Pestalotiopols E–J, Six New Polyketide Derivatives from a Marine Derived Fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. SWMU-WZ04-1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Material
3.3. Fermentation, Extraction, and Isolation
3.4. Mo2(AcO)4-Induced CD
3.5. Preparation of (S)- and (R)-MTPA Esters of 2
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.7. Antimicrobial Assay
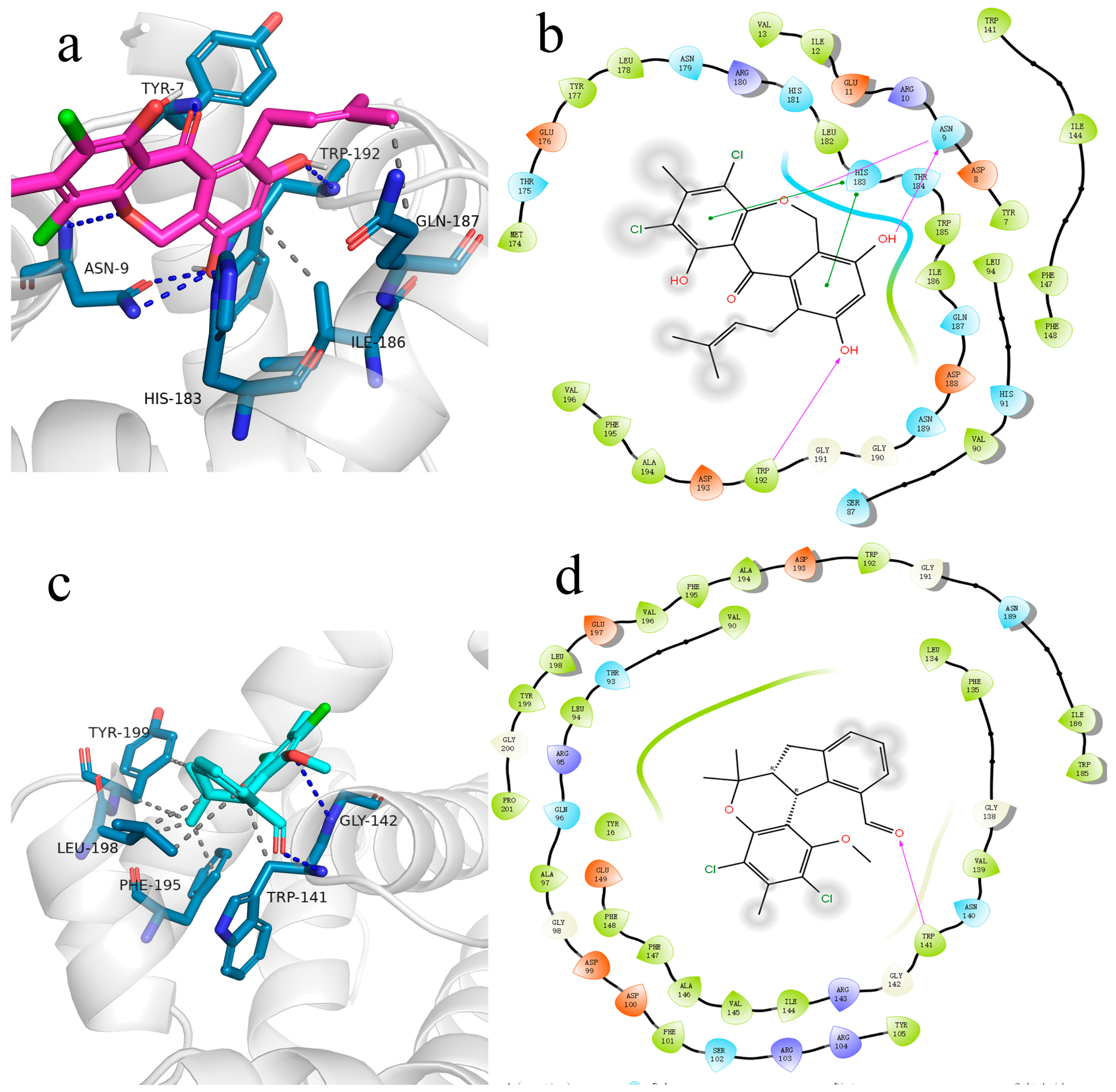
3.8. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Lu, J.; Qiu, P.; Wang, T.; Ding, L. Marine sponge-associated fungi as potential novel bioactive natural product sources for drug discovery. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1966–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Bai, X.L.; Chen, J.W.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, H. Exploring structural diversity of microbe secondary metabolites using OSMAC strategy: A literature review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hindra; Elliot, M.A. Unlocking the trove of metabolic treasures: Activating silent biosynthetic gene clusters in bacteria and fungi. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Fu, X.J.; Niu, H.; Chen, S.W.; Liu, F.F.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lei, H. Recent advances on Pestalotiopsis genus: Chemistry, biological activities, structure–activity relationship, and biosynthesis. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2023, 46, 449–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.R.; Filho, J.G.S.; Hoover, A.R.; King, J.B.; Ellis, T.K.; Powell, D.R.; Cichewicz, R.H. Chemical epigenetics alters the secondary metabolite composition of guttate excreted by an atlantic-forest-soil-derived Penicillium citreonigrum. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristina, P.R.; Aleu, J.; Rosa, D.P. Cryptic metabolites from marine-derived microorganisms using OSMAC and epigenetic approaches. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Ding, L.J.; Wang, N.; Xu, J.Z.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, B.; He, S.; Wu, B.; Jin, H.X. Isolation and characterization of two new metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. LS34 by OSMAC approach. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Gong, Y.H.; Gong, J.J.; Liu, J.J.; Chen, C.M.; Gu, L.H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.P.; Zhu, H.C.; Zhang, Y.H. Fungal polyketides with three distinctive ring skeletons from the fungus Penicillium canescens uncovered by OSMAC and molecular networking strategies. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 4973–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, R.M.A.; Monica, T.M.; Cristina, C.; Antonio Hernandez, D.; Antonio, F.M.; Jose, M.S.L. OSMAC approach and cocultivation for the induction of secondary metabolism of the fungus Pleotrichocladium opacum. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 39873–39885. [Google Scholar]
- Victor Rodriguez, M.A.; Francisco Romero, M.; Cristina, C.; Antonio Hernandez, D.; Antonio Fernandez, M.; Jose, M.; Sanchez, L. Induction of new aromatic polyketides from the marine actinobacterium Streptomyces griseorubiginosus through an OSMAC approach. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 526. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, H.P.; Liu, J.K. Sesquiterpenes with diverse skeletons from histone deacetylase inhibitor modified cultures of the basidiomycete Cyathus stercoreus (Schwein.) De Toni HFG134. Phytochemistry 2022, 195, 113048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.F.; Li, J.Y.; Wei, C.W.; Deng, X.L.; Xu, J. Chemical epigenetic modifiers enhance the production of immunosuppressants from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus isolated from Cynodon dactylon. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 4481–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.Y.; Hou, X.W.; Fu, J.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Zhao, Z.T.; Xu, D.; Lai, D.E.; Zhou, L.G. Recent advances in search of bioactive secondary metabolites from fungi triggered by chemical epigenetic modifiers. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Gan, L.S.; Mou, X.F.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Shao, C.L. Isolation, resolution and biological evaluation of pestalachlorides E and F containing both point and axial chirality. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22653–22658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y.; Li, D.; Shao, C.L.; Deng, D.S.; Wang, C.Y. (±)-Pestalachloride D, an antibacterial racemate of chlorinated benzophenone derivative from a soft coral-derived fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, S.; Muro, H.; Sasaki, K.; Nozoe, S.; Okuda, S.; Sato, Z.J. Isolations of phytotoxic substances produced by pyricularia oryzae cavara. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 37, 3537–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatasubbaiah, P.; Chilton, W.S. Toxins produced by the dogwood anthracnose fungus Discula sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillant, M.L.; Bernilion, J.; Favre-Bonvin, J.; Salin, N. New hexaketides related to sordariol in Sordaria macrospora. Z. Naturforschung C 1989, 44, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesting, J.R.; Olsen, L.; Staerk, D.; Tejesvi, M.V.; Kini, K.R.; Prakash, H.S.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Production of unusual dispiro metabolites in Pestalotiopsis virgatula endophyte cultures: HPLC-SPE-NMR, electronic circular dichroism, and time-dependent density-functional computation study. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2206–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Lin, X.P.; Han, L.; Ma, J.; Dong, K.L.; Wang, X.B.; Zhong, J.L.; Mu, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Huang, X.S. Polyketide derivatives from a marine-sponge-associated fungus Pestalotiopsis heterocornis. Phytochemistry 2017, 142, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, B.B.; Comezoglu, S.N.; Rao, M.M.; Pena, N.B. Isolation of macrocyclic trichothecenes from a large-scale extract of Baccharis megapotamica. J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.W.; Li, C.W.; Cui, C.B.; Hua, W.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q. Nine new and five known polyketides derived from a deep sea-sourced Aspergillus sp. 16-02-1. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3116–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayer, W.A.; Trifonov, L.S. Metabolites of Peniophora polygonia, part 2. Some aromatic compounds. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, B.B.; Wang, S.; Ammon, H.L. Trichoverroid stereoisomers. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, M.; Meyer, S.; Górecki, M.; Mandoli, A.; Bari, L.D.; Pescitelli, G.; Cimmino, A.; Cristofaro, M.; Clement, S. Pyriculins A and B, two monosubstituted hex-4-ene-2,3-diols and other phytotoxic metabolites produced by Pyricularia grisea isolated from buffelgrass (Cenchrus ciliaris). Chirality 2017, 29, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andolfi, A.; Cimmino, A.; Vurro, M.; Berestetskiy, A.; Troise, C.; Zonno, M.C.; Motta, A.; Evidente, A. Agropyrenol and agropyrenal, phytotoxins from Ascochyta agropyrina var. nana, a fungal pathogen of Elitrigia repens. Phytochemistry 2012, 79, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoye, T.R.; Jeffrey, C.S.; Shao, F. Mosher ester analysis for the determination of absolute configuration of stereogenic (chiral) carbinol carbons. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, I.; Kusumi, T.; Kashman, Y.; Kakisawa, H. High-field FT NMR application of Mosher’s method. The absolute configurations of marine terpenoids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 4092–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.Q.; Guo, H.Q.; Qiu, X.P.; Bai, X.L.; Yao, H.B.; Gao, L.X. Assignment of absolute configuration of cyclic secondary amines by NMR techniques using Mosher’s method: A general procedure exemplified with (-)-isoanabasine. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2006, 44, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, T.; Ooi, T.; Ohkubo, Y.; Yabuuchi, T. The modified Mosher’s method and the sulfoximine method. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 79, 965–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Wei, X.Y.; Qin, X.C.; Chen, H.; Lin, X.P.; Zhang, T.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Liao, S.R.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; et al. Two new prenylated phenols from endogenous fungus Pestalotiopsis vaccinii of mangrove plant Kandelia candel (L.) Druce. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.Z.; Lv, J.J.; Zhang, X.X.; Qiao, Y.J.; Yan, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhu, H.T.; Luo, H.R.; Yang, C.R.; et al. Triterpenoids with promoting effects on the differentiation of PC12 cells from the steamed roots of Panax notoginseng. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Aobulikasimu, N.; Zhang, Z.G.; Liu, C.B.; Cao, B.X.; Lin, B.; Guan, P.P.; Mu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Han, L. Amycolasporins and dibenzoyls from lichen-associated Amycolatopsis hippodromi and their antibacterial and antiinflammatory activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, N.; Jiang, Y.; Han, L.; Chen, X.; Ma, J.; Qu, X.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Jiang, C.; et al. Bafilomycins and odoriferous sesquiterpenoids from Streptomyces albolongus isolated from Elephas maximus feces. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Itabashi, T.; Wakana, D.; Takeda, H.; Yaguchi, T.; Kawai, K.; Hosoe, T. Isolation and structure elucidation of new phthalide and phthalane derivatives, isolated as antimicrobial agents from Emericella sp. IFM57991. J. Antibiot. 2015, 69, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.N.; Park, E.J.; Mbwambo, Z.H.; Santarsiero, B.D.; Mesecar, A.D.; Fong, H.H.S.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Kinghorn, A.D. New chemical constituents of euphorbia quinquecostata and absolute configuration assignment by a convenient Mosher ester procedure carried out in NMR tubes. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieser, M.J.; Hui, Y.H.; Rupprecht, J.K.; Kozlowski, J.F.; Wood, K.V.; McLaughlin, J.L.; Hanson, P.R.; Zhuang, Z.P.; Hoye, T.R. Determination of absolute configuration of stereogenic carbinol centers in annonaceous acetogenins by 1H- and 19F-NMR analysis of Mosher ester derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10203–10213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouda, K.; Ooi, T.; Kusumi, T. Application of the modified Mosher’s method to linear 1,3-diols. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 3005–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
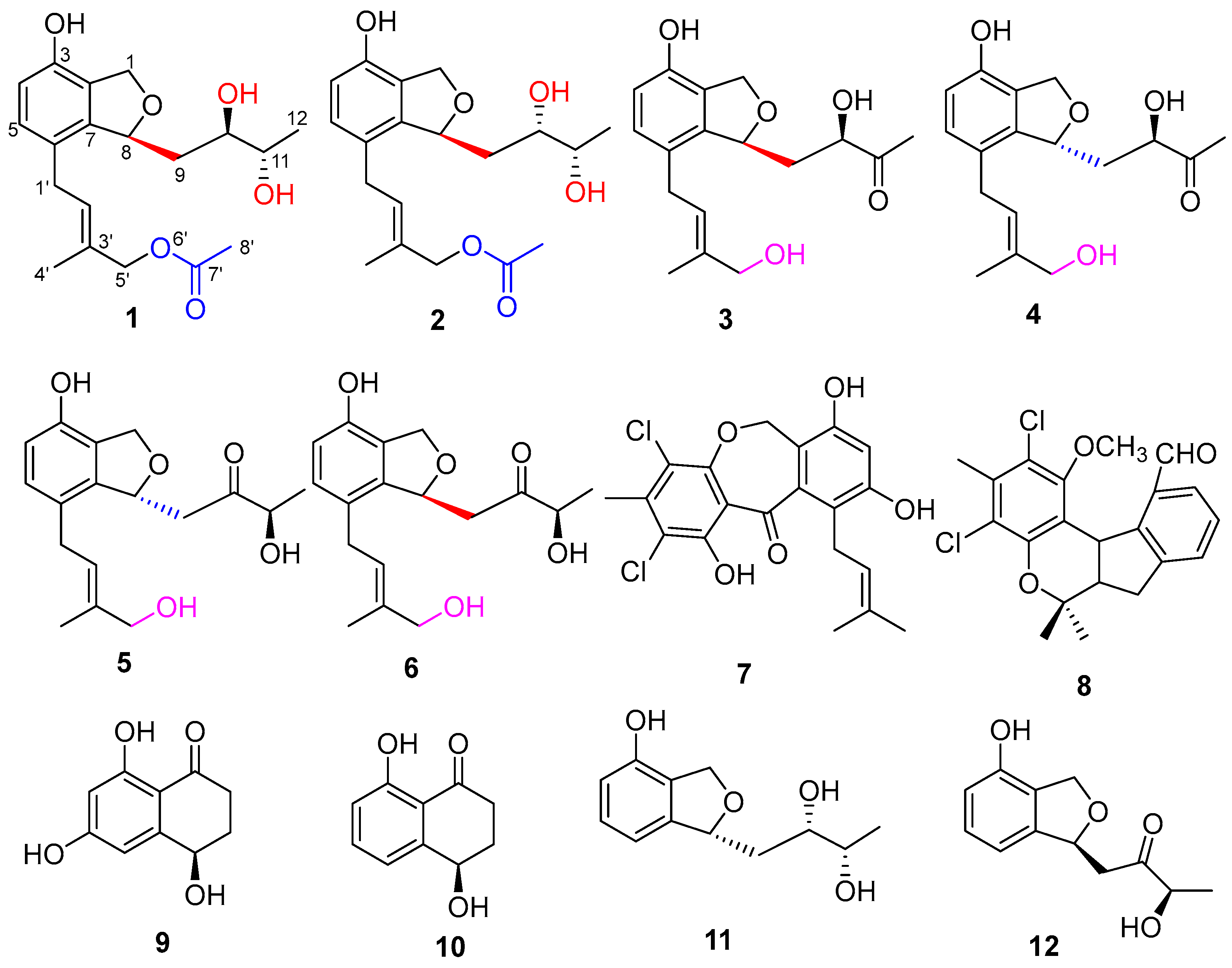


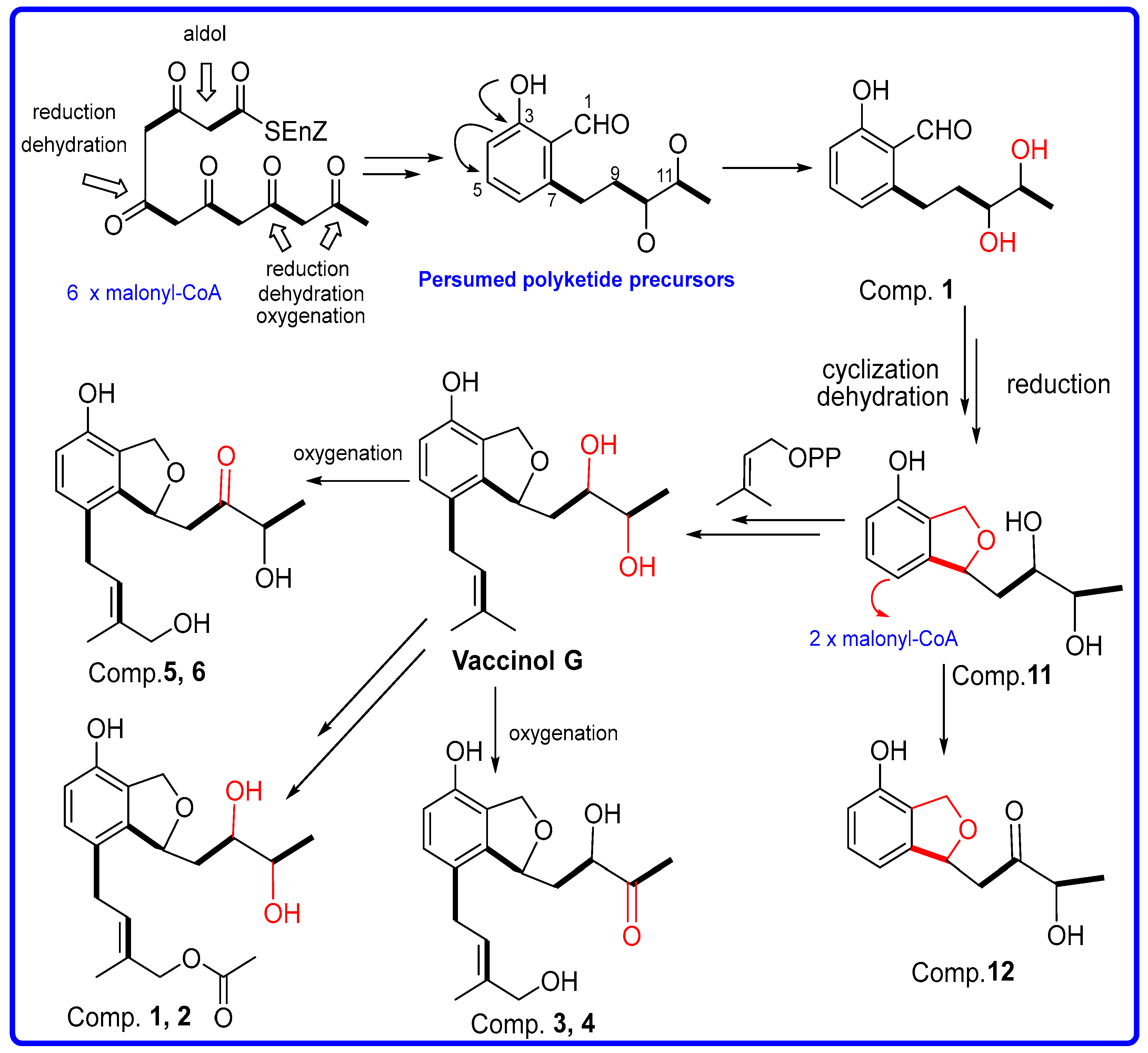
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) |
| 1 | 71.0, CH | 5.04, dd (12.3, 2.7) | 69.6, CH | 5.08, dd (12.2, 2.6) | 71.2, CH | 5.06, dd (12.2, 2.7) |
| 4.95, d (12.3) | 4.99, d (12.2) | 4.96, d (12.2) | ||||
| 2 | 126.0, C | 124.5, C | 126.1, C | |||
| 3 | 151.1, C | 149.9, C | 151.2, C | |||
| 4 | 115.4, CH | 6.60, d (8.1) | 114.1, CH | 6.63, d (8.0) | 115.6, CH | 6.61, d (8.2) |
| 5 | 130.4, CH | 6.87, d (8.1) | 129.2, CH | 6.88, d (8.0) | 130.7, CH | 6.89, d (8.2) |
| 6 | 125.9, C | 124.5, C | 126.5, C | |||
| 7 | 143.4, C | 141.6, C | 142.8, C | |||
| 8 | 82.3, CH | 5.53, brd (10.4) | 83.4, CH | 5.48, brd (10.2) | 81.5, CH | 5.51, m |
| 9 | 39.1, CH2 | 1.83, ddd (14.3, 10.4, 2.0) | 37.3, CH2 | 2.11, ddd (14.8, 3.9, 2.4) | 39.7, CH2 | 1.87, ddd (14.5, 4.9, 2.4) |
| 1.62, ddd (14.3, 10.4, 2.2) | 1.70, dd (14.8, 6.0) | 1.90, ddd (14.5, 9.8, 7.1) | ||||
| 10 | 73.3, CH | 3.71, ddd (10.4, 4.7, 2.1) | 74.4, CH | 3.69, m | 76.5, CH | 4.35, dd (9.9, 2.9) |
| 11 | 71.7, CH | 3.61, qd (6.4, 4.7) | 69.9, CH | 3.75, qd (6.2, 1.6) | 213.5, C | |
| 12 | 18.9, CH3 | 1.14, d (6.4) | 17.3, CH3 | 1.19, d (6.2) | 25.8, CH3 | 2.18, s |
| 1’ | 31.0, CH2 | 3.27, dd (16.0, 7.0) | 29.8, CH2 | 3.30, dd (16.0, 7.0) | 31.2, CH2 | 3.24, dd (16.0, 6.9) |
| 3.35, dd (16.0, 7.4) | ||||||
| 2’ | 128.8, CH | 5.57, brt (7.2) | 127.3, CH | 5.54, d (7.1) | 127.1, CH | 5.30, t (7.6) |
| 3’ | 132.3, C | 131.0, C | 136.6, C | |||
| 4’ | 14.3, CH3 | 1.75, s | 12.6, CH3 | 1.75, s | 21.5, CH3 | 1.80, s |
| 5’ | 71.0, CH2 | 4.48, s | 62.8, CH2 | 4.69, s | 61.4, CH2 | 4.19, d (12.2), |
| 4.20, d (12.2), | ||||||
| 7’ | 172.8, C | 171.5, C | ||||
| 8’ | 20.8, CH3 | 2.03, s | 20.2, CH3 | 2.05, s | ||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) |
| 1 | 71.4, CH | 5.05, dd (14.3, 2.2) | 70.1, CH | 5.06, dd (12.3, 2.5) | 69.6, CH | 5.03, dd (12.2, 2.3) |
| 4.95, d (14.3) | 4.96, d (12.3) | 4.92, d (12.2) | ||||
| 2 | 126.1, C | 125.0, C | 124.7, C | |||
| 3 | 151.1, C | 149.7, C | 149.7, C | |||
| 4 | 115.7, CH | 6.63, d (8.2) | 114.3, CH | 6.62, d (8.1) | 114.1, CH | 6.60, d (8.1) |
| 5 | 130.8, CH | 6.93, d (8.2) | 129.3, CH | 6.89, d (8.1) | 129.2, CH | 6.87, d (8.1) |
| 6 | 126.4, C | 125.6, C | 5.31, t (7.8) | 125.5, CH | 5.31, t (7.8) | |
| 7 | 142.0, C | 141.4, C | 140.6, C | |||
| 8 | 81.2, CH | 5.76, m | 79.9, CH | 5.74, m | 79.4, CH2 | 5.72, m |
| 9 | 44.3, CH2 | 2.91, d (9.6) | 43.1, CH2 | 2.88, m | 38.6, CH2 | 2.23, m |
| 2.85, dd (16.2, 2.0) | ||||||
| 10 | 74.4, CH | 4.23, q (7.0) | 211.8, C | 211.5, CH | ||
| 11 | 212.7, C | 74.7, CH | 4.28, q (7.0) | 73.3, CH | 4.24, q (7.0) | |
| 12 | 19.5, CH3 | 1.29, d (7.0) | 18.1, CH3 | 1.29, d (7.0) | 17.9, CH3 | 1.33, d (7.0) |
| 1’ | 31.2, CH2 | 3.21, m, 3.25, m | 29.6, CH2 | 3.30, d (7.1) | 29.6, CH2 | 3.30, d (7.1) |
| 2’ | 124.8, CH | 5.46, t (7.0) | 125.0, CH | 5.20, t (7.1) | 125.3, CH | 5.22, t (7.1) |
| 3’ | 137, C | 135.4, C | 135.2, C | |||
| 4’ | 13.9, CH3 | 1.71, s | 20.2, CH3 | 1.81, s | 20.1, CH3 | 1.83, s |
| 5’ | 68.6, CH2 | 3.95, s | 60.0, CH2 | 4.16, s | 60.0, CH2 | 4.16, s |
| Comp. | Cytotoxicity (IC50 in μM) | Antibacterial Activities (MIC μg/mL) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1975 | 7860 | Hela | HepG2 | B. subtilis | S. aureas | E. coli | C. albicans | |
| 1 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 2 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 3 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 5 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 7 | 83.6 | >100 | 63.5 | 16.2 | 3.0 | 3.0 | >100 | >100 |
| 8 | >100 | 63.1 | 45.0 | 34.8 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | >100 |
| 9 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 10 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 11 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 12 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| Adriamycin | 1.48 | 2 | 2.6 | 2.2 | ||||
| a Ciprofloxacin | 0.25 a | 0.13 a | 0.13 a | |||||
| b Amphotericin | 1.0 b | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, L.; Teng, B.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhai, L.; Lin, J.; Lei, H. Pestalotiopols E–J, Six New Polyketide Derivatives from a Marine Derived Fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. SWMU-WZ04-1. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010015
Jiang L, Teng B, Zhang M, Chen S, Zhang D, Zhai L, Lin J, Lei H. Pestalotiopols E–J, Six New Polyketide Derivatives from a Marine Derived Fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. SWMU-WZ04-1. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Liyuan, Baorui Teng, Mengyu Zhang, Siwei Chen, Dan Zhang, Longfei Zhai, Jiafu Lin, and Hui Lei. 2024. "Pestalotiopols E–J, Six New Polyketide Derivatives from a Marine Derived Fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. SWMU-WZ04-1" Marine Drugs 22, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010015
APA StyleJiang, L., Teng, B., Zhang, M., Chen, S., Zhang, D., Zhai, L., Lin, J., & Lei, H. (2024). Pestalotiopols E–J, Six New Polyketide Derivatives from a Marine Derived Fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. SWMU-WZ04-1. Marine Drugs, 22(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010015





