Fish By-Product Collagen Extraction Using Different Methods and Their Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
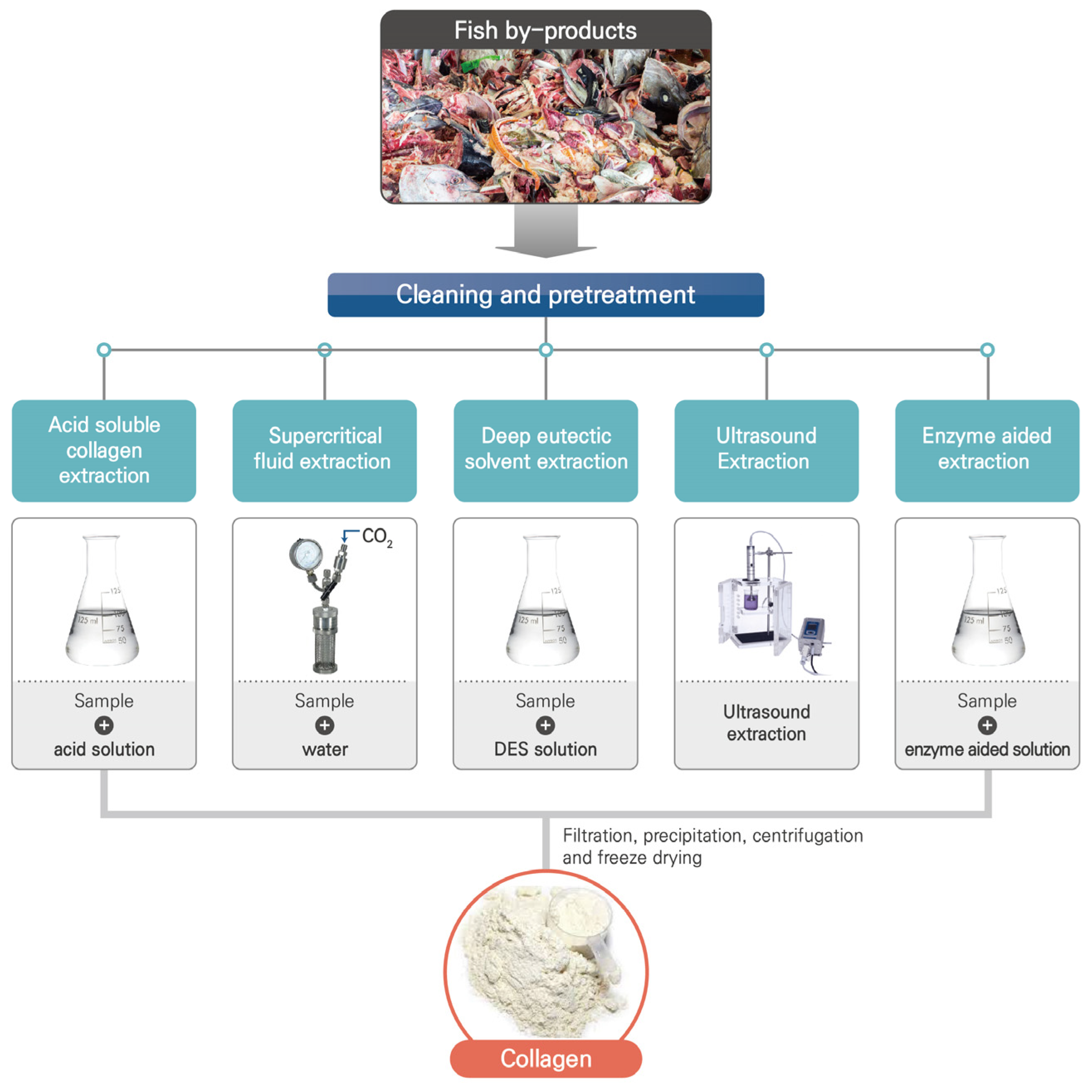
2. Extraction Techniques of Collagen from Fish By-Products
2.1. Acid-Soluble Collagen (ASC) Extraction
2.2. Enzyme-Soluble Collagen (ESC) Extraction
| Source of Collagen | Extraction Solvent | Extraction Conditions | Yield (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scales of tilapia | 30.2 M AcOH (CO2 bubble) | Time = 5 h Gas flow = 3 L/min S/L = 1/40 | 1.58 | [27] |
| Catfish skin | AcOH, HCl, citric acid and lactic acid | Time = 60 h T = 4 °C pH = 1.8–3.0 | 5–42.36 | [28] |
| Sole fish skin | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 32 h T = 25 °C S/L = 1/9 | 19 | [29] |
| Scales of seabass | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 48 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/10 | 0.38 | [41] |
| Grass carp skin | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 72 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/40 | 90 | [42] |
| Cod skin | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 72 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/10 | Not evaluated | [43] |
| Small-spotted catshark skin | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 34 h T = 25 °C | 61.24 | [33] |
| Skin of catla and rohu fish | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 48 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/60 | 69 (catla) 65 (rohu) | [44] |
| Tilapia skin and scale | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 24 h T = 4 °C pH = 7 | 3.2 (scale) 27.2 (skin) | [45] |
| Golden pompano skin and bone | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 48 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/40 | 21.81 (skin) 1.25 (bone) | [46] |
| Swim bladder of yellow tuna | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 48 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/10 | 1.07 | [47] |
| Skin of giant croaker | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 6–10 h T = 4 °C pH = 1–4 S/L = 1.45–1.65 Pepsin = 800–2400 U/g | 84.85 | [34] |
| Fins, scales, skins, bones, and swim bladders of bighead carp | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 36 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/10 Pepsin = 0.1% | 61.8 (fins) 58.1 (scales) 71 (skins) 57.1 (bone) 75.2 (swim bladders) | [35] |
| Nilem fish skin | 0.5–0.9 M AcOH | T = 4 °C Pepsin = 0.5–1.5% | 4.25–6.18 | [37] |
| Lophius litulon skin | 0.5 M AcOH | T = 4 °C Pepsin = 1–6% | Not evaluated | [48] |
| Tilapia skin | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 48 h T = 4 °C Pepsin = 0.5% | Not evaluated | [49] |
| Silver carp scales | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 10–60 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/10–1/50 Pepsin = 1.5% | 12.06 | [50] |
| Cod swim bladder | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 3 days T = 25 °C S/L = 1/10 Pepsin = 10% | 11.53 | [51] |
| Thornback ray skin | 0.2 M AcOH | Time = 18 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/10 Pepsin = 5 g/g | 30.16 | [52] |
| Skin of Alaska pollack | Water | Time = 18 h T = 55 °C Shaking frequency = 100 rpm Alcalase = 1% | 65.3 | [38] |
| Skin of Alaska pollack | Water | Time = 8 h T = 55 °C pH = 6.0 S/L = 1/6 Protamex = 0.2% | 85.95 | [39] |
| Skin of Clown featherback (Chitala ornata) | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 18 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/15 Ultrasound assisted Amplitude = 80% (10 min) Frequency = 20 kHz | 57.35 | [53] |
| Calipash of soft-shelled turtle | 0.5 M AcOH | Time = 24 h T = 4 °C S/L = 1/20 Ultrasound assisted Ultrasonic power = 200 W Frequency = 24 kHz (24 min) | 50.75 | [54] |
| Skin of sea bass | 0.1 M AcOH | T = 4 °C S/L = 1/200 Ultrasound assisted Amplitude = 80% (24 h) Frequency = 20 kHz | 90.40 | [55] |
| Skin of Atlantic cod fish | Deep eutectic solvent Composite of Urea (U) and lactic acid (LA) | U:LA ratio = 1.2 T = 4 °C S/L = 1/10 Time = 48 h | 6 | [56] |
| Skin of cod fish | Deep eutectic solvent Composite of Cholinium chloride (CC) and oxalic acid (OA) | CC:OA ratio = 1.1 Time = 2 h T = 65 °C | 96.01 (extraction efficiency) | [26] |
| Skin of Atlantic cod fish | Supercritical fluids Water (CO2 bubble) | T = 37 °C Pressure = 50 bars S/L = 1/20 Time = 3 h | 13.8 | [57] |
2.3. Ultrasound Extraction
2.4. Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Extraction
2.5. Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE)
3. Collagen Extraction Parameters
3.1. Time
3.2. Temperature
3.3. Solvent/Pepsin Concentration
4. Applications
4.1. Biomedical Applications
4.1.1. Wound Healing
4.1.2. Tissue Engineering
4.1.3. Drug Delivery
4.1.4. Cell Culture
4.2. Food Sector
4.2.1. Collagen Supplements
4.2.2. Collagen as Food Additives
4.2.3. Collagen in Drinks
4.3. Collagen in Cosmetics
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, R.; Grant, A.M.; Ma, R.; Zhang, S.; Tsukruk, V.V. Naturally-derived biopolymer nanocomposites: Interfacial design, properties and emerging applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2018, 125, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylingo, R.; Mania, S.; Panek, A.; Piątek, R.; Pawłowicz, R. Isolation and characterization of acid soluble collagen from the skin of african catfish (Clarias gariepinus), salmon (Salmo salar) and baltic cod (Gadus morhua). J. Biotechnol. Biomater. 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, F.; Ikram, M.; Shehzad, A.; Ghafoor, A. Marine collagen: An emerging player in biomedical applications. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4703–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Singla, A.; Lee, Y. Biomedical applications of collagen. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 221, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stover, D.A.; Verrelli, B.C. Comparative vertebrate evolutionary analyses of type I collagen: Potential of COL1a1 gene structure and intron variation for common bone-related diseases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, F.; Hussain, Z.; Tauseef, I.; Shehzad, A.; Wahid, F. A review on recent advances and applications of fish collagen. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, P.K.; Dandge, P.B. Isolation, characterization and valorizable applications of fish scale collagen in food and agriculture industries. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, F.; Datta, P.; Adhikari, B.; Dhara, S.; Ghosh, K.; Das Mohapatra, P.K. Collagen scaffolds derived from fresh water fish origin and their biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperman, L.; Michaeli, D. The immunogenicity of injectable collagen. II. A retrospective review of seventy-two tested and treated patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1984, 10, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperman, L.; Michaeli, D. The immunogenicity of injectable collagen. I. A 1-year prospective study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1984, 10, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-K.; Mendis, E. Bioactive compounds from marine processing byproducts–a review. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallela, R.; Venkatesan, J.; Bhatnagar, I.; Shim, Y.; Kim, S. Applications of Marine Collagen-Based Scaffolds in Bone Tissue Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Rome. 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org (accessed on 22 March 2018).
- Srikanya, A.; Dhanapal, K.; Sravani, K.; Madhavi, K.; Kumar, G.P. A study on optimization of fish protein hydrolysate preparation by enzymatic hydrolysis from tilapia fish waste mince. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 3220–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayannakidis, P.D.; Zotos, A. Fish processing by-products as a potential source of gelatin: A review. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, V.; Cruz, I.B.; Jorge, R.F.; Malcata, F.X.; Pintado, M.E.; Castro, P.M. Valorisation of natural extracts from marine source focused on marine by-products: A review. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2221–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Venkatesan, J. Introduction to marine biomaterials. In Marine Biomaterials. Characterization, Isolation and Application; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sripriya, R.; Kumar, R. A novel enzymatic method for preparation and characterization of collagen film from swim bladder of fish Rohu (Labeo rohita). Food Nutr. Sci. 2015, 6, 1468. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-K.; Wijesekara, I. Development and biological activities of marine-derived bioactive peptides: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Casas, D.E.; Aguilar, C.N.; Ascacio-Valdés, J.A.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Chávez-González, M.L.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C. Enzymatic hydrolysis and microbial fermentation: The most favorable biotechnological methods for the release of bioactive peptides. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2021, 3, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, C.; Shahidi, F. Marine Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Kim, D.; Park, S.-H.; Jung, J.; Cho, W.; Yu, A.R.; Lee, J. Fish Collagen Peptide (NaticolⓇ) Protects the Skin from Dryness, Wrinkle Formation, and Melanogenesis Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.; Park, J.; Lee, M.; Park, S.-H.; Jung, J.; Kim, J.; Eun, S.; Kim, J. Gly-Pro-Val-Gly-Pro-Ser Peptide Fish Collagen Improves Skin Moisture and Wrinkles with Ameliorated the Oxidative Stress and Pro-inflammatory Factors in Skin Photoaging Mimic Models. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 28, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, B.; Ramshaw, J.A. The collagen triple-helix structure. Matrix Biol. 1997, 15, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, C.; Wei, Q.; Ren, X. Selective extraction of collagen peptides with high purity from cod skins by deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7220–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, J. Extraction of type I collagen from tilapia scales using acetic acid and ultrafine bubbles. Processes 2021, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Chang, S.K. Isolation and characterization of collagen extracted from channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) skin. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, G.K.S.; Sharma, D.; Balakrishnan, R.M.; Ettiyappan, J.B.P. Extraction, optimization and characterization of collagen from sole fish skin. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 9, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuimbar, M.V.; Bhagwat, P.K.; Dandge, P.B. Extraction and characterization of acid soluble collagen from fish waste: Development of collagen-chitosan blend as food packaging film. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koochakzaei, A. Determination of Sulfuric Acid Effects on Degradation and Structural Changes of Gelatin Using Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Peak Deconvolution Analysis. Spectroscopy 2023, 38, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, N.; González, G.; Troncoso, E.; Zúñiga, R. Acid and enzyme-aided collagen extraction from the byssus of Chilean mussels (Mytilus chilensis): Effect of process parameters on extraction performance. Food Biophys. 2014, 9, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Vázquez, J.A.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Sotelo, C.G. Collagen extraction optimization from the skin of the small-spotted catshark (S. canicula) by response surface methodology. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zong, C.; Jin, S.; Zheng, J.; Chen, N.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, F.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y. Optimization of extraction conditions and characterization of pepsin-solubilised collagen from skin of giant croaker (Nibea japonica). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liang, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagen from fins, scales, skins, bones and swim bladders of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Deng, C. Characterization and comparison of collagen extracted from the skin of the Nile tilapia by fermentation and chemical pretreatment. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junianto, J.; Iskandar, I.; Rizal, A.; Damayanti, W. The influence of concentration of acetic acid and pepsin enzyme in nilem fish skin collagen extractionto the amount of rendement Produced. World News Nat. Sci. 2018, 21, 164–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.E.; Noh, S.-K.; Kim, M.J. Effects of Enzymatic-and Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction on Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Collagen Hydrolysate Fractions from Alaska Pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) Skin. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, A.; Li, Y.; Zheng, G. Enzymatic hydrolysis of Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) skin and antioxidant activity of the resulting hydrolysate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, Z.; Rakariyatham, K.; Yu, C.; Shahidi, F.; Zhou, D. Antioxidant activity and functional properties of Alcalase-hydrolyzed scallop protein hydrolysate and its role in the inhibition of cytotoxicity in vitro. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuaychan, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics of acid-and pepsin-soluble collagens from scale of seabass (Lates calcarifer). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wei, G.; Li, T.; Hu, J.; Lu, N.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Effects of alkaline pretreatments and acid extraction conditions on the acid-soluble collagen from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.M.; Marques, A.P.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Evaluation of the potential of collagen from codfish skin as a biomaterial for biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.K.; Nidheesh, T.; Suresh, P. Comparative study on characteristics and in vitro fibril formation ability of acid and pepsin soluble collagen from the skin of catla (Catla catla) and rohu (Labeo rohita). Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Yi, R.; Xu, N.; Gao, R.; Hong, B. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble collagen from scales and skin of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Duan, Q.; Liu, X.; Shen, X.; Li, C. Extraction and physicochemical characterization of pepsin soluble collagens from golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii) skin and bone. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2019, 28, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewdang, O.; Benjakul, S.; Kaewmanee, T.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics of collagens from the swim bladders of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares). Food Chem. 2014, 155, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Tian, X.; Tang, Y.; Ding, G.; Yang, Z.; Jin, H. Pepsin-soluble collagen from the skin of lophius litulo: A preliminary study evaluating physicochemical, antioxidant, and wound healing properties. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Jiang, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; An, X.; Li, Y. Preparation of self-assembled collagen fibrillar gel from tilapia skin and its formation in presence of acidic polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Kong, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W. Extraction and properties of acid-soluble collagen and pepsin-soluble collagen from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) scales: Prerequisite information for fishery processing waste reuse. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.O.; Alves, A.L.; Carvalho, D.N.; Martins, E.; Oliveira, C.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Acid and enzymatic extraction of collagen from Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) swim bladders envisaging health-related applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, I.; Jridi, M.; Nasri, R.; Dammak, A.; Hajji, M.; Nasri, M.; Barkia, A. Characteristics and functional properties of gelatin from thornback ray skin obtained by pepsin-aided process in comparison with commercial halal bovine gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Benjakul, S.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Nalinanon, S. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of collagen from clown featherback (Chitala ornata) skin: Yield and molecular characteristics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, L.; Cai, P.; Li, P.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Z.; Sun, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, D. Effect of ultrasound assisted extraction on the physicochemical and functional properties of collagen from soft-shelled turtle calipash. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, H.J.; Lee, N.H. Application of ultrasonic treatment to extraction of collagen from the skins of sea bass Lateolabrax japonicus. Fish. Sci. 2013, 79, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, M.; Martins, M.; Dias, A.C.; Ventura, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A. Uncovering the potential of aqueous solutions of deep eutectic solvents on the extraction and purification of collagen type I from Atlantic codfish (Gadus morhua). Green Chem. 2021, 23, 8940–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.O.; Martins, E.; Carvalho, D.N.; Alves, A.L.; Oliveira, C.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Collagen from Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) skins extracted using CO2 acidified water with potential application in healthcare. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, K.S.; Aznar, R.; O’Donnell, C.; Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound technology for the extraction of biologically active molecules from plant, animal and marine sources. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Lista, A.; Siekapen, M.M.; Ghaffari-Bohlouli, P.; Nie, L.; Alimoradi, H.; Shavandi, A. Fish collagen: Extraction, characterization, and applications for biomaterials engineering. Polymers 2020, 12, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, H.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A. Ionic liquid solutions as extractive solvents for value-added compounds from biomass. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4786–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruesgas-Ramón, M.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Durand, E. Application of deep eutectic solvents (DES) for phenolic compounds extraction: Overview, challenges, and opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, V.; Prieto, M.A.; Barros, L.; Coutinho, J.A.; Ferreira, I.C.; Ferreira, O. Enhanced extraction of phenolic compounds using choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents from Juglans regia L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 115, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, M.P.; Fernández, N.; Gaspar, F.B.; Bronze, M.d.R.; Duarte, A.R.C. Extraction of Biocompatible Collagen From Blue Shark Skins through the Conventional Extraction Process Intensification Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 937036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, E.; Mendiola, J.; Castro-Puyana, M. Supercritical Fluid Extraction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, K.; Rahman, M.; Azmir, J.; Mohamed, A.; Jahurul, M.; Sahena, F.; Zaidul, I. Experimental design of supercritical fluid extraction—A review. J. Food Eng. 2014, 124, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Trindade Alfaro, A.; Fonseca, G.G.; Balbinot, E.; de Souza, N.E.; Prentice, C. Yield, viscosity, and gel strength of wami tilapia (Oreochromis urolepis hornorum) skin gelatin: Optimization of the extraction process. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, R.C.; Marques, A.L.; Oliveira, S.M.; Diogo, G.S.; Pirraco, R.P.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Xavier, J.C.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H.; Mano, J.F. Extraction and characterization of collagen from Antarctic and Sub-Antarctic squid and its potential application in hybrid scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, M.; Agwa, M.; Saeed, H.; Khedr, S.M.; Morsy, O.; El-Demellawy, M.A. Fish scale collagen preparation, characterization and its application in wound healing. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, R.V.; James, S.L.; James, S.E. A review of tissue-engineered skin bioconstructs available for skin reconstruction. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandika, P.; Ko, S.-C.; Jung, W.-K. Marine-derived biological macromolecule-based biomaterials for wound healing and skin tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Qin, S. Comprehensive assessment of Nile tilapia skin (Oreochromis niloticus) collagen hydrogels for wound dressings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbialy, Z.I.; Atiba, A.; Abdelnaby, A.; Al-Hawary, I.I.; Elsheshtawy, A.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Fadl, S.E.; Assar, D.H. Collagen extract obtained from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) skin accelerates wound healing in rat model via up regulating VEGF, bFGF, and α-SMA genes expression. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Srivas, P.K.; Dadhich, P.; Das, B.; Maity, P.P.; Moulik, D.; Dhara, S. Accelerating full thickness wound healing using collagen sponge of mrigal fish (Cirrhinus cirrhosus) scale origin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Hong, P. Marine collagen peptides from the skin of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Characterization and wound healing evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.F.; Liu, H.; Yan, J.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.J. Characterization of collagen from haddock skin and wound healing properties of its hydrolysates. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 015022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Vázquez, J.A.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Sotelo, C.G. Hydrolysates of fish skin collagen: An opportunity for valorizing fish industry byproducts. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issains, F.B.; Trinanda, A.F.; Basyir, A.M.; Benaya, A.; Yuwono, A.H.; Ramahdita, G. Extraction of collagen Type-I from snakehead fish skin (Channa striata) and synthesis of biopolymer for wound dressing. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Long Island, NY, USA, 2019; p. 020013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Sui, B.; Mo, X.; Sun, J. Multifunctional and biomimetic fish collagen/bioactive glass nanofibers: Fabrication, antibacterial activity and inducing skin regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Yamaya, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Saito, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Koga, T.; Enari, H.; Suto, S.; Yotsuyanagi, T. The usefulness of the collagen and elastin sponge derived from salmon as an artificial dermis and scaffold for tissue engineerin. Biomed. Res. 2011, 32, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amal, B.; Veena, B.; Jayachandran, V.; Shilpa, J. Preparation and characterisation of Punica granatum pericarp aqueous extract loaded chitosan-collagen-starch membrane: Role in wound healing process. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, I.B.; Munde, S.J.; Shelke, S.; Ambekar, W.; Mallikarjuna Setty, C. Curcumin loaded fish scale collagen-HPMC nanogel for wound healing application: Ex-vivo and In-vivo evaluation. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2019, 68, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Wu, Q.; Long, H.; Hu, K.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Sun, M.; Dong, J.; Wei, X.; Suo, J. Development of chitosan/gelatin hydrogels incorporation of biphasic calcium phosphate nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 1636–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavandi, A.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Sun, Z.; Ali, M.A. Bio-scaffolds produced from irradiated squid pen and crab chitosan with hydroxyapatite/β-tricalcium phosphate for bone-tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, R.; Jones, E.; McGonagle, D.; Giannoudis, P.V. Bone regeneration: Current concepts and future directions. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.-S.; Ok, Y.-J.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Kwak, J.-Y.; Yoon, S. Marine collagen as a promising biomaterial for biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, J.; Zhang, J.; Bao, B.; Palaniyandi, K.; Wang, S.; Wenhui, W.; Robinson, J.S. Rheological, biocompatibility and osteogenesis assessment of fish collagen scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, N.; Xue, Y.; Ding, T.; Liu, X.; Mo, X.; Sun, J. Electrospun tilapia collagen nanofibers accelerating wound healing via inducing keratinocytes proliferation and differentiation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’heureux, N.; Pâquet, S.; Labbé, R.; Germain, L.; Auger, F.A. A completely biological tissue-engineered human blood vessel. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Saito, T. Effect of type I collagen derived from tilapia scale on odontoblast-like cells. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 12, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Ritch, R.; Lin, S.M.; Ni, M.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lu, Y.L.; Lai, H.J.; Lin, F.-H. A new fish scale-derived scaffold for corneal regeneration. Eur. Cells Mater. 2010, 19, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.M.; Haugh, M.G.; O’Brien, F.J. The effect of mean pore size on cell attachment, proliferation and migration in collagen–glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, S.; Sekar, S.; Katheem, M.F.; Krishnakumar, S.; Sastry, T.P. Fish scale collagen—A novel material for corneal tissue engineering. Artif. Organs 2012, 36, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyer, B.; Bernhardt, A.; Heinemann, S.; Stachel, I.; Meyer, M.; Gelinsky, M. Biomimetically mineralized salmon collagen scaffolds for application in bone tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.N.; Muthukumar, T.; Somanathan, N.; Sastry, T. Biocompatibility of Collagen Hybridized Porous Sulphonated Poly (Aryl ether ketone) Sponges for Bone Tissue Engineering. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2015, 29, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Raftery, R.M.; Woods, B.; Marques, A.L.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Silva, T.H.; Cryan, S.-A.; Reis, R.L.; O’Brien, F.J. Multifunctional biomaterials from the sea: Assessing the effects of chitosan incorporation into collagen scaffolds on mechanical and biological functionality. Acta Biomater. 2016, 43, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.; Choi, C.H.; Mun, F.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Jung, W.-K.; Jang, C.H.; Kim, G. A polycaprolactone/fish collagen/alginate biocomposite supplemented with phlorotannin for hard tissue regeneration. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Zainol, I.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Fauzi, M. Development of various composition multicomponent chitosan/fish collagen/glycerin 3D porous scaffolds: Effect on morphology, mechanical strength, biostability and cytocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Q.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Xin, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xu, T.; Cha, D.; Fan, B. Fabrication and evaluation of thermosensitive chitosan/collagen/α, β-glycerophosphate hydrogels for tissue regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Essen, T.H.; Lin, C.C.; Hussain, A.K.; Maas, S.; Lai, H.J.; Linnartz, H.; van den Berg, T.J.; Salvatori, D.C.; Luyten, G.P.; Jager, M.J.; et al. A fish scale–derived collagen matrix as artificial cornea in rats: Properties and potential. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 3224–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkasabgy, N.A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Shamma, R. Determination of cytocompatibility and osteogenesis properties of in situ forming collagen-based scaffolds loaded with bone synthesizing drug for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2018, 67, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, T.; Aravinthan, A.; Sharmila, J.; Kim, N.S.; Kim, J.-H. Collagen/chitosan porous bone tissue engineering composite scaffold incorporated with Ginseng compound K. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, G.; Seleenmary Sobhanadhas, L.S.; Sekar Jeyakumar, G.F.; Devi, V.; Sivagnanam, U.T.; Fardim, P. Fabrication of biohybrid cellulose acetate-collagen bilayer matrices as nanofibrous spongy dressing material for wound-healing application. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2512–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, F.; Guo, S.; Yang, J. Preparation of aminated fish scale collagen and oxidized sodium alginate hybrid hydrogel for enhanced full-thickness wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, G.S.; Marques, C.F.; Sotelo, C.G.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Pirraco, R.P.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. Cell-laden biomimetically mineralized shark-skin-collagen-based 3D printed hydrogels for the engineering of hard tissues. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3664–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, G.S.; Carneiro, F.; Freitas-Ribeiro, S.; Sotelo, C.G.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Pirraco, R.P.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. Prionace glauca skin collagen bioengineered constructs as a promising approach to trigger cartilage regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, R.; Jia, Z.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Xia, H.; Meng, D. Porous fish collagen for cartilage tissue engineering. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 6107. [Google Scholar]
- Woodrow, T.; Chant, T.; Chant, H. Treatment of diabetic foot wounds with acellular fish skin graft rich in omega-3: A prospective evaluation. J. Wound Care 2019, 28, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.d.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.K.; Yeo, K.P.; Chun, Y.Y.; Tan, T.T.Y.; Tan, N.S.; Angeli, V.; Choong, C. Fish scale-derived collagen patch promotes growth of blood and lymphatic vessels in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2017, 63, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Chen, M.-M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Wang, J.-H.; Chen, J.-D.; Zhang, Q.-Q.J.C.; Biointerfaces, S.B. Fish collagen-based scaffold containing PLGA microspheres for controlled growth factor delivery in skin tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerface 2015, 136, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Vu, M.Q.; Phan, T.T.; Vu, T.Q.; Vo, Q.A.; Bach, G.L.; Thai, H. Novel pH-sensitive hydrogel beads based on carrageenan and fish scale collagen for allopurinol drug delivery. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1795–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, D.M.; Campbell, A.M.; Park, C.R.; Halonen, J.; Zoladz, P.R. The temporal dynamics model of emotional memory processing: A synthesis on the neurobiological basis of stress-induced amnesia, flashbulb and traumatic memories, and the Yerkes-Dodson law. Neural Plast. 2007, 2007, 060803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.M.; Kang, H.Y.; Min, H.-J.; Lee, R.; Ikram, M.; Subhan, F.; Jin, S.W.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kwak, J.-Y.; Yoon, S. Bioactive fish collagen/polycaprolactone composite nanofibrous scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning for 3D cell culture. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 205, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, R.; Uemura, T.; Xu, Z.; Yamaguchi, I.; Ikoma, T.; Tanaka, J. Rapid oriented fibril formation of fish scale collagen facilitates early osteoblastic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King’Ori, A. A review of the uses of poultry eggshells and shell membranes. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2011, 10, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Wei, W.; Xiao, F.; Xu, J.H.; Bao, C.D.; Ni, L.Q.; Li, X.F. A randomized, double-blind, multicenter, controlled clinical trial of chicken type II collagen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2008, 59, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhou, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, B. Collagen and its derivatives: From structure and properties to their applications in food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shori, A.B.; Hong, Y.C.; Baba, A.S. Proteolytic profile, angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory activity and sensory evaluation of Codonopsis pilosula and fish collagen cheese. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamorano-Apodaca, J.C.; García-Sifuentes, C.O.; Carvajal-Millán, E.; Vallejo-Galland, B.; Scheuren-Acevedo, S.M.; Lugo-Sánchez, M.E. Biological and functional properties of peptide fractions obtained from collagen hydrolysate derived from mixed by-products of different fish species. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, R.; Perrechil, F.; Sato, A.; Cunha, R. Emulsifying properties of collagen fibers: Effect of pH, protein concentration and homogenization pressure. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Elavarasan, K.; Hanjabam, M.D.; Binsi, P.; Mohan, C.; Zynudheen, A.; Kumar, A.J.L. Marine collagen peptide as a fortificant for biscuit: Effects on biscuit attributes. LWT 2019, 109, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Shahidi, F. Gelatin hydrolysate from blacktip shark skin prepared using papaya latex enzyme: Antioxidant activity and its potential in model systems. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jridi, M.; Lassoued, I.; Nasri, R.; Ayadi, M.A.; Nasri, M.; Souissi, N. Characterization and potential use of cuttlefish skin gelatin hydrolysates prepared by different microbial proteases. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 461728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najumudeen, F. Avon Celebrates 20th Anniversary of Skincare Brand. 2012. Available online: http://thestar.com.my/metro/story.asp?file=/2012/7/18/central/11637420&sec=central (accessed on 4 October 2012).
- Takemori, T.; Yasuda, H.; Mitsui, M.; Shimizu, H. Collagen-Containing Food and Drink. U.S. Patent US20070009638A1, 11 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sibilla, S.; Godfrey, M.; Brewer, S.; Budh-Raja, A.; Genovese, L. An overview of the beneficial effects of hydrolysed collagen as a nutraceutical on skin properties: Scientific background and clinical studies. Open Nutraceuticals J. 2015, 8, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borumand, M.; Sibilla, S. Nutraceuticals. Effects of a nutritional supplement containing collagen peptides on skin elasticity, hydration and wrinkles. J. Med. Nutr. Nutraceuticals 2015, 4, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, B. Effects of collagen and collagen hydrolysate from jellyfish umbrella on histological and immunity changes of mice photoaging. Nutrients 2013, 5, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asserin, J.; Lati, E.; Shioya, T.; Prawitt, J. The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture and the dermal collagen network: Evidence from an ex vivo model and randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2015, 14, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.-C.; Chiu, C.-S.; Chan, Y.-J.; Guo, T.-P.; Lin, C.-C.; Wang, P.-C.; Lin, P.-Y.; Mulio, A.T.; Li, P.-H. An In Vivo Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of Blue Shark (Prionace glauca) Cartilage Collagen as a Cosmetic. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, E.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. In vivo skin hydrating efficacy of fish collagen from greenland halibut as a high-value active ingredient for cosmetic applications. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 11930:2019; Cosmetics Microbiology-Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Protection of a Cosmetic Product. International Organization of Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
| Fish Species | Source of Collagen | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) | Skin | Collagen extraction can increase b-fibroblast, TGF-β1 growth factor (b-FGF), fibroblast and myofibroblast proliferation, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) gene expression, and tricellularar matrix ECM production. | [72] |
| Tilapia and grey mullet | Scale | Extracted collagen converted to stable, high-strength fibers via self-aggregation and cross-linking, which assist optimal moisture level maintenance at the wound site, accelerating wound healing. | [68] |
| Melanogrammus aeglefinus | Skin | Fish skin-derived collagen on mice formed fibrin, which resulted in reduced clotting time, faster epithelialization, and shorter wound healing time. | [75] |
| Prionace glauca, Scyliorhinus canicula, Xiphias gladius, and Thunnus albacares | Skin | Collagen extraction significantly accelerated the wound healing of second-degree burns and generation of new skin appendage. | [76] |
| Snakehead fish (Channa striata) | Skin | New dressing for burn healing that has the potential to be used by cross-linking biopolymer collagen with alginate to form functional group—CONH. | [77] |
| Tilapia | Skin | Animal experiments indicated that collagen/bioactive glass (Col/BG) composites can accelerate rat skin wound healing. In addition, the Col/BG nanofibers promoted the proliferation, adhesion, and migration of human keratinocytes. | [78] |
| Salmon | Skin | The WST-1 assay reveled that the fibroblasts were well proliferated in the collagen and elastin sponge (CES). Grafting the CES and Terudermis (traditional collagen sponge) on the skin defects of rats revealed no significant difference observed between the CES and Terudermis. | [79] |
| Rachycentrn canadum (cobia) | Skin | Chitosan–collagen–starch membranes (CCSMs) loaded with Punica granatum extract showed reduced wound surface area and enhanced epithelial cell proliferation with no scar after wound healing. | [80] |
| Catla | Scale | Ex vivo permeation studies showed that the formulate (curcumin-loaded fish scale collagen)–hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC K100) nanogel exhibited high concentrations and a low irritation score, confirming the prepared formulate’s function in wound healing. | [81] |
| Fish Species | Source of Collagen | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tilapia | Scales | Corneal tissue engineering | [90] |
| Shark | Cartilage | Bone tissue engineering | [91] |
| Lates calcarifer | Scales | Corneal tissue engineering | [92] |
| Salmon | Skin | Bone tissue engineering | [93] |
| Lates calcarifer | Scales | Bone tissue engineering and bone implant | [94] |
| Salmon | Skin | Bone tissue engineering | [95] |
| Flat fish (Paralichthys olivaceus) | Skin | Bone tissue engineering | [96] |
| Tilapia | Scales | Skin tissue engineering and regeneration | [97] |
| Tilapia | Scales | Dental tissue engineering | [89] |
| African catfish, salmon, and Baltic cod | Skin | Tissue engineering | [2] |
| Flatfish (P. olivaceus) | Skin | Skin tissue engineering | [70] |
| Haddock | Skin | Tissue engineering | [98] |
| Fresh tilapia | Scales | Artificial cornea | [99] |
| Salmon | Skin | Bone and cartilage tissue engineering | [95] |
| Fish | - | Bone tissue engineering | [100] |
| Lates calcarifer | Scales | Bone tissue engineering | [101] |
| Salmon—S. salar and African catfish—C. gariepinu | - | Tissue engineering | [2] |
| Arothron stellatus fish | - | Skin tissue engineering | [102] |
| Larimichthys crocea | Scales | Skin tissue engineering | [103] |
| Shark | Skin | Bone tissue engineering | [104] |
| Blue shark | Skin | Cartilage tissue engineering | [105] |
| Tilapia | Skin | Cartilage tissue engineering | [106] |
| North Atlantic cod | Skin | Skin tissue engineering | [107] |
| Larimichthys crocea | Scale | Skin tissue engineering | [103] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaikwad, S.; Kim, M.J. Fish By-Product Collagen Extraction Using Different Methods and Their Application. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020060
Gaikwad S, Kim MJ. Fish By-Product Collagen Extraction Using Different Methods and Their Application. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaikwad, Sunita, and Mi Jeong Kim. 2024. "Fish By-Product Collagen Extraction Using Different Methods and Their Application" Marine Drugs 22, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020060
APA StyleGaikwad, S., & Kim, M. J. (2024). Fish By-Product Collagen Extraction Using Different Methods and Their Application. Marine Drugs, 22(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020060





