Abstract
Marine products are among the most promising sources of biologically active molecules. Aplysinopsins, tryptophan-derived marine natural products, were isolated from different natural marine sources including sponges, stony corals (hard corals) especially genus scleractinian, as well as sea anemone, in addition to one nudibranch. Aplysinopsins were reported to be isolated from different marine organisms related to various geographic areas such as Pacific, Indonesia, Caribbean, and Mediterranean regions. This review gives an up-to-date overview of marine alkaloid aplysinopsins: their various sources, their synthesis, and the fact that many aplysinopsin derivatives are biologically active compounds.
1. Introduction
Marine organisms produce thousands of organic compounds, many of which have an exceptionally high biological activity [1]. Aplysinopsins are tryptophan-derived marine natural products [2], whose name derives from the marine sponge Thorecta aplysinopsis. Aplysinopsin (1) was firstly isolated and chemically elucidated by Kazlauskas et al. [3]. Aplysinopsins have also been purified from other sponges, including Verongia spengelii [4], Dercitus sp. [5], Hyrtios erecta [6], Smenospongia aurea [7], Thorectandra, Smenospongia, and Verongula rigida [8,9]. Additionally, aplysinopsins were previously isolated from mollusk, Phestilla melanobrachia mollusk [10], and corals such as Tubastrea coccinea [10], Tubastraea aurea [11], Dendrophyllia sp. [12], Tubastraea faulkneri [13], and Thorectandra sp. [14].
Aplysinopsins possess an array of biological activities, such as, antimalarial [15,16], antimicrobial [16,17], monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor [18], anti-depressant [19], and antiviral [20]. Recently, it has been shown that aplysinopsins act as a blood–brain barrier permeable scaffold for anti-cholinesterase and anti-BACE-1 activity (beta-site amyloid-precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1) [21]. Additionally, aplysinopsin and its derivatives were found to possess significant anticancer activity against several cancer cell lines, including multidrug resistance (MDR) cell lines, leukemia, and breast, colon, and uterine cancer cell lines [22,23]. This review gives an up-to-date overview of marine alkaloid aplysinopsins: their origin, isolation sources, synthesis, analogs, and bioactivity.
2. Different Sources and Chemical Structures of Aplysinopsins
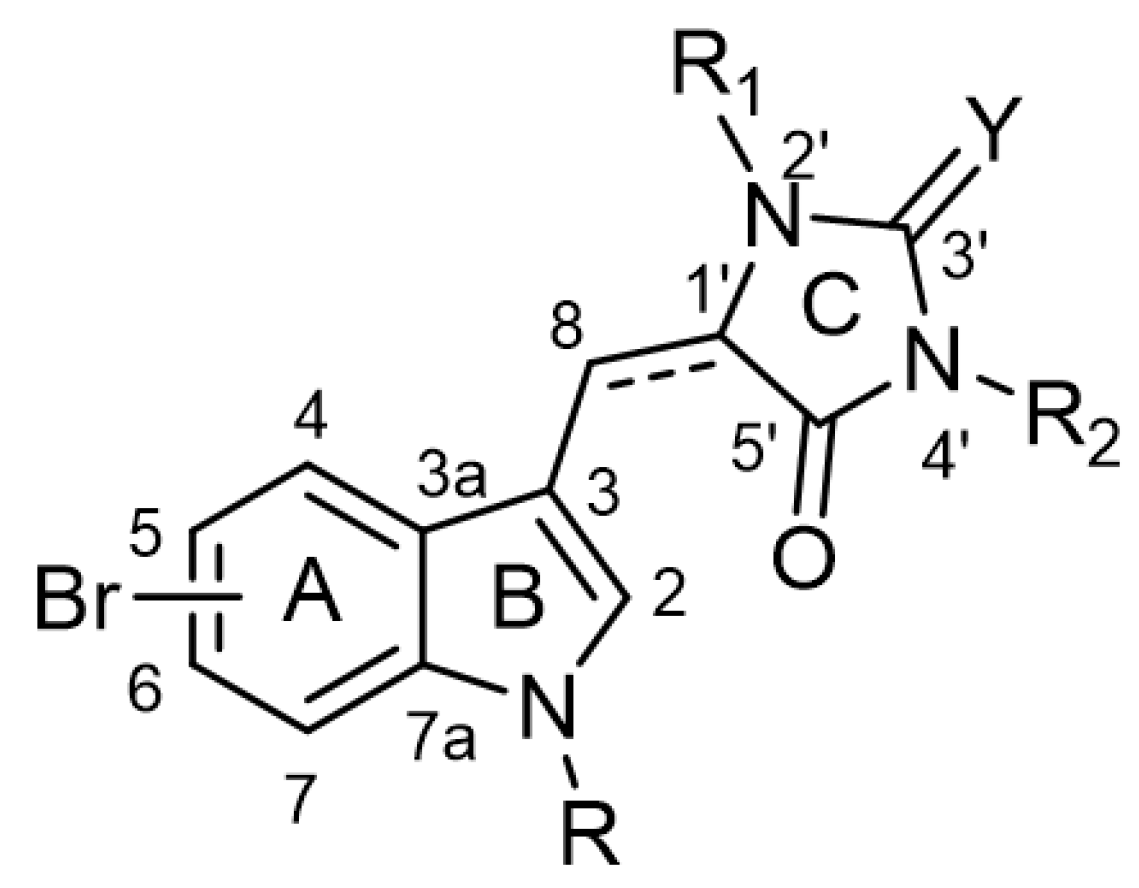
The chemical backbone of the natural aplysinopsins include a simple configuration of monomeric aplysinopsin-type structures and their brominated derivatives at the A ring, variation in the structure of the C ring, the presence and configuration of the C-8-C-1′ double bond, the oxidation state of the 2-aminoimidazoline fragment and N-alkylated at the B ring (Figure 1), in addition to the aplysinopsin dimers form.
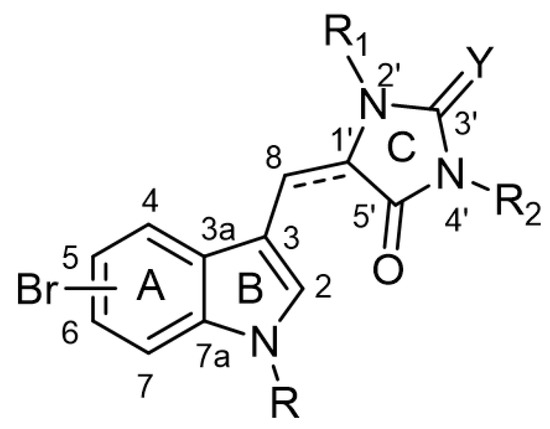
Figure 1.
The chemical configuration of monomeric aplysinopsin-type structures shows detailed segmentation of the rings, carbon numbering, and type of bonds.
Aplysinopsin, (E)-5-((1H-indol-3-yl)methylene)-2-imino-1,3-dimethylimidazo-li-din-4-one (1), was first isolated from the sponge genus Thorecta of the Australian Great Barrier Reef by Kazlauskas et al. [3]. Sequentially, aplysinopsin and its derivatives have been reported in many other marine organisms from various geographic areas (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4) [2].

Table 1.
Monomeric aplysinopsin-type structures and their brominated derivatives.

Table 2.
Aplysinopsins substituted at the nitrogen atom.

Table 3.
Aplysinopsins with a single C-8-C-1′ bond.

Table 4.
Aplysinopsin dimers.
3. Synthesis
The simple chemical structures of aplysinopsin motivated many researchers to prepare aplysinopsin-type structures in order to enrich various analogs and to study their activity besides the mode of action via their structure–activity relationships. Several synthetic approaches towards aplysinopsin-type structures have been reported.
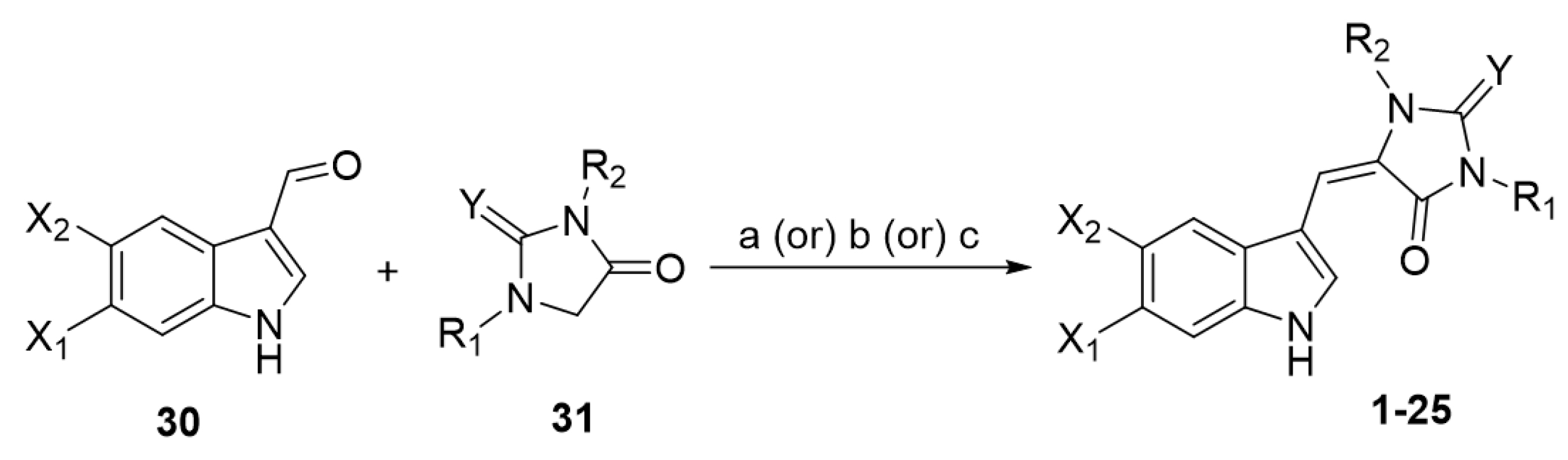
The synthetic approaches toward the preparation of monomeric aplysinopsin-type structures involve the condensation reaction of the appropriate 3-formylindole 30 with a five-membered ring 31, an imidazolidinone, by fusion [5,25] or boiling in acetic acid in the presence of sodium acetate [24] or boiling in piperidine [35] (Scheme 1).
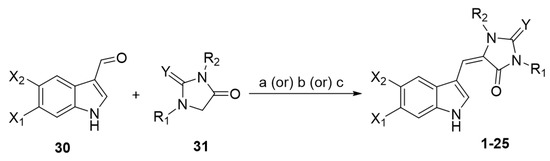
Scheme 1.
General procedure for the preparation of monomeric aplysinopsin-type structures. Reagents and conditions: (a) fusion; (b) AcOH, sodium acetate, boiling; (c) piperidine, boiling.
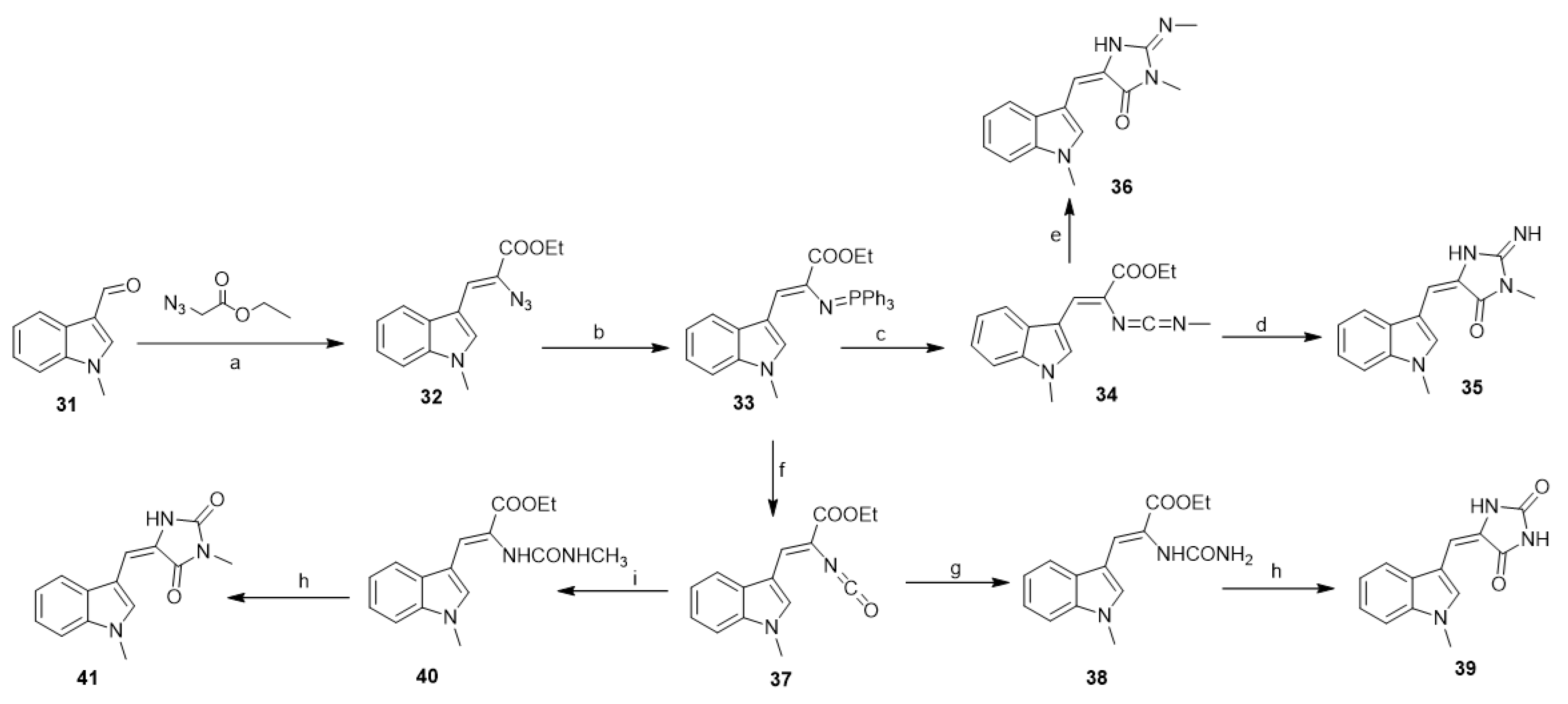
Molina et al. developed a simple and general entry to aplysinopsin alkaloids by tandem aza-Wittig/heterocumulene-mediated annelation [36]. Thus, ethyl 2-azido-3-(1-methylindol-3-yl)prop-2-enoate (32), available from 3-formyl-1-methyl indole (31) and ethyl azidoacetate, reacts with triphenylphosphine in dry dichloromethane to give the iminophosphorane (33). Compound (33), on the reaction with methyl isocyanate at room temperature, gave the carbodiimide (34). The reaction of (34) with ammonium acetate in acetonitrile afforded (35) in a 40% yield, while the reaction of (34) with methylamine in toluene at 45 °C afforded 2′-demethyl-3′-methylaplysinopsin (36) (Scheme 2). On the other hand, the reaction of (33) with carbon dioxide in dry toluene at 90 °C afforded the isocyanate (37) in a 80% yield. The reaction of the isocyanate (37) with ammonium acetate in acetonitrile at room temperature afforded the urea derivative (38) (78%), which undergoes cyclization using acetic anhydride and provided the 3′-deimino-2′,4′-bis(demethyl)-3′-oxo aplysinopsin (39) in a 50% yield. Similarly, compound (37), by the reaction with methylamine and further cyclization by the action of acetic anhydride, led to the formation of (41) in a 50% overall yield (Scheme 2).
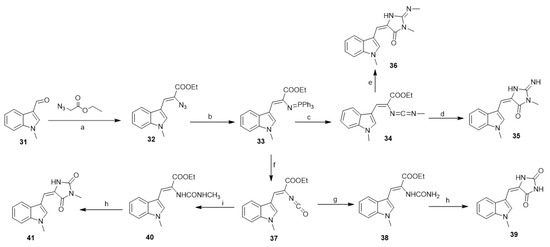
Scheme 2.
Aplysinopsin-type alkaloids by tandem aza-Wittig/heterocumulene-mediated annelation. Reagents and conditions: (a) ethanol, piperidine, reflux; (b) Ph3P, CH2C12, 0 °C; (c) methylisocyanate, toluene, N2, rt, 35 h; (d) CH3COONH4, CH3CN, 45 °C, 14 h; (e) methylamine, toluene, 45 °C, 14 h; (f) CO2, dry toluene, 90 °C; (g) CH3COONH4, CH3CN, room temperature (rt); (h) Ac2O, reflux; (i) methylamine, CH3CN, rt.
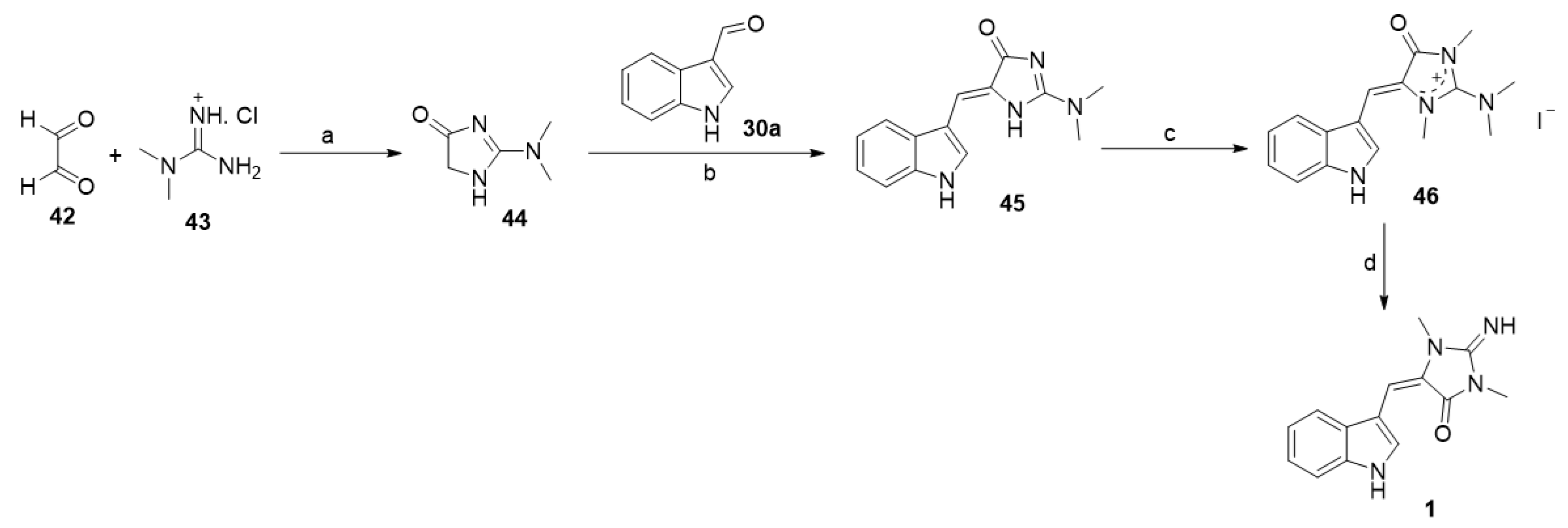
Poisson et al. reported an alternative method to prepare aplysinopsin (1) (Scheme 3) [37]. In detail, the reaction of dimethyl guanidine hydrochloride (43) with glyoxal (42) afforded the corresponding 2-(dimethylamino)-1,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one (44). The base catalyzed reaction of (44) with indole-3-carboxaldehyde (30a) yielded (Z)-5-((1H-indol-3-yl)methylene)-2-(dimethylamino)-1,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one (45). The methylation of (45) with methyl iodide, followed by basic hydrolysis using KOH (1N), provided aplysinopsin (1) (Scheme 3) [37].
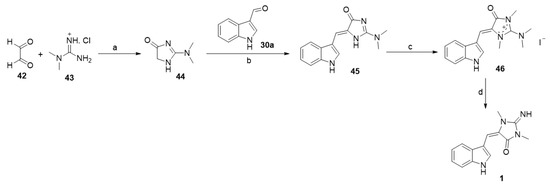
Scheme 3.
Synthesis of aplysinopsin (1) from dimethyl guanidine hydrochloride. Reagents and conditions: (a) H2O, reflux, 8 h; (b) piperidine, reflux, 2 h; (c) MeI, DMF, rt, 48 h; (d) KOH (1N), EtOH, reflux, 2 h.
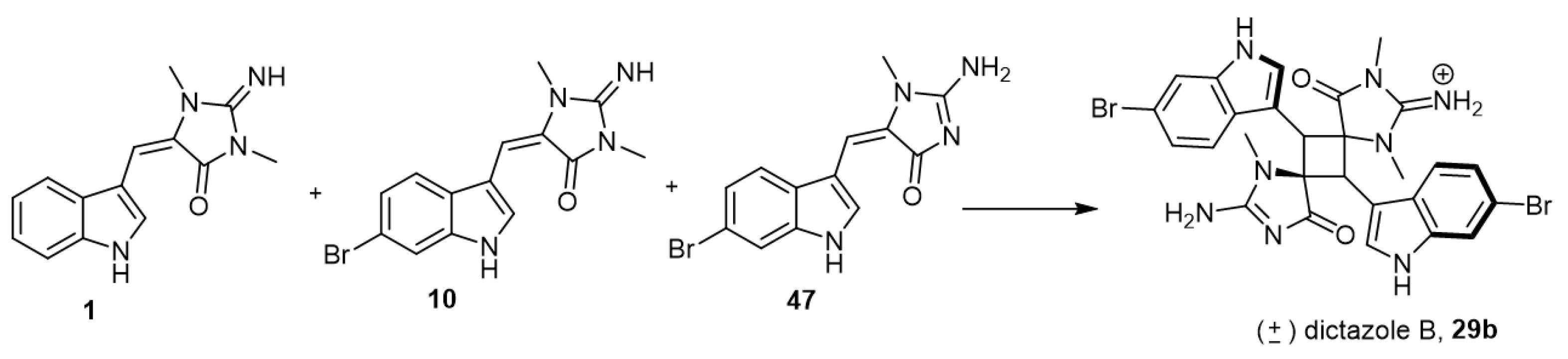
Skiredj et al. reported the synthesis of dictazole B (29b), an example of aplysinopsin dimers, as shown in Scheme 4 [38]. After several trials and reaction optimization, Skiredj et al. reached the best route to obtain dictazole B via irradiation with artificial sunlight of the three monomers 1, 10, and 47, in the presence of bismuth(III) triflate (Bi(OTf)3) (Scheme 4).
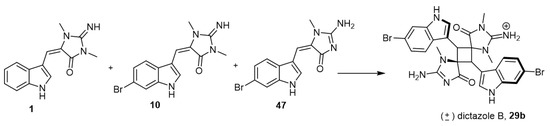
Scheme 4.
Synthesis of dictazole B (29b). Reagents and conditions: DMF, hν, 10 (1 equiv.), 47 (1 equiv.), Bi(OTf)3 (1 equiv.), 14 h, 14% yield.
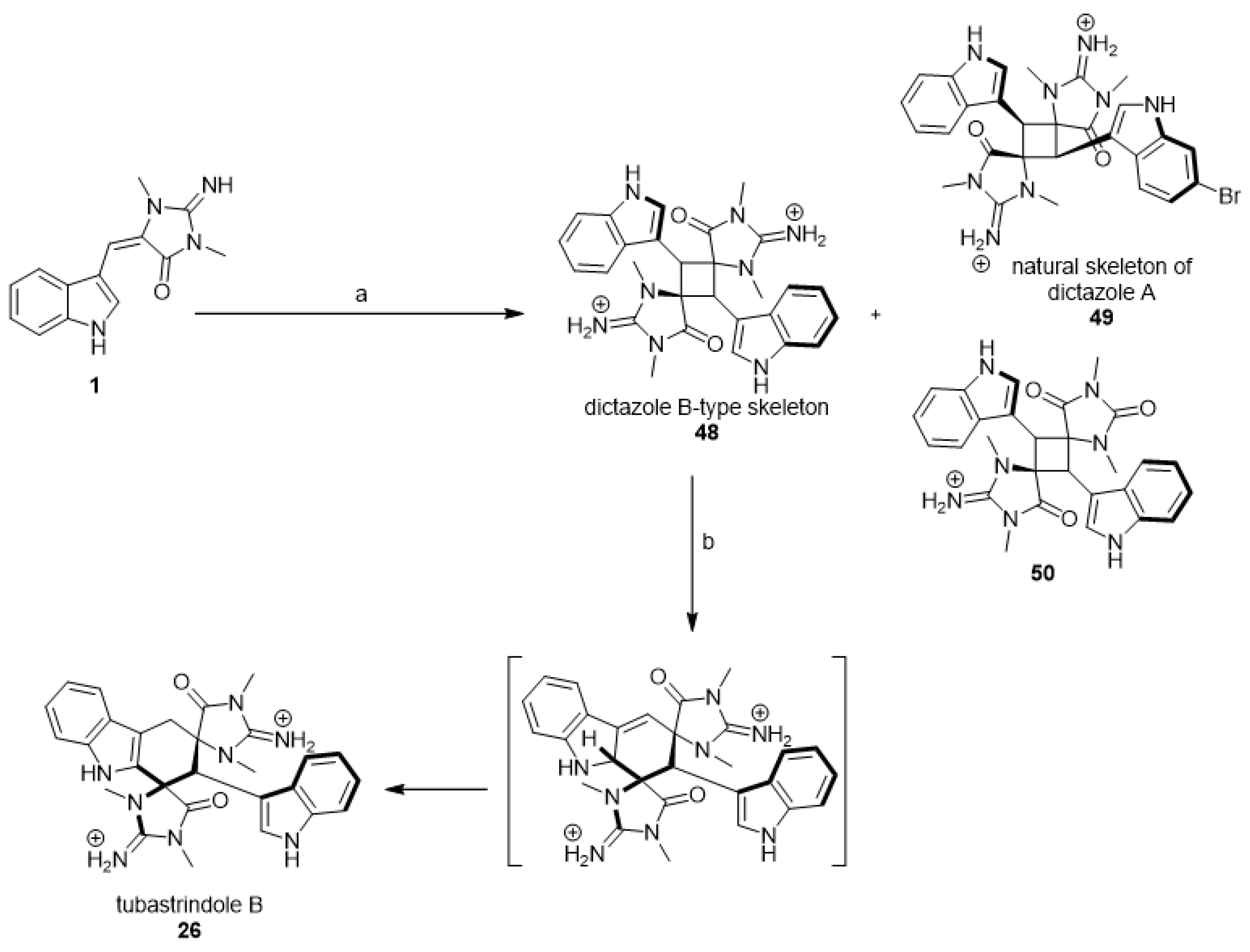
Additionally, in 2014 and 2015, Skiredj et al. reported the total synthesis of the cycloaplysinopsin-type, tubastrindole B (26) (Scheme 5), via a ring-expansion cascade of a dictazole-type precursor [39,40]. In detail, the cyclobutane (48) was produced by photochemical [2 + 2] homodimerization of aplysinopsin (1). Two minor compounds, 49 and 50, have been isolated in addition to compound 48. Compound (48) has been isolated by HPLC with a 16% yield to be involved in the next step. The ring-expansion of compound (48) in water with TFA under heating for 85 s and under microwave irradiation gave tubastrindole B (26) with a 40% yield (Scheme 5).

Scheme 5.
Synthesis of (±)-tubastrindole B (26) via biosynthetically relevant precursors. Reagent and conditions: (a) light 14 h, 0.5 equiv., CuOTf-toluene complex, DMF; (b) MW, 110 °C, 85 s, TFA, H2O.
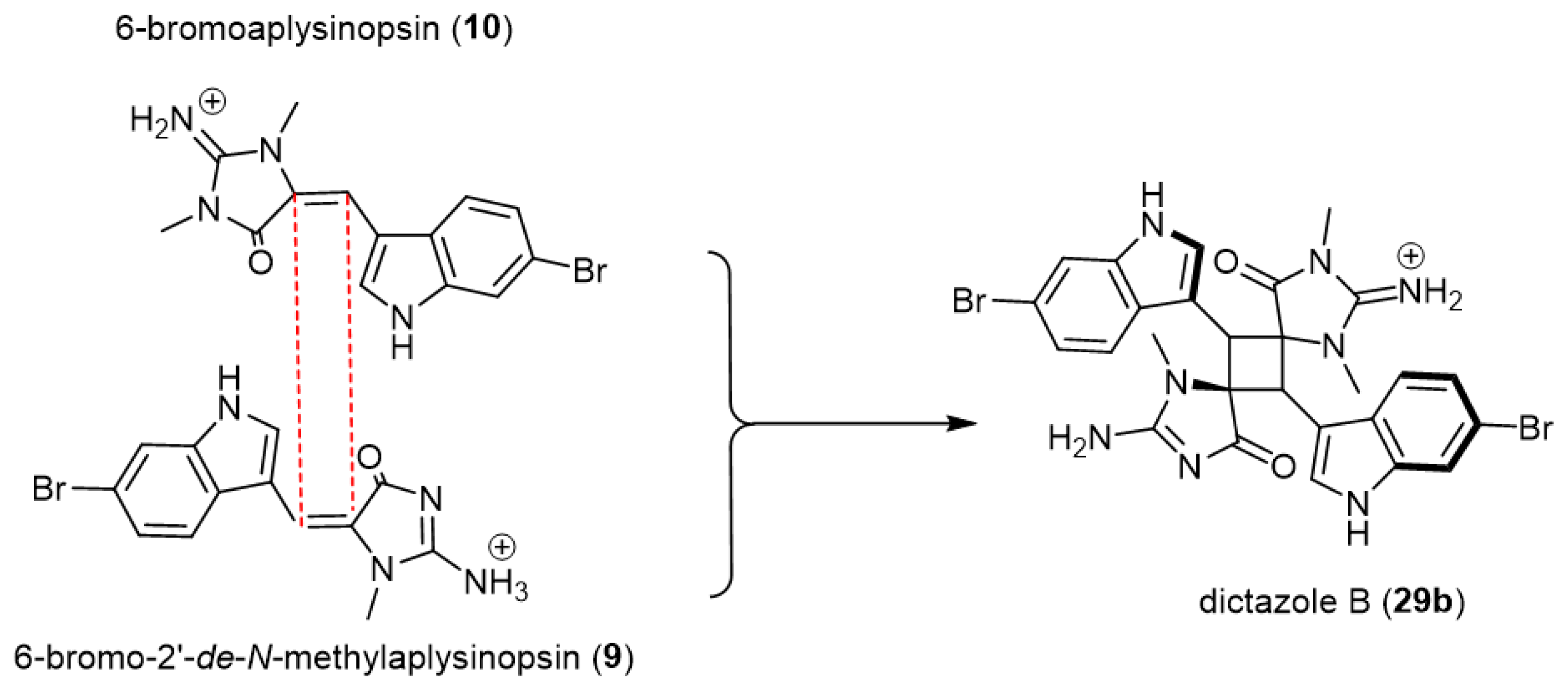
In advanced research for the same research team, Skiredj and his group [41] have developed an unprecedented DNA-templated [2 + 2] photodimerization process for synthesizing spiro-fused cyclobutane-containing compounds including the natural heterodimer dictazole B (29b) (Scheme 6).
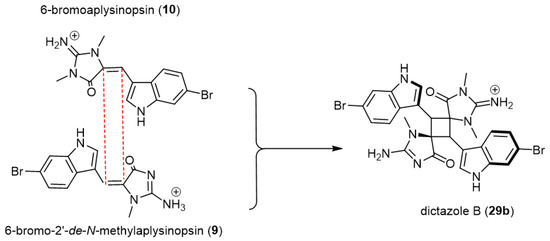
Scheme 6.
DNA-templated [2 + 2] photodimerization process for synthesizing dictazole B (28). Reagents and conditions: hν (λ = 280–315 nm), st-DNA, MOPS buffer/DMSO (3:1), pH 6.5.
The method was developed based on the dimerization of (E)-aplysinopsin (1), which was previously shown to be unproductive in solution [39]. Upon this developed technique, exposure of 6-bromo-2′-de-N-methylaplysinopsin (9) and 6-bromoaplysinopsin (10), tryptophan-derived olefin, to light in the presence of salmon testes DNA (st-DNA) reproducibly afforded the corresponding homo-dimerized spiro-fused cyclobutane, Dictazole B (29b), with an excellent yield of 16% (Scheme 6). Through this, compartmentalization properties offered by DNA could facilitate bypassing the inability of the monomers to self-organize in solution and ultimately promote the target cycloaddition.
4. Aplysinopsins Analogs
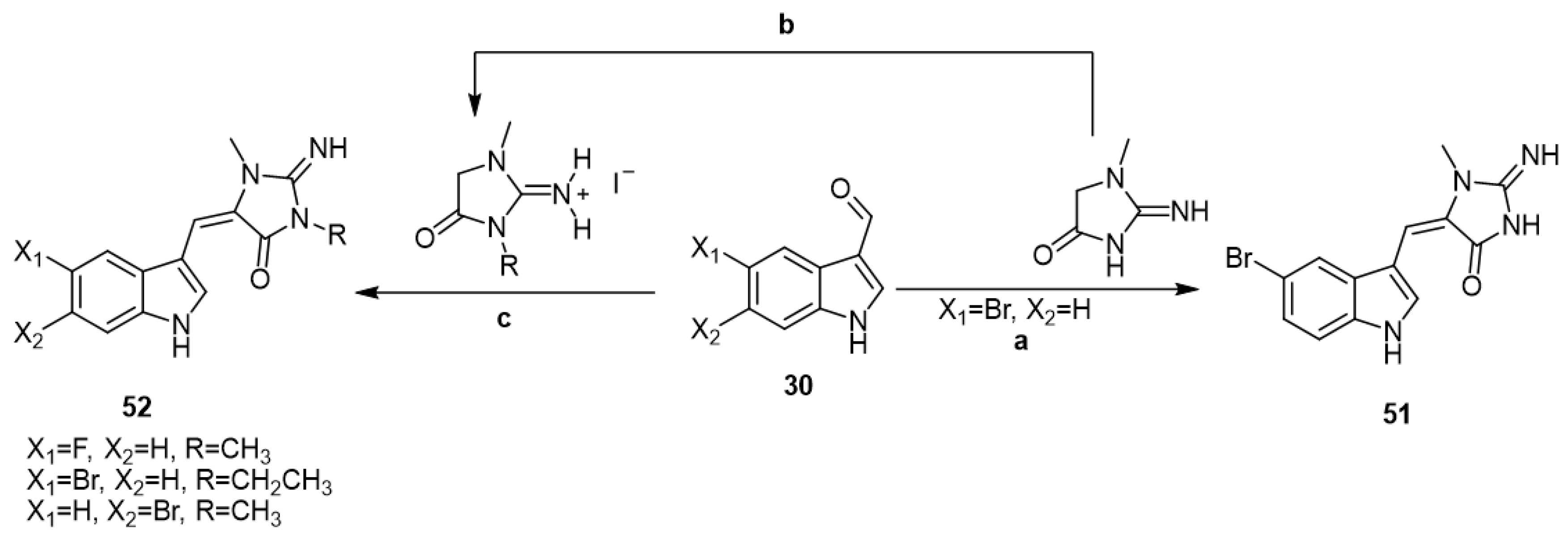
In 2009, various aplysinopsin analogs 51 and 52 were synthesized by the reaction of indole-3-carboxaldehyds 30, namely, 5-bromo, 5-fluoro, and 6-brom-1H-indole-3-carboxaldehydes, with either creatinine or 2-imino-1,3-dimethyl-imidazolidin-4-one or 2-imino-1-methyl-3-ethylimidazolidin-4-one (Scheme 7) [42].
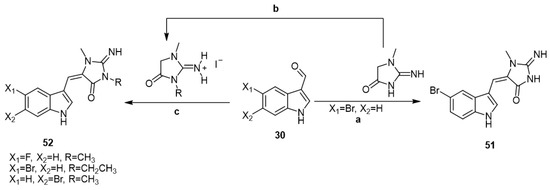
Scheme 7.
Reagents and conditions: (a) Bunsen burner, heat, 153 °C, 10 min; (b) alkyl iodide, EtOH, reflux, 7 days; (c) Bunsen burner, heat, 153 °C, 10 min.
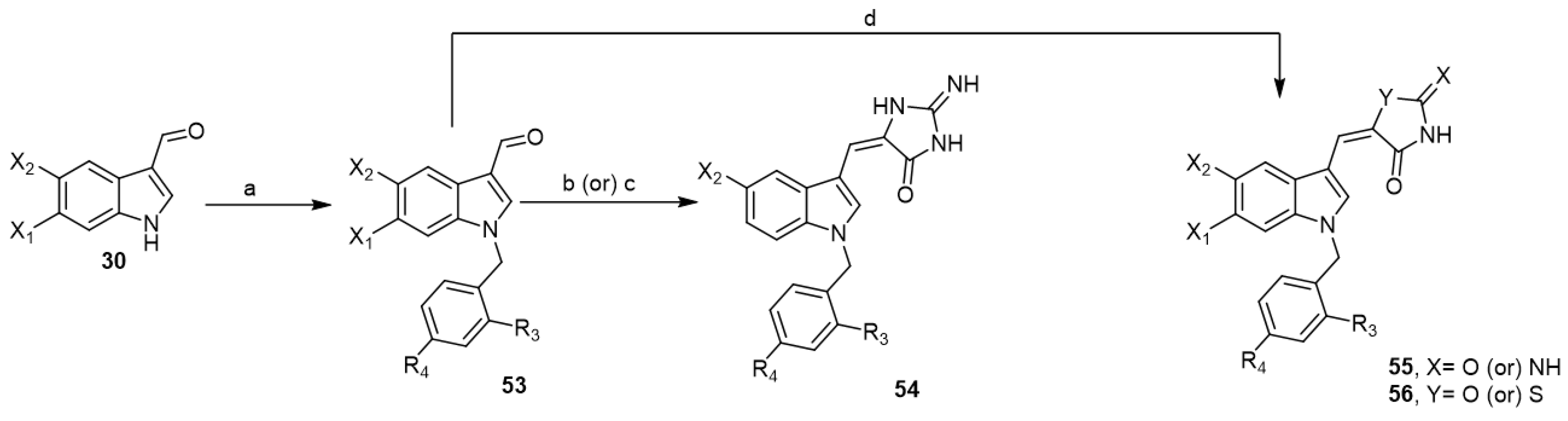
The preparation of an N-benzyl-1H-indoles to be N-benzyl aplysinopsin analogs was of interest to a group of researchers as potential anticancer agents. In 2010, they reported a series of substituted (Z)-5-(N-benzylindol-3-ylmethylene)imidazolidine-2,4-dione analogs 54 using microwave irradiation and conventional heating methods (Scheme 8) [23].
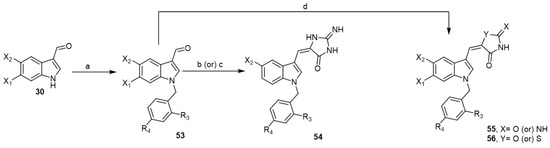
Scheme 8.
Synthesis of N-benzyl aplysinopsin analogs. Reagents and conditions: (a) appropriate benzyl halide, aq. NaOH solution (50%), triethylbenzylammonium chloride (TEBA), DCM, rt, 2 h; (b) hydantoin, ammonium acetate, acetic acid, microwave irradiation, 40–60 s; (c) hydantoin, ammonium acetate, acetic acid, 115–116 °C, 8–12 h; (d) hydantoin or 2-iminothiazolidin-4-one, ammonium acetate, acetic acid, microwave irradiation, 30–60 s.
In 2011, they developed a series of substituted (Z)-5-((1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene)imidazolidin-2,4-diones 55 and (Z)-5-((1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-yl) methyl-ene)-2-iminothiazolidin-4-ones 56 utilizing microwave irradiation method (Scheme 8) [22]. These analogs were evaluated for in vitro cytotoxicity against a panel of human tumor cell lines. Several of these analogs showed potent growth inhibition against melanoma UACC-257, OVCAR-8 ovarian, and MCF-7 breast cancer cells besides significant cytotoxicity. Therefore, these analogs could be regarded as useful lead compounds for further structural optimization as antitumor agents [22,23].
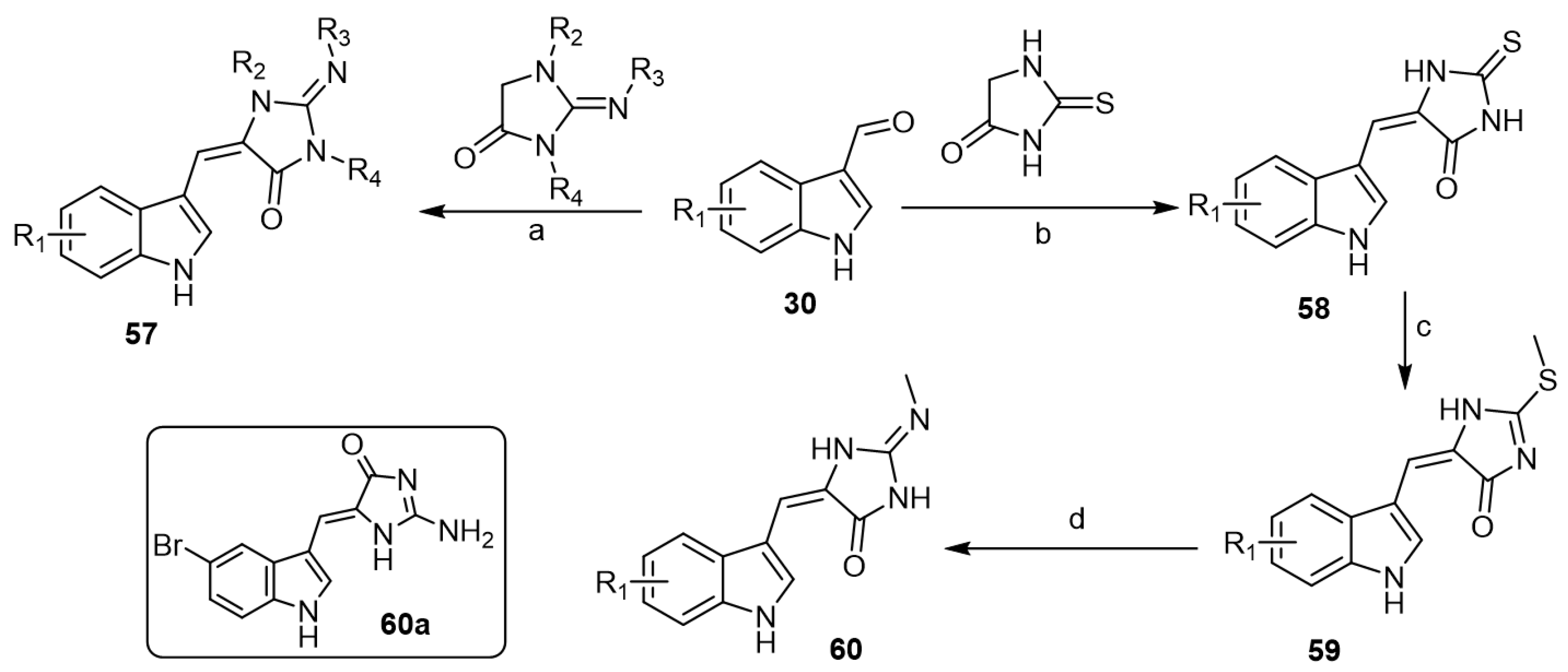
On the other hand, Cummings et al. reported low-molecular weight aplysinopsin analogs that served as a chemical scaffold for synthesizing compounds capable of differentiating between cloned human 5-HT2C and 5-HT2A receptor subtypes [43]. First, indole aldehydes 30 were reacted with the appropriate imidazolidinones to afford the corresponding aplysinopsin analogs 57 (Scheme 9). Additionally, aplysinopsin analogs 58 were obtained via condensation of indole aldehydes 30 with thiohydantoin followed by methylation of intermediate thiones 58 to afford the corresponding thioethers 59. Thioethers were allowed to react with methylamine to yield the corresponding N-methylamine aplysinopsin analogs 60 (Scheme 9). The prepared analogs have been evaluated in the chick anxiety–depression model. In vitro receptor binding assays showed that analogs revealed high affinity with selectivity for 5-HT2B over 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C. Regarding the in vivo studies of aplysinopsins using different depression models, aplysinopsins were unable to reproduce the in vitro efficacy in an animal model. However, one compound, (Z)-2-amino-5-((5-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl) methylene)-1H-imidazol-4(5H)-one (60a), showed a modest antidepressant effect in the later stages of the evaluation period.
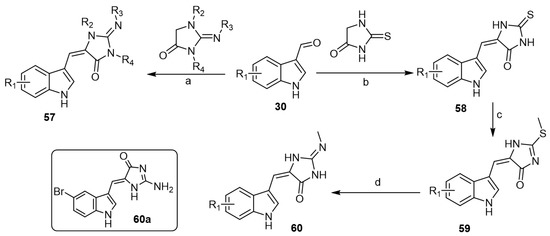
Scheme 9.
Synthesis of low-molecular weight aplysinopsin analogs. Reagents and conditions: (a) piperidine, reflux, 2 h; (b) ETA, EtOH, reflux, 1 h; (c) CH3I, NaOH, MeOH, rt, 18 h; (d) CH3NH2, EtOH, sealed vessel, 70 °C, 24 h.
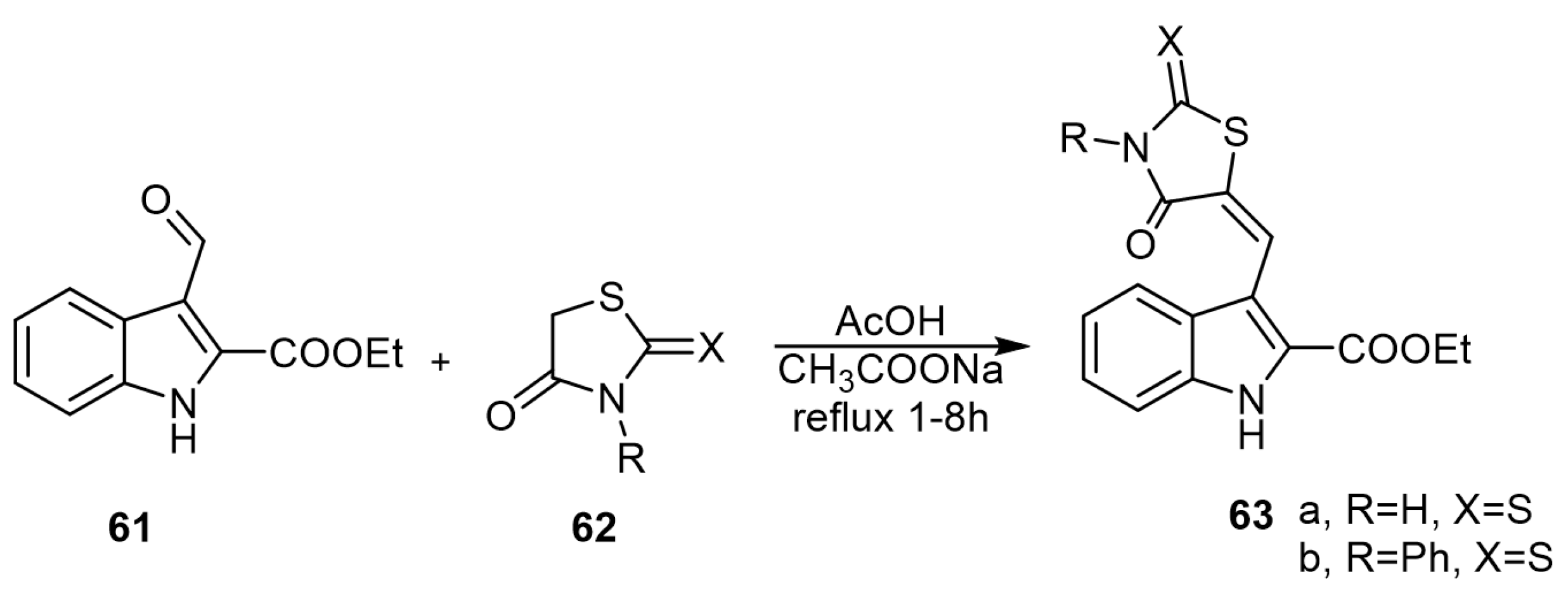
JakŠe et al. reported various aplysinopsin-thiohydantoin analogs via the reaction of ethyl 3-formyl-1H-indole-2-carboxylate (61) with the active methylene group of 2-thiohydantoin (62) in a mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate (Scheme 10) [44].
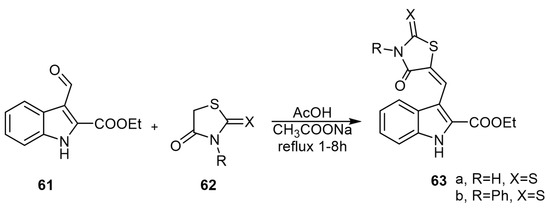
Scheme 10.
Synthesis of aplysinopsin-thiohydantoin analogs. Reagents and conditions: AcOH, CH3COONa, reflux 1–8 h.
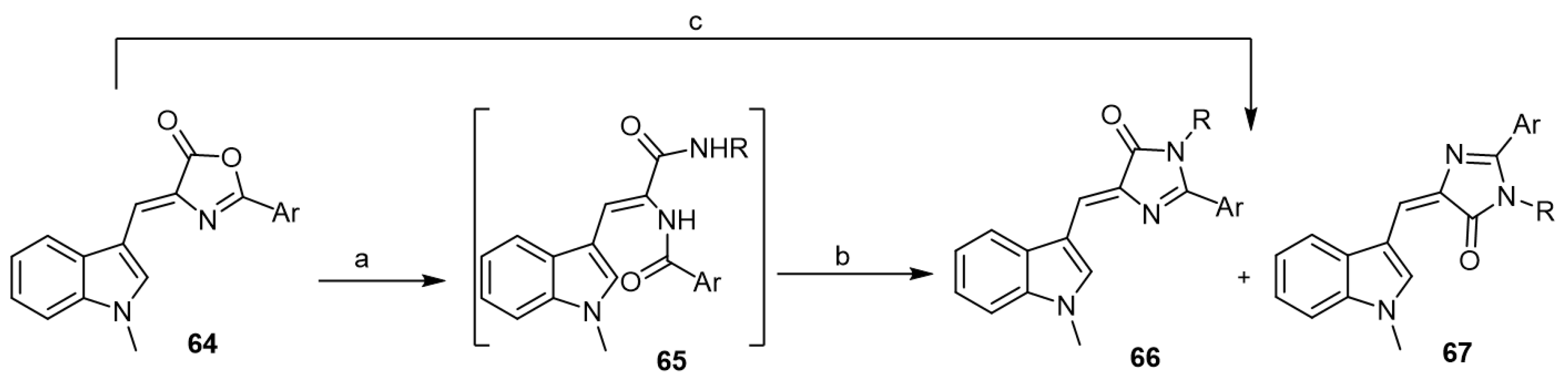
In 2016, Suzdalev and Babakova developed an efficient approach toward the synthesis of aplysinopsin analogs from 4-[(1H-indol-3-yl)-methylene]-1,3-oxazol-5(4H)-ones (64) [45]. The reaction of Z-isomers of oxazolones 64 with primary amines under reflux in dimethylformamide or ethylene glycol led to the formation of imidazolone derivatives 66 and 67 (Scheme 11).
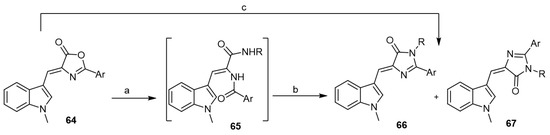
Scheme 11.
Synthesis of aplysinopsin analogs starting from 1,3-oxazol-5(4H)-ones. Reagents and conditions: (a) RNH2, reflux, acetonitrile, 1 h; (b) heat, dimethylformamide, 10 h (or) ethylene glycol, 30 min; (c) RNH2, reflux, dimethylformamide, 10 h (or) ethylene glycol, 30 min.
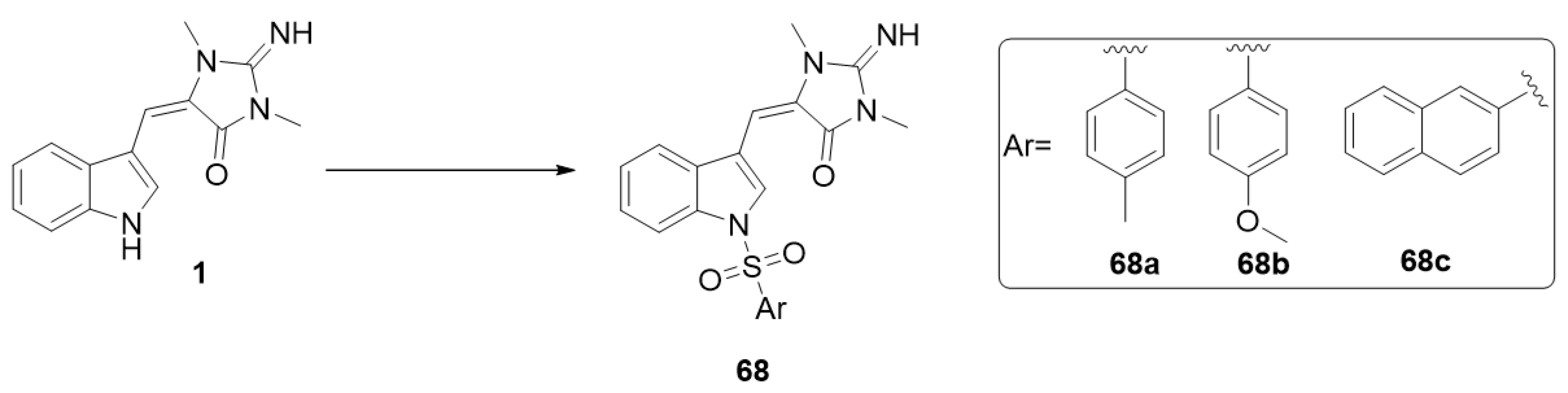
In 2021, Nuthakki et al. reported the insertion of sulphonamide moieties on the indole ring of aplysinopsin (1) and studied the effect of the obtained analogs on cholinesterases and beta-site amyloid-precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE-1) [21]. Aplysinopsin (1) inhibits electric eel acetylcholinesterase (AChE), equine serum butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), and human BACE-1 with IC50 values of 33.9, 30.3, and 33.7 μM, respectively, and it also showed excellent BBB permeability (8.92 × 10−6). The N-sulphonamide derivative 68b displayed better cholinesterase inhibition and was found to effectively permeate the BBB (Pe > 5 × 10−6 cm/s). The sulphonamide derivatives were prepared by the reaction of aplysinopsin (1) with different substituted sulphonyl chlorides in the presence of 4-dimethyl-aminopyridine (DMAP) and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) (Scheme 12) [21].
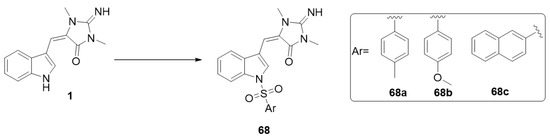
Scheme 12.
Synthesis of sulphonyl aplysinopsin analogs. Reagents and conditions: ArSO2Cl (1.1 equiv.), DMAP (0.05 equiv.), DIPEA (1.5 equiv.), methylene chloride, rt, 20 h.
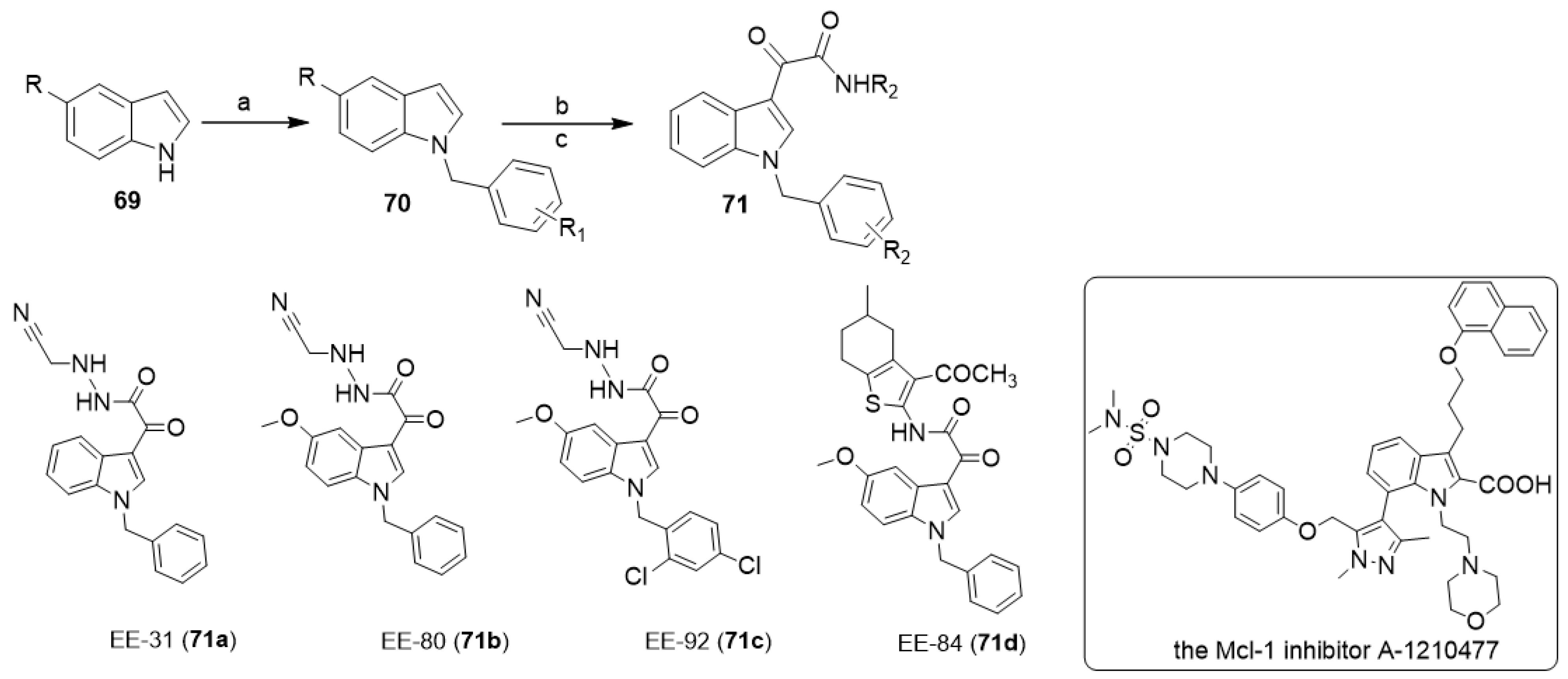
In 2021, Diederich and co-workers synthesized a series of aplysinopsin analogs EE (71) via the reaction of indole derivatives 69 with oxalyl chloride followed by the reaction with alkyl or arylamines (Scheme 13) [35]. Through the in vitro and in vivo proliferation and viability screening of the newly synthesized aplysinopsin analogs on myelogenous leukemia cell lines and zebrafish toxicity tests, as well as the analysis of differential toxicity in noncancerous RPMI 1788 cells and PBMCs, they identified EE-84 (71d) as a promising novel drug candidate against chronic myeloid leukemia. Furthermore, they proved that EE-84 induced a senescent-like phenotype in K562 cells in line with its cytostatic effect. Finally, they demonstrated the synergistic cytotoxic effect of EE-84 with a BH3 mimetic, the Mcl-1 inhibitor A-1210477, against imatinib-sensitive and -resistant K562 cells, highlighting the inhibition of antiapoptotic BCL2 proteins as a promising novel senolytic approach against chronic myeloid leukemia [35].
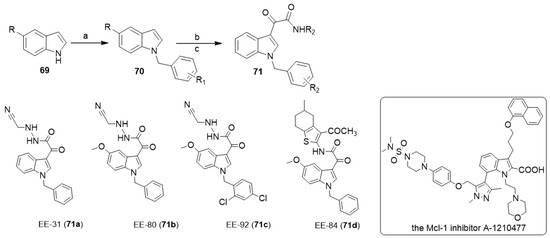
Scheme 13.
Chemical structures of aplysinopsin analogs (EE-31, EE-80, EE-84, EE-92), and the Mcl-1 inhibitor A-1210477. Reagents and conditions: (a) benzyl chlorides, NaH, DMF; (b) oxalyl chloride, dry ethyl ether, 40 °C; (c) alkyl or arylamines, dry THF, TEA, stirring, 3 h.
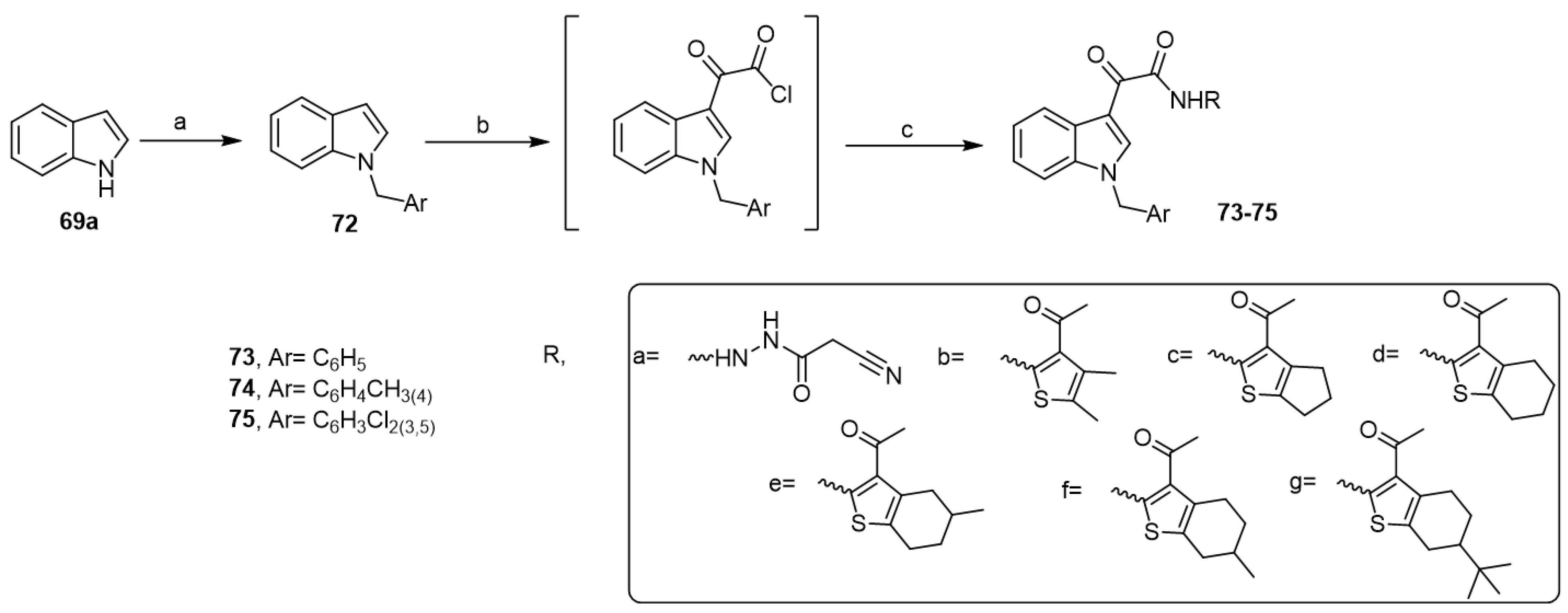
Recently, El-Sawy et al. synthesized a new series of aplysinopsin analogs under the previous reaction conditions (Scheme 14) and investigated their cytotoxic activity against prostate cancer [46]. Five analogs showed high antitumor activity via suppressing the expression of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl2, simultaneously increasing the expression of the pro-apoptotic genes p53, Bax, and Caspase 3. The inhibition of BCL2 led to the activation of BAX, which in turn activated Caspase 3, leading to apoptosis. This dual mechanism of action via apoptosis and cell cycle arrest induction was responsible for the antitumor activity of the aplysinopsin analogs.
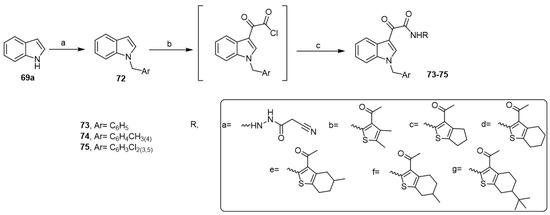
Scheme 14.
Synthesis of aplysinopsin analogs. Reagents and conditions: (a) benzyl chlorides, NaH, DMF; (b) oxalyl chloride, dry ethyl ether, 40 °C; (c) alkyl or arylamines (a–g), dry THF, TEA, stirring, 3 h.
5. Biological Activity
Aplysinopsins possess an array of biological activities (Table 5).

Table 5.
Biological activities of aplysinopsins.
6. Conclusions
Aplysinopsins are one of the most celebrated bicyclic arenas in the scientific literature, and they are tryptophan-derived marine natural products. Aplysinopsins represented the skeleton of indole and imidazolidin-4-ones cores that have been obtained from various sources of marine organisms. This survey touched upon the various sources of aplysinopsins, their synthesis, and the fact that many aplysinopsin derivatives are biologically active molecules. Aplysinopsins have been listed as anti-cancer, antimicrobial, inhibitors of monoamine oxidase (MAO), antidepressant, and serotonin receptors modulator. These facts open the field for scientific researchers to synthesize new aplysinopsin analogs to enrich their activity. An interesting observation is that the indole ring of aplysinopsin is considered an essential core of their structures. Therefore, future work should be focused on the optimization of the targeted imidazolidinone core.
Author Contributions
Resources, writing—original draft preparation, E.R.E.-S.; writing—review and editing, E.R.E.-S. and G.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
E.R.E.-S. appreciates the support she received from the National Research Center (Egypt) and the support provided by the University of Lorraine (France).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Karthikeyan, A.; Joseph, A.; Nair, B.G. Promising bioactive compounds from the marine environment and their potential effects on various diseases. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialonska, D.; Zjawiony, J.K. Aplysinopsins—Marine Indole Alkaloids: Chemistry, Bioactivity and Ecological Significance. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.T.; Quinn, R.J.; Wells, R.J. Aplysinopsin, a new tryptophan derivative from a sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kh, H.; Fj, S. Aplysinopsin: Antineoplastic Tryptophan Derivative from the Marine Sponge Verongia Spengelii. Lloydia 1977, 40, 479–481. [Google Scholar]
- Djura, P.; Faulkner, D.J. Metabolites of the marine sponge Dercitus species. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Ye, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Takashima, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Kitagawa, I.; Kobayashi, M. Novel Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase (nNOS) Selective Inhibitor, Aplysinopsin-Type Indole Alkaloid, from Marine Sponge Hyrtios erecta. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1372–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.-F.; Schetz, J.A.; Kelly, M.; Peng, J.-N.; Ang, K.K.H.; Flotow, H.; Leong, C.Y.; Ng, S.B.; Buss, A.D.; Wilkins, S.P.; et al. New Antiinfective and Human 5-HT2 Receptor Binding Natural and Semisynthetic Compounds from the Jamaican Sponge Smenospongia aurea. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segraves, N.L.; Crews, P. Investigation of Brominated Tryptophan Alkaloids from Two Thorectidae Sponges: Thorectandra and Smenospongia. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanowska, A.J.; Rao, K.V.; Childress, S.; El-Alfy, A.; Matsumoto, R.R.; Kelly, M.; Stewart, G.S.; Sufka, K.J.; Hamann, M.T. Secondary Metabolites from Three Florida Sponges with Antidepressant Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, R.K.; Klein, D.; Kinnel, R.B.; Li, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Marine natural products: The past twenty years and beyond. Pure Appl. Chem. 1982, 54, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusetani, N.; Asano, M.; Matsunaga, S.; Hashimoto, K. Bioactive marine metabolites—XV. Isolation of aplysinopsin from the Scleractinian coral Tubastrea aurea as an inhibitor of development of fertilized sea urchin eggs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1986, 85, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guella, G.; Mancini, I.; Zibrowius, H.; Pietra, F. Novel Aplysinopsin-Type Alkaloids from Scleractinian Corals of the Family Dendrophylliidae of the Mediterranean and the Philippines. Configurational-assignment criteria, stereospecific synthesis, and photoisomerization. Helvetica Chim. Acta 1988, 71, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.G.; Sweatman, H. Chemical warfare among scleractinians: Bioactive natural products from Tubastraea faulkneri Wells kill larvae of potential competitors. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 251, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwagawa, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Okamura, H.; Nakatani, M.; Doe, M.; Takemura, K. Three novel bis(indole) alkaloids from a stony coral, Tubastraea sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 2533–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaromin, A.; Czopek, A.; Parapini, S.; Basilico, N.; Misiak, E.; Gubernator, J.; Zagórska, A. Synthesis and Antiplasmodial Activity of Novel Bioinspired Imidazolidinedione Derivatives. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, P.-E.; Pichon, E.; Moriou, C.; Clerc, P.; Trépos, R.; Frederich, M.; De Voogd, N.; Hellio, C.; Gauvin-Bialecki, A.; Al-Mourabit, A. New Antimalarial and Antimicrobial Tryptamine Derivatives from the Marine Sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.C.; Resende, D.I.S.P.; da Costa, P.M.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Sousa, E. Tryptophan derived natural marine alkaloids and synthetic derivatives as promising antimicrobial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 209, 112945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, A.; Tu, L.C.; Yang, I.; Lim, K.-M.; Nam, S.-J. Marine natural products with monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory activity. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewellyn, K.; Bialonska, D.; Loria, M.J.; White, S.W.; Sufka, K.J.; Zjawiony, J.K. In vitro structure–activity relationships of aplysinopsin analogs and their in vivo evaluation in the chick anxiety–depression model. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7083–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkedjieva, J.; Konaklieva, M.; Dimitrova-Konaklieva, S.; Ivanova, V.; Stefanov, K.; Popov, S. Antiinfluenza Virus Effect of Extracts from Marine Algae and Invertebrates. Z. Naturforschung. C J. Biosci. 2000, 55, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuthakki, V.K.; Yadav Bheemanaboina, R.R.; Bharate, S.B. Identification of aplysinopsin as a blood-brain barrier permeable scaffold for anti-cholinesterase and anti-BACE-1 activity. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 107, 104568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penthala, N.R.; Yerramreddy, T.R.; Crooks, P.A. Synthesis and in vitro screening of novel N-benzyl aplysinopsin analogs as potential anticancer agents. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1411–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi Reddy, Y.; Narsimha Reddy, P.; Koduru, S.; Damodaran, C.; Crooks, P.A. Aplysinopsin analogs: Synthesis and anti-proliferative activity of substituted (Z)-5-(N-benzylindol-3-ylmethylene)imidazolidine-2,4-diones. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3570–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymiak, A.A.; Rinehart, K.L.; Bakus, G.J. Constituents of morphologically similar sponges: Aplysina and Smenospongia Species. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Lanzotti, V.; Magno, S.; Novellino, E. Tryptophan Derivatives from a Mediterranean Anthozoan, Astroides calycularis. J. Nat. Prod. 1985, 48, 924–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Miyagawa-Kohshima, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Naya, Y. Characterization of Compounds That Induce Symbiosis Between Sea Anemone and Anemone Fish. Science 1986, 234, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Nishi, J.; Ishibashi, M.; Kobayashi, J. Two New Tryptophan-Derived Alkaloids from the Okinawan Marine Sponge Aplysina sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djura, P.; Stierle, D.B.; Sullivan, B.; Faulkner, D.J.; Arnold, E.V.; Clardy, J. Some metabolites of the marine sponges Smenospongia aurea and Smenospongia (Ident.Polyfibrospongia) echina. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Guella, G.; Zibrowius, H.; Pietra, F. On the origin of quasi-racemic aplysinopsin cycloadducts, (bis)indole alkaloids isolated from scleractinian corals of the family Dendrophylliidae. Involvement of enantiodefective Diels–Alderases or asymmetric induction in artifact processes involving adventitious catalysts? Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 8757–8762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Delberghe, F.; Liron, F.; Guillaume, M.; Valentin, A.; Guyot, M. An antiplasmodial new (bis)indole alkaloid from the hard coral Tubastraea sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balansa, W.; Islam, R.; Gilbert, D.F.; Fontaine, F.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.; Piggott, A.M.; Lynch, J.W.; Capon, R.J. Australian marine sponge alkaloids as a new class of glycine-gated chloride channel receptor modulator. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4420–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwagawa, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Yokogawa, Y.; Okamura, H.; Nakatani, M.; Doe, M.; Morimoto, Y.; Takemura, K. Aplysinopsin Dimers from a Stony Coral. Tubastraea aurea. Heterocycles 2008, 75, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Jiménez, J.I.; Kelly, M.; Barnes, S.; Lorenzo, P.; Williams, P. Dictazolines A and B, Bisspiroimidazolidinones from the Marine Sponge Smenospongia cerebriformis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Jiménez, J.I.; Kelly, M.; Williams, P.G. Dictazoles: Potential Vinyl Cyclobutane Biosynthetic Precursors to the Dictazolines. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 2399–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Kim, S.; El-Sawy, E.R.; Cerella, C.; Orlikova-Boyer, B.; Kirsch, G.; Christov, C.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Anti-Leukemic Properties of Aplysinopsin Derivative EE-84 Alone and Combined to BH3 Mimetic A-1210477. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, P.; Fresneda, P.M.; Almendros, P. A simple and general entry to Aplysinopsine-type alkaloids by tandem Aza-Wittig/heterocumulene-mediated annelation. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 4491–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkafouki, A.; Ardisson, J.; Kunesch, N.; Lacombe, L.; Poisson, J.E. Synthesis of 2-dimethylaminoimidazole derivatives: A new access to indolyl-imidazole alkaloids of marine origin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 5325–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiredj, A.; Beniddir, M.A.; Joseph, D.; Leblanc, K.; Bernadat, G.; Evanno, L.; Poupon, E. Spontaneous Biomimetic Formation of (±)-Dictazole B under Irradiation with Artificial Sunlight. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6419–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiredj, A.; Beniddir, M.; Joseph, D.; Leblanc, K.; Bernadat, G.; Evanno, L.; Poupon, E. A Unified Bioinspired “Aplysinopsin Cascade”: Total Synthesis of (±)-Tubastrindole B and Related Biosynthetic Congeners. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 4980–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiredj, A.; Beniddir, M.A.; Joseph, D.; Bernadat, G.; Evanno, L.; Poupon, E. Harnessing the Intrinsic Reactivity within the Aplysinopsin Series for the Synthesis of Intricate Dimers: Natural from Start to Finish. Synthesis 2015, 47, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchemin, N.; Skiredj, A.; Mansot, J.; Leblanc, K.; Vasseur, J.-J.; Beniddir, M.A.; Evanno, L.; Poupon, E.; Smietana, M.; Arseniyadis, S. DNA-Templated [2 + 2] Photocycloaddition: A Straightforward Entry into the Aplysinopsin Family of Natural Products. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 11960–11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.E.; Canseco, D.C.; Dolliver, D.D.; Schetz, J.A.; Fronczek, F.R. Synthesis and Characterization of Aplysinopsin Analogs. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2009, 39, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.F.; Canseco, D.C.; Sheth, P.; Johnson, J.E.; Schetz, J.A. Synthesis and structure–affinity relationships of novel small molecule natural product derivatives capable of discriminating between serotonin 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C receptor subtypes. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 4783–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakše, R.; Bevk, D.; Golobič, A.; Svete, J.; Stanovnik, B. Synthesis and Transformations of Ethyl 3-Formyl-1H-indole-2-carboxylate. Preparation of Aplysinopsin and β-Carboline Thiohydantoin Analogues. Z. Nat. B 2006, 61, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzdalev, K.F.; Babakova, M.N. Synthesis of Analogues of Indole Alkaloids from Sea Sponges—Aplysinopsins by the Reaction of Amines with (4Z)-4-[(1H-indol-3-yl)-methylene]-1,3-oxazol-5(4H)-ones. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2016, 53, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sawy, E.R.; El-Shahid, Z.A.; Soliman, A.A.F.; Nassrallah, A.; Abdelwahab, A.B.; Kirsch, G.; Abdelmegeed, H. Synthetic Analogs of Marine Alkaloid Aplysinopsin Suppress Anti-Apoptotic Protein BCL2 in Prostate Cancer. Molecules 2023, 28, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuthakki, V.K.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Bharate, S.B. Identification of embelin, a 3-undecyl-1,4-benzoquinone from Embelia ribes as a multitargeted anti-Alzheimer agent. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passemar, C.; Saléry, M.; Soh, P.N.; Linas, M.-D.; Ahond, A.; Poupat, C.; Benoit-Vical, F. Indole and aminoimidazole moieties appear as key structural units in antiplasmodial molecules. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.J.; Murphy, P.T. 5-(Indol-3-Ylmethylene)-1,3-Dimethyl-2-Methylamino-4-Imidazolidinone. U.S. Patent US4195179A, 25 March 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Baird-Lambert, J.; Davis, P.A.; Taylor, K.M. Methylaplysinopsin: A natural product of marine origin with effects on serotonergic neurotransmission. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1982, 9, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).