Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary Analysis, and Expression Patterns of Cathepsin Superfamily in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) following Aeromonas salmonicida Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
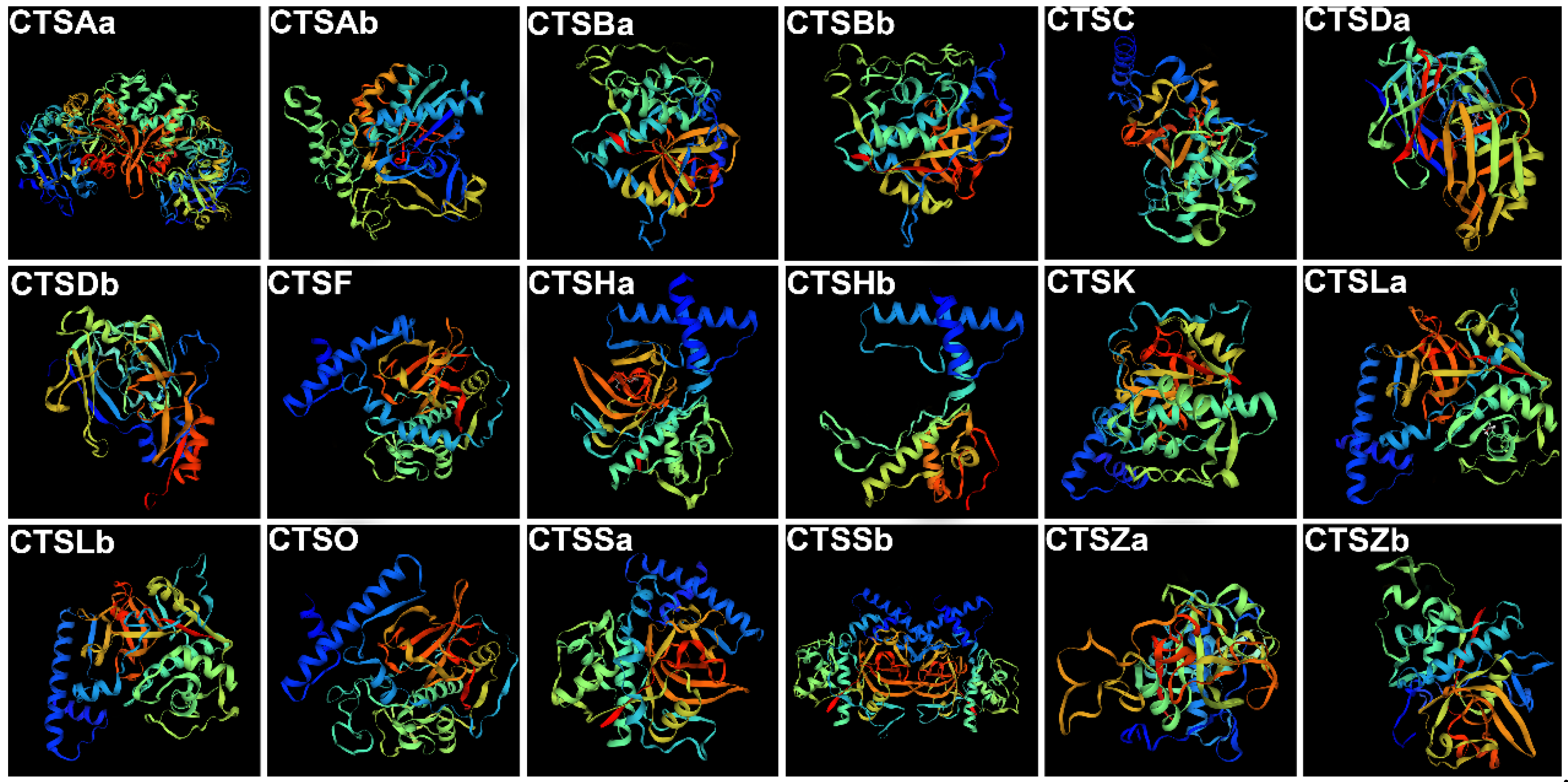
2.1. Identification of S. schlegelii Cathepsins
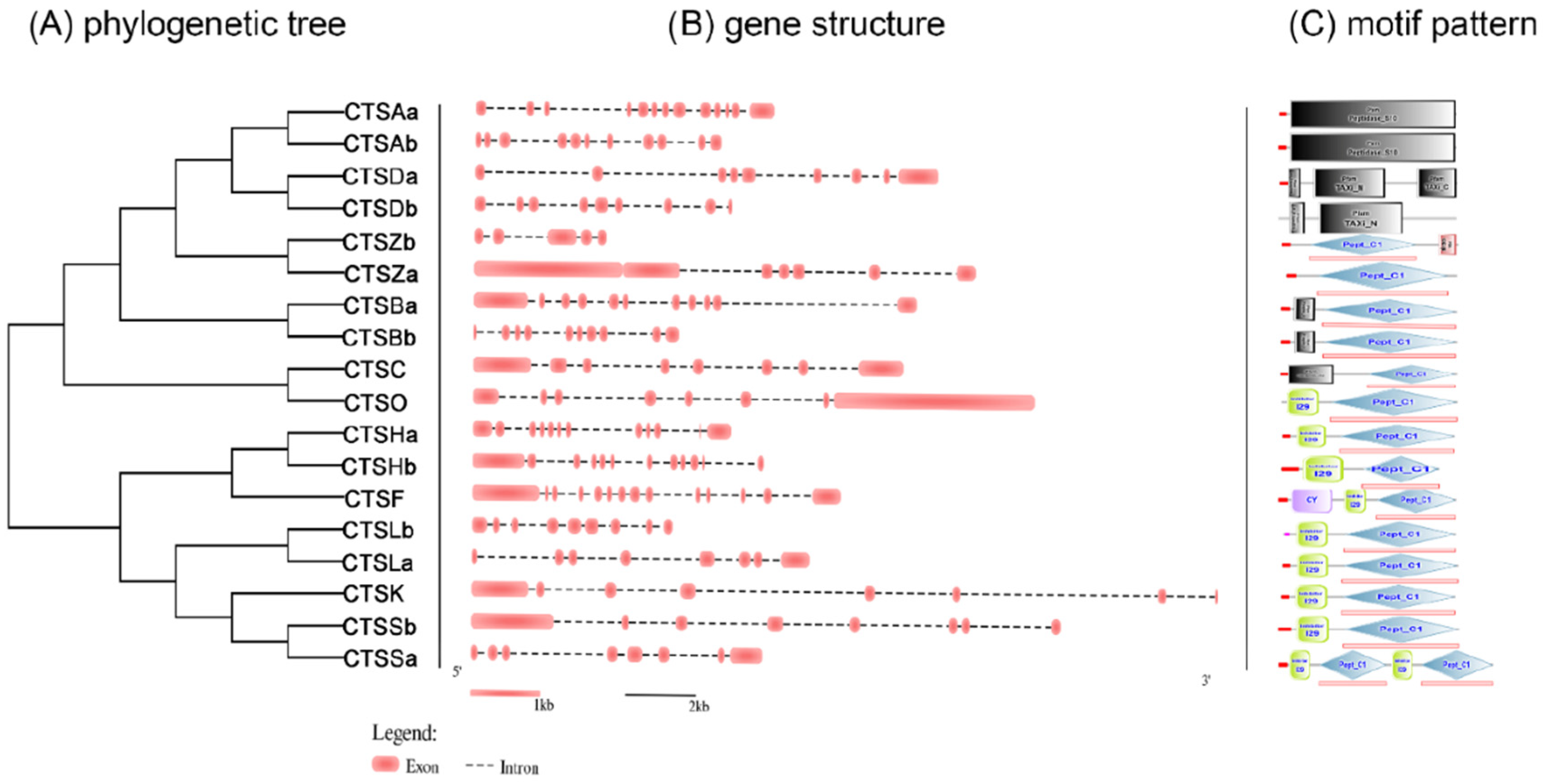
2.2. Gene Structure Analysis of S. schlegelii Cathepsins
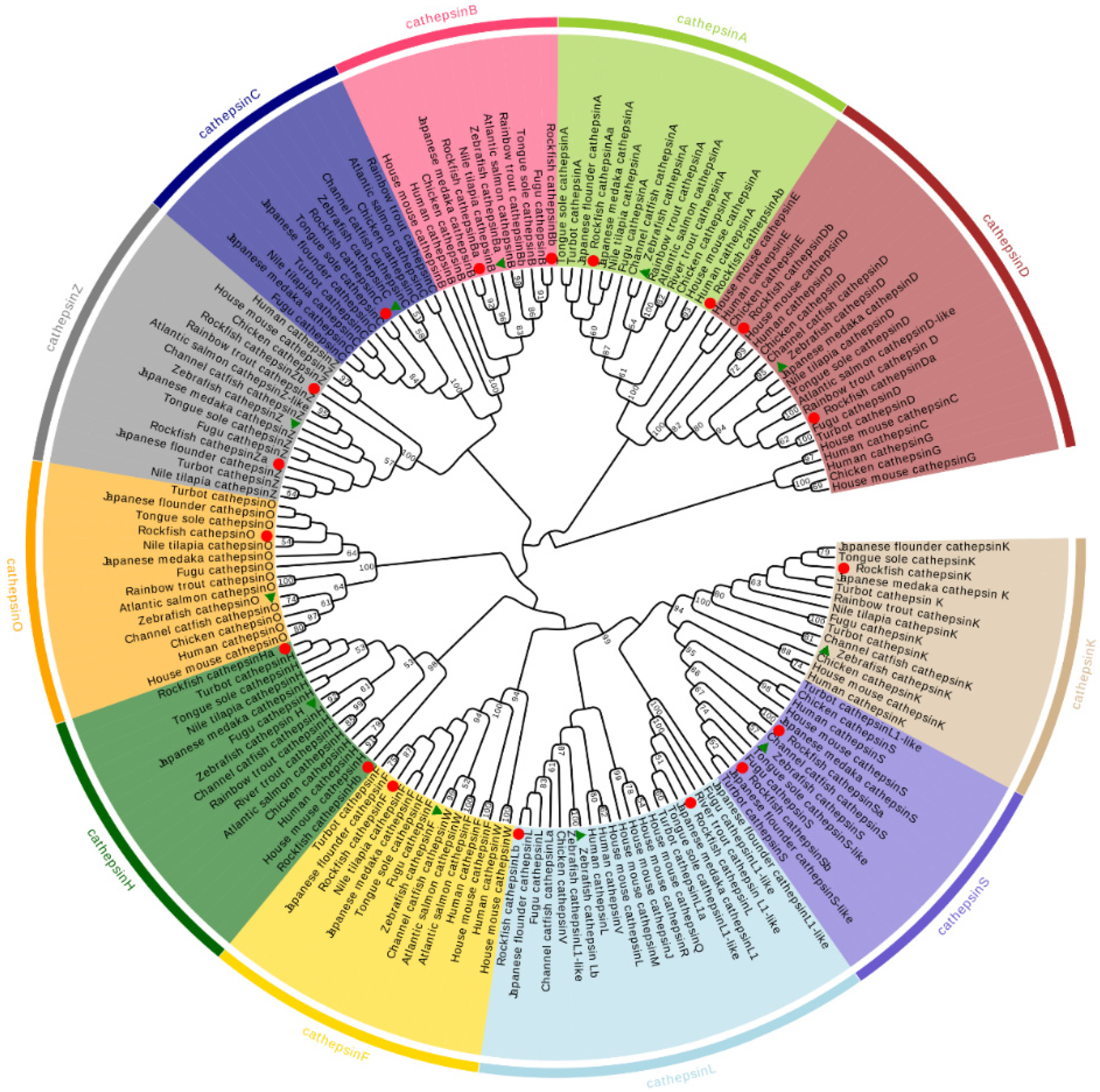
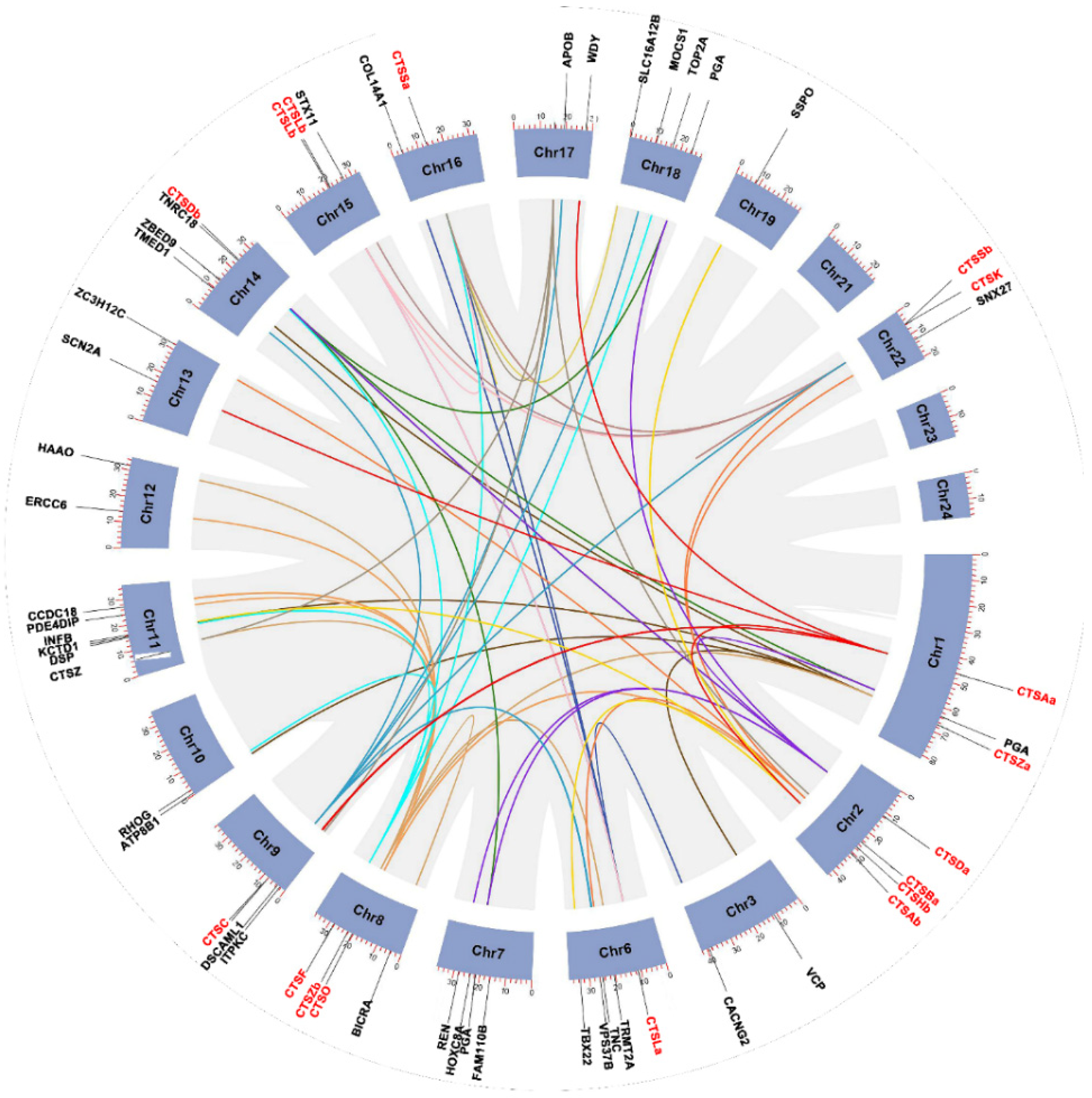
2.3. Phylogenetic and Synteny Analysis of S. schlegelii Cathepsins
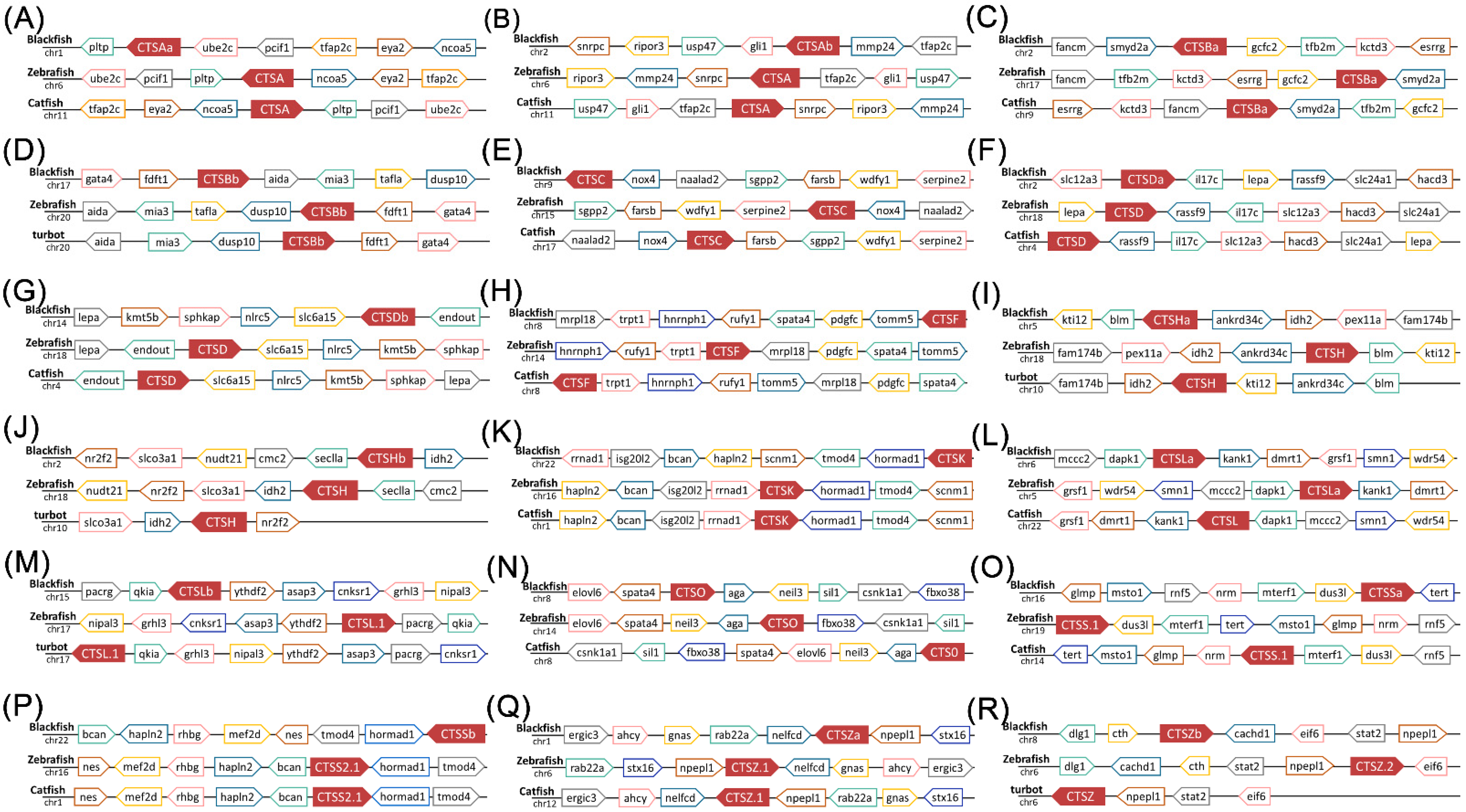
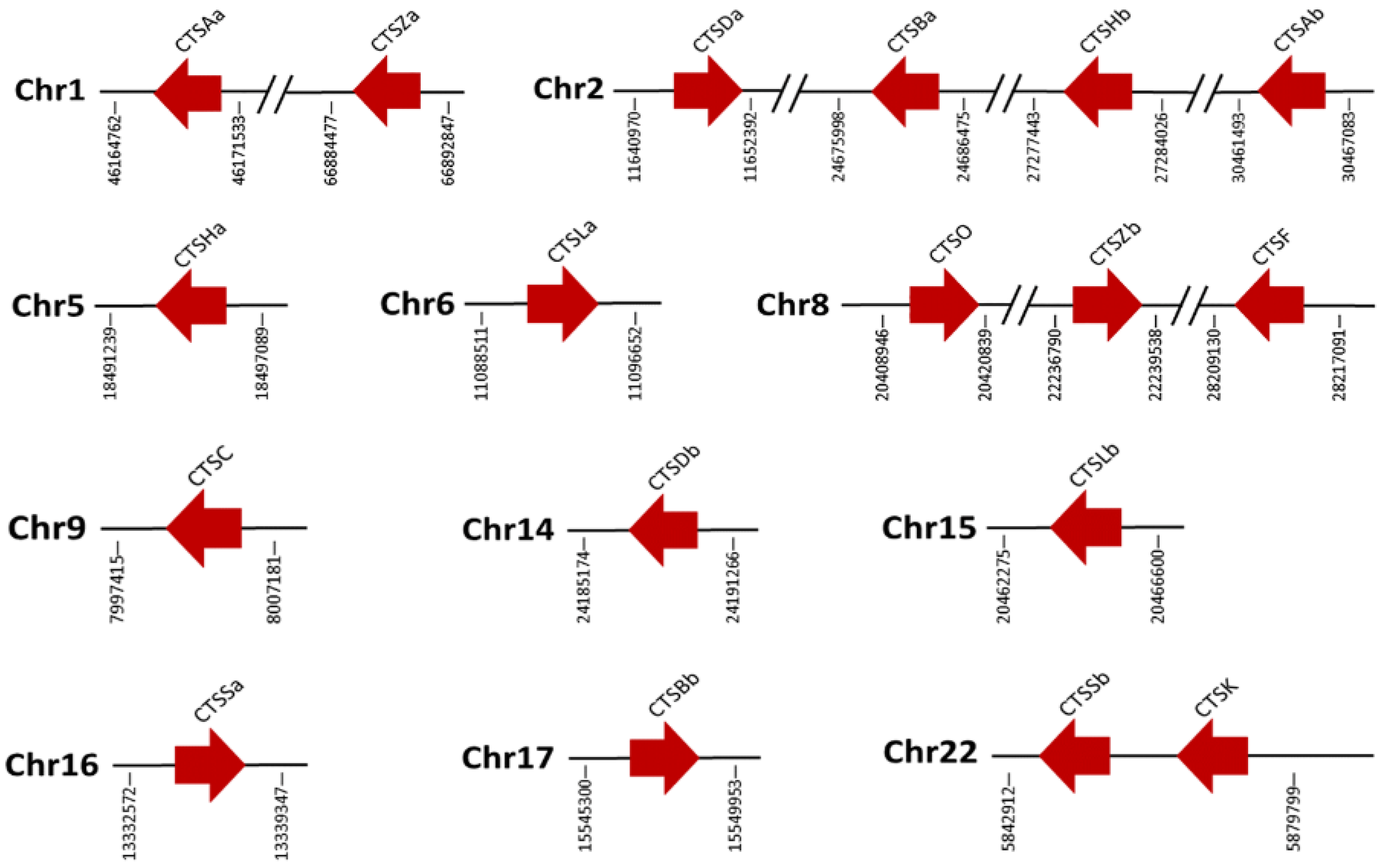
2.4. Genomic Clusters of S. schlegelii Cathepsins
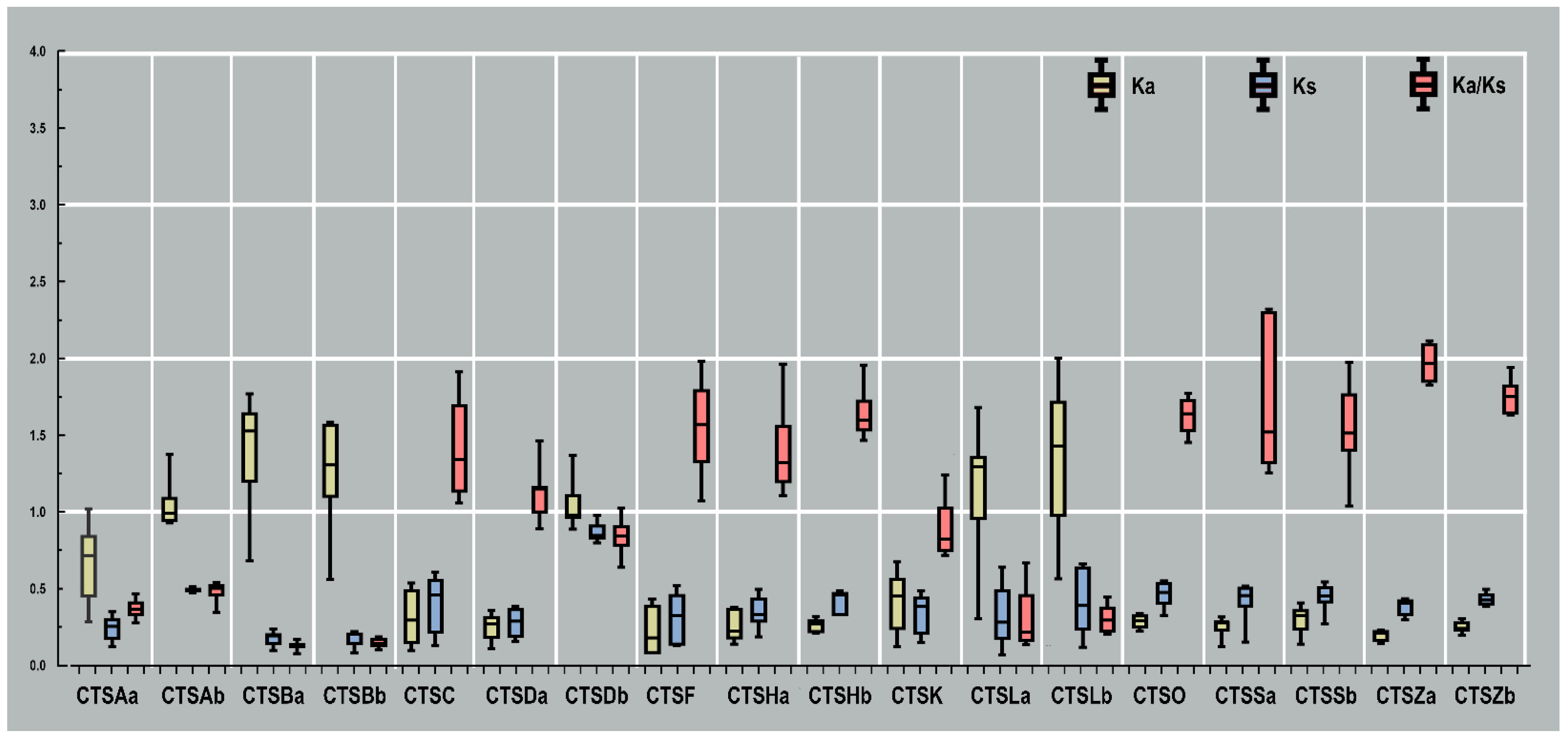
2.5. Evolutionary Rate Analysis
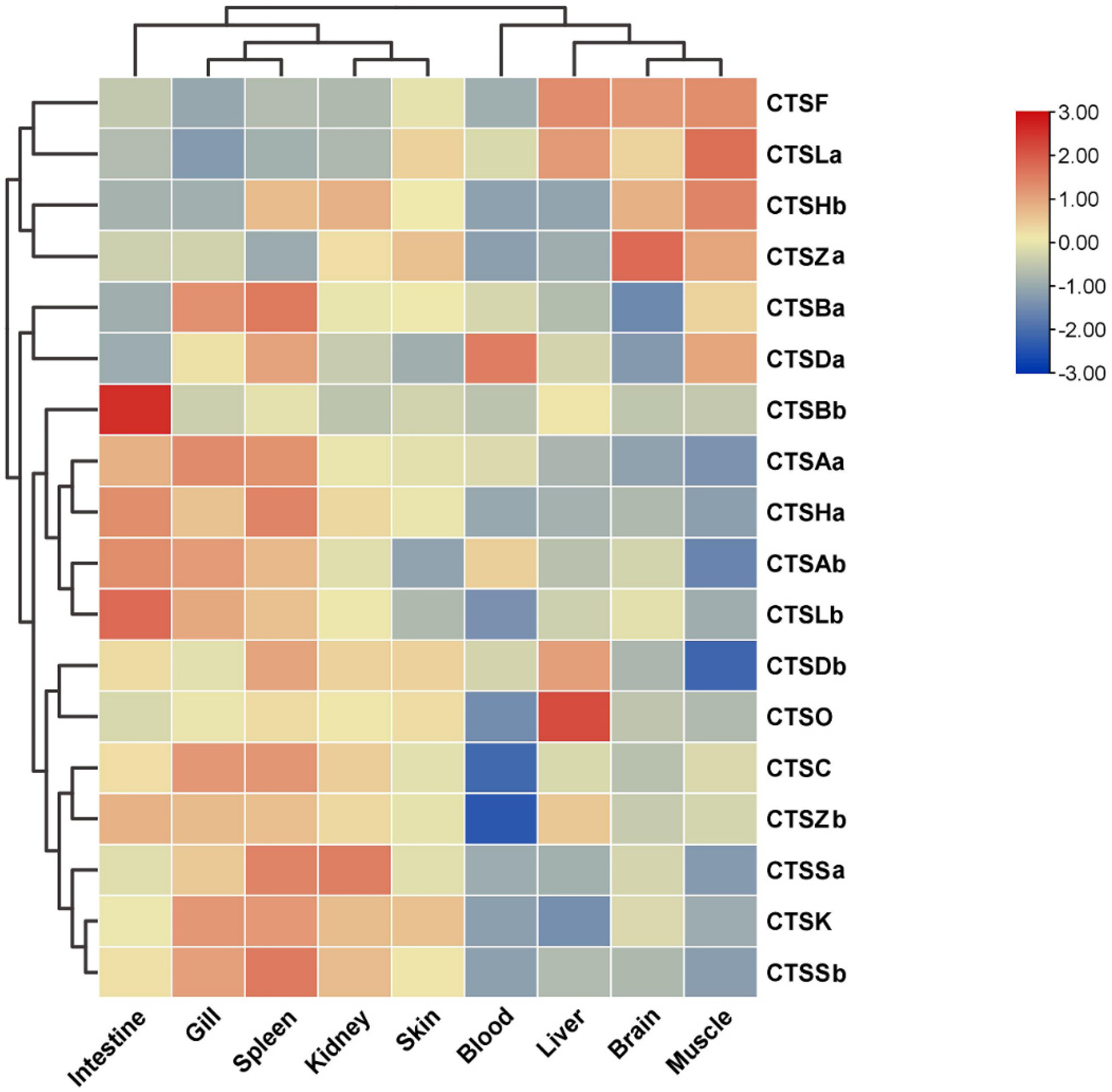
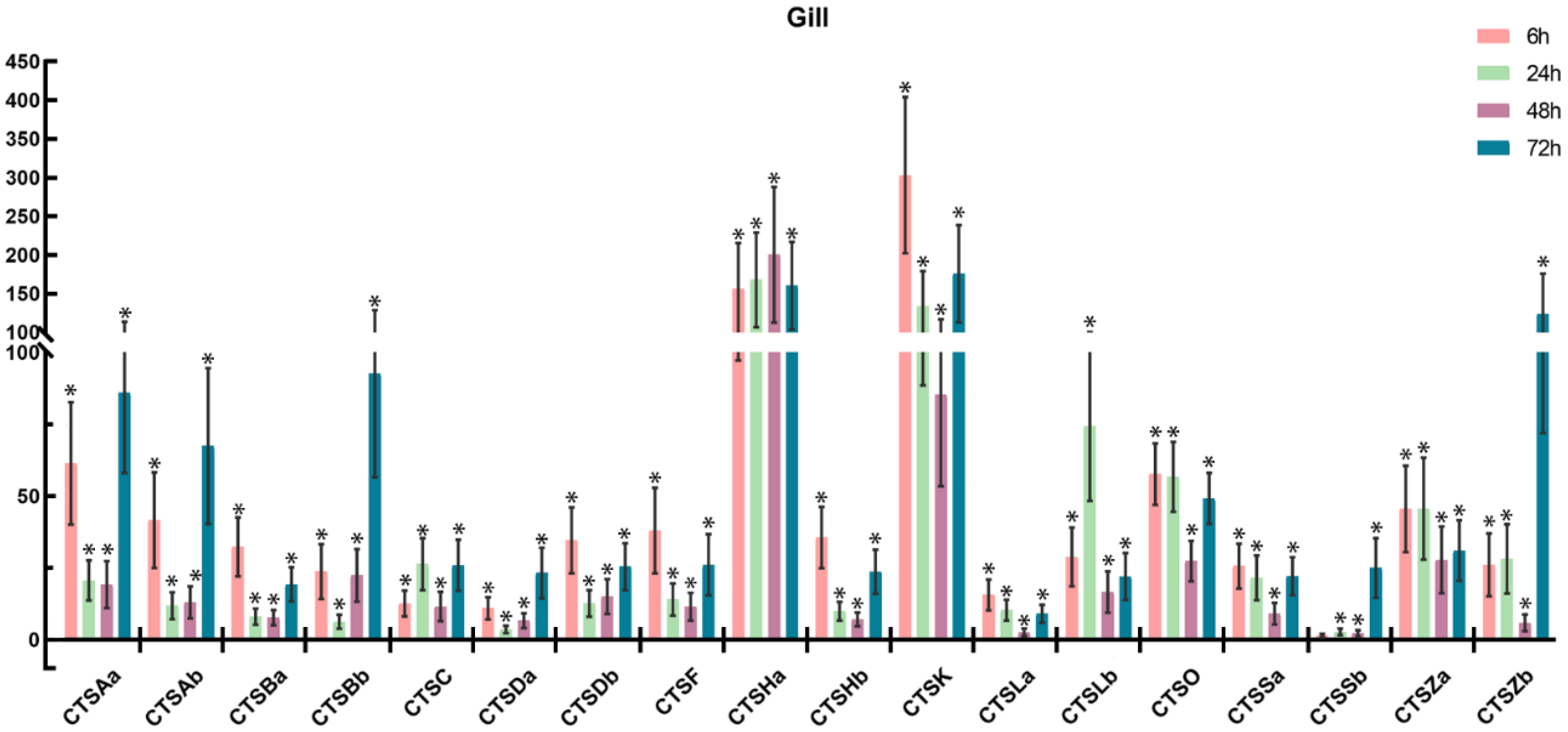
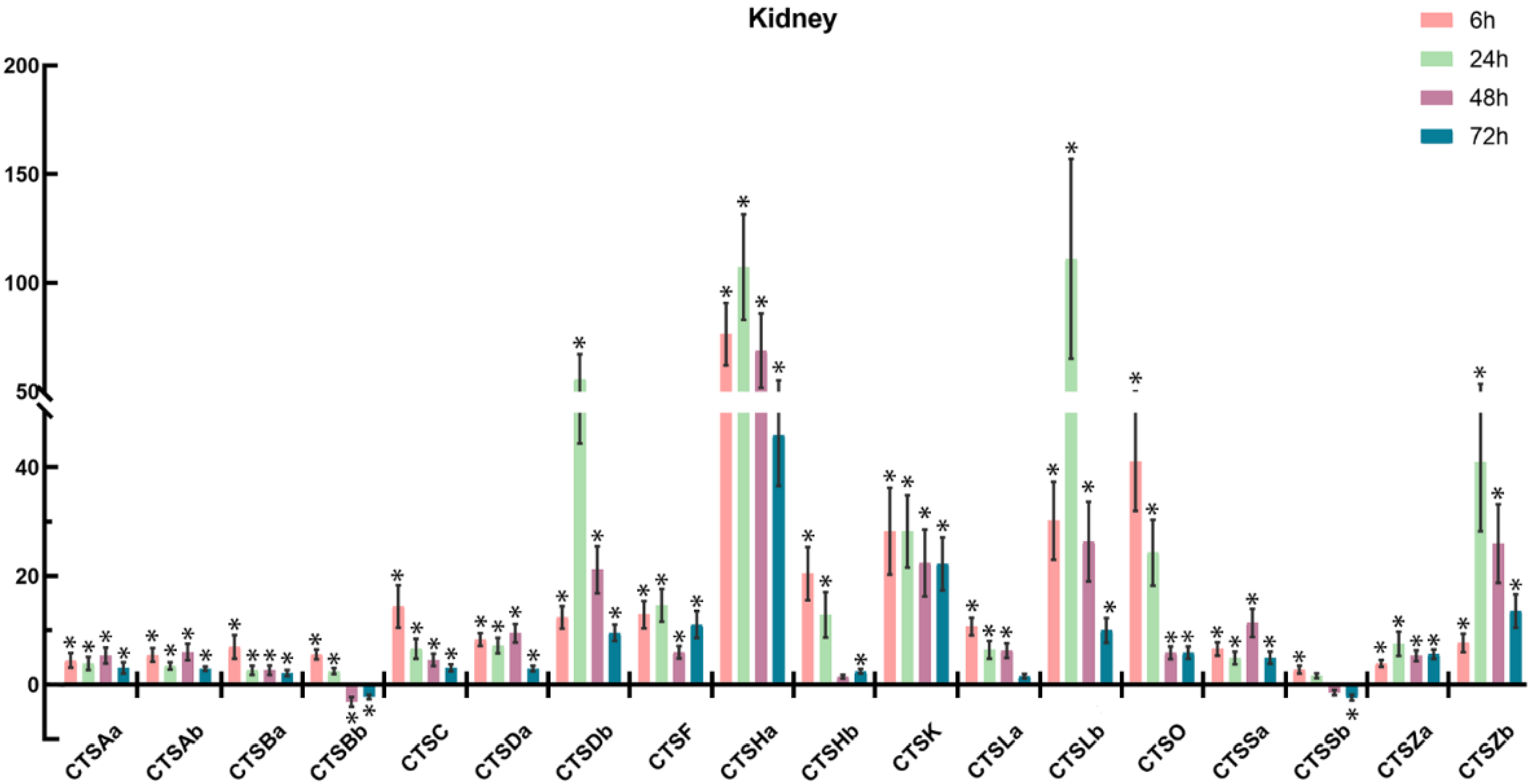
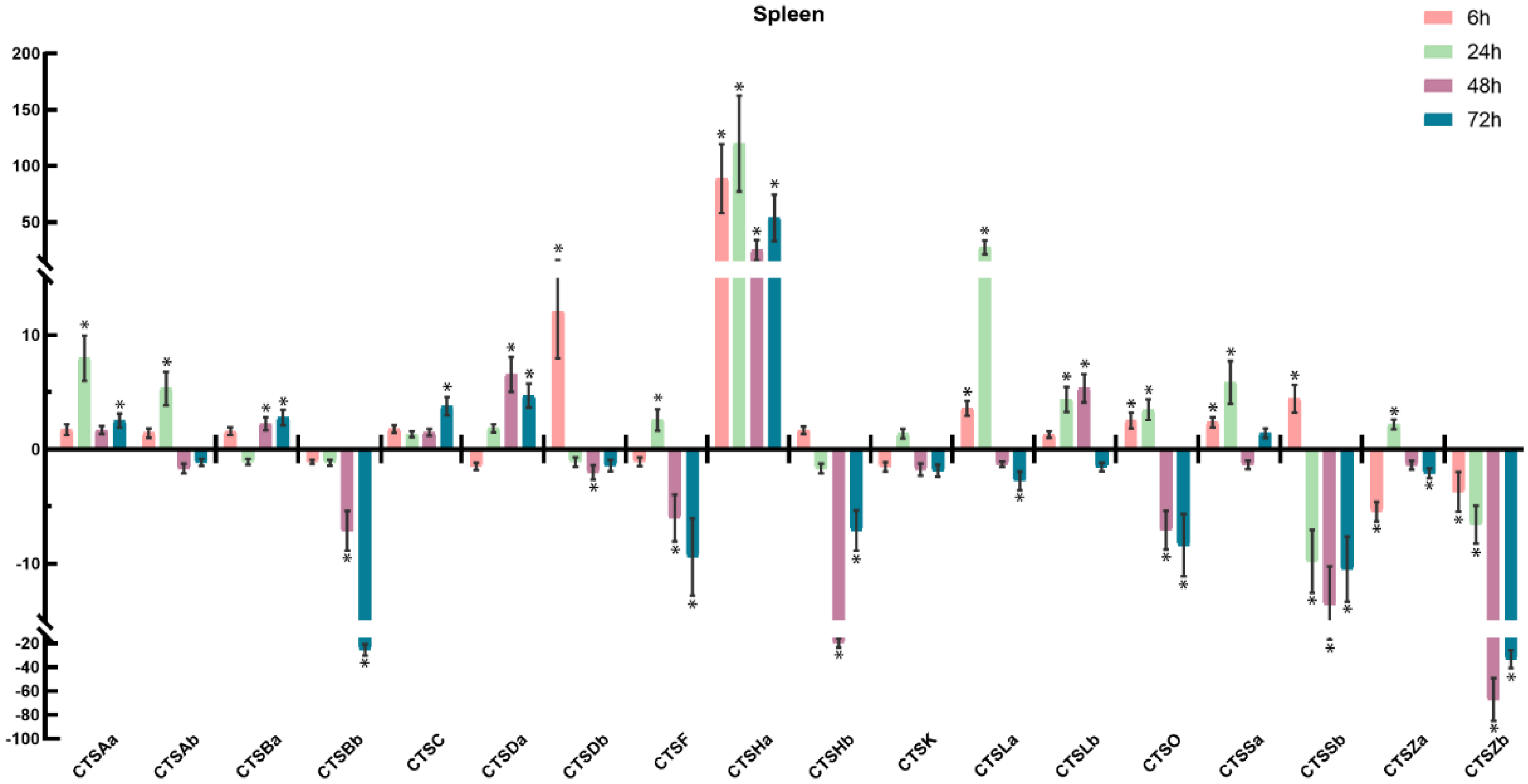
2.6. Expression Profiles of Cathepsins after A. salmonicida Infection
2.7. PPI Network Construction of Cathepsins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Gene Identification
4.2. Sequence Analysis
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. Synteny and Schematic Genomic Organization Analysis
4.5. Evolutionary Rate Analyses
4.6. Sample Collection of Healthy S. schlegelii
4.7. Bacterial Challenge and Sample Collection
4.8. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGrath, M. The lysosomal cysteine proteases. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1999, 28, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Honey, K.; Rudensky, A. Lysosomal cysteine proteases regulate antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uinuk-Ool, T.; Takezaki, N.; Kuroda, N.; Figueroa, F.; Sato, A.; Samonte, I.; Mayer, W.; Klein, J. Phylogeny of antigen-processing enzymes: Cathepsins of a cephalochordate, an agnathan and a bony fish. Scand. J. Immunol. 2003, 58, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kornfeld, S.; Mellman, I. The Biogenesis of Lysosomes. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1989, 5, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, A.; Rawlings, N.; Woessner, J. Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Isahara, K.; Ohsawa, Y.; Kanamori, S.; Shibata, M.; Waguri, S.; Sato, N.; Gotow, T.; Watanabe, T.; Momoi, T.; Urase, K.; et al. Regulation of a novel pathway for cell death by lysosomal aspartic and cysteine proteinases. Neuroscience 1999, 91, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.; Ahn, S.; Kim, N.; Seo, J.; Kim, M.; Park, N.; Kim, J.; Chung, J.; Lee, H.H. Molecular cloning, expression analysis and enzymatic characterization of cathepsin K from olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 154, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, V.; Stoka, V.; Vasiljeva, O.; Renko, M.; Sun, T.; Turk, B.; Turk, D. Cysteine cathepsins: From structure, function and regulation to new frontiers.Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colbert, J.; Matthews, S.; Miller, G.; Watts, C. Diverse regulatory roles for lysosomal proteases in the immune response. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 2955–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrer, K.; Peiffer, S.; DiTomas, M. Two distinct gene subfamilies within the family of cysteine protease genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3063–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, A.; Deveraux, Q.; Turk, B.; Sali, A. Comprehensive search for cysteine cathepsins in the human genome. Biol. Chem. 2004, 385, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. Families of Serine Peptidases. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 244, 19–61. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, D.; Turk, B.; Turk, V. Papain-like lysosomal cysteine proteases and their inhibitors: Drug discovery targets? Biochem. Soc. Symp. 2003, 70, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo, A.; Mann, L.; Bonten, E.; d’Azzo, A.; Dice, J.F. Cathepsin A regulates chaperone-mediated autophagy through cleavage of the lysosomal receptor. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petrera, A.; Kern, U.; Linz, D.; Gomez-Auli, A.; Hohl, M.; Gassenhuber, J.; Sadowski, T.; Schilling, O. Proteomic Profiling of Cardiomyocyte-Specific Cathepsin A Overexpression Links Cathepsin A to the Oxidative Stress Response. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 3188–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomgran, R.; Zheng, L.; Stendahl, O. Cathepsin-cleaved Bid promotes apoptosis in human neutrophils via oxidative stress-induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, F.; Saitoh, S.; Fukui, R.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanimura, N.; Konno, K.; Kusumoto, Y.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Miyake, K. Cathepsins are required for Toll-like receptor 9 responses. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.D.; Martins, A.; Khazaie, K.; Han, J.; Chan, B.; Kim, S.O. Cathepsin B is involved in the trafficking of TNF-alpha-containing vesicles to the plasma membrane in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qnla, B.; Skc, D.; Igc, D.; Hlz, A.; Mnac, D.; Lsd, A. The red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii cathepsin C, participates in the innate immune response to the viral and bacterial pathogens-ScienceDirect. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 436–444. [Google Scholar]
- Liaudet-Coopman, E.; Beaujouin, M.; Derocq, D.; Garcia, M.; Glondu-Lassis, M.; Laurent-Matha, V.; Prébois, C.; Rochefort, H.; Vignon, F. Cathepsin D: Newly discovered functions of a long-standing aspartic protease in cancer and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2006, 237, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bond, J.S.; Butler, P.E. Intracellular proteases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 333–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Qian, J.; Keppler, D.; Cardoso, W. Cathespin H is an Fgf10 target involved in Bmp4 degradation during lung branching morphogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22176–22184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.W.; Du, X.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, J.J.; Gu, H.J. Identification and characterization of a cathepsin K homologue that interacts with pathogen bacteria in black rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, N.; Cao, M.; Li, C. Characterization of the immune roles of cathepsin L in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) mucosal immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 97, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, G.; Ferrando, A.A.; Puente, X.S.; Sánchez, L.; López-Otín, C. Human cathepsin O. Molecular cloning from a breast carcinoma, production of the active enzyme in Escherichia coli, and expression analysis in human tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Malcangio, M.J. Microglial signalling mechanisms: Cathepsin S and Fractalkine. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 234, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudensky, A.; Beers, C. Lysosomal cysteine proteases and antigen presentation. Cytokines Potential Ther. Targets Inflamm. Ski. Dis. 2006, 56, 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Mall, M.; Schultz, C. A new player in the game: Epithelial cathepsin S in early cystic fibrosis lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 126–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, J.; Sekirnik, A.; Premzl, A.; Bergant, V.Z.; Langerholc, T.; Repnik, U.; Turk, B.; Werle, B.; Golouh, R.; Jeras, M.; et al. Carboxypeptidases cathepsins X and B display distinct protein profile in human cells and tissues. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 306, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabra, M.; Cerdà, J. Ovarian cysteine proteinases in the teleost Fundulus heteroclitus: Molecular cloning and gene expression during vitellogenesis and oocyte maturation. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2004, 67, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, H.; Klesius, P. Channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, cysteine proteinases: Cloning, characterisation and expression of cathepsin H and L. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Ahn, S.; Lee, A.; Seo, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.; Chung, J.; Lee, H. Cloning, expression analysis and enzymatic characterization of cathepsin S from olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 157, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallaire-Dufresne, S.; Tanaka, K.H.; Trudel, M.V.; Lafaille, A.; Charette, S.J. Virulence, genomic features, and plasticity of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida, the causative agent of fish furunculosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 169, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S.I.; Jung, S.J.; Kim, W.S.; Nishizawa, T.; Yoshimizu, M.J. A new genotype of lymphocystivirus, LCDV-RF, from lymphocystis diseased rockfish. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reith, M.E.; Singh, R.K.; Curtis, B.; Boyd, J.M.; Bouevitch, A.; Kimball, J.; Munholland, J.; Murphy, C.; Sarty, D.; Williams, J.; et al. The genome of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449: Insights into the evolution of a fish pathogen. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, P.; Kwon, H.; Elvitigala, D.; Wan, Q.; Lee, J. Identification and characterization of cystatin B from black rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii, indicating its potent immunological importance. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 104, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.H.; He, S.W.; Du, X.; Xie, B.; Hu, Y.H. Characterization, expression, enzymatic activity, and functional identification of cathepsin S from black rockfish Sebastes schlegelii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, R.; Wang, R.; Xu, T. Comparative genomic of the teleost cathepsin B and H and involvement in bacterial induced immunity of miiuy croaker. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.; Zhang, X.J. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of cathepsin D gene from turbot Scophthalmus maximus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Press, C.M.; Fish, E. The morphology of the immune system in teleost fishes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1999, 9, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, W.R.; Xiang, L.X.; Shao, J. Cloning and characterisation of two natural killer enhancing factor genes (NKEF-A and NKEF-B) in pufferfish, Tetraodon nigroviridis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Konagaya, S. Cysteine protease inhibitor in egg of chum salmon. J. Biochem. 1991, 110, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Cao, M.; Zhang, L.; Fu, Q.; Yang, N.; Tan, F.; Song, L.; Su, B.; Li, C. Characterization and initial functional analysis of cathepsin K in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harikrishnan, R.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.; Han, Y.; Jang, I.; Balasundaram, C.; Heo, M. Immune response and expression analysis of cathepsin K in goldfish during Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doggett, T.A.; Harris, J.E. The ontogeny of gut-associated lymphoid tissue in Oreochromis-mossambicus. J. Fish Biol. 1987, 31, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, C.; Hwang, S.; Jeong, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.; Shim, S. Molecular characterisation and expression analysis of the cathepsin H gene from rock bream (Oplegnathus fasciatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.R.; He, H.S.; Zhang, C.W.; Xu, X.M.; Zeng, Z.P.; Yuan, J.P.; Hong, Y.H.; Wang, J.H. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of cathepsin B from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Cao, Z.; Qin, Q.; Liu, C.; Guo, W. Functional characterization of cathepsin B and its role in the antimicrobial immune responses in golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 123, 104128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Yang, N.; Gao, C.; Tian, M.; Zhou, S.; Mu, X.; Sun, F.; Li, C. Characterization, expression signatures and microbial binding analysis of cathepsin A in turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. (SmCTSA). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 81, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, R.; Dong, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gui, J.F. Expressional induction of Paralichthys olivaceus cathepsin B gene in response to virus, poly I:C and lipopolysaccharide. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Song, L.; Tan, F.; Su, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.; Peatman, E. Identification and mucosal expression analysis of cathepsin B in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) following bacterial challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Kurz, U.; Schultz, J.; Lim, C.; Wiederanders, B.; Schilling, K. The alpha1/2 helical backbone of the prodomains defines the intrinsic inhibitory specificity in the cathepsin L-like cysteine protease subfamily. FEBS Lett. 2000, 469, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santamaría, I.; Velasco, G.; Pendás, A.M.; Fueyo, A.; López-Otín, C. Cathepsin Z, a Novel Human Cysteine Proteinase with a Short Propeptide Domain and a Unique Chromosomal Location. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16816–16823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiraiwa, M. Cathepsin A/protective protein: An unusual lysosomal multifunctional protein. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 1999, 56, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Azzo, A.; Hoogeveen, A.; Reuser, A.J.; Robinson, D.; Galjaard, H. Molecular defect in combined beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase deficiency in man. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 4535–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinogradova, V.M.; Michaud, L.; Mezentsev, V.A.; Lukong, E.K.; El-Alfy, M.; Morales, R.C.; Potier, M.; Pshezhetsky, V.A. Molecular mechanism of lysosomal sialidase deficiency in galactosialidosis involves its rapid degradation. Biochem. J. 1998, 330, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Noort, J.; van der Drift, A.C. The selectivity of cathepsin D suggests an involvement of the enzyme in the generation of T-cell epitopes. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 14159–14164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecaille, F.; Kaleta, J.; Brömme, D. Human and Parasitic Papain-Like Cysteine Proteases: Their Role in Physiology and Recent Developments in Inhibitor Design. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4459–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Cao, M.; Yang, N.; Huo, H.; Yan, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, C. CC chemokines and their receptors in black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii): Characterization, evolutionary analysis, and expression patterns after Aeromonas Salmonicida infection. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Gao, C.; Cao, M.; Yang, N.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Fu, Q. CXC chemokines and their receptors in black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii): Characterization, evolution analyses, and expression pattern after Aeromonas salmonicida infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, R.; Lian, H.; Zhong, X.; Yang, Q.; Shu, H. ZCCHC3 modulates TLR3-mediated signaling by promoting recruitment of TRIF to TLR3. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, J.; Kiryu, I.; Köllner, B.; Yoshiura, Y.; Ototake, M. MHC class II invariant chain homologues in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2003, 15, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodi, A.; Brett, S.; Nordeng, T.; Sidhu, S.; Batchelor, R.; Lombardi, G.; Bakke, O.; Lechler, R. The invariant chain inhibits presentation of endogenous antigens by a human fibroblast cell line. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.; Nepom, G.; Richert, J.; Biddison, W.; McFarland, H. Identification of a specific HLA DR2 Ia molecule as a restriction element for measles virus-specific HLA class II-restricted cytotoxic T cell clones. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 161, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, M.; Xiu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Yang, N.; Su, B.; Li, C. Identification of Antimicrobial Peptide Genes in Black Rockfish Sebastes schlegelii and Their Responsive Mechanisms to Edwardsiella tarda Infection. Biology 2021, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, N.; Fu, Q.; Li, C. Full length transcriptome profiling reveals novel immune-related genes in black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, V.; Kosarev, P.; Seledsov, I.; Vorobyev, D. Automatic annotation of eukaryotic genes, pseudogenes and promoters. Genome Biol. 2006, 7 (Suppl. S1), S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkins, M.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.; Williams, K.; Appel, R.; Hochstrasser, D. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. In 2-D Proteome Analysis Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 112, pp. 531–552. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, L.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.; Wass, M.; Sternberg, M. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Yang, N.; Tian, M.; Cai, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Cao, M.; Xue, T.; Li, C. Genome-wide identification, expression signature and immune functional analysis of two cathepsin S (CTSS) genes in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 102, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.; Yan, X.; Yang, N.; Fu, Q.; Xue, T.; Zhao, S.; Hu, J.; Li, Q.; Song, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Genome-wide characterization of Toll-like receptors in black rockfish Sebastes schlegelii: Evolution and response mechanisms following Edwardsiella tarda infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-DDCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Genes | CDS (aa) | PI | MW (kDa) | Ori | Chr | Location | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTSAa | 472 | 5.26 | 53.32 | − | 1 | 46,164,762–46,171,533 | 34.42 | 84.62 | C2408H3630N624O706S22 |
| CTSAb | 459 | 5.41 | 51.37 | − | 2 | 30,461,493–30,467,083 | 29.89 | 74.34 | C2333H3442N600O679S19 |
| CTSBa | 330 | 5.38 | 36.06 | − | 2 | 24,675,998–24,686,475 | 32.27 | 69.42 | C1599H2412N424O486S22 |
| CTSBb | 330 | 5.20 | 36.06 | + | 17 | 15,545,300–15,549,953 | 31.46 | 70.94 | C1590H2411N433O487S21 |
| CTSC | 454 | 5.78 | 50.63 | − | 9 | 7,997,415–8,007,181 | 33.78 | 70.13 | C2282H3423N591O656S31 |
| CTSDa | 396 | 6.88 | 42.50 | + | 2 | 11,640,970–11,652,392 | 35.19 | 89.65 | C1936H3023N501O573S16 |
| CTSDb | 339 | 8.41 | 36.97 | − | 14 | 24,185,174–24,191,266 | 40.74 | 94.07 | C1665H2617N437O483S15 |
| CTSF | 474 | 5.57 | 53.02 | − | 8 | 28,209,130–28,217,091 | 39.98 | 76.96 | C2354H3652N628O715S26 |
| CTSHa | 325 | 5.53 | 36.41 | − | 5 | 18,491,239–18,497,089 | 35.70 | 60.00 | C1614H2404N430O494S21 |
| CTSHb | 215 | 5.47 | 24.66 | − | 2 | 27,277,443–27,284,026 | 42.11 | 67.53 | C1110H1650N290O326S12 |
| CTSK | 330 | 5.56 | 36.41 | − | 22 | 5,860,447–5,879,799 | 32.01 | 72.39 | C1592H2468N444O490S23 |
| CTSLb | 333 | 5.02 | 36.63 | − | 15 | 20,462,275–20,466,600 | 34.81 | 74.11 | C1610H2471N435O508S18 |
| CTSLa | 336 | 5.62 | 38.08 | + | 6 | 11,088,511–11,096,652 | 29.14 | 66.43 | C1688H2558N462O511S18 |
| CTSO | 335 | 8.06 | 37.27 | + | 8 | 20,408,946–20,420,839 | 32.89 | 75.07 | C1664H2531N461O489S14 |
| CTSSa | 640 | 8.00 | 71.66 | + | 16 | 13,332,572–13,339,347 | 42.08 | 80.86 | C3192H4925N891O924S34 |
| CTSSb | 337 | 5.72 | 37.17 | − | 22 | 5,842,912–5,857,384 | 35.35 | 66.32 | C1629H2496N448O503S24 |
| CTSZa | 357 | 6.72 | 39.68 | − | 1 | 66,884,477–66,892,847 | 41.59 | 67.45 | C1746H2660N492O533S19 |
| CTSZb | 301 | 6.44 | 33.46 | + | 8 | 22,236,790–22,239,538 | 31.76 | 67.01 | C1497H2240N398O440S19 |
| Gene Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | GTGCGTGACATCAAGGAGAAGC | TGTTGTAGGTGGTCTCGTGGA |
| CTSAa | GAGCTGGTGATGAGAGATCTTG | GACGGACGTTCAGGTTTAGAG |
| CTSAb | GTGAATGTGGCCTTTGGTATTG | GGGTGTTTCCTGTCGTTCTTA |
| CTSBa | CACTCCCAGCTACAAAGTAGAC | CTACTGGGCCGTTCTTGTATAG |
| CTSBb | TGGGCTGTTATGGTGGTTATC | AGCCGACATTGGAGTTATACAG |
| CTSC | GTACACTGAAGATGGCCCTAAG | TGGAGGTACTGGTTTCACTTTC |
| CTSDa | GCTTGCTTCACCGCAAATATAA | GACAGACTGCCACTTCCATAC |
| CTSDb | CCCTCCATTCACTGCTCTTT | GGAGAACTCTGTGCCATTCTT |
| CTSF | GGGATCCGCTACACCATAAC | GTTTCTGCAACTCGGGATAGA |
| CTSHa | CCTCTGACTTCATGCACTACTC | TGCCGTTCTCTTGTCCATAC |
| CTSHb | GCTCTTCCTACCCTCTACCTTTA | CGTGTGTGTGTATGTTGTCTCT |
| CTSK | GGAGGAGGATACATGACCAATG | GCCATGCCTGTTGAATTGTAG |
| CTSLa | ACGGAGGGATAGACACAGAA | CGTCACCTTGTTTCACATCAAC |
| CTSLb | GGCTGGCACAGTAGGAAATA | CATTGAATGCTCCAGGTTGTG |
| CTSO | CCTCAGTCAGAGTATCCCTACA | CACTGAAGTCATGTGCAGTAAAG |
| CTSSa | GTGGAAGAAGACACACGAGAAG | AGGTTGTGCATGGTGATGAG |
| CTSSb | CTGGGCACTATGGAAGAAGATG | CCAAGGAGGTTTCCAGGTTATG |
| CTSZa | GGCAGATCGCATCAACATTAAG | GATCTCCTCCATGGCAACTAC |
| CTSZb | GAACCAGCACATCCCTAAGT | CGTGTTGGACGGACAGATAA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, D.; Tao, X.; Cao, M.; Li, C.; Fu, Q. Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary Analysis, and Expression Patterns of Cathepsin Superfamily in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) following Aeromonas salmonicida Infection. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080504
Li Y, Li X, Zhang P, Chen D, Tao X, Cao M, Li C, Fu Q. Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary Analysis, and Expression Patterns of Cathepsin Superfamily in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) following Aeromonas salmonicida Infection. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(8):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080504
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuqing, Xingchun Li, Pei Zhang, Defeng Chen, Xinran Tao, Min Cao, Chao Li, and Qiang Fu. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary Analysis, and Expression Patterns of Cathepsin Superfamily in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) following Aeromonas salmonicida Infection" Marine Drugs 20, no. 8: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080504
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, X., Zhang, P., Chen, D., Tao, X., Cao, M., Li, C., & Fu, Q. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary Analysis, and Expression Patterns of Cathepsin Superfamily in Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) following Aeromonas salmonicida Infection. Marine Drugs, 20(8), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080504






