Comparison of Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Acid-Soluble and Pepsin-Soluble Collagens from Blacktip Reef Shark Skin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
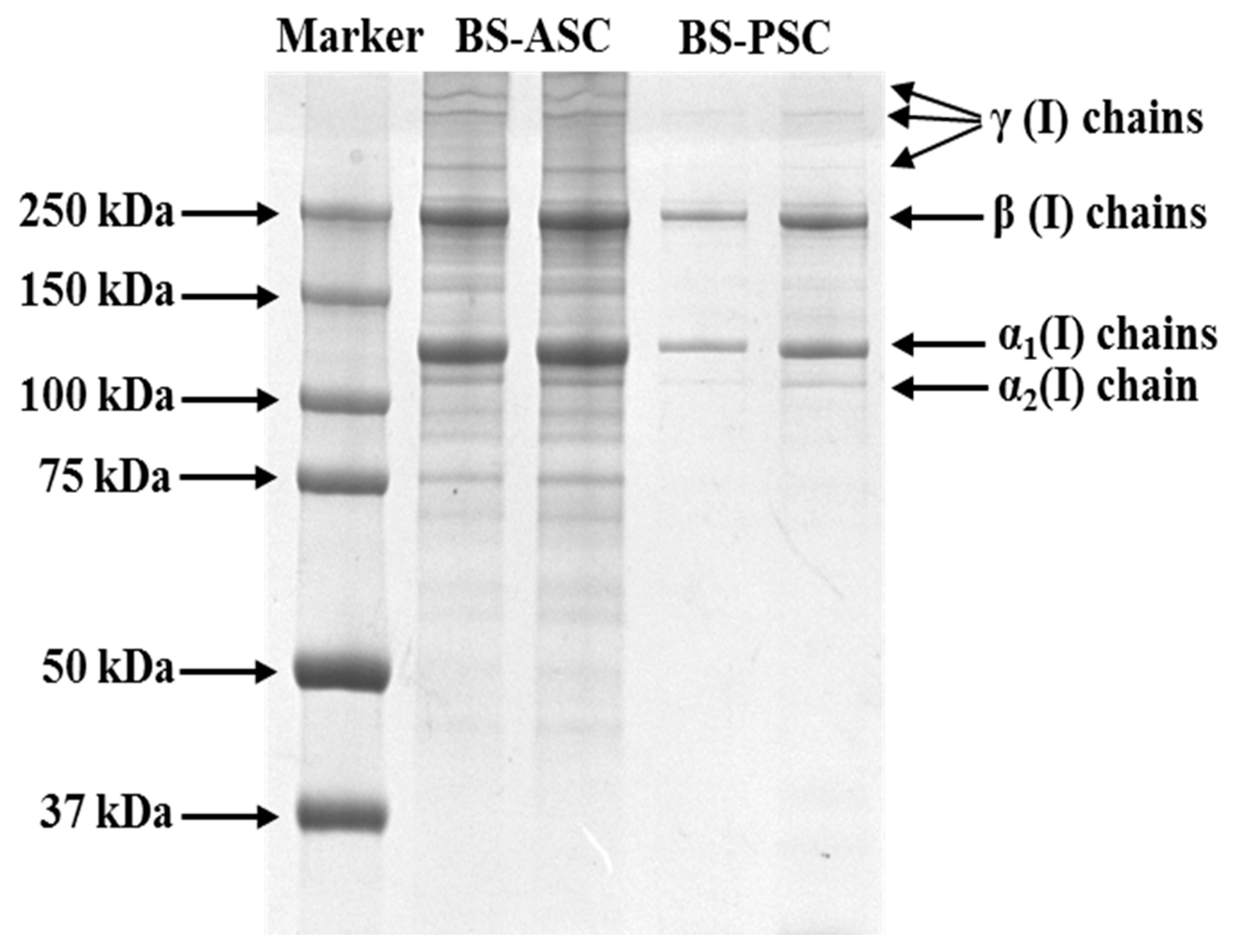
2.1. Protein Pattern of Collagens
2.2. Amino Acid Composition of Collagens
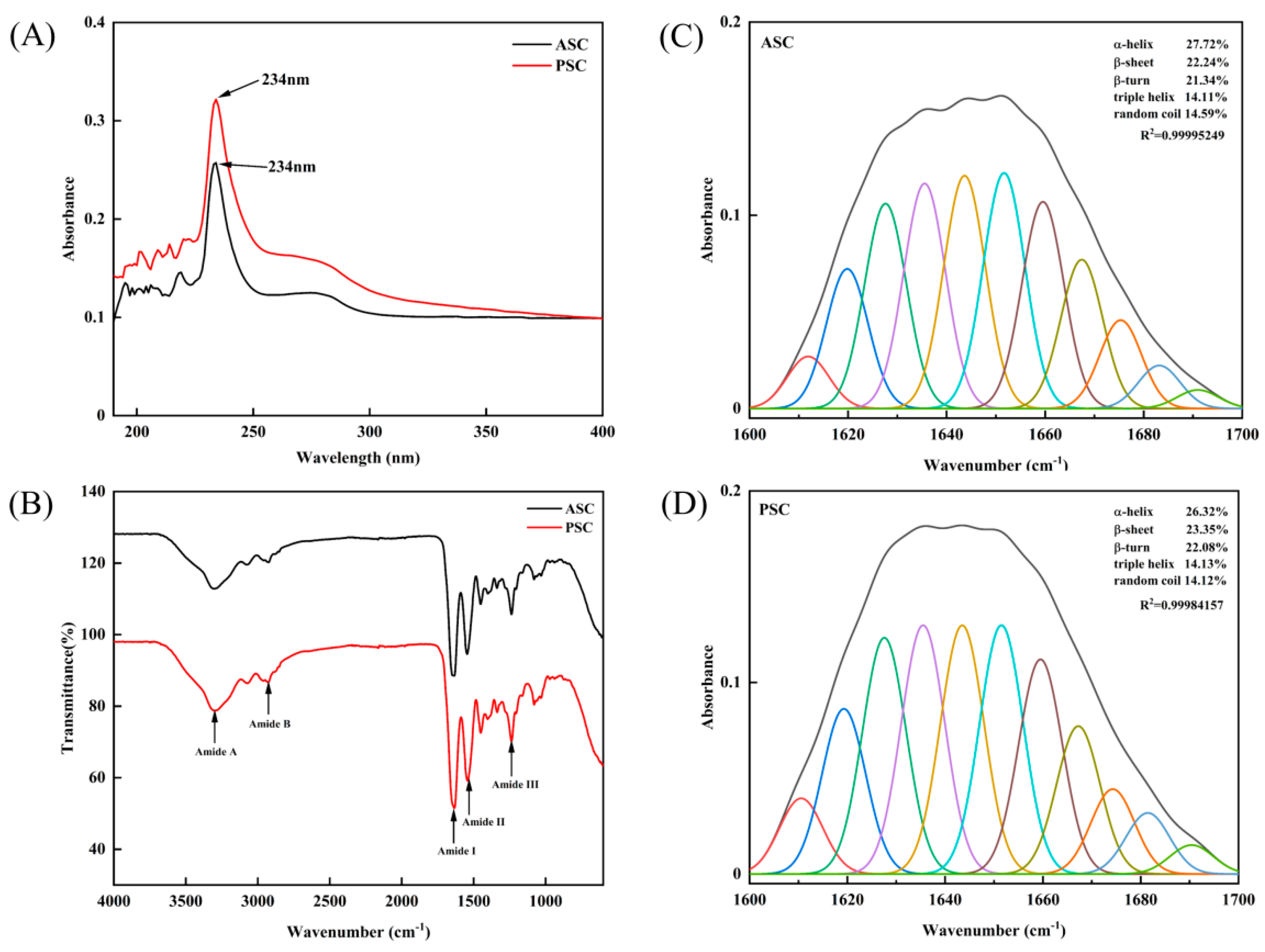
2.3. Maximum Absorption of Collagens
2.4. Secondary Structure Analysis
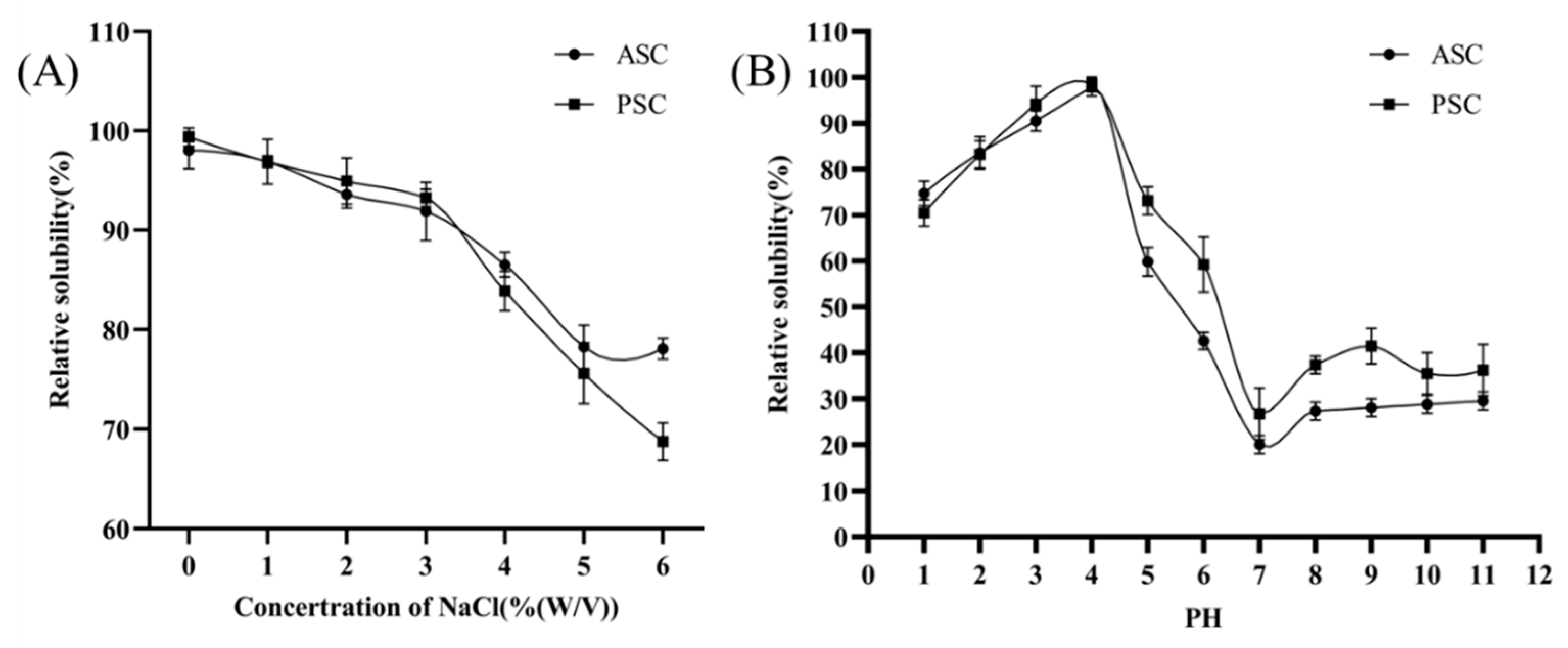
2.5. Solubility against pH and Salt
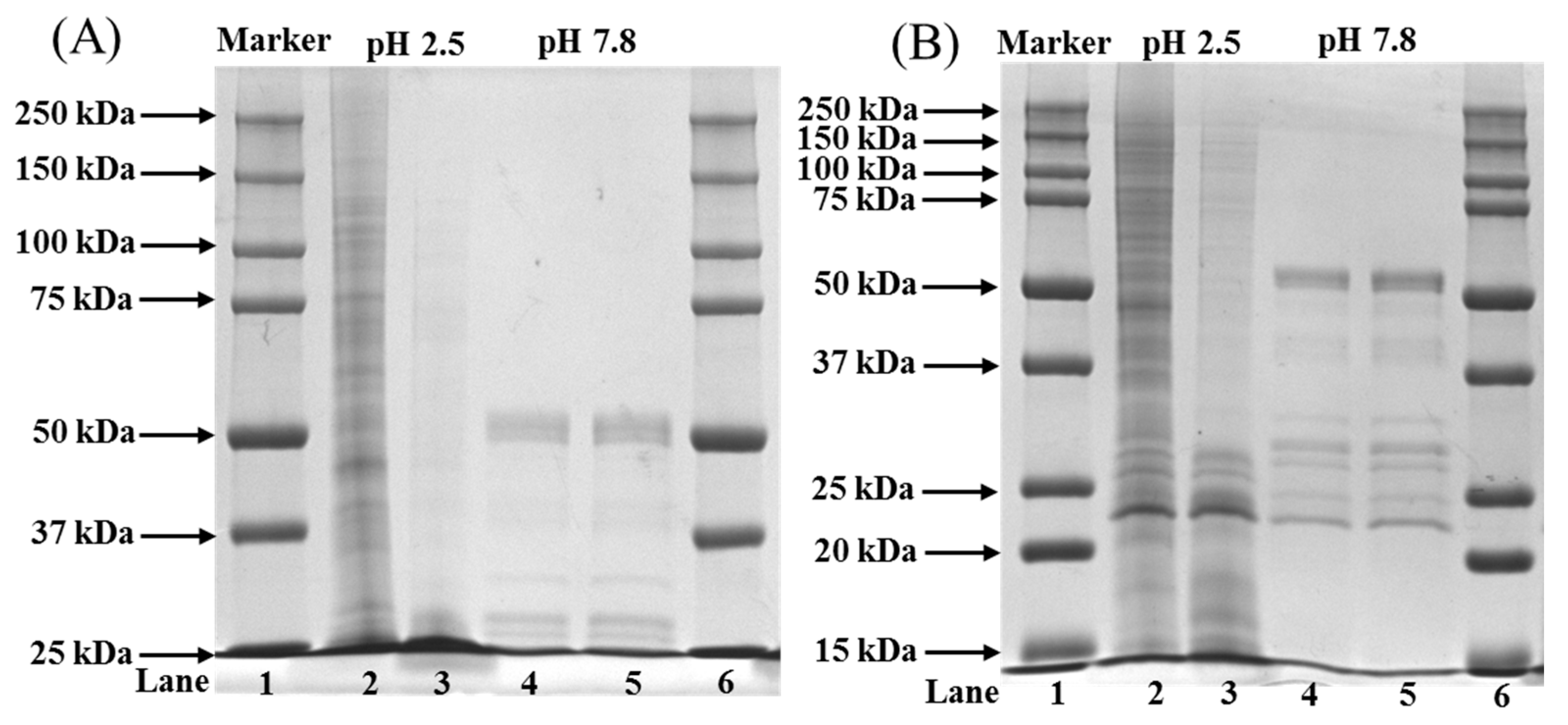
2.6. Peptide Mapping
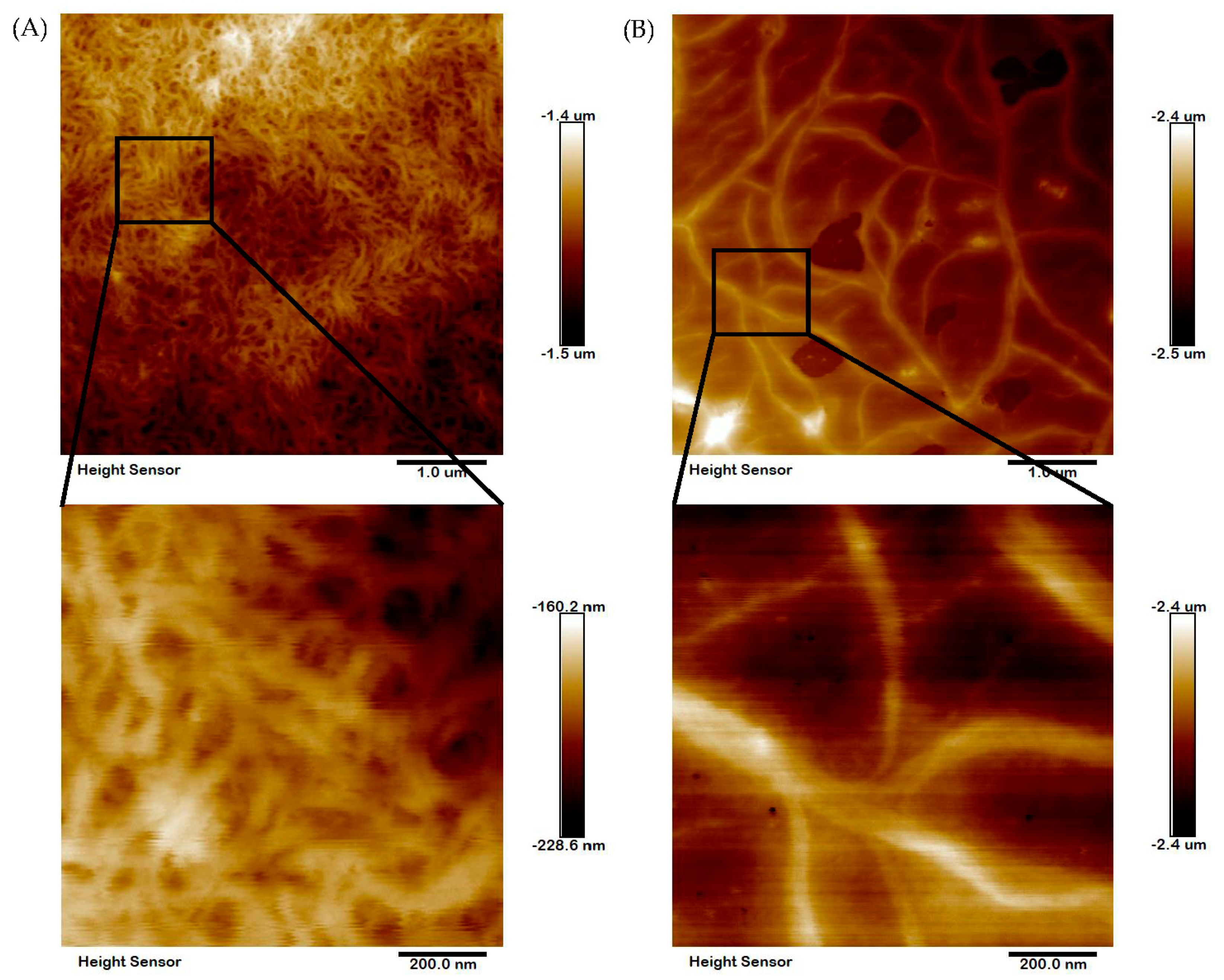
2.7. Microstructural Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
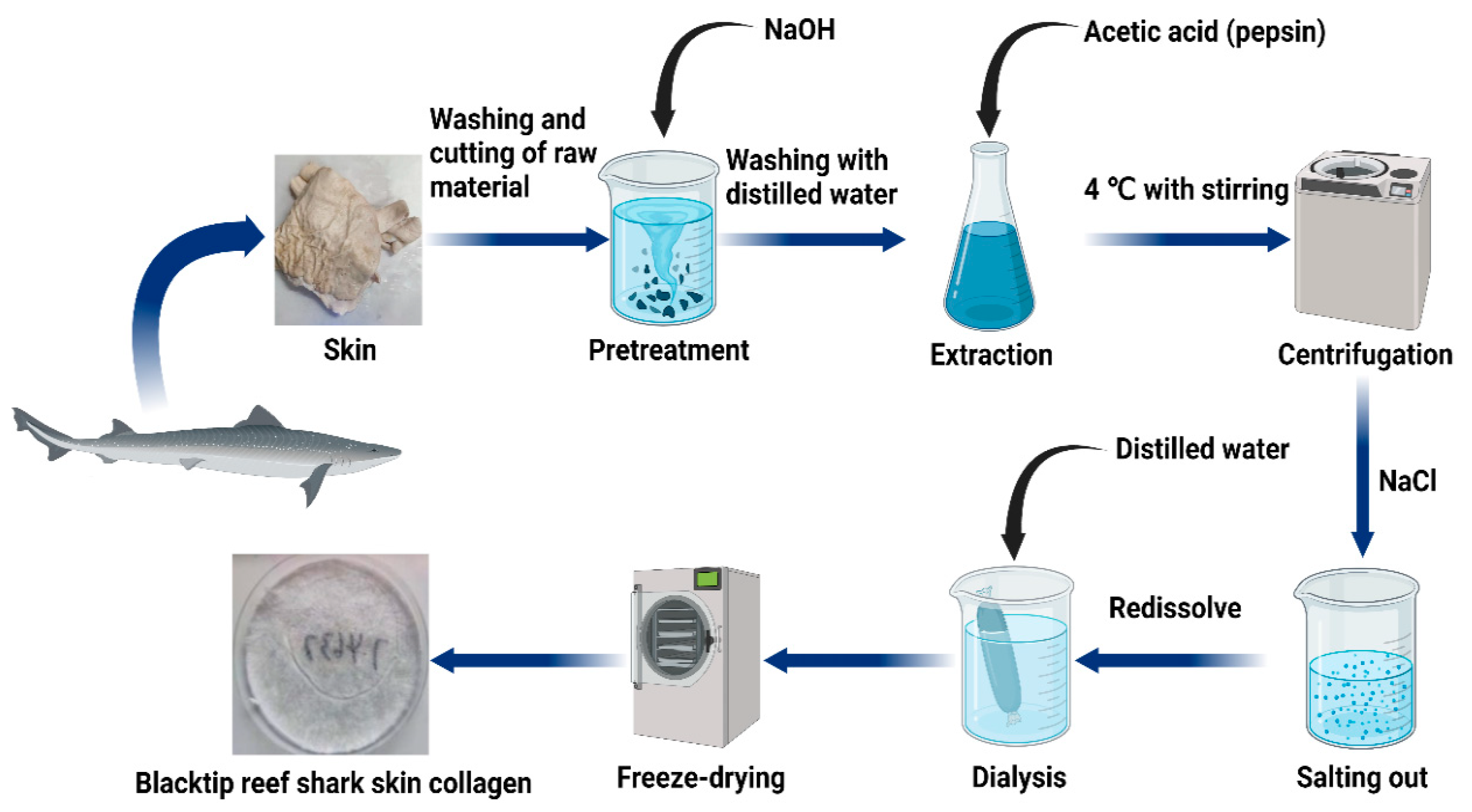
4.2. Raw Materials and Pre-Treatment
4.3. Preparation of Acid-Soluble and Pepsin-Soluble Collagen
4.4. Molecular Pattern
4.5. Amino Acid Composition
4.6. UV Absorption
4.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.8. Relative Solubility
4.8.1. Effect of pH
4.8.2. Effect of NaCl
4.9. Peptide Mapping
4.10. Microstructural Analysis
4.11. Atomic Force Microscope Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jafari, H.; Lista, A.; Siekapen, M.M.; Ghaffari-Bohlouli, P.; Nie, L.; Alimoradi, H.; Shavandi, A. Fish Collagen: Extraction, Characterization and Applications for Biomaterials Engineering. Polymers 2020, 12, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A. Collagen of Extracellular Matrix from Marine Invertebrates and Its Medical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, Y.-S.; Ok, Y.-J.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Kwak, J.-Y.; Yoon, S. Marine Collagen as a Promising Biomaterial for Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Jeevithan, E.; Bao, B.; Wang, S.; Gao, K.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W. Structural characterization, in-vivo acute systemic toxicity assessment and in-vitro intestinal absorption properties of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin acid and pepsin solublilized type I collagen. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-S.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhou, D.-Q. Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics and Fibril Formation Ability of Collagens Extracted from the Skin of Farmed River Puffer (Takifugu obscurus) and Tiger Puffer (Takifugu rubripes). Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhuimbar, M.V.; Bhagwat, P.K.; Dandge, P.B. Extraction and characterization of acid soluble collagen from fish waste: Development of collagen-chitosan blend as food packaging film. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, H.; Putriani, S.; Safithri, M.; Tarman, K. Isolation and allergenicity of protein collagen from parang-parang fish skin (Cirocentrus dorab). In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Food and Agriculture (ICoFA), Bali, Indonesia, 2–3 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, M.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Qin, S.; Wu, W. Extraction and characterization of type I collagen from skin of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and its potential application in biomedical scaffold material for tissue engineering. Process Biochem. 2018, 74, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Kodama, Y.; Miwa, K.; Kishimoto, K.; Hoshikawa, E.; Haga, K.; Sato, T.; Mizuno, J.; Izumi, K. Manufacturing micropatterned collagen scaffolds with chemical-crosslinking for development of biomimetic tissue-engineered oral mucosa. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, G.; Kuttalam, I.; Mukundan, S.; Lonchin, S. Valorization of toxic discarded fish skin for biomedical application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 323, 129147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika Rajasree, S.R.; Gobalakrishnan, M.; Aranganathan, L.; Karthih, M.G. Fabrication and characterization of chitosan based collagen/gelatin composite scaffolds from big eye snapper Priacanthus hamrur skin for antimicrobial and anti-oxidant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurilmala, M.; Suryamarevita, H.; Hizbullah, H.H.; Jacoeb, A.M.; Ochiai, Y. Fish skin as a biomaterial for halal collagen and gelatin. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Peng, X.-L.; Li, H.-R.; Liu, J.-X.; Cheng, J.-S.-Y.; Qi, X.-Y.; Ye, S.-J.; Gong, H.-L.; Zhao, X.-H.; Yu, J.; et al. Marine-Derived Collagen as Biomaterials for Human Health. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the cartilages of brownbanded bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium punctatum) and blacktip shark (Carcharhinus limbatus). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kishimura, H.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and Characterisation of collagen from the skin of brownbanded bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium punctatum). Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, B.B.; Bendit, E.G.; Blout, E.R. Infrared spectroscopy of collagen and collagen-like polypeptides. Biopolymers 1975, 14, 937–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Krimm, S. Normal vibrations of crystalline polyglycine I. Biopolymers 1972, 11, 1817–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Characterisation of acid soluble collagen from skins of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 85, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Choo, L.P.; Watson, P.H.; Halliday, W.C.; Mantsch, H.H. Beware of Connective Tissue Proteins: Assignment and Implications of Collagen Absorptions in Infrared Spectra of Human Tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 1995, 1270, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Moody, M.W.; Portier, R.J.; Bell, J.; Schexnayder, M.A.; Losso, J.N. Biochemical properties of black drum and sheepshead seabream skin collagen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 8088–8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Xue, C.; Chang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Collagen fibrils of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) are heterotypic. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalinanon, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H.; Osako, K. Type I collagen from the skin of ornate threadfin bream (Nemipterus hexodon): Characteristics and effect of pepsin hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reategui-Pinedo, N.; Salirrosas, D.; Sanchez-Tuesta, L.; Quinones, C.; Jauregui-Rosas, S.R.; Barraza, G.; Cabrera, A.; Ayala-Jara, C.; Martinez, R.M.; Baby, A.R.; et al. Characterization of Collagen from Three Genetic Lines (Gray, Red and F1) of Oreochromis niloticus (Tilapia) Skin in Young and Old Adults. Molecules 2022, 27, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Yi, R.; Xu, N.; Gao, R.; Hong, B. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble collagen from scales and skin of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petibois, C.; Gouspillou, G.; Wehbe, K.; Delage, J.-P.; Deleris, G. Analysis of type I and IV collagens by FT-IR spectroscopy and imaging for a molecular investigation of skeletal muscle connective tissue. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic study of acid soluble collagen and gelatin from skins and bones of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 86, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Z.; Wen, H.; Hong, B.; Lin, R.; Chen, W.; Xie, Q.; Le, Q.; Yi, R.; Wu, H. Compositional and structural characteristics of pepsin-soluble type I collagen from the scales of red drum fish, Sciaenops ocellatus. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha, R.; Ramasami, T. Influence of hydrogen bond, hydrophobic and electrovalent salt linkages on the transition temperature, enthalpy and activation energy in rat tail tendon (RTT) collagen fibre. Thermochim. Acta 1999, 338, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highberger, J.H. The isoelectric point of collagen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1939, 61, 2302–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, A.D.; Davis, S. Modelling charge across pH and the isoelectric point of bovine collagen during leather manufacture. In Proceedings of the IULTCS Congress 2019: “Benign by Design”-Leather, the Future through Science and Technology, Dresden, Germany, 25–28 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-R.; Wang, B.; Chi, C.-f.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Gong, Y.-d.; Tang, J.-J.; Luo, H.-y.; Ding, G.-f. Isolation and characterization of acid soluble collagens and pepsin soluble collagens from the skin and bone of Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorous niphonius). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, M.Z.; Karim, A.A.; Ahmed, F.; Latiff, A.A.; Gan, C.-Y.; Ghazali, F.C.; Sarker, M.Z.I. Isolation and characterization of pepsin-solubilized collagen from the integument of sea cucumber (Stichopus vastus). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeruraj, A.; Arumugam, M.; Ajithkumar, T.; Balasubramanian, T. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the outer skin of squid (Doryteuthis singhalensis). Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongjareonrak, A.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Tanaka, M. Isolation and characterization of collagen from bigeye snapper (Priacanthus macracanthus) skin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, S.; Yamada, Y.; Miyagi, T.; Yoshinaka, R. Histological changes in collagen related to textural development of prawn meat during heat processing. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.-x.; Xue, C.-h.; Li, Z.-j.; Zhang, Y.-q.; Dong, P.; Fu, X.-y.; Gao, X. Characterization and subunit composition of collagen from the body wall of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Li, G. Isolation and characterisation of collagens from the skin of largefin longbarbel catfish (Mystus macropterus). Food Chem. 2009, 115, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, J.; Lee, J.W.; Wang, S.; Henrotin, Y.; Mate Sanchez de Val, J.E.; Regenstein, J.M.; Lim, S.Y.; Bao, B.; Wu, W. Evaluation of Differentiated Bone Cells Proliferation by Blue Shark Skin Collagen via Biochemical for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevithan, E.; Wu, W.; Wang, N.; Lan, H.; Bao, B. Isolation, purification and characterization of pepsin soluble collagen isolated from silvertip shark (Carcharhinus albimarginatus) skeletal and head bone. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Bi, C.; Ding, M.; Xie, J.; Xu, C.; Qiao, R.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Polymorphism and stability of nanostructures of three types of collagens from bovine flexor tendon, rat tail, and tilapia skin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Amino Acid | Acid Soluble Collagen | Pepsin Soluble Collagen |
|---|---|---|
| Leucine (Leu) | 23.24 ± 0.13 a | 20.52 ± 0.41 b |
| Isoleucine (Ile) | 18.05 ± 0.70 a | 17.24 ± 0.01 b |
| Phenylalanine (Phe) | 11.07 ± 0.34 a | 10.73 ± 0.16 a |
| Valine (Val) | 21.53 ± 1.04 a | 19.45 ± 0.09 b |
| Methionine (Met) | 3.37 ± 0.16 a | 3.21 ± 0.15 a |
| Tyrosine (Tyr) | 1.69 ± 0.32 a | 1.06 ± 0.14 b |
| Alanine (Ala) | 103.94 ± 0.07 a | 105.04 ± 0.05 b |
| Threonine (Thr) | 20.46 ± 0.53 a | 19.91 ± 0.27 b |
| Glutamic acid (Glu) | 66.63 ± 0.29 a | 64.74 ± 0.06 b |
| Glycine (Gly) | 292.95 ± 0.46 a | 283.86 ± 0.19 b |
| Serine (Ser) | 38.49 ± 0.15 a | 36.22 ± 0.15 b |
| Aspartic acid (Asp) | 38.30 ± 0.28 a | 36.43 ± 0.10 b |
| Arginine (Arg) | 43.86 ± 0.2 a | 43.00 ± 0.15 b |
| Lysine (Lys) | 21.13 ± 0.54 a | 20.41 ± 0.34 b |
| Histidine (His) | 7.14 ± 0.32 a | 6.50 ± 0.20 b |
| Proline (Pro) | 195.84 ± 0.47 a | 202.22 ± 0.37 b |
| Hydroxyproline (Hyp) | 92.3 ± 0.16 a | 109.46 ± 0.13 b |
| Total | 1000.00 | 1000.00 |
| Imino acid | 288.14 ± 0.31 a | 311.68 ± 0.24 b |
| Region | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignment | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASC | PSC | |||
| Amide A | 3298 | 3298 | N-H stretch | Doyle et al. [16] |
| Amide B | 2926 | 2930 | CH2 asymmetrical stretch | Abe and Krimm [17] |
| Amide I | 1639 | 1639 | C=O stretch | Muyonga et al. [18] |
| Amide II | 1542 | 1546 | N-H bend coupled with C-N stretch | Jackson et al. [19] |
| Amide III | 1237 | 1237 | N-H in-plane bend | Jackson et al. [19] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, B.; Hou, C.; Bao, B.; Pan, Z.; de Val, J.E.M.S.; Elango, J.; Wu, W. Comparison of Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Acid-Soluble and Pepsin-Soluble Collagens from Blacktip Reef Shark Skin. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060376
Ge B, Hou C, Bao B, Pan Z, de Val JEMS, Elango J, Wu W. Comparison of Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Acid-Soluble and Pepsin-Soluble Collagens from Blacktip Reef Shark Skin. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(6):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060376
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Baolin, Chunyu Hou, Bin Bao, Zhilin Pan, José Eduardo Maté Sánchez de Val, Jeevithan Elango, and Wenhui Wu. 2022. "Comparison of Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Acid-Soluble and Pepsin-Soluble Collagens from Blacktip Reef Shark Skin" Marine Drugs 20, no. 6: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060376
APA StyleGe, B., Hou, C., Bao, B., Pan, Z., de Val, J. E. M. S., Elango, J., & Wu, W. (2022). Comparison of Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Acid-Soluble and Pepsin-Soluble Collagens from Blacktip Reef Shark Skin. Marine Drugs, 20(6), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060376







