Antiviral Cyclopropane Acids from Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sydowii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Strain, Identification, and Fermentation
3.3. Extraction, Isolation, and Purification
3.4. Anti-Influenza Virus H1N1 Assay
3.5. Cytotoxicity Test
3.6. Computational Method
3.6.1. NMR Calculation of Compound 1
3.6.2. ECD Calculations of Compounds 1–4
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Y.; Gao, X.; Yue, J. Attractive natural products with strained cyclopropane and/or cyclobutane ring systems. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Mandalapu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q. Biosynthesis of cyclopropane in natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 926–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackmann, F.; de Meijere, A. Natural occurrence, syntheses, and applications of cyclopropyl-group-containing α-amino acids. 2. 3,4- and 4,5-methanoamino acids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4538–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Y.; Shi, J. A minor diterpenoid with a new 6/5/7/3 fused-ring skeleton from Euphorbia micractina. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3950–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Lei, C.; Xiao, W.; Yang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, H. Isolation and characterization of biogenetically related highly oxygenated nortriterpenoids from Schisandra chinensis. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 2079–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, K.; Abe, T.; Arai, D.; Okamoto, M.; Shimizu, I.; de Voogd, N.J.; Fusetani, N.; Nakao, Y. Cinanthrenol A, an estrogenic steroid containing phenanthrene nucleus, from a marine sponge Cinachyrella sp. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 1539–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, E.V.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Andriyashenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Aminin, D.L.; Stonik, V.A. Phrygiasterol, a cytotoxic cyclopropane-containing polyhydroxysteroid, and related compounds from the Pacific starfish Hippasteria phrygiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, B.-W.; Tsai, Y.-Y.; Shih, S.-P.; Hwang, T.-L.; Dai, C.-F.; Wang, S.-Y.; Sheu, J.-H. New bioactive steroids from the soft coral Klyxum flaccidum. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12546–12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Teng, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, G.; Zhu, W. New quinazolinone alkaloids within rare amino acid residue from coral-associated fungus, Aspergillus versicolor LCJ-5-4. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kariya, R.; Seo, T.; Minami, A.; Oikawa, H. Biosynthesis of the structurally unique polycyclopropanated polyketide–nucleoside hybrid jawsamycin (FR-900848). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5423–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Chinthanom, P.; Veeranondha, S.; Supothina, S.; Luangsa-ard, J.J. Novel cyclopropyl diketones and 14-membered macrolides from the soil fungus Hamigera avellanea BCC 17816. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 11028–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.H.; Lee, Y.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J. Bioactive lipids from the sponge Spirastrella abata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, L.J.; Buck, J.P.; Tremblay, A.E.; Buist, P.H. Configurational analysis of cyclopropyl fatty acids isolated from Escherichia coli. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, L.J.; Buist, P.H. The absolute configuration of methyl dihydrosterculate: An unusual phytofatty acid isolated from the seed oil of Litchi chinensis. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2004, 15, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Tashiro, T.; Akasaka, K.; Ohrui, H.; Fattorusso, E. Determination of the absolute configuration at the two cyclopropane moieties of plakoside A, an immunosuppressive marine galactosphingolipid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 3719–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.A.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, I.-S.; Sung, C.K.; Hong, J.; Sim, C.J.; Im, K.S.; Jung, J.H. Lyso-PAF analogues and lysophosphatidylcholines from the marine sponge Spirastrella abata as inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1554–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starratt, A.N.; Caveney, S. Four cyclopropane amino acids from Ephedra. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rijke, D.; Ter Heide, R.; Boelens, H. New compounds with small rings in essential oils. Perfum. Flavor. 1982, 7, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Liu, D.; Hu, X.; Proksch, P.; Shao, Z.; Lin, W. Spiromastixones A−O, antibacterial chlorodepsidones from a deep-sea-derived Spiromastix sp. fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Fan, Z.; Xie, C.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Z.; Liu, G.; Yang, X. Spirograterpene A, a tetracyclic spiro-diterpene with a fused 5/5/5/5 ring system from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium granulatum MCCC 3A00475. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2174–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, D.; Shao, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Eremophilane-type sesquiterpenoids in a deep-sea fungus Eutypella sp. activated by chemical epigenetic manipulation. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 7310–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Xia, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Yi, Z.; Xie, C.; Peng, G.; Luo, Z.; Shao, Z.; Yang, X. Aphidicolin chemistry of the deep-sea-derived fungus Botryotinia fuckeliana MCCC 3A00494. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2307–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Xie, C.; Xia, J.; Liu, Q.; Peng, G.; Liu, G.; Yang, X. Botryotins A–H, tetracyclic diterpenoids representing three carbon skeletons from a deep-sea-derived Botryotinia fuckeliana. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, G.; Chen, T.; Hong, B.; Pei, S.; Shao, Z. Phenolic bisabolane and cuparene sesquiterpenoids with anti-inflammatory activities from the deep-sea-derived Aspergillus sydowii MCCC 3A00324 fungus. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 105, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, T.; Hong, B.; Pei, S.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, G. New monoterpenoids and polyketides from the deep-sea sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii MCCC 3A00324. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Chen, Z.; Pei, S.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Hong, B. Acremolin D, a new acremolin alkaloid from the deep-sea sediment derived Aspergillus sydowii fungus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Grimblat, N.; Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Beyond DP4: An improved probability for the stereochemical assignment of isomeric compounds using quantum chemical calculations of NMR shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Nam, M.; Hwang, G.-S.; Ryu, D.H. Enantioselective cyclopropanation with α-alkyl-α-diazoesters catalyzed by chiral oxazaborolidinium ion: Total synthesis of (+)-hamavellone B. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Si, L.; Liu, D.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, D.; Lin, W. Spiromastilactones: A new class of influenza virus inhibitors from deep-sea fungus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 108, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhn, T.; Schaumlöffel, A.; Hemberger, Y.; Pescitelli, G. Pescitelli, SpecDis Version 1.71, Berlin, Germany. 2017. Available online: http:/specdis-software.jimdo.com (accessed on 17 July 2020).
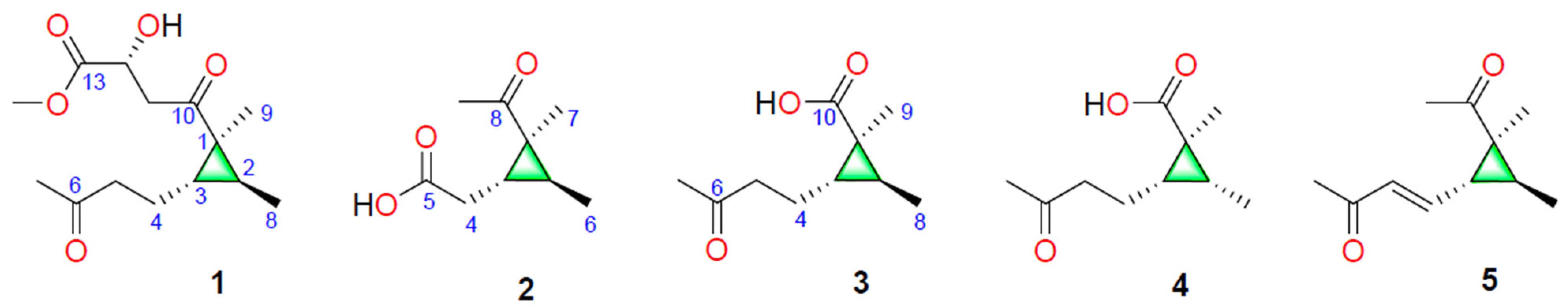
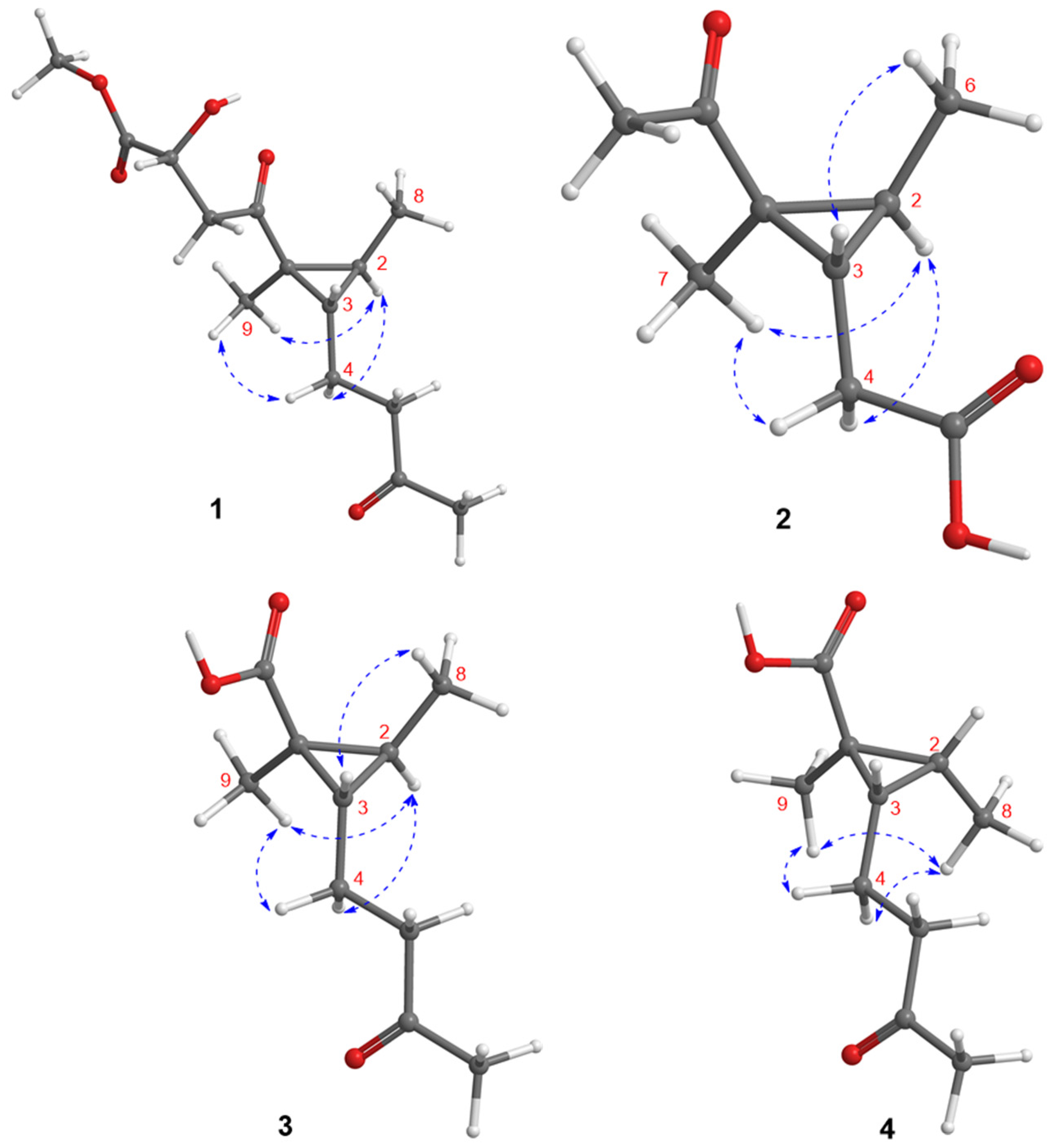
 ) and key HMBC (
) and key HMBC (  ) correlations of 1–3.
) correlations of 1–3.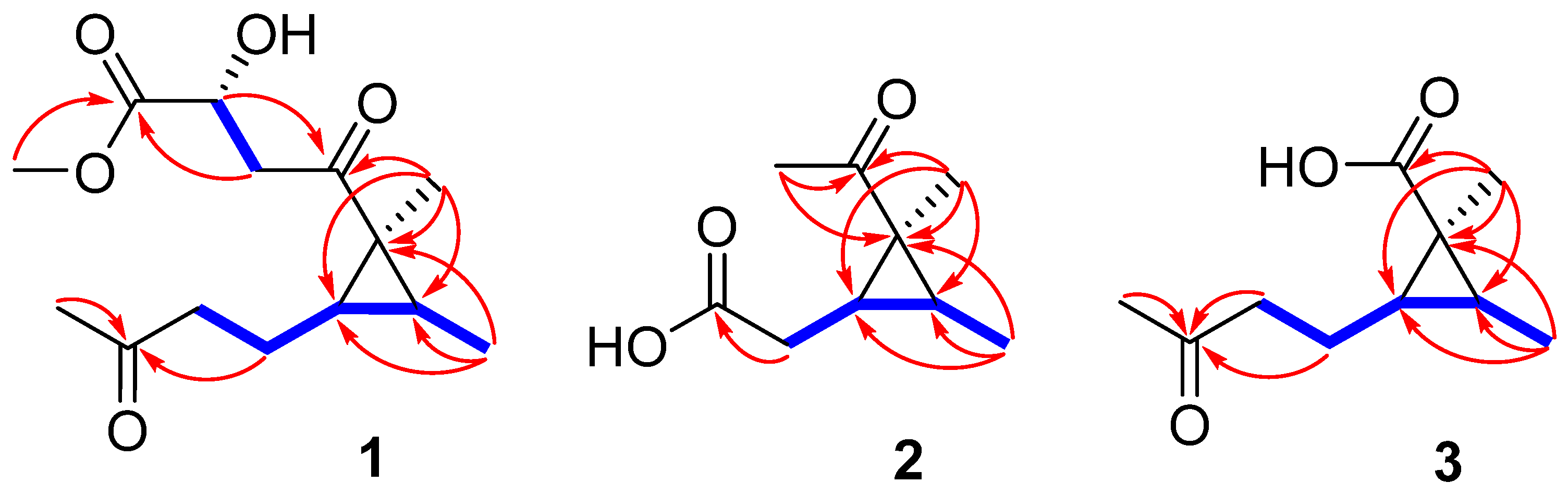
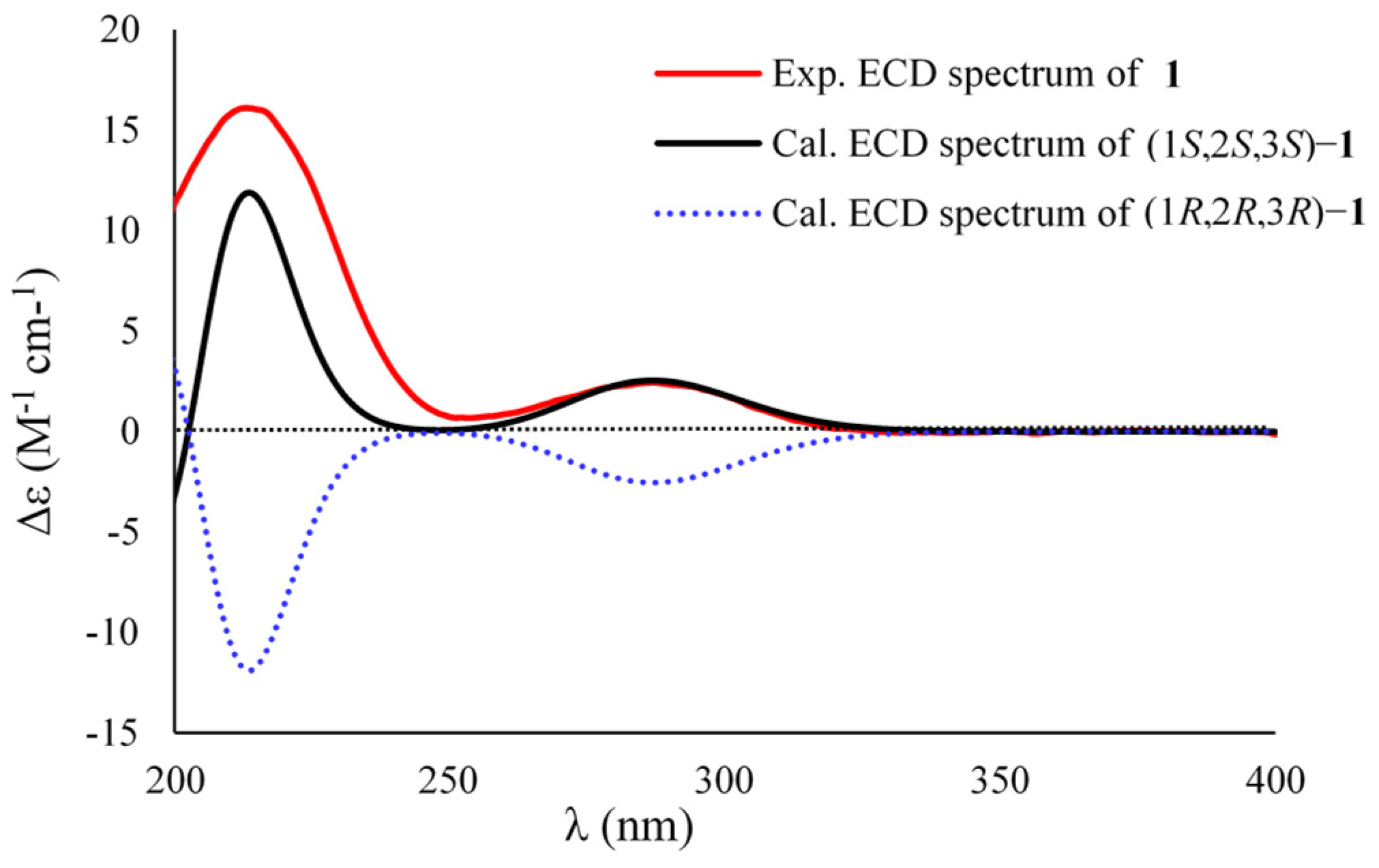
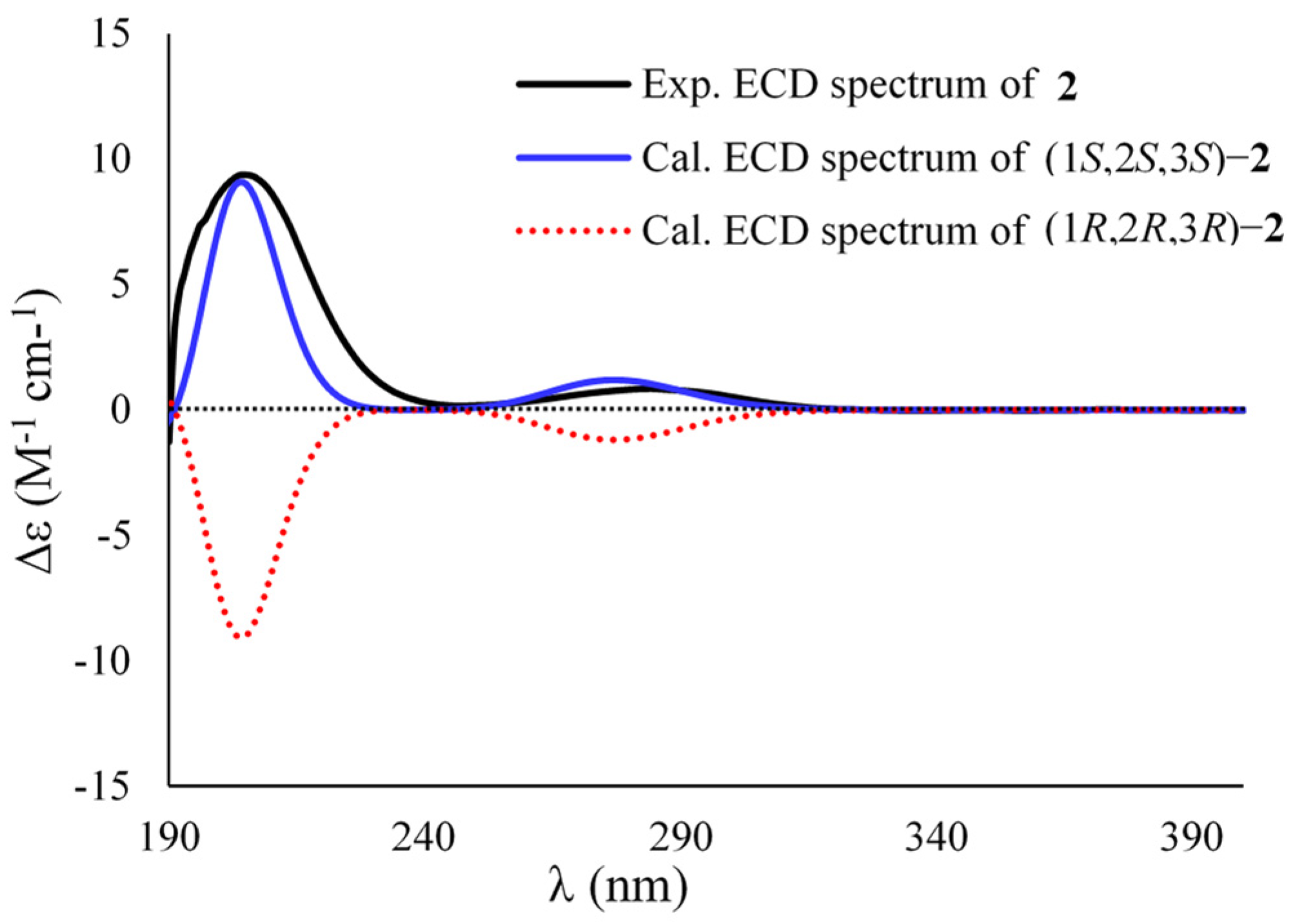

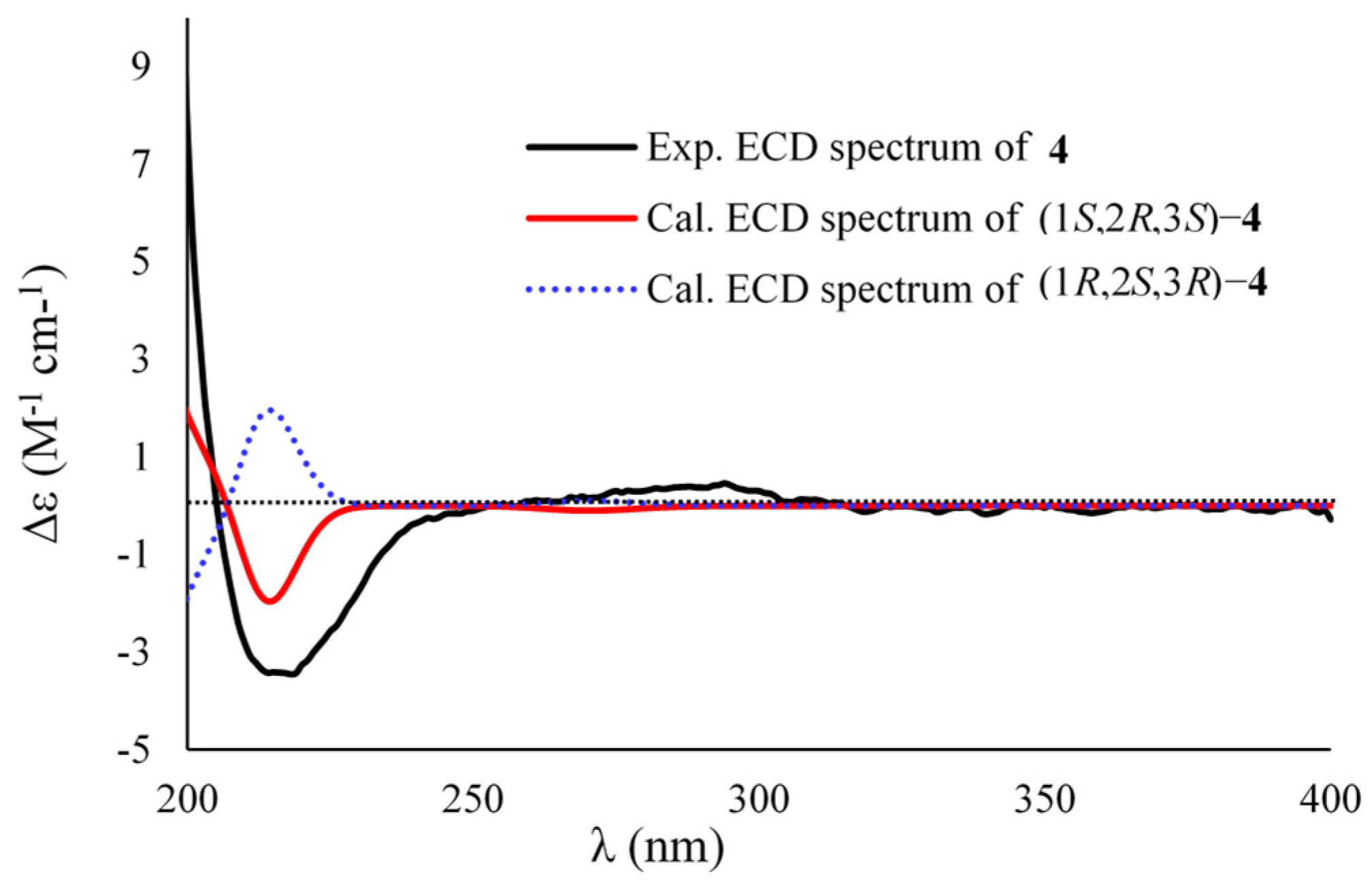
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.93, m | 0.99, m | 0.81, m | 1.53, m |
| 3 | 1.51, q (7.1) | 1.81, q (7.2) | 1.36, q (7.1) | 1.43, dt (9.5, 7.3) |
| 4 | 1.64, m | 2.46, dd (16.7, 7.3); 2.35, dd (16.7, 7.7) | 1.65, m | 1.59, m |
| 5 | 2.57, t (7.4) | 2.60, t (7.3) | 2.58, t (7.5) | |
| 6 | 1.04, d (5.6) | |||
| 7 | 2.16, s | 1.43, s | 2.17, s | 2.17, s |
| 8 | 0.98, d (5.8) | 1.16, d (6.2) | 1.03, d (6.5) | |
| 9 | 1.43, s | 2.27, s | 1.28, s | 1.15, s |
| 11 | 3.14, dd (17.8, 4.3); 2.99, dd (17.8, 6.6) | |||
| 12 | 4.51, dd (6.6, 4.3) | |||
| OCH3 | 3.73, s |
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 36.9, C | 36.5, C | 29.2, C | 25.5, C |
| 2 | 34.9, CH | 33.9, CH | 31.5, CH | 24.3, CH |
| 3 | 33.0, CH | 29.2, CH | 32.8, CH | 29.7, CH |
| 4 | 24.1, CH2 | 34.4, CH2 | 24.1, CH2 | 18.7, CH2 |
| 5 | 44.0, CH2 | 176.6, C | 44.0, CH2 | 43.7, CH2 |
| 6 | 211.5, C | 12.0, CH3 | 211.5, C | 211.3, C |
| 7 | 30.0, CH3 | 16.5, CH3 | 29.9, CH3 | 29.9, CH3 |
| 8 | 12.3, CH3 | 211.2, C | 13.0, CH3 | 7.8, CH3 |
| 9 | 15.6, CH3 | 29.6, CH3 | 15.7, CH3 | 8.7, CH3 |
| 10 | 209.1, C | 178.1, C | 180.7, C | |
| 11 | 46.2, CH2 | |||
| 12 | 67.9, CH | |||
| 13 | 175.9, C | |||
| OCH3 | 52.6, CH3 |
| Compounds | IC50 (μM) | CC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26.7 ± 0.9 | >100 |
| 2 | 29.5 ± 1.4 | >100 |
| 3 | 77.2 ± 0.5 | >100 |
| 4 | 66.4 ± 1.7 | >100 |
| 5 | 35.8 ± 3.2 | >100 |
| OSV | 18.1 ± 1.2 | >100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, S.; Huang, S.; Hong, B.; Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, G. Antiviral Cyclopropane Acids from Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sydowii. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070410
Niu S, Huang S, Hong B, Huang Q, Liu X, Shao Z, Zhang G. Antiviral Cyclopropane Acids from Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sydowii. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(7):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070410
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Siwen, Shuhuan Huang, Bihong Hong, Qixi Huang, Xiupian Liu, Zongze Shao, and Gaiyun Zhang. 2022. "Antiviral Cyclopropane Acids from Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sydowii" Marine Drugs 20, no. 7: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070410
APA StyleNiu, S., Huang, S., Hong, B., Huang, Q., Liu, X., Shao, Z., & Zhang, G. (2022). Antiviral Cyclopropane Acids from Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sydowii. Marine Drugs, 20(7), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20070410







