Pyrrole-Containing Alkaloids from a Marine-Derived Actinobacterium Streptomyces zhaozhouensis and Their Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
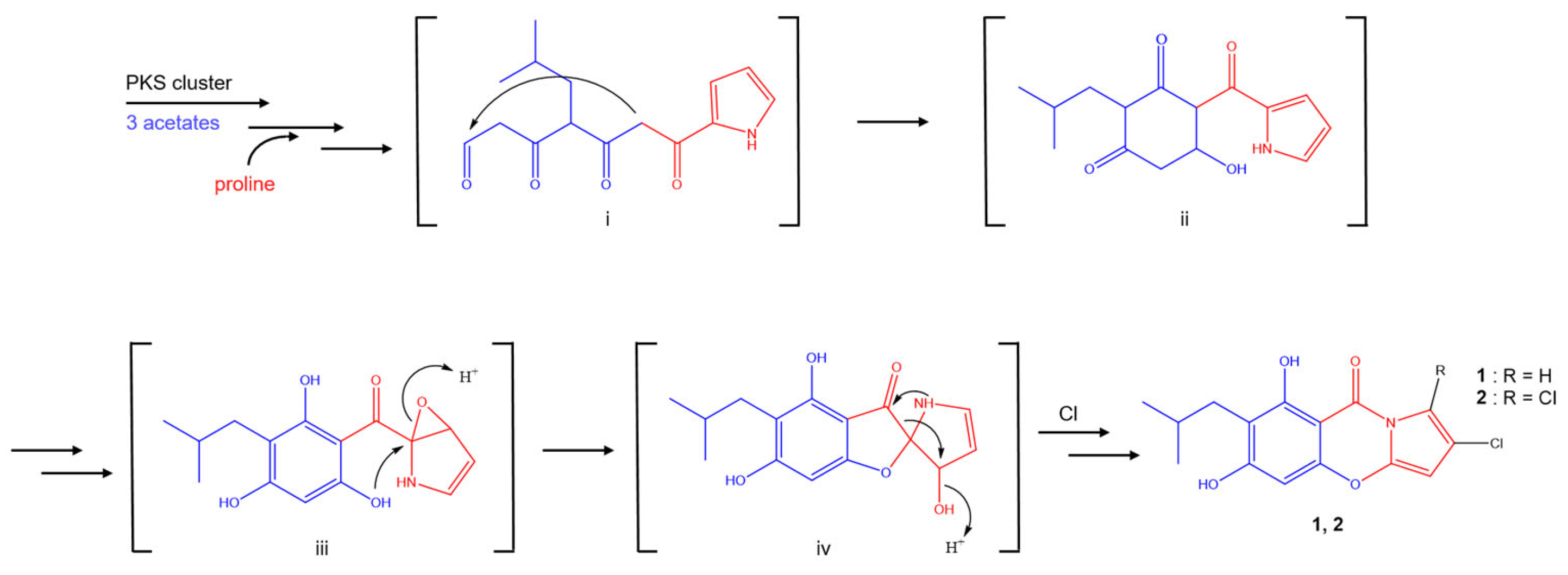
2.1. Structure Elucidation
2.2. Bioactivities
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Isolation of the Microorganisms from Marine Sediment Samples
3.3. Isolation and Identification of the Strain 208DD-064
3.4. Small-Scale Cultivation of the Strain 208DD-064 and the Test for Nutrient Supply Effect
3.5. Fermentation of the Strain 208DD-064 and Extraction and Isolation of Metabolites
3.6. Antibacterial Assay
3.7. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay for Cytotoxicity Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, R.E.; Mahmud, A.S.; Miller, I.F.; Rajeev, M.; Rasambainarivo, F.; Rice, B.L.; Takahashi, S.; Tatem, A.J.; Wagner, C.E.; Wang, L.F.; et al. Infectious disease in an era of global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. P T A Peer-Rev. J. Formul. Manag. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance: The Most Critical. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240062702 (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Takahashi, Y.; Nakashima, T. Actinomycetes, an Inexhaustible Source of Naturally Occurring. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mast, Y.; Stegmann, E. Actinomycetes: The Antibiotics Producers. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinos, G.P. The macrolide antibiotic renaissance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2967–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.; Cooper, M.A. Aminoglycoside Antibiotics in the 21st Century. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, A.; Buta, E.L. The Development of Third-Generation Tetracycline Antibiotics and New Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Deng, S.; Jiang, T. Recent developments in the identification and biosynthesis of antitumor drugs derived from microorganisms. Eng. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girão, M.; Ribeiro, I.; Ribeiro, T.; Azevedo, I.C.; Pereira, F.; Urbatzka, R.; Leão, P.N.; Carvalho, M.F. Actinobacteria Isolated From Laminaria ochroleuca: A Source of New Bioactive Compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, L.; Pipite, A.; Subramani, R.; Owen, J.; Keyzers, R.A.; Taufa, T. Streptomyces: Still the Biggest Producer of New Natural Secondary Metabolites, a Current Perspective. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 418–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, H.J.; Rutledge, P.J. Recently Discovered Secondary Metabolites from Streptomyces Species. Molecules 2022, 27, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanowska-Karamyan, A.J.; Hamann, M.T. Marine Indole Alkaloids: Potential New Drug Leads for the Control of Depression and Anxiety. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4489–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seipp, K.; Geske, L.; Opatz, T. Marine Pyrrole Alkaloids. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, J. Cytotoxic Furan- and Pyrrole-Containing Scalarane Sesterterpenoids Isolated from the Sponge Scalarispongia sp. Molecules 2019, 24, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, K.-C.; Chin, E.J.; Wibowo, M.; Tan, Z.Y.; Yang, L.-K.; Seow, D.C.; Leong, C.-Y.; Ng, V.W.; Ng, S.-B.; Kanagasundaram, Y. Antibacterial Spirotetronate Polyketides from an Actinomadura sp. Strain A30804. Mar. Drugs 2022, 27, 8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.T.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S.; Howard-Jones, A.R. Biological formation of pyrroles: Nature’s logic and enzymatic machinery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zeng, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Micromonospora: A Prolific Source of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites with Therapeutic Potential. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8735–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaine, G.; Ture, A.; Pedroni, J.; Smits, G. Isolation, chemistry, and biology of pyrrolo[1,4]benzodiazepine natural products. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 5–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateev, E.; Georgieva, M.; Zlatkov, A. Pyrrole as an Important Scaffold of Anticancer Drugs: Recent Advances. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 25, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trew, S.J.; Wrigley, S.K.; Pairet, L.; Sohal, J.; Shanu-Wilson, P.; Hayes, M.A.; Martin, S.M.; Manohar, R.N.; Chicarelli-Robinson, M.I.; Kau, D.A.; et al. Novel streptopyrroles from Streptomyces rimosus with bacterial protein histidine kinase inhibitory and antimicrobial activities. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breinholt, J.; Gürtler, H.; Kjær, A.; Nielsen, S.E.; Olsen, C.E.J.A.C.S. Streptopyrrole: An antimicrobial metabolite from Streptomyces armeniacus. Acta Chem. Scand. 1998, 52, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, E.; Trew, S.J.; Wrigley, S.K.; Pairet, L.; Hayes, M.A.; Martin, S.; Kau, D.A. Microorganism Capable of Producing Compounds Where Pyrrole Is Fused with 4-oxo-1,3-benzoxazine and Method of Use as Antibacterial and Antifungal. Patent No. WO 98/25931, 20 November 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Raggatt, M.E.; Simpson, T.J.; Wrigley, S.K. Biosynthesis of XR587 (streptopyrrole) in Streptomyces rimosus involves a novel carbon-to-nitrogen rearrangement of a proline-derived unit. Chem. Commun. 1999, 11, 1039–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couturier, C.; Bauer, A.; Rey, A.; Schroif-Dufour, C.; Broenstrup, M. Armeniaspiroles, a new class of antibacterials: Antibacterial activities and total synthesis of 5-chloro-Armeniaspirole A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 6292–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Yan, J.; Jia, J.; Xue, J.; Qu, X.; Hu, Y.; Deng, Z.; Bi, H.; Zhu, D. Characterization of the Biosynthetic Gene Cluster for the Antibiotic Armeniaspirols in Streptomyces armeniacus. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, C.; Wink, J.; Kurz, M.; Kogler, H.; Olivan, H.; Sablé, S.; Heyse, W.; Gerlitz, M.; Toti, L.; Nußer, A.; et al. Isolation and structural elucidation of armeniaspirols A-C: Potent antibiotics against gram-positive pathogens. Chemistry 2012, 18, 16123–16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobek, J.; Šmídová, K.; Čihák, M. A Waking Review: Old and Novel Insights into the Spore Germination in Streptomyces. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 11th ed.; CLSI Standard M07; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.-K.; Lee, H.-S.; Kang, J.S.; Shin, H.J. Dokdolipids A−C, Hydroxylated Rhamnolipids from the Marine-Derived Actinomycete Actinoalloteichus hymeniacidonis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
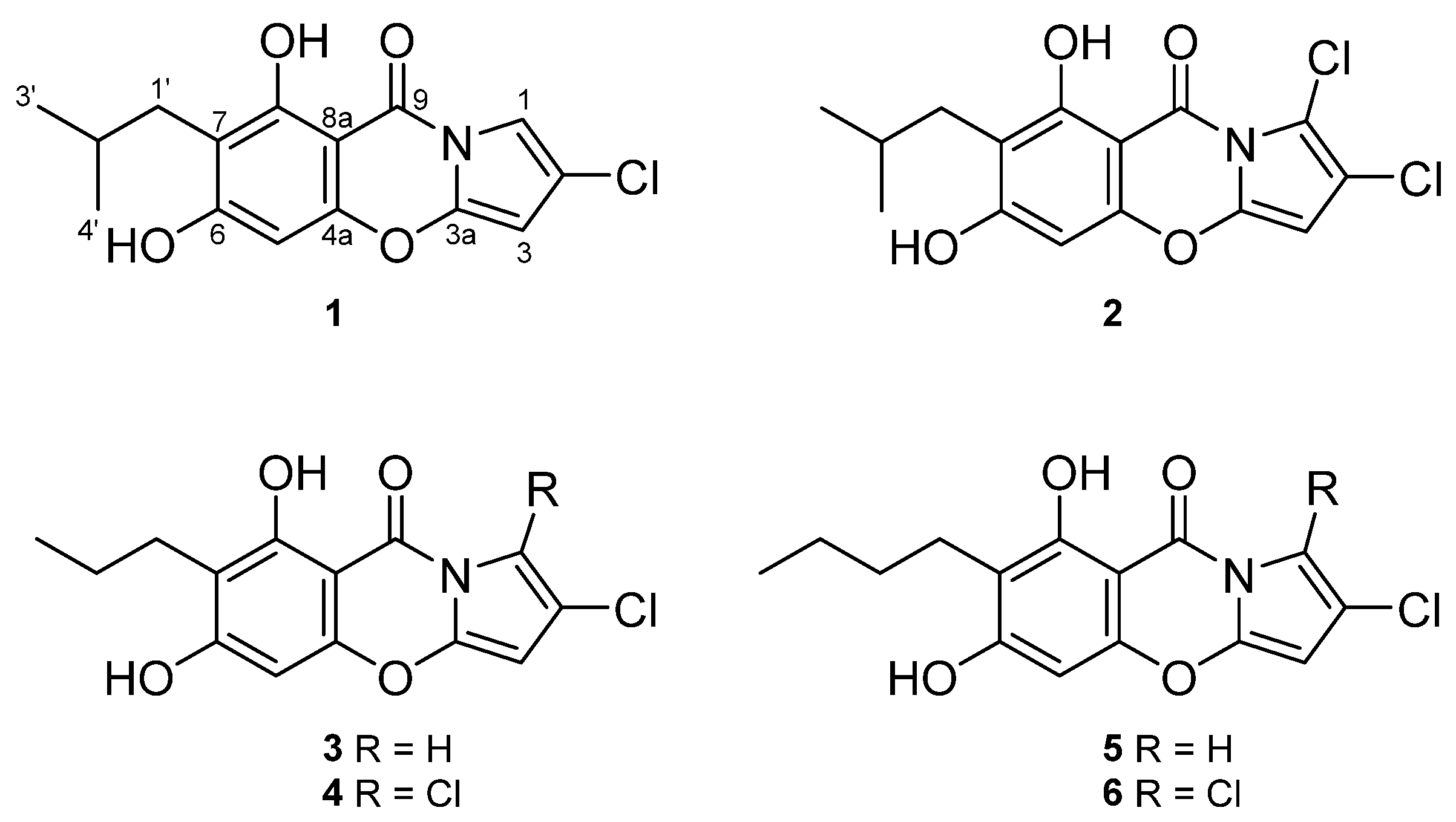


| No | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH, Mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | |
| 1 | 7.18, d (2.1) | 105.0, CH | 105.1, C | |
| 2 | 119.3, C | 117.3, C | ||
| 3 | 5.87, d (2.1) | 90.9, CH | 5.95, s | 90.3, CH |
| 3a | 142.5, C | 141.7, C | ||
| 4a | 154.9, C | 154.5, C | ||
| 5 | 6.29, s | 94.2, CH | 6.25, s | 94.1, CH |
| 6 | 165.8, C | 166.3, C | ||
| 7 | 112.7, C | 113.0, C | ||
| 8 | 161.3, C | 161.6, C | ||
| 8a | 93.2, C | 93.5, C | ||
| 9 | 159.8, C | 160.9, C | ||
| 1′ | 2.50, d (7.3) | 32.0, CH2 | 2.50 d (7.3) | 32.0, CH2 |
| 2′ | 1.97, m | 29.1, CH | 1.97, m | 29.1, CH |
| 3′ | 0.91, d (6.7) | 22.9, CH3 | 0.91, d (6.7) | 22.9, CH3 |
| 4′ | 0.91, d (6.7) | 22.9, CH3 | 0.91, d (6.7) | 22.9, CH3 |
| Strains | MIC (µM) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Kanamycin | |
| Bacillus subtilis | 0.8 | 2.9 | 0.9 | 24.5 | 6.5 | 5.9 | 1.0 |
| Micrococcus luteus | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 4.1 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 1.5 | <0.5 |
| Escherichia coli | - | - | - | - | - | - | <0.5 |
| Salmonella typhimurium | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4.1 |
| Klebsiella pneumonia | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.0 |
| Cell Lines | GI50 (µM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 5 | Adriamycin | |
| ACHN | 4.9 | 6.0 | 10.5 | 0.17 |
| MDA-MB-231 | 6.5 | 7.1 | 10.7 | 0.14 |
| PC-3 | 6.3 | 7.7 | 10.4 | 0.15 |
| NUGC-3 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 10.4 | 0.15 |
| NCI-H23 | 6.1 | 6.8 | 10.8 | 0.13 |
| HCT-15 | 6.6 | 7.7 | 10.7 | 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, C.-S.; Kang, J.S.; Kwon, J.-H.; Anh, C.V.; Shin, H.J. Pyrrole-Containing Alkaloids from a Marine-Derived Actinobacterium Streptomyces zhaozhouensis and Their Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030167
Heo C-S, Kang JS, Kwon J-H, Anh CV, Shin HJ. Pyrrole-Containing Alkaloids from a Marine-Derived Actinobacterium Streptomyces zhaozhouensis and Their Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(3):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030167
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Chang-Su, Jong Soon Kang, Joo-Hee Kwon, Cao Van Anh, and Hee Jae Shin. 2023. "Pyrrole-Containing Alkaloids from a Marine-Derived Actinobacterium Streptomyces zhaozhouensis and Their Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities" Marine Drugs 21, no. 3: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030167
APA StyleHeo, C.-S., Kang, J. S., Kwon, J.-H., Anh, C. V., & Shin, H. J. (2023). Pyrrole-Containing Alkaloids from a Marine-Derived Actinobacterium Streptomyces zhaozhouensis and Their Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities. Marine Drugs, 21(3), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030167







