Abstract
Marine meroterpenoids have attracted a great deal of attention from synthetic research groups due to their attractive and varied biological activities and their unique and diverse structures. In most cases, however, further biological studies have been severely limited mainly to the scarcity of natural supply and because almost none of the reported syntheses methods has enabled unified access for a large number of marine meroterpenoids with aureane and avarane skeletons. Based on our previous publications and the study of recent manuscripts on marine meroterpenoids, we have conceived a unified strategy for these fascinating marine compounds with aureane or avarane skeletons using available drimane compounds as starting materials. The key step is a biosynthetic sequence of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts. This strategy is of great synthetic value to access marine meroterpenoids through easy chemical synthetic procedures. Finally, several retrosynthetic proposals are made for the future synthesis of several members of this class of meroterpenoids, focused on consolidating these 1,2-rearrangements as a versatile and unified strategy that could be widely used in the preparation of these marine meroterpenoids.
1. Introduction
Most marine sesquiterpene hydroquinones/quinones, which have been isolated from marine organisms, particularly from sponges and algae, possess an aureane skeleton or an avarane skeleton (Figure 1a), [1,2,3,4]. Biosynthetically, these avarane and aureane skeletons arise from 1,2-rearrangements of the drimane skeleton [2] (Figure 1a). In turn, natural compounds with avarane skeletons have been divided into two groups depending on their configuration at the C-5 position. The first one groups the avaranes, Δ3, while the second one includes the trans-avarane Δ4(13) (trans-decalin system) or cis-avarane Δ4(14) (cis-decalin system) (Figure 1a). Representative marine sesquiterpene structures with aureane and avarane skeletons are depicted in Figure 1b–e.
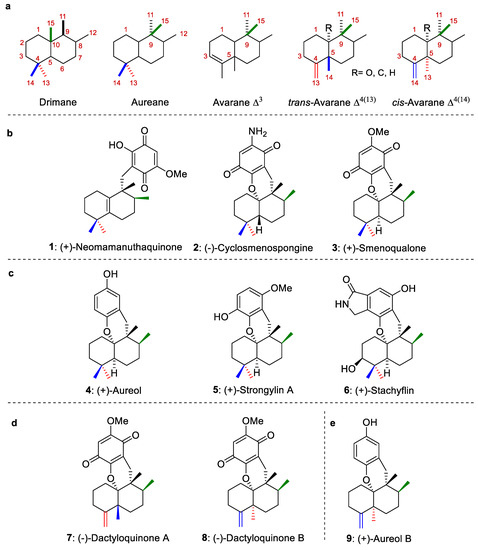
Figure 1.
(a): Sesquiterpene skeletons. (b): Representative examples of sesquiterpene structures with aureane (quinone) skeletons. (c): Representative examples of sesquiterpene structures with aureane (hydroquinone) skeletons. (d): Representative examples of sesquiterpene structures with avarane (quinone) skeletons. (e): Representative examples of sesquiterpene structures with avarane (hydroquinone) skeletons.
Many marine sesquiterpene quinones/hydroquinones exhibit a wide array of very interesting pharmacological properties, such as antiviral, cytotoxic, antimicrobial, antiinflamatory, antifungal and immunomodulation activities [2]. However, on many occasions, the study of the biological properties of these compounds has been limited due to the scarcity of marine natural supplies. This limitation is also due to the fact that the synthetic methodologies developed for these compounds are limited to individual compounds [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14], and only the one described by Magauer and co-workers [15] allows access to a whole family of these fascinating marine natural products. Therefore, the development of an efficient strategy for the scalable construction of complex marine meroterpenoids with aureane and avarane skeletons is desirable from the viewpoint of pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, and medicinal chemistry.
Regarding their biogenesis [10,16,17,18,19], it was postulated that aureane skeleton formation presumably involves the diastereoselective cyclization of a polyene 10 to generate the tertiary carbocation I, which then would undergo a sequence of stereospecific 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts to give a new carbocation II (pathway a, Scheme 1). Depending on the nature of the R group, carbocation II could evolve into a tetrasubstituted alkene (12) or could undergo intramolecular attack by a hydroxy group present in the substituent R (usually an aromatic ring) to form a polycyclic system (11). Based on this biosynthetic proposal, different research groups have successfully synthesized different marine meroterpenoids with an aureane skeleton 11–12 [10,12,14,20,21]. Recently, the preparation of compounds with an avarane skeleton 13–14 has been reported using a quinone derivative of compound 12 through a cyclization reaction catalyzed by a Lewis acid, which causes the migration of the methyl groups, leading to two different configurations at the C-5 carbon (pathway b, Scheme 1) [14].
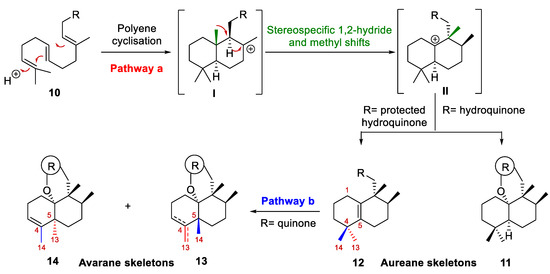
Scheme 1.
Proposed biosynthesis of the aureane skeleton (10, 11 and 12). Progress in research on the synthesis of an avarane skeleton from an aureane skeleton (12, 13 and 14).
In this context, rearrangement reactions [22,23,24,25] offer a versatile way to generate the target structures through the bond reorganization of the intermediate precursors. Rearrangement reactions allow the straightforward formation of the core skeletons, the control of stereochemistry, and the identification of potential commercially available synthons.
This article is focused on the synthetic efforts toward the compounds with aureane skeletons 12a–d (Scheme 2). These compounds are formed from drimanes prepared from available starting material. The process involves a sequence of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts as keys. Compounds 12a–d are valuable intermediates for the synthesis of marine meroterpenoids with aureane or avarane skeletons, such as 1–9. The above-mentioned key step can be considered a versatile, efficient, and promising unified methodology for the synthesis of meroterpenoids with aureane or avarane skeletons, including the control of the geometry of the stereocenters, the oxidative states, and the retrosynthetic relationships. In this way, compounds 12a–d, as will be mentioned later, can be prepared through a short route from available drimanes, a process that is desirable considering the concept of step economy.
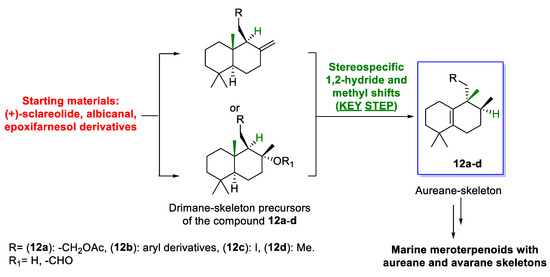
Scheme 2.
Conceptual model for the unified synthesis of marine meroterpenoids with aureane and avarane skeletons using 1,2-rearrangements as key step.
2. Synthesis of the Tetracyclic Alkenes 12a–d
2.1. George’s Synthesis of Compound 12a
In 2012, George´s group [10] reported the enantioselective synthesis of 12a via a biosynthetically inspired stereospecific sequence of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts of 16 (Scheme 3). The reduction of commercially available (+)-sclareolide (15) afforded a diol. The selective acetylation of diol using Ac2O in pyridine afforded the acetate ester 16 (84% yield over two steps). Aureane compound 12a arose from 1,2-rearrangements of drimane compound 16 using BF3·Et2O as a Lewis acid (70% yield). This key rearrangement proceeded via stereospecific 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts and yielded the desired compound 12a in a good yield. As will be discussed in Section 3, this rearrangement occurs through the formation of a tertiary carbocation at C-8, which can then undergo a sequence of stereospecific 1,2-hydrogen and methyl shifts. With the aureane compound 12a in their hands, George´s group [10] carried out the synthesis of the marine natural product (+)-aureol (4). First, alcohol 17 was prepared by the hydrolysis of acetate 12a (83% yield). The excision of one carbon atom with a Grieco–Sharpless elimination followed by oxidative cleavage gave 19. The resulting dialcohol underwent oxidative cleavage with NaIO4, leading to the aldehyde 19 (46% yield, two steps). Coupling aldehyde 19 with the aryllithium derivative of 20 formed a mixture of diastereomeric benzylic alcohols 21. The reduction of compound 21 gave the deoxygenated compound 22 (78% yield over two steps). After treatment of compound 22 with TBAF hydroquinone, 23 was synthesized (86% yield). Finally, the reaction of compound 23 with BF3·Et2O gave (+)-aureol (4) with a yield of 66%. This final cyclization to obtain the marine tetracyclic meroterpenoid aureol (4) had been previously described by Marcos and co-workers [8] in their synthesis of (−)-aureol. In conclusion, the aureane intermediate 12a was obtained through 1,2-rearrangements of the drimane compound 16 using BF3·Et2O as key step. This intermediate 12a was the key compound for the total synthesis of (+)-aureol (4). Compound 4 was first isolated from a marine sponge [26] and possesses potent biological activities, including anti-influenza A virus activity [27], selective cytotoxicity against human tumour cells [28], antibiotic activity [15], and the ability to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 [29].
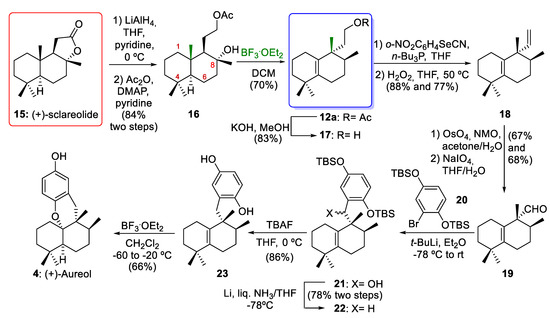
Scheme 3.
George´s synthesis of intermediate 12a and total synthesis of (+)-aureol (4). BF3·Et2O = boron trifluoride etherate; DMAP = 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine; NM O = N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide; TBAF = tetrabutylammonium fluoride.
2.2. Rosales Martínez’s Synthesis of Compound 12b
Due to the fascinating chemical structures and biological properties of marine meroterpenoids, our research group and the group led by Prof. Oltra [12,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] began to develop methodologies for the total synthesis of this group of natural marine compounds. Along with Gansäuer group [37,38], we have contributed to the acquisition of marine meroterpenoids through the diastereoselective radical cyclization of epoxypolyenes catalyzed by Cp2TiCl as a new green monoelectronic transfer complex [39,40]. Subsequently, specifically during the synthesis of marine (±)-aureol (4), we reported the first example of a Lewis acid-mediated rearrangement of drimane skeleton 29 bearing an exo-olefin at C-8 to obtain a compound with the aureane skeleton 12b (Scheme 4). Initially, our synthesis of compound 12b with an aureane skeleton was carried out by the Cp2TiCl-catalyzed radical cascade cyclization of the epoxyfarnesol derivative (27), which was obtained from epoxyfarnesol (24) [12]. In this way, the mesylation of compound 24, followed by bromination with LiBr at 0 °C and the addition of 2,5-dimethoxyphenylmagnesium bromide (26), furnished the epoxyfarnesol derivative 27. Radical cascade cyclization of 27 gave the trans-fused decalin 28 possessing an exo-cyclic double bond on C-8 in a 48% yield. This cyclization catalyzed by titanocene(III) is highly diastereoselective, and four stereocenters are formed with a desired relative configuration. Furthermore, the same methodology can be used for the enantiomerically pure preparation of optically active 28 if the Sharpless asymmetric cis-hydroxylation of farnesyl acetate is used for the preparation of 24, as described in the synthesis of β-onocerin [41]. Another advantage of titanocene(III)-catalyzed cascade cyclization of epoxyfarnesol derivative 27 is the generation of a compound with the presence of a hydroxyl group at C-3, which is present in interesting marine products such as (+)-stachyflin (6) (Figure 1) [42]. The deoxygenation of alcohol 28 was carried out using a two-step sequence (Scheme 4): first, the preparation of a thiocarbonate and later, its treatment with n-Bu3SnH and AIBN, leading to compound 29 in an 86% yield (two steps). Inspired by the biosynthetic hypothesis, we proposed that the treatment of 29 with BF3·Et2O could originate a rearrangement sequence of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts. The reaction gave the desired tetrasubstituted alkene 12b with an aureane skeleton in 63% yield, together with the undesired tetracyclic compound 30 in 30% yield. Later, Li and co-workers [14] optimized this rearrangement starting from the same drimane skeleton but with an alcohol group at the C-8 position, noting that the undesired compound 30 could be inhibited at low temperatures to improve the yield of compound 12b. With 12b in our hands, we completed the synthesis of marine (±)-aureol (4). This tetracyclic compound 4 was prepared from 12b in three steps. The removal of the methoxy groups was achieved through a two-step oxidative (AgO, HNO3)/reductive (Pd/C, H2) sequence, which afforded the phenolic compound 31 in an 82% yield. Finally, the cyclization of hydroquinone 31, under the same conditions reported by George and co-workers [10], gave (±)-aureol (4) in 62% yield.
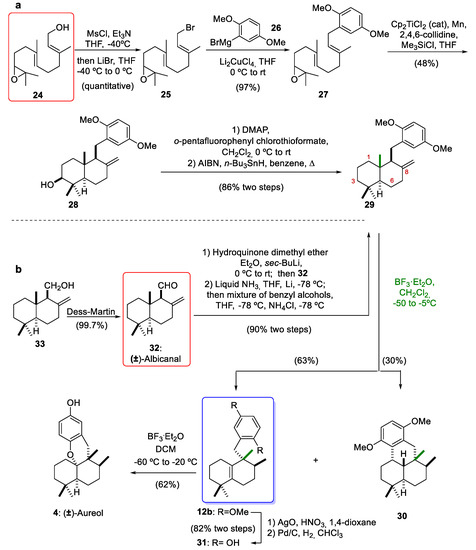
Scheme 4.
Rosales Martínez´s synthesis of compound 12b by (a): Cp2TiCl-catalyzed radical cyclization of 27 or by (b): nucleophilic addition of 2-lithiohydroquinone dimethyl ether to 32, and total synthesis of (±)-aureol (4). Cp2TiCl2 = Bis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium(IV) dichloride; DMAP = 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine; AIBN = 2,2´-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile); BF3·Et2O = boron trifluoride etherate.
Later, in order to consolidate the stereospecific 1,2-rearrangements as an excellent strategy towards compounds with aureane skeletons but using drimanes as starting materials, compound 29 was synthesized by the 1,2-addition of 2-lithiohydroquinone dimethyl ether to commercially available albicanal (32) [21]. Aldehyde 32 can also be prepared by the oxidation of albicanol (33), which can be obtained by the radical cyclization of epoxyfarnesyl acetate [30]. The C-C bond-forming reaction afforded a mixture of diastereomeric benzylic alcohols. Reduction of these alcohols with lithium in liquid NH3/THF followed by treatment with NH4Cl solution gave the drimane intermediate 29 in a 90% yield (two steps). Both procedures (the radical cascade cyclization of epoxyfarnesol derivatives catalyzed by titanocene(III) and the 1,2-addition of aryllithium derivatives to albicanal (32)) can provide compounds with a drimane skeleton with adequate functionalization of the aromatic ring to obtain highly valuable natural meroterpenoids through 1,2-rearrangements mediated by a Lewis acid as a key step (see Section 4).
2.3. Wu´s Synthesis of Compound 12c
In 2018, Wu and co-workers [20] reported an efficient and short synthesis of 12c as a precursor of aureol (4), employing the commercially available (+)-sclareolide (15) as a starting material (Scheme 5). Again, the key step for the synthesis of 12c, which has an aureane skeleton, was the stereospecific 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts of the drimane compound 34. In this way, (+)-sclareolide (15) was readily converted to intermediate 34 in two steps, including the reduction of the starting material using diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBAL-H) to give 35 and the C-C bond cleavage conditions reported by Suarez´s group (I2/PIDA/hν) [43] of 35 to afford 34. These conditions led to the formation of the formate derivative of iododrimanol 34 in a 76% overall yield. When drimane 34 was treated with BF3·Et2O, the tetrasubstituted alkene 12c and the undesired compound 36 were obtained in 63% and 20% yields. The drimane 34, which is equipped with a versatile iodine functionality, can be employed as a common precursor of marine meroterpenoids with aureane or avarane skeletons, as it allows the incorporation of the aromatic ring either through the 1,2-addition of aryllithium derivatives or through the Negishi coupling of aryl derivatives, as will be discussed in Section 4. With tetrasubstituted alkene 12c and an aryl Grignard reagent 37, the tricyclic compound 12b was prepared, which is an advanced intermediate in the synthesis of aureol (4), as reported by our research group [12].
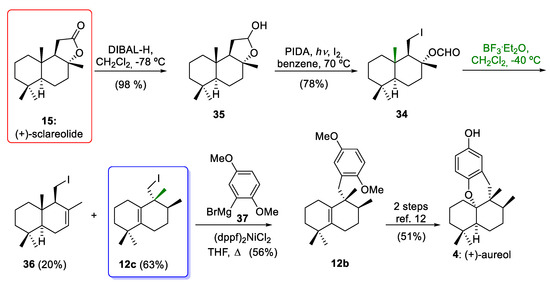
Scheme 5.
Wu´s synthesis of intermediate 12c and formal synthesis of (±)-aureol (4). DIBAL-H = diisobutylaluminium hydride; PIDA = phenyliodine(III) diacetate (dppf)2NiCl2 = [1,1´-bis(diphenylphospino)ferrocene]dichloronickel(II); BF3·Et2O = borontrifluoride etherate.
2.4. Li’s Synthesis of Compound 12b
Recently, Li and co-workers [14] reported the rearrangement of a drimane skeleton to an aureane skeleton employing as starting material commercially available (+)-sclareolide (15) (Scheme 6). In addition, for the first time, this research group included a promising study that provides new and hopeful ideas for the synthesis of compounds with an avarane skeleton from compounds with an aureane skeleton. This study provides a new pathway for the synthesis of avarane compounds using cyclization mediated by a Lewis acid.
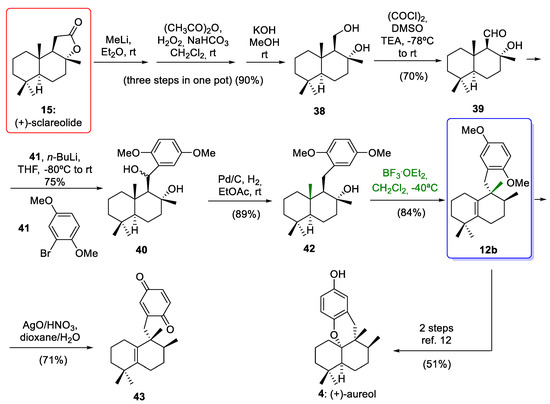
Scheme 6.
Preparation of compound 12b via stereospecific 1,2-rearrangements and formal synthesis of (+)-aureol (4). (CH3CO)2O = acetic anhydride; (COCl)2 = oxalyl chloride; BuLi = butyllithium; TEA = triethanolamine; BF3·Et2O = boron trifluoride etherate.
(+)-Sclareolide (15) was converted to diol 38 using a one-pot, three-step sequence in 90% yield over three steps. The oxidation of diol 38 gave aldehyde 39 in a 70% yield. The cross-coupling reaction between an aryllithium derivative of 41 and aldehyde 39 led to diastereomeric benzyl alcohol 40 in 75% yield. Deoxygenation of benzyl alcohol 40 by hydrogenolysis afforded tertiary alcohol 42, which led to the aureane compound 12b upon treatment with BF3·Et2O through a stereospecific rearrangement of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts. This key step gave the desired compound 12b with an aureane skeleton in a moderate yield. This moderate yield was obtained when the rearrangement was carried out at −50 °C and low reaction times. Optimization of the reaction conditions, using the same Lewis acid at −40 °C and 11 h of reaction, afforded the compound 12b in a higher yield (84%). As the tetrasubstituted olefin 12b is an intermediate in the total synthesis of aureol (4) reported by Rosales Martínez and co-workers [12], this work constitutes a formal synthesis of this interesting marine natural product (Scheme 6).
As we have already mentioned, the most notable milestone in the work published by Li and co-workers [14] was the preparation of tetracyclic meroterpenoids with an avarane skeleton. These compounds were obtained by a bioinspired Lewis acid-catalyzed cyclization reaction of quinone 43 (prepared from compound 12b) with the concomitant migration of C-4 Me-groups through 1,2-rearrangement leading to compounds with an avarane skeleton (Scheme 7).
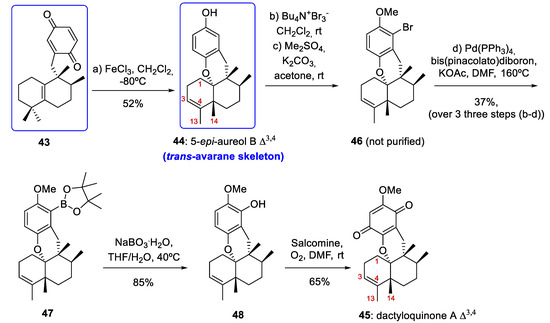
Scheme 7.
Preparation of compound 44 with an avarane skeleton and synthesis of dactyloquinone A Δ3,4 (45). DMF = dimethylformamide; salcomine = N,N´-bis(salicylidene)ethylenediaminocobalt(II).
Therefore, in this study, the authors simultaneously described the preparation of compounds with aureane (compound 12b, Scheme 6) and avarane (compound 44, Scheme 7) skeletons. This finding supports the affirmation that the bioinspired sequence of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts in compounds with a drimane skeleton is a general strategy that unifies the synthesis of a large group of marine meroterpenoids with aureane and avarane skeletons, starting from commercially available compounds with drimane skeletons.
In this way, when tetrasubstituted olefin 12b was treated with AgO/HNO3, quinone 43 was obtained in a yield of 71% (Scheme 6). Several Lewis acids were tested for the cascade reaction that allows the cyclization/rearrangement of the quinone 43 into 44. After optimization, treatment of 43 in a gram scale (2.0 g) with FeCl3 at −80 °C afforded the trans-avarane compound 44 in 52% yield with satisfactory stereoselectivity (Scheme 7). This trans-avarane compound 44 was used as starting material for the synthesis of non-natural dactyloquinone A Δ3,4 (45) (Scheme 7). From 44, the sequence was a selective bromination followed by methylation, a Miyaura borylation, and two final oxidations with NaBO3 and O2/salcomine. As a result, dactyloquinone A Δ3,4 (45) was obtained in a 20% overall yield from 46 (Scheme 7).
On the other hand, the reaction of the quinone 43 at the gram scale (1.5 g) with AgOTf at room temperature in CH2Cl2 afforded an inseparable mixture of 5-epi-aureol B Δ3,4 (44), aureol B Δ3,4 (49), and 5-epi-aureol B (50) in a 60% combined yield (Scheme 8). When this mixture was treated under the conditions reported in Scheme 7, dactyloquinone A Δ3,4 (45), dactyloquinone A (7), and dactyloquinone B Δ3,4 (51) (7:1:1) were obtained with a total yield of 17% (Scheme 8). Compounds 7 and 45 proved to be inseparable by HPLC purification.
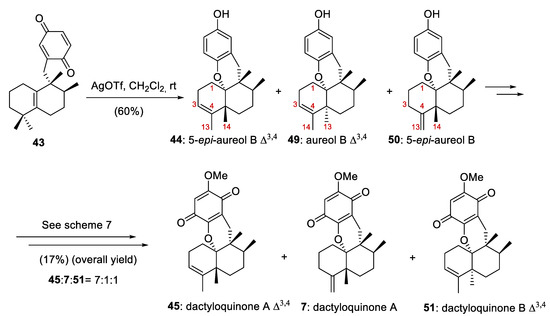
Scheme 8.
Preparation of of 5-epi-aureol B Δ3,4 (44), aureol B Δ3,4 (49), 5-epi-aureol B (50), dactyloquinone A Δ3,4 (45), dactyloquinone A (7) and dactyloquinone B Δ3,4 (51).
Dactyloquinone A (7) is a marine sesquiterpenoid quinone isolated from marine sponges [44] in very small amounts, limiting the study of its biological properties.
3. Probable Reaction Mechanism for BF3·Et2O Mediated 1,2-Hydride and Methyl Shifts to Generate Aureane Compounds 12a–d
Although mechanistic studies of the rearrangements of drimanes via sequential 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts have not been performed in detail [21], the remarkable stereocontrolled rearrangements of drimanes 16, 29, 34, and 52 can be rationalized by the mechanistic route shown in Scheme 9, which is based on the proposed mechanism for similar acid-catalyzed rearrangements [45,46]. From drimanes 16, 29, 34, and 52, the reaction process would involve four possible carbocationic intermediates I–IV. The cationic rearrangements would initially involve a proton transfer since it is known that pure Lewis acids are not ideal initiators in alkene cationic polymerization [47]. Additionally, it is known that BF3·Et2O is a very moisture-sensitive Lewis acid, and over time the HF that generates from the hydrolysis of BF3 will react with an excess of this Lewis acid to produce HBF4, which is a strong acid, and possibly trigger the cationic rearrangement. Thus, when the hydroxyl group of the drimanes (16, 52), the formate group of drimane 34, or the exocyclic double bond of drimane 29 is activated by a proton, the tertiary carbocation I is generated, which then would furnish the carbocationic intermediate II by migration of the C-9 hydrogen to the C-8 carbocation center. From a stereochemical point of view, the configuration of C-9 allows a 1,2-hydrogen shift on the α-face of the intermediate I to generate the intermediate II or trisubstituted alkene 36 after losing a proton at C-7 (this undesirable product was obtained when iododrimanol formate 34 was used as starting material in the rearrangement reaction). Carbocationic intermediate II would undergo a 1,2-methyl shift from the methyl group C-10 to the carbocationic center C-9 within the β-face of the molecule to furnish the carbocationic intermediate III, in which the loss of a proton at C-5 leads to the desirable compounds 12a–d (pathway a, Scheme 9).
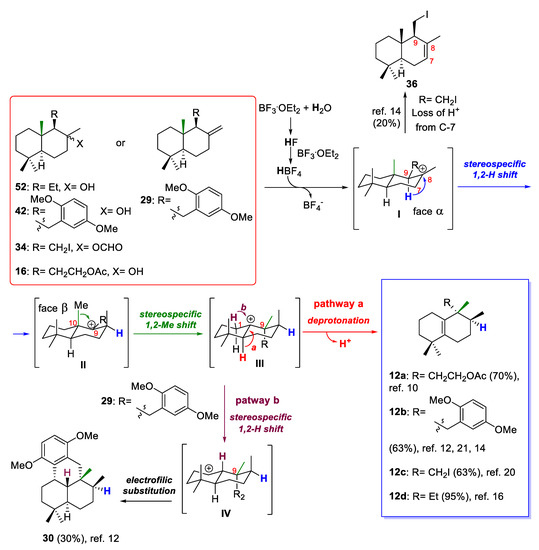
Scheme 9.
Probable reaction mechanism for BF3·Et2O-promoted 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts from compounds with drimane skeletons 16, 29, 34, 42 and 52.
On the other hand, it has been observed that when the C-11 of the starting material was linked to an aromatic derivative ring (29), the carbocationic intermediate III underwent a 1,2-hydride shift from the C-1 position to give the intermediate IV (pathway b, Scheme 9), the carbocation of which was trapped by the aromatic ring by electrophilic substitution to afford the undesirable minor tetracyclic compound 30. In both pathways, a proton is liberated, which can react with a more non-activated hydroxyl group or exocyclic alkene in the starting drimanes 16, 29, 34, and 52 to follow the catalytic cycle.
The simultaneous generation of tetrasubstituted alkene 12a–d and sub-products 30 and 36 suggests that these 1,2-rearrangements are not part of a concerted reaction. These rearrangements would proceed via an unconcerted mechanism involving a series of rapidly interconverting carbocationic intermediates. The major products with aureane skeletons (12a–d) are shown in Scheme 9, together with the best yields obtained after optimization of the 1,2-rearrangement reactions of the different starting drimanes (see the references shown in Scheme 9). The optimization of this rearrangement towards the formation of compounds with aureane skeletons is the result of many factors, which mainly include Lewis acid equivalents, temperature and reaction time [14]. The non-optimization of the rearrangement towards aureane skeletons generates mainly drimanes with a trans-decalin structure and a tetra (Δ8) or tri-substituted double bond (Δ7) [16].
4. Future Perspectives
Although we have successfully discussed different synthetic routes for marine meroterpenoids with aureane or avarane skeletons from available drimanes, with the key step being a cascade of 1,2-rearrangements, the alternative synthesis of other marine compounds with similar structures is desirable to illustrate the flexibility of this rearrangement as a key step. The precursor drimanes of compounds with aureane or avarane skeletons can be prepared by a convergent synthetic route, where the C-C bond between the drimane skeleton and the aromatic ring is formed either through a Negishi coupling or the 1,2-addition of an arylmetal derivative, or, alternatively, by a linear synthetic route using as starting material epoxipolyene derivatives. The synthetic value of the stereospecific 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts is demonstrated by the reported or future synthesis of select members of marine meroterpenoids in a concise and practical manner.
As we have commented in Section 2, using as starting material drimanes 16, 29, and 34 synthesized by a convergent or linear route, marine aureol (4) has been obtained efficiently using as a key step a 1,2-rearrangement mediated by BF3·Et2O. The important epimerization of aureol (4) into 5-epi-aureol (53) reported by Magauer and co-workers [15] opened the door to the preparation of other marine aureane skeletons with a trans-decalin structure, such as 5-epi-smenoqualone (55) and (−)-cyclosmenospongine (2) (Scheme 10).
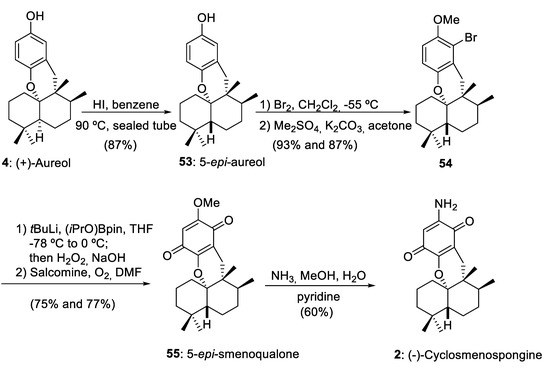
Scheme 10.
Preparation of 5-epi-smenoqualone (55) and (−)-cyclosmenospongine (2) from aureol (4). Salcomine = N,N´-bis(salicylidene)ethylenediaminocobalt(II). (iPrO)Bpin = isopropoxy pinacolborane.
The sequence including the epimerization of (+)-aureol (4), selective bromination and subsequent methylation, boronation-oxidation, and final aminolysis furnished (−)-cyclomenospongine (2) with a 24% overall yield from aureol (4). Tetracyclic meroterpenoid (−)-cyclomenospongine (2) is a natural compound isolated from a marine source [48] and with remarkable biological activity [15]. Magauer and co-workers have realized an important contribution to the synthesis of this compound using a highly modular synthetic strategy [15,49,50].
In addition to the synthesis of (+)-aureol (4) and (−)-cyclosmenospongine (2), other marine meroterpenoids with aureane skeletons can be easily prepared using the 1,2-rearrangements widely discussed in this article as a key step. In this way, the future syntheses of (+)-stachyflin (6), (+)-neomamanuthaquinone (1), and (+)-stronglyn A (5) are described below.
The retrosynthetic analysis of (+)-stachyflin (6) (Scheme 11) is based on: (a) the acid-mediated cyclization of the intermediate obtained from 56 after selective deprotection using Magauer´s conditions [15], (b) the key rearrangement reaction of 57 to give 56 using BF3·Et2O, (c) Cp2TiCl-catalyzed cascade cyclization of the epoxyfarnesol derivative 58 and protection of the OH group at C-3 to give 57, and (d) the cross-coupling reaction between the bromide 25 and isoindoline derivative 59 to afford 58. Alternatively, compound 57 could be obtained through a coupling reaction between drimane 60 and the isoindoline derivative 59. The trans-decalin 60 could be obtained through the titanocene(III)-catalyzed cascade cyclization of the epoxyfarnesol derivative 61.
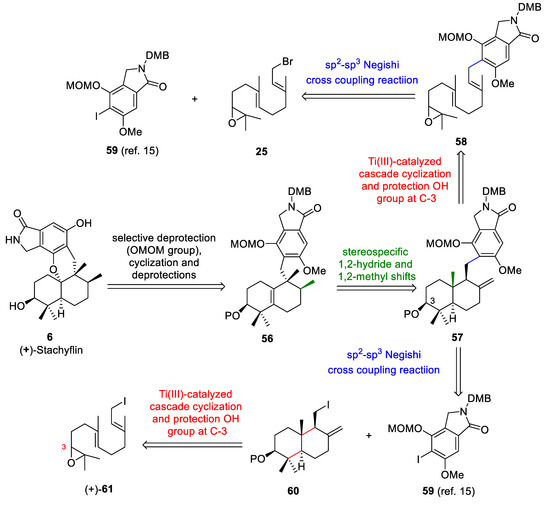
Scheme 11.
Retrosynthetic analysis of (+)-stachyflin (6).
(+)-Stachyflin (6) is a marine meroterpenoid with a fascinating chemical structure and biological activities [15]. It has been published that the anti-influenza A virus activity of this compound is 250 times higher than that of zanamivir (IC50 = 0.75 mM) and 1760 times higher than that of amantadine (IC50 = 5.3 mM) [42,51]. This compound was isolated from a marine fungus by the Shionogi research group [52]. The total synthesis of this compound has been reported by several research groups [5,7,9,15].
The retrosynthetic analysis of (+)-strongylin A (5) is outlined in Scheme 12. This retrosynthetic sequence is based on: (a) the selective deprotection and biomimetic acid-mediated cyclization of the hydroquinone of 62 to form 5, (b) a biosynthetically inspired sequence of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts of 63 to form 62, and (c) a cross-coupling reaction between abicanal 32 and aryllithium 64 to afford a mixture of benzyl alcohols, which after removal of the free hydroxy groups would give 63. Albicanal (32) can be synthesized by the oxidation of albicanol (33), which is easily prepared through the Cp2TiCl-catalyzed radical cyclization of epoxyfarnesyl acetate, as previously reported by us and others [21,30,53].
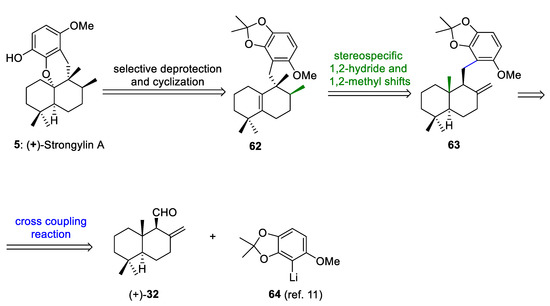
Scheme 12.
Retrosynthetic analysis of (+)-strongylin A (5).
(+)-Strongylin A (5) has been isolated from marine sponges [54,55] and possesses interesting biological activities [15,54]. The first total synthesis of (+)-strongylin A was reported by Katoh and co-workers [11] and later by Magauer and co-workers [15] through a modular synthetic strategy.
The retrosynthetic analysis of (+)-neomamanuthaquinone (1) and (+)-smenoqualone (3) is shown in Scheme 13. This retrosynthetic route is based on: (a) the selective deprotection of the methoxy groups of 65 to generate 1, (b) the addition of NaOMe to the quinone ring of 43 to afford 65, (c) the deprotection of both methoxy groups in 12b to produce 43, (d) stereospecific 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts to transform 29 into 12b, and (e) a C-C bond formation reaction between albicanal (32) and 2-lithiohydroquinonedimethylether (66). As neomamanuthaquinone (1) is the preliminary intermediate in Marcos´s synthesis of (−)-smenoqualone [8], the retrosynthetic analysis shown in Scheme 13 constitutes a formal synthesis of (+)-smenoquealone (3) (Scheme 13).
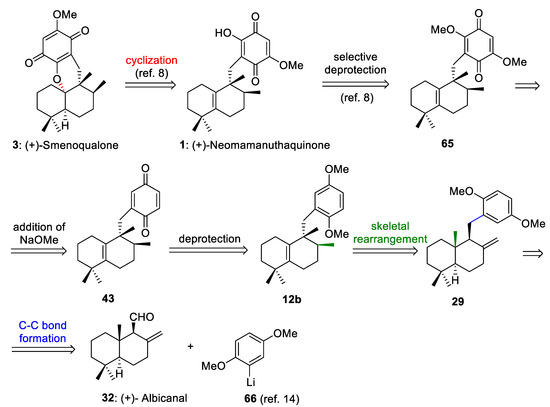
Scheme 13.
Retrosynthetic analysis of (+)-neomamanuthaquinone (1) and (+)-smenoqualone (3).
(+)-Neomamanuthaquinone (1) is a marine quinone isolate from marine sponges [56], which shows cytotoxic [56], hemolytic [57] and antioxidant activities [58]. The enantiomer of this interesting marine natural compound was synthesized by Marcos et al. [8].
(+)-Smenoquealone (3) is another tetracyclic meroterpenoid with biological activity isolated from a marine sponge [59]. This compound has been synthesized by several research groups [8,13,15].
5. Conclusions
In summary, we have established a synthetic strategy for the preparation of a large number of marine natural products with aureane and avarane skeletons. The key step of this synthetic strategy is a biosynthetically inspired rearrangement of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts from available drimanes obtained from (+)-sclareolide (15), albicanal (32), and epoxy farnesol (24). This article reviews the total synthesis of aureol (4), (−)-cyclomenospongine (2), and (−)-dactyloquinone A (7) and proposes future syntheses for (+)-neomamanuthaquinone.(1) (+)-smenoqualone (3), (+)-strongylin A (5), and (+)-stachyflin (6) using the aforementioned rearrangement as a key step. Consequently, this general synthetic strategy demonstrates its versatility and power for the construction of natural marine compounds with aureane and avarane skeletons that could be used to address relevant biological issues.
Author Contributions
A.R.M.: design and coordination of the project, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. R.N.R.-M.: writing—review. I.R.-G.: writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Antonio Rosales Martínez acknowledges the financial support of the University of Sevilla (Projects 2020/00001014, 2021/00000422: Proyectos a Consolidación de Grupos de la Junta de Andalucía. Ignacio Rodriguez-García acknowledges the financial support received from Universidad de Almería and Junta de Andalucía (Conserjería de Transformación Económica, Industria, Conocimiento y Universidades) and Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) for the Projects UALFEDER 2020-FQM-B1989, project PY20_01027 and project CEIA3 PYC20 RE 060 UAL, and also for the Horizon 2020-Research and Innovation Framework Programme of the European Commission for the project 101022507 LAURELIN.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Antonio Rosales Martínez acknowledges the University of the Sevilla for his position as professor.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ueda, K.; Uemura, D. Studies in Natural Products Chemistry. Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 35, pp. 57–100. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, I.S.; Conde, A.; Moro, R.F.; Basabe, P.; Diez, D.; Urones, J.G. Quinone/Hydroquinone Sesquiterpenes. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2010, 7, 230–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, M.; Imperatore, C.; D’Aniello, F.; Aiello, A. Meroterpenes from Marine Invertebrates: Structures, Occurrence, and Ecological Implications. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1602–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, P.A.; Hernández, Á.P.; San Feliciano, A.; Castro, M.Á. Bioactive Prenyl-and Terpenyl-Quinones/Hydroquinones of Marine Origin. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taishi, T.; Takechi, S.; Mori, S. First total synthesis of (±)-stachyflin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 4347–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Suzuki, A.; Nakatani, M.; Fuchikami, T.; Inoue, M.; Katoh, T. An efficient synthesis of (+)-aureol via boron trifluoride etherate-promoted rearrangement of (+)-arenarol. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6929–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Sakurai, J.; Abe, H.; Katoh, T. Total synthesis of (+)-stachyflin: A potential anti-influenza A virus agent. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4055–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, I.S.; Conde, A.; Moro, R.F.; Basabe, P.; Díez, D.; Urones, J.G. Synthesis of quinone/hydroquinone sesquiterpenes. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 8280–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, J.; Kikuchi, T.; Takahashi, O.; Watanabe, K.; Katoh, T. Enantioselective total synthesis of (+)-stachyflin: A potential anti-influenza A virus agent isolated from a microorganism. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 2011, 2948–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, K.K.W.; Pepper, H.P.; Bloch, W.M.; George, J.H. Total synthesis of (+)-aureol. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4710–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamishima, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Katoh, T. Total synthesis of (+)-strongylin A, a rearranged sesquiterpenoid hydroquinone from a marine sponge. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 4558–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, A.; Muñoz-Bascón, J.; Roldan-Molina, E.; Rivas Bascón, N.; Padial, N.M.; Rodríguez-Maecker, R.; Rodríguez-García, I.; Oltra, J.E. Synthesis of (±)-aureol by bioinspired rearrangements. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 1866–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, T.; Atsumi, S.; Saito, R.; Narita, K.; Katoh, T. Unified synthesis of the marine sesquiterpene quinones (+)-smenospongine, (-)-ilimaquinone, (+)-smenospongine, and (+)-isospongiaquinone. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3837–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, D. Bio-inspired construction of a tetracyclic ring system with avarane skeleton: Total synthesis of dactyloquinone A. Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 4705–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildermuth, R.; Speck, K.; Haut, F.-L.; Mayer, P.; Karge, B.; Broenstrup, M.; Magauer, T. A modular synthesis of tetracyclic meroterpenoid antibiotics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.H.; McArdle, M.; Baldwin, J.E.; Adlington, R.M. Biomimetic rearrangements of simplified labdane diterpenoids. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 6321–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugelshofera, C.L.; Magauer, T. Dyotropic rearrangements in natural products synthesis and biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.H. Biomimetic dearomatization strategies in the total synthesis of meroterpenoid natural products. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudry, C.M.; Malerich, J.P.; Trauner, D. Biosynthetic and Biomimetic Electrocyclizations. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4757–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Li, H.-J.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-C. A six-step synthetic approach to marine natural product (+)-aureol. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales Martínez, A.; Enríquez, L.; Jaraíz, M.; Pozo Morales, L.; Rodríguez-García, I.; Díaz Ojeda, E. A Concise Route for the Synthesis of Tetracyclic Meroterpenoids: (±)-Aureol Preparation and Mechanistic Interpretation. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.M. Molecular Rearrangements in Organic Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, G.; Zu, L. Natural product total synthesis using rearrangement reactions. Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 5383–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S. Recent applications of the 1,2-carbon atom migration strategy in complex natural product total synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2272–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delayre, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J. Natural Product Synthesis Enabled by Domino Processes Incorporating a 1,2-Rearrangement Step. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djura, P.; Stierle, D.B.; Sullivan, B.; Faulkner, D.J.; Arnold, E.; Clardy, J. Some metabolites of the marine sponges Smenospongia aurea and Smenospongia (polyfibrospongia) echina. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.E.; Cross, S.S.; Burres, N.S.; Koehn, F. Novel Antiviral and Antitumor Terpene Hydroquinones and Methods of Use. PCT WO 9112250A1, 22 August 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Longley, R.E.; McConnell, O.J.; Essich, E.; Harmody, D.J. Evaluation of Marine Sponge Metabolites for Cytotoxicity and Signal Transduction Activity. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhetri, B.K.; Tedbury, P.R.; Sweeney-Jones, A.M.; Mani, L.; Soapi, K. Marine Natural Products as Leads against SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, A.; López-Sánchez, C.; Álvarez-Corral, M.; Muñoz-Dorado, M.; Rodríguez-García, I. Total Synthesis of (±)-Euryfuran Through Ti(III) Catalyzed Radical Cyclization. Lett. Org. Chem. 2007, 4, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, A.; Muñoz-Bascón, J.; Moráles-Álcazar, V.M.; Castilla-Alcalá, J.A.; Oltra, J.E. Ti(III)-catalyzed, concise synthesis of marine furanospongian diterpenes. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 12922–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, A.; Muñoz-Bascón, J.; López-Sánchez, C.; Álvarez-Corral, M.; Muñoz-Dorado, M.; Rodríguez-García, I.; Oltra, J.E. Ti-Catalyzed Homolytic Opening of Ozonides: A sustainable C-C Bond-Forming Reaction. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 4171–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, A.; Foley, L.A.R.; Padial, N.M.; Muñoz-Bascón, J.; Sancho-Sanz, I.; Roldán-Molina, E.; Pozo-Morales, L.; Irías-Álvarez, A.; Rodríguez-Maecker, R.; Rodríguez-García, I.; et al. Diastereoselective Synthesis of (±)-ambroz by Titanium(III)-Catalyzed Radical Tandem Cyclization. Synlett 2016, 27, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales Martinez, A.; Pozo Morales, L.; Diaz Ojeda, E. Cp2TiCl-catalyzed, concise synthetic approach to marine natural product (±)-cyclozonarone. Synth. Commun. 2019, 49, 2554–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales Martínez, A.; Pozo Morales, L.; Díaz Ojeda, E.; Castro Rodríguez, M.; Rodríguez-García, I. The Proven Versatility of Cp2TiCl. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 1311–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales Martínez, A.; Rodríguez-García, I.; López-Martínez, J. Divergent Strategy in Marine Tetracyclic Meroterpenoids. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gansäuer, A.; Rosales, A.; Justicia, J. Catalytic epoxypolyene cyclization via radicals: Highly diastereoselective formal synthesis of puupehedione and 8-epi-puupehedione. Synlett 2006, 6, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansäuer, A.; Justicia, J.; Rosales, A.; Worgull, B.; Rinker, B.; Cuerva, J.M.; Oltra, J.E. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Allylic Substitution and Titanocene-Catalyzed Epoxypolyene Cyclization as a Powerful Tool for the Preparation of Terpenoids. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 2006, 4115–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Rodríguez, M.; Rodríguez García, I.; Rodríguez Maecker, R.N.; Pozo Morales, L.; Oltra, J.E.; Rosales Martínez, A. Cp2TiCl: An Ideal Reagent for Green Chemistry? Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales Martínez, A.; Castro Rodríguez, M.; Rodríguez-García, I.; Pozo Morales, L.; Rodríguez Maecker, R.N. Titanocene dichloride: A new green reagent in organic chemistry. Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, A.F.; Herrador, M.M.; del Moral, J.F.Q.; Arteaga, P.; Arteaga, J.F.; Piedra, M.; Sánchez, E.M. Reductive Coupling of Terpenic Allylic Halides Catalyzed by Cp2TiCl: A Short and Efficient Asymetric Synthesis of Onocerane Triterpenes. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 2301–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, K.; Kouzuki, S.; Yoshimoto, J.; Kawamura, Y.; Tani, H.; Iwata, T.; Terui, Y.; Nakai, H.; Yagi, S.; Hattori, N.; et al. Stachyflin and acetylstachyflin, novel anti-influenza a virus substances, produced by Stachybotrys sp. RF-7260. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concepción, J.I.; Francisco, C.G.; Freire, R.; Hernández, R.; Salazar, J.A.; Suárez, E. Iodosobenzene Diacetate, an Efficient Reagent for the Oxidative Decarboxylation of Carboxylic Acids. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitome, H.; Nagasawa, T.; Miyaoka, H.; Yamada, Y.; van Soest, R.W.M. New Sesquiterpenoid Quinones from the Okinawan Marine Sponge Dactylospongiaelegans. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1506–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, S.; Capon, R.J. Marine Sesquiterpene Quinones and Hydroquinones: Acid-Catalyzed Rearrangements and Stereochemical Investigations. Aust. J. Chem. 1994, 47, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J. The Acid-Catalyzed Rearrangement and Absolute Stereochemistry of Isospongiaquinone. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraher, C.E., Jr. Ionic Chain-Reaction and Complex Coordinative Polymerization (Addition Polymerization). In Polymer Chemistry, 6th ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Utkina, N.K.; Denisenko, V.A.; Scholokova, O.V.; Virovaya, M.V.; Prokof’eva, N.G. Cyclosmenospongine, a new sesquiterpenoid aminoquinone from an Australian marine sponge Spongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speck, K.; Wildermuth, R.; Magauer, T. The Acid-Catalyzed Rearrangement and Absolute Stereochemistry of Isospongiaquinone. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14131–14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speck, K.; Magauer, T. Evolution of a Polyene Cyclization Cascade for the Total Synthesis of (-)-Cyclosmenospongine. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, K.; Kouzuki, S.; Kamigauchi, T. Stachyflin and acetylstachyflin, novel anti-influenza A virus substances, produced by Stachybotrys sp. RE-7260. II. Synthesis and Preliminary Structure-Activity Relationships of Stachyflin Derivatives. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamigauchi, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Tani, H.; Kawamura, Y.; Horibe, I. Sesquiterpene Derivatives Having Antiviral Activity. PCT WO 9711947 A1, 3 April 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Matthias Göhl, M.; Seifert, K. Synthesis of the Sesquiterpenes Albicanol, Drimanol, and Drimanic Acid, and the Marine Sesquiterpene Hydroquinone Deoxyspongiaquinol. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 6975–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.E.; Rueth, S.A.; Cross, S.S. An Antiviral Sesquiterpene Hydroquinone from the Marine Sponge Strongylophora hartmani. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coval, S.J.; Conover, M.A.; Mierzwa, R.; King, A.; Puar, M.S.; Phife, D.W.; Pai, J.-K.; Burrier, R.E.; Ahn, H.-S.; Boykow, G.C.; et al. Wiedendiol-A and -B, chlolesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors from the marine sponge Xestospongia wiedenmayeri. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1995, 5, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, K.W.L.; Jankam, A.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Suksamrarn, A.; Garson, M.J. Stereochemical evaluation of sesquiterpene quinones from two sponges of the genus Dactylospongia and the implication for enantioselective processes in marine terpene biosynthesis. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 6341–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokof'eva, N.G.; Utkina, N.K.; Chaikina, E.L.; Makarchenko, A.E. Biological activities of marine sesquiterpenoid quinones: Structure-activity relationships in cytotoxic and hemolytic assays. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 139B, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkina, N.K.; Makarchenko, A.E.; Shchelokova, O.V.; Virovaya, M.V. Antioxidant activity of phenolic metabolites from marine sponges. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2004, 40, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L.; Martin, M.-T.; Guyot, M. Smenoqualone, a Novel Sesquiterpenoid from the Marine Sponge Smenospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 8079–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).