Tissue Distribution and Metabolization of Ciguatoxins in an Herbivorous Fish following Experimental Dietary Exposure to Gambierdiscus polynesiensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Dietary Toxin Exposure
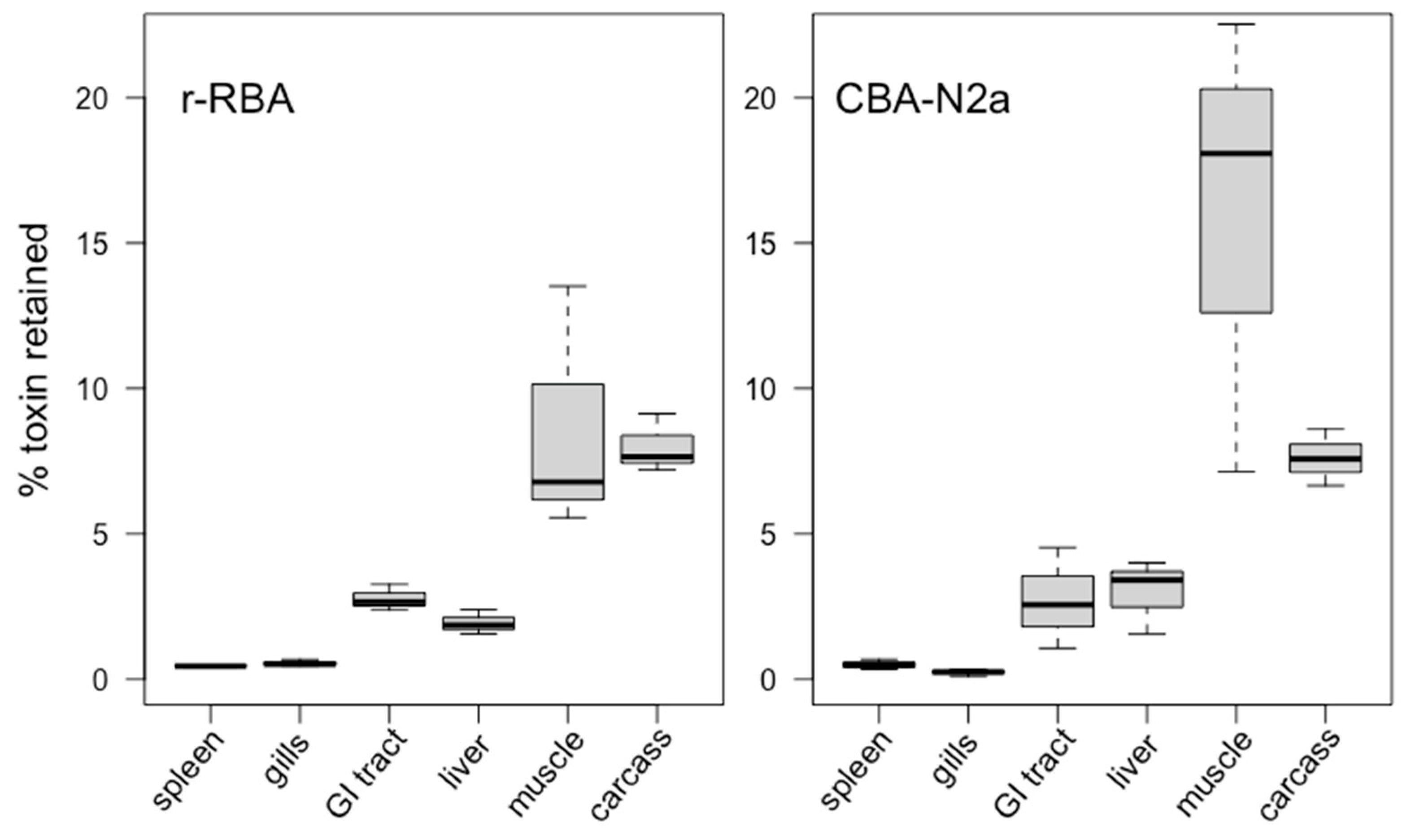
2.2. Toxin Tissue Distribution
2.2.1. Tissue Concentrations
2.2.2. Tissue Burden
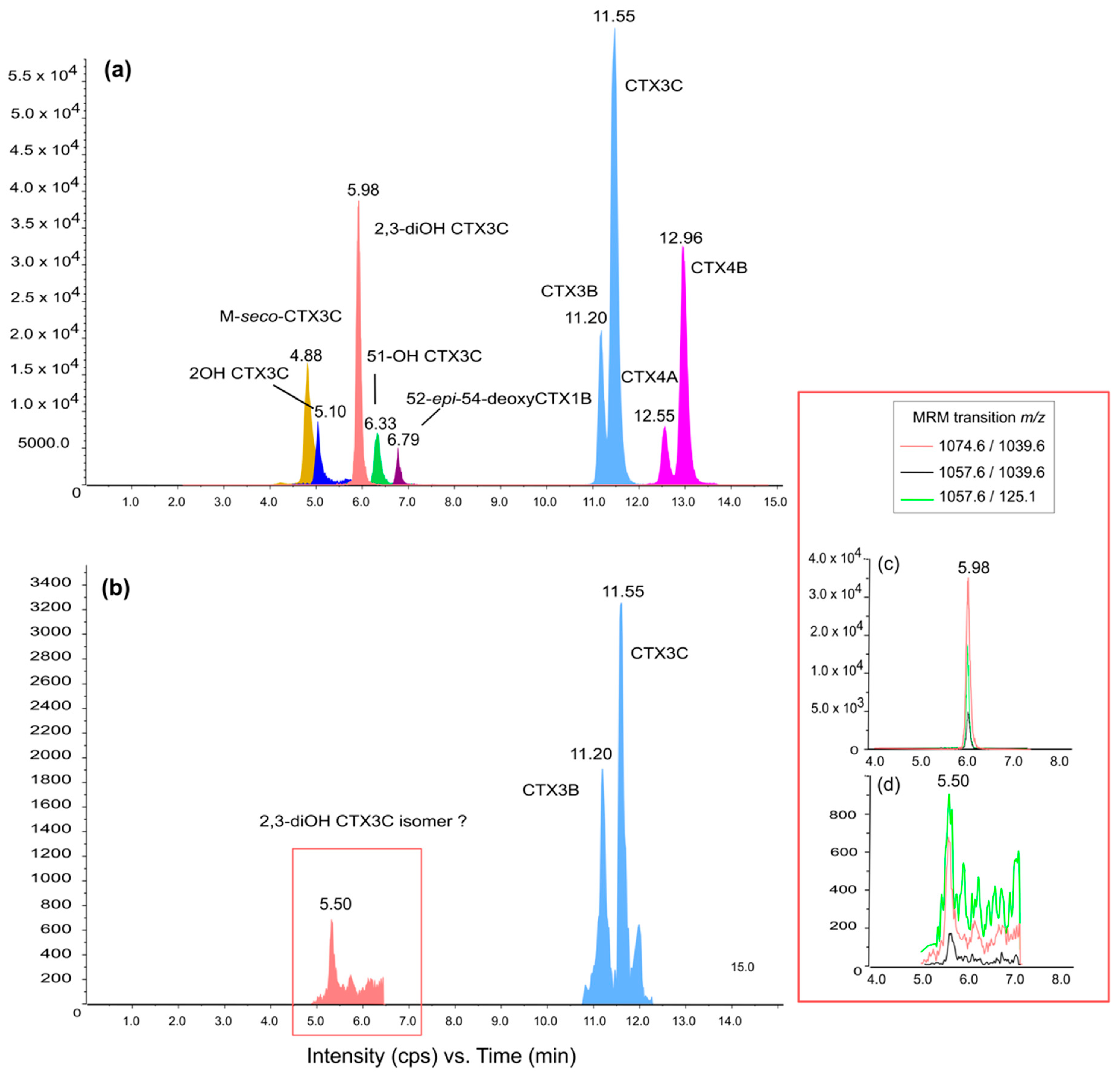
2.3. Toxin Metabolization
3. Discussion
3.1. Toxin Tissue Distribution
3.2. Toxin Metabolization
3.3. Toxin Tissue Burden
3.4. Implications for Trophic Transfer and Seafood Safety
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Model
4.1.1. Study Species
4.1.2. Fish Maintenance
4.1.3. Gel Food Preparation
4.1.4. Fish Exposure
4.2. Toxin Determination
4.2.1. Sample Extraction
4.2.2. Radioligand-Receptor Binding Assay (r-RBA)
4.2.3. Neuro2a Cytotoxicity Assay (CBA-N2a)
4.2.4. Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
4.3. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adachi, R.; Fukuyo, Y. The thecal structure of a marine toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus gen. et sp. nov. collected in a ciguatera-endemic area. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1979, 45, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Nakajima, I.; Bagnis, R.; Adachi, R. Finding of a dinoflagellate as a likely culprit of ciguatera. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1977, 43, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.; Qiu, D.; Lopes, R.M.; Lin, S. Fukuyoa paulensis gen. et sp. nov., a new genus for the globular species of the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, L.; Dewailly, E.; Baden, D.G. The epidemiology of marine harmful algal blooms. Epidemiology 2000, 11, S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.A.; Fernandez, M.; Backer, L.C.; Dickey, R.W.; Bernstein, J.; Schrank, K.; Kibler, S.; Stephan, W.; Gribble, M.O.; Bienfang, P.; et al. An updated review of ciguatera fish poisoning: Clinical, epidemiological, environmental, and public health management. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Tartaglione, L.; Friedemann, M.; Spielmeyer, A.; Kappenstein, O.; Bodi, D. Ciguatera mini review: 21st century environmental challenges and the interdisciplinary research efforts rising to meet them. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litaker, R.W.; Vandersea, M.W.; Faust, M.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Nau, A.W.; Holland, W.C.; Chinain, M.; Holmes, M.J.; Tester, P.A. Global distribution of ciguatera causing dinoflagellates in the genus Gambierdiscus. Toxicon 2010, 56, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, G.; Farrell, H.; Murray, S. Gambierdiscus, the cause of ciguatera fish poisoning: An increased human health threat influenced by climate change. In Climate Change and Marine and Freshwater Toxins; Botana, L.M., Louzao, C., Vilarino, N., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2015; p. 508. ISBN 311038261X/9783110382617. [Google Scholar]
- Aligizaki, G.; Fraga, S.; Nikolaidis, K. Is Gambierdiscus expanding to new areas? Harmful Algae 2008, 36, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Darius, H.T.; Quod, J.P.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatera poisonings: A global review of occurrences and trends. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Caillaud, A.; Diogène, J.; Raho, N.; Zapata, M. Gambierdiscus excentricus sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a benthic toxic dinoflagellate from the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean). Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Sato, S.; Tawong, W.; Sakanari, H.; Uehara, K.; Shah, M.M.R.; Suda, S.; Yasumoto, T.; Taira, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. Genetic diversity and distribution of the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae) in coastal areas of Japan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Smith, K.F.; Murray, S.; Harwood, D.T.; Trnski, T.; Munday, R. The epiphytic genus Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae) in the Kermadec Islands and Zealandia regions of the southwestern Pacific and the associated risk of ciguatera fish poisoning. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laza-Martínez, A.; David, H.; Riobó, P.; Miguel, I.; Orive, E. Characterization of a Strain of Fukuyoa paulensis (Dinophyceae) from the Western Mediterranean Sea. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2016, 63, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, M.P.; Brewer, T.D.; Johnstone, R.; Fleming, L.E.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera fish poisoning in the Pacific Islands (1998 to 2008). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliño, L.; Costa, P.R. Global impact of ciguatoxins and ciguatera fish poisoning on fish, fisheries and consumers. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dolah, F.M. Marine algal toxins: Origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haro, L.; Pommier, P.; Valli, M. Emergence of imported ciguatera in Europe: Report of 18 cases at the poison control centre of Marseille. J. Toxicol.-Clin. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehane, L.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera: Recent advances but the risk remains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 61, 91–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Holmes, M.J. Origin and transfer of toxins involved in ciguatera. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. 1993, 106, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdalet, E.; Fleming, L.E.; Gowen, R.; Davidson, K.; Hess, P.; Backer, L.C.; Moore, S.K.; Hoagland, P.; Enevoldsen, H. Marine harmful algal blooms, human health and wellbeing: Challenges and opportunities in the 21st century. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2016, 96, 61–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, P.A.; Feldman, R.L.; Nau, A.W.; Kibler, S.R.; Wayne Litaker, R. Ciguatera fish poisoning and sea surface temperatures in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. Toxicon 2010, 56, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausing, R.J.; Chinain, M.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y. Practical sampling guidance for determination of ciguatoxin in fish. In Guide for Designing and Implementing a Plan to Monitor Toxin-Producing Microalgae; Reguera, B., Alonso, R., Moreira, A., Méndez, S., Dechraoui-Bottein, M.-Y., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO and International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Paris, France; Vienna, Austria, 2016; pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, D.; Kerbrat, A.S.; Darius, H.T.; Rossi, F.; Yeeting, B.; Haddad, M.; Golubic, S.; Pauillac, S.; Chinain, M. Ciguatera Shellfish Poisoning (CSP): A new ecotoxicological phenomenon from cyanobacteria to humans via giant clams. In Food Chains: New Research; Jensen, M.A., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Toulouse, France, 2012; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Vandersea, M.W.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P.; et al. Toxicological investigations on the sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla (Toxopneustidae, Echinoid) from Anaho Bay (Nuku Hiva, French Polynesia): Evidence for the presence of Pacific ciguatoxins. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Vandersea, M.W.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P.; et al. Tectus niloticus (Tegulidae, gastropod) as a novel vector of ciguatera poisoning: Detection of Pacific ciguatoxins in toxic samples from Nuku Hiva Island (French Polynesia). Toxins 2018, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, Y.L.; Wai, T.C.; Murphy, M.B.; Chan, W.H.; Wu, J.J.; Lam, J.C.W.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S. Pacific ciguatoxins in food web components of coral reef systems in the Republic of Kiribati. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14070–14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Clausing, R.J.; Vandersea, M.; Chamero-Lago, D.; Gómez-Batista, M.; Hernández-Albernas, J.I.; Chomérat, N.; Rojas-Abrahantes, G.; Litaker, R.W.; Tester, P.; et al. Ciguatoxin occurrence in food-web components of a Cuban coral reef ecosystem: Risk-assessment implications. Toxins 2019, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, M.; Sasaki, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Yasumoto, T.; Naoki, H.; Iwashita, T.; Matsunaga, S. Structure of Maitotoxin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 2060–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Holmes, M.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Jones, A. Lonspray mass spectrometry of ciguatoxin-1, maitotoxin-2 and -3, and related marine polyether toxins. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui Bottein, M.Y.; Wacksman, J.J.; Ramsdell, J.S. Species selective resistance of cardiac muscle voltage gated sodium channels: Characterization of brevetoxin and ciguatoxin binding sites in rats and fish. Toxicon 2006, 48, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molgó, J.; Gaudry-Talarmain, Y.M.; Legrand, A.M.; Moulian, N. Ciguatoxin extracted from poisonous moray eels Gymnothorax javanicus triggers acetylcholine release from Torpedo cholinergic synaptosomes via reversed Na+–Ca2+ exchange. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 160, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, G.M.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatoxins: Cyclic polyether modulators of voltage-gated ion channel function. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 82–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Report of the Expert Meeting on Ciguatera Poisoning. Rome, 19–23 November 2018; Food Safety and Quality, No.9; FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dechraoui Bottein, M.Y.; Wang, Z.; Ramsdell, J.S. Toxicokinetics of the ciguatoxin P-CTX-1 in rats after intraperitoneal or oral administration. Toxicology 2011, 284, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikehara, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Yasumoto, T. Biooxidation of ciguatoxins leads to species-specific toxin profiles. Toxins 2017, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudge, E.M.; Miles, C.O.; Ivanova, L.; Uhlig, S.; James, K.S.; Erdner, D.L.; Fæste, C.K.; McCarron, P.; Robertson, A. Algal ciguatoxin identified as source of ciguatera poisoning in the Caribbean. Chemosphere 2023, 330, 138659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Inafuku, Y.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T. Detailed LC-MS/MS analysis of ciguatoxins revealing distinct regional and species characteristics in fish and causative alga from the Pacific. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8886–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti Howell, C.; Roué, M.; Ung, A.; Henry, K.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Viallon, J.; Darius, H.T. Ciguatera poisoning in French Polynesia: A review of the distribution and toxicity of Gambierdiscus spp., and related impacts on food web components and human health. Harmful Algae 2023, 129, 102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Poli, M.A.; Norton, R.S.; MacLeod, J.K.; Sheil, M.M. Purification and characterization of ciguatoxins from moray eel (Lycodontis javanicus, Muraenidae). Toxicon 1991, 29, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, M.; Legrand, A.M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Fukui, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and configurations of ciguatoxin from the moray eel Gymnothorax javanicus and its likely precursor from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4380–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M. Multiple ciguatoxins in the flesh of fish. Toxicon 1992, 30, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledreux, A.; Brand, H.; Chinain, M.; Bottein, M.Y.D.; Ramsdell, J.S. Dynamics of ciguatoxins from Gambierdiscus polynesiensis in the benthic herbivore Mugil cephalus: Trophic transfer implications. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosteson, T.R.; Ballantine, D.L.; Durst, H.D. Seasonal frequency of ciguatoxic barracuda in southwest Puerto Rico. Toxicon 1988, 26, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliño, L.; Costa, P.R. Differential toxin profiles of ciguatoxins in marine organisms: Chemistry, fate and global distribution. Toxicon 2018, 150, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.H.; Mak, Y.L.; Wu, J.J.; Jin, L.; Sit, W.H.; Lam, J.C.W.; Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Murphy, M.B. Spatial distribution of ciguateric fish in the Republic of Kiribati. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaboriau, M.; Ponton, D.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M. Ciguatera fish toxicity in French Polynesia: Size does not always matter. Toxicon 2014, 84, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshiro, N.; Yogi, K.; Asato, S.; Sasaki, T.; Tamanaha, K.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Inafuku, Y. Ciguatera incidence and fish toxicity in Okinawa, Japan. Toxicon 2010, 56, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, A.M. Ciguatera toxins: Origin, transfer through the food chain and toxicity to humans. In Proceedings of the Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernandez, M., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Xunta de Galicia, Spain, 1998; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.J. The changing face of ciguatera. Toxicon 2001, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roué, M.; Darius, H.T.; Picot, S.; Ung, A.; Viallon, J.; Gaertner-Mazouni, N.; Sibat, M.; Amzil, Z.; Chinain, M. Evidence of the bioaccumulation of ciguatoxins in giant clams (Tridacna maxima) exposed to Gambierdiscus spp. cells. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roué, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Hess, P.; Amzil, Z.; Chinain, M. Tissue distribution and elimination of ciguatoxins in Tridacna maxima (Tridacnidae, bivalvia) fed Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Toxins 2018, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausing, R.J.; Losen, B.; Oberhaensli, F.R.; Darius, H.T.; Sibat, M.; Hess, P.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Chinain, M.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.Y. Experimental evidence of dietary ciguatoxin accumulation in an herbivorous coral reef fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Venables, B.; Lewis, R.J. Critical review and conceptual and quantitative models for the transfer and depuration of ciguatoxins in fishes. Toxins 2021, 13, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J. Origin of ciguateric fish: Quantitative modelling of the flow of ciguatoxin through a marine food chain. Toxins 2022, 14, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J. Model of the origin of a ciguatoxic grouper (Plectropomus leopardus). Toxins 2023, 15, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Fouc, M.T.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Pauillac, S.; Laurent, D. Ciguatera risk management in French Polynesia: The case study of Raivavae Island (Australes Archipelago). Toxicon 2010, 56, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darius, H.T.; Paillon, C.; Mou-Tham, G.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Revel, T.; Viallon, J.; Vigliola, L.; Ponton, D.; Chinain, M. Evaluating age and growth relationship to ciguatoxicity in five coral reef fish species from French Polynesia. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.T.; Robertson, A. Depuration kinetics and growth dilution of Caribbean ciguatoxin in the omnivore Lagodon rhomboides: Implications for trophic transfer and ciguatera risk. Toxins 2021, 13, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Henao, A.; García-álvarez, N.; Padilla, D.; Ramos-Sosa, M.; Sergent, F.S.; Fernández, A.; Estévez, P.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Diogène, J.; Real, F. Accumulation of C-CTX1 in muscle tissue of goldfish (Carassius auratus) by dietary experience. Animals 2021, 11, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, I.D.P.; Sdiri, K.; Taylor, A.; Viallon, J.; Gharbia, H.B.; Mafra Júnior, L.L.; Swarzenski, P.; Oberhaensli, F.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; et al. Experimental evidence of ciguatoxin accumulation and depuration in carnivorous lionfish. Toxins 2021, 13, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Mak, Y.L.; Chang, Y.H.; Xiao, C.; Chen, Y.M.; Shen, J.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Lam, P.K.S. Uptake and depuration kinetics of Pacific ciguatoxins in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4475–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, S.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Darius, H.T.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M. Intraspecific variability in the toxin production and toxin profiles of in vitro cultures of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) from French Polynesia. Toxins 2019, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yon, T.; Sibat, M.; Réveillon, D.; Bertrand, S.; Chinain, M.; Hess, P. Deeper insight into Gambierdiscus polynesiensis toxin production relies on specific optimization of high-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Talanta 2021, 232, 122400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottein, M.Y.D.; Kashinsky, L.; Wang, Z.; Littnan, C.; Ramsdell, J.S. Identification of ciguatoxins in Hawaiian monk seals monachus schauinslandi from the northwestern and main Hawaiian Islands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5403–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish--Emerging toxins: Ciguatoxin group. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1627–1665. [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Natural Toxins. In Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Control Guidance; US Food and Drug Administration: College Park, MD, USA, 2019; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Darius, H.T.; Drescher, O.; Ponton, D.; Pawlowiez, R.; Laurent, D.; Dewailly, E.; Chinain, M. Use of folk tests to detect ciguateric fish: A scientific evaluation of their effectiveness in Raivavae Island (Australes, French Polynesia). Food Addit. Contam.-Part A 2013, 30, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernoux, J.P.; Lahlou, N.; El Andaloussi, S.A. A study of the distribution of ciguatoxin in individual Caribbean fish. Acta Trop. 1985, 42, 225–233. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2865878/ (accessed on 29 November 2023). [PubMed]
- Darius, H.T.; Ponton, D.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Ung, A.; Tchou Fouc, M.; Chinain, M. Ciguatera risk assessment in two toxic sites of French Polynesia using the receptor-binding assay. Toxicon 2007, 50, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Sosa, M.J.; García-Álvarez, N.; Sanchez-Henao, A.; Padilla, D.; Sergent, F.S.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Diogène, J.; Caballero, M.J.; Fernández, A.; Real, F. Ciguatoxin-like toxicity distribution in flesh of amberjack (Seriola spp.) and dusky grouper (Epinephelus marginatus). Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Sosa, M.J.; García-álvarez, N.; Sanchez-Henao, A.; Sergent, F.S.; Padilla, D.; Estévez, P.; Caballero, M.J.; Martín-Barrasa, J.L.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Diogène, J.; et al. Ciguatoxin detection in flesh and liver of relevant fish species from the Canary Islands. Toxins 2022, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowska, M.; Protasowicki, M. Distribution of metals (Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu) in fish tissues in two lakes of different trophy in Northwestern Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, F.P.; Savassi, L.A.; Santos, H.B.; Gomes, M.V.T.; Bazzoli, N. Bioaccumulation of mercury, cadmium, zinc, chromium, and lead in muscle, liver, and spleen tissues of a large commercially valuable catfish species from Brazil. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2016, 88, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, O.; Misery, L.; Talagas, M.; Le Garrec, R. Immune effects of the neurotoxins ciguatoxins and brevetoxins. Toxicon 2018, 149, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Nagasawa, H.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Asakura, H.; Yasumoto, T. Characteristic distribution of ciguatoxins in the edible parts of a grouper, Variola louti. Toxins 2021, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Legrand, A.-M.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and structure of ciguatoxin-4A, a new ciguatoxin precursor, from cultures of dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus and parrotfish Scarus gibbus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Wang, Z.; Ponton, D.; Laurent, D.; Pauillac, S. Growth and toxin production in the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) in culture. Toxicon 2010, 56, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibat, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Chinain, M.; Hess, P. Detection of Pacific ciguatoxins using liquid chromatography coupled to either low or high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeder, K.; Erler, K.; Kibler, S.; Tester, P.; Van The, H.; Nguyen-Ngoc, L.; Gerdts, G.; Luckas, B. Characteristic profiles of ciguatera toxins in different strains of Gambierdiscus spp. Toxicon 2010, 56, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisapia, F.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Litaker, R.W.; Fraga, S.; Nishimura, T.; Adachi, M.; Nguyen-Ngoc, L.; Séchet, V.; Amzil, Z.; et al. Toxicity screening of 13 Gambierdiscus strains using neuro-2a and erythrocyte lysis bioassays. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechraoui, M.Y.; Naar, J.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.M. Ciguatoxins and brevetoxins, neurotoxic polyether compounds active on sodium channels. Toxicon 1999, 37, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogi, K.; Sakugawa, S.; Oshiro, N.; Ikehara, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of toxins involved in ciguatera fish poisoning in the Pacific by LC/MS. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, V.; Soliño, L.; Leroy, P.; David, E.; Velge, P.; Dragacci, S.; Krys, S.; Flores Quintana, H.; Diogène, J. Contribution to the risk characterization of ciguatoxins: LOAEL estimated from eight ciguatera fish poisoning events in Guadeloupe (French West Indies). Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, Y.; Ohta, A.; Yin, X.; Ishizaki, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Doi, H.; Ishibashi, T. Difference in uptake of tetrodotoxin and saxitoxins into liver tissue slices among pufferfish, boxfish and porcupinefish. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, D.L.; Galbraith, R.M.; McMillan, J.P.; Higerd, T.B. Preliminary immunologic studies of ciguatera poisoning. Arch. Intern. Med. 1983, 143, 1931–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, I.; Lewis, R.J.; Vernoux, J.P. Ciguatera fish poisoning in the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean: Reconciling the multiplicity of ciguatoxins and analytical chemistry approach for public health safety. Toxins 2023, 15, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, R.W.; Plakas, S.M. Ciguatera: A public health perspective. Toxicon 2010, 56, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinain, M.; Faust, M.A.; Pauillac, S. Morphology and molecular analyses of three toxic species of Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae): G. pacificus, sp. nov., G. australes, sp. nov., and G. polynesiensis, sp. nov. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Germain, M.; Deparis, X.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.M. Seasonal abundance and toxicity of the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae), the causative agent of ciguatera in Tahiti, French Polynesia. Mar. Biol. 1999, 135, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chateau-Degat, M.L.; Chinain, M.; Cerf, N.; Gingras, S.; Hubert, B.; Dewailly, É. Seawater temperature, Gambierdiscus spp. variability and incidence of ciguatera poisoning in French Polynesia. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Clausing, R.J.; Rañada, M.L.; Alonso-Hernández, C.M.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.Y. A radioligand receptor binding assay for ciguatoxin monitoring in environmental samples: Method development and determination of quality control criteria. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 192, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y.; Clausing, R.J. Receptor binding assay for the analysis of marine toxins: Detection and mode of action. In CAC: Recent Advances in the Analysis of Marine Toxins; Diogène, J., Campàs, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 277–301. [Google Scholar]
- Detection of Harmful Algal Toxins Using the Radioligand Receptor Binding Assay: A Manual of Methods; IAEA-TECDOC-1729; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2013.
- Poli, M.A.; Mende, T.J.; Baden, D.G. Brevetoxins, unique activators of voltage-sensitive sodium channels, bind to specific sites in rat brain synaptosomes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1986, 30, 129–135. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2426567/ (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Manger, R.L.; Leja, L.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Hungerford, J.M.; Wekell, M.M. Tetrazolium-based cell bioassay for neurotoxins active on voltage-sensitive sodium channels: Semiautomated assay for saxitoxins, brevetoxins, and ciguatoxins. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 214, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui, M.Y.B.; Tiedeken, J.A.; Persad, R.; Wang, Z.; Granade, H.R.; Dickey, R.W.; Ramsdell, J.S. Use of two detection methods to discriminate ciguatoxins from brevetoxins: Application to great barracuda from Florida Keys. Toxicon 2005, 46, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.T.; Revel, T.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Cruchet, P.; Longo, S.; Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; et al. Comparative study on the performance of three detection methods for the quantification of Pacific ciguatoxins in French Polynesian strains of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| r-RBA Assay | CBA-N2a Assay | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue | Tissue Weight (g) | Concentration (ng CTX3C equiv g−1 TE) | Tissue Burden (ng CTX3C equiv) | Tissue Weight (g) | Concentration (ng CTX3C equiv g−1 TE) | Tissue Burden (ng CTX3C equiv) | ||
| spleen | mean ± SD | 0.065 ± 0.018 | 98.06 ± 12.17 | 6.21 ± 0.85 | 0.049 ± 0.007 | 129.0 ± 34.9 | 6.47 ± 2.17 | |
| min | 0.053 | 84.05 | 5.62 | 0.04 | 106.02 | 4.41 | ||
| max | 0.086 | 105.97 | 7.19 | 0.06 | 169.19 | 8.73 | ||
| liver | mean ± SD | 1.25 ± 0.29 | 18.09 ± 1.71 | 22.55 ± 5.43 | 1.39 ± 0.11 | 27.41 ± 11.30 | 38.25 ± 16.36 | |
| min | 0.89 | 15.84 | 15.98 | 1.29 | 14.36 | 19.87 | ||
| max | 1.58 | 20.08 | 30.70 | 1.51 | 34.00 | 51.23 | ||
| GI tract | mean ± SD | 3.59 ± 0.53 | 9.87 ± 0.16 | 35.48 ± 5.77 | 3.22 ± 0.18 | 10.85 ± 7.22 | 34.78 ± 22.28 | |
| min | 3.12 | 9.76 | 30.52 | 3.11 | 4.35 | 13.57 | ||
| max | 4.16 | 10.05 | 41.81 | 3.42 | 18.63 | 58.00 | ||
| muscle | mean ± SD | 27.64 ± 11.79 | 4.04 ± 0.79 | 114.0 ± 56.5 | 21.90 ± 1.60 | 9.13 ± 4.12 | 203.8 ± 101.4 | |
| min | 18.15 | 3.40 | 61.79 | 20.47 | 4.46 | 91.34 | ||
| max | 46.26 | 5.34 | 177.01 | 23.62 | 12.21 | 288.38 | ||
| gills | mean ± SD | 1.18 ± 0.48 | 6.43 ± 0.93 | 7.52 ± 2.73 | 0.89 ± 0.13 | 3.29 ± 1.53 | 2.99 ± 1.50 | |
| min | 0.80 | 5.76 | 4.81 | 0.76 | 1.82 | 1.39 | ||
| max | 2.02 | 7.97 | 11.70 | 1.03 | 4.88 | 4.35 | ||
| eyes | mean ± SD | *** | 1.15 ± 0.065 | 1.47 ± 0.47 | 1.69 ± 0.55 | |||
| min | 1.09 | 1.04 | 1.14 | |||||
| max | 1.22 | 1.97 | 2.24 | |||||
| brain | mean ± SD | *** | 0.260 ± 0.019 | 1.22 ± 0.87 | 0.330 ± 0.256 | |||
| min | 0.25 | 0.41 | 0.10 | |||||
| max | 0.28 | 2.14 | 0.61 | |||||
| gall bladder | mean ± SD | *** | 0.090 ± 0.024 | 0.650 ± 0.12 | 0.061 ± 0.027 | |||
| min | 0.07 | 0.56 | 0.04 | |||||
| max | 0.12 | 0.79 | 0.09 | |||||
| carcass | mean ± SD | 28.97 ± 9.54 | 3.59 ± 0.55 | 102.4 ± 12.8 | 24.49 ± 3.12 | 3.98 ± 1.89 * | 97.44 ± 12.44 * | |
| min | 21.43 | 3.25 | 92.33 | 21.43 | 85.24 * | |||
| max | 49.35 | 4.22 | 116.9 | 27.68 | 110.1 * | |||
| viscera combined | mean ± SD | 4.95 ± 0.73 | 12.9 ± 0.76 | 64.1 ± 12.5 | 4.75 ± 0.12 | 16.7 ± 7.77 | 79.6 ± 37.3 | |
| min | 4.49 | 12.0 | 54.1 | 4.65 | 8.56 | 39.8 | ||
| max | 5.79 | 13.5 | 78.1 | 4.88 | 24.0 | 114.0 | ||
| whole body | mean ± SD | 59.36 ± 10.71 | 4.46 ± 0.38 | 283.84 ± 64.47 | 55.43 ± 1.44 | 7.00 ± 2.33 ** | 385.76 ± 120.84 ** | |
| min | 47.91 | 4.09 | 239.75 | 54.33 | 4.32 ** | 246.75 ** | ||
| max | 73.77 | 4.85 | 357.83 | 57.06 | 8.57 ** | 465.72 ** | ||
| (A) r-RBA Assay | (B) CBA-N2a Assay | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue 1 | Tissue 2 | Estimate | Lower CI | Upper CI | Adjusted p-Value | Estimate | Lower CI | Upper CI | Adjusted p-Value | |
| brain | spleen | 127.8 | 90.1 | 165.4 | <0.001 | |||||
| eyes | spleen | −0.8 | −38.5 | 36.8 | <0.001 | |||||
| gallbladder | spleen | 9.4 | −28.3 | 47.0 | <0.001 | |||||
| GI | spleen | 88.2 | 78.5 | 97.8 | <0.001 | 1.8 | −35.8 | 39.5 | <0.001 | |
| gills | spleen | 91.6 | 83 | 100 | <0.001 | 25.9 | −11.7 | 63.6 | <0.001 | |
| liver | spleen | 80 | 71.3 | 88.6 | <0.001 | 7.7 | −30.0 | 45.3 | <0.001 | |
| muscle | spleen | 94 | 85.4 | 103 | <0.001 | 127.5 | 89.9 | 165.2 | <0.001 | |
| carcass | spleen | 95.1 | 86.9 | 103 | <0.001 | |||||
| gills | liver | 11.7 | 4.18 | 19.1 | <0.001 | |||||
| muscle | liver | 14 | 6.57 | 21.5 | <0.001 | |||||
| carcass | liver | 15.1 | 8.2 | 22 | <0.001 | |||||
| M | L | G | GI | Sp | Gb | E | B | C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r-RBA | mean | 37.52 | 8.75 | 2.49 | 12.64 | 1.93 | 37.30 | |||
| sd | 10.25 | 0.54 | 0.20 | 1.38 | 0.51 | 9.38 | ||||
| CBA-N2a | mean | 50.33 | 9.65 | 0.85 | 8.53 | 1.80 | 0.02 | 0.48 | 0.11 | 28.24 |
| sd | 12.54 | 1.75 | 0.51 | 3.98 | 0.78 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 14.29 | |
| overall means | mean | 43.93 | 9.20 | 1.67 | 10.59 | 1.85 | 0.02 | 0.48 | 0.11 | 32.77 |
| sd | 12.41 | 1.26 | 0.96 | 3.49 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 11.90 |
| M | L | G | GI | Sp | Gb | E | B | C | By Fish | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r-RBA | mean | 8.62 | 1.94 | 0.55 | 2.77 | 0.45 | -- | -- | -- | 8.00 | 22.17 |
| sd | 4.29 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 1.00 | 5.04 | ||||
| CBA-N2a | mean | 15.91 | 2.99 | 0.23 | 2.72 | 0.51 | 0.005 | 0.132 | 0.026 | 7.61 | 30.13 |
| sd | 7.92 | 1.28 | 0.12 | 1.74 | 0.17 | 0.002 | 0.043 | 0.020 | 0.97 | 9.44 | |
| overall means | mean | 12.3 | 2.46 | 0.39 | 2.74 | 0.48 | 0.005 | 0.132 | 0.026 | 7.80 | 26.15 |
| sd | 6.96 | 1.03 | 0.20 | 1.14 | 0.12 | 0.002 | 0.043 | 0.020 | 0.91 | 8.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clausing, R.J.; Ben Gharbia, H.; Sdiri, K.; Sibat, M.; Rañada-Mestizo, M.L.; Lavenu, L.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M.; Bottein, M.-Y.D. Tissue Distribution and Metabolization of Ciguatoxins in an Herbivorous Fish following Experimental Dietary Exposure to Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010014
Clausing RJ, Ben Gharbia H, Sdiri K, Sibat M, Rañada-Mestizo ML, Lavenu L, Hess P, Chinain M, Bottein M-YD. Tissue Distribution and Metabolization of Ciguatoxins in an Herbivorous Fish following Experimental Dietary Exposure to Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleClausing, Rachel J., Hela Ben Gharbia, Khalil Sdiri, Manoëlla Sibat, Ma. Llorina Rañada-Mestizo, Laura Lavenu, Philipp Hess, Mireille Chinain, and Marie-Yasmine Dechraoui Bottein. 2024. "Tissue Distribution and Metabolization of Ciguatoxins in an Herbivorous Fish following Experimental Dietary Exposure to Gambierdiscus polynesiensis" Marine Drugs 22, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010014
APA StyleClausing, R. J., Ben Gharbia, H., Sdiri, K., Sibat, M., Rañada-Mestizo, M. L., Lavenu, L., Hess, P., Chinain, M., & Bottein, M.-Y. D. (2024). Tissue Distribution and Metabolization of Ciguatoxins in an Herbivorous Fish following Experimental Dietary Exposure to Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Marine Drugs, 22(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010014