Cold-Azurin, a New Antibiofilm Protein Produced by the Antarctic Marine Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. TAE6080
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Production of AntiBiofilm and Anti-Adhesive Molecules Active against S. epidermidis Biofilm
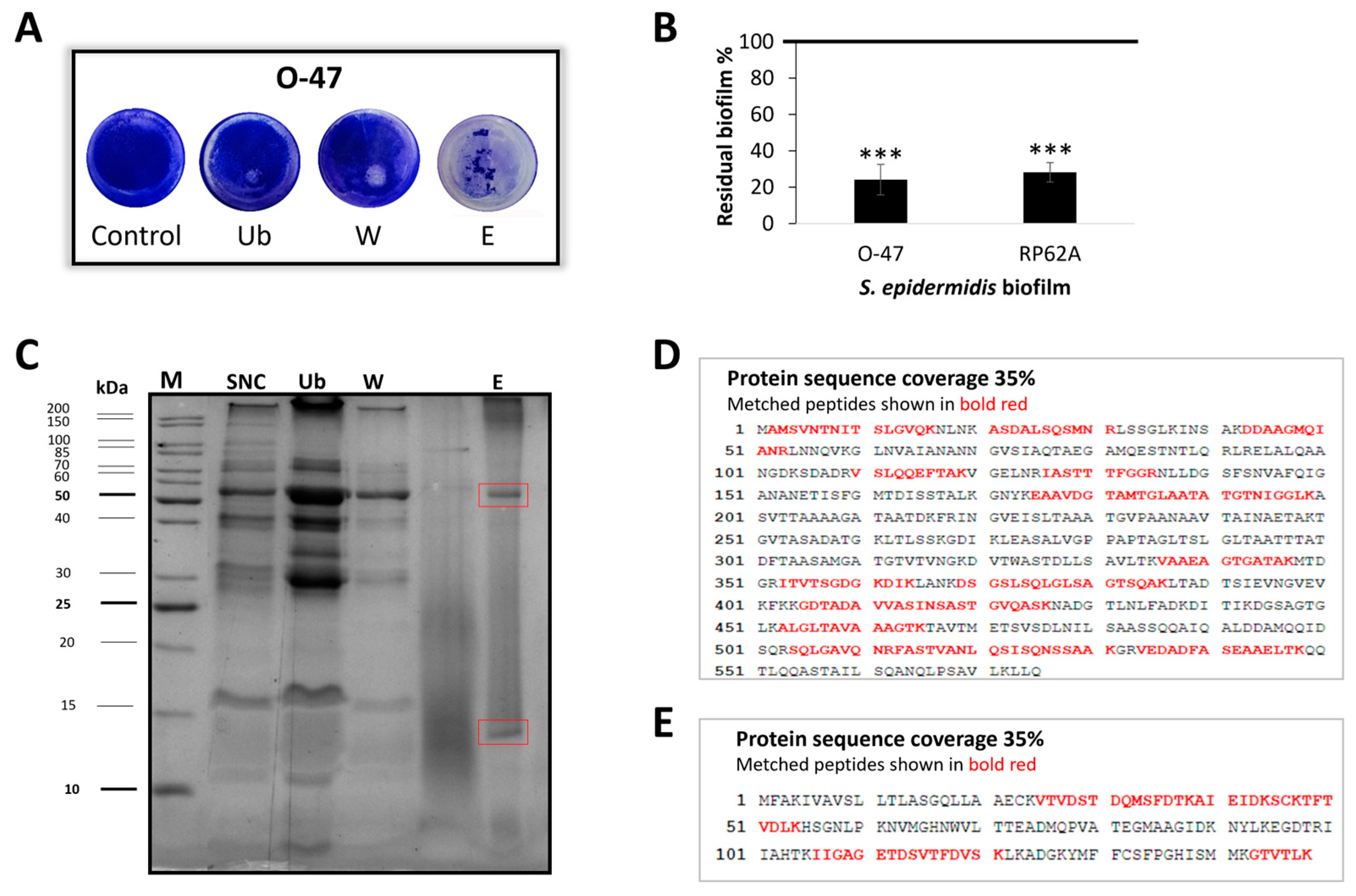
2.2. Purification of Anti-Adhesive and Antibiofilm Molecule
2.3. Cold-Azurin Identification
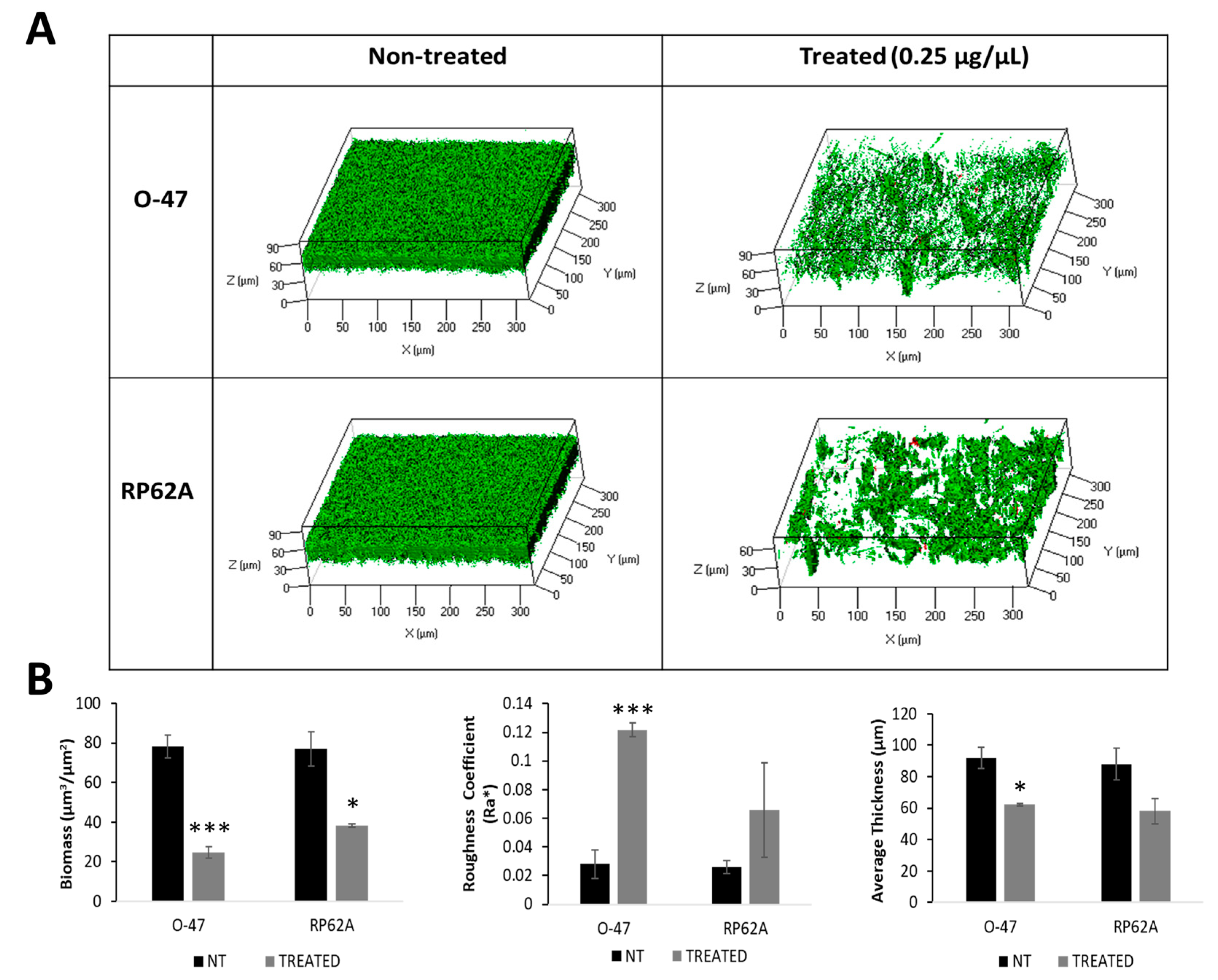
2.4. Recombinant Cold-Azurin Production and Purification
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. TAE6080 Cell-Free Supernatant Preparation
4.3. Surface Coating Assay
4.4. Biofilm Inhibiting Assay
4.5. Proteinase K Treatment
4.6. Large-Scale Growth
4.7. Adsorption Chromatography
4.8. SDS-PAGE
4.9. In Situ Hydrolysis, LC-MS/MS Analysis and Protein Identification
4.10. Pseudomonas sp. TAE6080 Periplasmic Protein Extraction
4.11. Recombinant Cold-Azurin Protein Production
4.12. Confocal Microscopy
4.13. Statistics and Reproducibility of Results
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SN TAE6080 | Pseudomonas sp. TAE6080 cell-free supernatant |
| G | Pseudomonas sp. TAE6080 culture medium |
| SNC | Retentate fraction obtained after the ultrafiltration of TAE6080 cell-free supernatant |
| Ub | Unbound fraction obtained from adsorption chromatography, |
| W | Fractions obtained from adsorption chromatography during the washing steps |
| E or P | Fractions obtained from adsorption chromatography elution step with methanol |
| OS | Pseudomonas sp. TAE6080 periplasmic extract by osmotic shock method |
| Sol | soluble fraction obtained after TAE6080 cell-pellet lysis |
References
- Moriarty, T.F.; Kuehl, R.; Coenye, T.; Metsemakers, W.J.; Morgenstern, M.; Schwarz, E.M.; Riool, M.; Zaat, S.A.J.; Khana, N.; Kates, S.L.; et al. Orthopaedic Device-Related Infection: Current and Future Interventions for Improved Prevention and Treatment. EFORT Open Rev. 2016, 1, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, B.F.; Carson, L. Bioactive Biomaterials for Controlling Biofilms; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2015; ISBN 9780857097224. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, S.W.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; Otto, M. Different Drugs for Bad Bugs: Antivirulence Strategies in the Age of Antibiotic Resistance. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrocola, G.; Campoccia, D.; Motta, C.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R.; Speziale, P. Colonization and Infection of Indwelling Medical Devices by Staphylococcus aureus with an Emphasis on Orthopedic Implants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranjec, C.; Angeles, D.M.; Mårli, M.T.; Fernández, L.; García, P.; Kjos, M.; Diep, D.B. Staphylococcal Biofilms: Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, T.D.; Tejera, N.; McNamara, I.; Langridge, G.C.; Wain, J.; Poolman, M.; Singh, D. Genome-Scale Metabolic Modelling Approach to Understand the Metabolism of the Opportunistic Human Pathogen Staphylococcus epidermidis RP62A. Metabolites 2022, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.; Rohde, H.; Vilanova, M.; Cerca, N. Fighting Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm-Associated Infections: Can Iron Be the Key to Success? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 798563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffari, F.; Gurram, B. Molecular and Phenotypic Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Clones of Staphylococcus epidermidis in Iranian Hospitals: Clonal Relatedness to Healthcare-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Isolates in Northern Europe. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents Antibiot. Resist. Bact. Biofilms 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, G.R.d.S.; Viana, N.B.; Gómez, F.; Pontes, B.; Frases, S. The Mechanical Properties of Microbial Surfaces and Biofilms. Cell Surf. 2019, 5, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, B.; Baillie, G.S.; Douglas, L.J. Mixed Species Biofilms of Candida albicans and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 51, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilli, E.; Luisa, M.; Gennaro, T. Biofilm as an Adaptation Strategy to Extreme Conditions. Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. e Nat. 2022, 33, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artini, M.; Papa, R.; Vrenna, G.; Lauro, C.; Ricciardelli, A.; Casillo, A.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E.; Selan, L. Cold-Adapted Bacterial Extracts as a Source of Anti-Infective and Antimicrobial Compounds against Staphylococcus aureus. Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, R.; Selan, L.; Parrilli, E.; Tilotta, M.; Sannino, F.; Feller, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Artini, M. Anti-Biofilm Activities from Marine Cold Adapted Bacteria against Staphylococci and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casillo, A.; Papa, R.; Ricciardelli, A.; Sannino, F.; Ziaco, M.; Tilotta, M.; Selan, L.; Marino, G.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Long-Chain Fatty Aldehyde from Antarctic Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 against Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi, C.; D’Angelo, C.; Calvanese, M.; Ricciardelli, A.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E.; Fondi, M. Genome Analysis of a New Biosurfactants Source: The Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020. Mar. Genom. 2022, 61, 100922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, C.; Casillo, A.; Melchiorre, C.; Lauro, C.; Corsaro, M.M.; Carpentieri, A.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E. CATASAN Is a New Anti-Biofilm Agent Produced by the Marine Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, R.; Vrenna, G.; D’angelo, C.; Casillo, A.; Relucenti, M.; Donfrancesco, O.; Corsaro, M.M.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Assanti, V.T.G.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Anti-Virulence Activity of the Cell-Free Supernatant of the Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. Tae2020 against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Clinical Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, C.; D’Angelo, C.; Calvanese, M.; Ricciardelli, A.; Sellitto, A.; Giurato, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Weisz, A.; Parrilli, E.; Fondi, M. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Pseudomonas Sp. TAE6080, a Strain Capable of Inhibiting Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm. Mar. Genom. 2021, 60, 100887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, C.; Gerke, C.; Somerville, G.A.; Fischer, E.R.; Otto, M. Quorum-Sensing Control of Biofilm Factors in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raue, S.; Fan, S.H.; Rosenstein, R.; Zabel, S.; Luqman, A.; Nieselt, K.; Götz, F. The Genome of Staphylococcus epidermidis O47. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondino, S.; San Martin, F.; Buschiazzo, A. 3D Cryo-EM Imaging of Bacterial Flagella: Novel Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Cell Motility. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.J.; Seib, K.L.; Edwards, J.L.; Apicella, M.A.; McEwan, A.G.; Jennings, M.P. Azurin of Pathogenic Neisseria spp. Is Involved in Defense against Hydrogen Peroxide and Survival within Cervical Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 8444–8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydorn, A.; Nielsen, A.T.; Hentzer, M.; Sternberg, C.; Givskov, M.; Ersboll, B.K.; Molin, S. Quantification of Biofilm Structures by the Novel Computer Program COMSTAT. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Kamp, M.; Silvestrini, M.C.; Brunori, M.; Van Beeumen, J.; Hali, F.C.; Canters, G.W. Involvement of the Hydrophobic Patch of Azurin in the Electron-transfer Reactions with Cytochrome C551 and Nitrite Reductase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 194, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Breslawec, A.P.; Liang, T.; Deng, Z.; Kuperman, L.L.; Yu, Q. Strategy to Combat Biofilms: A Focus on Biofilm Dispersal Enzymes. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artini, M.; Cicatiello, P.; Ricciardelli, A.; Papa, R.; Selan, L.; Dardano, P.; Tilotta, M.; Vrenna, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Giardina, P.; et al. Hydrophobin Coating Prevents Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm Formation on Different Surfaces. Biofouling 2017, 33, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savelieff, M.G.; Lu, Y. CuA Centers and Their Biosynthetic Models in Azurin. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 15, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, D.; Besson, S.; Brondino, C.D.; Pereira, E.; De Castro, B.; Moura, I. Two Azurins with Unusual Redox and Spectroscopic Properties Isolated from the Pseudomonas chlororaphis Strains DSM 50083T and DSM 50135. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijgenboom, E.; Busch, J.E.; Canters, G.W. In Vivo Studies Disprove an Obligatory Role of Azurin in Denitrification in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Show That Azu Expression Is under Control of RpoS and ANR. Microbiology 1997, 143, 2853–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Webb, S.P.; Ivanic, J.; Jensen, J.H. Determinants of the Relative Reduction Potentials of Type-1 Copper Sites in Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8010–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, G.; Giardina, P.; Bianco, C.; Scaloni, A.; Capasso, A.; Sannia, G. A Novel White Laccase from Pleurotus ostreatus. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 31301–31307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fialho, A.M.; Stevens, F.J.; Das Gupta, T.K.; Chakrabarty, A.M. Beyond Host-Pathogen Interactions: Microbial Defense Strategy in the Host Environment. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Yuan, C.; Sun, R.; Wang, K.; Tang, B. Revealing the Underestimated Anticancer Effect of Azurin by Mechanical Unfolding. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4809–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshi, B.; Barzelighi, H.M.; Daraei, B. The Anti-Adhesive and Anti-Invasive Effects of Recombinant Azurin on the Interaction between Enteric Pathogens (Invasive/Non-Invasive) and Caco-2 Cells. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.; Fialho, A.M.; Ratner, D.; Gupta, P.; Hong, C.S.; Kahali, S.; Yamada, T.; Haldar, K.; Murphy, S.; Cho, W.; et al. Azurin, Plasmodium falciparum Malaria and HIV/AIDS: Inhibition of Parasitic and Viral Growth by Azurin. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, A.; Mahfouz, M.; Fialho, A.M.; Yamada, T.; Granja, A.T.; Zhu, Y.; Hashimoto, W.; Schlarb-Ridley, B.; Cho, W.; Das Gupta, T.K.; et al. Cupredoxin-Cancer Interrelationship: Azurin Binding with EphB2, Interference in EphB2 Tyrosine Phosphorylation, and Inhibition of Cancer Growth. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Jiang, W.; Zuo, J.; Shi, D.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Liu, Z.; Xing, Q. Structural Basis of Bacterial Effector Protein Azurin Targeting Tumor Suppressor P53 and Inhibiting Its Ubiquitination. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.J.; Kuemmel, C.; Babnigg, G.; Collart, F.R. Efficient Recognition of Protein Fold at Low Sequence Identity by Conservative Application of Psi-BLAST: Application. J. Mol. Recognit. 2005, 18, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. Surface Proteins of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Peña, S.; Martínez-García, S.; Rodríguez-Martínez, S.; Cancino-Diaz, M.E.; Cancino-Diaz, J.C. Overview of Staphylococcus epidermidis Cell Wall-Anchored Proteins: Potential Targets to Inhibit Biofilm Formation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, H.; Mack, D.; Rohde, H. Structural Basis of Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm Formation: Mechanisms and Molecular Interactions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarawsky, A.E.; Johns, S.L.; Schuck, P.; Herr, A.B. The Biofilm Adhesion Protein Aap from Staphylococcus epidermidis Forms Zinc-Dependent Amyloid Fibers. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4411–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dai, J.; Wu, Y.; Qu, D.; Ma, G.; Fang, X. Staphylococcus epidermidis Small Basic Protein (Sbp) Forms Amyloid Fibrils, Consistent with Its Function as a Scaffolding Protein in Biofilms. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14296–14311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhan, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Rao, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Mupirocin Enhances the Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis in an AtlE-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Mishra, P. Engineered Recombinant EGFP-Azurin Theranostic Nanosystem for Targeted Therapy of Prostate Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 6066–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hazmi, N.E.; Naguib, D.M. Microbial Azurin Immobilized on Nano-Chitosan as Anticancer and Antibacterial Agent Against Gastrointestinal Cancers and Related Bacteria. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2022, 53, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinteros, M.A.; Bonilla, J.O.; Alborés, S.V.; Villegas, L.B.; Páez, P.L. Biogenic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stability and Biocompatibility Mediated by Proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punj, V.; Das Gupta, T.K.; Chakrabarty, A.M. Bacterial Cupredoxin Azurin and Its Interactions with the Tumor Suppressor Protein P53. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowrishankar, S.; Pandian, S.K. Modulation of Staphylococcus Epidermidis (RP62A) Extracellular Polymeric Layer by Marine Cyclic Dipeptide-Cyclo(L-Leucyl-L-Prolyl) Thwarts Biofilm Formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardelli, A.; Casillo, A.; Papa, R.; Monti, D.M.; Imbimbo, P.; Vrenna, G.; Artini, M.; Selan, L.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Pentadecanal Inspired Molecules as New Anti-Biofilm Agents against Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biofouling 2018, 34, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Angelo, C.; Trecca, M.; Carpentieri, A.; Artini, M.; Selan, L.; Tutino, M.L.; Papa, R.; Parrilli, E. Cold-Azurin, a New Antibiofilm Protein Produced by the Antarctic Marine Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. TAE6080. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020061
D’Angelo C, Trecca M, Carpentieri A, Artini M, Selan L, Tutino ML, Papa R, Parrilli E. Cold-Azurin, a New Antibiofilm Protein Produced by the Antarctic Marine Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. TAE6080. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(2):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020061
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Angelo, Caterina, Marika Trecca, Andrea Carpentieri, Marco Artini, Laura Selan, Maria Luisa Tutino, Rosanna Papa, and Ermenegilda Parrilli. 2024. "Cold-Azurin, a New Antibiofilm Protein Produced by the Antarctic Marine Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. TAE6080" Marine Drugs 22, no. 2: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020061
APA StyleD’Angelo, C., Trecca, M., Carpentieri, A., Artini, M., Selan, L., Tutino, M. L., Papa, R., & Parrilli, E. (2024). Cold-Azurin, a New Antibiofilm Protein Produced by the Antarctic Marine Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. TAE6080. Marine Drugs, 22(2), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020061









