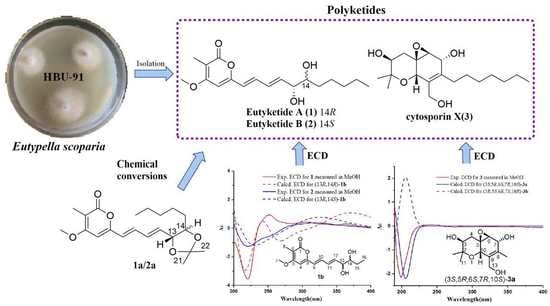
Anti-inflammatory Polyketides from the Marine-Derived Fungus Eutypella scoparia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
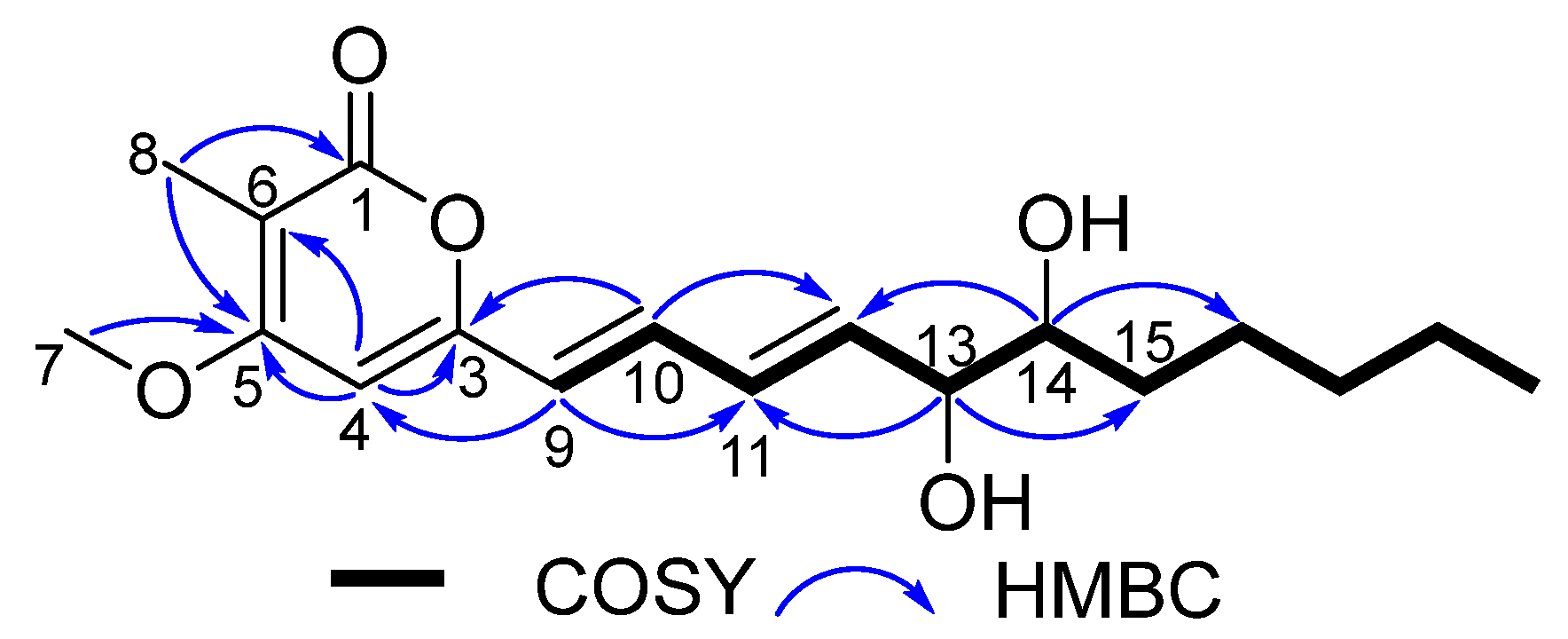
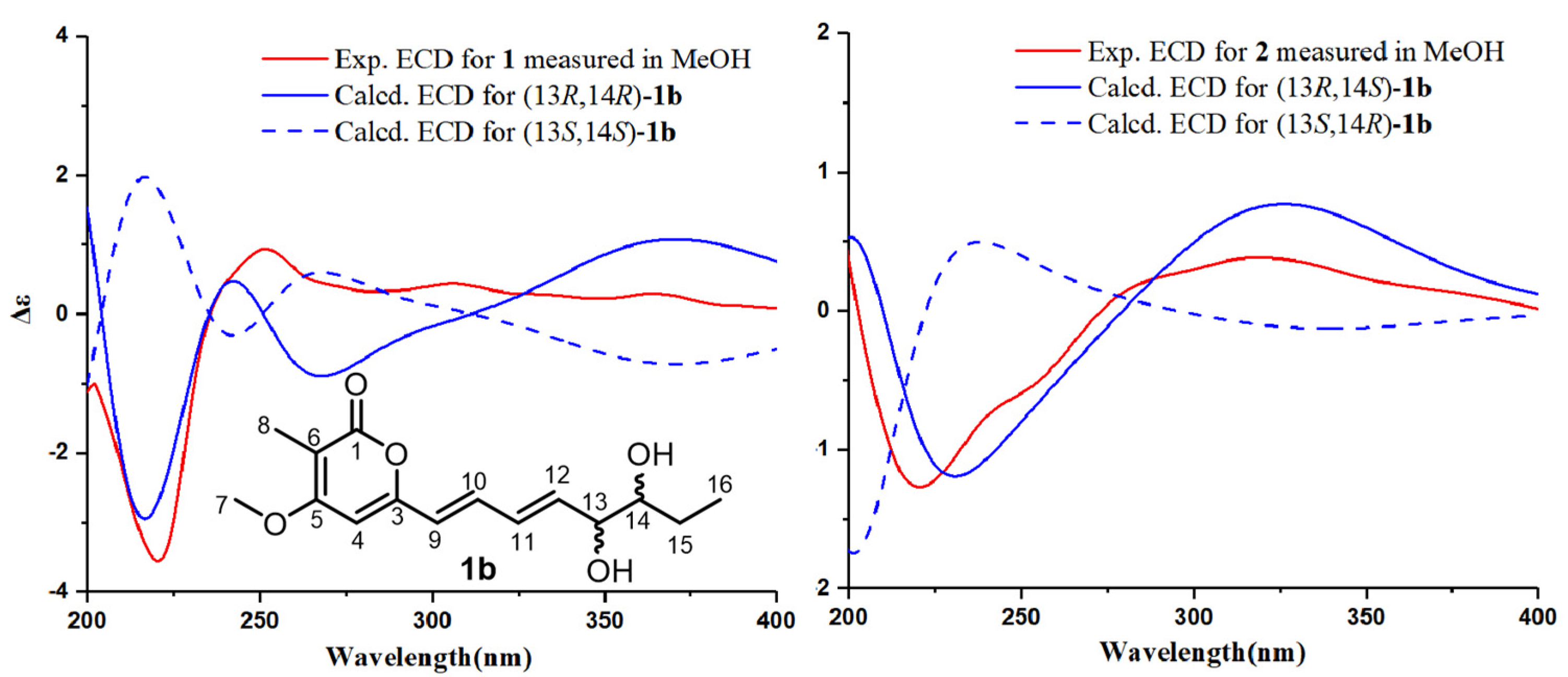
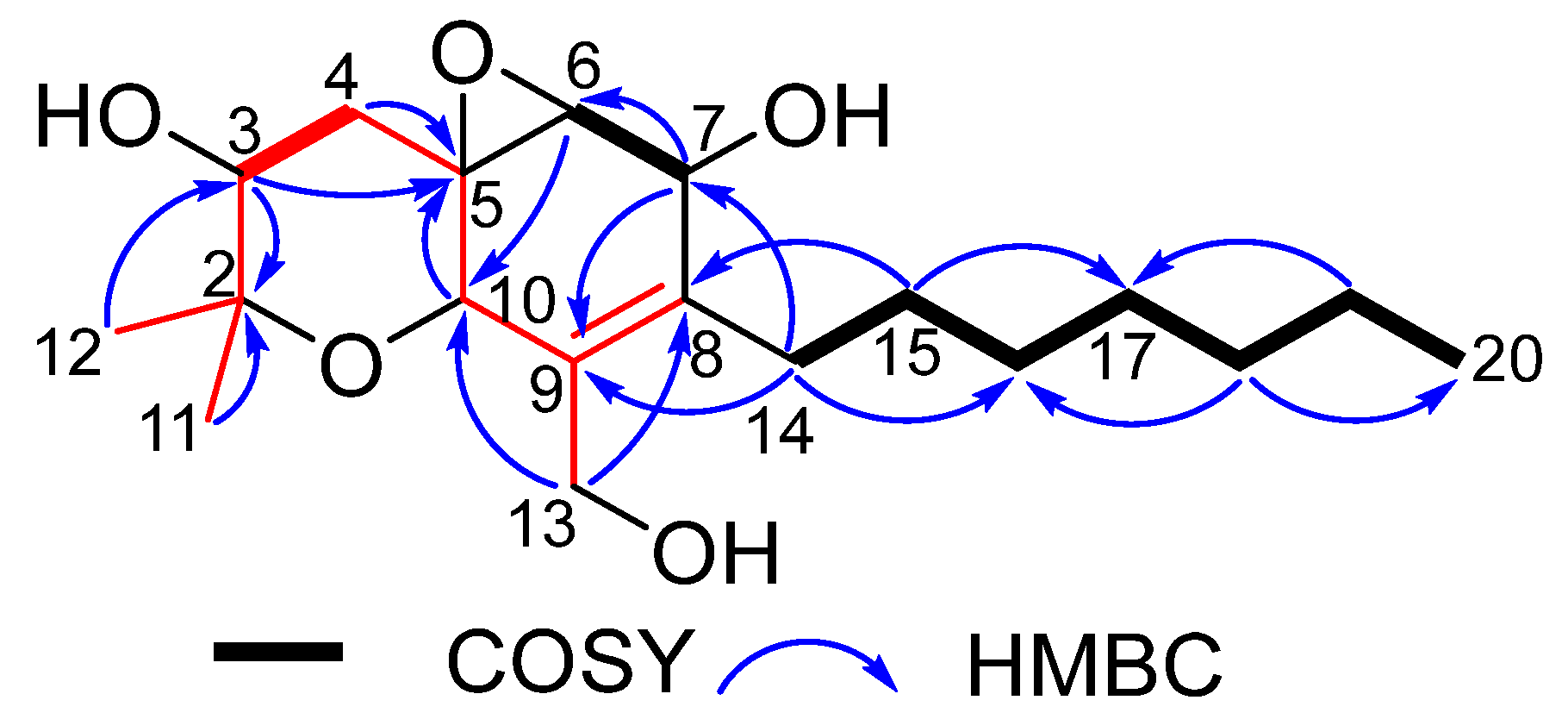
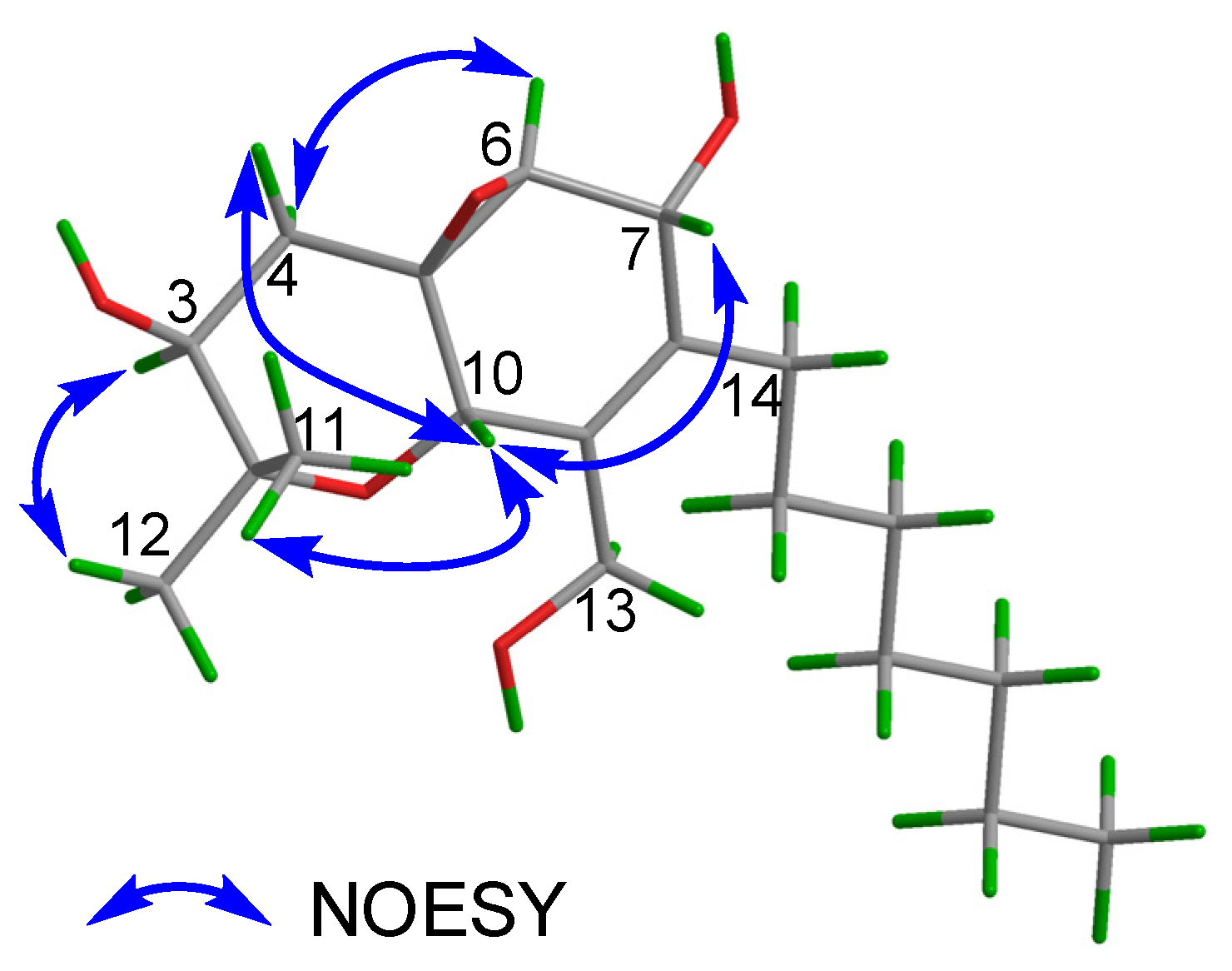
2.1. Structural Elucidation
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Isolation of Fungal Material
3.2.1. Fungal Material
3.2.2. Fermentation and Purification
3.2.3. Acetonide Formation of 1 and 2
3.3. Computational Section
3.4. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
3.5. Inhibition of NO Production Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciavatta, M.L.; Lopez-Gresa, M.P.; Gavagnin, M.; Nicoletti, R.; Manzo, E.; Mollo, E.; Guo, Y.W.; Cimino, G. Cytosporin-related compounds from the marine-derived fungus Eutypella scoparia. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 5365–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergero, R.; Girlanda, M.; Varese, G.C.; Intili, D.; Luppi, A.M. Psychrooligotrophic fungi from arctic soils of Franz Joseph Land. Polar Biol. 1999, 21, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Q. Fungi and associated tree diseases in Melville Island, Northern Territory, Australia. Aust. Syst. Bot. 1996, 9, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Palasarn, S.; Lapanun, S.; Chanthaket, R.; Boonyuen, N.; Lumyong, S. γ-Lactones and ent-eudesmane sesquiterpenes from the endophytic fungus Eutypella sp. BCC 13199. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1720–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongcharoen, W.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Phongpaichit, S.; Rungjindamai, N.; Sakayaroj, J. Pimarane diterpene and cytochalasin derivatives from the endophytic fungus Eutypella scoparia PSU-D44. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongprapan, T.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Saithong, S.; Phongpaichit, S.; Poonsuwan, W.; Sakayaroj, J. Cytotoxic cytochalasins from the endophytic fungus Eutypella scoparia PSU-H267. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 13, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang., L. Manufacture Method and Application of Diaporthein B in Antitumor agents. CN Patent 102168119A, 31 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Tan, G.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Q.; Ye, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, W. Cytotoxic pimarane-type diterpenes from the marine sediment-derived fungus Eutypella sp. FS46. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, D.; Tao, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Dan, F.; Zhang, W. Two new polyketides from a marine sediment-derived fungus Eutypella scoparia FS26. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, D.; Tao, M.; Chen, Y.; Dan, F.; Zhang, W. Scopararanes C–G: New oxygenated pimarane diterpenes from the marine sediment-derived fungus Eutypella scoparia FS26. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, F.; Meng, Z.H.; Mu, X.; Yue, Y.F.; Zhu, H.J. Absolute configuration of bioactive azaphilones from the marine-derived fungus Pleosporales sp. CF09-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Meng, Z.H.; Wang, P.; Luo, D.Q.; Zhu, H.J. Dipleosporalones A and B, dimeric azaphilones from a marine-derived Pleosporales sp. fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Yue, Y.F.; Feng, L.X.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. Asperienes A–D, bioactive sesquiterpenes from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus flavus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.C.; Xu, L.L.; Yang, R.Y.; Yang, M.Y.; Hu, L.D.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. Anti-vibrio indole-diterpenoids and C-25 epimeric steroids from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium janthinellum. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, Z.H.; Sun, T.T.; Zhao, G.Z.; Yue, Y.F.; Chang, Q.H.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. Marine-derived fungi as a source of bioactive indole alkaloids with diversified structures. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Shao, C.L. The intriguing chemistry and biology of sulfur-containing natural products from marine microorganisms (1987–2020). Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 488–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Q.; Xia, J.M.; Xie, C.L.; Luo, Z.H.; Shao, Z.; Liu, G.; Yang, X.W. Polyketides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421 showed potent antifood allergic activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mándi, A.; Kurtán, T. Applications of OR/ECD/VCD to the structure elucidation of natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ding, S.S.; Zhu, A.; Cao, F.; Zhu, H.J. Bioactive azaphilone derivatives from the fungus Talaromyces aculeatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2199–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Katayama, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Ichihara, A. Total synthesis of (−)-solanapyrone a via enzymatic Diels−Alder reaction of prosolanapyrone. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 8748–8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayone, W.C.; Honma, M.; Kanamaru, S.; Noguchi, S.; Tanaka, K.; Nehira, T.; Hashimoto, M. Stereochemical investigations of isochromenones and isobenzofuranones isolated from Leptosphaeria sp. KTC 727. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayone, W.C.; Kanamaru, S.; Honma, M.; Tanaka, K.; Nehira, T.; Hashimoto, M. Absolute stereochemistry of novel isochromanone derivatives from Leptosphaeria sp. KTC 727. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 2390–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Elimat, T.; Raja, H.A.; Figueroa, M.; Falkinham, J.O., III.; Oberlies, N.H. Isochromenones, isobenzofuranone, and tetrahydronaphthalenes produced by Paraphoma radicina, a fungus isolated from a freshwater habitat. Phytochemistry 2014, 104, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn, T.; Schaumlöffel, A.; Hemberger, Y.; Bringmann, G. SpecDis: Quantifying the comparison of calculated and experimental electronic circular dichroism spectra. Chirality 2013, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griess, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite and [15N] in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 165.0, C | - | 165.0, C | - |
| 3 | 157.3, C | - | 157.2, C | - |
| 4 | 96.1, CH | 6.07, s | 96.2, CH | 6.06, s |
| 5 | 165.8, C | - | 165.8, C | - |
| 6 | 103.2, C | - | 103.3, C | - |
| 7 | 56.4, CH3 | 3.87, s | 56.4, CH3 | 3.87, s |
| 8 | 8.9, CH3 | 1.93, s | 9.0, CH3 | 1.93, s |
| 9 | 122.8, CH | 6.08, d (15.0) | 123.0, CH | 6.07, d (15.2) |
| 10 | 134.8, CH | 7.13, dd (15.0, 11.5) | 134.7, CH | 7.13, dd (15.2, 11.1) |
| 11 | 130.8, CH | 6.42, dd (15.0, 11.5) | 130.7, CH | 6.44, dd (15.2, 11.1) |
| 12 | 137.5, CH | 6.05, dd (15.0, 6.0) | 138.7, CH | 6.01, dd (15.2, 6.2) |
| 13 | 75.2, CH | 4.23, dd (6.0, 4.2) | 74.4, CH | 4.05, m |
| 14 | 74.6, CH | 3.72, m | 74.7, CH | 3.51, m |
| 15 | 32.2, CH2 | 1.42, m | 33.2, CH2 | 1.47, m |
| 16 | 25.7, CH2 | 1.31, m; 1.50, m | 25.4, CH2 | 1.48, m |
| 17 | 31.9, CH2 | 1.29, m | 31.9, CH2 | 1.30, m |
| 18 | 22.7, CH2 | 1.30, m | 22.7, CH2 | 1.29, m |
| 19 | 14.1, CH3 | 0.88, t (6.6) | 14.1, CH3 | 0.88, t (6.6) |
| No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 77.2, C | - |
| 3 | 73.5, CH | 3.67, d (12.0) |
| 4 | 35.6, CH2 | 2.23, dd (13.2, 5.4); 1.67, dd (13.2, 5.4) |
| 5 | 56.1, C | - |
| 6 | 60.1, CH | 3.24, d (3.6) |
| 7 | 67.2, CH | 4.26, d (3.6) |
| 8 | 128.3, C | - |
| 9 | 138.1, C | - |
| 10 | 68.6, CH | 4.40, s |
| 11 | 16.3, CH3 | 1.32, s |
| 12 | 28.0, CH3 | 1.30, s |
| 13 | 62.2, CH2 | 4.24, d (12.0); 4.04, d (12.0) |
| 14 | 30.6, CH2 | 2.27, m; 2.16, m |
| 15 | 29.0, CH2 | 1.33, m; 1.42, m |
| 16 | 29.8, CH2 | 1.25, m |
| 17 | 29.2, CH2 | 1.26, m |
| 18 | 31.9, CH2 | 1.24, m |
| 19 | 22.7, CH2 | 1.27, m |
| 20 | 14.2, CH3 | 0.87, t (6.6) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.-H.; Du, H.-F.; Gao, W.-B.; Li, W.; Cao, F.; Wang, C.-Y. Anti-inflammatory Polyketides from the Marine-Derived Fungus Eutypella scoparia. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080486
Zhang Y-H, Du H-F, Gao W-B, Li W, Cao F, Wang C-Y. Anti-inflammatory Polyketides from the Marine-Derived Fungus Eutypella scoparia. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(8):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080486
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ya-Hui, Hui-Fang Du, Wen-Bin Gao, Wan Li, Fei Cao, and Chang-Yun Wang. 2022. "Anti-inflammatory Polyketides from the Marine-Derived Fungus Eutypella scoparia" Marine Drugs 20, no. 8: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080486
APA StyleZhang, Y.-H., Du, H.-F., Gao, W.-B., Li, W., Cao, F., & Wang, C.-Y. (2022). Anti-inflammatory Polyketides from the Marine-Derived Fungus Eutypella scoparia. Marine Drugs, 20(8), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080486