Abstract
For making full use of aquatic by-products to produce high value-added products, Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) cartilages were degreased, mineralized, and separately hydrolyzed by five kinds of proteases. The collagen hydrolysate (SCH) generated by Alcalase showed the strongest 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH·) and hydroxide radical (HO·) scavenging activity. Subsequently, thirteen antioxidant peptides (SCP1-SCP3) were isolated from SCH, and they were identified as GPTGED, GEPGEQ, GPEGPAG, VPPQD, GLEDHA, GDRGAEG, PRGFRGPV, GEYGFE, GFIGFNG, PSVSLT, IELFPGLP, LRGEAGL, and RGEPGL with molecular weights of 574.55, 615.60, 583.60, 554.60, 640.64, 660.64, 885.04, 700.70, 710.79, 602.67, 942.12, 714.82, and 627.70 Da, respectively. GEYGFE, PSVSLT, and IELFPGLP showed the highest scavenging activity on DPPH· (EC50: 1.27, 1.05, and 1.38 mg/mL, respectively) and HO· (EC50: 1.16, 0.97, and 1.63 mg/mL, respectively), inhibiting capability of lipid peroxidation, and protective functions on H2O2-damaged plasmid DNA. More importantly, GEYGFE, PSVSLT, and IELFPGLP displayed significant cytoprotection on HUVECs against H2O2 injury by regulating the endogenous antioxidant enzymes of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) to decrease the contents of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA). Therefore, the research provided better technical assistance for a higher-value utilization of Siberian sturgeon cartilages and the thirteen isolated peptides—especially GEYGFE, PSVSLT, and IELFPGLP—which may serve as antioxidant additives for generating health-prone products to treat chronic diseases caused by oxidative stress.
1. Introduction
The balanced relationship between the endogenous antioxidant defense system and reactive oxygen species (ROS) will be broken under the toxic environment in the cells [1,2,3]. Excessive ROS can cause DNA mutation, enzyme inactivation, and membrane phospholipid oxidation, which further lead to oxidative stress, inducing cell necrosis or apoptosis, tissue injury, and pathologic transformations of the human body [4,5,6]. Such oxidative damage significantly increases the incidence of chronic diseases, including arthritis, hypertension, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease [7,8,9,10]. Many antioxidant chemical compounds can play highly effective functions to prevent and to cure those diseases and to clear away excessive ROS in the human body [11,12]. However, synthetic antioxidants have shown a potential toxicity risk and their applications are strictly regulated [13,14]. Therefore, researchers are focusing their research interests on natural active molecules and their derivatives, such as flavonoids, triterpenoid, quinones, and alkaloids [12,15,16,17]. Remarkably, antioxidant peptide (AP) originated from food proteins, which captured worldwide interest because of their advantages in environmental protection and in sustainability, and their small molecular weight (MW) and low toxic side effects [1,9,12].
Collagen and its derivatives, including gelatin, hydrolysate, and peptide, are traditionally produced from animal bones and skins, and they have served as multifunctional ingredients applied in food, cosmetics, photographic, and pharmaceuticals products. The global market volume of gelatin/collagen is expected to exceed 650 kilo-tones, which is approximately 4 billion US dollars by 2024 [18,19,20,21]. However, those products generated from mammalian resources have aroused the wide concern of customers because of the increasing number of infectious diseases and dietary restriction in Islam, Judaism and Hinduism [22,23]. Therefore, collagen and its derivatives from fish by-products are considered to be ideal substitutes due to good bioactivity, high nutrition, weak antigenicity, excellent moisture retention, and good biocompatibility properties [18,24,25,26].
Recently, collagen peptides from aquatic organism drew great interest from the food, medicine, and cosmetics industries because of their multiple functions, including free radical scavenging activity, lipid peroxidation inhibition ability, cytoprotection, and ultraviolet damage protection [21,24,27,28]. For example, bioactive peptides from collagen hydrolysates of giant croaker swim bladders [29], sea cucumber [30], and redlip croaker scales [11] could significantly accelerate the proliferation of HUVECs, RAW264.7, and HepG2 cells, and protect them against the oxidative damage of H2O2 by increasing the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and reducing the levels of ROS and malondialdehyde (MDA). Gelatin peptides from Pacific cod had a significant protective effect on ultraviolet-A (UVA) damaged cells and skins by up-regulating the levels of SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px [31,32,33]. Similarly, collagen peptides from silver carp skins showed a stronger beneficial effect than casein derived peptides and tea poly-phenols on alleviating the UV-caused unusual lesions of skin compositions and antioxidant indices in the serum and in the skins [34]. In addition, collagen peptides from the croceine croaker swim bladders showed a favorable anti-fatigue function in mice by increasing antioxidase activities to reduce ROS damage, enhancing the lactic dehydrogenase activity to get rid of excessive lactic acid to further alleviate the development of physical fatigue [35].
Sturgeon, belonging to the family Acipenseridae, is the common name of 27 kinds of cartilaginous fish, and its farmed production in China is approximately 4.4 million tons accounting for nearly 80% of world production [36,37]. In the receiving process of sturgeon eggs, cartilage, which accounts for 10% of the sturgeon’s weight, becomes a by-product. Therefore, active substances in sturgeon cartilage, such as chondroitin sulfate [38], collagen [39,40], and anti-inflammatory peptides [41], were studied constantly to replace shark cartilage, which is used in health and functional products. The Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baerii Brandt, inhabits large Siberian rivers from the Ob to the Kolyma and Lake Baikal, and it is one of the important breeding varieties in China. In this experiment, antioxidant collagen peptides from the cartilage of the Siberian sturgeon (A. baerii) were prepared and identified. Moreover, their protective function on H2O2 injured HUVECs was evaluated.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation of Collagen Hydrolysate of Siberian Sturgeon Cartilage (SCH)
The effects of five kinds of proteases on the DPPH· and HO· scavenging rates of collagen hydrolysates of Siberian sturgeon cartilage are presented in Figure 1. At 10.0 mg/mL, the DPPH· and HO· scavenging rates of collagen hydrolysate generated by Alcalase were 47.43 ± 1.86% and 72.22 ± 2.11%, which were observably stronger than the rates of collagen hydrolysates produced using papain, flavorzyme, trypsin, and pepsin, respectively (p < 0.05). Compared with microbial fermentation, chemical degradation, and solvent extraction, enzymatic hydrolysis is one of the most popular and useful ways to generate bioactive hydrolysates from protein resources due to its easy manipulation, high efficiency, and eco-friendly features [1,42,43]. In addition, the specificity of protease is the very key property determining the MW, amino acid sequence, and bioactivity of the prepared hydrolysates because of their different cleavage sites [1,11]. In addition, multiple endonuclease enzymes, exonuclease enzymes, and their combinations are generally selected to degrade different proteins to generate active hydrolysates [1,9]. The present results supported the previous reports that the selectivity of enzymes significantly affected the peptide component and the bioactivities of prepared hydrolysates [1,14]. In consequence, the collagen hydrolysate of Siberian sturgeon cartilage prepared using Alcalase was named SCH and selected for further experimentation.
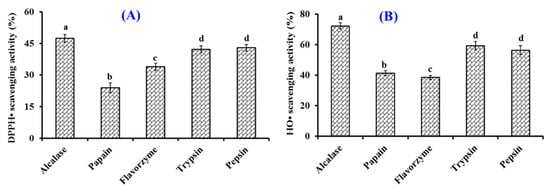
Figure 1.
Effects of Alcalase, papain, pepsin, flavorzyme, and trypsin on radical scavenging activity of collagen hydrolysates from Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) cartilages. (A) 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH·) scavenging activity; (B) hydroxide radical (HO·) scavenging activity. All data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate results. a–d Values with different letters indicate significant difference (p < 0.05).
2.2. Purification of APs from SCH
2.2.1. Fractionation of SCH by Ultrafiltration
Using 3.0 kDa ultrafiltration membranes, SCH was fractionated into two peptide components (SCH-1 and SCH-2) and their radical scavenging rates are shown in Figure 2. At 5.0 mg/mL, the DPPH· and HO· scavenging rates of SCH-1 were 38.52 ± 1.69% and 45.37 ± 1.97%, which were significantly stronger than those activities of SCH and SCH-2 (p < 0.05). The changes of amino acid composition and MW could significantly modulate the bioactivity of peptides, and their average MWs could adversely affect the antioxidant capability of enzymatic hydrolysates [44,45]. The current result agreed well with the previous finding that peptide components with smaller MWs from skipjack roe [46,47,48], skate cartilage [49], Bacillus amyloliquefaciens [50], Tolithes ruber [51], croceine croaker muscle [13], and Tilapia skin [31] possessed the highest antioxidant activity. Then, SCH-1 was chosen for further purification.
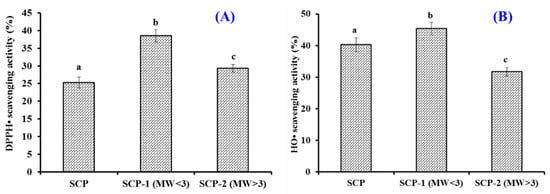
Figure 2.
Radical scavenging activity of SCH and its two fractions by ultrafiltration. (A) DPPH· scavenging activity; (B): HO· scavenging activity. All data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate results. a–c Values with different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
2.2.2. Gel Filtration Chromatography (GFC)
Figure 3A showed that three peptide subfracitons (SCH-1a, SCH-1b, and SCH-1c) were isolated from SCH-1 based on their MWs. At 5.0 mg/mL, the DPPH· and HO· scavenging rates of SCH-1b were 56.64 ± 2.69% and 66.79 ± 2.65%, which were significantly higher than those of SCH, SCH-1, and other subfracitons (p < 0.05) (Figure 3B). As a kind of size exclusion chromatography, GFC is generally applied to either fractionate active ingredients or to remove an impurity with a particular size range from a complex mixture of components [1,9,52]. Therefore, GFC is frequently employed to isolate peptides with different MWs from marine protein hydrolysates [1,47,53]. In the experiment, the MW of SCH-1b was bigger than that of SCH-1c, but its radical scavenging rates were significantly higher than those of SCH-1c (p < 0.05), which suggested that the bioactivities of APs are not only influenced by MW but also amino acid composition and sequence [1,42].
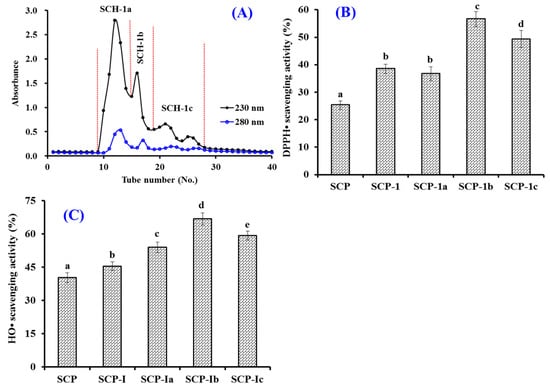
Figure 3.
Chromatogram map of SCH-1 on a Sephadex G-25 column (A) and the scavenging activity of SCH-1 and its fractions (SCH-1a, SCH-1b, and SCH-1c) on DPPH· (B) and HO· (C). All data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate results. a–e Values with different letters indicate significant difference (p < 0.05).
2.2.3. RP-HPLC Separation of SCH-1b
SCH-1 with high radical scavenging activity was further purified by RP-HPLC and its chromatogram is shown in Figure 4. On the chromatographic peaks of SCH-1, thirteen peptide peaks with retention times of 4.58 min (SCP1), 8.98 min (SCP2), 10.73 min (SCP3), 13.01 min (SCP4), 18.03 min (SCP5), 21.02 min (SCP6), 21.75 min (SCP7), 24.81 min (SCP8), 33.85 min (SCP9), 39.79 min (SCP10), 42.52 min (SCP11), 44.18 min (SCP12), and 45.62 min (SCP13), respectively, were purified from SCH-1b (Table 1). Based on the hydrophobic and the hydrophilic properties, RP-HPLC employing an ODSC18 column can effectively isolate APs with high purity from different protein hydrolysates of aquatic resources, such as croaker (Otolithes ruber) [51], tuna [46,54], red stingray [55], Pacific Cod [32,33], shortclub cuttlefish [56], Euphausia superba [57], and mackerel (Scomber japonicus) [58]. Then, thirteen peptides (SCP1 to SCP13) were corrected and lyophilized for further structure identification.
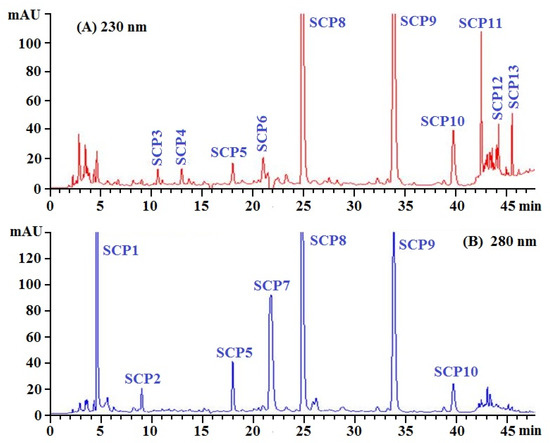
Figure 4.
Elution profile of the subfraction (SCH-1b) by RP-HPLC using a linear gradient of acetonitrile (0.06% trifluoroacetic acid) at 230 nm (A) and 280 nm (B).

Table 1.
Retention time, amino acid sequences, and molecular mass of thirteen APs (SCP1- SCP13) from collagen hydrolysate of Siberian sturgeon cartilage.
2.3. Determination of Amino Acid Sequences of Thirteen Isolated APs (SCP1 to SCP13)
Using a Protein Sequencer and an ESI/MS, the amino acid sequences and the MWs of thirteen isolated APs (SCP1 to SCP13) were determined and the results are shown in Table 1. The sequences of SCP1 to SCP13 were identified as Gly-Pro-Thr-Gly-Glu-Asp (GPTGED, SCP1), Gly-Glu-Pro-Gly-Glu-Gln (GEPGEQ, SCP2), Gly-Pro-Glu-Gly-Pro-Ala-Gly (GPEGPAG, SCP3), Val-Pro-Pro-Gln-Asp (VPPQD, SCP4), Gly-Leu-Glu-Asp-His-Ala (GLEDHA, SCP5), Gly-Asp-Arg-Gly-Ala-Glu-Gly (GDRGAEG, SCP6), Pro-Arg-Gly-Phe-Arg-Gly-Pro-Val (PRGFRGPV, SCP7), Gly-Glu-Tyr-Gly-Phe-Glu (GEYGFE, SCP8), Gly-Phe-Ile-Gly-Phe-Asn-Gly (GFIGFNG, SCP9), Pro-Ser-Val-Ser-Leu-Thr (PSVSLT, SCP10), Gly-Ile-Glu-Leu-Phe-Pro-Gly-Leu-Pro (GIELFPGLP, SCP11), Leu-Arg-Gly-Glu-Ala-Gly-Leu (LRGEAGL, SCP12), and Arg-Gly-Glu-Pro-Gly-Leu (RGEPGL, SCP13) with MWs of 574.55, 615.60, 583.60, 554.60, 640.64, 660.64, 885.04, 700.70, 710.79, 602.67, 942.12, 714.82, and 627.70 Da, respectively, and their determined MWs were well consistent with their theoretical mass (Table 1).
2.4. Antioxidant Activity of Thirteen Isolated APs (SCP1 to SCP13)
2.4.1. Radical Scavenging Activity of Thirteen Isolated APs (SCP1 to SCP13)
Figure 5A shows that the DPPH· scavenging rates of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 were 77.03 ± 2.08%, 80.09 ± 2.15%, and 71.1 ± 2.14%, respectively, which were significantly higher than those of ten other isolated collagen APs but still lower than that (95.37 ± 3.25%) of ascorbic acid. In addition, the half clearance concentrations (EC50 values) of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 were 1.27, 1.05, and 1.38 mg/mL, respectively, which were significantly less than those of APs from skipjack tuna milt (GRVPRV: 4.13 mg/mL; AQRPR 1.80 mg/mL) [59], loach (PSYV: 17.0 mg/mL) [60], Antarctic krill (NVPDM: 4.88 mg/mL; NGPDPRPSQQ: 7.05 mg/mL; TFPIYDPQ: 2.15 mg/mL) [61], and hairtail muscle (QNDER: 4.95 mg/mL) [62].
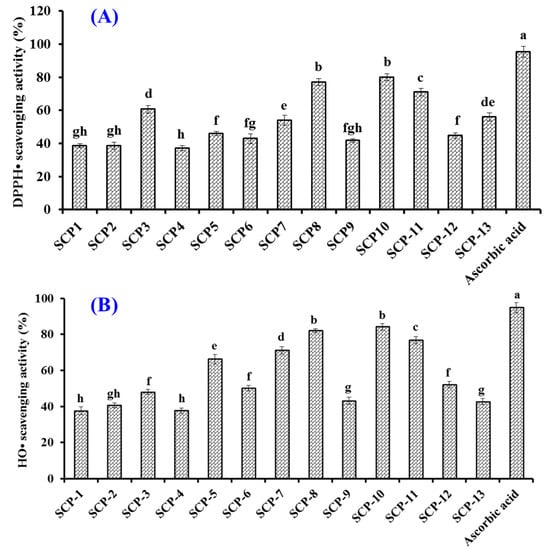
Figure 5.
DPPH· (A) and HO· (B) scavenging rates of thirteen isolated APs (SCP1–SCP13) from collagen hydrolysate of Siberian sturgeon cartilages. All data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate results. a–h Values with different letters indicate significant difference (p < 0.05).
Figure 5B showed that the HO· scavenging rates of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 were 81.94 ± 1.05%, 84.11 ± 1.82%, and 76.78 ± 1.92%, respectively, which were significantly higher than those of ten other isolated collagen APs but still lower than that (94.84 ± 2.79%) of ascorbic acid. The EC50 values of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on HO· were 1.16, 0.97, and 1.63 mg/mL, respectively, which were significantly less than those of APs from skipjack tuna milts (GRVPRV: 5.78 mg/mL; AQRPR 2.80 mg/mL) [59] and roes (SGE: 2.76 mg/mL; QAEP: 2.10 mg/mL) [48], miiuy croaker muscle (NFWWP: 2.39 mg/mL; YFLWP: 2.47 mg/mL) [63], Antarctic krill (NVPDM: 1.84 mg/mL; NWDDMRIVAV: 2.61 mg/mL) [61], Misgurnus anguillicaudatus (PSYV: 2.64 mg/mL) [60], and grass carp skin (VGGRP: 2.06 mg/mL; PYSFK: 2.28 mg/mL) [64]. The present results suggested that SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 could effectively scavenge excess HO· to inhibit the oxidative stress in cells and biological tissues.
MW can significantly affect the antioxidant abilities of APs because a smaller size is beneficial to them in getting into cells or into tissues and playing their roles [50,65,66]. In the study, thirteen isolated APs (SCP1 to SCP13) range from pentapeptides to nonapeptides and their MWs range from 554.60 to 942.12 Da, respectively, which are very helpful for them to approach and to effectively scavenge excess free radicals.
Hydrophobic and aromatic amino acids, such as Leu, Ile, Tyr, Pro, and Phe, play key roles in the activity of APs. These two kinds of amino acids are able to improve the peptides’ solubility in lipids, which further facilitate the combination between APs and free radicals and promote the antioxidant capabilities of APs [1,9,50]. Leu, Thr, Ala, Ile, and Val were reported to play key roles in the antioxidant capabilities of HFGBPFH, ILGATIDNSK, GADIVA, and GAEGFIF, respectively [61,67,68]. Aromatic amino acids could restrain the extension of the radical-mediated peroxide domino effect by changing free radicals into more stable phenoxy radicals [63,69]. Pro residue in sequences of LDEPDPL and PHH was beneficial to their antioxidant activity because Pro residue could improve the flexibility of peptides and directly scavenge singlet oxygen by its pyrrolidine ring [59,70,71]. Therefore, Tyr and Phe in SCP8, Phe and Ile in SCP10, and Ile, Leu, Phe, and Pro in SCP11 should play key roles for their antioxidant activities.
Hydrophilic amino acids are the key factor for the scavenging abilities of APs on mental ions and hydroxide radicals [48]. Glu/Gln, Asp/Asn, and Lys residues had strong positive impacts on the antioxidant activities of QDHKA, AEHNH, LDEPDPLI, AEDKKLIQ, and NTDGSTDYGILQINSR [48,72,73]. Gly residue in WMGPY, EMGPA, GADIVA, and GAEGFIF could increase the flexibility of peptide skeleton and directly neutralize ROS by acting as a single hydrogen donor [25,74]. Therefore, Gly and Glu in SCP8, Gly and Asn in SCP10, and Gly and Glu in SCP11 were important to their antioxidant capabilities.
2.4.2. Lipid Peroxidation Inhibition Ability
Compared with the blank control group, the absorbance values of the SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 groups at 500 nm were significantly decreased when the temperature was kept at 40 °C for 7 days in the linoleic acid system (Figure 6). More importantly, the inhibiting capabilities of SCP10 drew near the variation trend of glutathione (GSP). Lipid oxidation is a very complex chemical reaction, which is affected by multiple factors. Therefore, lipid peroxidation inhibition assay was generally applied to compare and to analyze the antioxidant abilities of peptides from marine protein resources, such as Antarctic krill [61], channel catfish [75], miiuy croaker [63], and croceine croaker [13]. These results suggested that SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 have significant protective ability on unsaturated fatty acid against peroxidation.
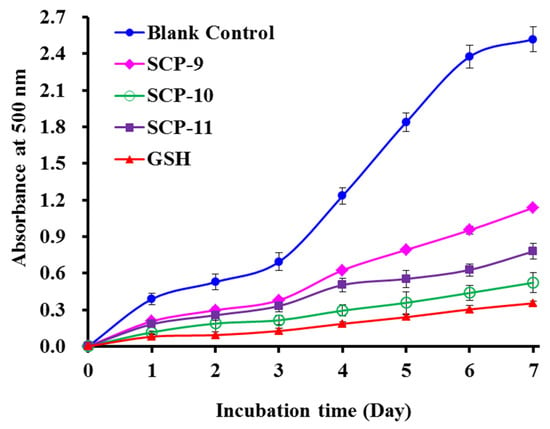
Figure 6.
Lipid peroxidation inhibition capability of three isolated APs (SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11) from collagen hydrolysate of Siberian sturgeon cartilages. All data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate results.
2.4.3. Protective Activity of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 against H2O2-damaged Plasmid DNA
The protective abilities of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on plasmid DNA (pBR322DNA) against H2O2 damage were determined and presented in Figure 7. Plasmid DNA keeps the supercoiled (SC) form under normal conditions (Figure 7, lane 6), but the supercoiled (SC) form will translate into a relaxed open circular (OC) form when free radicals split one phosphodiester chain of pBR322 DNA. Moreover, the open circular (OC) form will turn into the linear (LIN) form when excess free radicals split the second breakage near the first splitting breakage. In this experiment, the plasmid DNA strands was split by HO·, produced from the chemical reaction of FeSO4 and H2O2, and converted into the OC and the LIN forms [61,76]. Lane 5 indicated that most of the SC forms of plasmid DNA were mutated to LIN forms, which suggested that the chemical reaction generated excessive HO·, which further broke the double-strand of pBR322 DNA. Lane 2 to Lane 4 displayed that the content of SC form of pBR322 DNA was obvious more than that of the model group (Lane 5), which suggested that SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 have a remarkable effect on protecting plasmid DNA against oxidative damage by scavenging superfluous HO·, and this result agreed well with the previous finding that SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 could effectively scavenge HO· to protect biomolecules. In addition, SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 may serve as a radical scavenger in health products to prevent and to treat these degenerative diseases caused by free radicals.
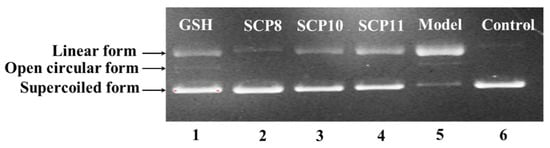
Figure 7.
The protective effects of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on the H2O2-damaged plasmid DNA (pBR322DNA). Lane 1, DNA + FeSO4 + H2O2 + GSH (200 μM); Lane 2, DNA + FeSO4 + H2O2 + SCP8 (200 μM); Lane 3, DNA + FeSO4 + H2O2 + SCP10 (200 μM); Lane 4, DNA + FeSO4 + H2O2 + SCP11 (200 μM); Lane 5, pBR322DNA + FeSO4 + H2O2; Lane 6, the native pBR322DNA.
2.4.4. Cytoprotection of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on H2O2-Induced HUVECs
Effects of H2O2, SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on the Viability of HUVECs
To establish the cell model of oxidative damage, HUVECs were treated with different concentrations of H2O2 (0~600 μM). Figure 8A indicated that the viability of HUVECs showed a significant downward trend at the H2O2 concentrations, which increased from 0 to 600 μM and dropped to 49.06 ± 1.96% at the concentration of 200 μM. Therefore, the H2O2 concentration of 200 μM was chosen to establish the cell model of oxidative damage [66].
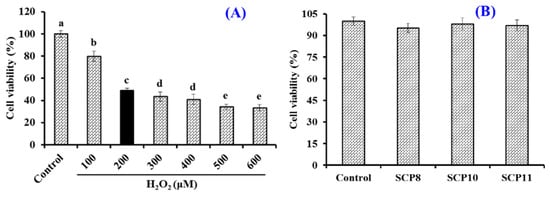
Figure 8.
Effects of H2O2 concentration (A) and isolated peptides (SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11) (B) on the viability of HUVECs. All data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate results. a–e Values with different letters indicate significant difference (p < 0.05).
The Effects of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 at 200 μM on the viability of HUVECs were studied by the MTT method and the data is shown in Figure 8B. No significant difference was found between the blank control and the peptide groups, which indicated that SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 had no significant cytotoxicity to HUVECs. Therefore, the concentration of 200 μM was determined for the subsequent cytoprotection experiment of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11.
Effect of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on the Cell Viability and the ROS Level of H2O2-Injured HUVECs
As shown in Figure 9A, the HUVEC viability of the SCP10 group was 69.36 ± 2.97% at 200 μM, which was significantly higher than those of the model (49.06 ± 1.96%), SCP8 (62.4 ± 2.87%), and SCP11 (57.59 ± 3.21%) groups (p < 0.05), and it was lower than that of the positive control (86.03 ± 3.57%) (p < 0.001) (Figure 9A). Figure 9B and Figure 10 show the effects of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on the ROS level of H2O2-injured HUVECs. The ROS levels of the SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 groups were significantly decreased from 445.5 ± 14.57% to 302.2 ± 16.8%, 269.8 ± 11.5%, and 317.6 ± 6.4% for the control group, respectively (p < 0.001). These data indicated that SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 could significantly scavenge ROS to protect HUVECs against H2O2 injury.
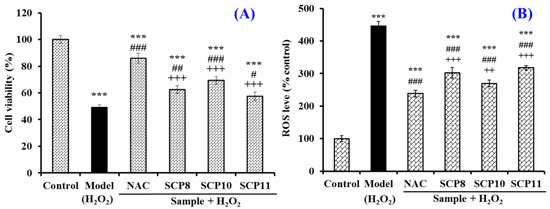
Figure 9.
Effects of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on the cell viability (A) and ROS level (B) of H2O2-injured HUVECs. N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine (NAC) was used as the positive control. All data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate results. *** p < 0.001 vs. blank group; ### p < 0.001, ## p < 0.01 and # p < 0.05 vs. model group; +++ p < 0.001, ++ p < 0.01 vs. NAC + H2O2 group.
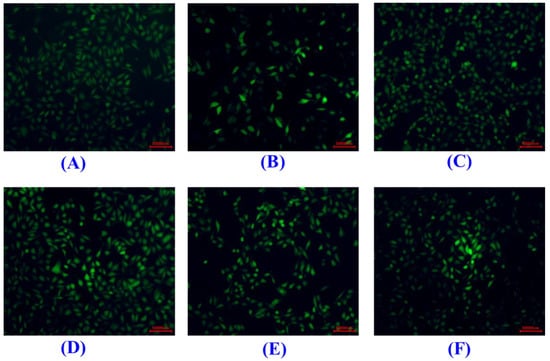
Figure 10.
Determination of ROS contents in HUVECs by DCFH-DA staining. (A) Control; (B) H2O2-induced cell model; (C) Positive control (NAC); (D) SCP8; (E) SCP10; (F) SCP11. The scale bar was 50,000 nm.
Effects of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on the Levels of Antioxidases and MDA of H2O2-Injured HUVECs
As shown in Figure 11A, the activity of SOD in the SCP10 group was 165.1 ± 11.2 U/mg prot, which was significantly higher than those in the model (107.8 ± 7.3 U/mg prot) and the SCP8 (147.2 ± 12.6 U/mg prot) and SCP11 (121.9 ± 10.8 U/mg prot) groups (p < 0.001), respectively. Similarly, the activity of GSH-Px in the SCP10 group (55.77 ± 2.48 U/mg prot) was significantly higher than those in the model (41.74 ± 2.36 U/mg prot) and the SCP8 (51.46 ± 2.65 U/mg prot) and the SCP11 (46.8 ± 1.82 U/mg prot) groups (p < 0.001), respectively (Figure 11B). However, the activity of antioxidases in the SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 groups was significantly lower than those in the positive control group (p < 0.05). In addition, SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 could significantly reduce the MDA contents of H2O2-injured HUVECs. Compared with the model group (10.84 ± 0.72 nmol/mg prot), the MDA contents of the SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 groups were gradually reduced to 8.22 ± 0.45, 7.37 ± 0.69, and 9.07 ± 0.84 nmol/mg prot at 200 μM, respectively (p < 0.05) (Figure 11C). Nonetheless, the MDA contents of the SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 groups were significantly higher than that (6.05 ± 0.54 nmol/mg prot) of the positive control group.
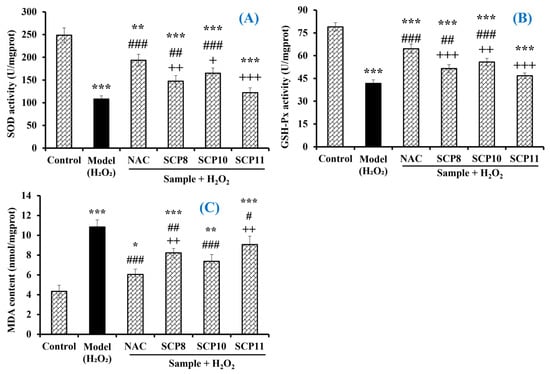
Figure 11.
Effects of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on the levels of SOD (A), GSH-Px (B), and MDA (C) in H2O2-injured HUVECs. All data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01 and * p < 0.05 vs. blank group; ### p < 0.001, ## p < 0.01, and # p < 0.05 vs. model group; + + + p < 0.001 and ++ p < 0.01 and + p < 0.05 vs. NAC+H2O2 group.
In an abnormal environment, excess ROS generated in cells can induce DNA mutations, loss of protein structures, and lipid peroxidation of cell membrane [4,8,24]. Those oxidative stress states are closely linked to many chronic diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, inflammation, etc. [10,12,52]. Therefore, excess ROS must be eliminated promptly and efficiently by endogenous antioxidant defense systems to decrease such oxidative damage [1,53]. Presently, some bioactive peptides show remarkable protection on cells and tissues by alleviating the oxidative and the inflammatory responses. For example, LCGEC could suppress the apoptosis of HaCaT cells by altering the Nrf2 pathway [47]. To decrease the contents of ROS and MDA, FWKVV, FMPLH, and FPYLRH could significantly up-regulate the levels of SOD and GSH-Px in H2O2-injured HUVECs [66,77]. By regulating the NF-κB/caspase pathways and enhancing antioxidase activities, EVSGPGLSPN could protect PC12 cells against H2O2-induced neurotoxicity [78].
In addition, small natural products have been identified as being capable of directly interacting with the Cys residues of Keap1 and thus resulting in the dissociation of Keap1 from Nrf2, which finally promotes Nrf2 nuclear accumulation and activates the Nrf2 pathway [79,80]. Moreover, a number of peptides have been identified to be capable of binding to Keap1, especially the Glu residues that form electrostatic interactions with R380, R415, and R483 and the Asp residue that forms an intramolecular interaction to stabilize the β-hairpin conformation of the structure [81]. The binding site of Keap1 in the Kelch domain can be divided into five subcysts, P1-P5, which can combine with the Neh2 domain of Nrf2 to promote its ubiquitination [82]. The five subcysts are P1 (Arg415, Ile461, Gly423, Phe478, Arg483, Ser508), P2 (Ser363, Arg380, Asn382, Asp422), P3 (Gly509, Ser555, Ala556, Gly571, Ser602, Gly603), P4 (Tyr525, Gln530, Tyr572), and P5 (Tyr334, Phe577), respectively. Wang et al. reported that the Glu residue of peptide EDYGA from the soft-shelled turtle could directly bind to the Arg415 residue on the Kelch domain of Keap1 to form a hydrogen bond [81]. Similarly, the Glu residues in an amino acid sequence of RDPEER from watermelon seed could combine with Asn382, Arg380, and Tyr334 on the Kelch domain of Keap1 to form hydrogen bonds [83]. Tonolo et al. found that the Ser residues in the amino acid sequence of APSFSDIPNPIGSENSE from fermented milk could bind to Arg415 and Ser363 residues on the Kelch domain of Keap1 to form a hydrogen bond to activate the Nrf2 pathway [84]. The Thr residues in the amino acid sequence of NTVPAKSCQAQPTTM could bind to the Ser602 residue in the Kelch domain of Keap1 to form a hydrogen bond [81]. Furthermore, Li et al. reported that the Thr residue of the peptide VTSALVGPR from the urechis unicinctus visceral could bind to Gly423 on the Kelch domain of Keap1 to form a hydrogen bond and to activate the Nrf2 pathway [85]. The EAMAPKHK from fermented rubbing cheese could regulate the Nrf2 pathway through its Pro residue combining with Asp422 on the Kelch domain of Keap1 to form a hydrogen bond [86]. In addition, the Gly residue in an amino acid sequence of PVLGPVR could combine with Ile461 on the Kelch domain of Keap1 to form a hydrogen bond [86]. Then, those amino acid residues in the amino acid sequences of APs occupy the active site of Nrf2 in the Kelch domain of Keap1, competitively inhibit Nrf2 binding, promote Nrf2 into the nucleus, further activate the Keap1/Nrf2 signal pathway, and protect cells from oxidative stress.
According to the introduced literature, we speculated that Gly and Glu in SCP8 (GEYGFE), Pro and Ser in SCP10 (PSVSLT), and Glu, Pro, and Gly in SCP11 (IELFPGLP) should play key roles in protecting HUVECs against H2O2 injury by regulating the endogenous antioxidant defense systems (Nrf2 pathway) to scavenge excess ROS, and their mechanism of action will be explored in our future studies.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemical Reagents
Cartilages of Siberian sturgeon (A. baerii) were kindly provided by Thousand Island Lake Sturgeon Technology Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China). HUVECs were purchased from the Cell Bank of Type Culture Collection of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT), trypsin, Alcalase, NAC, DPPH, papain, and pepsin were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Trading Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Flavorzyme and Sephadex G-25 was purchased from Shanghai Source Poly Biological Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Collagen peptides of SCP1 to SC13 with a purity higher than 98% were synthesized in Shanghai Apeptide Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
3.2. Preparation of Collagen Hydrolysate from Siberian Sturgeon Cartilages
The Siberian sturgeon cartilages were thawed, broken, homogenized, and degreased using the method described by Luo et al. [37]. In short, the cartilage was cut into approximately 0.5 cm2 pieces, homogenized, added into a NaOH solution (0.1 M) with a cartilage/solution ratio of 1:8 (w/v) and uninterruptedly stirred for 6 h, and the NaOH solution was substituted every three hours. Subsequently, the degreased cartilages were rinsed using cold tap water three times and demineralized using EDTA-2Na (0.5 M) with a cartilage/solution ratio of 1:8 (w/v) for two days, and the EDTA-2Na solution was changed every 12 h. The pretreated cartilage was rinsed using cold tap water three times.
Pretreated cartilages were suspended in a buffer solution to prepare the 10% (w/v) sample slurry. After that, the mixed solution was separately hydrolyzed for 6.5 h with 3.0% dose of Alcalase (pH 9.0, 50 °C), papain (pH 7.0, 50 °C), trypsin (pH 8.0, 37.0 °C), flavorzyme (pH 7.5, 45 °C), and pepsin (pH 2.0, 37.0 °C), respectively. The collagen hydrolysate solutions were put in a 95 °C water bath for 15 min to inactivate proteases, centrifuged at 6000× g for 20 min, dialyzed, and lyophilized. The activities of the prepared collagen hydrolysates were evaluated using DPPH· and HO· scavenging assays [45]. Then, the collagen hydrolysate produced using Alcalase revealed the maximum activity among the five hydrolysates, and it was named SCH.
3.3. Purification of APs from SCH
APs were prepared from SCH according to the following designed isolated process (Figure 12).
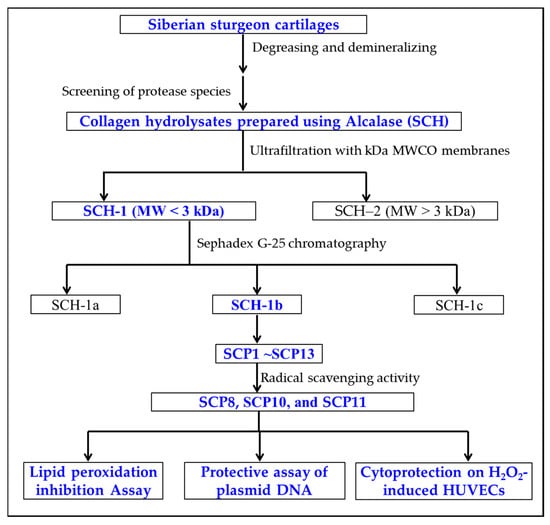
Figure 12.
The flow chart of preparation and activity evaluation of APs from collagen hydrolysate (SCH) of Siberian sturgeon cartilages.
The SCH solution was fractionated using a 3 kDa MW cut-off ultrafiltration membrane and two resulting components, defined as SCH-1 (MW < 3 kDa), and SCH-2 (MW > 3 kDa) were collected, dialyzed, freeze-dried, and their radical scavenging activity was detected.
A total of 10 mL of SCH-1 solutions (50.0 mg/mL) were injected into the chromatography column of Sephadex G-25 (2.6 cm × 150 cm) and washed out by phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH 7.2), with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The effluent solution was collected every 2 min and measured at 230 and 280 nm. Finally, three peptide components (SCH-1a, SCH-1b, and SCH-1c) were enriched, desalted, freeze-dried, and their radical scavenging activity was detected.
The SCH-1b (20 μL, 100.0 μg/mL) was pre-treated with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane and purified by a HPLC column of Waters Symmetry C18 (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 µm) using a gradient of acetonitrile containing 0.06% trifluoroacetic acid. The sample was isolated with a flow velocity of 0.8 mL/min and monitored at 230 and 280 nm. In the end, thirteen APs (SCP1 to SCP13) were purified from SCH-1b on the basis of the chromatographic peaks.
3.4. Analysis of Sequences and MWs of Thirteen APs (SCP1 to SCP13)
The N-terminal amino-acid sequences of thirteen APs (SCP1 to SCP13) were determined by the Edman degradation method using an Applied Biosystems 494 protein sequencer (Foster City, CA, USA). The MWs of thirteen APs (SCP1 to SCP13) were measured by a Q-TOF MS coupled to an electrospray ionization (ESI) source.
3.5. Radical Scavenging, Lipid Peroxidation Inhibition, and Plasmid DNA Protective Assays
3.5.1. Radical Scavenging Assays
The DPPH· and the HO· scavenging assays were performed on the previous methods, and the EC50 value was set as the AP dose, resulting in a 50% decrease of the initial radical concentration [14,45].
DPPH· Scavenging Activity
Two milliliters of samples consisting of distilled water and different concentrations of the analytes were placed in cuvettes, and 500 μL of an ethanolic solution of DPPH (0.02%) and 1.0 mL of ethanol were added. A control sample containing the DPPH solution without the sample was also prepared. In the blank, the DPPH solution was substituted with ethanol. The antioxidant activity of the sample was evaluated using the inhibition percentage of the DPPH radical with the following equation:
where A is the absorbance rate of the sample, A0 is the control group absorbance, and A′ is the blank absorbance.
DPPH radical scavenging activity (%) = (A0 + A′ − A)/A0 × 100%
HO· Scavenging Activity
A total of 1.0 mL of a 1.87 mM 1,10-phenanthroline solution and 2.0 mL of the sample were added to a screw-capped tube and mixed. Then, 1.0 mL of a FeSO4·7H2O solution (1.87 mM) was added to the mixture. The reaction was initiated by adding 1.0 mL of H2O2 (0.03%, v/v). After incubating at 37 °C for 60 min in a water bath, the absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured at 536 nm against a reagent blank. The reaction mixture without any antioxidant was used as the negative control, and a mixture without H2O2 was used as the blank. The hydroxyl radical scavenging activity (HRSA) was calculated using the following formula:
where As, An, and Ab are the absorbance values determined at 536 nm of the sample, negative control, and blank after the reaction, respectively.
HRSA (%) = [(As − An)/(Ab − An)] × 100%
3.5.2. Lipid Peroxidation Inhibition Assay
Lipid peroxidation inhibition assays were operated on the reported methods [11,14]. Briefly, a sample (5.0 mg) was dissolved in 10 mL of 50 mM PBS (pH 7.0) and added to 0.13 mL of a solution of linoleic acid and 10 mL of 99.5% ethanol. Then, the total volume was adjusted to 25 mL with deionized water. The mixture was incubated in a conical flask with a screw cap at 40 °C in a dark room, and the degree of oxidation was evaluated by measuring ferric thiocyanate values. The reaction solution (100 μL) incubated in the linoleic acid model system was mixed with 4.7 mL of 75% ethanol, 0.1 mL of 30% ammonium thiocyanate, and 0.1 mL of 20 mM ferrous chloride solution in 3.5% HCl. After 3 min, the thiocyanate value was measured at 500 nm, following color development with FeCl2 and thiocyanate at different intervals during the incubation period at 40 °C.
3.5.3. Protective Assay on Plasmid DNA
The protective effects of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11, on supercoiled plasmid DNA (pBR322) were measured using the previous method [11]. In brief, 15 μL of reaction mixtures containing 5 μL of PBS (10 mM, pH 7.4), 2 μL of FeSO4 (1.0 mM), 1μL of pBR322 (0.5 μg), 5 μL of the peptide (SCP8, SCP10, or SCP11, respectively), and 2 μL of H2O2 (1.0 mM) were incubated at 37 °C. After 0.5 h incubation, the reaction was terminated by adding 2 μL of a loading buffer containing glycerol (50%, v/v), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (40 mM), and bromophenol blue (0.05%). The resulted reaction mixtures were subsequently electrophoresed on 1% agarose gel containing 0.5 μg/mL EtBr for 50 min (60 V), and the DNA in the agarose gel was photographed under ultraviolet light.
3.6. Protective Function of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on H2O2-Injured HUVECs
3.6.1. Cell Culture and Viability Determination
The HUVECs were cultured according to the described method by Cai et al. [66] and Wang et al. [77]. In brief, HUVECs with the density of 1.0 × 105 cells/well were seeded into a 96-well plate containing 100 μL of culture media. After incubated for 24 h, 20 μL of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 solutions dissolved in the DMEM medium were separately added in the sample groups with the final concentration of 200 μg/mL. In addition, peptide was substituted by PBS (pH 7.2) in the control group. After incubated for 24 h, 20 μL of MTT was added into the plate and OD490 nm was measured after 4 h. The cell viability was calculated on the basis of the following formula:
Cell viability (%) = (ODsample/ODcontrol)×100.
3.6.2. Protection of SCP8, SCP10, and SCP11 on H2O2-Injured HUVECs
HUVECs with the density of 1.0 × 105 cells/well were seeded into a 96-well plate containing 100 μL of culture media. After 24 h, the supernatant in the HUVECs wells was aspirated and H2O2 was added, and its final concentrations, respectively, reached 0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, and 600 μM. After 24 h, cell viability was determined according to the above method and the H2O2 concentration that induced cell viability by approximately 50% was chosen to establish the oxidative damage model of HUVECs [66,77].
After culturing for 24 h, the supernatant in the HUVECs wells was wiped off. Subsequently, 100 µL of the peptide samples at the final concentrations of 200 µM were joined in the protection groups. After 8 h, the peptide sample was cleared and H2O2 at 200 µM was put in the model and the peptide sample groups and then treated for 24 h. A total of 100 µL of NAC (1.5 mM) was used as the positive control group. The blank control group used 20 μL PBS instead of the peptide solution.
3.6.3. Determination of ROS, MDA, and Antioxidases
The levels of ROS in the blank control, model, and sample groups were measured on the reported method and expressed as a percentage of the of blank control [66].
The activity of SOD and GSH-Px and the content of MDA were measured using assay kits in accordance with the protocols of the Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China), and the levels of SOD and GSH-Px were indicated as U/mg prot.
3.7. Statistical Analysis
The data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD, n = 3). An ANOVA test was used to analyze the differences between the means of each group, using SPSS 19.0 (Statistical Program for Social Sciences, SPSS Corporation, Chicago, IL, USA). A Duncan’s test was used to determine the significance between different groups (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, or p < 0.001).
4. Conclusions
In the study, thirteen APs were isolated from the collagen hydrolysate of Siberian sturgeon cartilages produced using Alcalase and identified as GPTGED, GEPGEQ, GPEGPAG, VPPQD, GLEDHA, GDRGAEG, PRGFRGPV, GEYGFE, GFIGFNG, PSVSLT, IELFPGLP, LRGEAGL, and RGEPGL, respectively. Among them, GEYGFE, PSVSLT, and IELFPGLP showed the highest radical scavenging activity, lipid peroxidation inhibiting capability, and protection on H2O2-injured HUVECs and on plasmid DNA. Therefore, this research provides free technical support for higher-valued utilizing fish by-products. More importantly, thirteen isolated collagen APs, especially GEYGFE, PSVSLT, and IELFPGLP, may act as antioxidant additives for generating health products to treat chronic diseases caused by oxidative stress. Moreover, the antioxidant mechanism of GEYGFE, PSVSLT, and IELFPGLP will be systematically researched in our follow-up study.
Author Contributions
Y.S.: conceptualization, data curation, and formal analysis. Y.-T.Q.: investigation, methodology, validation, and writing—original draft. Y.-M.W.: conceptualization, data curation, and formal analysis. C.-F.C.: investigation, methodology, and validation. B.W.: resources, funding acquisition, supervision, and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82073764) and the Ten-thousand Talents Plan of Zhejiang Province (No. 2019R52026).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
DPPH·, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical; HO·, hydroxide radical; ROS, reactive oxygen species; AP, antioxidant peptide; MW, molecular weight; SCH, Collagen hydrolysate of Siberian Sturgeon Cartilage; GFC, Gel Filtration Chromatography; SCP1, Gly-Pro-Thr-Gly-Glu-Asp (GPTGED); SCP2, Gly-Glu-Pro-Gly-Glu-Gln (GEPGEQ); SCP3, Gly-Pro-Glu-Gly-Pro-Ala-Gly (GPEGPAG); SCP4, Val-Pro-Pro-Gln-Asp (VPPQD); SCP5, Gly-Leu-Glu-Asp-His-Ala (GLEDHA); SCP6, Gly-Asp-Arg-Gly-Ala-Glu-Gly (GDRGAEG) SCP7, Pro-Arg-Gly-Phe-Arg-Gly-Pro-Val (PRGFRGPV); SCP8, Gly-Glu-Tyr-Gly-Phe-Glu (GEYGFE); SCP9, Gly-Phe-Ile-Gly-Phe-Asn-Gly (GFIGFNG); SCP10, Pro-Ser-Val-Ser-Leu-Thr (PSVSLT); SCP11, Gly-Ile-Glu-Leu-Phe-Pro-Gly-Leu-Pro (GIELFPGLP); SCP12, Leu-Arg-Gly-Glu-Ala-Gly-Leu (LRGEAGL); SCP13, Arg-Gly-Glu-Pro-Gly-Leu (RGEPGL); GSP, glutathione; SC, supercoiled; OC, open circular; LIN, linear; HUVECs, Human umbilical vein endothelial cells; MTT, 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.
References
- Sila, A.; Bougatef, A. Antioxidant peptides from marine by-products: Isolation, identification and application in food systems. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vliet, A.; Janssen, H.; Anathy, V. Oxidative stress in chronic lung disease: From mitochondrial dysfunction to dysregulated redox signaling. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 63, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, E.P.; Mariz, P.N.; Rigazio, C.S.; Santamaría, M.H.; Corral, R.S. Honokiol attenuates oxidative stress-dependent heart dysfunction in chronic Chagas disease by targeting AMPK/NFE2L2/SIRT3 signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 156, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello, V.C.; Simon, F.; Trollet, C.; Santibañez, J.F. Oxidative stress in disease and aging: Mechanisms and therapies. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 6, 4310469. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Yu, H.; Yang, Z.; Hu, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.K.; Peng, J. Gly-Pro-Ala peptide and FGSHF3 exert protective effects in DON-induced toxicity and intestinal damage via decreasing oxidative stress. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, W.H.; Wang, P.; Chi, C.F. Antioxidant peptides from Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) hydrolysate: Preparation, identification and cytoprotection on H2O2-induced oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 86, 104701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Li, T.; Ding, G.F. Antioxidant and anticancer peptides from protein hydrolysate of blood clam (Tegillarca granosa) muscle. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 15, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della, M.D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H. Plant protein-derived antioxidant peptides: Isolation, identification, mechanism of action and application in food systems: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, D.; Takaki, A.; Oyama, A.; Adachi, T.; Wada, N.; Onishi, H.; Okada, H. Oxidative stress management in chronic liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhao, G.X.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from collagen hydrolysate of redlip croaker (Pseudosciaena polyactis) scales: Preparation, characterization, and cytoprotective effects on H2O2-damaged HepG2 cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, R.; Dong, Y.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Lin, S.; Sun, N. Advances in the activity evaluation and cellular regulation pathways of food-derived antioxidant peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 122, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Ren, X.J.; Deng, S.G.; Wu, C.W. Purification and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolyzate of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) muscle. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.H.; Luo, Q.B.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, B. Preparation, identification, and activity evaluation of ten antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of swim bladders of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy). J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hritcu, L.; Ionita, R.; Postu, P.A.; Gupta, G.K.; Turkez, H.; Lima, T.C.; Carvalho, C.U.S.; De Sousa, D.P. Antidepressant flavonoids and their relationship with oxidative stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 5762172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macáková, K.; Afonso, R.; Saso, L.; Mladěnka, P. The influence of alkaloids on oxidative stress and related signaling pathways. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 134, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Jo, M.H.; Choe, K.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, S.; Saeed, K.; Kim, M.W.; Kim, M.O. Cycloastragenol, a triterpenoid saponin, regulates oxidative stress, neurotrophic dysfunctions, neuroinflammation and apoptotic cell death in neurodegenerative conditions. Cells 2021, 10, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Nikoo, M.; Boran, G.; Zhou, P.; Regenstein, J.M. Collagen and gelatin. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 527–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand View Research. (June 2016). Gelatin Market Size Expected to Reach $4.08 Billion by 2024. Available online: http://www.grandviewresearch.com/pressrelease/global-gelatin-market (accessed on 13 June 2016).
- Nurilmala, M.; Hizbullah, H.H.; Karnia, E.; Kusumaningtyas, E.; Ochiai, Y. Characterization and antioxidant activity of collagen, gelatin, and the derived peptides from yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) skin. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al, N.S.; Dayah, A.A.; Hasan, I.; Daghmash, R. Cosmetic, biomedical and pharmaceutical applications of fish gelatin/hydrolysates. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, S.M.K.; Hossain, M.A.M.; Sagadevan, S.; Amin, M.A.; Johan, M.R. Halal and kosher gelatin: Applications as well as detection approaches with challenges and prospects. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.M.; Yang, X.R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Gelatin and antioxidant peptides from gelatin hydrolysate of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) scales: Preparation, identification and activity evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Felician, F.F.; Xia, C.; Qi, W.; Xu, H. Collagen from marine biological sources and medical applications. Chem Biodivers. 2018, 15, 1700557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, G.X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Qiu, Y.T.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Identification and active evaluation of antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysates of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) head. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.B.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Eight peptides from collagen hydrolysate fraction of Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorous niphonius) skin: Isolation, identification, and antioxidant activity in vitro. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Jo, Y.J. Static hydrothermal processing and fractionation for production of a collagen peptide with anti-oxidative and anti-aging properties. Process Biochem. 2019, 83, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Verma, A.K.; Patel, R. Collagen extraction and recent biological activities of collagen peptides derived from sea-food waste: A review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 18, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Tian, X.; Xu, B.; Yuan, F.; Gong, J.; Yang, Z. Collagen peptides from swim bladders of giant croaker (Nibea japonica) and their protective effects against H2O2-induced oxidative damage toward human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, S.J.; Yang, Z.S.; Jin, H.X. Preparation of antioxidant peptide by microwave-assisted hydrolysis of collagen and its protective effect against H2O2-induced damage of RAW264.7 cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, Y. Antiphotoaging effect and purification of an antioxidant peptide from tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) gelatin peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Hou, H. Protective effect of gelatin polypeptides from pacific cod (Gadus Macrocephalus) against UV irradiation-induced damages by inhibiting inflammation and improving transforming growth factor-β/smad signaling pathway. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 162, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Hou, H.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, Q.; Si, L.; Li, B. Protective effect of gelatin peptides from pacific cod skin against photoaging by inhibiting the expression of MMPs via MAPK signaling pathway. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 165, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, X.; Meng, M.; Luo, Y.; Li, B. The anti-photoaging effect of antioxidant collagen peptides from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) skin is preferable to tea polyphenols and casein peptides. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Zeng, L.; Yang, Z.S.; Huang, F.F.; Ding, G.F.; Wang, B. Anti-Fatigue effect by peptide fraction from protein hydrolysate of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) swim bladder through inhibiting the oxidative reactions including DNA damage. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gui, M.; Song, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, R.; Ma, C. Chemical characteristics and antithrombotic effect of chondroitin sulfates from sturgeon skull and sturgeon backbone. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 123, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.B.; Chi, C.F.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, B. Physicochemical properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the cartilage of Siberian sturgeon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31427–31438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Ren, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B. Structural characterization and proliferation activity of chondroitin sulfate from the sturgeon, Acipenser schrenckii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3005–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, B.; Poungchawanwong, S.; Hou, H. Structural feature and self-assembly properties of type II collagens from the cartilages of skate and sturgeon. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.S.; Tu, C.W.; Kuo, H.C.; Sun, P.P.; Tsai, M.L. Type II Collagen from cartilage of Acipenser baerii promotes wound healing in human dermal fibroblasts and in mouse skin. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chu, Q.; Wu, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W.; Jin, W.; Gao, R. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity of peptides from ethanol-soluble hydrolysates of sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii) cartilage. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 689648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.Q.; Luo, Q.B.; Suo, S.K.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Preparation, characterization, and cytoprotective effects on HUVECs of fourteen Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysate of tuna processing by-products. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 868681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.L.; Luo, Q.B.; Suo, S.K.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Preparation, identification, molecular docking study and protective function on HUVECs of Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptides from protein hydrolysate of Skipjack tuna muscle. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Hu, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Luo, H. Influence of different hydrolysis processes by trypsin on the physicochemical, antioxidant, and functional properties of collagen hydrolysates from Sphyrna lewini, Dasyatis akjei, and Raja porosa. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 616–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Chi, C.; Luo, H.; Gong, Y.; Ding, G. Influence of average molecular weight on antioxidant and functional properties of collagen hydrolysates from Sphyrna lewini, Dasyatis akjei and Raja porosa. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intarasirisawat, R.; Benjakula, S.; Wu, J.; Visessanguan, W. Isolation of antioxidative and ACE inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysate of skipjack (Katsuwana pelamis) roe. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Huang, Z.; Tang, S.; Lu, C.; Wan, H.; Zhou, J. The novel peptides ICRD and LCGEC screened from tuna roe show antioxidative activity via Keap1/Nrf2-ARE pathway regulation and gut microbiota modulation. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, L.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Twelve antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) roe prepared by flavourzyme: Purification, sequence identification, and activity evaluation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 813780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B. Preparation and identification of antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of skate (Raja porosa) cartilage. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 25, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Hee, C.Y.; Seok, C.Y.; Alam, M.B.; Han, L.S.; Cheol, Y.J. A novel antioxidant peptide, purified from bacillus amyloliquefaciens, showed strong antioxidant potential via Nrf2 mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, R.A.; Kumar, N.S.S.; Ganesh, R.J. In vitro and in vivo studies on the antioxidant activity of fish peptide isolated from the croaker (Otolithes ruber) muscle protein hydrolysate. Peptides 2012, 35, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from the protein hydrolysate of monkfish (Lophius litulon) muscle: Purification, identification, and cytoprotective function on HepG2 cells damage by H2O2. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sridhar, K.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. Recent developments on production, purification and biological activity of marine peptides. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Luo, H.Y. Influence of amino acid compositions and peptide profiles on antioxidant capacities of two protein hydrolysates from Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) dark muscle. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2580–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, L.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Four antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of red stingray (Dasyatis akajei) cartilages: Isolation, identification, and in vitro activity evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sudhakar, S.; Nazeer, R.A. Preparation of potent antioxidant peptide from edible part of shortclub cuttlefish against radical mediated lipid and DNA damage. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Park, S.Y.; Han, E.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, D.S.; Je, J.Y.; Ahn, C.B.; Ahn, G. Isolation of an antioxidant peptide from krill protein hydrolysates as a novel agent with potential hepatoprotective effects. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 67, 103889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, K.M.I.; Sohn, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, J.S. Identification and characterization of novel antioxidant peptides from mackerel (Scomber japonicus) muscle protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of skipjack tuna milt: Purification, identification, and cytoprotection on H2O2 damaged human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Process Biochem. 2022, 113, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhao, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ren, J. Purification and identification of antioxidative peptides from loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) protein hydrolysate by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhao, G.X.; Suo, S.K.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Purification, identification, activity evaluation, and stability of antioxidant peptides from alcalase hydrolysate of Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) proteins. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.B.; Cho, Y.S.; Je, J.Y. Purification and anti-inflammatory action of tripeptide from salmon pectoral fin byproduct protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, B. Ten new pentapeptides from protein hydrolysate of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) muscle: Preparation, identification, and antioxidant activity evaluation. LWT 2019, 105, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, S.; Li, J. Purification and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 16, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonolo, F.; Moretto, L.; Grinzato, A.; Fiorese, F.; Folda, A.; Scalcon, V. Fermented soy-derived bioactive peptides selected by a molecular docking approach show antioxidant properties involving the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Cytoprotective effect of antioxidant pentapeptides from the protein hydrolysate of swim bladders of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) against H2O2-mediated human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) injury. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 20, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajapakse, N.; Mendis, E.; Jung, W.K.; Je, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Purification of a radical scavenging peptide from fermented mussel sauce and its antioxidant properties. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Zhou, A.; Miao, J.; Liu, J.; Benjakul, S. A novel antioxidant peptide purified frecom defatted round scad (Decapterus maruadsi) protein hydrolysate extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheih, I.C.; Wu, T.K.; Fang, T.J. Antioxidant properties of a new antioxidative peptide from algae protein waste hydrolysate in different oxidation systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3419–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Jin, D.H.; Ogawa, T.; Muramoto, K.; Hatakeyama, E.; Yasuhara, T.; Nokihara, K. Antioxidative properties of tripeptide libraries prepared by the combinatorial chemistry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3668–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, O.K.; Ha, G.E.; Han, G.S.; Seol, K.H.; Kim, H.W.; Jeong, S.G.; Oh, M.H.; Park, B.Y.; Ham, J.S. Novel antioxidant peptide derived from the ultrafiltrate of ovomucin hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7294–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarpoor, Y.M.; Asoodeh, A.; Chamani, J. A novel antioxidant and antimicrobial peptide from hen egg white lysozyme hydrolysates. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Si, D.; Ahmad, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R. A novel antioxidative peptide derived from chicken blood corpuscle hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Qiu, Y.T.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Preparation and characterization of gelatin and antioxidant peptides from gelatin hydrolysate of Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) bone stimulated by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theodore, A.E.; Raghavan, S.; Kristinsson, H.G. Antioxidative activity of protein hydrolysates prepared from alkaline-aided channel catfish protein isolates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7459–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.X.; Yang, X.R.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from the protein hydrolysate of Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorous niphonius) muscle by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion and their in vitro activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant mechanisms of the oligopeptides (FWKVV and FMPLH) from muscle hydrolysate of miiuy croaker against oxidative damage of HUVECs. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9987844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, F. Potential mechanisms mediating the protective effects of a peptide from walnut (Juglans mandshurica Maxim) against hydrogen peroxide induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3491–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.C.; Ji, J.A.; Jiang, Z.Y.; You, Q.D. The Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as a potential preventive and therapeutic target: An update. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 924–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G. Peptide and small molecule inhibitors of the Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, W.; Sadiq, F.A.; Wang, S.; Caiqin, L.; Jianchang, J. Involvement of Nrf2 and Keap1 in the activation of antioxidant responsive element (ARE) by chemopreventive agent peptides from soft-shelled turtle. Process Biochem. 2020, 92, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.; José, A.M.G. Molecular recognition between potential natural inhibitors of the Keap1-Nrf2 complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.T.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, H.H.; Duan, Y.Q.; Ma, H.L. Study on the structure–activity relationship of watermelon seed antioxidant peptides by using molecular simulations. Food Chem. 2021, 2021, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonolo, F.; Fiorese, F.; Moretto, L.; Folda, A.; Scalcon, V.; Grinzato, A.; Ferro, S.; Arrigoni, G.; Bindoli, A.; Feller, E.; et al. Identification of new peptides from fermented milk showing antioxidant properties: Mechanism of action. Antioxidants. 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Lu, J.; Asakiya, C.; Huang, K.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; He, X. Extraction and identification of three new urechis unicinctus visceral peptides and their antioxidant activity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.Q.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, D.D.; Fan, Y.Z.; Shi, Y.; Huang, A.X. Novel ACE inhibitory, antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides identified from fermented rubing cheese through peptidomic and molecular docking. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).