The Marine Natural Compound Aplysinamisine I Selectively Induces Apoptosis and Exhibits Synergy with Taxol™ in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Spheroids
Abstract
1. Introduction
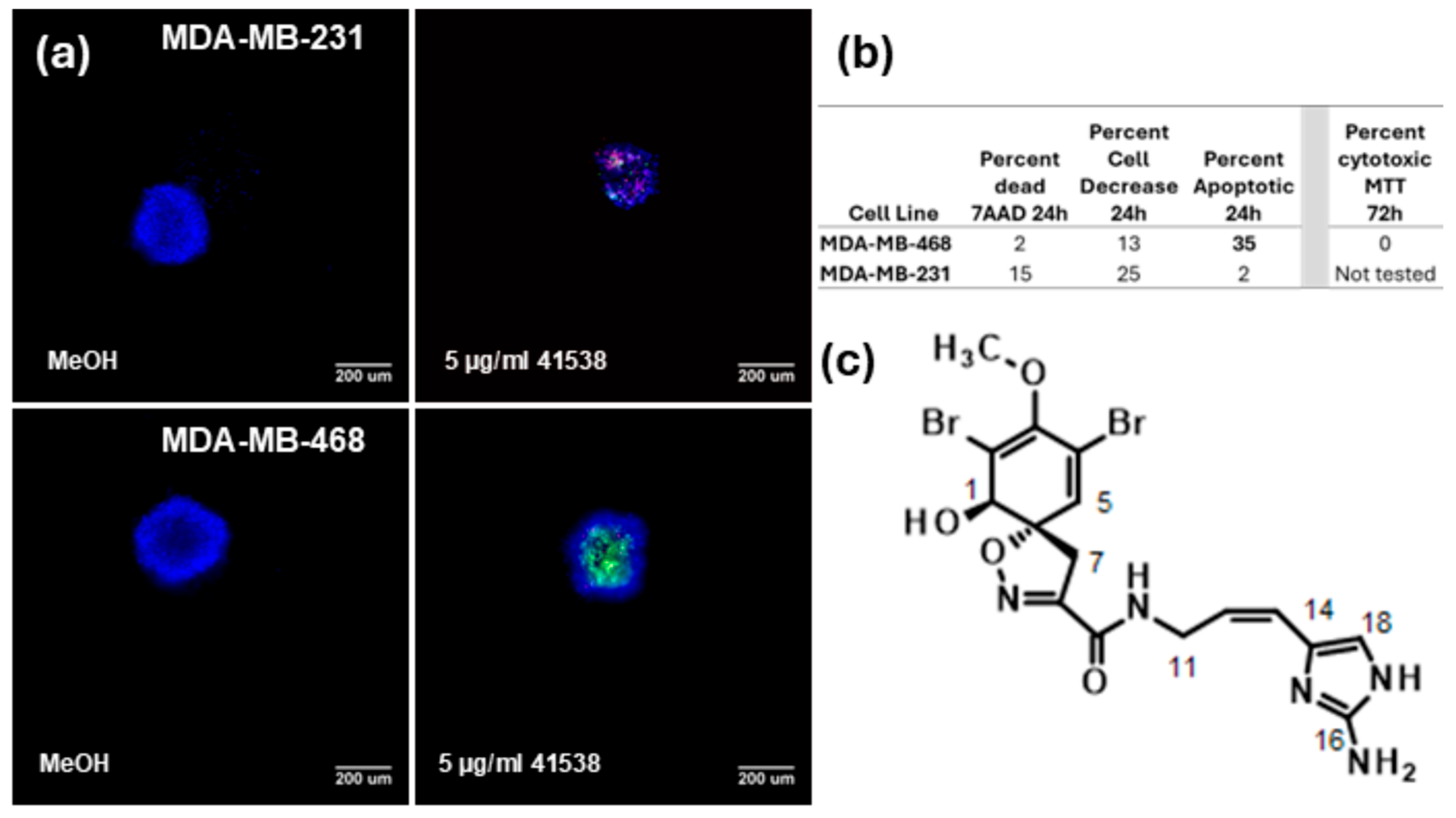
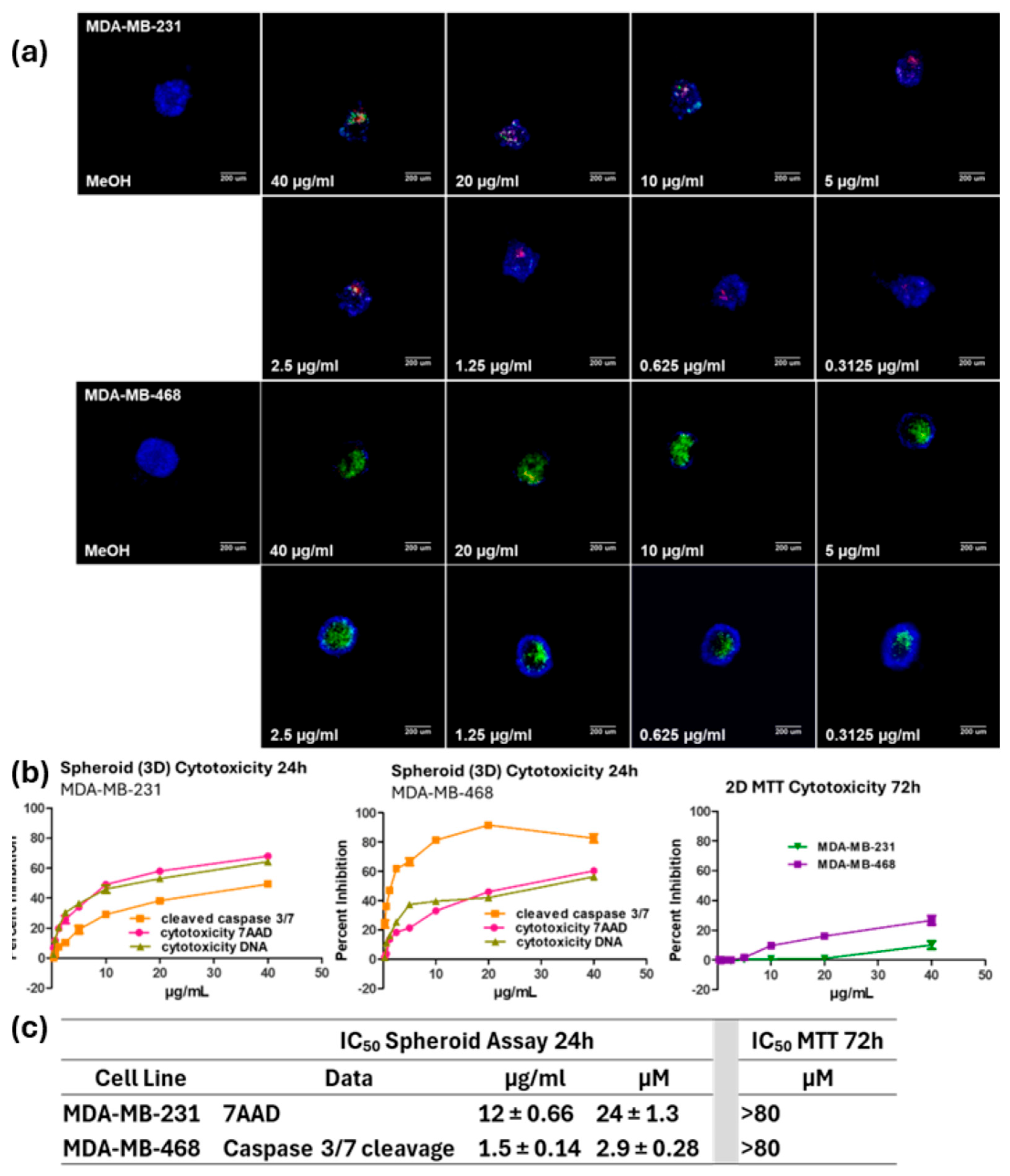
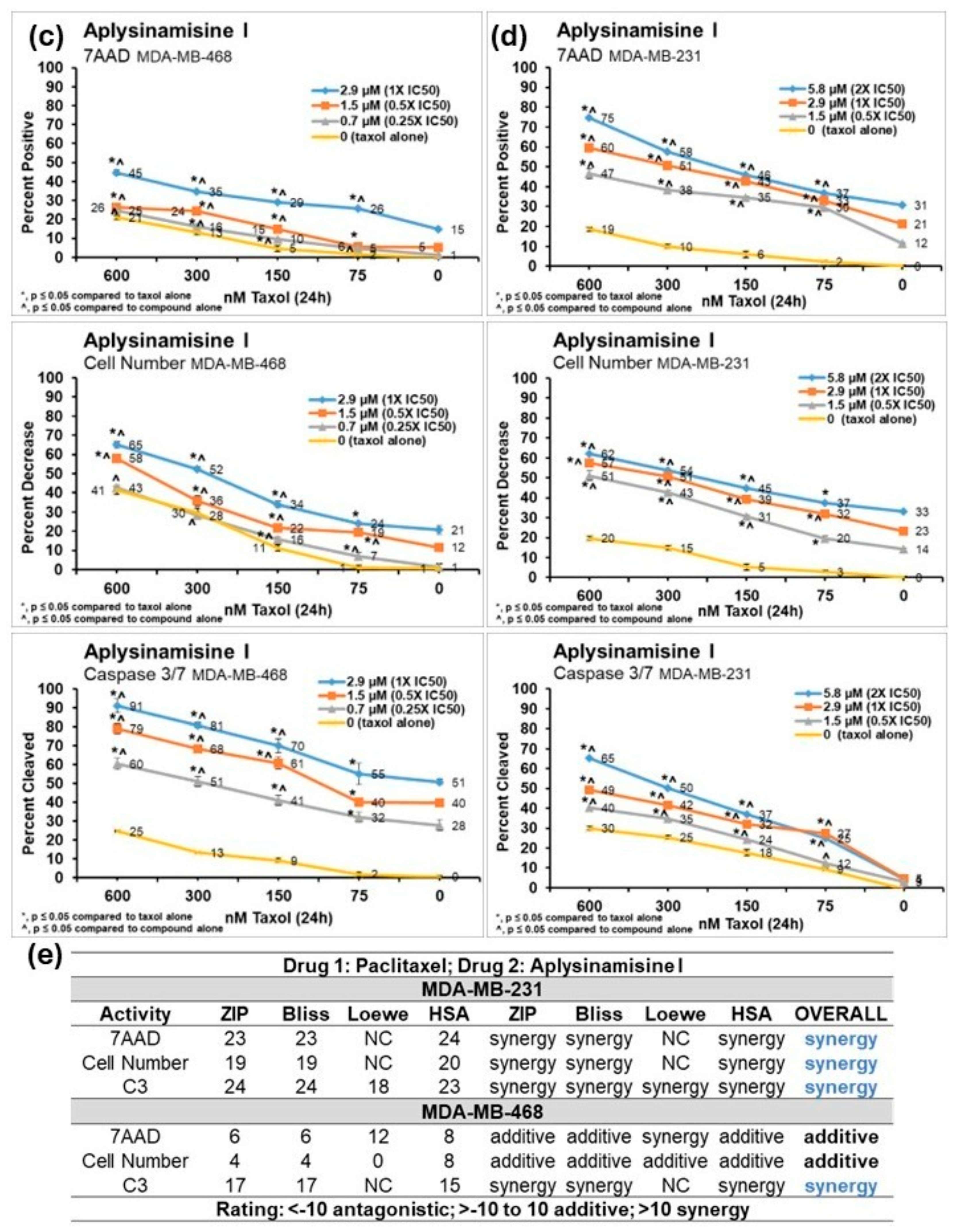
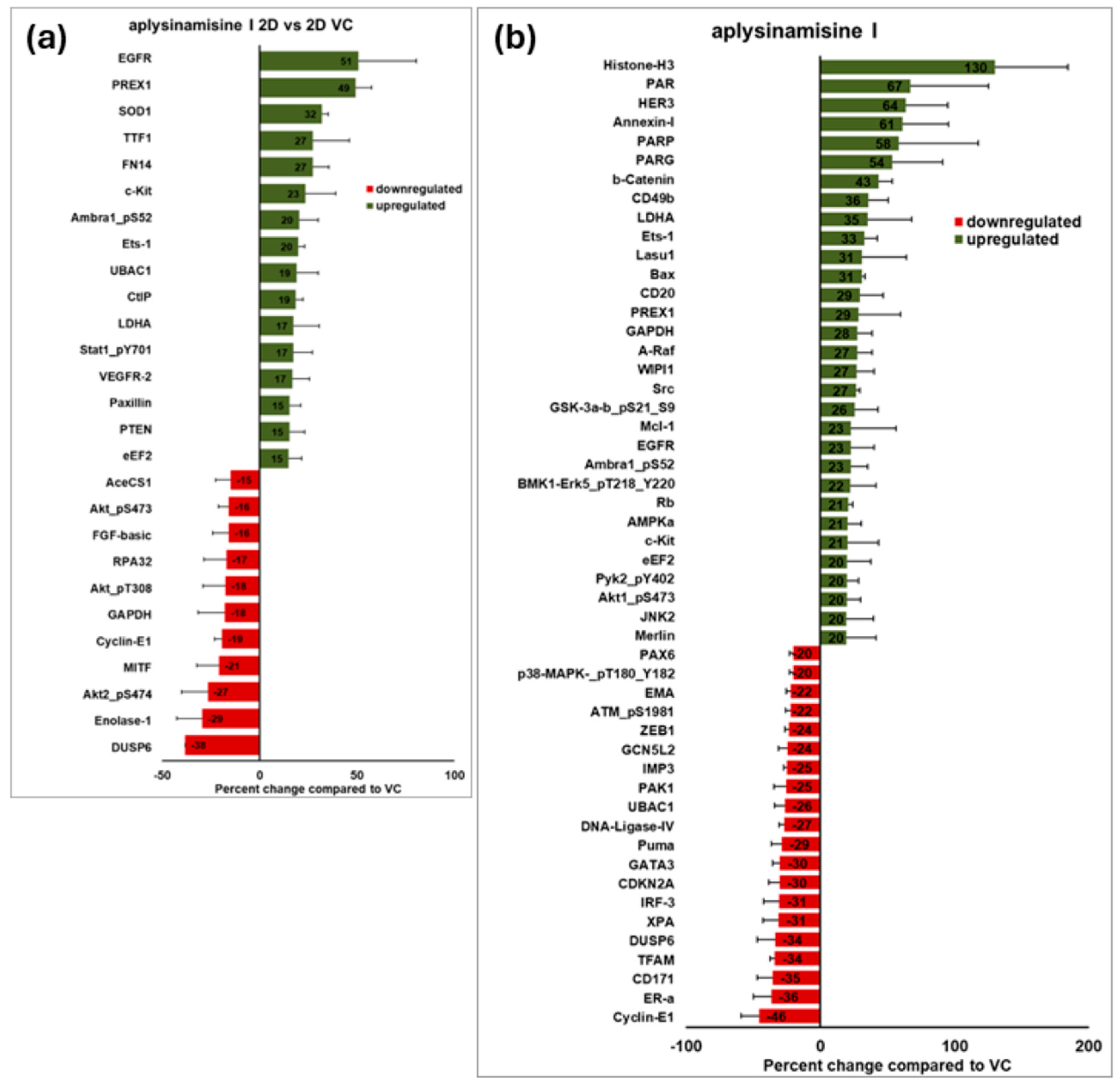
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Material
4.2. Purification of Aplysinamisine I
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Three-Dimensional Spheroid Multiparametric Assay
4.5. Two-Dimensional Cell Viability Assay (MTT)
4.6. IC50 Determination
4.7. Combination Experiments with Taxol™ and Synergy Determination
4.8. Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA)
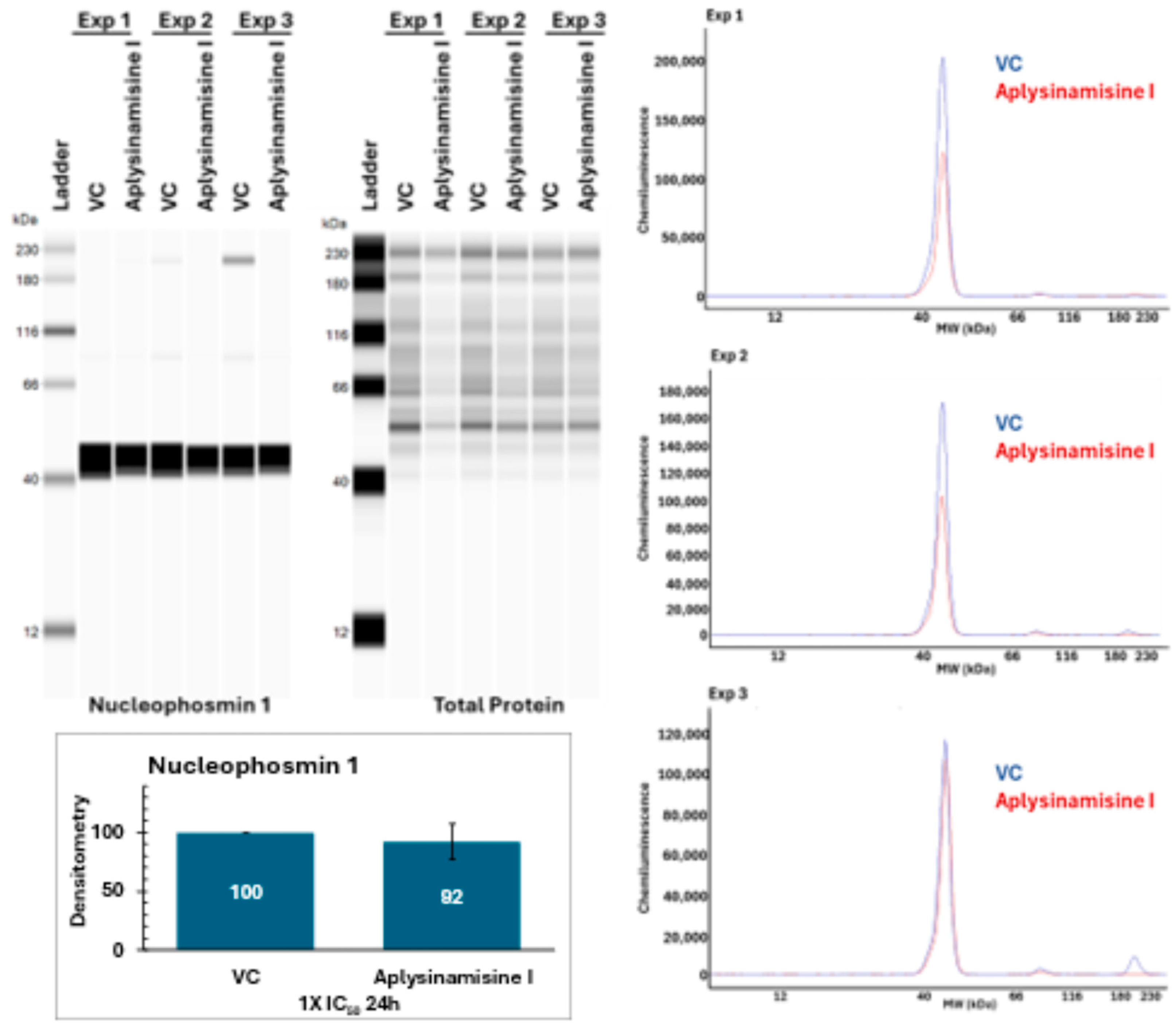
4.9. Simple Western
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TNBC | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |
| 7AAD | 7-amino actinomycin D |
| C3 | Cleaved caspase 3/7 |
| MTT | 3-[4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl]-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide |
References
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/2025-cancer-facts-figures.html (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- American Cancer Society. About Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/breast-cancer/about/types-of-breast-cancer/triple-negative.html (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Hirschhaeuser, F.; Menne, H.; Dittfeld, C.; West, J.; Mueller-Klieser, W.; kunz-Schughart, L.A. Multicellular tumor spheroids: An underestimated tool is catching up again. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 148, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, R.; Broglie, J.J.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L. Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, E.A.; Pitts, T.P.; Winder, P.L.; Wright, A.E. The Marine Natural Product Furospinulosin 1 Induces Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Spheroids, But Not in Cells Grown Traditionally with Longer Treatment. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, A.; Schlederer, M.; Pudelko, K.; Stadler, M.; Walter, S.; Unterleuthner, D.; Unger, C.; Kramer, N.; Hengstschlager, M.; Kenner, L.; et al. Comparison of cancer cells in 2D vs 3D culture reveals differences in AKT-mTOR-S6K signaling and drug responses. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 203–218. [Google Scholar]
- Muguruma, M.; Teraoka, S.; Miyahara, K.; Ueda, A.; Asaoka, M.; Okazaki, M.; Kawate, T.; Kuroda, M.; Miyagi, Y.; Ishikawa, T. Differences in drug sensitivity between two-dimensional and three-dimensional culture systems in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 533, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, E.A.; Peterson, T.A.; Wright, A.E. The Marine Natural Compound Dragmacidin D Selectively Induces Apoptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Spheroids. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.D.; Pina, I.C. The Structures of Aplysinamisine-I, Aplysinamisine-Ii, and Aplysinamisine-Iii—New Bromotyrosine-Derived Alkaloids from the Caribbean Sponge Aplysina-Cauliformis. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustacchi, G.; De Laurentiis, M. The role of taxanes in triple-negative breast cancer: Literature review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 4303–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: Visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W488–W493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 interactions for cancer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 1223–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Jang, M.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, E.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, I.A.; et al. High EGFR gene copy number predicts poor outcome in triple-negative breast cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.D.; Mao, F.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Y.L.; Guan, J.H.; Shen, S.J.; Pan, B.; Wang, C.J.; et al. Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-Trisphosphate Dependent Rac Exchange Factor 1 (PREX1) is a Novel Predictor of Prognosis for Breast Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Case Series. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 6554–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, M.L.; Shah, N.; Kenny, T.C.; Jenkins, E.C.; Germain, D. SOD1 is essential for oncogene-driven mammary tumor formation but dispensable for normal development and proliferation. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5751–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingen, T.A.; Chen, Y.; Suhrke, P.; Stefansson, I.M.; Gundersen, M.D.; Akslen, L.A. Expression of thyroid transcription factor-1 is associated with a basal-like phenotype in breast carcinomas. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, N.; Carter, J.M.; Deka, K.; Tan, B.K.T.; Sim, Y.; Tan, S.M.; Li, Y.H. TWEAK/Fn14 signalling driven super-enhancer reprogramming promotes pro-metastatic metabolic rewiring in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; McCuaig, R.D.; Sutton, C.R.; Tan, A.H.Y.; Jeelall, Y.; Bean, E.G.; Dai, J.; Prasanna, T.; Batham, J.; Malik, L.; et al. Nuclear-Biased DUSP6 Expression is Associated with Cancer Spreading Including Brain Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Chen, Q.X.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhou, M.; Ren, Y.X.; Tang, L.Y.; Ren, Z.F. Association of Enolase-1 with Prognosis and Immune Infiltration in Breast Cancer by Clinical Stage. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Lambring, C.B. Akt Isoforms: A Family Affair in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Kim, S.; Lee, M.W.; Jeon, H.J.; Ryu, H.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, H.J. MITF Promotes Cell Growth, Migration and Invasion in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by Activating the RhoA/YAP Signal Pathway. Cancers 2021, 13, 2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Kong, Q.; Su, P.; Duan, M.; Xue, M.; Li, X.; Tang, J.N.; Gao, Z.T.; Wang, B.B.; Li, Z.B.; et al. Regulation of Hippo signaling and triple negative breast cancer progression by an ubiquitin ligase RNF187. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobet, S.G.; van der Vegt, B.; Jongeneel, E.; Bense, R.D.; Zwager, M.C.; Schröder, C.P.; Everts, M.; Fehrmann, R.S.N.; de Bock, G.H.; van Vugt, M.A.T.M. Cyclin E expression is associated with high levels of replication stress in triple-negative breast cancer. npj Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, R.M.; Arun, B. PARP Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Including Those With BRCA Mutations. Cancer J. 2021, 27, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandullo-Sanchez, L.; Ocana, A.; Pandiella, A. HER3 in cancer: From the bench to the bedside. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2022, 41, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearanpan, L.; Nordin, F.J.; Siew, E.L.; Kumolosasi, E.; Mohamad Hanif, E.A.; Masre, S.F.; Chua, E.W.; Cheng, H.S.; Rajab, N.F. A Cell-Based Systematic Review on the Role of Annexin A1 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doberstein, K.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Bretz, N.P.; Schirmer, U.; Harari, A.; Witzel, I.; Ben-Arie, A.; Hubalek, M.; Muller-Holzner, E.; Reinold, S.; et al. L1CAM is expressed in triple-negative breast cancers and is inversely correlated with androgen receptor. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Qu, C.; Tian, Y.; Wen, Y.; Xia, S.; Ma, M. The HIF-1/SNHG1/miR-199a-3p/TFAM axis explains tumor angiogenesis and metastasis under hypoxic conditions in breast cancer. Biofactors 2021, 47, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Narayan, R.; Corsello, S.M.; Peck, D.D.; Natoli, T.E.; Lu, X.; Gould, J.; Davis, J.F.; Tubelli, A.A.; Asiedu, J.K.; et al. A Next Generation Connectivity Map: L1000 Platform and the First 1,000,000 Profiles. Cell 2017, 171, 1437–1452.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenical, W.; Jensen, P.R.; Cheng, X.C. Avrainvillamide, a Cytotoxic Marine Natural Product, and Derivatives Thereof. U.S. Patent 6,066,635, 23 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, J.E.; Siegrist, R.; Myers, A.G. The natural product avrainvillamide binds to the oncoprotein nucleophosmin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14444–14451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, M.; Chen, Y.; Gilbert, L.A.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Krenning, L.; Menchon, G.; Rai, A.; Cho, M.Y.; Stern, J.J.; Prota, A.E.; et al. Pharmaceutical-Grade Rigosertib Is a Microtubule-Destabilizing Agent. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 191–198.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.Y.; Du, J.L.; Yang, P.M. Repositioning VU-0365114 as a novel microtubule-destabilizing agent for treating cancer and overcoming drug resistance. Mol. Oncol. 2024, 18, 386–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seashore-Ludlow, B.; Rees, M.G.; Cheah, J.H.; Cokol, M.; Price, E.V.; Coletti, M.E.; Jones, V.; Bodycombe, N.E.; Soule, C.K.; Gould, J.; et al. Harnessing Connectivity in a Large-Scale Small-Molecule Sensitivity Dataset. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1210–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Annika, G.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.I.; Weng, S.; Gollub, J.; Jin, H.; Botstein, D.; Cherry, J.M.; Sherlock, G. GO::TermFinder--open source software for accessing Gene Ontology information and finding significantly enriched Gene Ontology terms associated with a list of genes. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3710–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, A.; Franceschini, M.; Chiarella, S.; Rocchio, S.; Travaglini-Allocatelli, C.; Federici, L. Molecules that target nucleophosmin for cancer treatment: An update. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 44821–44840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gao, X.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Shi, Q.; Wu, M. Nucleophosmin/B23 inhibits Eg5-mediated microtubule depolymerization by inactivating its ATPase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19060–19067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, J.K.; Paquet, N.; Adams, M.N.; Boucher, D.; Bolderson, E.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Nucleophosmin: From structure and function to disease development. BMC Mol. Biol. 2016, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, J.; Hamann, M.T. The marine bromotyrosine derivatives. Alkaloids Chem. Biol. 2005, 61, 59–262. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Kawachi, T.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Hypoxia-selective growth inhibition of cancer cells by furospinosulin-1, a furanosesterterpene isolated from an Indonesian marine sponge. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, E.A. Regulated Cell Death Signaling Pathways and Marine Natural Products That Target Them. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.; Wang, X.; Ye, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Qin, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Long, Q.; et al. NPM1 upregulates the transcription of PD-L1 and suppresses T cell activity in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfatti, M.C.; Gerratana, L.; Dalla, E.; Isola, M.; Damante, G.; Di Loreto, C.; Puglisi, F.; Tell, G. APE1 and NPM1 protect cancer cells from platinum compounds cytotoxicity and their expression pattern has a prognostic value in TNBC. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2019, 38, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Peng, C.; Liang, W.; Lin, H. Knockdown of nucleophosmin 1 suppresses proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cells through activating CDH1/Skp2/p27kip1 pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisendi, S.; Mecucci, C.; Falini, B.; Pandolfi, P.P. Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ji, J.; Yu, L.R.; Veenstra, T.; Wang, X.W. Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of nucleophosmin and its potential regulation by peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase. J. Mol. Biochem. 2015, 4, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Destouches, D.; Page, N.; Hamma-Kourbali, Y.; Machi, V.; Chaloin, O.; Frechault, S.; Birmpas, C.; Katsoris, P.; Beyrath, J.; Albanese, P.; et al. A simple approach to cancer therapy afforded by multivalent pseudopeptides that target cell-surface nucleoproteins. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3296–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzis, J.A.; Leone, P.d.A.; Hooper, J.N.; Quinn, R.J. Ianthesine E, a new bromotyrosine-derived metabolite from the Great Barrier Reef sponge Pseudoceratina sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 22, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusama, T.; Tanaka, N.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Gonoi, T.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Bromopyrrole alkaloids from a marine sponge Agelas sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivascu, A.; Kubbies, M. Diversity of cell-mediated adhesions in breast cancer spheroids. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 31, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirenko, O.; Mitlo, T.; Hesley, J.; Luke, S.; Owens, W.; Cromwell, E.F. High-Content Assays for Characterizing the Viability and Morphology of 3D Cancer Spheroid Cultures. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2015, 13, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadevaia, S.; Lu, Y.; Morales, F.C.; Mills, G.B.; Ram, P.T. Identification of optimal drug combinations targeting cellular networks: Integrating phospho-proteomics and computational network analysis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6704–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibes, R.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Hennessy, B.; Andreeff, M.; Mills, G.B.; Kornblau, S.M. Reverse phase protein array: Validation of a novel proteomic technology and utility for analysis of primary leukemia specimens and hematopoietic stem cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Aplysinamisine I | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound Perturbagens with Enrichment Scores Most Similar | ||||
| Rank | Score | ID | Name | Description |
| 2 | 97.69 | BRD-K39569857 | avrainvillamide-analog-3 | nucleophosmin inhibitor |
| 7 | 96.66 | BRD-K61691971 | avrainvillamide-analog-1 | nucleophosmin inhibitor |
| 8 | 96.02 | BRD-K35687265 | ON-01910 | microtubule destabilizing agent |
| 14 | 94.77 | BRD-K37456065 | VU-0365114-2 | microtubule destabilizing agent |
| 17 | 94.05 | BRD-A18043272 | phensuximide | Succinimide antiepileptic |
| 22 | 92.21 | BRD-K37865504 | LY-2183240 | tubulin polymerization modulator |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guzmán, E.A.; Peterson, T.A.; Harmody, D.K.; Wright, A.E. The Marine Natural Compound Aplysinamisine I Selectively Induces Apoptosis and Exhibits Synergy with Taxol™ in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Spheroids. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100380
Guzmán EA, Peterson TA, Harmody DK, Wright AE. The Marine Natural Compound Aplysinamisine I Selectively Induces Apoptosis and Exhibits Synergy with Taxol™ in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Spheroids. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(10):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100380
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuzmán, Esther A., Tara A. Peterson, Dedra K. Harmody, and Amy E. Wright. 2025. "The Marine Natural Compound Aplysinamisine I Selectively Induces Apoptosis and Exhibits Synergy with Taxol™ in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Spheroids" Marine Drugs 23, no. 10: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100380
APA StyleGuzmán, E. A., Peterson, T. A., Harmody, D. K., & Wright, A. E. (2025). The Marine Natural Compound Aplysinamisine I Selectively Induces Apoptosis and Exhibits Synergy with Taxol™ in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Spheroids. Marine Drugs, 23(10), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100380







