An Octopus-Derived Peptide with Antidiuretic Activity in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
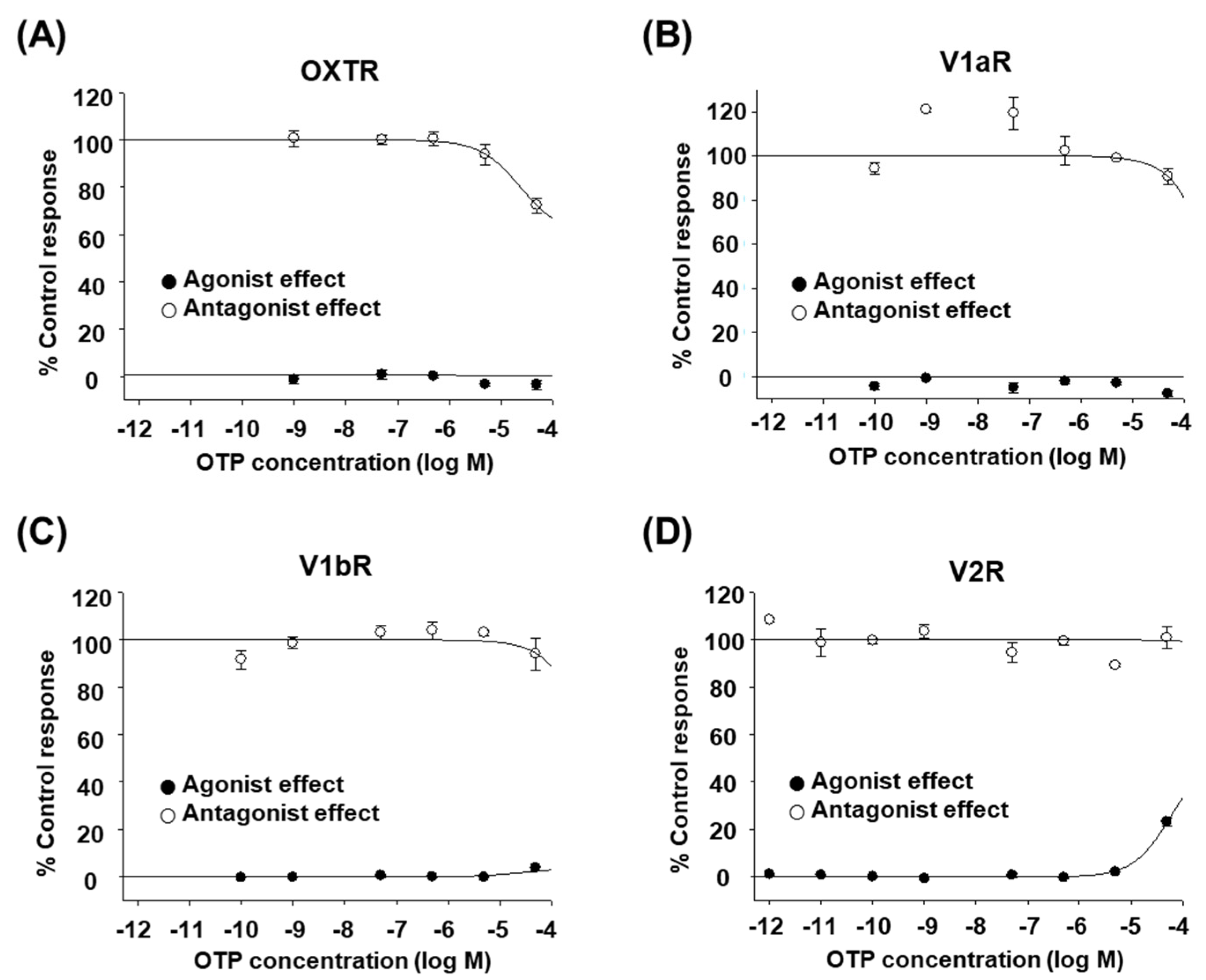
2.1. OTP Does Not Affect Human OXT/AVP Receptors
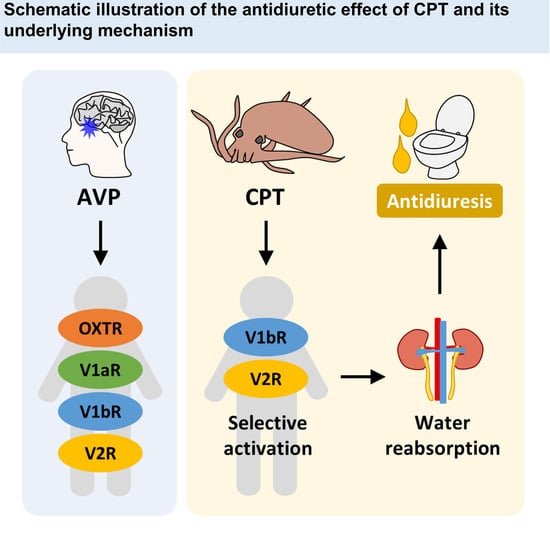
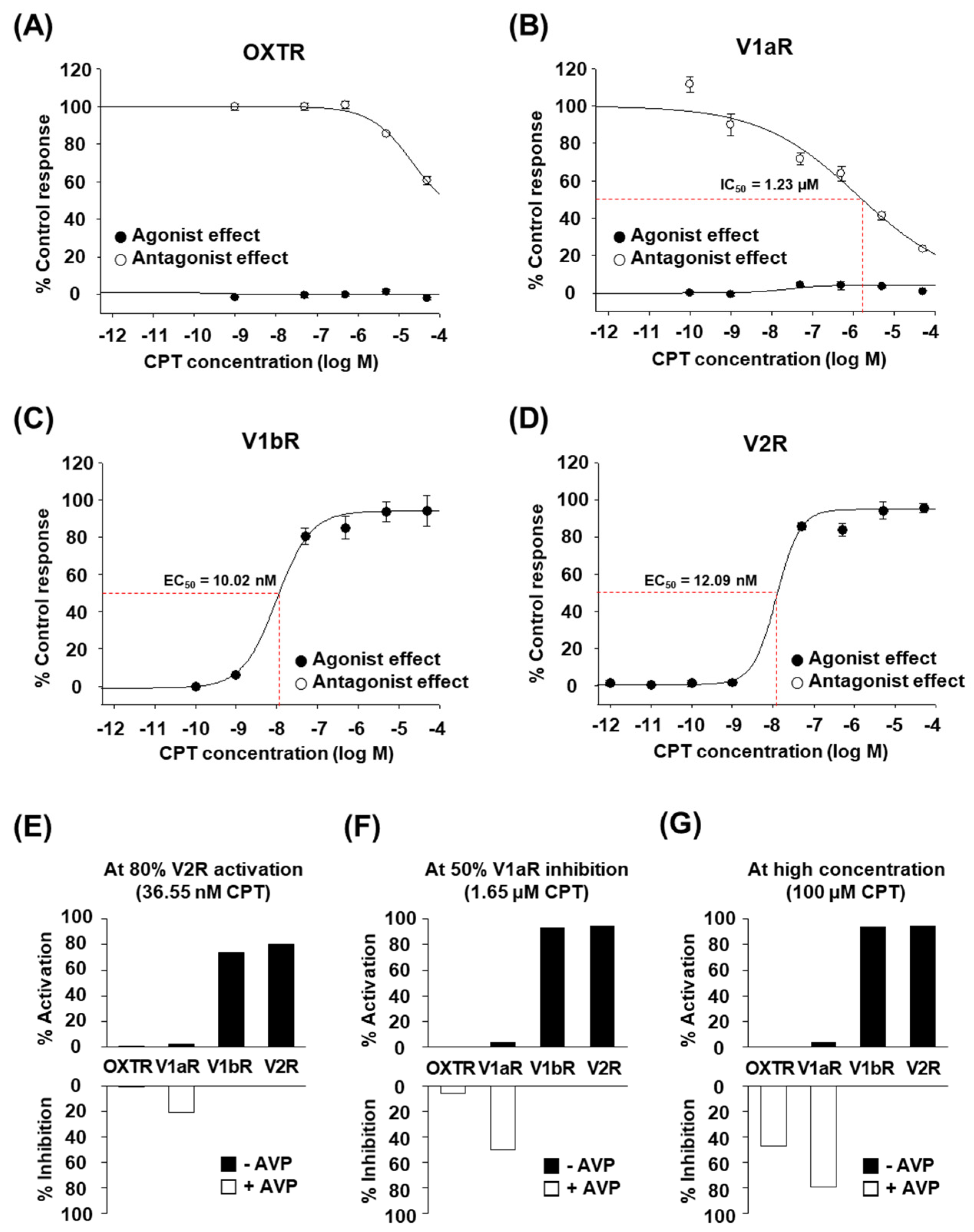
2.2. CPT Selectively Activates Human V1bR and V2R
2.3. A Single Tail Intravenous Injection of CPT Reduced the Collected Urine Output in SD Rats
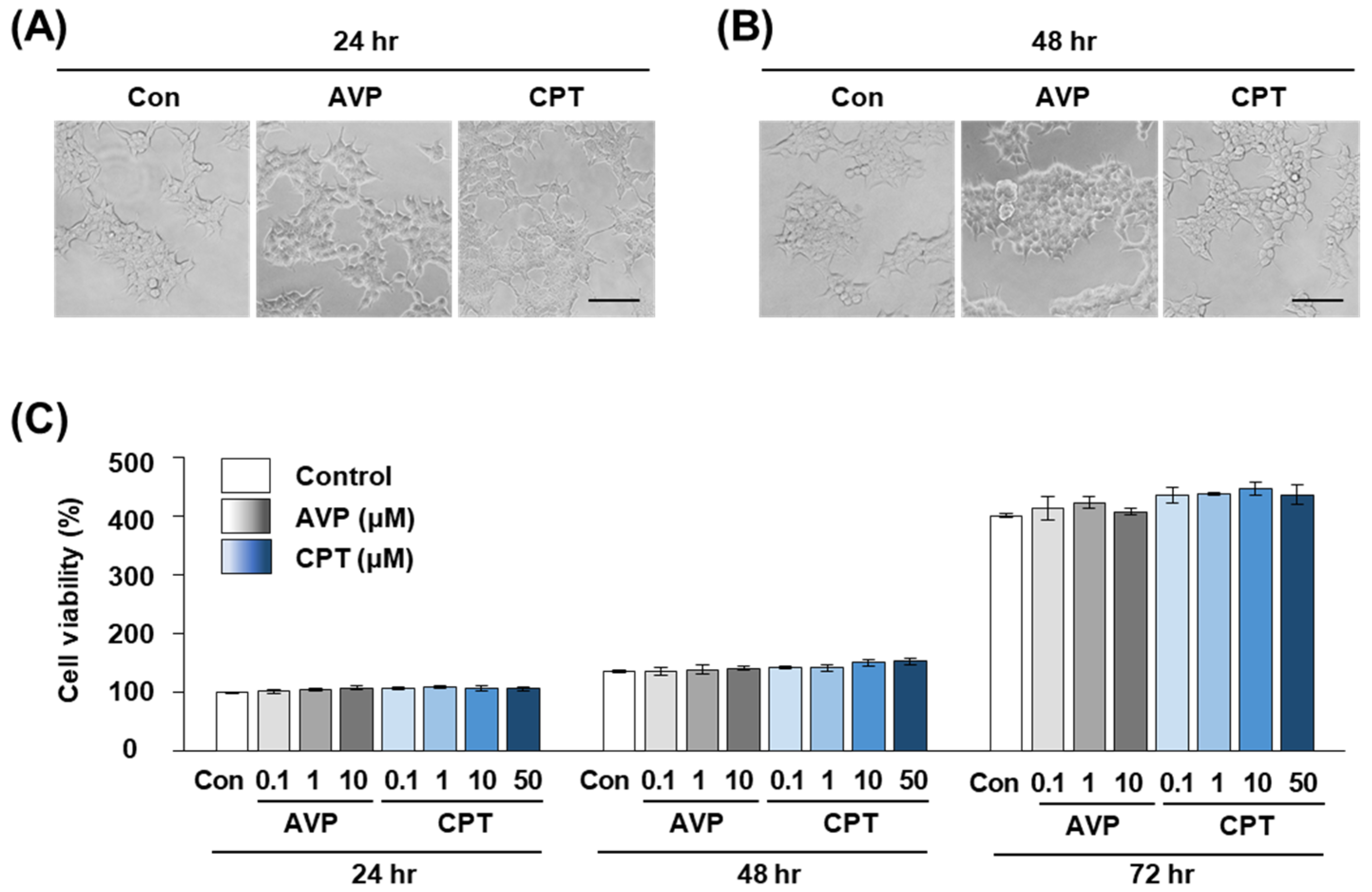
2.4. CPT Does Not Alter the Viability of HEK293T Human Kidney Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptides
4.2. In Vitro Assay
4.2.1. In Vitro OXT/AVP Receptor Functional Assay
4.2.2. CCK-8 Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Antidiuretic Experiments
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gimpl, G.; Fahrenholz, F. The oxytocin receptor system: Structure, function, and regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 629–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Vigneaud, V.; Ressler, C.; Trippett, S. The sequence of amino acids in oxytocin, with a proposal for the structure of oxytocin. J. Biol. Chem. 1953, 205, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneaud, V.d.; Lawler, H.C.; Popenoe, E.A. Enzymatic cleavage of glycinamide from vasopressin and a proposed structure for this pressor-antidiuretic hormone of the posterior pituitary. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 4880–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baribeau, D.A.; Anagnostou, E. Oxytocin and vasopressin: Linking pituitary neuropeptides and their receptors to social neurocircuits. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, C.S. The oxytocin–vasopressin pathway in the context of love and fear. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurek, B.; Neumann, I.D. The oxytocin receptor: From intracellular signaling to behavior. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1805–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treschan, T.A.; Peters, J.; Warltier, D.C. The vasopressin system: Physiology and clinical strategies. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2006, 105, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Tahara, A.; Sugimoto, T. 1-desamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (DDAVP) as an agonist on V1b vasopressin receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997, 53, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching-Gonzalez, A.; Meza-Valle, C.; Muñoz-Báez, K.; Medrano-Carreazo, J.; Agrawal, A.; Mishra, R.; Shrivastava, A.; Janjua, T.; Moscote-Salazar, L.R. Desmopressin in Critically Ill Neurosurgical Patients: An Overview. J. Transl. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 2, 23. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, T.S.; Shah, A.D. Desmopressin. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, M.; Misicka, A.; Olma, A.; Bankowski, K.; Stoev, S.; Chini, B.; Durroux, T.; Mouillac, B.; Corbani, M.; Guillon, G. Oxytocin and vasopressin agonists and antagonists as research tools and potential therapeutics. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 24, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumi, T.; Ukena, K.; Matsushima, O.; Ikeda, T.; Fujita, T.; Minakata, H.; Nomoto, K. Annetocin, an annelid oxytocin-related peptide, induces egg-laying behavior in the earthworm, Eisenia foetida. J. Exp. Zool. 1996, 276, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odekunle, E.A.; Semmens, D.C.; Martynyuk, N.; Tinoco, A.B.; Garewal, A.K.; Patel, R.R.; Blowes, L.M.; Zandawala, M.; Delroisse, J.; Slade, S.E. Ancient role of vasopressin/oxytocin-type neuropeptides as regulators of feeding revealed in an echinoderm. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, C.W. Physiology of invertebrate oxytocin and vasopressin neuropeptides. Exp. Physiol. 2014, 99, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, C.W.; Koehbach, J.; Muttenthaler, M. Exploring bioactive peptides from natural sources for oxytocin and vasopressin drug discovery. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Croker, D.; Daly, N.L.; Andersson, A.; Muttenthaler, M.; Lumsden, N.G.; Craik, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Guillon, G.; Lewis, R.J. Conopressin-T from Conus tulipa reveals an antagonist switch in vasopressin-like peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7100–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giglio, M.G.; Muttenthaler, M.; Harpsøe, K.; Liutkeviciute, Z.; Keov, P.; Eder, T.; Rattei, T.; Arrowsmith, S.; Wray, S.; Marek, A. Development of a human vasopressin V 1a-receptor antagonist from an evolutionary-related insect neuropeptide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takuwa-Kuroda, K.; Iwakoshi-Ukena, E.; Kanda, A.; Minakata, H. Octopus, which owns the most advanced brain in invertebrates, has two members of vasopressin/oxytocin superfamily as in vertebrates. Regul. Pept. 2003, 115, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, G. A new peptide of the oxytocin/vasopressin family isolated from nerves of the cephalopod Octopus vulgaris. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 134, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakata, H. Oxytocin/vasopressin and gonadotropin-releasing hormone from cephalopods to vertebrates. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1200, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Ogawa, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Akada, C.; Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, T.; Minakata, H.; Sakamoto, H. Osmotic/ionic status of body fluids in the euryhaline cephalopod suggest possible parallel evolution of osmoregulation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, I.; Leprince, J.; Chichery, R.; Vaudry, H.; Agin, V. Vasopressin/oxytocin-related peptides influence long-term memory of a passive avoidance task in the cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2010, 93, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, A.; O’Carroll, A.-M.; Brownstein, M.J.; Lolaft, S.J. Molecular cloning and expression of a rat Via arginine vasopressin receptor. Nature 1992, 356, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaoral, M.; Kolc, J.; Šorm, F. Amino acids and peptides. LXXI. Synthesis of 1-deamino-8-D-γ-aminobutyrine-vasopressin, 1-deamino-8-D-lysine-vasopressin, and 1-deamino-8-D-arginine-vasopressin. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1967, 32, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cort, J.; Schück, O.; Stříbrná, J.; Jošt, K.; Mulder, J.L. Role of the disulfide bridge and the C-terminal tripeptide in the antidiuretic action of vasopressin in man and the rat. Kidney Int. 1975, 8, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dehoorne, J.L.; Raes, A.M.; Van Laecke, E.; Hoebeke, P.; Vade Walle, J.G. Desmopressin toxicity due to prolonged half-life in 18 patients with nocturnal enuresis. J. Urology. 2006, 176, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgaard, J.P.; Østerberg, O.; Holdrup, L. Re: Desmopressin Toxicity Due to Prolonged Half-Life in 18 Patients With Nocturnal Enuresis. J. Urology. 2007, 177, 1204–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzicka, H.; Björkman, S.; Lethagen, S.; Sterner, G. Pharmacokinetics and antidiuretic effect of high-dose desmopressin in patients with chronic renal failure. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 92, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agersø, H.; Seiding Larsen, L.; Riis, A.; Lövgren, U.; Karlsson, M.O.; Senderovitz, T. Pharmacokinetics and renal excretion of desmopressin after intravenous administration to healthy subjects and renally impaired patients. Brit. J. Clinl. Pharmaco. 2004, 58, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, U. Pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism in the elderly. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Sasaki, S.; Tsuganezawa, H.; Monkawa, T.; Kitajima, W.; Konishi, K.; Fushimi, K.; Marumo, F.; Saruta, T. Expression and distribution of aquaporin of collecting duct are regulated by vasopressin V2 receptor in rat kidney. J. Clin. Invest. 1994, 94, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.L.; Miranda, C.A.; Knepper, M.A. Vasopressin and the regulation of aquaporin-2. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2013, 17, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hus-Citharel, A.; Bouby, N.; Corbani, M.; Mion, J.; Mendre, C.; Darusi, J.; Tomboly, C.; Trueba, M.; Serradeil-Le Gal, C.; Llorenss-Cortes, C.; et al. Characterization of a functional V1B vasopressin receptor in the male rat kidney, evidence for crosstalk between V1B and V2 receptor signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2021, 321, F305–F321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttenthaler, M.; King, G.F.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henninot, A.; Collins, J.C.; Nuss, J.M. The current state of peptide drug discovery: Back to the future? J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 1382–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimica, N.; Wegienka, L.C.; Forsham, P.H. Lypressin nasal spray: Usefulness in patients who manifest allergies to other antidiuretic hormone preparations. JAMA 1968, 203, 802–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, A.; Tsukada, J.; Tomura, Y.; Wada, K.i.; Kusayama, T.; Ishii, N.; Yatsu, T.; Uchida, W.; Tanaka, A. Pharmacologic characterization of the oxytocin receptor in human uterine smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, A.; Saito, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Tomura, Y.; Wada, K.i.; Kusayama, T.; Tsukada, J.; Ishii, N.; Yatsu, T.; Uchida, W. Pharmacological characterization of the human vasopressin receptor subtypes stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaumer, M. Vasopressin receptors. Horm. Brain Behav. 2002, 3, 803–810. [Google Scholar]
- Cotte, N.; Balestre, M.-N.; Phalipou, S.; Hibert, M.; Manning, M.; Barberis, C.; Mouillac, B. Identification of residues responsible for the selective binding of peptide antagonists and agonists in the V2 vasopressin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 29462–29468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Sequence | Purity | Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxytocin (OXT) | CYIQNCPLG-NH2 (disulfide bond) | >98% | Mammals |
| Vasopressin (AVP) | CYFQNCPRG-NH2 (disulfide bond) | >98% | Mammals |
| Desmopressin (DP) | Mpr-YFQNCP(D-Arg)G-NH2 (disulfide bond) | >95% | Synthetic (From AVP, deamination of 1-C and substitution of 8-D-R) |
| Cephalotocin (CTP) | CYFRNCPIG-NH2 (disulfide bond) | >98% | O. vulgaris |
| Octopressin (OTP) | CYWTSCPIG-NH2 (disulfide bond) | >98% | O. vulgaris |
| Receptors | Cell Lines | Stimulus (Full Activation) | Incubation | Measured Component | Detection Method | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OXTR (h) (agonist effect) | ECV304 | none (1 µM OXT) | RT | intracellular [Ca2+] | Fluorimetry | [37] |
| OXTR (h) (antagonist effect) | ECV304 | 30 nM OXT | RT | intracellular [Ca2+] | Fluorimetry | |
| V1aR (h) (agonist effect) | CHO | none (1 µM AVP) | RT | intracellular [Ca2+] | Fluorimetry | [38] |
| V1aR (h) (antagonist effect) | CHO | 10 nM AVP | RT | intracellular [Ca2+] | Fluorimetry | |
| V1bR (h) (agonist effect) | RBL | none (0.1 µM AVP) | RT | intracellular [Ca2+] | Fluorimetry | [39] |
| V1bR (h) (antagonist effect) | RBL | 5 nM AVP | RT | intracellular [Ca2+] | Fluorimetry | |
| V2R (h) (agonist effect) | CHO | none (1 nM AVP) | 30 min RT | cAMP | HTRF | [40] |
| V2R (h) (antagonist effect) | CHO | 0.03 nM AVP | 30 min RT | cAMP | HTRF |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, S.-H.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, C.-H.; Jo, S.; Woo, D.H. An Octopus-Derived Peptide with Antidiuretic Activity in Rats. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050328
Kim Y-J, Lee JH, Jung S-H, Kim KH, Choi C-H, Jo S, Woo DH. An Octopus-Derived Peptide with Antidiuretic Activity in Rats. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(5):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050328
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ye-Ji, Jei Ha Lee, Seung-Hyun Jung, Ki Hyun Kim, Chang-Hoon Choi, Seonmi Jo, and Dong Ho Woo. 2022. "An Octopus-Derived Peptide with Antidiuretic Activity in Rats" Marine Drugs 20, no. 5: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050328
APA StyleKim, Y.-J., Lee, J. H., Jung, S.-H., Kim, K. H., Choi, C.-H., Jo, S., & Woo, D. H. (2022). An Octopus-Derived Peptide with Antidiuretic Activity in Rats. Marine Drugs, 20(5), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050328