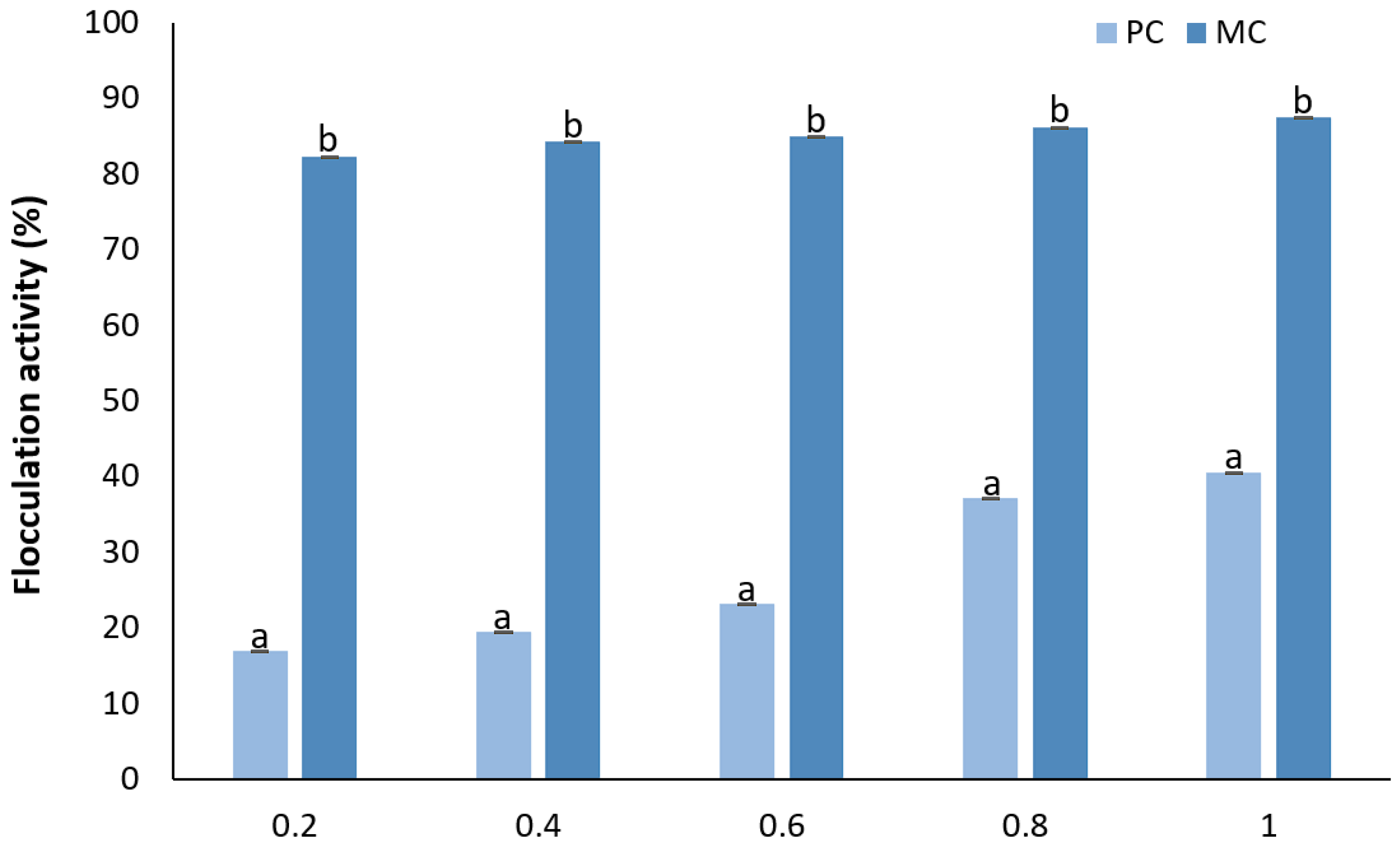
2.12.4. Determination of Flocculation Activity
3. Discussion
3.1. Growth Rate of Culture, Biomass and EPS Production, and Lactose Reduction During Cultivation
3.2. Protein and Sugar Contents
3.3. Fatty Acids Profile of the Biomass
3.4. Antioxidant Activity and Total Polyphenol Contents of the Biomass and EPS
3.5. Chlorophyll and Carotenoids Contents of Biomass
3.6. Functional Properties of EPS
3.6.1. Foaming Capacity and Stability
3.6.2. Emulsifying Capacity and Stability
3.6.3. Water Holding Capacity & Oil Holding Capacity
3.6.4. Flocculation Activity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microalga Cultures
4.2. Cheese Whey (CW) and Microalgae Cultivation
4.2.1. Pretreatment of CW
4.2.2. Algae Cultivation with CW
4.3. Biomass Harvest and EPS Extraction
4.4. Determination of the Lactose Content
4.5. Analysis on EPS
4.5.1. Characterization of EPSs with FT-IR
4.5.2. Determination of the Total Protein Contents of the EPSs and Microalgal Biomass
4.5.3. Determination of the Total Sugar Content of the EPS
4.5.4. Antioxidant Activity of EPSs
4.5.5. Determination of Total Polyphenol Content (TPC)
4.5.6. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of EPS
Foaming Capacity and Stability
Determination of Emulsification Capacity
Determination of the Water Holding Capacity (WHC) & Oil Holding Capacity (OHC)
Flocculation Activity of EPS
4.6. Analysis on Microalgal Biomass
4.6.1. Determination of Total Protein Content
4.6.2. Fatty Acids Profile of Biomass
4.6.3. Determination of Chlorophyll and Carotenoids Content
4.6.4. Antioxidant Activity and Total Polyphenol Content (TPC) of Microalgal Biomass
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nazos, T.; Stratigakis, N.-C.; Spantidaki, M.; Spantidaki, A.; Ghanotakis, D. Characterization of Cheese whey Effluents and Investigation of Their Potential to be used as a Nutrient Substrate for Chlorella Biomass Production. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 3643–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Aadil, R.M.; Ahmed, H.; Rahman, U.U.; Soares, B.C.V.; Souza, S.L.Q.; Pimentel, T.C.; Scudino, H.; Guimarães, J.T.; Esmerino, E.A.; et al. Treatment and utilization of dairy industrial waste: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, D.; Suwal, S.; Ray, C.; Tiwari, B.K.; Jensen, P.E.; Poojary, M.M. Valorization of dairy side-streams for the cultivation of microalgae for value added food products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 104386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2022–2031; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Dairy Market Review: Overview of Global Dairy Market and Policy Developments in 2021; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, F.; Prazeres, A.R.; Rivas, J. Cheese whey wastewater: Characterization and treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 445–446, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesovs, S.; Semjonovs, P. Microalgal conversion of whey and lactose containing substrates: Current state and challenges. Biodegradation 2023, 34, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavov, A.K. General Characteristics and Treatment Possibilities of Dairy Wastewater—A Review. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 55, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolganyuk, V.; Belova, D.; Babich, O.; Prosekov, A.; Ivanova, S.; Katserov, D.; Patyukov, N.; Sukhikh, S. Microalgae: A Promising Source of Valuable Bioproducts. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Tiji, Y.; Fields, F.J.; Mayfield, S.P. Microalgae as a future food source. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 41, 107536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, H.F.; Oswald, W.J.; Gotaas, H.B.; Lynch, V. Algae Symbiosis in Oxidation Ponds: I. Growth Characteristics of “Euglena Gracilis” Cultured in Sewage. Sew. Ind. Wastes 1951, 23, 1337–1355. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, M.R.O.B.; Moura, Y.A.S.; Converti, A.; Porto, A.L.F.; Viana Marques, D.d.A.; Bezerra, R.P. Assessment of the potential of Dunaliella microalgae for different biotechnological applications: A systematic review. Algal Res. 2021, 58, 102396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.; Inácio, L.G.; Afonso, C.; Maranhão, P. The microalga Dunaliella and its applications: A review. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 4, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanette, C.; Mariano, A.; Yukawa, Y.; Mendes, I.; Spier, M. Microalgae mixotrophic cultivation for β-galactosidase production. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Zheng, Y. Overview of microalgal extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and their applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babiak, W.; Krzemińska, I. Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) as Microalgal Bioproducts: A Review of Factors Affecting EPS Synthesis and Application in Flocculation Processes. Energies 2021, 14, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korcz, E.; Varga, L. Exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria: Techno-functional application in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, L.; Ben Ouada, H.; Zili, F.; Mazhoud, N.; Ammar, J. Evaluation of Arthrospira platensis extracellular polymeric substances production in photoautotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic conditions. Folia Microbiol. 2013, 58, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, A.; Xiong, Y.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Radicetti, E.; Umair, M.; Shoukat, M.; Khan, M.K.I.; Aadil, R.M. Recent Advances in the Production of Exopolysaccharide (EPS) from Lactobacillus spp. and Its Application in the Food Industry: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Morgado, M.; Amador-Espejo, G.G.; Pérez-Cortés, M.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A. Microalgae and cyanobacteria polysaccharides: Important link for nutrient recycling and revalorization of agro-industrial wastewater. Appl. Food Res. 2023, 3, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.; Silva, P.; Melo, R.; Ferreira, M.; Porto, A.; Bezerra, R. Microalgal production under mixotrophic conditions using cheese whey as substrate. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2022, 44, e62512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.Y.; Tawfeek, F.E.-Z.; Eltanahy, E.; Mansour, T.A.; Khalil, Z. Enhancement of Growth, Lipid, and Carbohydrate Production of the Egyptian isolate Dunaliella salina SA20 Using Mozzarella Cheese Whey as a Growth Supplement. Egypt. J. Bot. 2022, 63, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, P. Extracellular polymeric substances, a key element in understanding biofilm phenotype. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Saikaly, P.E. Physicochemical Properties of Extracellular Polymeric Substances Produced by Three Bacterial Isolates from Biofouled Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 668761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Bayona, K.C.; Garcés, L.A. Effect of different media on exopolysaccharide and biomass production by the green microalga Botryococcus braunii. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçer, A.T.; İnan, B.; Kaptan Usul, S.; Özçimen, D.; Yılmaz, M.T.; Işıldak, İ. Exopolysaccharides from microalgae: Production, characterization, optimization and techno-economic assessment. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harimawan, A.; Ting, Y.-P. Investigation of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) properties of P. aeruginosa and B. subtilis and their role in bacterial adhesion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecozzi, M.; Pietroletti, M.; Scarpiniti, M.; Acquistucci, R.; Conti, M.E. Monitoring of marine mucilage formation in Italian seas investigated by infrared spectroscopy and independent component analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 6025–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geun Goo, B.; Baek, G.; Jin Choi, D.; Il Park, Y.; Synytsya, A.; Bleha, R.; Ho Seong, D.; Lee, C.-G.; Kweon Park, J. Characterization of a renewable extracellular polysaccharide from defatted microalgae Dunaliella tertiolecta. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Li, D.; Rong, S.; Su, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Acharya, K. Characterization of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) fractions produced by Microcystis aeruginosa under the stress of linoleic acid sustained-release microspheres. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21091–21102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, W.-Z.; Li, A.-F.; Li, T. Comparison on characterization and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharides from two Porphyridium strains. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 2983–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M.; Yousef, N. Optimization of production and intrinsic viscosity of an exopolysaccharide from a high yielding Virgibacillus salarius BM02: Study of its potential antioxidant, emulsifying properties and application in the mixotrophic cultivation of Spirulina platensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Gan, L.; Li, X.; He, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Tian, Y. Characterization of Structural and Physicochemical Properties of an Exopolysaccharide Produced by Enterococcus sp. F2 From Fermented Soya Beans. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 744007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Jha, B. Isolation and characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from micro-algae Dunaliella salina under salt stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3382–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qamar, S.A.; Asgher, M.; Bilal, M. Sustainable Production, Optimization, and Partial Characterization of Exopolysaccharides by Macrococcus brunensis. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 6847–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casá, N.E.; Lois-Milevicich, J.; Alvarez, P.; Mateucci, R.; de Escalada Pla, M. Chlorella vulgaris cultivation using ricotta cheese whey as substrate for biomass production. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velu, P.; Peter, M.J.; Sanniyasi, E. Effect of Various Carbon Sources on Biochemical Production in Marine Microalgae Nannochloropsis salina (Eustigmatophyceae), Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyceae) and Tetraselmis suecica (Chlorodendrophyceae). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, F. Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides from Chlorella zofingiensis and Chlorella vulgaris with anti-colorectal cancer activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Li, Y.; Lan, C.Q. Production and Rheological Studies of Microalgal Extracellular Biopolymer from Lactose Using the Green Alga Neochloris oleoabundans. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Zurano, A.; Villaró-Cos, S.; Ciardi, M.; Acién-Fernández, F.G.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M.; Lafarga, T. Assessment of the mixotrophic production of Chlorella vulgaris using milk whey as a nutrient source. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 36, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.I.B.; Chagas, B.M.E.; Sassi, R.; Medeiros, G.F.; Aguiar, E.M.; Borba, L.H.F.; Silva, E.P.E.; Neto, J.C.A.; Rangel, A.H.N. Mixotrophic cultivation of Spirulina platensis in dairy wastewater: Effects on the production of biomass, biochemical composition and antioxidant capacity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A.P.; Fernandes, B.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.; Dragone, G. Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris using industrial dairy waste as organic carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, K.B.; Ozcan, Y.; Mercan Dogan, N.; Bozkaya, O.; Ide, S. Characterization and Production of Extracellular Polysaccharides (EPS) by Bacillus Pseudomycoides U10. Environments 2018, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.B.F.; Azero, E.G.; Teixeira, C.M.L.L.; Andrade, C.T. Influence of culture conditions on the production of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) by Arthrospira platensis. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2020, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Hyun, S.-H.; Suh, H.W.; Hong, S.-J.; Cho, B.-K.; Lee, C.-G.; Lee, H.; Choi, H.-K. Fatty acids and global metabolites profiling of Dunaliella tertiolecta by shifting culture conditions to nitrate deficiency and high light at different growth phases. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tang, H.; Ma, H.; Holland, T.C.; Ng, K.Y.S.; Salley, S.O. Effect of nutrients on growth and lipid accumulation in the green algae Dunaliella tertiolecta. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lari, Z.; Abrishamchi, P.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Soltani, N. Differential carbon partitioning and fatty acid composition in mixotrophic and autotrophic cultures of a new marine isolate Tetraselmis sp. KY114885. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, M.A.; Gomaa, M. Pretreated fucoidan and alginate from a brown seaweed as a substantial carbon source for promoting biomass, lipid, biochemical constituents and biodiesel quality of Dunaliella salina. Renew. Energy 2020, 157, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şirin, P.A.; Serdar, S. Effects of nitrogen starvation on growth and biochemical composition of some microalgae species. Folia Microbiol. 2024, 69, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaman, S.N.A.; Nagao, N.; Yusoff, F.M.; Tan, S.W.; Yeap, S.K. A comparison of the morphological and biochemical characteristics of Chlorella sorokiniana and Chlorella zofingiensis cultured under photoautotrophic and mixotrophic conditions. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Riofrío, G.; García-Márquez, J.; Casas-Arrojo, V.; Uribe-Tapia, E.; Abdala-Díaz, R.T. Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Effects on Tumor Cells of Exopolysaccharides from Tetraselmis suecica (Kylin) Butcher Grown Under Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Conditions. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiris, K.; Van Colen, W.; Wilches, I.; León-Tamariz, F.; De Cooman, L.; Muylaert, K. Impact of nutrient stress on antioxidant production in three species of microalgae. Algal Res. 2015, 7, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Riofrío, G.; Casas-Arrojo, V.; Pino-Selles, R.; García-Márquez, J.; Abdala-Díaz, R.T.; Uribe-Tapia, E. Adaptation of autotrophic to heterotrophic culture of Porphyridium purpureum (Bory) K.M. Drew & R. Ross: Characterization of biomass and production of exopolysaccharides. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 3603–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Peralta, C.; Maldonado-Pereira, L.; Cantú-Lozano, D.; Medina-Meza, I.G. Mixotrophic cultivation boost nutraceutical content of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis. agriRxiv 2022, 2022, 20220173394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelekan, A.O.; Olurin, T.O.; Ezeani, A.O. Antioxidant Activities of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Commercial Yoghurt Samples. Adv. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-L.; Huang, T.-H.; Liang, T.-W.; Fang, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-L. Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides and antioxidant from Paenibacillus sp. TKU023. New Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.; Sany, H.; El-Sayed, A.E.-K.B.; El-Bahbohy, R.M.; Mohamed, H.I.; Amin, A. Growth Performance and Biochemical Composition of Desmodesmus sp. Green Alga Grown on Agricultural Industries Waste (Cheese Whey). Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.E.S.; Martini, M.; Altomonte, I.; Salari, F.; Nardoni, S.; Sorce, C.; Silva, F.L.H.D.; Andreucci, A. Production of Chlorella protothecoides biomass, chlorophyll and carotenoids using the dairy industry by-product scotta as a substrate. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 11, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.-G.; Lin, Y.-H.; Zhao, D.-X.; Wu, Y.-K.; Yan, R.-R.; Zhao, H.-B.; Tan, Z.-L.; Jia, S.-R.; Han, P.-P. Comparisons of Functional Properties of Polysaccharides from Nostoc flagelliforme under Three Culture Conditions. Polymers 2019, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongi, W.; Cordeiro, N.; Pinchetti, J.L.G.; Ouada, H.B. Functional, rheological, and antioxidant properties of extracellular polymeric substances produced by a thermophilic cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya sp. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, I.; Ktari, N.; Triki, M.; Bkhairia, I.; Ben Slima, S.; Sassi Aydi, S.; Aydi, S.; Abdeslam, A.; Ben Salah, R. Physicochemical, techno-functional, and antioxidant properties of a novel bacterial exopolysaccharide in cooked beef sausage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Malik, S.; Mehwish, H.M.; Ali, M.W.; Hussain, N.; Khurshid, M.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Chen, Y. Isolation and functional characterization of exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum S123 isolated from traditional Chinese cheese. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3061–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Kumar, R.S.; Yuvaraj, N.; Paari, K.A.; Pattukumar, V.; Arul, V. Production and purification of a novel exopolysaccharide from lactic acid bacterium Streptococcus phocae PI80 and its functional characteristics activity in vitro. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillard, R.R.L. Culture of Phytoplankton for Feeding Marine Invertebrates. In Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals: Proceedings—1st Conference on Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals Greenport; Smith, W.L., Chanley, M.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 29–60. ISBN 978-1-4615-8714-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ciempiel, W.; Czemierska, M.; Szymańska-Chargot, M.; Zdunek, A.; Wiącek, D.; Jarosz-Wilkołazka, A.; Krzemińska, I. Soluble Extracellular Polymeric Substances Produced by Parachlorella kessleri and Chlorella vulgaris: Biochemical Characterization and Assessment of Their Cadmium and Lead Sorption Abilities. Molecules 2022, 27, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Zhao, F.; Feng, J.; Liu, Q.; Nan, F.; Xie, S. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from a newly isolated self-flocculating microalga Neocystis mucosa SX with different methods. Algal Res. 2019, 40, 101479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Yuan, T.; Shimizu, K.; Liu, Y.; Lee, D.-J. Insight into the rapid biogranulation for suspended single-cell microalgae harvesting in wastewater treatment systems: Focus on the role of extracellular polymeric substances. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miros, S.; Kiani, H.; Eckhardt, H.-G.; Blanco, A.; Mulcahy, S.; McDonnell, H.; Tiwari, B.K.; Halim, R. Mechanism of lactose assimilation in microalgae for the bioremediation of dairy processing side-streams and co-production of valuable food products. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongi, W.; Cordeiro, N.; Pinchetti, J.L.G.; Sadok, S.; Ben Ouada, H. Extracellular polymeric substances with high radical scavenging ability produced in outdoor cultivation of the thermotolerant chlorophyte Graesiella sp. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, V.; Ramachandran, S.; Balahmar, R.M.; Pandian, S.R.K.; Sivasubramaniam, S.D.; Nellaiah, H.; Sundar, K. In vitro evaluation of anticancer properties of exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus acidophilus in colon cancer cell lines. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2016, 52, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cheng, J.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, S.; Sun, Y. Foaming and Physicochemical Properties of Commercial Protein Ingredients Used for Infant Formula Formulation. Foods 2022, 11, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, N.; Hossain, T.J.; Ali, F.; Das, T.; Dhar, K.; Nafiz, I.H. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and emulsification properties of exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria of bovine milk: Insights from biochemical and genomic analysis. LWT 2023, 186, 115263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Peng, B.; Tian, Y. Preparation, characterization and functional properties of a novel exopolysaccharide produced by the halophilic strain Halomonas saliphila LCB169T. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanmani, P.; Yuvapriya, S. Exopolysaccharide from Bacillus sp. YP03: Its properties and application as a flocculating agent in wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, A.; Budenkova, E.; Babich, O.; Sukhikh, S.; Ulrikh, E.; Ivanova, S.; Prosekov, A.; Dolganyuk, V. Production, Purification, and Study of the Amino Acid Composition of Microalgae Proteins. Molecules 2021, 26, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Fallon, J.V.; Busboom, J.R.; Nelson, M.L.; Gaskins, C.T. A direct method for fatty acid methyl ester synthesis: Application to wet meat tissues, oils, and feedstuffs. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, Y.; Su, M.; Kyaw, K. Extraction and Determination of Chlorophyll Content from Microalgae. 2017. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Extraction-And-Determination-Of-Chlorophyll-Content-Oo-Su/bee975ee7eea78e2713837cab316c2c103eafdef (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Farobie, O.; Anis, L.A.; Nurcahyani, P.R.; Hartulistiyoso, E.; Rahman, D.Y.; Fatriasari, W.; Nafisyah, A.L.; Amrullah, A.; Aziz, M. Extraction of Bio-pigments from the Green Microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa Under Different Solvent Ratios. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1187, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Pei, H.; Xiang, W.; Li, T.; Lin, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, C.; Wu, H. Rapid Screening of Microalgae as Potential Sources of Natural Antioxidants. Foods 2023, 12, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Growth Rate (day−1) | Dry Biomass (g L−1) | EPSs (g L−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 0.29 a ± 0.014 | 0.30 a ± 0.001 | 1.99 a ± 0.002 |
| MC (20% CW) | 0.31 a ± 0.019 | 2.51 b ± 0.003 | 2.60 b ± 0.002 |
| Material | Result (%) |
|---|---|
| Proteins | 1.37 |
| Sugars | 4.20 |
| Fat | 0.25 |
| Carbohydrates | 4.29 |
| Dry matter | 6.54 |
| Moisture | 93.46 |
| Crude ash | 0.63 |
| Total dietary fibers | <0.30 |
| Lactose | 2.96 |
| Fatty Acid | PC | MC (20% CW) |
|---|---|---|
| C4:0 | 16.39 ± 0.36 | 35.57 ± 1.24 |
| C6:0 | 4.66 ± 0.15 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C8:0 | 3.75 ± 0.08 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C10:0 | 5.35 ± 0.1 | 5.51 ± 0.15 |
| C12:0 | 2.28 ± 0.02 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C13:0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 1.29 ± 0.05 |
| C14:0 | 4.38 ± 0.12 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C15:1 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 2.37 ± 0.08 |
| C16:0 | 27.93 ± 0.90 | 28.55 ± 0.80 |
| C16:1 | 7.79 ± 0.12 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C17:1 | 4.56 ± 0.08 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C18:0 | 4.02 ± 0.05 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C18:1n9c | 8.26 ± 0.06 | 4.82 ± 0.06 |
| C18:2n6t | 2.79 ± 0.02 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C18:2n6c | 1.8 ± 0.02 | 5.32 ± 0.08 |
| C18:3n3 | 6.04 ± 0.09 | 16.56 ± 1.08 |
| SFAs a | 68.76 ± 1.78 | 70.92 ± 2.24 |
| UFAs b | 31.24 ± 0.39 | 29.07 ± 1.3 |
| MUFAs c | 20.61 ± 0.26 | 7.19 ± 0.14 |
| PUFAs d | 10.63 ± 0.13 | 21.88 ± 1.16 |
| Chlorophyll (mg g−1) | Carotenoids (mg g−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| PC | 20.85 a ± 0.05 | 21.55 a ± 0.11 |
| MC (20% CW) | 7.31 b ± 0.06 | 8.07 b ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsotsouli, K.; Didos, S.; Koukaras, K.; Argiriou, A. Mixotrophic Cultivation of Dunaliella tertiolecta in Cheese Whey Effluents to Enhance Biomass and Exopolysaccharides (EPS) Production: Biochemical and Functional Insights. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030120
Tsotsouli K, Didos S, Koukaras K, Argiriou A. Mixotrophic Cultivation of Dunaliella tertiolecta in Cheese Whey Effluents to Enhance Biomass and Exopolysaccharides (EPS) Production: Biochemical and Functional Insights. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(3):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030120
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsotsouli, Konstantina, Spyros Didos, Konstantinos Koukaras, and Anagnostis Argiriou. 2025. "Mixotrophic Cultivation of Dunaliella tertiolecta in Cheese Whey Effluents to Enhance Biomass and Exopolysaccharides (EPS) Production: Biochemical and Functional Insights" Marine Drugs 23, no. 3: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030120
APA StyleTsotsouli, K., Didos, S., Koukaras, K., & Argiriou, A. (2025). Mixotrophic Cultivation of Dunaliella tertiolecta in Cheese Whey Effluents to Enhance Biomass and Exopolysaccharides (EPS) Production: Biochemical and Functional Insights. Marine Drugs, 23(3), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030120








