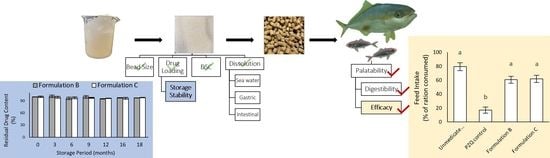
Effects of Formulation on the Palatability and Efficacy of In-Feed Praziquantel Medications for Marine Finfish Aquaculture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bead Characterisation
2.1.1. Bead Size and Drug Loading
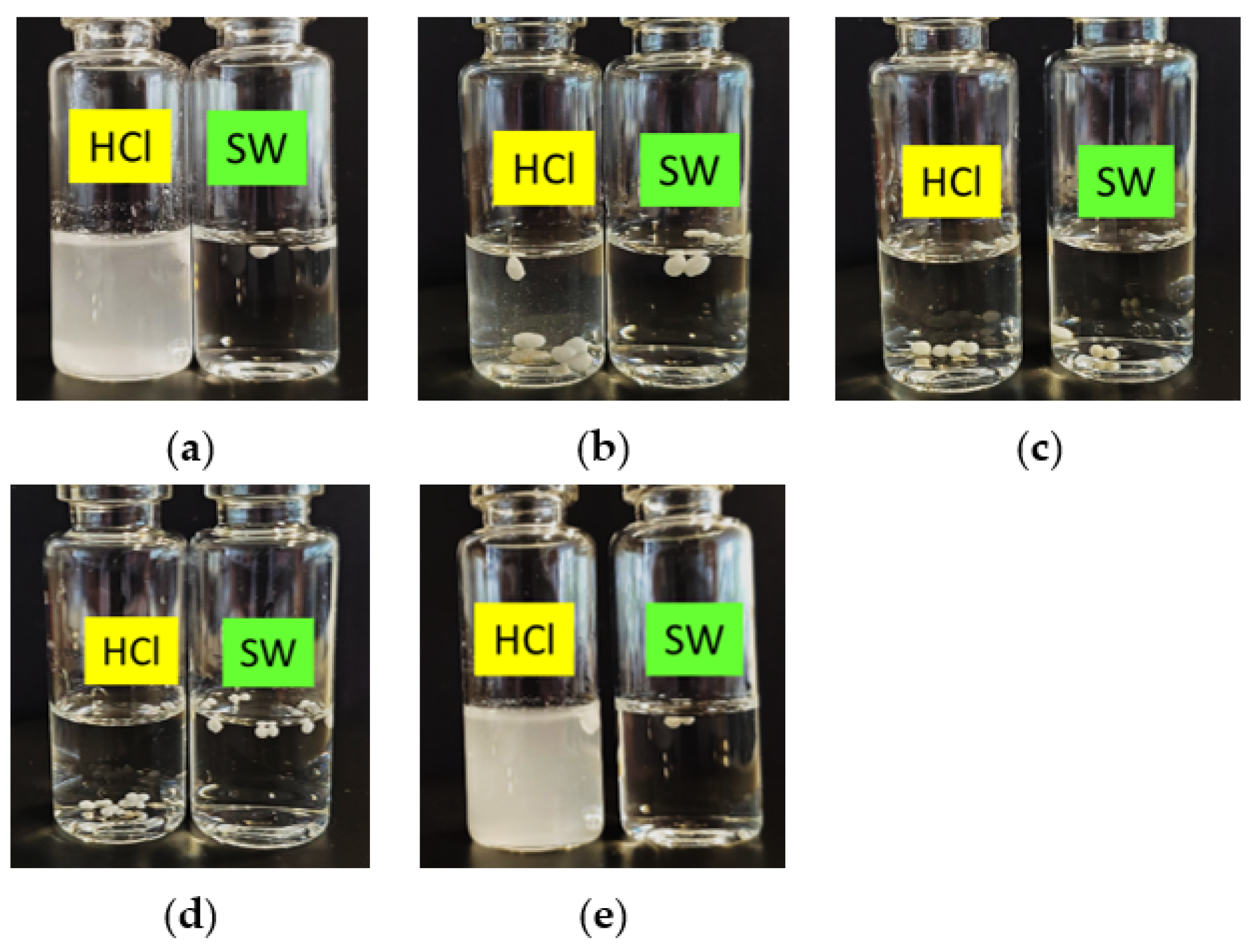
2.1.2. In Vitro Disintegration Profile
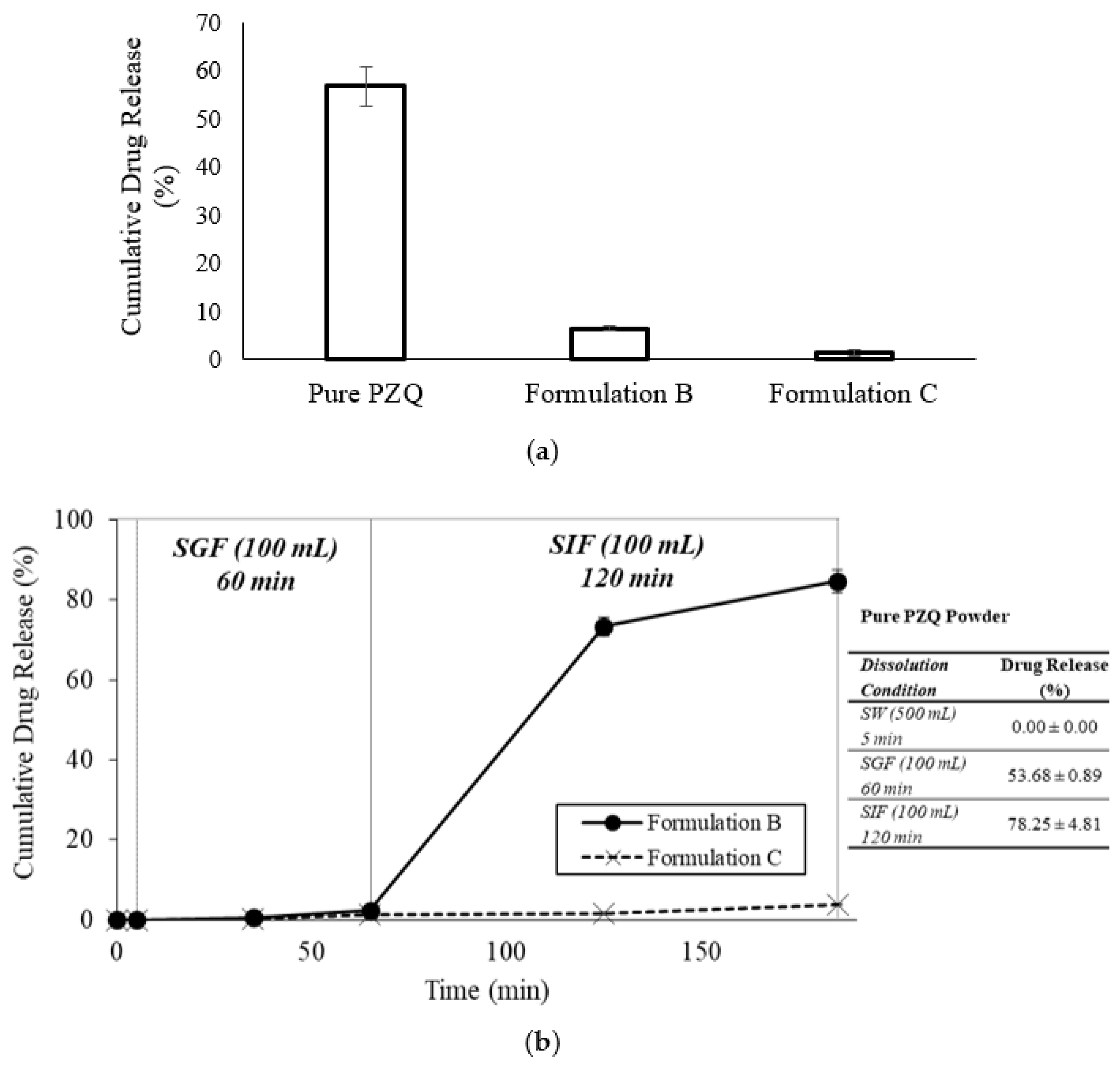
2.1.3. In Vitro Dissolution Profile of Formulation B and Formulation C
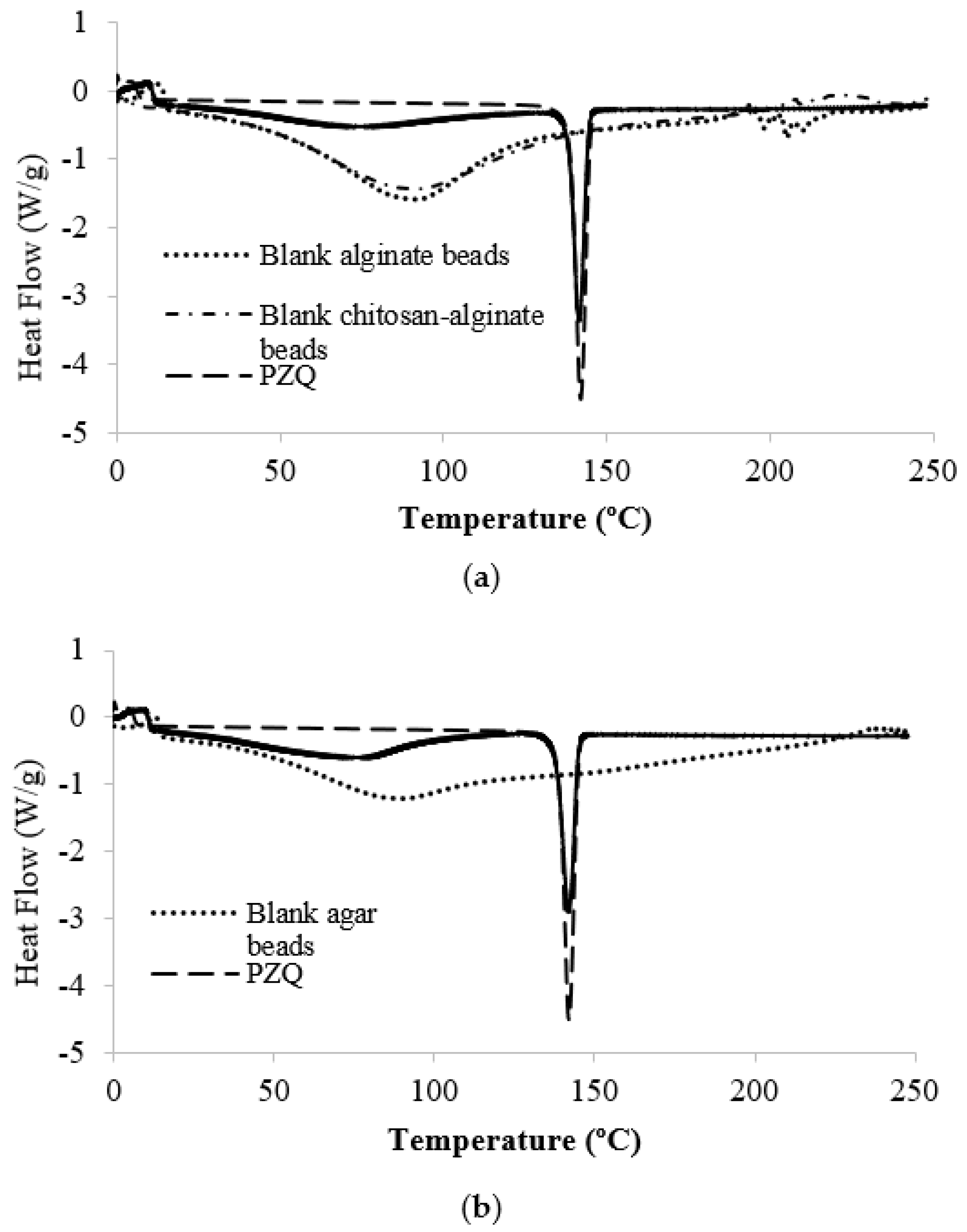
2.1.4. PZQ Compatibility with Matrix Materials in Formulations B and C
2.2. Storage Stability of Formulations B and C BEADS at Ambient Temperature
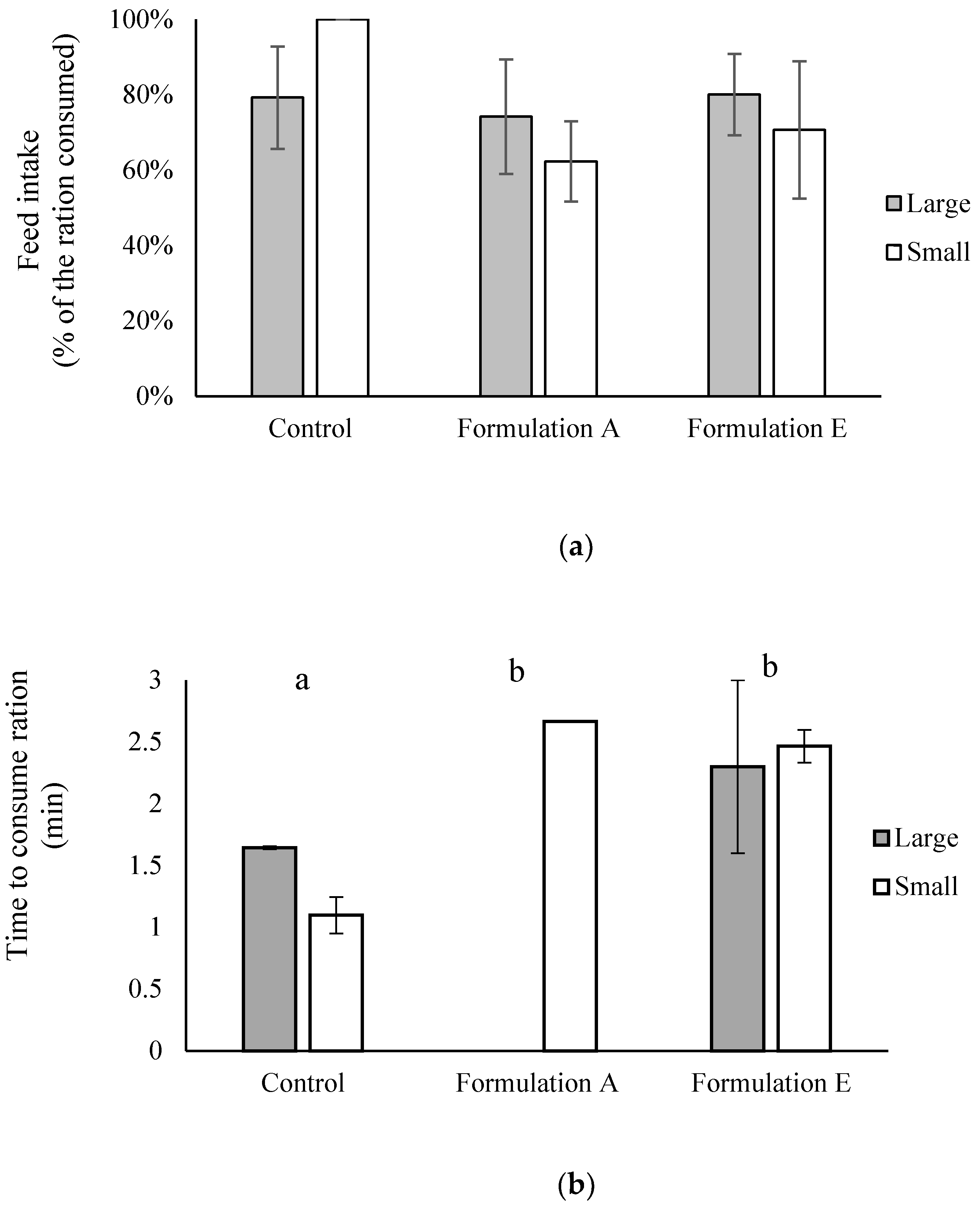
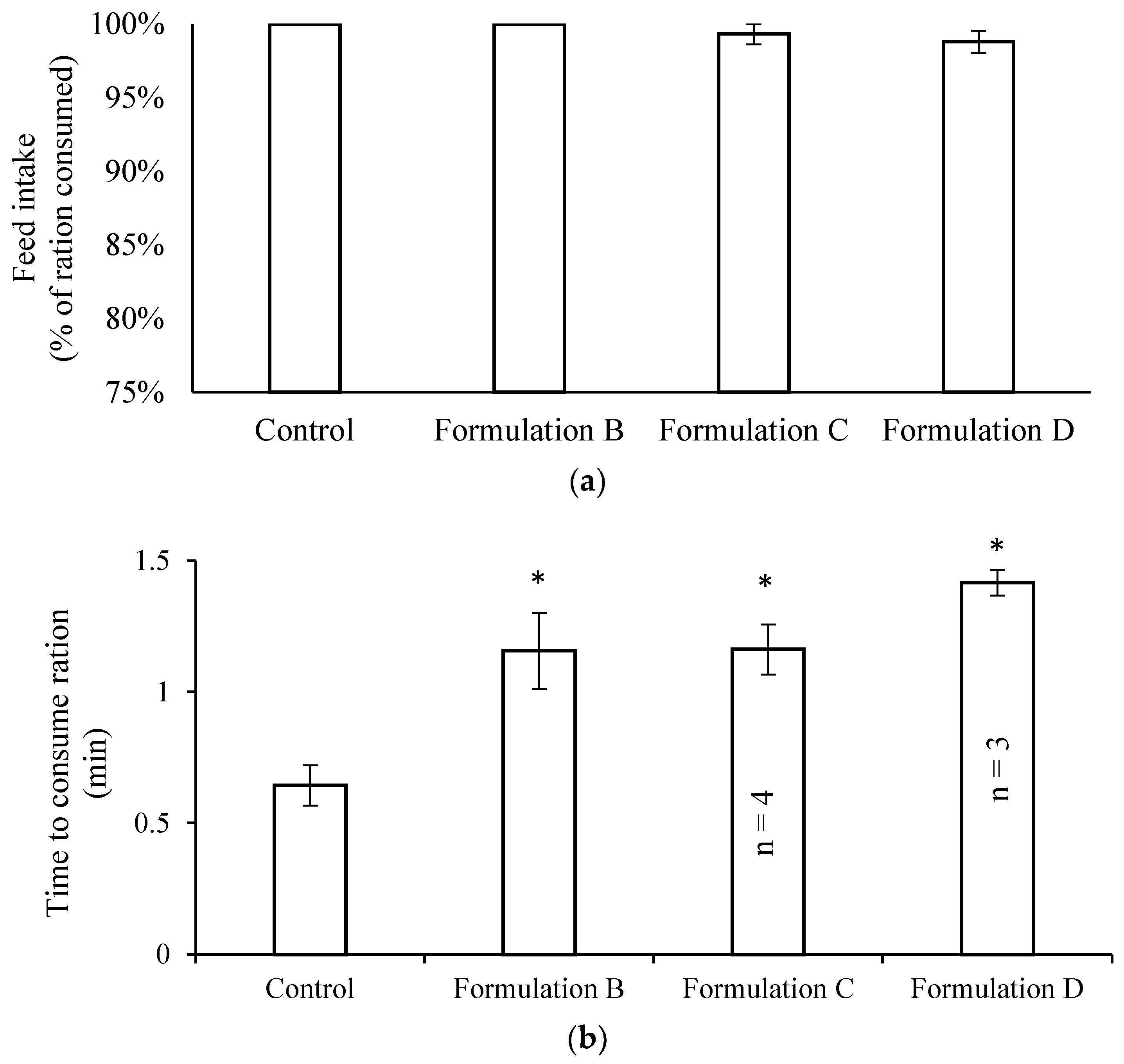
2.3. Palatability and Digestibility of Formulations A, B, C, D, and E in Healthy (Uninfected) Fish
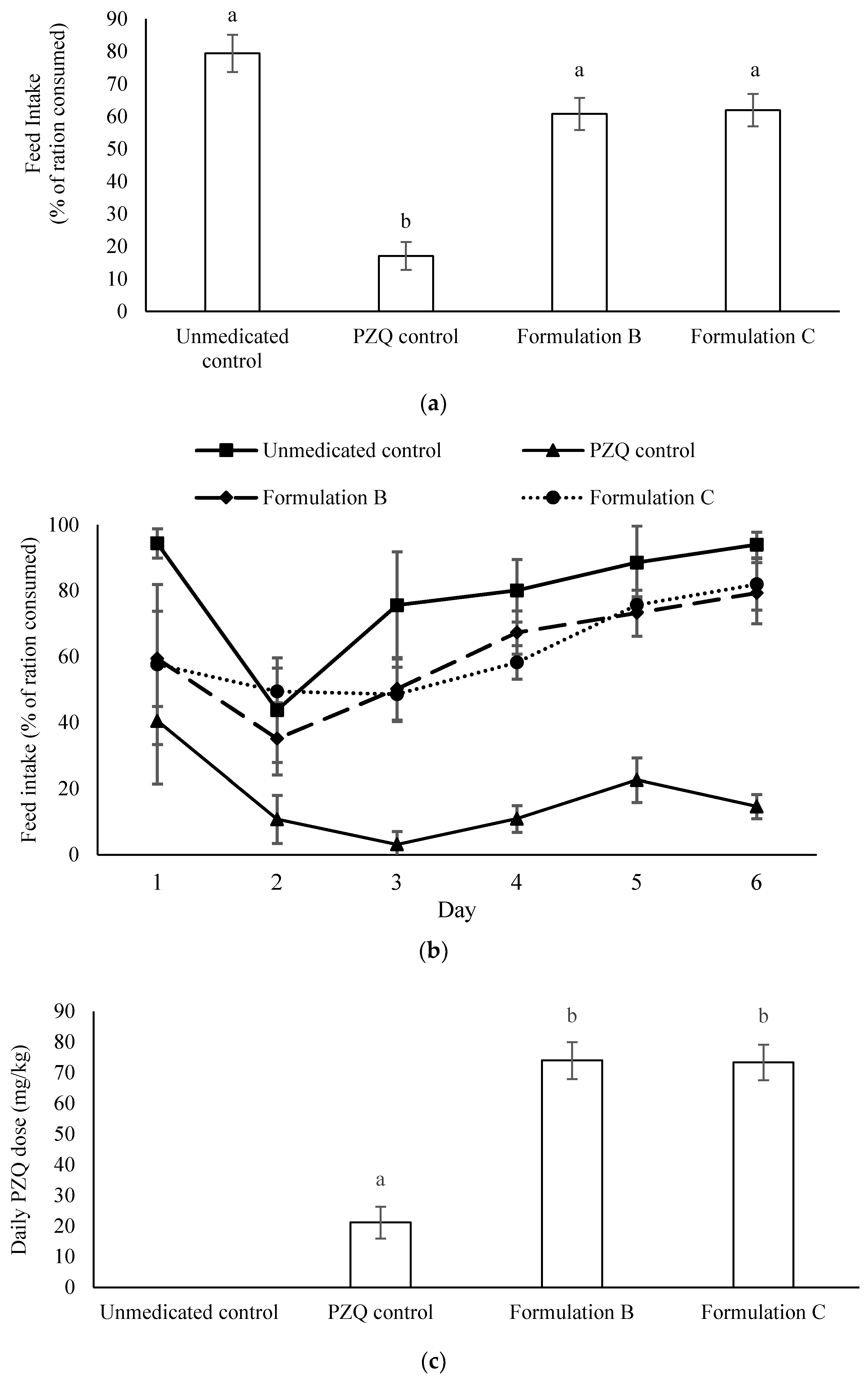
2.4. Palatability and Efficacy of Formulations B and C in Parasite-Infected Fish
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Bead Preparation
4.2.1. Chitosan-Based Beads (Formulation A and Formulation E)
4.2.2. Alginate/Chitosan-Based Beads (Formulation B and Formulation D)
4.2.3. Agar-Based Beads (Formulation C)
4.2.4. Scaled-Up Manufacture
4.3. Bead Characterisation
4.3.1. Bead Diameter
4.3.2. Drug Loading and Stability on Storage
4.3.3. In Vitro Disintegration Profile
4.3.4. In Vitro Dissolution Profile of Formulation B and Formulation C
4.3.5. Analysis by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.4. Palatability Assessment in Healthy Fish
4.5. Palatability and Efficacy Assessments in Parasite-Infected Fish
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shinn, A.; Pratoomyot, J.; Bron, J.; Paladini, G.; Brooker, E.; Brooker, A. Economic impacts of aquatic parasites on global finfish production. Glob. Aquac. Advocate 2015, 2015, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hoai, T.D. Reproductive strategies of parasitic flatworms (Platyhelminthes, Monogenea): The impact on parasite management in aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 421–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, I.D.; Chisholm, L.A. Diseases Caused by Monogenea. In Fish Diseases; Science Publishers, Inc.: Enfield, UK, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 683–816. [Google Scholar]
- Partridge, G.J.; Michael, R.J.; Thuillier, L. Praziquantel form, dietary application method and dietary inclusion level affect palatability and efficacy against monogenean parasites in yellowtail kingfish. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 109, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirazawa, N.; Tsubone, S.; Takano, R. Anthelmintic effects of 75ppm hydrogen peroxide treatment on the monogeneans Benedenia seriolae, Neobenedenia girellae, and Zeuxapta japonica infecting the skin and gills of greater amberjack Seriola dumerili. Aquaculture 2016, 450, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, L.D.; Pilmer, L.; Stephens, F.J.; Lim, Z.X.; Arthur, P.G.; Gholipourkanani, H.; Partridge, G.J. The effect of hydrogen peroxide concentration and water temperature on yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi in a repeated bathing treatment. Aquaculture. in review.
- Gaikowski, M.P.; Rach, J.J.; Ramsay, R.T. Acute toxicity of hydrogen peroxide treatments to selected lifestages of cold-, cool-, and warmwater fish. Aquaculture 1999, 178, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M. Praziquantel. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2009, 18, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.D.; Guerrant, R.L. Praziquantel: A Major Advance in Anthelminthic Therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 1983, 99, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahl, G.; Mehlhorn, H. Treatment of fish parasites. Z. Parasitenkd. 1985, 71, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, G.J.; Rao, S.; Woolley, L.D.; Pilmer, L.; Lymbery, A.J.; Prestidge, C.A. Bioavailability and palatability of praziquantel incorporated into solid-lipid nanoparticles fed to yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 218, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Partridge, G.J.; Burge, T.; Lymbery, A.J. A comparison of the palatability of racemic praziquantel and its two enantioseparated isomers in yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi (Valenciennes, 1833). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.; Darwish, A. Efficacy of 6-, 12-, and 24-h Praziquantel Bath Treatments against Asian Tapeworms Bothriocephalus acheilognathi in Grass Carp. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2009, 71, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, C.; Riley, A. Anthelmintic treatment of fish via stomach tube. Fish. Manag. 1982, 13, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forwood, J.M.; Harris, J.O.; Deveney, M.R. Efficacy of bath and orally administered praziquantel and fenbendazole against Lepidotrema bidyana Murray, a monogenean parasite of silver perch, Bidyanus bidyanus (Mitchell). J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forwood, J.M.; Bubner, E.J.; Landos, M.; D’Antignana, T.; Deveney, M.R. Praziquantel treatment for yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi): Dose and duration safety study. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, C.; Jesudoss Chelladurai, J.; Starling, D.; Jones, D.; Brewer, M. Efficacy of injectable praziquantel for elimination of trematode metacercariae in bluegills (Lepomis macrochirus) and quantification of parasite death by propidium iodide staining. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 117, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.E.; Ernst, I.; Chambers, C.B.; Whittington, I.D. Efficacy of orally administered praziquantel against Zeuxapta seriolae and Benedenia seriolae (Monogenea) in yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 77, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirazawa, N.; Akiyama, K.; Umeda, N. Differences in sensitivity to the anthelmintic praziquantel by the skin-parasitic monogeneans Benedenia seriolae and Neobenedenia girellae. Aquaculture 2013, 404, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn, A.P.; Pratoomyot, J.; Bron, J.E.; Paladini, G.; Brooker, E.E.; Brooker, A.J. Economic costs of protistan and metazoan parasites to global mariculture. Parasitology 2015, 142, 196–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicuro, B.; Luzzana, U. The State of Seriola spp. Other Than Yellowtail (S. quinqueradiata) Farming in the World. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2016, 24, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K. Marine parasitology with special reference to Japanese fisheries and mariculture. Vet. Parasitol. 1996, 64, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, K.S.; Ernst, I.; Whittington, I.D. Risk assessment for metazoan parasites of yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi (Perciformes: Carangidae) in South Australian sea-cage aquaculture. Aquaculture 2007, 271, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, I.; Whittington, I.D.; Corneillie, S.; Talbot, C. Effects of temperature, salinity, desiccation and chemical treatments on egg embryonation and hatching success of Benedenia seriolae (Monogenea: Capsalidae), a parasite of farmed Seriola spp. J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilmer, L. Novel Methods of Improving the Palatability of Feeds Containing Praziquantel for Commercially Cultured Yellowtail Kingfish. Ph.D. Thesis, Murdoch University, Perth, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Forwood, J.M.; Bubner, E.J.; Landos, M.; Deveney, M.R.; D’Antignana, T. Praziquantel delivery via moist pellets to treat monogenean parasites of yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi: Efficacy and feed acceptance. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2016, 121, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurienzo, P. Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2435–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takka, S.; Gürel, A. Evaluation of Chitosan/Alginate Beads Using Experimental Design: Formulation and In Vitro Characterization. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2010, 11, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sosnik, A. Alginate Particles as Platform for Drug Delivery by the Oral Route: State-of-the-Art. ISRN Pharm. 2014, 2014, 926157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ching, S.H.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Alginate gel particles—A review of production techniques and physical properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.-C.; Wang, Y.-L.; Wang, K. A pH-responsive composite hydrogel beads based on agar and alginate for oral drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, V.; Majumdar, D.K. Entrapment of α-Amylase in Agar Beads for Biocatalysis of Macromolecular Substrate. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 936129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murata, Y.; Maeda, T.; Miyamoto, E.; Kawashima, S. Preparation of chitosan-reinforced alginate gel beads—Effects of chitosan on gel matrix erosion. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 96, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aral, C.; Akbuğa, J. Alternative approach to the preparation of chitosan beads. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 168, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Helw, A.E.-R.; El-Said, Y. Preparation and characterization of agar beads containing phenobarbitone sodium. J. Microencapsul. 1988, 5, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storebakken, T.; Austreng, E. Binders in fish feeds: II. Effect of different alginates on the digestibility of macronutrients in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 1987, 60, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüello-Guevara, W.; Molina-Poveda, C. Effect of binder type and concentration on prepared feed stability, feed ingestion and digestibility of Litopenaeus vannamei broodstock diets. Aquac. Nutr. 2013, 19, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, G.J.; Southgate, P.C. The effect of binder composition on ingestion and assimilation of microbound diets (MBD) by barramundi Lates calcarifer Bloch larvae. Aquac. Res. 1999, 30, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Arini, S.K.; Giron, D.; Leuenberger, H. Solubility Properties of Racemic Praziquantel and Its Enantiomers. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 1998, 3, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, R.R.; Mertins, O.; Tavares-Dias, M.; Flores-Gonzales, A.P.; Patta, A.C.M.F.; Ramirez, C.A.; Rigoni, V.L.; Mathews, P.D. High compliance and effective treatment of fish endoparasitic infections with oral drug delivery nanobioparticles: Safety of intestinal tissue and blood parameters. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, P.D.; Patta, A.C.M.F.; Madrid, R.R.M.; Ramirez, C.A.B.; Pimenta, B.V.; Mertins, O. Efficient Treatment of Fish Intestinal Parasites Applying a Membrane-Penetrating Oral Drug Delivery Nanoparticle. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.W.; Ching, A.L.; Liew, C.V.; Heng, P.W.S. Mechanistic Study on Hydration and Drug Release Behavior of Sodium Alginate Compacts. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Matysiak, S. Effect of pH on chitosan hydrogel polymer network structure. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7373–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danulat, E. Digestibility of chitin in cod, Gadus morhua, in vivo. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1987, 41, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahtat, D.; Mahlous, M.; Benamer, S.; Khodja, A.N.; Oussedik-Oumehdi, H.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Oral delivery of insulin from alginate/chitosan crosslinked by glutaraldehyde. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, M.I.; Karim, E.I.A.; Ibrahim, K.E.E.; Ahme, B.M.; Saeed, A.E.M.; Hamid, A.E.M.E. Photo-thermal stability of praziquantel. Saudi Pharm. J. 2004, 12, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, M.; Salem, M.; Gaber, M.; Nour, A. Effect of Chitosan Supplemented Diet on Survival, Growth, Feed Utilization, Body Composition & Histology of Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). World J. Eng. Technol. 2015, 3, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Stationery Office. British Pharmacopoeia 2019; The Stationery Office: London, UK, 2018; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Solovyev, M.M.; Kashinskaya, E.N.; Izvekova, G.I.; Glupov, V.V. pH values and activity of digestive enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract of fish in Lake Chany (West Siberia). J. Ichthyol. 2015, 55, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguara, S.; Jauncey, K.; Agius, C. Enzyme activities and pH variations in the digestive tract of gilthead sea bream. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 62, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, M.R.C.; Loebenberg, R.; Almukainzi, M. Simulated Biological Fluids with Possible Application in Dissolution Testing. Dissolution Technol. 2011, 18, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, P.; Kortejärvi, H.; Liimatainen, A.; Ojala, K.; Kangas, H.; Hirvonen, J.; Tanninen, V.P.; Peltonen, L. Use of conventional surfactant media as surrogates for FaSSIF in simulating in vivo dissolution of BCS class II drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumoto, T. Yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata. In Nutrient Requirements and Feeding of Finfish for Aquaculture; CABI Publishing: Surrey, UK, 2002; pp. 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Formulation (Polymer Matrix) | Drug Loading (% w/w, n = 3) | Diameter of Dry Beads (mm, n = 20) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 g-Batch | 100 g-Batch | ||
| A (chitosan complexed for 3 h) | 82.5 ± 0.1 | N/A | 1.89 ± 0.26 |
| B (alginate and chitosan) | 74.7 ± 3.4 | 78.2 ± 0.3 | 3.03 ± 0.35 |
| C (agar) | 77.8 ± 0.1 | 80.2 ± 1.5 | 1.80 ± 0.26 |
| D (alginate and Cremophor® RH40) | 83.9 ± 1.3 | 86.1 ± 0.4 | 1.36 ± 0.29 |
| E (chitosan complexed overnight) | 81.5 ± 1.1 | N/A | 1.86 ± 0.28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, E.K.Y.; Partridge, G.J.; Woolley, L.D.; Pilmer, L.; Lim, L.Y. Effects of Formulation on the Palatability and Efficacy of In-Feed Praziquantel Medications for Marine Finfish Aquaculture. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050323
Tang EKY, Partridge GJ, Woolley LD, Pilmer L, Lim LY. Effects of Formulation on the Palatability and Efficacy of In-Feed Praziquantel Medications for Marine Finfish Aquaculture. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(5):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050323
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Edith K. Y., Gavin J. Partridge, Lindsey D. Woolley, Luke Pilmer, and Lee Yong Lim. 2022. "Effects of Formulation on the Palatability and Efficacy of In-Feed Praziquantel Medications for Marine Finfish Aquaculture" Marine Drugs 20, no. 5: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050323
APA StyleTang, E. K. Y., Partridge, G. J., Woolley, L. D., Pilmer, L., & Lim, L. Y. (2022). Effects of Formulation on the Palatability and Efficacy of In-Feed Praziquantel Medications for Marine Finfish Aquaculture. Marine Drugs, 20(5), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050323