Obtainment of Two Monomorphic Nematocysts from Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and Comparative Analysis of the Biological Activities of Their Contents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
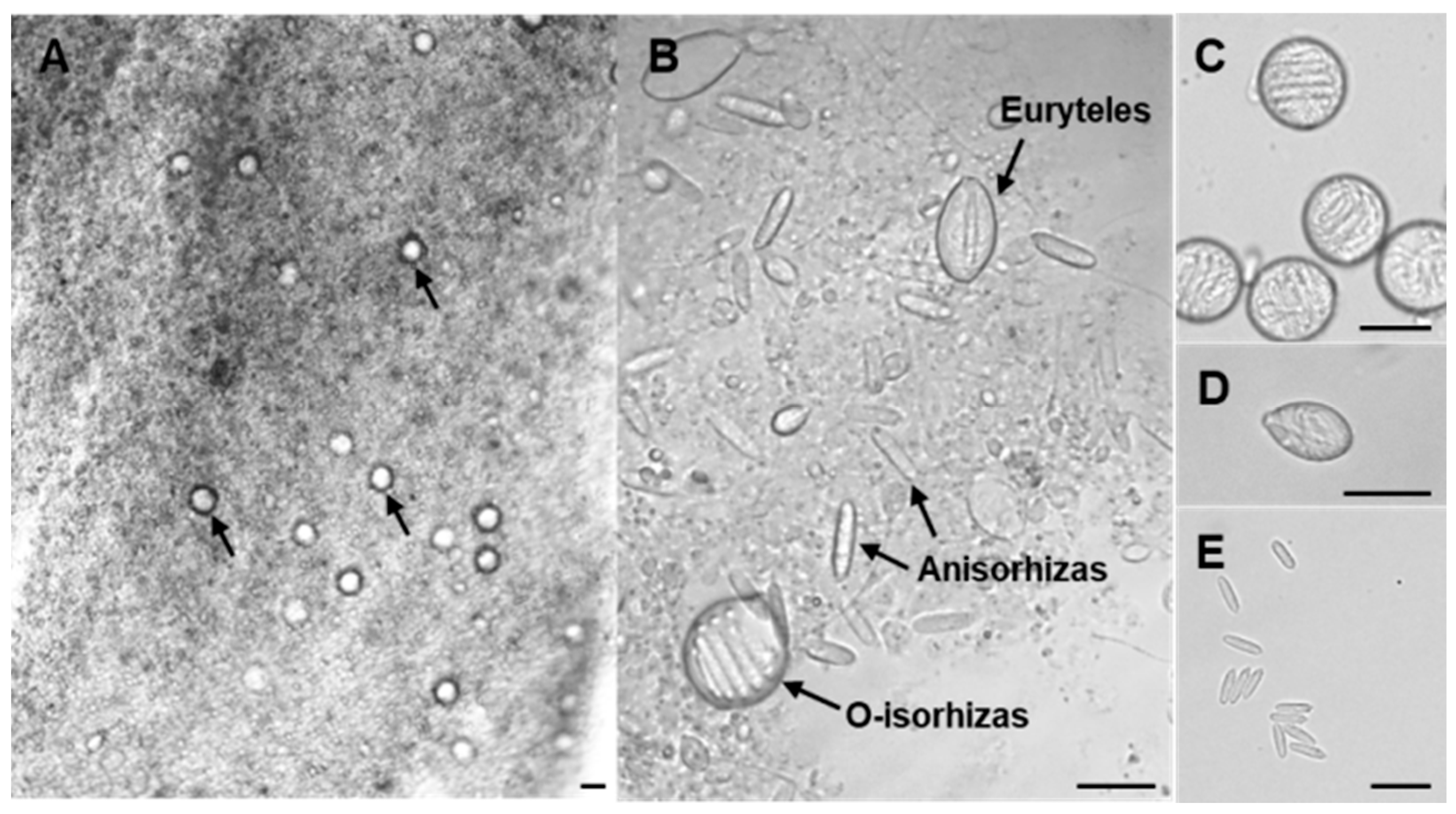
2.1. Microscopic Morphology of N. nomurai Nematocysts
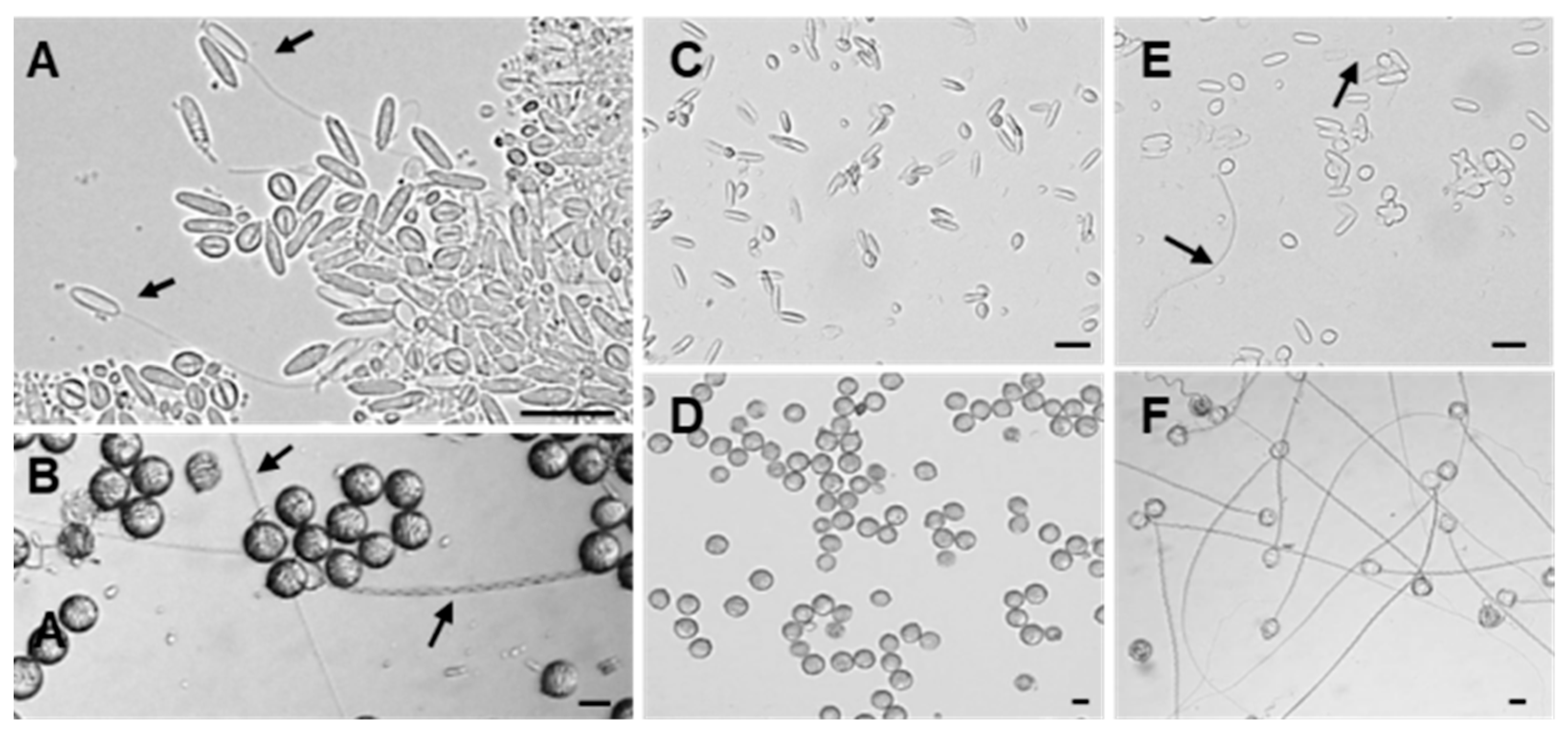
2.2. Discharge Abilities of Anisorhizas and O-Isorhizas
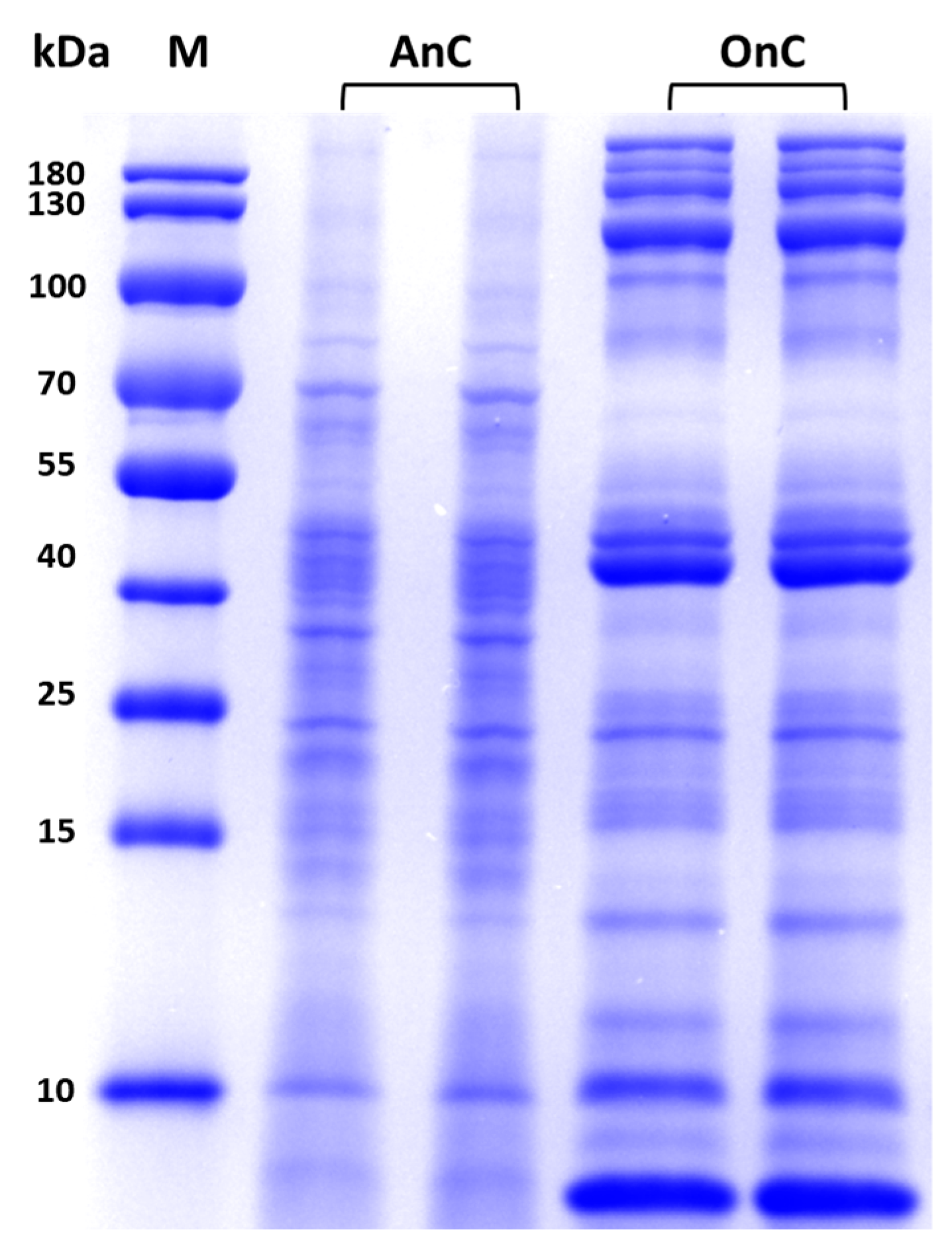
2.3. Protein Composition in Nematocysts
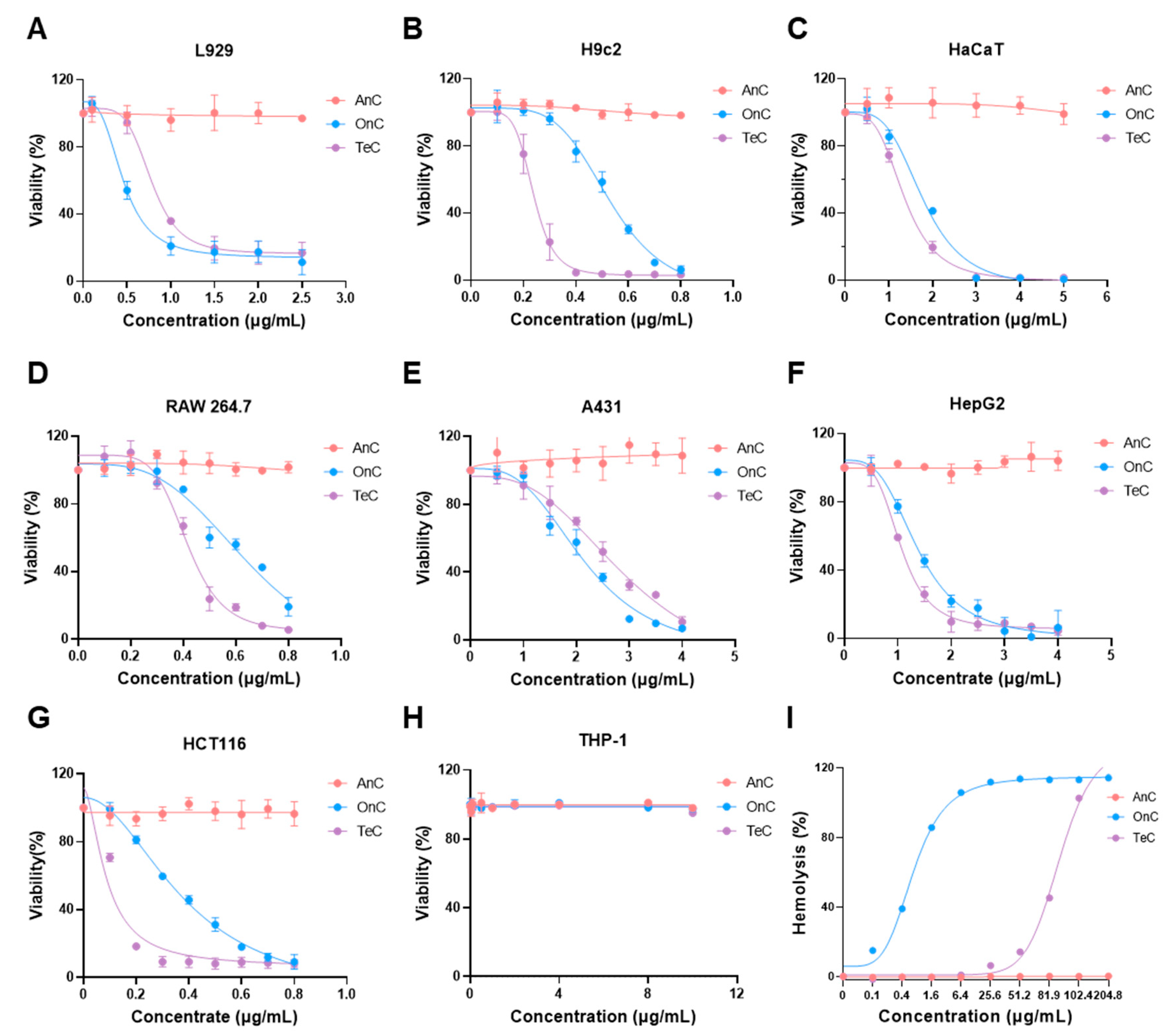
2.4. Cytotoxicity of AnC and OnC
2.5. Hemolytic Effects of AnC and OnC
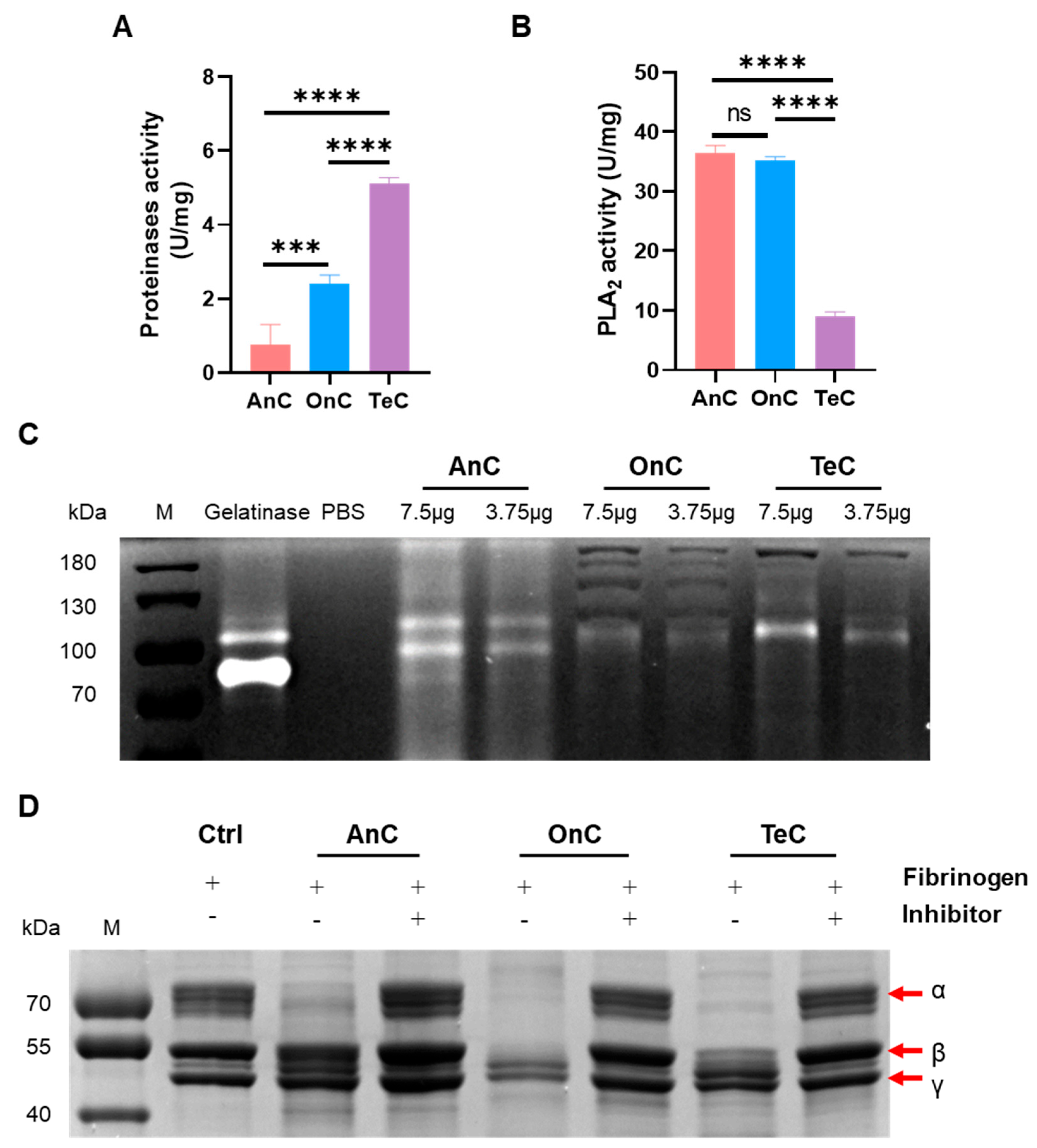
2.6. Enzyme Activity of AnC and OnC
2.6.1. Protease Activity
2.6.2. Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) Activity
2.6.3. Serine Protease Activity
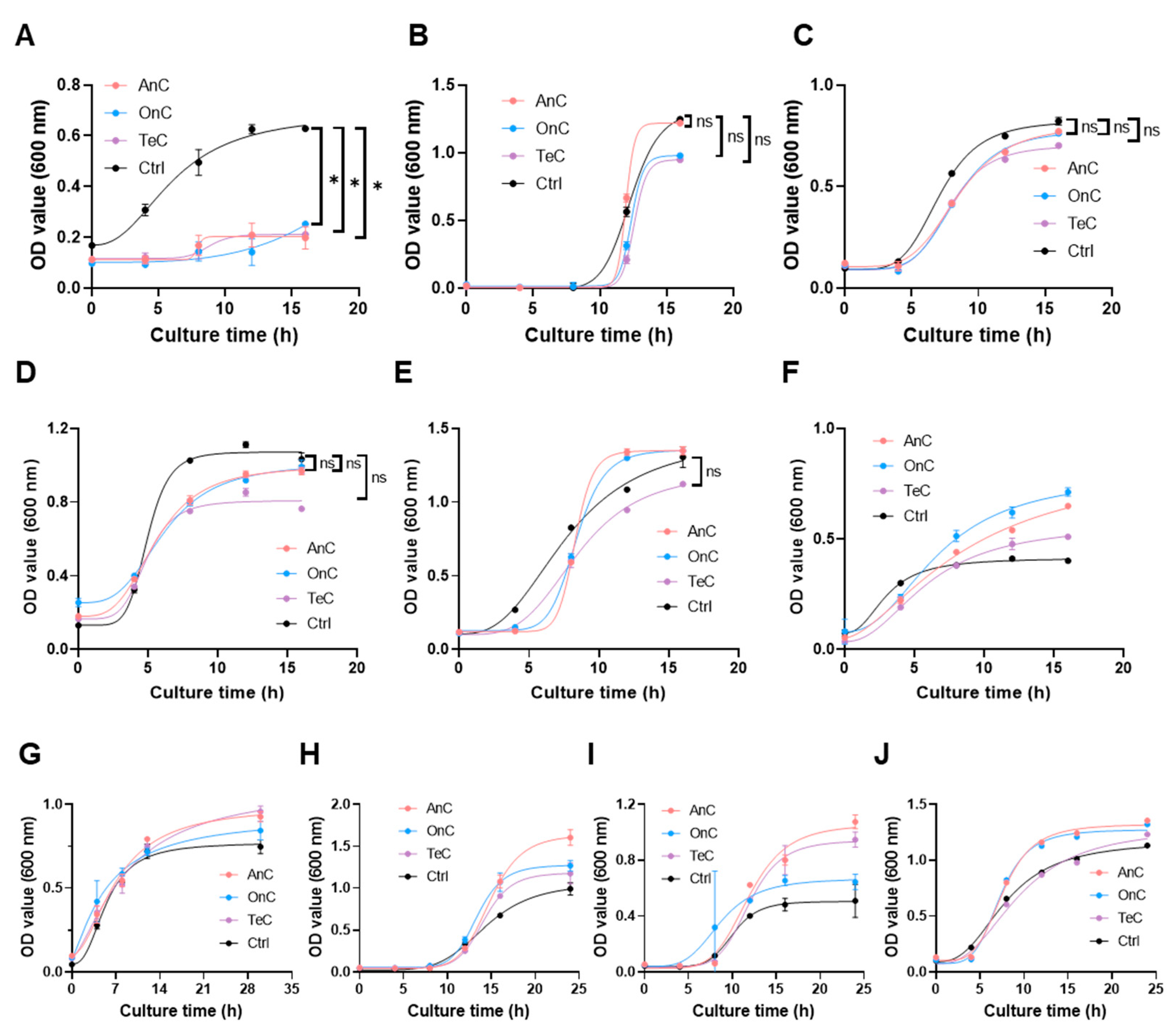
2.7. Antimicrobial Activity of AnC and OnC
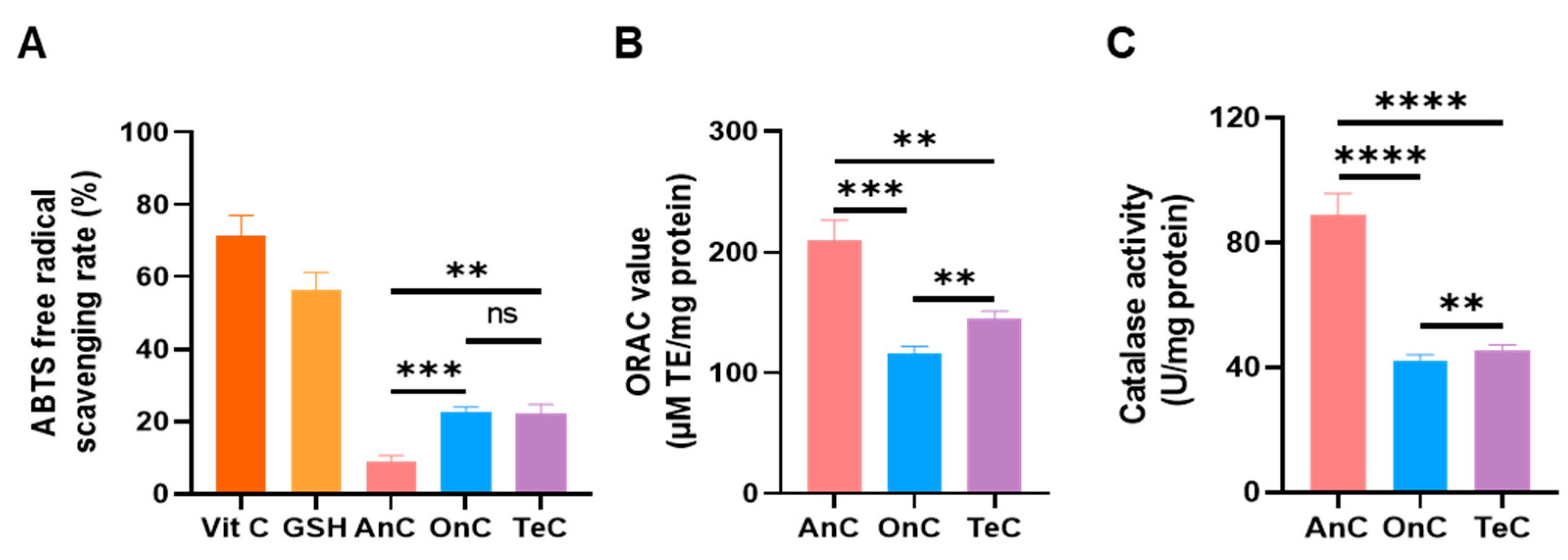
2.8. Antioxidant Activity of AnC and OnC
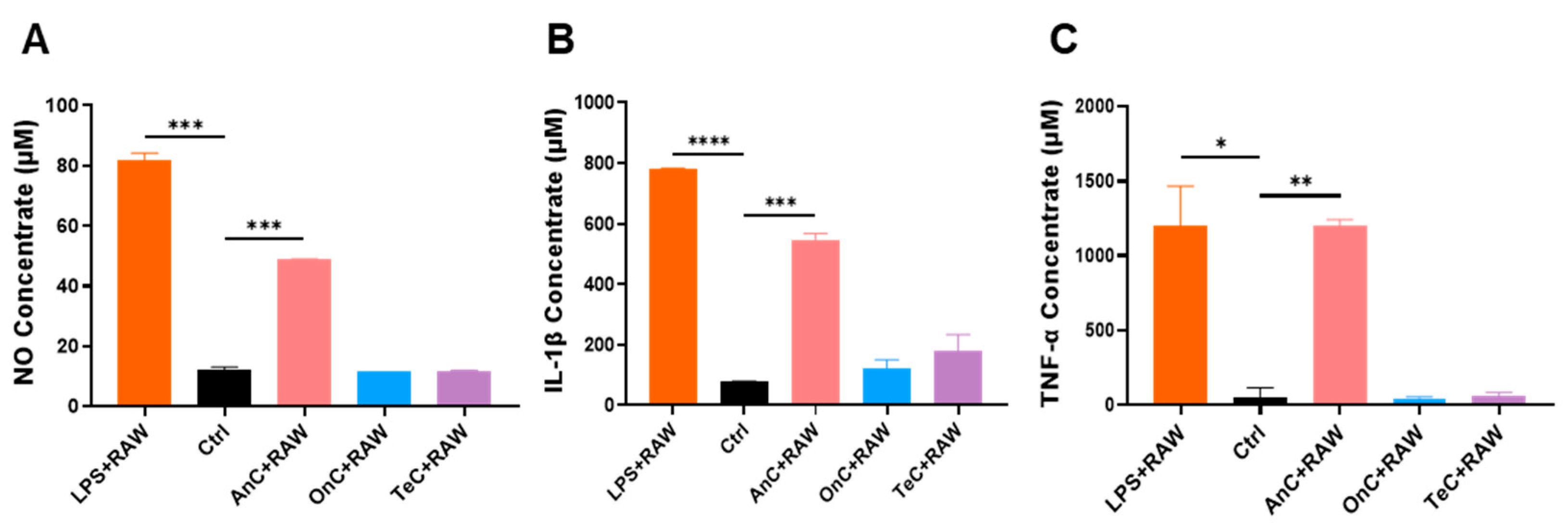
2.9. Proinflammatory Effects of AnC and OnC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Jellyfish Collection
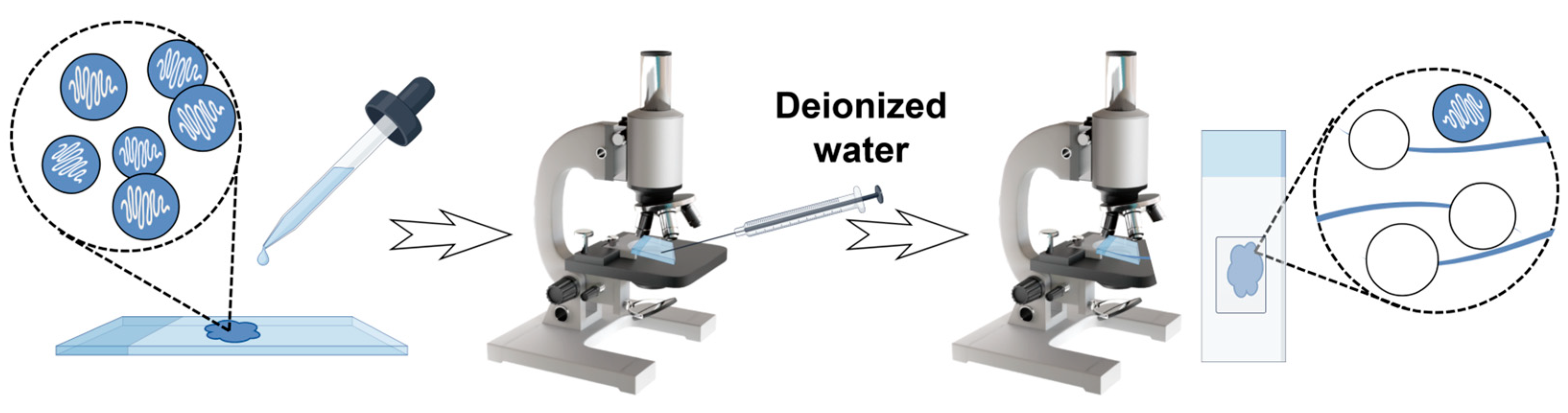
4.3. Isolation and Purification of Two Monomorphic Nematocysts
4.3.1. Isolation and Purification of Anisorhizas
4.3.2. Isolation and Purification of O-Isorhizas
4.4. Nematocyst Content Extraction and SDS-PAGE Analysis
4.5. Assessment of Nematocyst Discharge Capacity
4.6. N. nomurai Tentacle Extraction
4.7. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.8. Enzyme Activity Assays
4.8.1. Protease Activity Assay Using Azocasein
4.8.2. Zymography of Proteases
4.8.3. PLA2 Activity
4.8.4. Fibrinogenolytic Assay
4.9. Hemolysis Assays
4.10. Antimicrobial Activity
4.11. Antioxidant Activity Assay
4.11.1. ABTS+ Scavenging Assay
4.11.2. Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity
4.11.3. Catalase Activity Assay
4.12. Nitric Oxide Measurement and Cytokine Assay
4.12.1. Nitric Oxide Measurement
4.12.2. Cytokine Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AnC | Anisorhizas nematocyst content |
| OnC | O-isorhizas nematocyst content |
| TeC | Tentacle extract content |
| NOBA | 4-nitro-3-octanoyloxybenzoic acid |
| T-AOC | Total Antioxidant Capacity |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| ORAC | Oxygen radical absorbance capacity |
| AMPs | Antimicrobial peptides |
| TE | Trolox equivalent |
| CAT | Catalase |
References
- Kim, J.H.; Han, S.B.; Durey, A. Fatal Pulmonary Edema in a Child after Jellyfish Stings in Korea. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2018, 29, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remigante, A.; Costa, R.; Morabito, R.; La Spada, G.; Marino, A.; Dossena, S. Impact of Scyphozoan Venoms on Human Health and Current First Aid Options for Stings. Toxins 2018, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, M.-J.; Lee, H.; Bae, S.; Heo, Y.; Choudhary, I.; Yoon, W.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Modulation of Jellyfish Nematocyst Discharges and Management of Human Skin Stings in Nemopilema nomurai and Carybdea mora. Toxicon 2016, 109, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killi, N.; Mariottini, G.L. Cnidarian Jellyfish:Ecological Aspects, Nematocyst Isolation, and Treatment Methods of Sting. In Marine Organisms as Model Systems in Biology and Medicine; Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 65, pp. 477–513. [Google Scholar]
- Killi, N.; Mariottini, G.L.; Tekin, İ.; Azaiez, K. Neurotoxic Effects of Alicia mirabilis and Aurelia aurita Venoms on Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896: Behavioural Results. J. Biol. Res.-Boll. Della Soc. Ital. Di Biol. Sper. 2025, 98, 12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Hua, X.; Danso, B.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; et al. Insights into the Discovery and Intervention of Metalloproteinase in Marine Hazardous Jellyfish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, M.M.; Eissa, N.; Althobaiti, F.; Fayad, E.; Abu Almaaty, A.H. Nomad Jellyfish Rhopilema nomadica Venom Induces Apoptotic Cell Death and Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Balde, A.; Nazeer, R.A. A Review on Animal Venom-Based Matrix Metalloproteinase Modulators and Their Therapeutic Implications. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 157, 114703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Bae, S.; Hwang, D.H.; Prakash, R.L.M.; Kim, J.-H.; Hong, I.-H.; Kim, W.H.; Rho, I.R.; Kim, E.; Kang, C. Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom Attenuates Phenotypic Modulation of PDGF BB-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and κ-Carrageenan-Induced Rat Tail Thrombosis. Toxicon 2023, 233, 107266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, A.A.; Giglio, M.L.; Hurwitz, K.; Kadler, R.; Espino, S.S.; Raghuraman, S.; Olivera, B.M. Elucidation of Medusozoan (Jellyfish) Venom Constituent Activities Using Constellation Pharmacology. Toxins 2024, 16, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Cai, S.; Li, P. Isolation and Characterization of Lethal Proteins in Nematocyst Venom of the Jellyfish Cyanea nozakii Kishinouye. Toxicon 2010, 55, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrette, T.J.; Cullen, P.; Little, M.; Peiera, P.L.; Seymour, J.E. Temperature Effects on Box Jellyfish Venom: A Possible Treatment for Envenomed Patients? Med. J. Aust. 2002, 177, 654–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, I.; Burnett, J.W. Techniques Applicable for Purifying Chironex Fleckeri (Box-Jellyfish) Venom. Toxicon 1990, 28, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, B.L.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; He, Q.; Zhang, L. Unique Diversity of Sting-Related Toxins Based on Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis of the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata and Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitatani, R.; Yamada, M.; Kamio, M.; Nagai, H. Length Is Associated with Pain: Jellyfish with Painful Sting Have Longer Nematocyst Tubules than Harmless Jellyfish. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstein, T.; Tardent, P. An Ultrahigh-Speed Analysis of Exocytosis: Nematocyst Discharge. Science 1984, 223, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Piriatinskiy, G.; Zeevi, D.; Ben-David, J.; Yossifon, G.; Shavit, U.; Lotan, T. The Nematocyst’s Sting Is Driven by the Tubule Moving Front. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20160917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajollahi, S.; Dennis, P.B.; Crosby, M.G.; Slocik, J.M.; Pelton, A.T.; Hampton, C.M.; Drummy, L.F.; Yang, S.J.; Silberstein, M.N.; Gupta, M.K.; et al. Disulfide Crosslinked Hydrogels Made from the Hydra Stinging Cell Protein, Minicollagen-1. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass-Simon, G.; Scappaticci, A.A. The Behavioral and Developmental Physiology of Nematocysts. Can. J. Zool. 2002, 80, 1772–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostman, C. A Guideline to Nematocyst Nomenclature and Classification, and Some Notes on the Systematic Value of Nematocysts. Sci. Mar. 2000, 64, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, C. 26—Nematocysts as Taxonomic Criteria Within the Family Campanulariidae, Hydrozoa. In The Biology of Nematocysts; Hessinger, D.A., Lenhoff, H.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1988; pp. 501–517. ISBN 978-0-12-345320-4. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, J. Predation on Zooplankton by Large Jellyfish, Aurelia, Cyanea and Aequorea, in Prince William Sound, Alaska. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 246, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariscal, R.N. Nematocysts. In Coelenterate Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1974; pp. 129–178. ISBN 978-0-12-512150-7. [Google Scholar]
- Calder, D.R. Nematocysts of the Coronate Scyphomedusa, Linuche Unguiculata, with a Brief Reexamination of Scyphozoan Nematocyst Classification. Chesap. Sci. 1974, 15, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.H.; Seymour, J.E. Venom Ontogeny, Diet and Morphology in Carukia Barnesi, a Species of Australian Box Jellyfish That Causes Irukandji Syndrome. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, P. Functional Elucidation of Nemopilema nomurai and Cyanea nozakii Nematocyst Venoms’ Lytic Activity Using Mass Spectrometry and Zymography. Toxins 2017, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Jia, X.; Potriquet, J.; Kumar, D.; Dash, D.; Kvaskoff, D.; Mulvenna, J. Transcriptome and Venom Proteome of the Box Jellyfish Chironex fleckeri. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K. Jellyfish Blooms in China: Dominant Species, Causes and Consequences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Li, R.; Teng, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, W.; Gao, K.; Li, A.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Yu, H.; et al. Exploring the Efficacy of Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives in Mitigating Jellyfish Toxin-Induced Skin Damage: Insights into Protective and Reparative Mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.-Y.; Wang, M.-K.; Hou, X.-C.; Wang, Z.-F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Danso, B.; Wei, D.-B.; Shou, Z.-Y.; Xiao, L.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Tentacle Extract and Nematocyst Venom: Toxicity, Mechanism, and Potential Intervention in the Giant Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.-S.; Yoon, W.D.; Lim, D.; Hart, A.J.; Hodgson, W.C. Cardiovascular Effects of Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) Jellyfish Venom in Rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 167, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Li, P. Topical Exposure to Nemopilema nomurai Venom Triggers Oedematogenic Effects: Enzymatic Contribution and Identification of Venom Metalloproteinase. Toxins 2021, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yue, Y.; Yin, X.; Li, R.; Yu, H.; Li, P. Identifying and Revealing the Geographical Variation in Nemopilema nomurai Venom Metalloprotease and Phospholipase A2 Activities. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Yue, Y.; Yu, C.; Geng, H.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai Causes Myotoxicity through the Metalloprotease Component of Venom. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asirvatham, R.D.; Hwang, D.H.; Prakash, R.L.M.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Pharmacoinformatic Investigation of Silymarin as a Potential Inhibitor against Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Metalloproteinase Toxin-like Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yu, H.; Teng, L.; Geng, H.; Li, R.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. NnM469, a Novel Recombinant Jellyfish Venom Metalloproteinase from Nemopilema nomurai, Disrupted the Cell Matrix. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Yue, Y.; Yu, C.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Effects of Toxin Metalloproteinases from Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai Nematocyst on the Dermal Toxicity and Potential Treatment of Jellyfish Dermatitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtovirta, J.; Vartio, T. Type IV Collagenases in Human Amniotic Fluids and Amnion Epithelial Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1994, 1206, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.H.; Lee, H.; Choudhary, I.; Kang, C.; Chae, J.; Kim, E. Protective Effect of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) on Toxic Metalloproteinases-Mediated Skin Damage Induced by Scyphozoan Jellyfish Envenomation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Balandin, S.V.; Aleshina, G.M.; Tagaev, A.A.; Leonova, Y.F.; Krasnodembsky, E.D.; Men’shenin, A.V.; Kokryakov, V.N. Aurelin, a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from Jellyfish Aurelia aurita with Structural Features of Defensins and Channel-Blocking Toxins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 348, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganthi, K.; Bragadeeswaran, S. Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Activities of Jellyfish (Chrysaora quinquecirrha) Venom. In Prospects in Bioscience: Addressing the Issues; Sabu, A., Augustine, A., Eds.; Springer India: Mumbai, India, 2012; pp. 283–292. ISBN 978-81-322-0809-9. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Landa, J.L.; Zapata-Pérez, O.; Cedillo-Rivera, R.; Segura-Puertas, L.; Simá-Alvarez, R.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J. Antimicrobial, Antiprotozoal, and Toxic Activities of Cnidarian Extracts from the Mexican Caribbean Sea. Pharm. Biol. 2007, 45, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, A.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Geng, X.; Wan, J.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Yang, J. Identification and Characterization of a Novel GAPDH-Derived Antimicrobial Peptide from Jellyfish. J. Pept. Sci. 2025, 31, e70011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Inhibitory Effect of Metalloproteinase Inhibitors on Skin Cell Inflammation Induced by Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai Nematocyst Venom. Toxins 2019, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Yue, Y.; Li, P. Combined Proteome and Toxicology Approach Reveals the Lethality of Venom Toxins from Jellyfish Cyanea nozakii. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3904–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’ambra, I.; Lauritano, C. A Review of Toxins from Cnidaria. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouiaei, M.; Yanagihara, A.A.; Madio, B.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Fry, B.G. Ancient Venom Systems: A Review on Cnidaria Toxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 2251–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, E.A.; Cao, J.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G. Phospholipase A2 Enzymes: Physical Structure, Biological Function, Disease Implication, Chemical Inhibition, and Therapeutic Intervention. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Kudo, I. Phospholipase A2. J. Biochem. 2002, 131, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Ilies, M.A. The Phospholipase A2 Superfamily: Structure, Isozymes, Catalysis, Physiologic and Pathologic Roles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.E.; Dennis, E.A. Phospholipase A2 Structure/Function, Mechanism, and Signaling. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S237–S242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, F.S.; Swenson, S. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaoba, O.T.; Karina Dos Santos, P.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S.; Ferreira de Souza, D.H. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases (SVMPs): A Structure-Function Update. Toxicon X 2020, 7, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.R.; Daneri, A.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J. Cholestasis-Induced Fibrosis Is Reduced by Interferon Alpha-2a and Is Associated with Elevated Liver Metalloprotease Activity. J. Hepatol. 2000, 33, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, S.; Markland, F.S. Snake Venom Fibrin(Ogen)Olytic Enzymes. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1021–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J. Snake Venoms and Coagulopathy. Toxicon 2005, 45, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M. Serine Proteases Affecting Blood Coagulation and Fibrinolysis from Snake Venoms. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005, 34, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.K.; Lee, H.; Heo, Y.; Pyo, M.J.; Choudhary, I.; Han, C.H.; Yoon, W.D.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. In Vitro Characterization of Jellyfish Venom Fibrin(Ogen)Olytic Enzymes from Nemopilema nomurai. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornara, L.; Mariottini, G.L.; Giordani, P.; Smeriglio, A.; Trombetta, D.; Guida, L.; Lavorano, S.; Burlando, B. Modulatory Activities of Plant Extracts on Jellyfish Cytotoxicity. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2020, 31, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fan, L.; Pan, H.; Li, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, Y. Antimicrobial Peptides from Marine Animals: Sources, Structures, Mechanisms and the Potential for Drug Development. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1112595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, S.M.; Dos Santos Freitas, F.; Lourenço da Fonseca, E.; Vicente, A.C.P. Vibrio Mimicus Lineage Carrying Cholera Toxin and Vibrio Pathogenicity Island, United States and China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Maeda, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Ogawa, S.; Fukuda, K.; Nagatsuka, N.; Nagao, K.; Ueno, S. Antioxidant Activity of the Giant Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai Measured by the Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity and Hydroxyl Radical Averting Capacity Methods. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 4, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, E.; Menon, V.P. In Vitro Radical Scavanging Activities of Chrysaora quinquecirrha Nematocyst Venom. Drug Discov. Ther. 2009, 3, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Suganthi, K.; Bragadeeswaran, S.; Kumaran, N.S.; Thenmozhi, C.; Thangaraj, S. In Vitro Antioxidant Activities of Jelly Fish Chrysaora quinquecirrha Venom from Southeast Coast of India. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, S347–S351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, S.A.; Vasantharaja, R.; Govindaraju, K. Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of Nematocyst Venom Protein of Five Scyphozoan Chrysaora Jellyfish’s Species from the Coastal Waters of Tamil Nadu, India. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 22989–22999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Qin, N.; Zhu, B.; Xia, X. Jellyfish Skin Polysaccharides Enhance Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulate the Gut Microbiota in Mice with DSS-Induced Colitis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10121–10135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Su, M.; Song, S.-J.; Hong, J.; Kim, S.; Im, D.S.; Jung, J.H. A Bile Acid Derivative with PPARγ-Mediated Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Steroids 2018, 137, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Su, M.; Song, S.-J.; Hong, J.; Chung, H.Y.; Jung, J.H. An Anti-Inflammatory PPAR-γ Agonist from the Jellyfish-Derived Fungus Penicillium chrysogenum J08NF-4. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, F.; Sinclair, A.J.; Li, D. Protective Effects of a Lipid Extract from Hard-Shelled Mussel (Mytilus coruscus) on Intestinal Integrity after Lipopolysaccharide Challenge in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhu, X.; Mei, L.; Song, X.; Liu, X.; Song, Z.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Mytilus coruscus α-d-Glucan (MP-A) in Activated Macrophage Cells via TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK Pathway Inhibition. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bao, C.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, H.J. Green Lipped Mussel Oil Complex Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide Stimulated Inflammation via Regulating Nuclear Factor-κB and Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases Signaling in RAW264.7 Murine Macrophages. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, I.; Mohideen, H.S.; Nazeer, R.A. A Meretrix Meretrix Visceral Mass Derived Peptide Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Responses in RAW264.7 Cells and Adult Zebrafish Model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Chen, M.-F.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Sun, S.; Qian, Z.-J. Boiled Abalone Byproduct Peptide Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity in HT1080 Cells and HUVECs by Suppressing the Metastasis and Angiogenesis in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8855–8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Zou, S.; Song, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, L. Protective Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) against the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai Envenoming. Toxins 2023, 15, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, L. β Adrenergic Receptor/cAMP/PKA Signaling Contributes to the Intracellular Ca2+ Release by Tentacle Extract from the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Maeda, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Tamura, Y.; Koizumi, T. Antioxidant Activity of Fish Sauces Including Puffer (Lagocephalus wheeleri) Fish Sauce Measured by the Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity Method. Mol. Med. Rep. 2010, 3, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, J.; Zhou, D.; Zou, S.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, S.; et al. Obtainment of Two Monomorphic Nematocysts from Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and Comparative Analysis of the Biological Activities of Their Contents. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110421
Lyu Y, Huang Y, Song J, Zhou D, Zou S, Li J, Wang F, Wang Q, Hu Y, Zhu S, et al. Obtainment of Two Monomorphic Nematocysts from Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and Comparative Analysis of the Biological Activities of Their Contents. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(11):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110421
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Yongfei, Yichao Huang, Juxingsi Song, Dayuan Zhou, Shuaijun Zou, Jie Li, Fan Wang, Qianqian Wang, Yanan Hu, Shaoqian Zhu, and et al. 2025. "Obtainment of Two Monomorphic Nematocysts from Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and Comparative Analysis of the Biological Activities of Their Contents" Marine Drugs 23, no. 11: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110421
APA StyleLyu, Y., Huang, Y., Song, J., Zhou, D., Zou, S., Li, J., Wang, F., Wang, Q., Hu, Y., Zhu, S., Luo, S., Gan, X., Zhang, L., & Liu, G. (2025). Obtainment of Two Monomorphic Nematocysts from Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and Comparative Analysis of the Biological Activities of Their Contents. Marine Drugs, 23(11), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110421






