Marmaricines A-C: Antimicrobial Brominated Pyrrole Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Agelas sp. aff. marmarica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Purification of Compounds 1–3
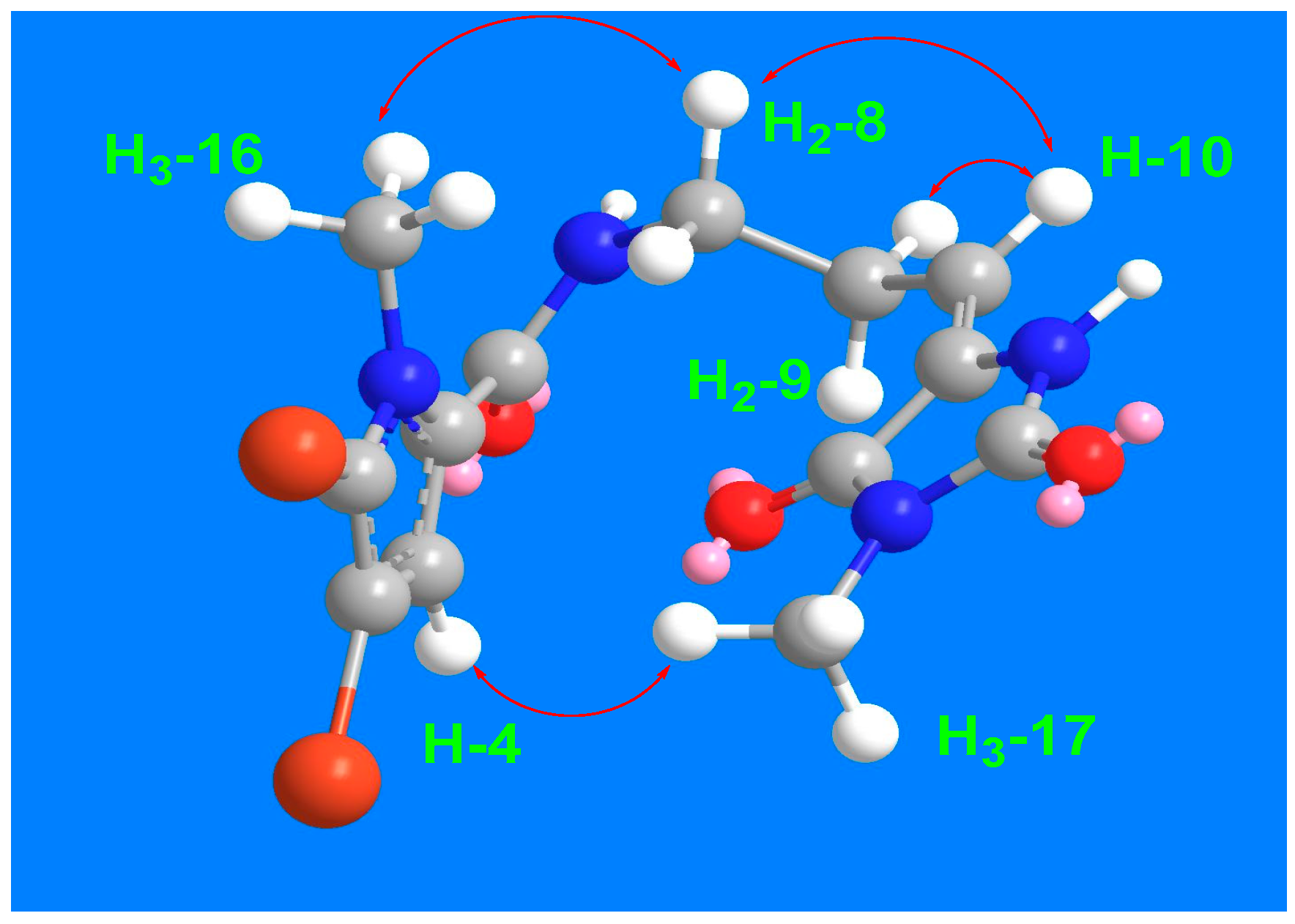
2.2. Structure of Compound 1
2.3. Structure of Compound 2
2.4. Structure of Compound 3
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Materials
3.3. Purification of the Compounds
3.4. Spectral Data of 1–3
3.4.1. Marmaricine A (1)
3.4.2. Marmaricine B (2)
3.4.3. Marmaricine C (3)
3.5. Antimicrobial Activities of the Compounds
3.5.1. Disk Diffusion Assay
3.5.2. Evaluation of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
3.5.3. Determination of the Minimum Bactericidal Concentrations (MBCs)
3.5.4. Assessment of the Minimum Fungicidal Concentrations (MFCs)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stehli, F.G.; Wells, J.W. Diversity and Age Patterns in Hermatypic Corals. Syst. Zool. 1971, 20, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBattista, J.D.; Roberts, M.B.; Bouwmeester, J.; Bowen, B.W.; Coker, D.J.; Lozano-Cortés, D.F.; Choat, J.H.; Gaither, M.R.; Hobbs, J.P.A.; Khalil, M.T.; et al. A Review of Contemporary Patterns of Endemism for Shallow Water Reef Fauna in the Red Sea. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, G.O.; Burt, J.A. The changing dynamics of coral reef science in Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaet, J.L.; Thorrold, S.R.; Berumen, M.L. A Review of Elasmobranch Research in the Red Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, F.J. Climate and Oceanography. In Red Sea; Edwards, A.J., Head, S., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 45–68. [Google Scholar]
- Voolstra, C.R.; Miller, D.J.; Ragan, M.A.; Hoffmann, A.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Bourne, D.; Ball, E.; Ying, H.; Foret, S.; Takahashi, S.; et al. The ReFuGe 2020 Consortium—Using “Omics” Approaches to Explore the Adaptability and Resilience of Coral Holobionts to Environmental Change. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 68. [Google Scholar]
- van Soest, R.W.M.; Beglinger, E.J. Tetractinellid and Hadromerid Sponges of the Sultanate of Oman. Zool. Meded. 2008, 82, 749–790. [Google Scholar]
- Berumen, M.L.; Hoey, A.S.; Bass, W.H.; Bouwmeester, J.; Catania, D.; Cochran, J.E.; Khalil, M.T.; Miyake, S.; Mughal, M.R.; Spät, J.L.; et al. The Status of Coral Reef Ecology Research in the Red Sea. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.K.; Voigt, O.; Erpenbeck, D.; Wörheide, G.; Berumen, M.L. Sponges of the Red Sea. In Coral Reefs of the Red Sea. Coral Reefs of the World; Voolstra, C., Berumen, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, M.-J.; Li, M.; Ma, H.; Li, P.-L.; Li, G.-Q. Secondary metabolites from marine sponges of the Genus Agelas: A Comprehensive Update Insight on Structural Diversity and Bioactivity. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 7789–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forenza, S.; Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Fattorusso, E. New Bromopyrrole Derivatives from the Sponge Agelas oroides. Chem. Commun. 1971, 18, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, E.; Devlin, J.P. Agelasine: A Novel Quaternary 9-Methyladenine from the Sponge Agelas dispar. Can. J. Chem. 1975, 53, 1690–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafieri, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Clathramides, Unique Bromopyrrole Alkaloids from the Caribbean Sponge Agelas clathrodes. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 13713–13720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, M.; Lichte, E.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Köck, M. New Bromopyrrole Alkaloid from the Marine Sponge Agelas wiedenmayeri. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusama, T.; Tanaka, N.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Gonoi, T.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Bromopyrrole Alkaloids from a Marine Sponge Agelas sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Iwai, T.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Fromont, J.; Gonoi, T.; Kobayashi, J. Agelasines O–U, New Diterpene Alkaloids with a 9-N-Methyladenine Unit from a Marine Sponge Agelas sp. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9738–9744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bourne, G.T.; Christoph, C.A.; Leet, J.E.; Knight, J.C.; Pettit, R.K.; Chapuis, J.-C.; Doubek, D.L.; et al. Isolation and Structures of Axistatins 1–3 from the Republic of Palau Marine Sponge Agelas axifera Hentschel. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemoto, H.; Tsuda, M.; Kobayashi, J. Mukanadins A–C, New Bromopyrrole Alkaloids from Marine Sponge Agelas nakamurai. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1581–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroif-Gregoire, C.; Appenzeller, J.; Debitus, C.; Zaparucha, A.; Al-Mourabit, A. Debromokeramadine from the Marine Sponge Agelas cf. mauritiana: Isolation and Short Regioselective and Flexible Synthesis. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 3609–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, B.-B.; Yang, F.; Jiao, W.-H.; Hu, G.-H.; Yu, H.-B.; Han, B.-N.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; et al. Antifungal Bromopyrrole Alkaloids from the South China Sea Sponge Agelas sp. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 2964–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Wu, H.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y. Agelasine-A, -B, -C and -D, Novel Bicycle Diterpenoids with a 9-Methylladeninium Unit Possessing Inhibitory Effects on Na-K-ATPase from the Okinawan Sea Sponge Agelas sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 2989–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Faulkner, D.J. Antimicrobial Metabolites from a Pacific Sponge, Agelas sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 1819–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, B.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tang, X.-L.; Wang, Q.; Chu, M.-J.; Li, P.-L.; Li, G.-Q. Two New Diterpene Alkaloids from the South China Sea Sponge Agelas aff. Nemoechinata. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Wu, H.; Kobayashi, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y. Agelasidines, Novel Hypotaurocyamine Derivatives from the Okinawan Sea Sponge Agelas nakamurai Hoshinot. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 2494–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J.; Tanner, R.S.; Kelly-Borges, M. Agelasines H and I, 9-Methyladenine-Containing Diterpenoids from an Agelas Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vik, A.; Hedner, E.; Charnock, C.; Samuelsen, Ø.; Larsson, R.; Gundersen, L.-L.; Bohlin, L. (+)-Agelasine D: Improved Synthesis and Evaluation of Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Two Novel Pyrrole-Imidazole Alkaloids from the Mediterranean Sponge Agelas oroides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 9917–9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appenzeller, J.; Mihci, G.; Martin, M.-T.; Gallard, J.-F.; Menou, J.-L.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Hooper, J.; Petek, S.; Chevalley, S.; Valentin, A.; et al. Agelasines J, K, and L from the Solomon Islands Marine Sponge Agelas cf. mauritiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, K.; Ishibashi, M.; Shigemori, H.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Agelasine G, A New Antileukemic Alkaloid from the Okinawan Marine Sponge Agelas sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 766–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertiani, T.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ortlepp, S.; van Soest, R.W.M.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Hentschel, U.; Kozytska, S.; Müller, W.E.G.; Proksch, P. From Anti-Fouling to Biofilm Inhibition: New Cytotoxic Secondary Metabolites from Two Indonesian Agelas Sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, T.; Adachi, K.; Shizuri, Y. New Agelasine Compound from the Marine Sponge Agelas mauritiana as an Antifouling Substance Against Macroalgae. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Nakao, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Seiki, M.; Itoh, Y.; Yamashita, J.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Ageladine A: An Antiangiogenic Matrixmetalloproteinase Inhibitor from the Marine Sponge Agelas nakamurai. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15700–15701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A. Hemimycalins C–E; Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Alkaloids with Hydantoin and 2-Iminoimidazolidine-4-one Backbones from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale sp. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A. Pseudoceratonic Acid and Moloka’iamine Derivatives from the Red Sea Verongiid Sponge Pseudoceratina arabica. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Tanaka, N.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuji, D.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kojoma, M.; Itoh, K.; Kobayashi, J.; Kashiwada, Y. Agesasines A and B, Bromopyrrole Alkaloids from Marine Sponges Agelas spp. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yuan, T.; Lan, P.; White, L.V.; Chen, J.; Banwell, M.G. Syntheses and Preliminary Biological Evaluations of the Dibromopyrrole-Containing Marine Natural Products Agesasine A, Agesasine B, Longamide E and Various Congeners. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 26, e202300003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindel, L.; Hoffmann, H. Synthesis of rac-Midpacamide and the spiro-C yclization of Its Precursor. Liehigs Ann. 1997, 1997, 1525–1528. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 11th ed.; CLSI Standard M07; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 13th ed.; CLSI Standard M02; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kiehlbauch, J.A.; Hannett, G.E.; Salfinger, M.; Archinal, W.; Monserrat, C.; Carlyn, C. Use of the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards Guidelines for Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Testing in New York State Laboratories. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Shaala, L.A.; Genta-Jouve, G. Asperopiperazines A and B: Antimicrobial and cytotoxic dipeptides from a tunicate-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. DY001. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, J.F. The Disc Susceptibility Test. In Antibiotics in Laboratory Medicine; Lorian, V., Ed.; Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1980; pp. 24–54. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Shaala, L.A. Magnificines A and B, Antimicrobial Marine Alkaloids Featuring a tetrahydrooxazolo [3,2-a]azepine-2,5(3H, 6H)-dione Backbone from the Red Sea Sponge Negombata magnifica. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Position | δC, Type | δH (Mult., J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH (Mult., J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH (mult., J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 1 | 2 1 | 3 2 | ||||
| 1 | 12.65 (s) | 9.05 (brs) | ||||
| 2 | 104.9, C | 167.5, C | 111.9, C | |||
| 3 | 98.2, C | 120.3, C | 99.2, C | |||
| 4 | 112.9, CH | 6.90 (s) | 147.0, CH | 7.24 (t, 1.6) | 116.1, CH | 6.82 (s) |
| 5 | 128.6, C | 87.8, C | 129.4, C | |||
| 6 | 159.4, C | 167.3, C | 161.4, C | |||
| 7 | 8.14 (t, 5.6) | 8.21 (t, 5.9) | ||||
| 8 | 38.3, CH2 | 3.21 (q, 6.5) | 38.8, CH2 | 3.07 (q, 7.8) | 39.2, CH2 | 3.45 (t, 7.5) |
| 9 | 25.0, CH2 | 1.73 (quin., 7.1) | 24.7, CH2 | 1.65 (quin., 7.2) | 28.8, CH2 | 2.61 (q, 7.5) |
| 10 | 31.1, CH2 | 2.34 (t, 7.4) | 31.0, CH2 | 2.27 (t, 7.5) | 120.5, CH | 6.24 (t, 7.5) |
| 11 | 173.6, C | 173.6, C | 130.0, C | |||
| 12 | 51.7, CH3 | 3.57 (s) | 51.7, CH3 | 3.55 (s) | 163.1, C | |
| 13 | ||||||
| 14 | 154.0, C | |||||
| 16 | 36.4, CH3 | 3.90 (s) | ||||
| 17 | 26.5, CH3 | 3.20 (s) | ||||
| Compound | MRSA | C. albicans | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition Zone (mm) | MIC (μg/mL) | MBC (μg/mL) | Inhibition Zone (mm) | MIC (μg/mL) | MFC (μg/mL) | |
| 1 | 14 | 8 | 16 | NI 4 | NT | NT |
| 2 | 15 | 8 | 16 | 15 | 8 | 16 |
| 3 | 12 | 16 | 32 | 14 | 8 | 16 |
| Ciprofloxacin 1 | 15 | 0.25 | 1.0 | NT | NT | NT |
| Clotrimazole 2 | NT 3 | NT | NT | 18 | 0.125 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youssef, D.T.A.; Alqarni, A.S.; Almohammadi, A.M.; Abujamel, T.; Shaala, L.A. Marmaricines A-C: Antimicrobial Brominated Pyrrole Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Agelas sp. aff. marmarica. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020080
Youssef DTA, Alqarni AS, Almohammadi AM, Abujamel T, Shaala LA. Marmaricines A-C: Antimicrobial Brominated Pyrrole Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Agelas sp. aff. marmarica. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(2):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020080
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoussef, Diaa T. A., Areej S. Alqarni, Ameen M. Almohammadi, Turki Abujamel, and Lamiaa A. Shaala. 2025. "Marmaricines A-C: Antimicrobial Brominated Pyrrole Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Agelas sp. aff. marmarica" Marine Drugs 23, no. 2: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020080
APA StyleYoussef, D. T. A., Alqarni, A. S., Almohammadi, A. M., Abujamel, T., & Shaala, L. A. (2025). Marmaricines A-C: Antimicrobial Brominated Pyrrole Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Agelas sp. aff. marmarica. Marine Drugs, 23(2), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23020080









