Effect of Nitrogen, Salinity, and Light Intensity on the Biomass Composition of Nephroselmis sp.: Optimization of Lipids Accumulation (Including EPA)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
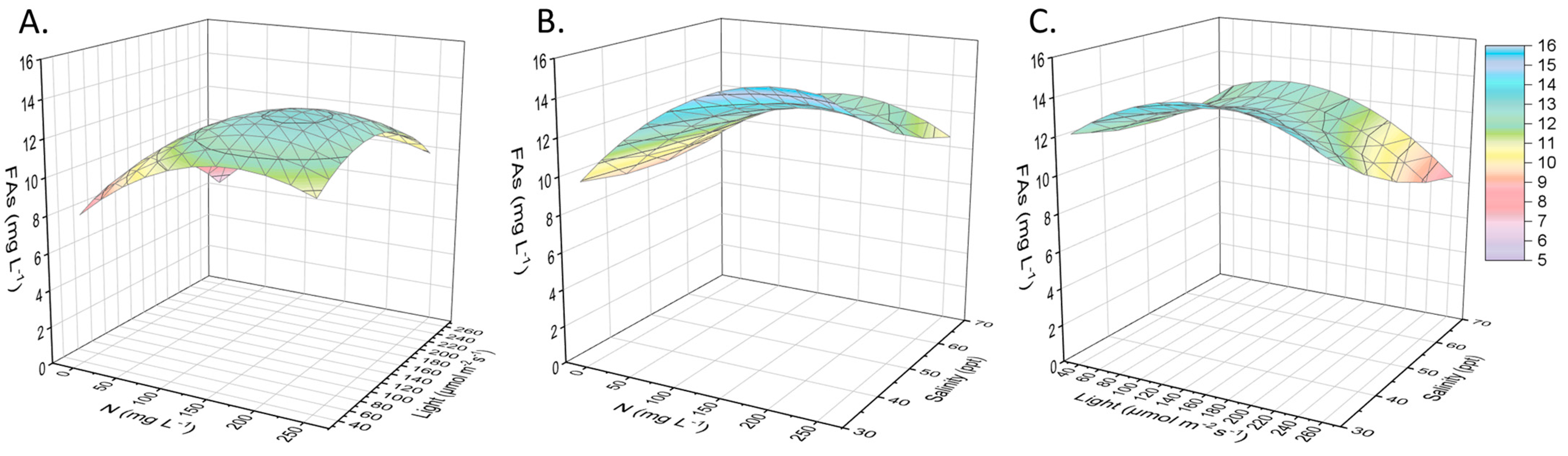
2.1. Biomass Adaptation and Lipids Concentration
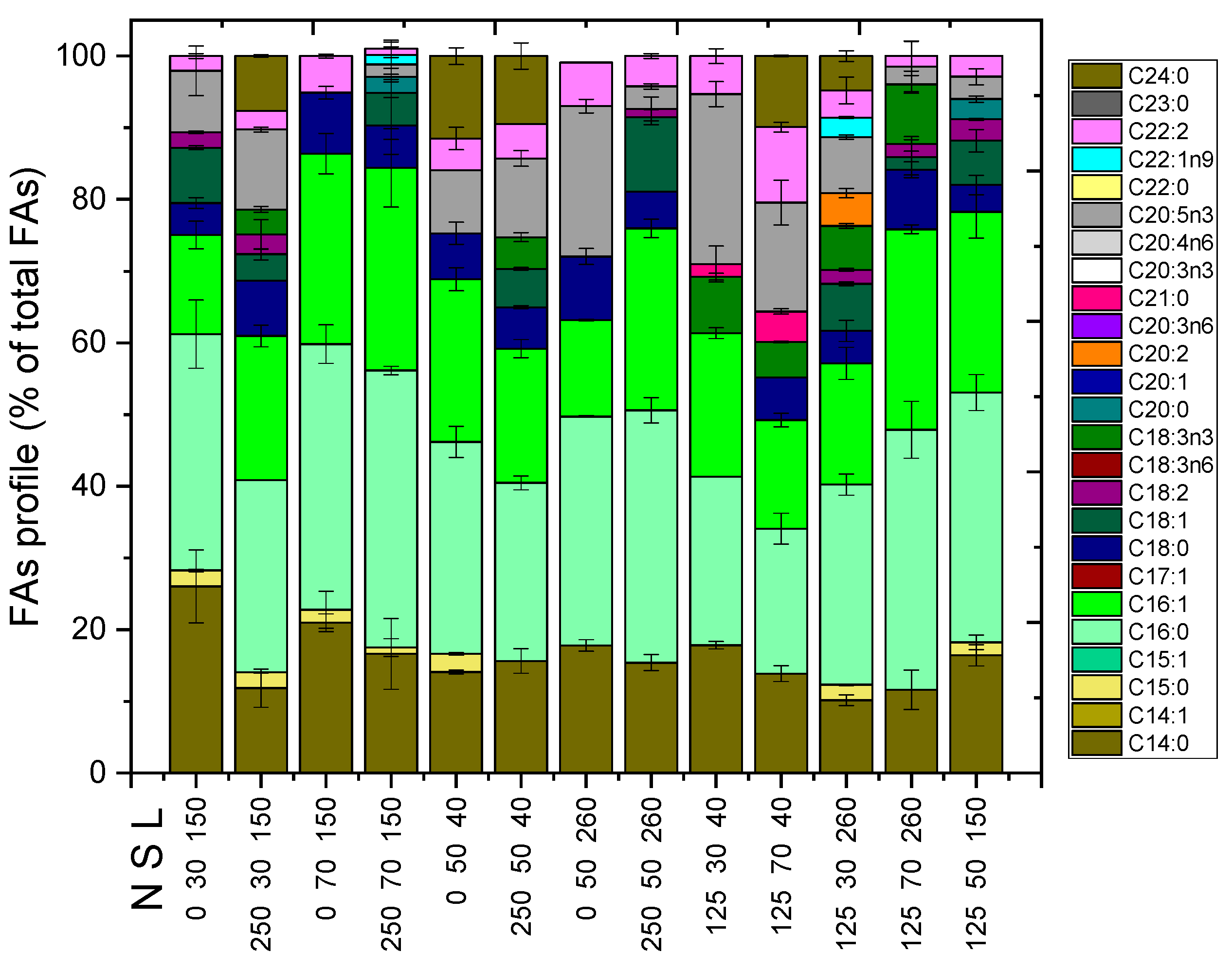
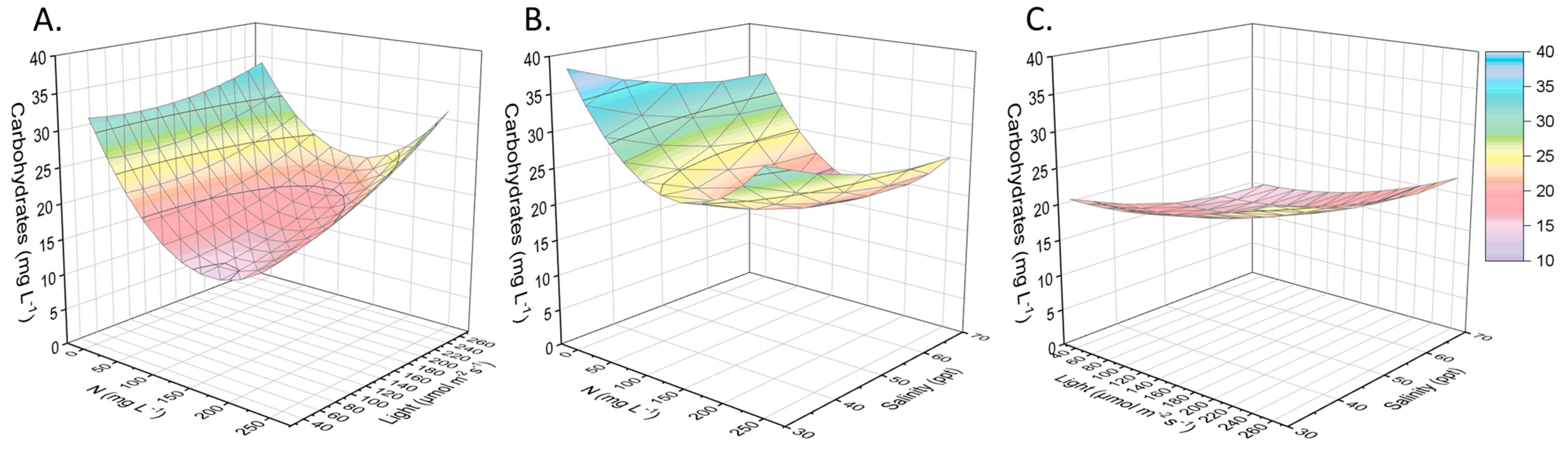
2.2. Other Compounds of Interest
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Nephroselmis sp. Cultivation Conditions
3.2. Second Stage Cultivation: Experimental Design and Conditions
3.3. Analytical Methods
3.3.1. Determination of Harvested Biomass, Total Solids, Volatile Solids, and Moisture
3.3.2. Fatty Acids Determination
3.3.3. Determination of Pigments, Proteins, and Carbohydrates Production
3.4. Analysis of Variance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borowitzka, M.A. Biology of microalgae. In Microalgae in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 23–72. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yildiz, I. The effect of salinity concentration on algal biomass production and nutrient removal from municipal wastewater by Dunaliella salina. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltanahy, E.; Torky, A. Microalgae as Cell Factories: Food and Feed-Grade High-Value Metabolites; The Royal Society of Chemistry Burlington House: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakarika, M.; Kornaros, M. Chlorella vulgaris as a green biofuel factory: Comparison between biodiesel, biogas and combustible biomass production. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Eisterhold, M.L.; Rindi, F.; Palanisami, S.; Nam, P.K. Isolation and screening of microalgae from natural habitats in the midwestern United States of America for biomass and biodiesel sources. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2014, 5, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotos, G.; Avramidou, D.; Mastropetros, S.G.; Tsigkou, K.; Kouvara, K.; Makridis, P.; Kornaros, M. Isolation, identification, and chemical composition analysis of nine microalgal and cyanobacterial species isolated in lagoons of Western Greece. Algal Res. 2023, 69, 102935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Saxena, R.C. An introduction to microalgae: Diversity and significance. In Handbook of Marine Microalgae; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hotos, G.N.; Avramidou, D. The Effect of Various Salinities and Light Intensities on the Growth Performance of Five Locally Isolated Microalgae [Amphidinium carterae, Nephroselmis sp., Tetraselmis sp.(var. red pappas), Asteromonas gracilis and Dunaliella sp.] in Laboratory Batch Cu. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lortou, U.; Panou, M.; Papapanagiotou, G.; Florokapi, G.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Kavoukis, S.; Iakovou, G.; Zalidis, G.; Triantafyllidis, K.; Gkelis, S. Beneath the Aegean Sun: Investigating Dunaliella Strains’ Diversity from Greek Saltworks. Water 2023, 15, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkelis, S.; Panou, M.; Konstantinou, D.; Apostolidis, P.; Kasampali, A.; Papadimitriou, S.; Kati, D.; Di Lorenzo, G.M.; Ioakeim, S.; Zervou, S.-K. Diversity, cyanotoxin production, and bioactivities of cyanobacteria isolated from freshwaters of Greece. Toxins 2019, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzovenis, I.; Fountoulaki, E.; Dolapsakis, N.; Kotzamanis, I.; Nengas, I.; Bitis, I.; Cladas, Y.; Economou-Amilli, A. Screening for marine nanoplanktic microalgae from Greek coastal lagoons (Ionian Sea) for use in mariculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Suda, S.; Kawachi, M.; Inouye, I. Phylogeny and ultrastructure of Nephroselmis and Pseudoscourfieldia (Chlorophyta), including the description of Nephroselmis anterostigmatica sp. nov. and a proposal for the Nephroselmidales ord. nov. Phycologia 2007, 46, 680–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Suda, S.; Nakayama, T.; Pienaar, R.N.; Chihara, M.; Inouye, I. Taxonomy of Nephroselmis viridis sp. nov.(Nephroselmidophyceae, Chlorophyta), a sister marine species to freshwater N. olivacea. J. Plant Res. 2011, 124, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, S. Light Microscopy and Electron Microscopy of Nephroselmis spinosa sp. nov.(Prasinophyceae, Chlorophyta) 1. J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.K.; Yun, H.S.; Hwang, B.S.; Kabra, A.N.; Jeon, B.H.; Choi, J. Mixotrophic cultivation of Nephroselmis sp. using industrial wastewater for enhanced microalgal biomass production. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulombier, N.; Nicolau, E.; Le Déan, L.; Barthelemy, V.; Schreiber, N.; Brun, P.; Lebouvier, N.; Jauffrais, T. Effects of nitrogen availability on the antioxidant activity and carotenoid content of the microalgae Nephroselmis sp. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.; Park, S.; Ji, M.-K.; Ha, G.-S.; Jeon, B.-H.; Choi, J. Biodiesel production potential of microalgae, cultivated in acid mine drainage and livestock wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, E.B.; Antoniosi Filho, N.R. Concepts and studies on lipid and pigments of microalgae: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, L.; Dietrich, T.; Marañón, I.; Villarán, M.C.; Barrio, R.J. Producing omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: A review of sustainable sources and future trends for the EPA and DHA market. Resources 2020, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-Q.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F. Fatty acid and lipid class composition of the eicosapentaenoic acid-producing microalga, Nitzschia laevis. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.M.A.; Kassim, K.A.; Shokravi, Z.; Jakarni, F.M.; Liu, H.Y.; Zaini, N.; Tan, L.S.; Islam, A.B.M.S.; Shokravi, H. Two-stage cultivation strategy for simultaneous increases in growth rate and lipid content of microalgae: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Chou, S.K.; Cao, S.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Z. An updated comprehensive techno-economic analysis of algae biodiesel. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanaarachchi, V.C.; Premaratne, M.; Ariyadasa, T.U.; Nimarshana, P.H.V.; Malik, A. Two-stage cultivation of microalgae for production of high-value compounds and biofuels: A review. Algal Res. 2021, 57, 102353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Ahn, Y.; Pandi, K.; Ji, M.-K.; Yun, H.-S.; Choi, J.-Y. Microalgae cultivation in pilot scale for biomass production using exhaust gas from thermal power plants. Energies 2019, 12, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayan, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Sirohi, R.; Sreekumar, N.; Sang, B.-I.; Sim, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Pandey, A. Production of microalgae with high lipid content and their potential as sources of nutraceuticals. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorgüven, E.; Özilgen, M. Thermodynamic efficiency of synthesis, storage and breakdown of the high-energy metabolites by photosynthetic microalgae. Energy 2013, 58, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tian, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Guan, W.; Guo, M.; Chu, J.; Zhuang, Y. A two-stage fed-batch heterotrophic culture of Chlorella protothecoides that combined nitrogen depletion with hyperosmotic stress strategy enhanced lipid yield and productivity. Process Biochem. 2017, 60, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.C.; Amaro, H.M.; Barbosa, C.R.; Pereira, R.D.; Malcata, F.X. Fatty acid composition of several wild microalgae and cyanobacteria, with a focus on eicosapentaenoic, docosahexaenoic and α-linolenic acids for eventual dietary uses. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2721–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Acién Fernández, F.G.; Cañizares Guerrero, E.; Hall, D.O.; Molina Grima, E. Overall assessment of Monodus subterraneus cultivation and EPA production in outdoor helical and bubble column reactors. J. Appl. Phycol. 2002, 14, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Rodríguez, J.; Cerón-García, M.C.; González-López, C.V.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M.; Contreras-Gómez, A.; Molina-Grima, E. A low-cost culture medium for the production of Nannochloropsis gaditana biomass optimized for aquaculture. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerón-García, M.C.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M.; Sánchez-Mirón, A.; García-Camacho, F.; Contreras-Gómez, A.; Molina-Grima, E. Mixotrophic growth of Phaeodactylum tricornutum on fructose and glycerol in fed-batch and semi-continuous modes. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzayisenga, J.C.; Farge, X.; Groll, S.L.; Sellstedt, A. Effects of light intensity on growth and lipid production in microalgae grown in wastewater. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangsomboon, S. Effect of light, nutrient, cultivation time and salinity on lipid production of newly isolated strain of the green microalga, Botryococcus braunii KMITL 2. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 109, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithtisarn, S.; Yokthongwattana, K.; Mahong, B.; Roytrakul, S.; Paemanee, A.; Phaonakrop, N.; Yokthongwattana, C. Comparative proteomic analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii control and a salinity-tolerant strain revealed a differential protein expression pattern. Planta 2017, 246, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, C.; Ballesteros, M. Linking microalgae and cyanobacteria culture conditions and key-enzymes for carbohydrate accumulation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulders, K.J.M.; Lamers, P.P.; Martens, D.E.; Wijffels, R.H. Phototrophic pigment production with microalgae: Biological constraints and opportunities. J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulombier, N.; Nicolau, E.; Le Déan, L.; Antheaume, C.; Jauffrais, T.; Lebouvier, N. Impact of Light Intensity on Antioxidant Activity of Tropical Microalgae. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Stand Methods 2012; Byrd Prepess Springfield: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780875532356. [Google Scholar]
- Koutra, E.; Kopsahelis, A.; Maltezou, M.; Grammatikopoulos, G.; Kornaros, M. Effect of organic carbon and nutrient supplementation on the digestate-grown microalga, Parachlorella kessleri. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastropetros, S.G.; Koutra, E.; Amouri, M.; Aziza, M.; Ali, S.S.; Kornaros, M. Comparative assessment of nitrogen concentration effect on microalgal growth and biochemical characteristics of two chlorella strains cultivated in digestate. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Run | Nitrogen (mg L−1) | Salinity (ppt) | Light (μmol m−2 s−1) | Biomass (mg/L) (Average ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 30 | 150 | 92.9 ± 22.5 A |
| 2 | 250 | 30 | 150 | 117.4 ± 8.1 A |
| 3 | 0 | 70 | 150 | 96.3 ± 8.6 A |
| 4 | 250 | 70 | 150 | 109.8 ± 5.6 A |
| 5 | 0 | 50 | 40 | 103.2 ± 1.4 A |
| 6 | 250 | 50 | 40 | 97.2 ± 9.4 A |
| 7 | 0 | 50 | 260 | 106.2 ± 11.4 A |
| 8 | 250 | 50 | 260 | 113.2 ± 9.8 A |
| 9 | 125 | 30 | 40 | 98.4 ± 0.9 A |
| 10 | 125 | 70 | 40 | 96.4 ± 6.1 A |
| 11 | 125 | 30 | 260 | 111.1 ± 0.3 A |
| 12 | 125 | 70 | 260 | 127.1 ± 26.5 A |
| 13 | 125 | 50 | 150 | 108.0 ± 20.9 A |
| 14 | 125 | 50 | 150 | 114.4 ± 1.4 A |
| 15 | 125 | 50 | 150 | 101.7 ± 2.2 A |
| Biomass Compounds | Equation (All Parameters) | Simplified Equation (Only Parameters of Statistical Significance) |
|---|---|---|
| Proteins (mg/L) | ||
| Carbohydrates (mg/L) | ||
| Pigments (mg/L) | ||
| FAs (mg/L) | ||
| EPA (% of FAs) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mastropetros, S.G.; Tsigkou, K.; Cladas, Y.; Priya, A.K.; Kornaros, M. Effect of Nitrogen, Salinity, and Light Intensity on the Biomass Composition of Nephroselmis sp.: Optimization of Lipids Accumulation (Including EPA). Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060331
Mastropetros SG, Tsigkou K, Cladas Y, Priya AK, Kornaros M. Effect of Nitrogen, Salinity, and Light Intensity on the Biomass Composition of Nephroselmis sp.: Optimization of Lipids Accumulation (Including EPA). Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(6):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060331
Chicago/Turabian StyleMastropetros, Savvas Giannis, Konstantina Tsigkou, Yannis Cladas, Arun Kumar Priya, and Michael Kornaros. 2023. "Effect of Nitrogen, Salinity, and Light Intensity on the Biomass Composition of Nephroselmis sp.: Optimization of Lipids Accumulation (Including EPA)" Marine Drugs 21, no. 6: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060331
APA StyleMastropetros, S. G., Tsigkou, K., Cladas, Y., Priya, A. K., & Kornaros, M. (2023). Effect of Nitrogen, Salinity, and Light Intensity on the Biomass Composition of Nephroselmis sp.: Optimization of Lipids Accumulation (Including EPA). Marine Drugs, 21(6), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060331