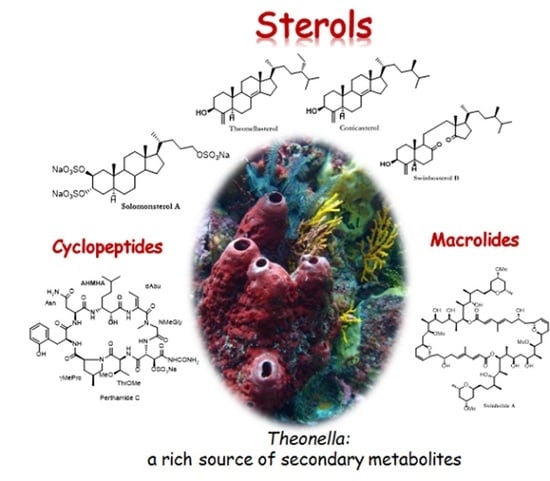
Theonella: A Treasure Trove of Structurally Unique and Biologically Active Sterols
Abstract
1. Introduction
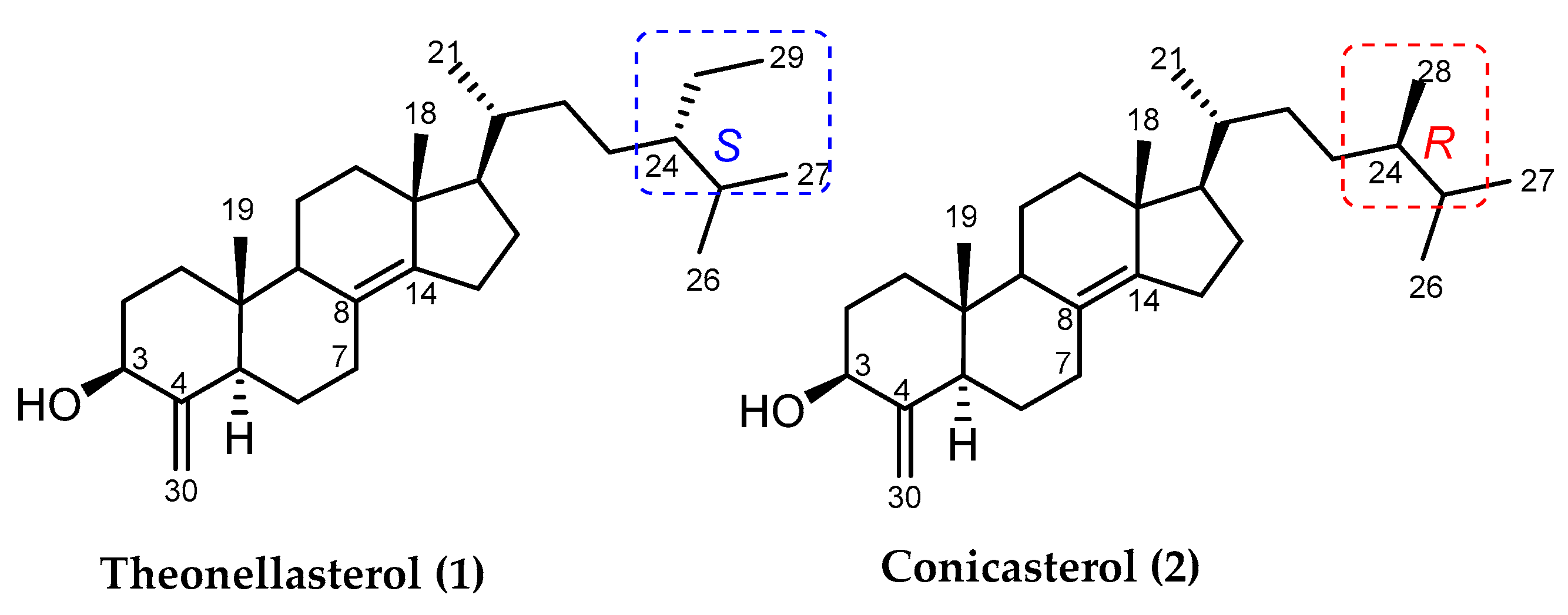
2. Sterols from Theonella spp.
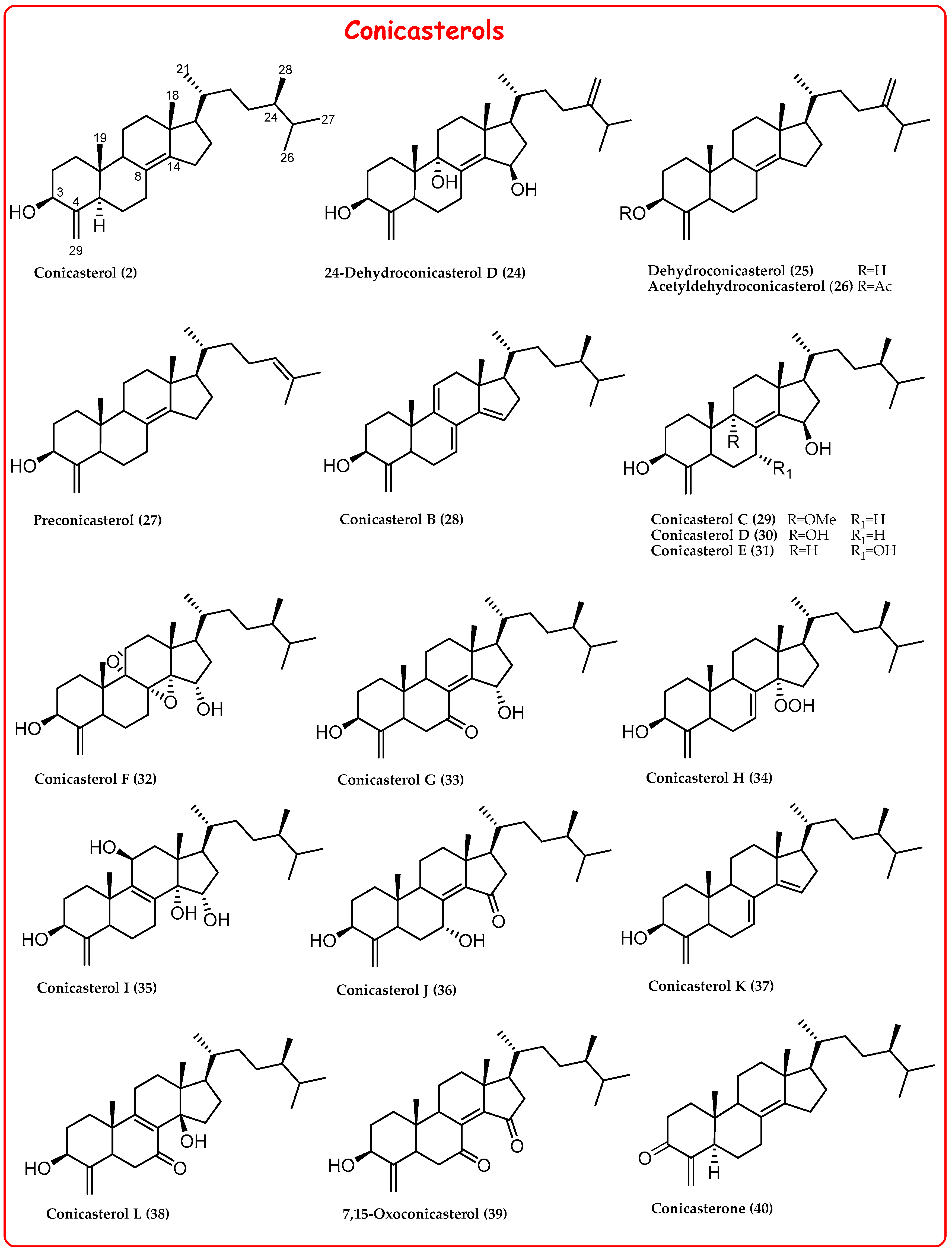
2.1. 4-Exo-Methylene Sterols
- ✓
- A keto group at C-3 in theonellasterone (23) and conicasterone (40);
- ✓
- The presence of additional hydroxyl groups at C-7, C-8, C-9, C-14, or C-15;
- ✓
- The presence of oxygenated functions at C-7 or C-15;
- ✓
- Epoxide groups at positions 8,14, 14,15, or 9,11;
- ✓
- Additional rare double bonds Δ7,8, Δ8,9, Δ9,11, and Δ14,15;
- ✓
- A peroxide group at C-14 in theonellasterol K (17) and conicasterol H (34) and an endoperoxide ring in theonellasterol-5,8-oxide (18).

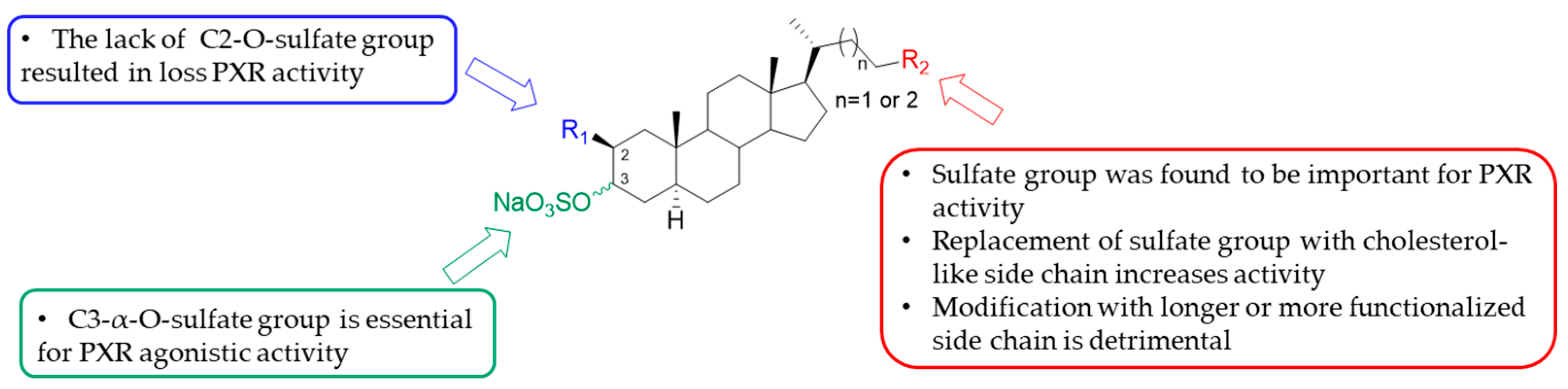
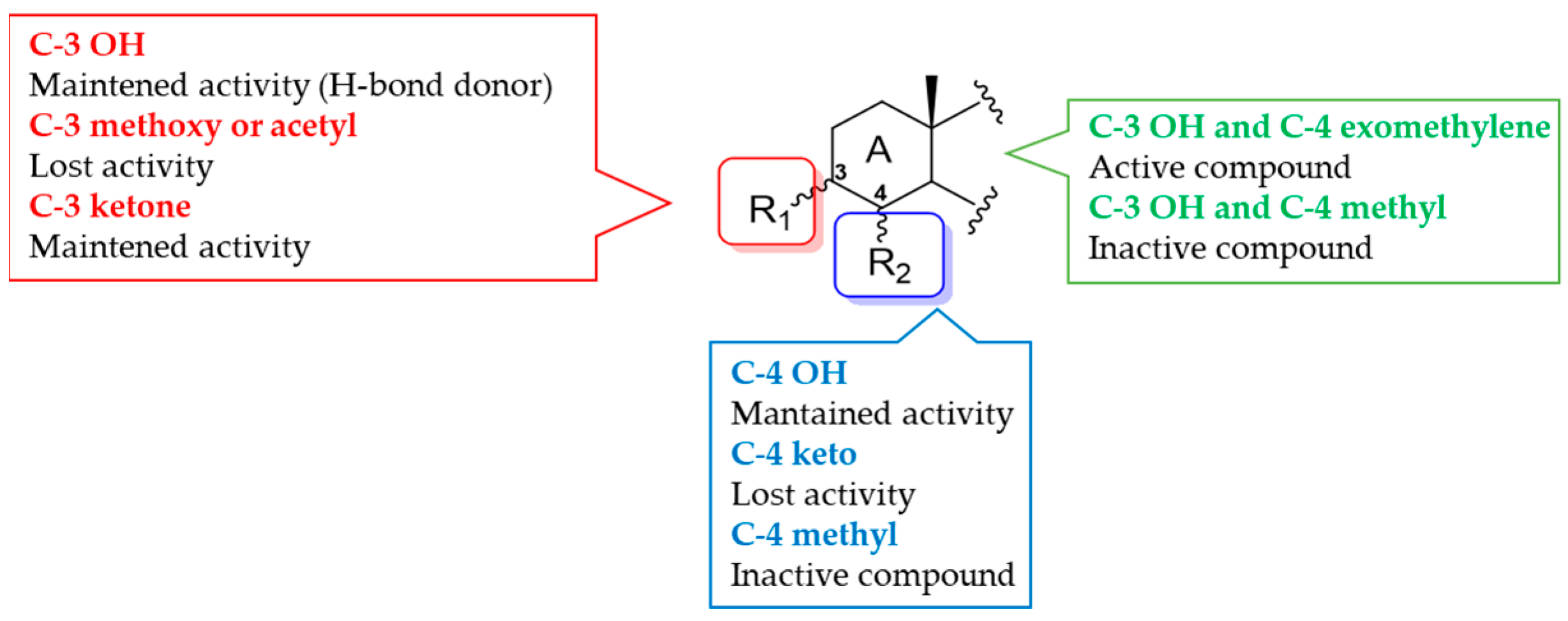
2.2. 4-Exo-Methylene Sterols as Modulators of NRs
- ✓
- The orientation of the hydroxyl group at C-3;
- ✓
- The A/B ring junction, which is trans in theonellasterol (1) and cis in CDCA;
- ✓
- The unsaturation between C-8 and C-14 in theonellasterol (1);
- ✓
- The lack of the carboxylic group at C-24 and the presence of an aliphatic side chain.

2.3. Unconventional Sterols as NRs Ligands
2.4. Sterols with Potential Anticancer Activity
3. Total Synthesis and Structural Modifications of Theonella-Inspired Sterols
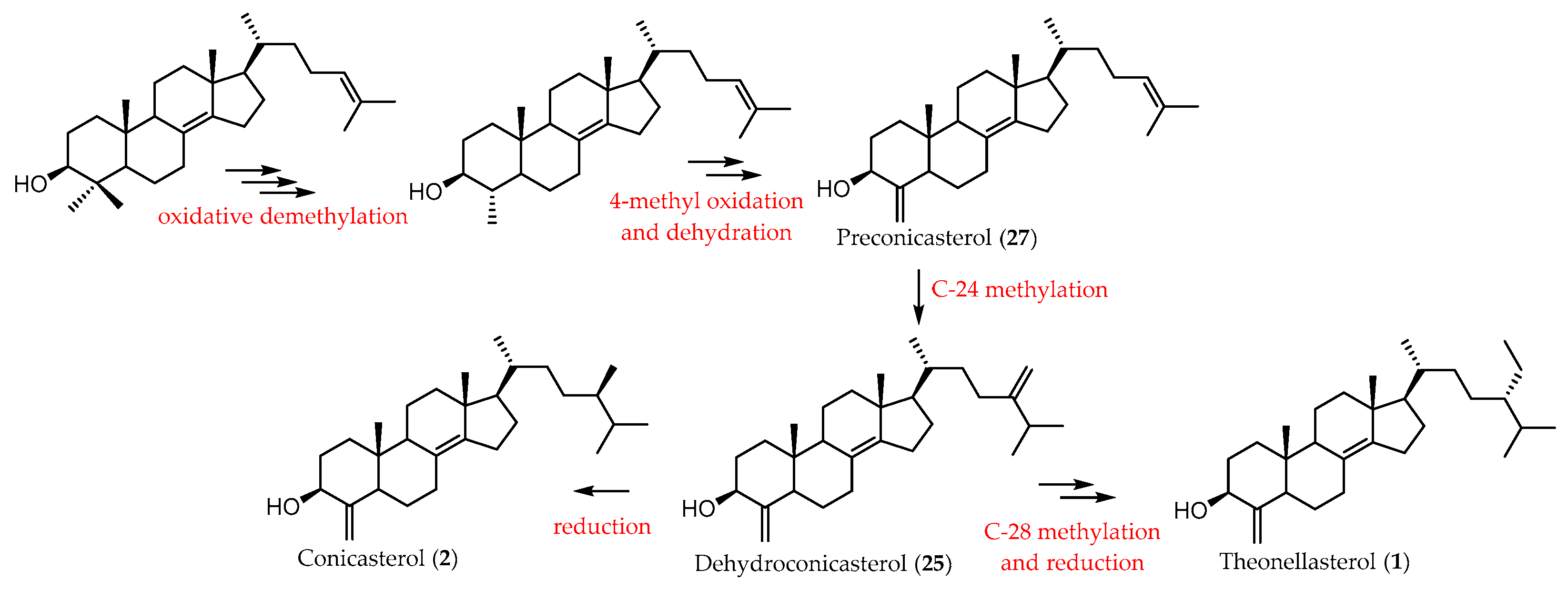
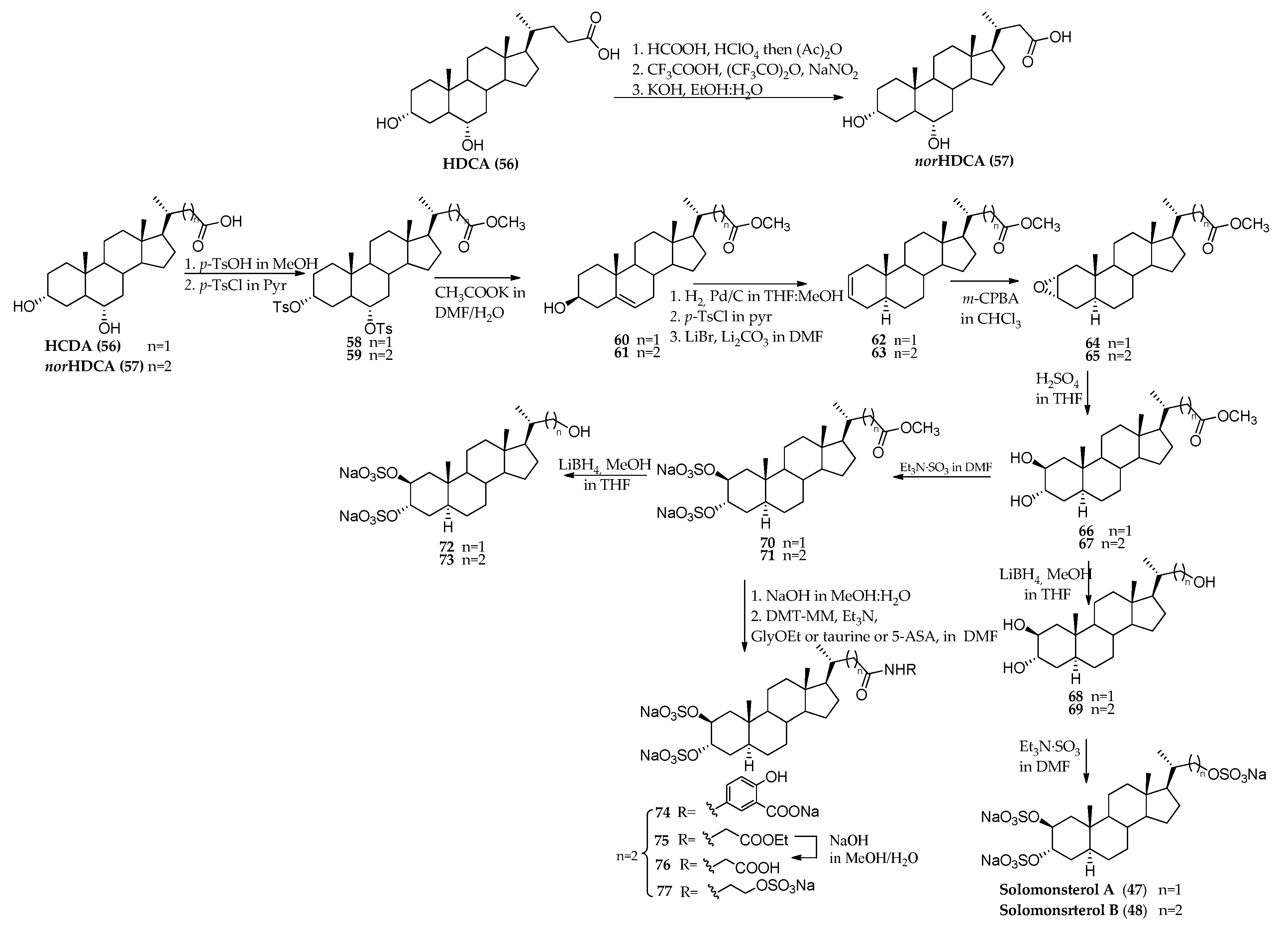
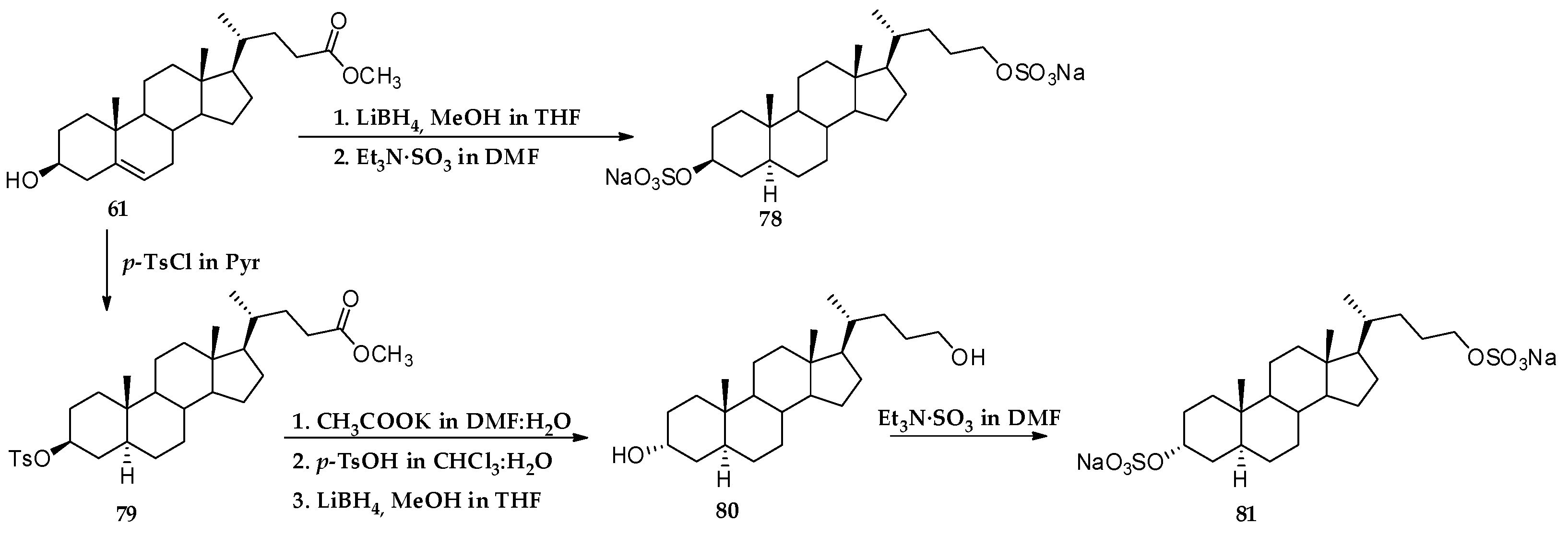
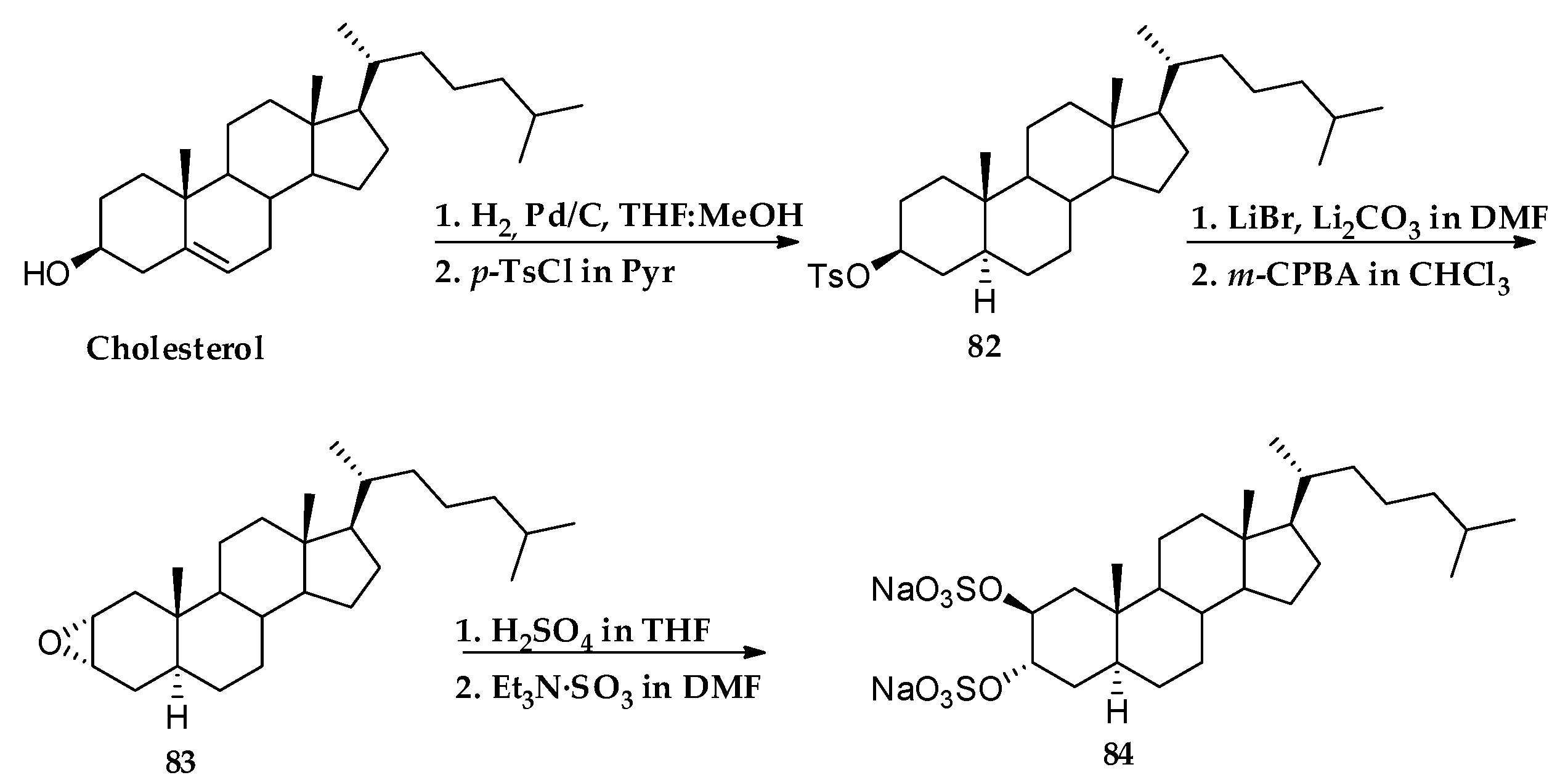
3.1. Total Synthesis of Solomonsterols and Their Analogues
3.2. Structural Modifications of 4-Exo-Methylene Sterols
3.2.1. Theonellasterol Series
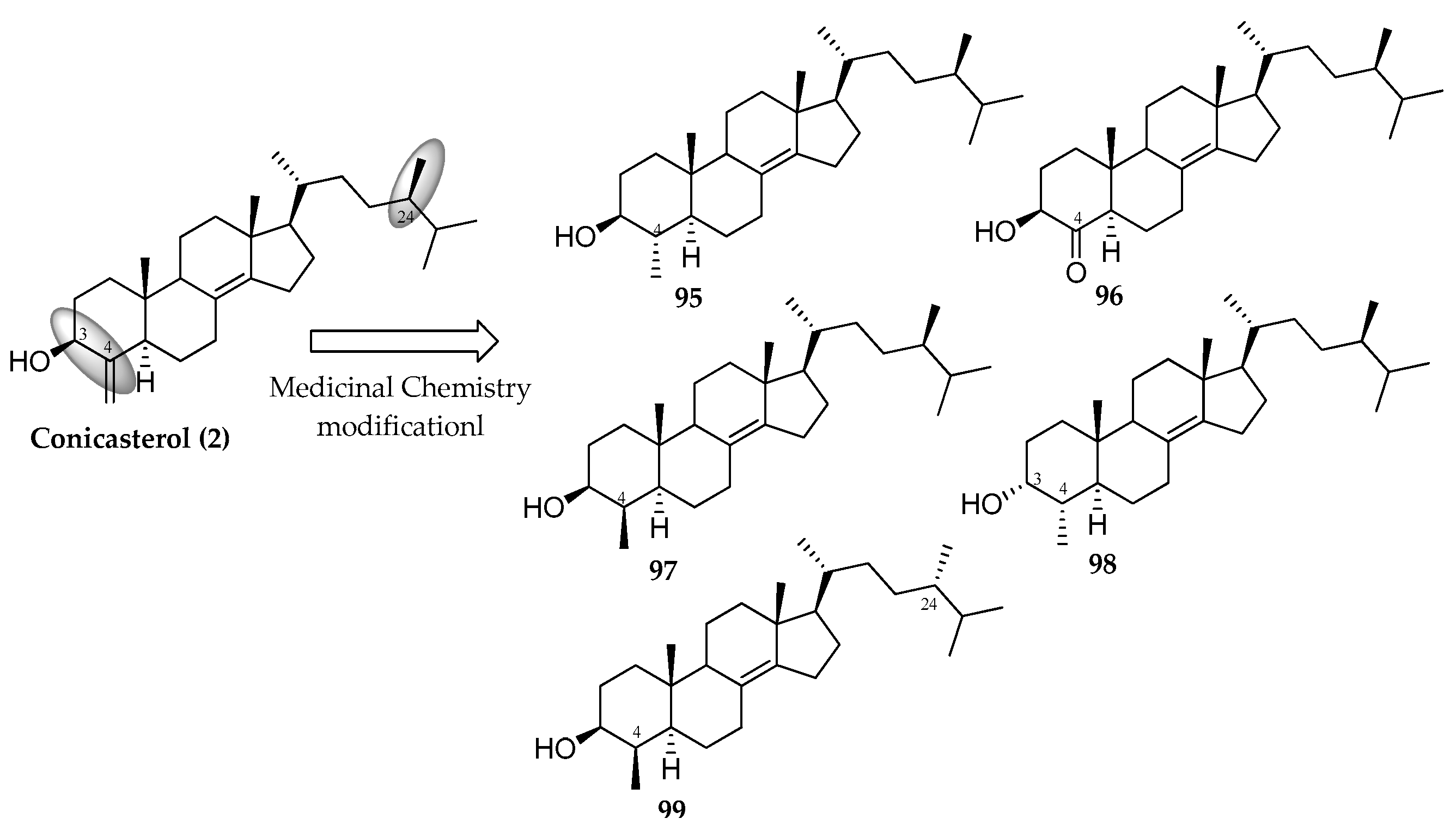
3.2.2. Conicasterol Series
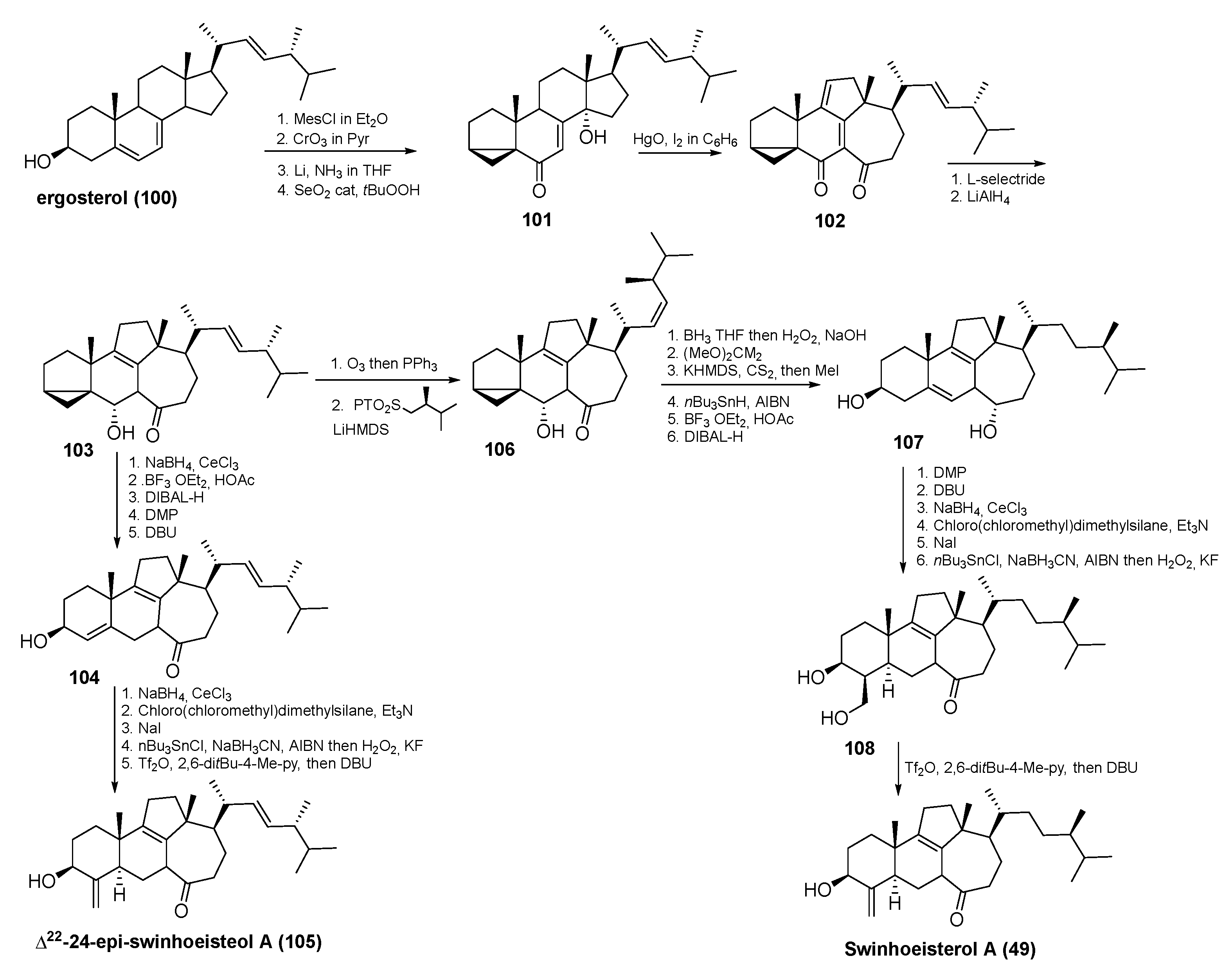
3.3. Total Synthesis of Swinhoeisterol A (49) and Its Analogue (105)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kho, E.; Imagawa, D.K.; Rohmer, M.; Kashman, Y.; Djerassi, C. Sterols in marine invertebrates. 22. Isolation and structure elucidation of conicasterol and theonellasterol, two new 4-methylene sterols from the red sea sponges Theonella conica and Theonella swinhoei. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 1836–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder, P.L.; Pomponi, S.A.; Wright, A.E. Natural products from the Lithistida: A review of the literature. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2643–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegerski, C.J.; Hammond, J.; Tenney, K.; Matainaho, T.; Crews, P. A serendipitous discovery of isomotuporin-containing sponge populations of Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marino, S.; Festa, C.; D’Auria, M.V.; Cresteil, T.; Debitus, C.; Zampella, A. Swinholide J, a potent cytotoxin from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinisi, A.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Dien, H.A.; Zampella, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Isoswinholide B and swinholide K, potently cytotoxic dimeric macrolides from Theonella swinhoei. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 5332–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; De Marino, S.; D’Auria, M.V.; Monti, M.C.; Bucci, M.; Vellecco, V.; Debitus, C.; Zampella, A. Anti-inflammatory cyclopeptides from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 2851–28571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; De Marino, S.; Sepe, V.; Monti, M.C.; Luciano, P.; D’Auria, M.V.; Debitus, C.; Bucci, M.; Vellecco, V.; Zampella, A. Perthamides C and D, two new potent anti-inflammatory cyclopeptides from a Solomon Lithistid sponge Theonella swinhoei. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 10424–10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-K.; Wang, D.; Bokesch, H.R.; Fuller, R.W.; Smith, E.; Henrich, C.J.; Durrant, D.E.; Morrison, D.K.; Bewley, C.A.; Gustafson, K.R. Swinhopeptolides A and B: Cyclic depsipeptides from the Sponge Theonella swinhoei that inhibit Ras/Raf Interaction. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, A.S.; Bugni, T.S.; Feng, X.; Harper, M.K.; Skalicky, J.J.; Mohammed, K.A.; Andjelic, C.D.; Barrows, L.R.; Ireland, C.M. Theopapuamide, a cyclic depsipeptide from a Papua New Guinea lithistid sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeyama, A.; Shoji, N.; Enoki, M.; Arihara, S. Swinhosterols A-C, 4-methylene secosteroids from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; De Marino, S.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Petek, S.; Zampella, A. Solomonsterols A and B from Theonella swinhoei. The first example of C-24 and C-23 sulfated sterols from a marine source endowed with a PXR agonistic activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Sun, P.; Jiang, N.; Riccio, R.; Lauro, G.; Bifulco, G.; Li, T.-J.; Gerwick, W.H.; Zhang, W. New steroids with a rearranged skeleton as (h) P300 inhibitors from the sponge Theonella swinhoei. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 2224–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, H.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Zhuang, C.-L.; Su, L.; Zheng, G.-L.; Zhang, W. Swinhoeisterols from the south China sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, C.A.; Faulkner, D.J. Lithistid sponges: Star performers or hosts to the stars. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2162–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, J. Metabolites from symbiotic bacteria. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 338–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, Y.-Y.; Tang, J.; Sun, F.; Lin, H.-W. New 4-methylidene sterols from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Fitoterapia 2018, 127, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Nagahamide A, an antibacterial depsipeptide from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3039–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; D’Amore, C.; Cipriani, S.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Monti, M.C.; Bifulco, G.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Discovery that theonellasterol a marine sponge sterol is a highly selective FXR antagonist that protects against liver injury in cholestasis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, S.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Debitus, C.; Zampella, A. Theonellasterols and Conicasterols from Theonella swinhoei. Novel marine natural ligands for human nuclear receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Mencarelli, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Total synthesis and pharmacological characterization of solomonsterol A, a potent marine pregnane-X-receptor agonist endowed with anti-inflammatory activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 4590–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; D’Amore, C.; Ummarino, R.; Renga, B.; D’Auria, M.V.; Novellino, E.; Sinisi, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Nakao, Y.; Limongelli, V.; et al. Insights on pregnane-X-receptor modulation. Natural and semisynthetic steroids from Theonella marine sponges. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 73, e126–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angawi, R.F.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Dien, H.A.; Fattorusso, E.; Scala, F.; Taglialatela Scafati, O. Dehydroconicasterol and aurantoic acid, a chlorinated polyene derivative, from the Indonesian sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2195–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgham, J.T.; Eick, G.N.; Larroux, C.; Deshpande, K.; Harms, M.J.; Gauthier, M.E.A.; Ortlund, E.A.; Degnan, B.M.; Thornton, J.W. Protein Evolution by Molecular Tinkering: Diversification of the nuclear receptor superfamily from a ligand dependent ancestor. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorucci, S.; Distrutti, E.; Bifulco, G.; D’Auria, M.V.; Zampella, A. Marine sponge steroids as nuclear receptor ligands. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Targeting nuclear receptors with marine natural products. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 601–635. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, J.A. Historical overview of nuclear receptors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 157, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, A.; Vilarem, M.J.; Maurel, P.; Pascussi, J.M. Xenoreceptors CAR and PXR activation and consequences on lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and inflammatory response. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencarelli, A.; Migliorati, M.; Barbanti, M.; Cipriani, S.; Palladino, G.; Distrutti, E.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S. Pregnane-X-receptor mediates the anti-inflammatory activities of rifaximin on detoxification pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizaki, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takizawa, D.; Negishi, M. New insights on the xenobiotic-sensing nuclear receptors in liver diseases—CAR and PXR. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Shah, Y.M.; Ma, X.; Pang, X.; Tanaka, T.; Kodama, T.; Krausz, K.W.; Gonzalez, F.J. Therapeutic role of rifaximin in inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical implication of human pregnane X receptor activation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carazo, A.; Mladenka, P.; Pávek, P. Marine ligands of the pregnane X receptor (PXR): An overview. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makishima, M.; Okamoto, A.Y.; Repa, J.J.; Tu, H.; Learned, R.M.; Luk, A.; Hull, M.V.; Lustig, K.D.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Shan, B. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science 1999, 284, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.J.; Blanchard, S.G.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Chandra, G.; Consler, T.G.; Kliewer, S.A.; Stimmel, J.B.; Willson, T.M.; Zavacki, A.M.; Moore, D.D.; et al. Bile acids: Natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science 1999, 284, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicciari, R.; Gioiello, A.; Costantino, G.; Sadeghpour, B.M.; Rizzo, G.; Meyer, U.; Parks, D.J.; Entrena-Guadix, A.; Fiorucci, S. Back door modulation of the farnesoid X receptor: Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a series of side chain modified chenodeoxycholic acid derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4208–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owsley, E.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Guggulsterone antagonizes farnesoid X receptor induction of bile salt export pump but activates pregnane X receptor to inhibit cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, T.P.; Montrose, C.; Houck, K.A.; Osborne, H.E.; Bocchinfuso, W.P.; Yaden, B.C.; Cheng, C.C.; Zink, R.W.; Barr, R.J.; Hepler, C.D.; et al. The hypolipidemic natural product guggulsterone is a promiscuous steroid receptor ligand. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Debitus, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Conicasterol E, a small heterodimer partner sparing farnesoid X receptor modulator endowed with a pregnane X receptor agonistic activity, from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.G.; Jones, C.R.; Zampella, A.; D’Auria, M.V.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Butts, C.P.; Bifulco, G. Quantitative NMR-derived interproton distances combined with quantum mechanical calculations of 13C chemical shifts in the stereochemical determination of conicasterol F, a nuclear receptor ligand from Theonella swinhoei. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margarucci, L.; Monti, M.C.; Tosco, A.; Esposito, R.; Zampella, A.; Sepe, V.; Mozzicafreddo, M.; Riccio, R.; Casapullo, A. Theonellasterone, a steroidal metabolite isolated from a Theonella sponge, protects peroxiredoxin-1 from oxidative stress reactions. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1591–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, A.; Fattorusso, F.; Menna, M. Steroids from sponges: Recent reports. Steroids 1999, 64, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, N.S.; Krishna, M.S.R.; Rao, S.R. Sterol ring system oxidation pattern in marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2005, 3, 84–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, S.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; Petek, S.; Fiorucci, S.; et al. 4-Methylenesterols from Theonella swinhoei sponge are natural pregnane-X-receptor agonists and farnesoid-X-receptor antagonists that modulate innate immunity. Steroids 2012, 77, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, S.; Renga, B.; Carino, A.; D’Auria, M.V.; Zampella, A.; Riccio, R.; Fiorucci, S.; Bifulco, G. Structural insights into Estrogen Related Receptor-b modulation: 4-Methylenesterols from Theonella swinhoei sponge as the first example of marine natural antagonists. Steroids 2014, 80, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marino, S.; Sepe, V.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; Petek, S.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Towards new ligands of nuclear receptors. Discovery of malaitasterol A, a unique bis-secosterol from marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4856–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.; Faulkner, D.J. 7α-Hydroxytheonellasterol, a cytotoxic 4-methylene sterol from the Philippines sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.K.; Chiang, C.Y.; Lu, M.C.; Chang, W.B.; Su, J.H. 4-Methylenesterols from a sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.-H.; Peng, B.-R.; Su, C.-H.; El-Shazly, M.; Sun, Y.-L.; Shih, M.-C.; Huang, Y.-T.; Yen, P.-T.; Wang, L.-S.; Su, J.-H. Anti-Proliferative potential of secondary metabolites from the marine sponge Theonella sp.: Moving from Correlation toward Causation. Metabolites 2021, 11, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, A.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, J.S.; Son, A.; Choi, C.; Lee, J. Oxygenated theonellastrols: Interpretation of unusual chemical behaviors using quantum mechanical calculations and stereochemical reassignment of 7α-hydroxytheonellasterol. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencarelli, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Cipriani, S.; Carino, A.; Sepe, V.; Perissutti, E.; D’Auria, M.V.; Zampella, A.; Distrutti, E.; et al. Solomonsterol A, a marine Pregnane-X-Receptor agonist, attenuates inflammation and immune dysfunction in a mouse model of arthritis. Mar. Drugs. 2014, 12, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. The first total synthesis of solomonsterol B, a marine Pregnane X Receptor agonist. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5187–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Lauro, G.; Bifulco, G.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Modification in the side chain of solomonsterol A: Discovery of cholestan disulfate as a potent pregnane-X-receptor agonist. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 6350–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; De Marino, S.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Nakao, Y.; et al. Preliminary structure-activity relationship on theonellasterol, a new chemotype of FXR antagonist, from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2448–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duecker, F.L.; Heinze, R.C.; Heretsch, P. Synthesis of swinhoeisterol A, dankasterone A and B, and periconiastone A by radical framework reconstruction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duecker, F.L.; Heinze, R.C.; Steinhauer, S.; Heretsch, P. Discoveries and challenges en route to swinhoeisterol A. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 9971–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Festa, C.; De Marino, S.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Theonella: A Treasure Trove of Structurally Unique and Biologically Active Sterols. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050291
Festa C, De Marino S, Zampella A, Fiorucci S. Theonella: A Treasure Trove of Structurally Unique and Biologically Active Sterols. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(5):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050291
Chicago/Turabian StyleFesta, Carmen, Simona De Marino, Angela Zampella, and Stefano Fiorucci. 2023. "Theonella: A Treasure Trove of Structurally Unique and Biologically Active Sterols" Marine Drugs 21, no. 5: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050291
APA StyleFesta, C., De Marino, S., Zampella, A., & Fiorucci, S. (2023). Theonella: A Treasure Trove of Structurally Unique and Biologically Active Sterols. Marine Drugs, 21(5), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050291