Abstract
Nowadays, the logarithmic production of existing well-known food materials is unable to keep up with the demand caused by the exponential growth of the human population in terms of the equality of access to food materials. Famous local food materials with treasury properties such as mangrove fruits are an excellent source to be listed as emerging food candidates with ethnomedicinal properties. Thus, this study reviews the nutrition content of several edible mangrove fruits and the innovation to improve the fruit into a highly economic food product. Within the mangrove fruit, the levels of primary metabolites such as carbohydrates, protein, and fat are acceptable for daily intake. The mangrove fruits, seeds, and endophytic fungi are rich in phenolic compounds, limonoids, and their derivatives as the compounds present a multitude of bioactivities such as antimicrobial, anticancer, and antioxidant. In the intermediary process, the flour of mangrove fruit stands as a supplementation for the existing flour with antidiabetic or antioxidant properties. The mangrove fruit is successfully transformed into many processed food products. However, limited fruits from species such as Bruguiera gymnorrhiza, Rhizophora mucronata, Sonneratia caseolaris, and Avicennia marina are commonly upgraded into traditional food, though many more species demonstrate ethnomedicinal properties. In the Middle East, A. marina is the dominant species, and the study of the phytochemicals and fruit development is limited. Therefore, studies on the development of mangrove fruits to functional for other mangrove species are demanding. The locally accepted mangrove fruit is coveted as an alternate food material to support the sustainable development goal of eliminating world hunger in sustainable ways.
1. Introduction
Prolonged drought and other natural disasters drive food shortages, and with the global COVID-19 pandemic over the last two years, the global food distribution has been left in disarray. Disruption of the food supply and poverty cause inequity in accessing nutritious food stocks [1,2]. Regarding the UN report in 2021, up to 811 million of the world’s population is threatened by undernourishment, which represents an increase from previous years, whilst the production rate and economic aspect continue to disturb the food stock and distribution [3,4]. Those massive obstacles obstruct the sustainable development program adopted by the UN, especially point 2, to ensure sustainable manufacturer and consumption patterns to negate world hunger [5]. Thus, the search for emerging alternative food sources with a nutrition balance is requested [6]. Even though it is not a staple food for many populations, the consumption of fruit is steadily growing for its health benefit, the daily intake of which can be considered useful in providing nutrition supplementation [7]. Some types of mangroves produce edible fruit. Though it is not categorized as a commonly cultivated plant, the mangrove fruit for many communities is consumed for its ethnomedicinal properties.
Mangroves are halophile plants with vital economic and ecological services [8]. The area is considered the most productive ecosystem, underlying the fisheries’ food web [9]. Mangrove areas are wood/timber producers, feeding–nesting ground for birds, and consumable fishery commodities such as fish and shellfish [10,11]. On the global scale, the mangrove area is a main natural contributor in managing the climate in complex ways, such as its carbon flux mechanism and sequestration scheme [12,13]. However, the mangrove area hides its useful function on a smaller scale, especially for human merit. The mangrove sediments are rich in nutrients due to the rapid decomposition of organic matters [14], and it holds financial worth up to USD 232.49 per hectare when transformed into fertilizer in the agroindustry sector [15,16]. However, the equilibrium between conservation and exploration is compulsory to contain the sustainability effort [17,18,19].
Various natural treasures are found, from deeply buried in the sediment to high up in the canopy within the mangrove forest. Many microorganisms as micro-producers reside within the ecosystem with their irreplaceable roles [20,21]. Mangrove plants are hosts for more than 850 fungi, while 38 are classified as endophytic symbionts [22]. Several associated bacteria are also well-recognized for synthesizing phytochemicals, such as compounds from Pseudoalteromonas xiamenensis for its antibiotic properties [23,24] and Streptomyces euryhalinus for its antioxidant properties [25]. Aside from the symbionts, all parts of mangroves have been used in folklore medicine since time immemorial [26]. The parts of Rhizophora mangle, Avicennia officinalis L., and Xylocarpus granatum J. Koenig are renowned for their pharmacological and ethnomedicinal usage [27,28,29]. Those bioactivities are assumed from the metabolite contents within the plant. Naphthofuranquinone with intense anti-trypanosomal activity is found in the twigs of A. lanata [30], while proanthocyanidins from leaves of Ceriops tagal show solid antioxidant activities [31]. Unfortunately, only 27 species of mangrove have been traditionally used [32]. Among parts of the mangrove, the fruit is a seducing subject for exploration. The fruit is known for its prowess in traditional medicine, such as treating asthma, bleeding, cough, febrifuge, hemorrhages, intestinal parasites, remedy piles, sprains, swelling, and ulcers [32]. Some mangrove fruits are also edible, assigning their compatibility to traditional food manufacturers with curative properties [33].
In arid areas such as the Middle East, green vegetation such as mangrove forest is scarce, and regions such as this require severe specific attention from the community and the government [34]. The satellite data show that mangrove forests in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and Bahrain remain stable with a slight increase [35], while an intense incline is observed in the United Arab Emirates. The plantation of mangroves has driven the increase in the mangrove coverage area during the past decade [36]. The investigation of attractive mangrove forest products such as the fruits will encourage the rehabilitation program in the region.
Thus, this study summarizes the nutrition content along with secondary metabolites from mangroves and the possibility of the fruit being upgraded into functional food. The review is narrated in several parts, beginning with the nutrition content of the mangrove fruit followed by the secondary metabolites. In addition, the exploration of the metabolites is also extended to seed and fungus symbionts in the fruit. The processing of the mangrove fruit is later described as conveying the intermediate and final process. The current progress of exploration of mangrove plants in the Middle East is also defined.
2. Nutrition Composition and Bioactivity of Mangrove Fruit Extract
The mangrove fruit contains diverse nutrition compositions concerning the species. Carbohydrate is the dominant nutrition in all mangrove fruit, while the protein and fat contents are varied (Figure 1). The total phenolic content (TPC) in the mangrove fruit is also widely investigated and, for most purposes, relates TPC with antioxidant activities [37,38]. TPC is positively correlated with the antioxidants; thus, the exploration probes for high TPC content in the fruit [39,40]. However, the evaluation is limited due to the extraction method (Figure 2), which may produce bias in the results. The TPC and other nutrient contents may be distinct among the fruit in the same species. Besides antioxidant activities, the mangrove fruit extract demonstrates other excellent bioactivities.
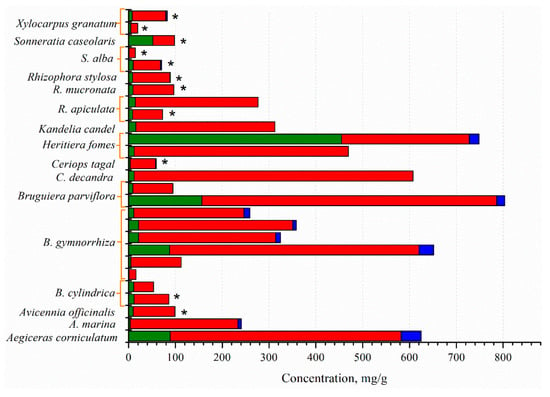
Figure 1.
The primary metabolites from some selected mangrove fruit:  , carbohydrate;
, carbohydrate;  , lipid;
, lipid;  , protein; *, carbohydrate is presented by total sugar and lipid is presented by fat. Modified from [41,42,43].
, protein; *, carbohydrate is presented by total sugar and lipid is presented by fat. Modified from [41,42,43].
 , carbohydrate;
, carbohydrate;  , lipid;
, lipid;  , protein; *, carbohydrate is presented by total sugar and lipid is presented by fat. Modified from [41,42,43].
, protein; *, carbohydrate is presented by total sugar and lipid is presented by fat. Modified from [41,42,43].
The molecular study of the fruit extract of A. officinalis revealed the potentiality of the extract in treating the worldwide emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Four compounds within the extract—methyl palminoleate, methyl linoleate, hexacosane, and triacontane—showed excellent binding affinity to the virus’ main proteases, such as Arg188, Cys145, Gln189, Glu166, and Met165 [44]. However, long clinical steps are still required to produce firm outcomes in administering the mangrove fruit extract to treat SARS-CoV-2.
The antibacterial activity of the mangrove extract comes from the synergistic relationship among secondary metabolites. The extract is rich in steroids, phenolic compounds, alkaloids, flavonoids, and other secondary metabolites. The enrichment of Artemia salina by extract of S. alba enhanced the resistance of giant tiger prawn against Vibrio harveyi. The enrichment of extract into A. salina escalates the steroid and phenol hydroquinone levels [45]. Alkaloid disrupts peptidoglycan in bacterial cell walls, leading to the death of cells, while phenol affects the cytoplasmic membrane and breaks the cell nucleus. Flavonoids modify the cell protein and DNA, resulting in the inhibition of the growth of the cell [46].
Extract of mangrove fruit exhibited antimicrobial activities (Table 1) due to many phytochemicals, such as the total phenolic content, flavonoid [47], saponin, tannin, alkaloids, and saponin [48]. The composition of those phytochemicals varies based on the extraction method and solvent used. The composition determines the bioactivity; therefore, selecting extraction procedures is crucial in achieving noticeable positive results. The common antibacterial mechanism is attributed to membrane cell disruption [49]. Despite the antibacterial activity, the extract also exhibits antiviral properties. The aqueous extract of B. gymnorrhiza demonstrates potent inhibition of Zika virus (ZIKV) infection on human epithelial A549 cells by preventing the binding of the virus to the host cell surface. The aqueous extract contains polyphenols that disrupt the lipid membrane (outer membrane) of the flavivirus [50]. The protein for the cell-binding receptor of ZIKV is targeted by cryptochlorogenic acid from the extract, leading to the virus’ death [51]. Moreover, the aqueous extract of R. mangle showed activity against various bacteria and depicted the cytotoxicity against human fibrosarcoma cell line HT1080 [52].
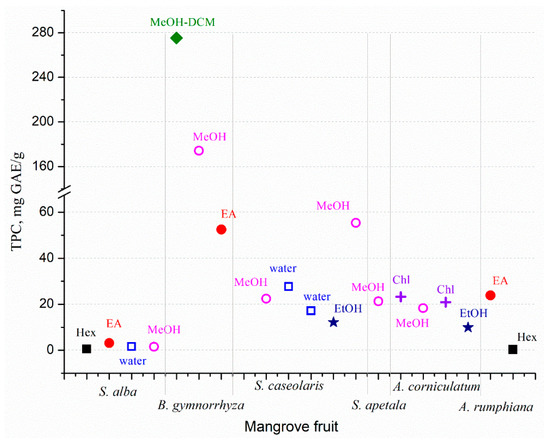
Figure 2.
Total phenolic content (TPC) from several mangrove fruit extracted using different solvents: Hex (hexane), EA (ethyl acetate), water, MeOH (methanol), DCM (dichloromethane), EtOH (ethanol), and Chl (chloroform). Modified from [37,38,39,40,53,54].
Various notable compounds are successfully identified from the extract of mangrove fruit. The eminent compound, such as (-)-17β-neriifolin, a cardiac glycoside, is found in the extract of Cerbera manghas with excellent heart stimulation function, effective in curing acute heart failure, at the same time show antiestrogenic, antiproliferative, and anticancer activities [55]. The fruit of B. gymnorrhiza contains isopimaradiene and 4-(2-aminopropyl) phenol. Isopimeradiene acts as antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial while 4-(2-aminopropyl) phenol shows high ROS scavenging activity, O2 scavenger, NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) stimulant, down-regulated cyclooxygenase-2 expression, and lowering of the nitrite level [38].
The administration of the mangrove fruit extract to animal models presents multiple vantages such as antioxidant [56], anti-atherosclerosis [57], antimicrobial [47,58], anti-diabetes [59], and hepatoprotective properties [60]. Excessive free-radical levels of diabetes trigger other diseases due to oxidative stress. Synthetic antioxidants are usually administered to reduce the oxidant level in the human body; however, side effects such as carcinogenicity should be addressed [61]. Mangrove fruit is a source of bioactive compounds with antioxidant activities. The antioxidant activity of the fruit is commonly related to the high content of vitamin C, anthocyanins, flavonoids, and polyphenols, which have hydrogen donating capabilities against free radicals such as nitric oxide (NO) [56]. The administration of methanol extract of the fruit of S. apetala to Long–Evans male rats inhibits the nitrite production in a dose-dependent manner. The extract acts as an insulin-like compound and modifies glucose utilization, enhances the transport of blood glucose to peripheral tissue, and stimulates the regeneration of the pancreas’ cells [40].

Table 1.
The antimicrobial activities of fruit extract from different types of mangrove species.
Table 1.
The antimicrobial activities of fruit extract from different types of mangrove species.
| Species | Solvent | Antimicrobial | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avicennia marina | Ethanol | Aspergillus fumigatus | [58] |
| Candida albicans | |||
| A. officinalis | Methanol | Escherichia coli | [47] |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |||
| Bacillus subtilis | |||
| Lactobacillus delbrueckii | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes | |||
| B. gymnorrhiza | Methanol | E. coli | [51] |
| P. aeruginosa | |||
| K. pneumoniae | |||
| S. aureus | |||
| Salmonella enteritidis | |||
| Sarcina lutea | |||
| Proteus mirabilis | |||
| Bacillus cereus | |||
| C. albicans | |||
| R. mangle | Ethanol | Enterococcus faecalis | [52] |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | |||
| Bacillus cereus | |||
| Streptococcus lactis | |||
| S. aureus | |||
| S. apetala | Methanol | E. coli | [40] |
| E. faecalis | |||
| Pseudomonas sp. | |||
| Shigella flexneri | |||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | |||
| S. caseolaris | Ethyl acetate | E. coli | [48] |
| C. albicans | |||
| Ethanol | E. coli | ||
| S. aureus | |||
| C. albicans | |||
| Methanol | S. aureus | [49,62] | |
| E. coli | |||
| C. albicans | |||
| P. aeruginosa | |||
| Acenobacter baumannii | |||
| Methanol:ethanol | E. coli | [63] | |
| Klebsiella sp. | |||
| Shigella boydii | |||
| S. sonnei | |||
| S. aureus | |||
| X. mekongensis | Methanol:ethanol | S. aureus | [63] |
The ethanolic extract of S. apetala shows anti-atherosclerosis in the male Wistar rat model [57]. The cholesterol levels, including LDL and HDL, are higher, and the formed foam is lower than the control animal [57]. Atherosclerosis is a vascular inflammatory disease characterized by lipid accumulation, fibrosis, and cell death in the arteries. The inflammation is mainly caused by high free-radical concentration ensuing in the incline of plasma lipid levels, such as LDL. LDL infiltrates the vascular sub-endothelium via impaired endothelium, which excites the oxidation process [64]. The oxidized LDL activates the endothelial cells expressed by leukocyte adhesion molecules such as vascular cell-adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) on the surface of the artery. The elevated oxidized LDL stimulates the production of ROS via nitric oxide activation. Typically, NO is a protective substance produced by the vascular endothelial cells; however, it enables pro-atherogenesis if produced by macrophages. Moreover, excessive ROS generation stimulates and activates Nf-kB p65 translocation, increasing the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1) and releasing the pro-inflammatory mediators by macrophages. Monocyte turns phagocytosis and macrophages of oxidized LDL to form foam cells [65,66,67]. Regarding its antioxidant property, the mangrove fruit extract prevents the excessive production of free radicals at the beginning of the mechanism [64].
The administration of the ethyl acetate extract of mangrove fruit X. moluccensi presented antidiabetic properties in a male albino Sprague–Dawley rat model; many blood parameters such as the blood glucose, serum fructosamine, serum triglycerides, and serum cholesterol levels declined. The extract improves phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase in the liver and kidneys while maintaining bodyweight [59]. The fruit of S. apetala displays hepatoprotective properties of male Kunming mice. The fruit extract’s antioxidative property improves the aspartate aminotransferase level in serum, reduces the alanine aminotransferase, and increases the survival rate. The hepatoprotective ability of the fruit extract in the liver is depicted by the incline in total antioxidant capacity and catalase, improvement in glutathione peroxidase and glutathione, and inhibition of myeloperoxidase, interleukin 6, and tumor necrosis factor-α. The antioxidant properties of the fruit extract are suspected to prevent the liver damage caused by oxidative stress from ROS [60].
3. Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Mangrove Fruit
The exploration and discovery of secondary metabolites in mangrove fruit are highly valued, mainly for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical purposes. The intensive investigation is organized to isolate the potent secondary metabolites. Protolimonoids and limonoids are common secondary metabolites found in mangrove fruit. Both compounds are triterpenoid with four rings and a β-substituted furanyl ring at the 17α position. The differences are observed in the sidechain and composition of the ring. The sidechain and all rings of the protolimonoids are intact; meanwhile, the sidechain of limonoid is furan with the substitution of lactone at ring D. Limonoids such as mexicanolide and phragmalin possess an opened and recycled skeleton in ring B, whilst phragmalin is indicated by specific C4, C29, and C1 bridges. Mexicanolides are a precursor for phragmalins. All limonoids are in the oxygen-containing group at C-3, C-4, C-7, C-16, and C-17 [68].
The genera Xylocarpus, Avicennia, and Sonneratia are commonly explored for their fruit phytochemistry. The fruit of those genera are famous for the biosynthesis of limonoids (Table 2) with similarities in their molecular structures (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). X. granatum is used in traditional medicine in southeast Asia to treat antifeedant, malaria, chlorella, diarrhea, and other diseases. Limonoids and derivatives such as polyoxyphragmalin and mexicanolide compounds are common isolates from X. granatum. The fruit of the mangrove is rich in polyoxyphragmalins; meanwhile, mexicanolides can be found either in seed or fruit [69]. Gedunin (1) isolated from the fruit of X. granatum inhibited the pharyngeal cancer FaDu, colon cancer DLD-1, lung cancer A549, ovarian cancer OVCAR-3, and PA-1. In ovarian cancer cells, the administration of 1 showed G2/M cell-cycle arrest, leading to cell death in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The death of cancer cells is promoted by disturbance in the regulation of cell-cycle protein, provoking nucleus fragmentation, pyknosis, and cell shrinkage. Compound 1 induced apoptosis by stimulating mitochondria to release cytochrome c, followed by proteolytic cleavage of many key proteins, including poly (ADP) ribose polymerase (RARP) [70].

Table 2.
The secondary metabolites from the fruit of mangroves and their bioactivity.
Figure 3.
The molecular structure of compounds 1–24.
Figure 4.
Molecular structure of compounds 25–43.
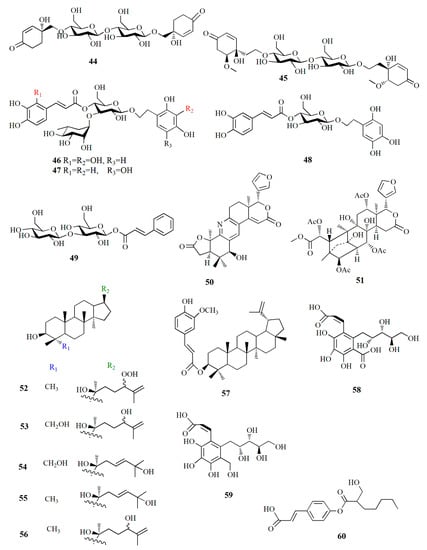
Figure 5.
Molecular structure of compounds 44–60.
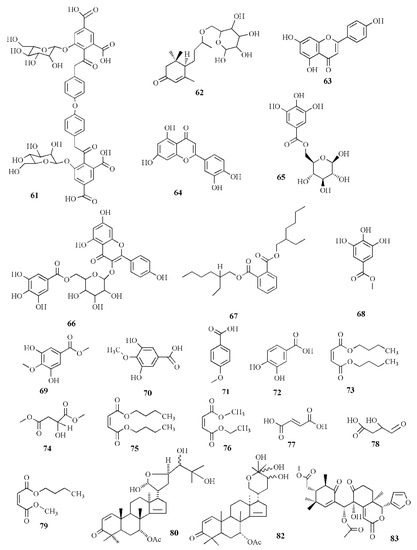
Figure 6.
Molecular structure of compounds 61–83.
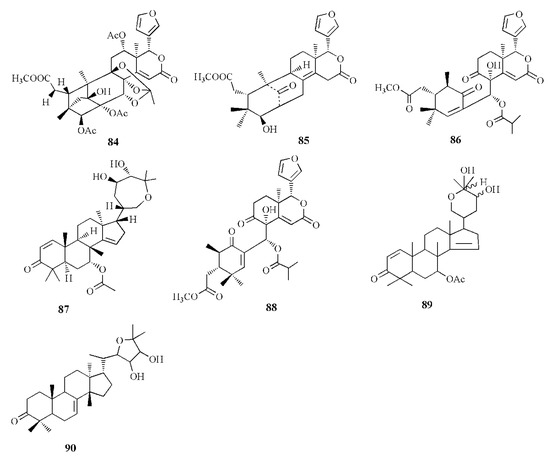
Figure 7.
Molecular structure of compounds 84–90.
Xyloccensin-type limonoids are isolated from various fruits of the genus Xylocarpus. The ethanol extract of X. granatum collected from Hainan, China, afforded 3β,8β-epoxymexicanolide, a rare oxidized limonoid. Xyloccensin K (2) has a 3,8-epoxy bridge, which is shown by the relationship between H-3 at δH 4.13 ppm and C-8 at δC 81.37 ppm. The α-configuration was depicted by the correlation between H-30 at δH 5.52 ppm, H-2 at δH 3.09 ppm, and H-3 and H-29 at δH 0.57 ppm. The extract also contains 6-acetoxycedrodorin (3) and xyloccensin W (4) (C29H36O10); 4 possesses β-furyl ring, acetyl, a methoxy, a hydroxyl, and a ketone function. Compounds 2–4 are similar in their ring skeleton, where the difference is demonstrated by the arrangement of the acetyl group attached to C-6 and C-30 [71].
Ethanol extract of X. granatum fruit from Hainan Island contained 3-deacetyl xyloccensin M (5) with a molecular formula of C27H36O8. Compound 5 has six rings, two esters, and carbon–carbon double bonds, and it has a similar structure to xyloccensin M. Another isolated compound, 3-deacetyl xyloccensin N (6) with a molecular formula, C27H36O8, has keto and ester carbonyl groups, hydroxyl, carbon double bond, one methoxycarbonyl group, and β-furyl moiety [87]. Compounds 5 and 6 are a pair of isomers of mexicanolides, and compound 6 is suspected as a biosynthetic intermediate of compound 5 [72]. These two compounds resembled mexicanolides isolated from the stem bark of X. granatum, namely xyloccensin M and xyloccensin N with the absence of the acetyl group [88]. Within X. granatum, xyloccensin X1 (7), C29H36O10, was observed with methoxycarbonyl at δH 3.74 ppm and δC at 53.5 and 172.6 ppm while the β-furyl ring at δH 6.57, 6.53, and 7.68 ppm related to carbons at δC 111.6, 121.6, 143.7, and 144.4 ppm. The extract also yielded xyloccensins X2 (8) with a molecular formula of C27H34O8. Compound 8 is similar to compound 7 without the 6-acetoxy group [73].
Ethanolic extract of X. granatum from Hainan, China contains xyloccensin Y (9) and xyloccensin Z1–Z2 (10–11). Compound 9, C33H42O15, is a hexacyclic with a β-furyl ring; three acetyls; a methoxy, methoxycarbonyl; and three methyls of the phragmalin nucleus. Compound 10 has a molecular formula of C33H42O14, and the backbone of its structure is similar to compound 9 without the hydroxyl group. Compound 11, C31H40O12, is similar to that of compound 10, except for the absence of the 12-acetoxy group. Phragmalins with an 8,9 hydroxy group are less common in the maliaseae plants. Limonoids have intact oxidized triterpene nuclei, and they are triterpene derivatives from a precursor 4,4,8-trimethyl-17-furanylsteroid backbone [74].
The ethanolic extract of X. granatum fruit confines xylogranatin A–D (12–15). Compound 12, C32H40O9, is mexicanolide with a β-furyl ring, tiglate group, a methoxycarbonyl group, a ketone, and an α,β- unsaturated δ-lactone ring D. Compound 13 (C34H42O11) is similar to 12 with the addition of an acetoxy group at δH 1.9 ppm and δC at 20.9, 170.2 ppm, and acetal carbon at δC 107.4 ppm with the absence of ketone carbon at δC 218.2 ppm. Compound 14 (C34H44O11) resembles 13 with the absence of the tiglate group and replaced by 2’-methyl-butanoate. Compound 15, C33H42O11, resembles compound 13 with the absence of a tiglate group and replaced by an isobutyrate group [75]. A phragmalin is isolated from ethanol extract of fruit X. granatum, namely xylogranatin E (16), C32H40O10, and it has a rare oxygen bridge of C1 to C29. The compound is characterized by six unsaturated units represented by six rings, β-furyl ring, a tiglate moiety, a methoxycarbonyl, and an α,β-unsaturated δ-lactone ring E [76].
Ethanol extraction of X. granatum fruit led to the isolation of several limonoids, i.e., xylocarpin A–I (17–21, 23–26) and 6-dehydroxyxylocarpin (22). Compound 17, C35H44O14, is characterized by a β-substituted furan ring at δH 7.45, 6.38, and 7.44 ppm, four oxymethines, seven methyls, and four acetyl groups. Compound 18 (C33H42O12) shares the same basic skeleton as 17, with the presence of a methylene group at δH 2.25 and 2.31 ppm, while it loses the C-6 oxymethine signal. Compound 19, C33H42O13, is similar to compound 17 with the shift of the C-1 signal to δC 81.5 ppm. Compound 20 is similar to compound 19, except for the presence of seven oxygenated carbons at δC 69.8, 77.3, 71.3, 73.4, 71.2, 76.4, and 88.0 ppm. Compound 21 is similar to compound 20 with the oxygenated carbons at C-1, C-3, C-6, C-8, C-12, and C-30; meanwhile, the significant downfield of H-6 was observed at δH 5.40 ppm. Compound 22, C35H44O14, is a phragmalin with a β-substituted furanyl group. Compound 23, C31H38O11, contains four tertiary methyl groups, two acetyl methyl groups, a methoxy group, and two oxymethine protons. Compound 23 possesses the same molecular formula as xylogranatin B with an acetoxy group at C-3 and tigloxy group at C-30. Compound 24, C32H38O10, is composed of three tertiary methyls and a β-substituted furan ring. Compound 25, C37H44O16, is uniquely characterized by 1,1,1-trioxyethyl moiety, as represented by the relationship between methyl singlet at δH 1.66 ppm and quaternary carbon at δC 119.2 ppm [69]. Ethanolic extract from X. granatum from Hainan, China, afforded pyrazine alkaloid xylogranatinin (27), C9H8N2O3. It is a bicyclic molecule with a pyridine ring that is configured as α,β-unsaturated lactam [77].
Ethanol extract of X. granatum fruit contains five protolimonoids, 2 limonoids, and 2 xylocarpins. Protoxylocarpin A (28), C32H50O6, is characterized by the presence of C=O and OH groups. Compound 28 shows characteristics of apotirucallane triterpene with the tetracyclic nucleus. Protoxylocarpin B (29) is similar to compound 28, except for the occurrence of the C17 shifting to δC 52.4 ppm and C21 to δC 103.3 ppm. The structure of Protoxylocarpin C (30), C34H54O6, resembles compound 28, with the addition of ether groups appearing at δC 56.5 ppm and 16.1 ppm. Ether groups are resumed from the link of the ether with HO-C25 moiety at δC 76.6 ppm. Protoxylocarpin D (31) is identical to holstinone B, with a difference being observed in the carbon shift of C21 at δC 104.6 ppm and C17 at δC 52.5 ppm. Protoxylocarpin E (32), C35H52O9, is an apotirucalla-1,14-dien-3-one analogue.
Xylocarpin J (33), C32H42O9, is a C3 epimer of xylocarpin A. Xylocarpin K (34), C37H46O17, is phragmalin limonoid and configured by five AcO groups. Xyloccensin M (35) is also isolated from the same extract. Compounds 28–33 and 35 showed weak-to-moderate activity against HCT-8, Bel-7402, BGC-823, and A2780 cell lines [78].
Protolimonoids and their fatty acid are isolated from the ethanol extract of X. granatum. Alkaline hydrolysis of the ethanol extract using sodium hydroxide produces two mixtures: a mixture of fatty acids, and a mixture of butyrospermol and β-sitosterol. The protolimonoids are identified as butyrospermols, i.e., butyrospermol 3β-O-palmitate, C46H80O2 (36), butyrospermol 3β-O-oleate, C48H82O2 (37), butyrospermol 3β-O-stearate, C48H84O2 (38), and butyrospermol 3β-O-linoleate C48H80O2 (39). The composition of the fatty acid mixture is 3.3% methyl myristate, 62.2% methyl palmitate, 20.1% methyl oleate, 9.8% methyl stearate, and 4.5% methyl linoleate [79]. Ethanolic extract of A. marina fruit from Guangxi province, China, contains caffeoyl derivatives such as maricaffeolylide A, C17H20O6; (40) and maricyclohexene A, C12H20O2 (41). The caffeoyl moiety of compound 40 is presented by proton at δH 7.02, 6.93, and 6.77 ppm, and it possesses an eight-membered lactone ring with two chiral centers. Compound 41 confirms its cyclohexene group as a positive cotton effect by CD spectrum at 205 nm. Compound 40 exhibited cellular antioxidant assay (CAA) with an EC50 value of 24±0.3 μM, and compound 41 showed an EC50 value of 339 ± 3 μM [80].
Jacaranone analogs marinoid F–I (42–45) are isolated from A. marina fruit from Beibu Gulf, China, using an ethanol–dichloromethane solution. Compound 42, C14H19ClO8, contains an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl group resonating at δH 6.22, 6.99, and 7.12 ppm; and two methylene groups at δH 2.08, 3.64, and 3.94 ppm. The compound is distinguished by its β-glucosyl group and para-quinol-type partial structure. Compound 43, C14H19ClO8, is similar to compound 42 except for the cotton effect (∆ε) of 42, which is –4.28 while that of compound 43 is +5.97. Compound 44, C26H38O15, possesses two cyclohexanone moieties with two β-glucosyl groups. Compound 45, C30H46O17, contains two cyclohexanone moieties and is considered an unsymmetrical dimer of cornoside analog. Compound 45 exhibited the strongest cellular antioxidant assay with an EC50 value of 26 μM, while compounds 42–44 were weak with EC50 values of 598, 4971, and 1103 μM, respectively [81].
Phenylethyl glycosides and cinnamoyl glycosides, named marinoid J–M (46–49), are isolated from the ethanol–dichloromethane extract of A. marina fruit collected from Beibu Gulf, China. Compound 46, C29H36O17, possesses 2,3,4-trihydroxyphenyl moiety and 2,3,4-trihydroxycinnamoy moiety in the AB system. Compound 47, C29H36O16, contains 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl moiety, two trans-olefinic protons in the AB-type system, and caffeoyl moiety. Compound 48, C23H26O12, presents trans-olefinic protons in AB-type, caffeoyl moiety, 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl moiety, and β-glucosyl. Compound 49, C21H28O12, is composed of two trans-olefinic protons in AB-type, phenyl moiety, two β-glucosyls, and cinnamoyl moiety. Cellular antioxidant assay of compounds 44–49 showed EC50 values of 23, 36.2, 114.5, and 247.8 μM, respectively [82].
A limonoid-based alkaloid granatione (50), C26H27NO6, is isolated from ethanol extract of X. granatum fruit, which possesses conjugated δ-lactones in rings E and B substituted furan ring. The cyclohexene D of the compound fused to the δ-lactone ring. Compound 50 has five aromatic signals on the carbon at δC 158.2, 124.3, 133.9, 130.5, and 156.6 ppm assigned as tetra-substituted pyridine units. The γ-lactone is formed by carbonyl carbon and a methylene group. Compound 50 was biosynthetically obtained from 9,10-seco-mexicanolide xylogranatin C as a precursor. A phragmalin xylocarpin L (51), C35H44O16, is isolated from the same extract [83].
Dammarane triterpenes are isolated from the hexane and dichloromethane extract of C. tagal collected at Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand. Cereotagaloperoxide (52), C30H52O4Na, is characterized by a tetracyclic dammarane with five methyl singlets and oxymethine proton. Cereotagalol A (53), C30H52O4, is similar to compound 52 with the addition of one hydroxymethylene group and the loss of a methyl group. Cereotagalol B (54) is similar to compound 53 in its tetracyclic moiety, and the difference was observed as two olefinic methine protons instead of terminal methylene protons. Isofouquierol (55), fouquierol (56), and 3β-E-feruloylbetulinic acid (57) are isolated from the same extract. Compound 57 showed cytotoxic activity against human breast cancer KB, human oral epidermoid carcinoma BC, and human small-cell lung cancer NIC-H187 cell line with IC50 values of 3.8, 3.0, and 1.8 μg/mL, respectively [84].
Alcoholic extract of S. apetala fruit produced types of sonneradons. Sonneradon A (58), C15H18O11, has an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl group from proton δH 8.07 and 7.52 ppm and carbon at δC 113.9, 149.1, and 172.8 ppm. Sonneradon B (59), C15H20O10, also possesses an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl group at proton δH 8.16; 7.41 ppm along with ortho-trihydroxyphenyl moiety and 2-deoxy-D-arabino-hexitol moiety. Sonneradon C (60), C17H22O5, contains two AB system proton signals at δH 6.80 and 7.58 ppm as 1,4-disubstituted phenyl moiety, and Sonneradon D (61) has the molecular formula C44H42O23. Other compounds have been identified, and these compounds are isolated from other types of plants, viz. ranuncoside (62), apigenin (63), luteoline (64), 6-O-galloyl-d-glucopyranose (65), O-B-(6-O-galloyl)-glucopyranoside (66), 2-ethylhexyl phthalate (67), methyl gallate (68), methyl 4-O-methylgallate (69), 4-O-methylgallic acid (70), 4-methoxybenzoic acid (71), 3,4-dihydrobenzoic acid (72), bibutyl malate (73), dimethyl malate (74), bibutyl malate (75), ethylmethyl malate (76), 2-butenedioic acid (77), 3-hydroxy-4-oxobutanoic acid (78), and butylmethyl malate (79). Compounds 58, 59, 61, 63, 74, and 79 significantly expanded the life span of nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as compound 58 was the most potent in the molecular docking analysis. Compounds 58, 59, 61, 63, 74, and 79 showed heat-stress properties due to the interaction between the key amino residues of HSF-1 such as GLN49, ASN74, and LYS80 of the DBD (N-terminal DNA-binding domain). Heat-shock transcription factor-1 (HSF-1) is used for modulating the life span of an organism, maintaining proteostasis, and the heat-shock response. Compound 58 significantly extended the lifespan of the N2 worm by 34.48±0.92% from 15.08 ± 0.74 days to 20.28 ± 0.84 days [85].
Acetonitrile extraction assisted with an ultrasonic water bath method was able to isolate some limonoids from the fruit of X. granatum. Piscidinol G (80), xylogranation D (81), spicatin (82), xylogranatin C (83), xyloccensin V (84), proceranolide (85), xylomexicanin D (86), Sapelin E acetate (87), xylomexicanin A (88), grandifoliolenone (89), and odoratone (90) are quantitatively detected using LC/MS [86].
4. The Secondary Metabolites from the Seed of Mangrove
The mangrove seed, the fruit’s flesh, and the pericarp are also consumed for their ethnomedicinal properties. The seed is rich in limonoid and its derivatives (Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14) have various bioactivities (Table 3). The extract of S. apetala seed demonstrated anti-diarrheal and antimicrobial activities against Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella dysenteriae, Salmonella Typhi, S. Paratyphi, and E. coli [63].
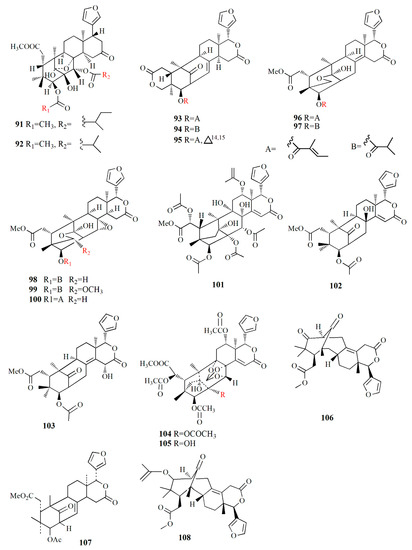
Figure 8.
Molecular structure of compounds 91–108.
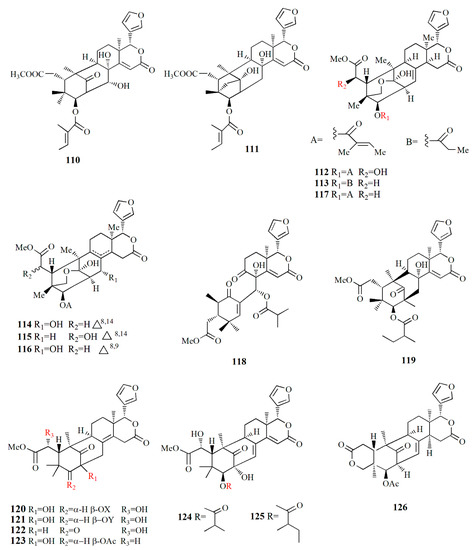
Figure 9.
Molecular structure of compounds 110–126.
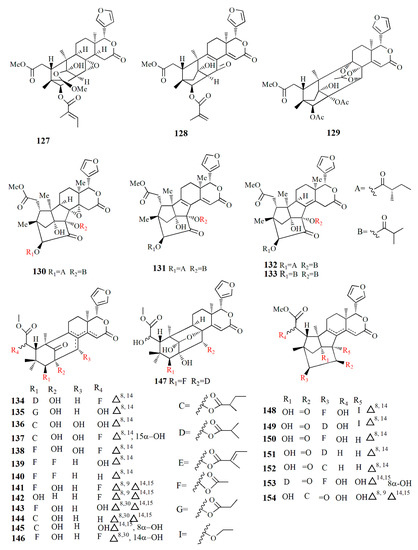
Figure 10.
Molecular structure of compounds 127–154.
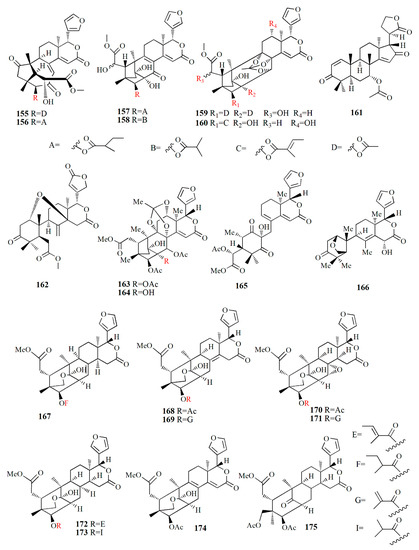
Figure 11.
Molecular structure of compounds 155–175.
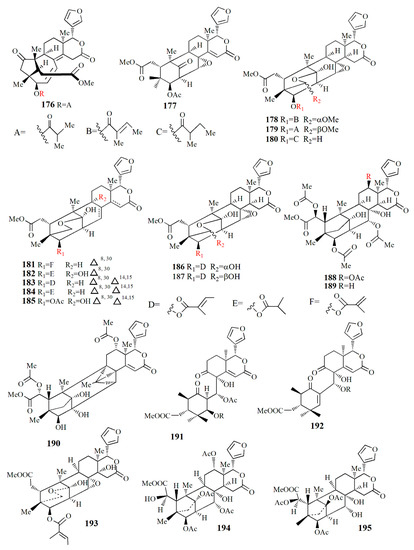
Figure 12.
Molecular structure of compounds 176–195.
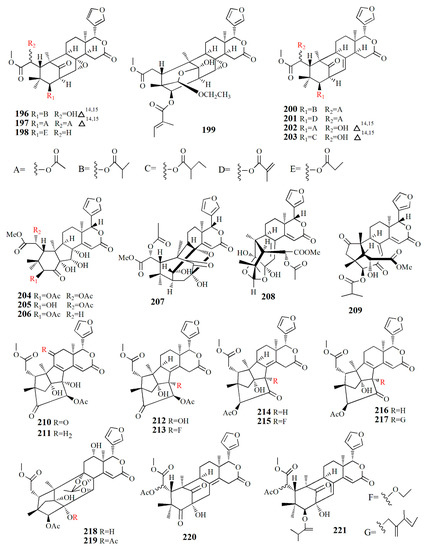
Figure 13.
Molecular structure of compounds 196–221.
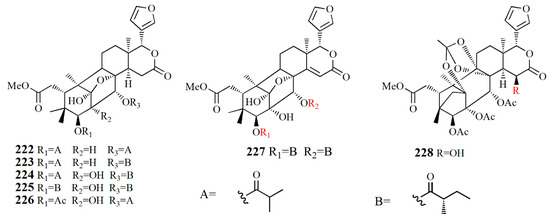
Figure 14.
Molecular structure of compounds 222–228.

Table 3.
The metabolites isolated from the seed of mangrove and their bioactivities.
Xyloccensin I (91), C34H46O12, and Xyloccensin J (92), C34H44O12, were observed in the nonpolar extract of fruit kernel of X. granatum and X. moluccensis. Usually, limonoids are superior to insect antifeedants; however, these compounds show no antikinase, antiviral or antimicrobial activity [89]. Limonoids godavarins A–J (93–99, 101–105), xyloccensin L (100), xyloccensin P–Q (104–105), angustidienolide (106), 6-deoxy-3-detigloyl-swietenine acetate (107), fissinolide (108), and methyl 3β-acetoxy-1-oxomeliaca-8(9),14-dienoate (109) were observed in the seed of X. moluccensis. Compound 93 is characterized by the presence of ∆8,30 double bonds. Compound 94 resembles compound 93 by the addition of an isobutyryl group and loss of the 3-tigloyl group. Compound 94 is identical to compound 93, except for the presence of a ∆14,15 double bond. Compound 95 is similar, with xylogranatinin E and the loss of a ∆14,15 double bond, while compound 96 is similar to compound 95 with the addition of the isobutyryl group. Compound 97 reflects xyloccensin L with the addition of the isobutyryl group, while compound 98 resembles that of compound 6 with the loss of the C-29 methylene group. Compound 99 is similar to granatumin G with the addition of two acetyl groups. Compound 100 is similar to xyloccensin X2 with the addition of the acetyl group. Compound 101 resembles 3-O-acetylswietenolide with an OH group located in C-15. Compounds 93, 96, 103, and 106–109 exhibited insecticidal and antifeedant activities [90].
A mexicanolide, 30α-hydroxyl xylogranatin A (110), C32H40O10, and a phragmalin, xylogranatin E2 (111), C32H40O9, were isolated from ethanol extract of the seed of X. granatum. Both compounds have a 3-O-β-tigloyl group. Compound 110 is similar to xylogranatin A with the addition of a hydroxyl group attached to C30, while compound 111 is similar to xylogranatin E without an oxygen bridge between C-1 and C-29 [91]. Ethanol extract of the species also contains thaigranatins A–E (112–116) and granatumin L (117). Compounds 112–116 contain an oxygen bridge between C1 and C19. Compound 112 contains a typical β-furyl ring, oxygenated methylene moiety, tigloyl group, and methoxycarbonyl moiety. Compound 113 is similar to compound 112 with the presence of 3-O-propionyl moiety instead of a 3-O-tigloyl group. Compound 114 and compound 115 are similar to godavarin D with the addition of a 30-OH group for compound 114 and a 6-OH group for compound 115. Compound 116 is similar to compound 114 with the presence of ∆8,9 double bonds instead of ∆8,14 double bonds. Compound 117 was active against HIV-1 with an inhibition rate of 67.10 ± 3.04 % at 20 μM. The derivatization of compound 117 is carried out by employing several protocols, i.e., oximization with hydroxylamine, esterification with diazomethane along with other organic compounds, and alkalization by KOH. However, among the derivatives, esterification by diazomethane of alkalinized compound 6 is the only active compound against HIV-1. The C3 substituent of the compound is the determining group for anti-HIV-1. Fatty acid ester in C3 is the best substituent compared to C=N or C=O [92].
∆14,15-mexicanolides were isolated from the ethanol extract of X. granatum seed, namely xylomexicanins A and B (118–119). Compound 118 contains an isobutytyloxy group, a methoxycarbonyl group, a hydroxyl group, and an α,β-unsaturated keto carbonyl group. Compound 119 resembles that of xylogranatin A, with the difference being in the replacement of tiglate moiety by 2’-methylbutanoyl moiety. Compound 118 exhibits antiproliferative activity against KT human tumor cell [93].
Moluccensins R–Y (120–121, 124–129), 6-hydroxymexicanolide (122), and 2-hydroxyfissinoide (123) were isolated from X. moluccensis. Compound 120 has isobutyryl moiety, and it resembles that of 2,6-dihydroxyfissinolide. Compound 121 is similar to 120, with the presence of 3-O-2-methylbutyryl moiety instead of a 3-O-isobutyl group. Compound 122 was first discovered as an oxidation product of swietenolide. Compound 124 resembles that of 120, with the addition of two conjugated double bonds: ∆8,9 and ∆14,15. Compounds 124 and 125 are structural analogues. Compound 126 is similar to godavarin A with a 3-O-acetyl moiety instead of the 3-O-tigloyl moiety. Compound 127 resembles that of godavarin G with the loss of isobutylryl moiety replaced by tigloyl moiety. Compound 128 is related to moluccensin G, with the disappearance of 1-O-isobutylryl moiety. Compound 129 is composed of phragmalin orthoester. Compounds 120, 122, and 123 exhibited antifeedant activities against the third-instar larvae of B. longissima [94].
The ethanol extract of X. moluccensis is rich in limonoids such as khayanolide and xylomolins. Khayanolides are mostly found in the Meliaceae genus Khaya, and they are a group of limonoids with the fused A/B ring from octahydro-1H-1,6-methanoindene moiety. Krishnolides A–D (130–133) were isolated from the mangrove seed X. moluccensis. Compound 130 has a heptacyclic structure and is similar to thaixylomolin K with the addition of 30-isobutyryloxy moiety, 3-(2-methyl)butyryloxy group, and 8,14-epoxy group, with the loss of C-30 methine moiety, 3-acetoxy group, and a ∆8,14 double bond. Compound 131 is similar to 130 with the presence of conjugated ∆8,9 and ∆14,15 double bonds instead of an 8,14-epoxy group. Compound 132 resembles that of compound 130 with the addition of a ∆8,14 double bond replacing the 8,14-epoxy group. Compound 133 is identical to 132, with the presence of isobutyryloxy moiety and the absence of the 3-(2-methyl)butyryloxy group. Compound 130 showed antivirus activity against the HIV-I virus with an inhibition rate of 79.75 ± 0.77% at 20 μM. The 8,14-epoxy group is responsible for the anti-HIV activity [95].
Ethanol extract of X. moluccensis yielded limonoids called xylomolins A1–A7, B1–B2, C1–C2, D–F, G1–G5, H–I, J1–J2, K1–K2, L1–L2, and M–N (134–162, respectively). Compounds 134–146 are mexicanolides characterized by one double bond or two conjugated double bonds. Compound 145 is a mexicanolide with a C1-O-C8 bridge. Compounds 146–151 contain khayanolides with ∆8,14 double bonds, compound 152 contains khayanolides with ∆14,15, and compound 153 contains khayanolides with ∆8,9, ∆14,15 conjugated double bonds. Compounds 154 and 155 are limonoids with the presence of (Z)-bicyclo[5.2.1]dec-3-en-8-one. Compounds 156 and 157 have 30-ketophragmalins identified by a conjugated double bond at ∆8,9 and ∆14,15. Compounds 158 and 159 are 8,9,30-ortho ester phragmalin, 160 is characterized by azadirone derivatives, and 161 is characterized by andirobin derivatives. Compound 162 showed weak antitumor activity against human triple-negative breast MD-MBA-231 cancer cells (IC50 value of 37.7 μM) [96].
Phragmalins 8,9,12-orthoesters, called thaixylomolins O–P (163, 164); 9,10-seco mexicanolide named thaixylomolin Q (165); and thaixylomolin R (166), a limonoid with 6-oxabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-one, were discovered in the seed of X. moluccensis. Compound 164 exhibited antitumor against ovarian A2780/T cell and A2780 with an IC50 value of 37.5 μM [97].
Limonoids named granatumins L–U (167–175) were isolated from the ethanol extract of X. granatum seed. Compound 167 is closely related to godavarin D with the presence of C8=C30 instead of C8=C14. Compound 162 is identical to compound 167 with the substitution of 3-O-2-methylbutanoyl moiety in place of the 3-O-tigloyl moiety. Compounds 168 and 169 are correlated with godavarin D with the presence of 3-O-Ac moiety and 3-O-methacryl instead of 3-O-tigloyl, respectively. Compound 170 is closely related to godavarin F with the presence of 3-O-Ac moiety in place of the 3-O-isobutyryl moiety. Compound 171 is similar to 5 with the addition of 3-O-methacryl moiety in the place of 3-O-Ac. Compound 172 is identical to 167 with the loss of the C8=C30 bond. Compound 173 is related to 172 with the substitution of 3-O-tigloyl moiety by 3-O-isobutyryl moiety. Compound 174 is correlated with godavarin K with the presence of 3-O-Ac moiety instead of 3-O-tigloyl. Compound 175 resembles that of xyloccensin N with the addition of a double bond at C8=C30 [105].
Methanol extract of X. granatum seed contained sundarbanxylogranins A–E (176–180). Compound 176 possesses bicycle[5.2.1]dec-3-en-8-one as a fused ring A/B. Compound 177 contains an 8α,30α-epoxy ring, and compounds 178–180 contain 29-OMe with different orientations. Compound 177 was active against HIV with an IC50 value of 23.14 ± 1.29 μM [99].
Granatumin X (181) and krishnagranatinins A–I (182–190) are isolated from the seed of X. granatum. Compound 182 is similar to granatumin Y, except for the presence of 3-O-isobutyryl moiety instead of the 3-O-tigloyl group. Compound 183 is similar to erythrocarpine D, with the substitution of the 3-O-tigloyl group in place of the 3-O-cinnamoyl group. Compound 184 resembles that of compound 183, with the addition of the 3-O-isobutyryl group replacing the 3-O-tigloyl group. Compound 185 is similar to that of 184, except for the addition of the 9-OH group and substitution of the 3-O-acetyl group in the position of the 3-O-isobutyryl group. Compounds 186 and 187 are a mixture and are determined in methylation. Compound 188 is similar to that of xylocarpin C with the presence of an acetoxy group in the 6-OH group position. Compound 189 is identical to compound 188 with the loss of the 12-acetoxy group. Compound 190 resembles that of 2,3-dideacetylxyloccensin S with the presence of an acetoxy group instead of the 6-hydroxy group. Compounds 188–190 inhibited the NF-κB signaling pathway [98].
Within ethanol extract of X. granatum extract, granaxylocarpins A–E (191–195) were isolated. Compounds 191 and 192 are mexicanolide-type limonoids with a 9,10-seco skeleton while compound 193 contains a 1,29-oxygen bridge and 8α,30α-epoxy ring. Compound 191 is similar to that of xylogranatin B with the loss of tigloyl moiety. Compound 192 resembles that of xylogranatin C with the substitution of C-30 tigloyloxyl moiety in place of C-30 acetoxyl. Compound 193 is identical to xyloccensin L with the addition of C-14 hydroxyl. Compound 194 is closely related to xyloccensin U with the presence of C-6-OH moiety. Compound 195 is similar to compound 194 with the addition of acetyl carbonyl and acetoxyl at C-6. Compounds 191 and 192 exhibited weak toxicity against P-388 murine leukemia with IC50 values of 9.3 and 4.9 μM, respectively [100].
Thaixylogranins A–H (196–203) were isolated in ethanol extract of seed of X. granatum as compounds 196–198, and 200–203 are mexicanolides. Compounds 196–199 contain an 8α,30α-epoxy ring while compounds 200–203 possess a C8=C30 bond. Compound 196 is a hexacyclic structure consisting of four ester groups, two carbons double bonds, and a ketone group. Compound 196 is identical to those of granatumin C with the presence of an isobutyryloxy group instead of the 3-tigloyloxy moiety. Compound 197 resembles that of compound 196 with the substitution of two acetoxy groups in the positions of 6-OH and 3-isobutytyloxy. Compound 198 is similar to that of xylocarpin with the presence of a propionyl group instead of a 3-O-acetyl group. Compound 199 is identical to moluccensin W with the presence of an ethoxy group instead of a 29-methoxy group. Compound 200 is similar to that of swietenin C with the substitution of 6-acetoxy moiety instead of 6-OH. Compound 201 is identical to that of swietenine acetate with the addition of methacryloyl moiety replacing the 3-O-tigloyl moiety. Compound 202 is identical to swielimonoid A with the presence of an acetoxy group in place of the 3-O-tygloyl group. Compound 203 resembles that of swielimonoid A with the presence of a 2-methylbutytyloxy group instead of the 3-O-tigloyl moiety. Compounds 196–203 showed weak cytotoxicity against breast cancer MDA-MB-231 with IC50 values of 49.4, 58.3, 53.6, 61.1, 57.9, 44.6, 40.6, and 38.5 μM [101].
Ethanol extract of X. moluccensis seed was found to contain stereo-structure limonoids, trangmolins A–F (204–209). Compounds 204–206 possess hexahydro-1H-inden-4-one while compound 4 contains hexahydro-2,6-methanobenzofuran-7-one. Compound 208 comprises a hexahydro-2H-2,8-epoxychromene while compound 209 is closely related to andhraxylocarpin A [102]. Types of khayanolides, thaixylomolins G–N (210–217), phragmalins (218–219), and mexicanolides (220–221) are isolated with ethanol from X. moluccensis. Compound 210 is similar to khayseneganin A with the addition of a C-11 carbonyl moiety, a 30-OH, and a 2-O-acetyl. Compound 211 resembles that of compound 210 except for the absence of the C-11 carbonyl moiety. Compound 212 is similar to compound 211 with the replacement of conjugated ∆8,9, ∆14,15 double bonds by ∆8,14 double bonds. Compound 213 is related to compound 212, with the C-30 hydroxy group being replaced by an ethoxy group. Compound 214 resembles that of compound 212, with the loss of 30-OH moiety in exchange for C-3 carbonyl moiety and the C-2 acetoxy group. Compound 215 is correlated with compound 214, with the addition of an ethoxy group. Compound 216 is similar to compound 214, with the replacement of ∆8,14 double bonds by conjugated ∆8,9- ∆14,15 double bonds. Compound 217 is identical to compound 216, except for the presence of tigloyloxy moiety. Compound 218 is related to xyloccensin U without 12-acetoxy moiety replaced by a hydroxyl group. Compound 219 is related to compound 218, with the presence of an acetoxy group instead of the 2-OH moiety. Compound 220 is identical to 2α-hydroxymexicanolide with the addition of 6-acetoxy moiety. Compound 221 relates to moluccensin T without 6-OH moiety. Compounds 212, 214, and 216 showed anti-H1N1 activities with IC50 values of 77.1 ± 8.7, 113.5 ± 8.6, and 121.5 ± 1.5 μM, respectively [103].
Xylorumphiins E–J (222–223, 225–228) and 2-hydroxyxylorumphhin F (224) were isolated from the seed of X. rumphii. Compound 222 is composed of six rings, two isobutyryl groups, a methoxycarbonyl, and β-substituted furan moiety. Compound 223 is similar to 222 with the presence of a 2-methylbutyryl group instead of isobutyryl moiety at C-30. Compound 224 is closely related to 223, except for the replacement of the methane group by oxygenated tertiary carbon. Compound 225 resembles that of compound 224, except for the replacement of the isobutyryl group by the 2-methylbutyryl group. Compound 226 is identical to xylorumphiin A with the presence of acetyl in place of the isobutyryl group. Compound 227 resembles that of 225 with the addition of ∆14,15 double bonds. Compound 228 is a phragmalin orthoester. Compounds 224 and 227 exhibited moderate anti-inflammatory activities with IC50 values of 24.5 and 3.13 μM [104].
5. The Endophytic Fungus in the Mangrove Fruit as a Source of Secondary Metabolites
The mangrove fruit is also a host for fungi. Endophytes inhabit the plant host without triggering problems for the host, sometimes providing nutrients or bioactive metabolites against the phytopathogenic bacteria. Like the fruit, the fungi also biosynthesize treasured phytochemicals for pharmaceutical applications. The isolation of pure fungus and the cultivation of those pure strains led to the discovery of several unique compounds with their bioactivities (Table 4, Figure 15, Figure 16 and Figure 17).

Table 4.
Metabolites of endophytic fungus from mangrove fruit and their bioactive properties.
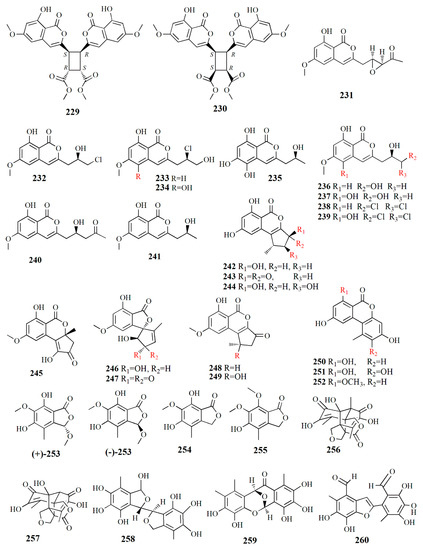
Figure 15.
Molecular structure of compounds 229–260.
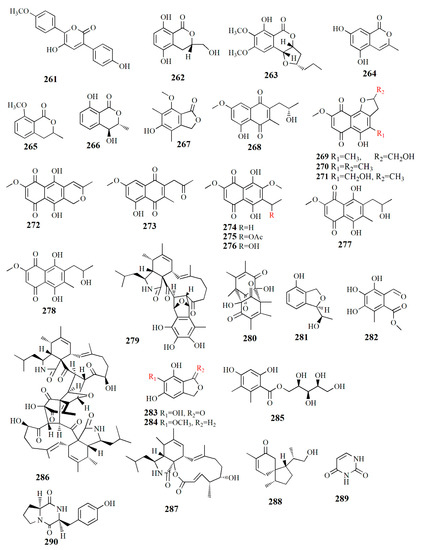
Figure 16.
Molecular structure of compounds 261–290.
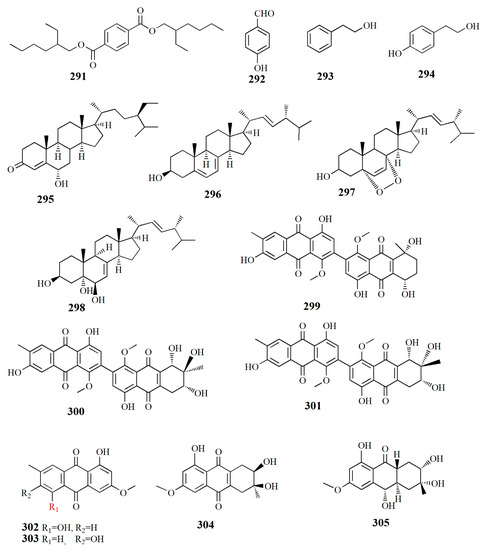
Figure 17.
Molecular structure of compounds 291–305.
Ten peniisocoumarins were isolated from the fungus P. commune from the fresh fruit of K. candel. Peniisocoumarin A (229), C28H24O12, has the isocoumarins’ nucleus configured by the correlation of H5 at δH 6.43 ppm to carbon C-5, C-6, C-8, and C-8a, chelated hydroxy group 8-OH at δH 10.81 ppm to C-8 and C-8a, and methoxy protons 6-OMe at δH 3.83 ppm to C-6. Peniisocoumarin B (230), C28H24O12, is similar to compound 229, with 14 carbons, and 7 non-protonated carbon, 3 sp2 methines, 2 sp3 methines, and 2 methoxyls. Compounds 229 and 230 are diastereoisomers with the difference in chemical shift of H-9 at δH 4.07 ppm instead of δH 4.11 ppm and H-10 at δH 3.94 instead of δH 4.00. Peniisocoumarins C (231), C15H14O6, was characterized by a hydroxy, two aromatic protons, an olefinic, methoxy group, methylene, and two methines. Peniisocoumarin D (232), C13H13ClO5, is similar to the isomarine skeleton of compound 231 with the presence of two methylene groups and one methine group. Peniisocoumarins E (233) is an isomer of compound 232 with a similarity in molecular formula; however, it is different in the side chain at C-3. Peniisocoumarin F (234), C13H13ClO6, is different from compound 233 in the hydroxy group at δH 7.85 ppm, the aromatic proton at δH 6.63 ppm, the olefinic proton at δH 6.78 ppm, and absence of aromatic proton at H-5. Peniisocoumarin G (235), C12H12O6, resembles that of orthosporin, an isocoumarin with a 2-hydroxypropyl sidechain [115], from fungus Drechslera siccans, yet it differs in hydroxy group 5-OH. Peniisocoumarin H (236), C13H14O6, is similar to diaportinol yet different in optical rotation and CD spectra. Diaportinol, C13H14O6, was first elucidated from the fungus Penicillium nagoivense [116]. Peniisocoumarin I (237) is a 5-hydroxylated analogue of compound 236, and peniisocoumarin J (239), C13H12O6, is similar to compound 236, yet it differs in the presence of the terminal methine group at H δH 6.21 ppm. Other detected compounds are 3-[-(R)-3,3-dichloro-2-hydroxypropyl]-8-hydroxy-6-methoxy-1H-isochromen-1-on1 (238); (+)-6-methyl-citreoisocoumarin (240), and (+)-diaporthin (241). These compounds have been in vitro tested for their bioactivities for metabolic disease, infectious disease, and cancer. In metabolic diseases such as diabetes type 2, α-glucosidase is essential in insulin signaling pathways, while in infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, MptpB is secreted into the human host to suppress the immune defense. Compounds 231, 235, 237, and 239 showed strong inhibition toward α-glucosidase compared to acarbose at IC50 values of 38.1–78.1 μM while 233, 234, and 239 show moderate activity of α-glucosidase with IC50 values of 102.4 and 158.4 μM. Compound 235 showed inhibition to Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein tyrosine phosphate B (MptpB) with an IC50 value of 20.7 μM. Others showed weak or no inhibitory against MptpB, embryonic kidney HEK293T, breast cancer MCF-7, cervical cancer HeLa, liver cancer HepG2, and lung cancer A549 [106].
Altenusin derivatives were isolated from Alternaria sp. SK6YW3L from the fresh fruit of S. caseolaris. Altenusin derivative 1 (242), C13H12O5, contains hydroxyl and carbonyl groups and has two meta-coupled aromatic protons at δH 6.33 and 6.44 ppm, one chelated hydroxyl at δH 11.31 ppm, one methyl at δH 1.27 ppm, one methylene at δH 2.19 and 2.25 ppm, one methine at δH 3.32 ppm, and one oxymethine at δH 5.21 ppm. Altenusin derivative 2 (243), C13H10O5, is similar to compound 242 with the addition of an α,β-conjugated keto carbonyl at δC 195.7 ppm and the absence of an oxymethine group. Altenusin derivative 3 (244), C13H12O6, is similar to 242 with the addition of oxymethine signal at δH 4.02 ppm and the absence of methylene. Altenusin derivative 4 (245), C14H12O6, is similar to compound 243, with the presence of a carbonyl group at C-8 and methyl group at C-9a. Altenusin derivative 5 (246), C14H14O6, resembles that of compound 247, except for the absence of α,β conjugated keto carbonyl signal and presence of oxymethyl. Compounds 247–252 are also isolated in the fungus. Talaroflavone (247), C14H12O6, was first isolated from Talaromyces flavus. Deoxyrubralactone (248), C14H12O5, was characterized by a methoxy group at δH 3.94 ppm, an aromatic proton, one aliphatic methane, methylene protons, one methoxy group, and one methyl group [117]. Rubralactone (249), C14H12O6, has one lactone carbonyl signal at 167.9 ppm, and this lactone carbonyl carbon correlated with the methoxy group and benzene ring [118]. 2-OH-AOH (250), alternariol (251), and anternariol methyl ether (252) were first discovered in the toxin fungus Alternaria [119]. Compounds 243, 244, and 250 display strong inhibition of α-glucosidase with IC50 values of 78.2, 78.1, and 64.7 μM, respectively. Compounds 242 and 249 also show weak inhibition with IC50 values of 235.2 and 194.4 μM, respectively. Compounds 245, 247, and 251 present moderate inhibition with IC50 values of 334, 348.4, and 474.3 μM, respectively. Alternaria is member of the ascomycetes family of fungi and is considered a plant pathogen; however, some ascomycetes can be used as a biocontrol of invasive species [107].
Endophytic fungus Epicoccum nigrum isolated from fresh fruit of mangrove A. ilicifolius L. yielded isobenxofuranone monomer and dimer derivatives. Racemic (+)-epicoccone C and (-)-epicoccone C (253), C11H12O6, possesses OH groups at δH 6.53 and 7.55 ppm and one oxymethine carbon at δC 103.8 ppm. In the separated–purified version, the compound was identified as 3S in (+)-1 and R in (-)-1. Therefore, compound 253 was recognized as (S)-5, 7-dihydroxy-3, 6-dimethoxy-4-methylisobenzofuran-1(3H)-one and (R)-5, 7-dihydroxy-3,6-dimethoxy-4-methylisobenzofuran-1(3H)-one. Epicoccone D (254), C10H10O5, is similar in the carbon framework of compound 25; however, 3-OMe in compound 253 is substituted by oxymethylene proton at C-3 in compound 254. Compound 254 is identified as 5,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-4-methylisobenzofuran-1(3H)-one. Epicoccone E (255), C11H12O5, is an isobenzofuranone monomer with 2 methoxy protons at δH 4.03 and 3.85 ppm. Compounds 255 and 254 are similar, the difference being in the replacement of hydroxy groups 7-OH by the methoxy group. Epicolactone A (256) is an isobenzofuranone dimer with the molecular formula C18H18O8. The 4-oxymethylenes of compound 256 are shown by the relationship between proton δH 4.5 and 4.25 ppm; 3.72 and 3.87 ppm; and 3.83 and 3.93 ppm. Compounds 257–260 are epicolactone, flavimycins A, epicocconigrone A, and epicoccolide B, respectively. Compounds (+)-253, 255, 259, and 260 show strong inhibition activity for α-glucosidase while compounds (-)-253, 254, 256, and 258 show moderate activity. The strong activity ranges from 32.3 to 63.3 μM and moderate activity from 130.2 and 252.4 μM. Compounds (+), (-)-253, 258, and 259 had strong oxidant activity with IC50 values from 10.2 to 15.3 μM. Compounds 254 and 260 show comparable activity to the positive control; the phenolic group and phenolic hydroxy group are responsible for the antioxidant activity [108].
Allantopyrone E (261), C18H14O5, is isolated from rice culture of Aspergillus versicolor from A. marina. Compound 261 is configured by two aromatic ring systems and α-pyrone moiety. The α-pyrone ring was established from the correlation of H-4 to C-2, C-3, and C-5 while the p-methoxy benzene ring was correlated with C-6. Thus, the compound was named 3,6-diaryl-5-hydroxy-a-pyrone. Compound 261 is derived from phenylalanine via ter-phenyl quinone polyporic acid. It presented a cytotoxic effect on HeLa cells with an IC50 value of 50.97±1.7 μM [109].
Botryoisocoumarin was detected from Botryosphaeria sp. KcF6 from the inner fruit of K. candel. 3S-5,8-dihydroxy-3-hydroxymethyldihydroisocoumarin or botryoisocoumarin A (262), C10H10O5, has a tetrasubstituted hydroquinone ring that is configured by two-ortho coupled protons, a methine signal, and methylene signals. The compound is similar to mullein, with the difference in the occurrence of a hydroxymethyl group instead of a methyl group. Compound 262 showed a strong COX-2 inhibitory IC50 value of 6.51 μM. COX-2 is an inducible enzyme activated by tumor promoters, endotoxins, mitogens, and cytokines. Monocerin (263) has been used as an insecticidal and antifungal, and it was first isolated from the fungus Microdochium bolleyi as an endophyte in the herbaceous plant Fagonia cretica [120]. Other isolated compounds from the fungus are 3-methyl-6,8-dihydroxyisocoumarin (264), 8-methoxymellein (265), trans-4-hydroxymellein (267), and 5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4,6-dimethyl phthalide (268). Compound 262 inhibited COX-2 activity (IC50 value of 6.51 μM) [110].
Naphthoquinone derivatives were successfully isolated from Talaromyces amestolkiae, an endophytic fungus of fresh fruit K. obovata. Talanaphthoquinone A (268), C15H15O5, has one methylene, one oxygenated methine, one methoxy, two methyl groups, two meta-coupled aromatics, and one phenolic hydroxy proton. Talanaphthoquinone B (269), C15H15O7, is similar to compound 268, with the difference in two quinone carbonyls at C δC 177.6 and 190.1 ppm. The extract also contains other compounds, such as: anhydrojavanicin (270), 2,3-dihydro-5-hydroxy-4-hydroxymethyl-8-methoxy-2- methylnaphtho[1,2-b]furan-6,9-dione (271), anhydrofusarubin (272), 2-acetonyl-3-methyl-5-hydroxy -7-methoxy-naphthazarin (273), 6-ethyl-2,7-dimethoxyjuglone (274), 6-[1-(acetyloxy)ethyl]-5-hydroxy-2,7-dimethoxy-1,4-naphthalenedione (275), 5-hydroxy- 6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-2,7-dimethoxy-1,4-naphthalenedione (276), solaniol (277), and javanicin (278). All of these compounds (268–278) showed strong inhibition against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated NO production in the murine macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7 cells) with IC50 values of 3.9, 49.7, 16.0, 22.6, 11.2, 5.2, 14.4, 7.7, 1.7, 7.5, 15.5, and 5.6 μM, respectively. Compound 275 reduced the mRNA expression of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1B, the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Those proteins are responsible for metabolic action during inflammation. The macrophage and monocyte produce the overexpression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-6B, TNF-α, and also prostaglandin E2 (PGE2); meanwhile, NO is produced by inflammatory factors such as COX-2 and iNOS. Overproduction of those compounds leads to inflammatory and cell disease. In normal conditions, inflammation is a response to tissue injury and infection. However, longer inflammation may cause diseases such as septic shock syndrome, a neurodegenerative disorder, or arthritis [111].
Fungus Mycosphaerella sp. from fruit Bruguiera gave compounds with α-glucosidase inhibition. Asperchalasine I (279), C33H41O7N, is configured by the presence of epicoccine moiety and cytochalasan moiety. Dibefurin B (280), C18H20O6, has carbonyls and a hydroxyl group. The phthalan ring present in epicoccine derivatives (R)-9-((R)-10-hydroxyethyl)-7,9-dihydroisobenzofuran-1-ol (281), C10H12O3, while aldehyde group and methyl ester appear in 2-methoxycarbonyl-4,5,6-trihydroxy- 3-methyl-benzaldehyde (282), C10H10O6. Other compounds were also isolated from the extract, such as epicoccone B (283), 1,3-dihydro-5-methoxy-7-methylisobenzofuran (284), paeciloside A (285), asperchalasine A (286), and aspochalasin I (287). Strong α-glucosidase inhibitory was shown by compounds 279 and 286 with IC50 values of 17.1, 26.7, and 15.7 μM while compounds 279, 282, and 284 had antioxidant activity with EC50 values of 16.3–85.8 μM [112].
The investigation of the fungi extracts of Pseudofusicoccum sp. J003 from fruit S. apetala led to the discovery of compounds, i.e., sesquiterpenoid acorenone C (288), alkaloid uracil (289), alkaloid cyclo-(L-Pro-L-Tyr) (290), phenolic bis-(2-ethylhexyl) terephthalate (291), phenolic 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde (292), phenolic 2-phenylethanol (293), phenolic 4-hydroxyphenethyl alcohol (294), steroid estigmast-4-en-6B-ol-3-ona (295), steroid ergosterol (296), steroid ergosterol peroxide (297), and steroid cerevisterol (298). Compound 288 showed AChE inhibitory activity with an inhibition rate of 23.34% at 50 μM. Compound 296 also showed an inhibition rate of 72.89% NO production at a concentration of 25 μM and human tumor cell lines HL-60 and SW480 with inhibition rates of 98.68% and 60.40%, respectively [113].
The fungus Alternaria sp. ZJ9-6B from the fruit Aegiceras corniculatum yielded at least seven compounds. Alterporriol K (299), C32H26O11, is constructed by a tetrahydroanthraquinone unit and an anthraquinone unit. Alterporriol L (300), C32H26O12, is similar to compound 299 with the addition of an oxymethine group and a hydroxyl group. Alterporriol M (301), C32H25O12, is identical to 300; both compounds are epimers, diastereomers, and atropisomers. Other isolated compounds from the extract are physcion (302), marcrospin (303), dactylariol (304), and tetrahydroaltersolanol B (305). Compound 299 showed cytotoxicity against human breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-435 (IC50 = 26.97 μM) and MCF-7 (IC50 = 13.11 μM). Compound 300 showed cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-435 (IC50 = 13.11 μM) and MCF-7 (IC50 = 20.04 μM) [114].
Two endophytic fungi, Cladosporium tenuissmum and E. nigrum, were isolated from the fresh fruit of S. apetala. The ethyl acetate extract of C. tenuissimum demonstrated antibacterial activity against E. coli, Micrococcus luteus, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus, while its methanolic extract depicted antimicrobial activity against E. coli, M. luteus, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and C. albicans. Ethyl acetate extract of E. nigrum showed antibacterial activity against M. luteus, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus, while the methanolic extract showed antibacterial against E. coli, M. luteus, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus [121].
6. The Mangrove Fruit in the Intermediary Stage of Processed Food
The supply-chain problem challenges the dominancy of wheat flour as a daily ingredient. Wheat grows worldwide as a major cereal source; however, the demand has increased exponentially. Wheat flour is crucial for bakeries and many household products [122]. Other emerging edible flours are required to supplement the demand with cost-effective and fortification functions. The flour from fruit is reliable in solving the problem of the world’s wheat stock [123]. Among the fruit, the flour of mangrove fruit is a proper candidate due to its richness in protein, carbohydrate, alkaloid, flavonoid, steroid, and other metabolites [124]. Many coastal communities utilize mangrove fruit flour for biscuits, flatbread, and crackers.
Usually, the mixture of mangrove flour and other ingredients produces unique characteristics. For instance, the mixture of wheat flour and B. gymnorrhiza flour (BGF) generates different functional and rheological properties, such as changes in the peak time, setback viscosity, final viscosity, and breakdown viscosity. The dominant factor affecting those properties is the water content [125,126]. The BGF is different from wheat flour in its amylopectin and amylose content. Flour with higher amylopectin conserved water more than flour with lower amylopectin [127]. BGF contains water-soluble fractions such as tannin, while tannin reduces the hydrophobicity of flour protein (gluten). Thus, the addition of BGF increases the water absorption capacity. During the production of mangrove flour, the size of particles in the final flour product is essential [128]. Flour with a finer particle size is better in making contact, frictional forces, and cohesive force than flour with a coarse particle size [129].
In the food innovation process, many types of wheat are mixed to offer a better product with acceptable texture and nutrition content. The mangrove fruit flour can be mixed with other types of flour such as sweet potato flour and maize starch, which affect the peak viscosity. The pasting temperature of the mixture of mangrove fruit flour and sweet potato flour exhibits no significant difference compared to the single-source pure four. The peak viscosity is the most sensitive parameter affected by the addition of mangrove fruit flour. During the mixture of mangrove flour and potato starch, the peak viscosities are significantly correlated with the breakdown viscosities. Meanwhile, the addition of the mangrove fruit reduces the viscosity of waxing maize starch. The peak viscosity is the maximum viscosity during cooking and affects the paste strength in response to gelatinization [130]. The pectin content within the mangrove flour is the substance determining the viscosity properties since pectin gives gelling properties to the mixture [131]. Pectin is the soluble dietary fiber in mangrove fruit, and lignin, hemicellulose, and cellulose are insoluble dietary fibers. Insoluble dietary fibers usually decline the sensory quality of the food, while soluble dietary fibers improve it. Thus, the ratio between insoluble and soluble dietary fibers is important in maintaining the quality of the food product [132].
Low viscosity indicates higher resistance to retrogradation, and the addition of mangrove fruit enhances the retrogradation. Retrogradation is a step wherein the gelatinized starch forms an ordered configuration by cooling to increase the crystallinity to create rigidness and firmness of the product [133,134]. The addition of mangrove can be used for a product with a high final viscosity, such as pudding. On the contrary, high viscosity is unfavorable for baked food due to high breakdown viscosity representing a lower ability to withstand heating and shear stress [135]. The mixture of mangrove flour and wheat flour provides no significant improvement in viscosity due to the interaction of starch and non-starch content (protein–fiber) of the wheat flour to increase swelling. The breakdown viscosity of the mixture between mangrove fruit flour and wheat flour is positively related to the peak viscosity. The starch content of mangrove four is negligible, the change in pasting viscosity is derived by the swelling of pectin, and the pectin does not bind or withdraw water from the starch [136]. To catch the whole scope of the safe usage of the mangrove fruit flour, the animal test and preliminary test on food making are investigated [132].
B. gymnorrhiza flour (BGF) is rich in pinitol, a strong antioxidant to restrain ulcerative colitis. Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory abdominal disease in the rectum and colon [137]. Ulcerative colitis is related to a limited oxidative response in the intestine [138]. The administration of the flour to male BALB/c mice maintains the bodyweight while declining the histological score, improving colon pathologic variation, restoring the colon length, and alleviating inflammatory mediators such as IFN-γ, IL-1B, L-6, and MDA levels. The BGF up-regulates the protein (mRNA) level of NQO1, HO-1, GCLM, GCLC, and nuclear Nrf2 while inhibiting the cytosolic Nrf2 and protein expression of Keap1. NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is responsible for the oxidative stress response either due to endogenous or environmental stress, and it is regulated by Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) [139]. The activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 signalling pathway is powerful in the therapeutic procedure of ulcerative colitis [140]. Nrf2 antioxidant enzymes to treat ulcerative colitis are the glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC), NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1), hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1), and glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier (GCLM). Moreover, BGF promotes the growth of probiotics such as Lactobacillus, Anaerotruncus, and Bifidobacterium in the gut while restraining pathogenic bacteria Streptococcus and Bacteroides. The balance of the flora community restrained the abnormality in intestinal mucosa and then minimized the oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a common inflammatory disease caused by pathogenic infection. BGF demonstrated the DPPH scavenging activity with an IC50 value of 20.45 μg/mL [141].
The administration of R. mucronata flour shows hypoglycemic activities and reduces the blood glucose of male Wistar rats. Even though the effect is incomparable to a standard drug, with glibenclamide, the response in blood and urine is similar. The antidiabetic activity is due to the dietary fiber content and the bioactive compound [142]. Ripe fruit flour of the mangrove declines the blood glucose in a dose-dependent manner while maintaining the bodyweight of streptozotocin-induced mice. Diabetic organisms favor losing the bodyweight since they burn fat rather than glucose. The flour contains 3.5% protein, 0.78% fat, 819 ppm tannin, and 46.1% dietary fiber including 38.6% insoluble fiber and 7.5% soluble fiber. The flour is low in fat and protein while high in carbohydrate and insoluble fiber. The high dietary fiber with soluble fiber helps to reduce plasma lipid in type 2 diabetes, reduce hyperinsulinemia, and maintain blood glucose levels [142].
The administration of the mixture of fruit flour with sweet potato, arrowroot starch, taro starch, potato starch, and cassava starch in the Wistar rat model produces different outcomes. The performance of each mixture is assessed by considering the glycemic index. The glycemic index of food determines the significance of carbohydrates in the diet and relates to the effect on blood glucose [143]. Food with a high glycemic index escalates the metabolic condition [144]. The best mixture is 20% mangrove fruit and 80% taro starch, resulting in a 7.39 glycemic load, 48.83 glycemic index, 2.72% crude fiber, 15.55% fat, and 2.58% protein. Food with a low glycemic index helps to restrain appetite, improving the glucose and fat level [145].
7. The Prospect of Mangrove Fruit in the Functional Food Development
Referring to sustainable development growth proposed by the United Nations, a new strategy is required to solve the world’s hunger either by a physical, political, or economic approach. In the physical aspect, the concepts of bioeconomy in the food industry arise by utilizing the material from renewable resources [146]. Fruits such as mangrove fruit come as an option with their richness of phytochemicals. However, it is worth noting that the exploration of mangrove fruit should be reflected in the conservation strategies in each region. The population of mangrove plants is decreasing based on the IUCN, viz., A. marina and B. gymnorrhiza. The massive exploitation of the fruit has to be in balance with the plantation and harvesting strategies. Nevertheless, the campaign on the usage of mangrove fruit as functional food will hopefully improve the communities’ understanding of the priceless value of the fruit and the mangrove forest itself. With the increasing awareness of the community of the mangrove fruit value, the conservatism effort will, naturally, increase. Studies on the food products derived from the mangrove fruit are intensively directed to date. Many processed foods derived from mangrove fruit are patented (Table 5), including ingredients [147,148,149], beverages [150,151,152], and even synthetic rice [153]. Though the market study still needs to be carried out, the literature depicts the potency of mangrove fruit to be processed into unique food.

Table 5.
Patents in the mangrove fruit transformation in food products.
About 27 species of mangrove are approved traditionally and pharmacologically for folklore medicine [32]. The medicine is derived from parts of mangrove such as the stem, bark, leave, root, or fruit. However, fruit from limited species are developed into traditional food (Figure 18), i.e., B. gymnorrhiza, R. mucronata, S. caseolaris, and A. marina. Juice-making is a simple and conventional way of processing fruit, a process that mainly involves pulping the fresh fruit [160]. The juice, which involves a heating process from ripened fruit S. caseolaris, contains 65 mg of vitamin C [161]. Heating is sometimes required to prepare the juice for sterilization purposes; however, the heating should be for the proper duration. The longer time of heating is highly likely to decompose metabolites. During the heating, the total polyphenol level increases from 0 minutes to 20 minutes and declines afterwards. Polyphenols are stored in the pectin network or cell wall, then the heating assists in breaking the cell wall [162]. However, boiling reduces the vitamin C from 187.46 to 151.92 mg/100 g and protein content from 52.78% to 38% [163]. Thus, the pulp of mangrove fruit S. caseolaris is developed into a fruit drink with that is high in phenolic compounds [164].
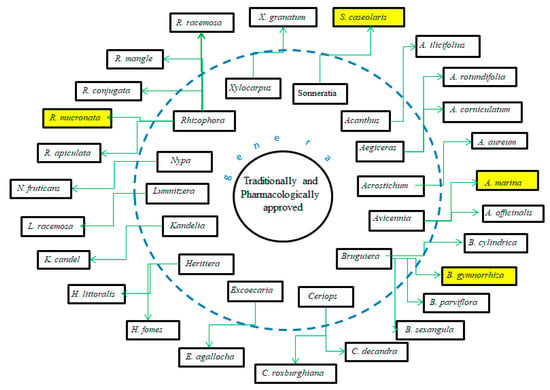
Figure 18.
Species of mangrove that are traditionally and pharmacologically proven for their ethnomedical properties; the yellow boxes are species common for traditional food. Modified from [32,128,141,165,166].
The juice of S. caseolaris is traditionally applied as an antiseptic and astringent to stop hemorrhages and treat coughs. The phenolic compound and antioxidant properties of unripe fruit are higher than ripe fruit. In the ripe fruit, the compound is degraded due to the biosynthesis pathway controlled by enzyme expression, environmental factors, and genetics. The antioxidant activity of the juice has a strong correlation with the total phenolic, flavonoid, and carotenoid content [39]. The juice of Barringtonia racemosa showed antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibition activities, while the juice of Thespesia populnea showed antihyperglycemic- and hypoglycemic-induced diabetes in the rabbit. Those fruits contain polyisoprenoids such as dolichols and polyprenol. The dolichols content differs among fruits, i.e., B. racemosa is comprised of C50–C110 and T. populnea is comprised of C65–C100. Polyprenol is only found in T. populnea (C55–C90). Dolichols are sugar-carrier lipids in the N-glycoprotein biosynthetic and GPI-anchored protein [167].
Other biscuits are made from the fruit of two mangrove plants, S. caseolaris and B. gymnorrizha, with antidiabetic and anticholesterol activity in male Wistar rats. The blood glucose level declines to 52.22% (109.91 mg/dL) as a result of the hypoglycemic effect of the bioactive compound and dietary fiber. The mangrove fruit flour from S. caseolaris has 63.70% dietary fiber and showed glucose inhibition [168]. The biscuit stays in a shorter time in the intestine than wheat flour biscuit, reducing glucose absorption. In diabetic rats, the bodyweight decreased by up to 6.32% due to the damage to B pancreas cells from alloxan induction. This stimulates the production of insulin and the glucose to be absorbed into the cell. The feeding of biscuits increased the body weight by up to 11.13%, showing a response to the enhancement of peripheral insulin sensitivity. The feeding reduced the cholesterol by 47% and LCL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglyceride by 50.47%. Dietary fiber controls the absorption and metabolism of lipid and glucose [169].
Another innovation is the food bar from local materials, and it provides advantageous dietary intake during an emergency such as flooding or an earthquake. As an emergency arises, convenient food with sufficient nutrient content is required. The availability of edible raw materials in the surrounding environment is important. The food bar made of mangrove fruit flour, soybean flour, and broccoli flour is beneficial in minimizing malnutrition in elderly people. The consumption of the food bar increases the bodyweight, and it is efficient in providing macronutrients [170].
Kombucha herbal from mangrove fruit R. mucronata showed antidiabetic and antioxidant activity by α-glucosidase inhibition with an IC50 value of 33.95 ppm. Kombucha is a traditional drink with a sweet-sour taste from the fermentation of a mixture of sugary herbs or tea by microbial tea starters [171]. The starter microorganism forms an elastic layer called "nata" or "tea mushroom" on the herb’s surface and tea liquid on the bottom. The microorganism is a consortium of bacteria and fungi. The bacteria are from the genera Acetobacter and Gluconobacter, while the yeast is Mycoderma, Mycotorula, Pichia, Kloeckera, Brettanomyces, Torulospora, Candida, Schizosaccharomyces, Saccharomycodes, Zygosaccharomyces, and Saccharomyces [172]. The beverage has a sour and sweet taste based on the type of starter, and the flavor comes from tannin transformation [173]. Kombucha herbal tea is famous for its antioxidant and antimicrobial activities [174]. A positive correlation between the tannin content with antidiabetic and antioxidant activity is observed in kombucha from mangrove fruit. The kombucha is prepared with 10% sugar addition and fermentation within 14 days. During the fermentation, the kombucha produces 19679.82 mg GAE/100g of total phenolic acid [175]. Mangrove fruit is also processed into other drinks such as tea and coffee. Tea and coffee from mangrove fruit contain quercetin-3-O-(2”-O-glucopyranoside)-galactopyranoside, dodecanoic, quercetin-3-O-galactopyranoside and L-alanine. Both extracts of tea and coffee from mangrove fruit demonstrate high antioxidant activities, i.e., tea mangrove with an IC50 value of 4.13 μg/mL and coffee mangrove with an IC50 value of 5.25 μg/mL [166].
S. caseolaris extract can be added as an additive or perseverance for palm olein by restraining lipid oxidation. Palm olein is vegetable oil as a fraction of palm oil after crystallization. Palm olein has low oxidative stability due to high (up to 55%) unsaturated fatty acid, mainly oleic acid (C18:1n9) and linoleic acid (C18:2n6). It is a challenge to maintain the quality of the oil for marketing purposes. The main problem is oxidation, leading to discoloration, an offensive odor, destructive vitamins, enzymes, and other nutrients. Minimizing the oxidation, the antioxidant is added, and a natural antioxidant is preferable due to its lower toxicity, even if it is more expensive. The antioxidative activities of the mangrove fruit extract are related to the total phenolic compounds. With the addition of mangrove fruit extract, the storage period increases with the increased formation of primary lipid oxidation product (hydroperoxide) [176].
8. The Possible Strategic Development for Mangrove Fruit as Functional Food Material
The mangrove fruits, indeed, show great potency in functional food development given their richness of phytochemicals and their potential for improvement as processed food. Traditional food based on edible mangrove fruit has long been applied in some South Asian and Southeast Asian countries. However, the search for the mangrove fruit candidate as functional food should well address the safety aspects regarding the fruit’s chemical content since some fruits may not be edible. Semi-mangrove Excoecaria agallocha L. and mangrove Heritiera littoralis are notorious examples of mangrove species producing poisonous compounds [177,178]. Even though the poison is merely produced in the bark of the mangrove, the phytochemical activities of the fruit need to be investigated. The latex from E. agallocha bark causes temporary blindness [177]; the leaf extract is used as dart poison and fish poison in many countries including Goa, Sarawak, and New Caledonia [179]. The latex of H. littoralis is also used as spearhead and arrowhead poison and fish poison [178]. Investigation is also required for other mangroves.
Concurrent with the poisonous latex from its bark, the seed of E. agallocha and H. littoralis is acknowledged for its ethnomedicinal properties. The bark of E. agallocha is rich of diterpene such as ent-3,4-seco-16α-hydroxyatis-4(19)-en-3-oic acid, which possesses anti-microfouling activity against Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes (EC50 value of 0.54 ± 0.01 ppm) [179]. E. agallocha is an important mangrove plant in East and Southeast Asia as a traditional remedy for dermatitis, conjunctivitis, epilepsy, and toothache. Various triterpenoids, flavonoids, and tannins are isolated from the species [180]. Meanwhile, the seed of H. littoralis is edible and consumed for traditional medicine in Andaman Island and Nicobar for treating diarrhea and dysentery [178]. Unfortunately, there are limitations in the literature for the fruit of both species.
It is worth noting that evaluating the toxicity and hazardous compounds within the mangrove fruit is important. On the phytochemical aspect, the compounds from mangrove fruit and other parts of the mangrove are toxic and can be utilized for larvicidal, acaricidal, and pesticidal applications. The leaf extract of R. mucronata has larvicidal potential against mosquito larvae, i.e., Aedes aegypti (LC50 = 0.11 mg/mL), Culex quinquefasciatus (LC50 = 0.13 mg/mL), and Anopheles stephensi (LC50 = 0.34 mg/mL). The active compounds with applications as larvicidals are phenols, tannins, saponins, flavonoids, and quinones [181]. The fruit of C. manghas shows acaricidal activity against female adults of Panonychus citri (LC50 = 3.39 g/L) [55]. The mangrove forest also has a remarkable area containing pollutants, including solid particles such as micro/nanoplastics [182], organic pollutants (e.g., PAHs, PCBs, and other POPs), and metals [183,184,185,186]. Those pollutants potentially accumulate within the mangrove plant [187]. Therefore, the evaluation of those hazardous compounds within the mangrove fruit is coveted prior to their development into functional food.
It is acknowledged that mangroves play a crucial role in aquatic environments. The fruit of mangroves provides nutritious food for animals such as birds, reptiles, and mammals living in the mangrove forest [188]. The harvesting of mangrove fruit for human consumption in conservation or protected areas has to consider the natural capacity to preserve the habitat and its inhabitants. Thus, when it is widely accepted by the society, other approaches to support the mangrove fruit utilization for human food are demanded. Though the mangroves are not considered cultivated plants, there are rehabilitation and mangrove reforestation success stories in many places. The B. gymnorrhiza plantation in south Florida in the 1940s is an excellent example in which the population growth rate reached 5.6% per year [189]. These successes reflect the potency of mangrove to potentially be cultivated for agricultural purposes (Figure 19). To cope with the mangrove fruit demand for human consumption, the fruit can be collected from man-made areas. The man-made area is divided into at least two actions: (1) a sole man-made mangrove ecosystem for agricultural purposes, and (2) the integrated mangrove-aquaculture area. The integrated mangrove-aquaculture or silvofishery are applied in many countries such as Indonesia, Vietnam, and Nigeria [190,191,192]. In Indonesia and Vietnam, the mangrove is planted in the water canal between platforms [193]. From these man-made areas, the mangrove fruit and other mangroves forest products can be extensively explored, even though the justified management should be applied. The type of planted mangrove can be selected considering the ecological aspects.
Figure 19.
The proposed strategy development for utilizing mangrove fruit for functional food production.
The harvested mangrove fruit has been subjected to chemical analysis to investigate the safety or hazardous chemical of the fruit [194]. The common phytochemical compounds from mangrove fruit, in high concentrations, expose a threat to human health; therefore, the amount is reduced during processing. A biscuit can be made from the mixture of mangrove fruit B. gymnorrhiza flour and soybean flour with a ratio of 7:2. The manufacturer modifies the chemical content during food processing by performing some treatment. Some mangrove fruit contains a high level of HCN and tannin that are unhealthy for the human body. Boiling and the addition of ash during biscuit production reduce the amount of HCN and tannin. The boiling process reduces the HCN and tannin content, while the addition of ash inhibits the metabolism rate of tannin. Tannin is decomposed to glucose, and gallic acid during the heating and rubbing ash absorbs the tannin. The addition of mangrove fruit increases the fat and protein contents to relatively higher amounts compared to commercial plain flour cookies [165]. Thus, the evaluation of chemical content from the mangrove fruit for functional food is commenced after the fruit harvesting and food production.
9. Current Studies of Mangrove Fruit in Middle East
Using the Landsat data, it can be seen that the mangrove forest in the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman increased from 1977 to 2017. The mangrove afforestation effort supported by government regulation shows a positive outcome in each of the Gulf countries during 1977–2017, i.e., Iran (from 4735 ha to 9403 ha), United Arab Emirates (from 1327 ha to 7926 ha), Oman (from 206 ha to 530 ha), Arabian Gulf of Saudi Arabia (from 97 ha to 837 ha), Qatar (from 16 ha to 1002 ha), and Bahrain (from 31 ha to 48 ha) [195].
Mangrove forest in the Red Sea, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, grows in a narrow or broad forest in coastal, nearshore, or offshore islands. Four species—A. marina, B. gymnorrhiza, C. tagal, and R. mucronata—are recorded along the Red Sea part of Saudi Arabia [196]. The mangrove forest in the Red Sea part of Saudi Arabia is mostly composed of A. marina with a small co-existence of R. mucronata. The mangrove forest is in a patchy pattern rather than continuous distribution. The mangroves are slow growers in the area due to environmental and anthropogenic stress such as pollution, poor soil texture, high salinity, and low precipitation. The Red Sea in the Arabian Peninsula is characterized as an arid and oligotrophic area [197]. The Landsat imaginary identified the slight increase by about 0.29% per year of mangrove stands from 1972 to 2013 due to rehabilitation efforts [198].
The rehabilitation effort of mangrove forests in the Red Sea in the Arabian Peninsula mainly introduce A. marina since the species is salt-tolerant up to 70 ppt, and the survival rate of the plantation reached 39% during two years of the program [199]. The growth of A. marina in the Red Sea is affected by the nitrogen limitation. The tallest trees are observed in the southern part of the Red Sea in the Arabian Peninsula, while the smallest is recorded in the central of the Red Sea. At the same time, the intermediate high is documented in the northern part of the Red Sea. The distribution follows the nitrogen concentration [200]. A. marina allocates its biomass belowground more than aboveground to cope with the nutrient limitation and hypersaline, anoxic, soft, and unstable sediment. The allocation of this belowground biomass is more significant in the arid area. The belowground biomass of A. marina in Shuaiba on the Saudi Arabian Red Sea coast is greater than in East Africa [201]. The photoperiods, temperature, humidity, and salinity affect the reproduction of A. marina in the central Red Sea of Saudi Arabia [202]. A. marina occupies 135 km2 of the coastal area. The forest is a low organic-carbon Corg sink due to extreme conditions such as the inclining soil respiration rate, the declining growth rate of mangrove, high temperature, poor nutrition, and low rainfall [203]. Mangrove forests in Yanbu (0.39 t C/ha) store more organic carbon than Umluj (0.12 t C/ha) and Ar-Rayis (0.11 t C/ha). Mangrove forest in Yanbu is a protected area, while the others are non-rehabilitation and non-conservation areas [204].
A. marina and R. mucronata are two species of mangrove discovered in the Red Sea part of the Egyptian coastal area [205], while A. marina is the only mangrove that grows in south Sinai, Gulf Aqaba, Egypt [206]. Mangrove on the Egyptian Red Sea coast is dominantly monospecific with A. marina. The variation in R. mucronata occurs on the Egyptian–Sudanese border coexisting with the dominant A. marina. The mangrove occupies 525 ha spreading in 28 locations on the Egyptian Red Sea coast [207]. On the Egyptian Red Sea coast, the growth of R. mucronata is higher when associated with A. marina compared with its pure stand. The soil composition (e.g., Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, and CaCO3), morphological characteristics, and tidal inundation determine the distribution pattern of mangrove species. The root system of both mangroves affects the survival rate [208]. The mangrove on the Red Sea Yemeni coast is denser than mangrove in the Red Sea southern Saudi Arabia part since they receive less anthropogenic stress. They grow in intertidal, lagoon, and estuarine areas, covering around 1610 ha. As in other parts of the Red Sea, the mangroves grow in a patchy pattern instead of in a continuous distribution [209]. A. marina is the dominant mangrove species but co-exists with small R. mucronata in Kamaran Island, Yemen. The mangrove in the offshore island is denser than the coastal area of the Arabian Peninsula [210].
In the Arabian Gulf, A. marina is also the dominant species. However, the growth of A. marina in the western part of Arabia Gulf is slow due to harsh environmental conditions and pollution, e.g., from the Gulf War oil spill in 1991 [211]. The plantation of A. marina in Qatar shows positive feedback after 23 years of the plantation program, with a density increase from 1100/ha to 2100/ha. The natural habitat covers 797.6 ha; the planted area is 182.9 ha on the east coast, while it is only 1 ha on the west coast. However, the natural mangrove is higher (1–6 m) compared to planted mangrove (1–3 m) [212]. Meanwhile, the mangrove area in Oman covers 0.33% of the coastline [213]. An impressive increase in mangrove forests is observed in the United Arab Emirates: mangrove forest in Khor al Beida is undisturbed and is in a natural condition [214].
The mangrove forest in the Middle East is relatively less dense with has fewer recorded species than in other parts of the world. The local community utilizes the mangrove plant as traditional medicine, and several studies on the bioactive compounds are also explored (Table 6). Extract of A. marina leaf from Safaga, Red Sea, Egypt, possesses antibiofilm formation against Pseudomonas fluorescens by preventing initial cell attachment at an IC50 value of 42.0–45.8 mg/mL [215]. Ethanol extract of A. marina from Saudi Arabia possesses antidiabetic activity by reducing the blood glucose level; methanolic extract of the aerial root shows antihyperglycemic properties. Aqueous extract of R. mucronata bark presents antihyperglycemic and hypoglycemic activities. Water extract of A. marina leaf in Iran also shows antidiabetic properties by reducing the serum levels in the liver [216]. The bark of A.marina from Jazan, Saudi Arabia, is traditionally used to treat diabetes and smallpox, to induce infertility in women, and as a pruritic [217]. However, the fruits’ development into functional food is limited.

Table 6.
Several studies of bioactive compounds from the mangrove forest in the Middle East.
10. Conclusions
Through various profound investigations, valuable nutrition data and many classes of metabolites with bioactive properties from the mangrove fruits have been discovered. The proximate of mangrove fruit differs regarding the type of the fruit and the crude extract possesses antioxidant activities related to the amount of total phenolic content. The extract of mangrove fruit to animal models exhibits antioxidant, anti-atherosclerosis, antimicrobial, anti-diabetic, and hepatoprotective properties. The mangrove fruit is also rich in limonoids, a group of terpenoid compounds that show antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anticancer properties. Interestingly, the seed and symbiont, endophytic fungus, are also a source of secondary metabolites with various bioactivities. Observed deeply, some compounds found in the seed are similar to those of compounds from the fruit, such as the class of xyloccensins; however, the class of compounds from the endophytic fungi is different from them both. It is suspected that the biosynthetic pathway of the compounds in the fruit resembles that of the seed, yet the endophytic fungi may possess distinct biosynthetic pathways.
The mangrove fruits exhibit an excellent prospect of transforming into high economic food products. The flour of the fruit contains sufficient proximates for supporting the daily intake of nutrition. The flour from mangrove fruit presents an antioxidant and anti-diabetes to animal rat models. The innovation in processing mangroves resulted in several edible food products from snacks such as biscuits or crackers; drinks such as kombucha, tea, and coffee; and even synthetic staple food such as rice. The food products derived from mangrove fruit show merit in animal rat models. Unfortunately, the study on the introduction of mangrove fruit to functional food is limited to only some species, such as B. gymnorrhiza, R. mucronata, S. caseolaris, and A. marina, though around 27 species are confirmed traditionally and pharmacologically for their ethnomedicinal properties. This limitation opens challenges to identifying the possibility of developing the other mangrove species into functional foods. The mangrove plant is also considered the traditional medicine in the Middle East, and A. marina is the dominant mangrove species in the region. The study of phytochemicals from the fruit of mangrove is limited, and the development of fruit into functional food is even more limited.
Thus, the mangrove fruits can be used as a functional food with health impacts. Some local communities have utilized mangrove fruit in the form of homemade food products for traditional medicine since time immemorial. The further development of food based on mangrove fruit still requires a long journey, such as the economic and market study as well the cultivation strategy. The introduction of food derived from mangrove fruit to a vast community may also improve the understanding of the importance of mangrove forests.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the manuscript. Conceptualization, F.B. and W.M.A.; methodology, E.A.A. and A.E.M.; validation, M.A.G., N.O.B., and H.S.A.; formal analysis, E.A.A. and A.E.M.; investigation, F.B.; resources, E.A.A., N.O.B., and H.S.A.; data curation, M.A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, F.B., W.M.A.; writing—review and editing, M.A.G., N.O.B., H.S.A., and W.M.A.; visualization, E.A.A. and A.E.M.; supervision, W.M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the marine chemistry department of King Abdulaziz University for use of their facilities. The authors also thank the blind reviewers and editorial board for the valuable comments and suggestions for the improvement of the manuscript. This publication received no funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chiwona-Karltun, L.; Amuakwa-Mensah, F.; Wamala-Larsson, C.; Amuakwa-Mensah, S.; Abu Hatab, A.; Made, N.; Taremwa, N.K.; Melyoki, L.; Rutashobya, L.K.; Madonsela, T.; et al. COVID-19: From health crises to food security anxiety and policy implications. Ambio 2021, 50, 794–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savary, S.; Akter, S.; Almekinders, C.; Harris, J.; Korsten, L.; Rötter, R.; Waddington, S.; Watson, D. Mapping disruption and resilience mechanisms in food systems. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 695–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer-Nawrocka, A.; Sadowski, A. Food security and food self-sufficiency around the world: A typology of countries. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio Osorio, L.L.; Flórez-López, E.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. The potential of selected agri-food loss and waste to contribute to a circular economy: Applications in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Molecules 2021, 26, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, J.A.; Rolim, P.M.; Damasceno, K.S.F.d.S.C.; de Sousa, F.C.; Nabas, R.C.; Seabra, L.M.A.J. From seed to flour: Sowing sustainability in the use of cantaloupe melon residue (Cucumis melo L. Var. Reticulatus). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason-D’Croz, D.; Bogard, J.R.; Sulser, T.B.; Cenacchi, N.; Dunston, S.; Herrero, M.; Wiebe, K. Gaps between fruit and vegetable production, demand, and recommended consumption at global and national levels: An integrated modelling study. Lancet Planet Health 2019, 3, e318–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, M.L. Whole fruits and fruit fiber emerging health effects. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, U.; Mitra, B.; Bhadra, K. Island Based Assemblage Pattern and Foraging Profile of Insect Flower Visitors on Aegialitis rotundifolia—A Near Threatened Mangrove Plant from Indian Sundarban. Neotrop. Entomol. 2022, 51, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänes, H.; Macreadie, P.I.; Rizzari, J.; Ierodioconou, D.; Reeves, S.E.; Dwyer, P.G.; Carnell, P.E. The value of estuarine producers to fisheries: A case study of Richmond River Estuary. Ambio 2022, 51, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Nabangchang, O.; Erdman, K.; Vanko, A.C.A.; Poudel, P.; Giri, C.; Vincent, J.R. Inferring economic impacts from a program’s physical outcomes: An application to forest protection in Thailand. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaranayake, W.M. Traditional and medicinal uses of mangroves. Mangroves Salt Marshes 1998, 2, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, H.A.; Bouroubi, Y.; Khomalli, Y.; Elyaagoubi, S.; Maanan, M.; Rhinane, H.; Maanan, M. The economic benefit of coastal blue carbon stocks in a Moroccan Lagoon ecosystem: A case study at Moulay Bousselham Lagoon. Wetlands 2022, 42, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Uribe, H.M.; López-Portillo, J.; Reverchon, F.; Hernández, M.E. Effect of degradation of a black mangrove forest on seasonal greenhouse gas emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 11951–11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazareth, D.R.; Gonsalves, M.-J. Influence of seasonal and environmental variables on the emission of methane from the mangrove sediments of Goa. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.A.; Badola, R. Valuing mangrove ecosystem services: Linking nutrient retention function of mangrove forests to enhanced agroecosystem production. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 16, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.H.; Song, Q.L.; Nie, F.H.; Wei, W.; Chen, M.M.; Zhang, M.; Lin, H.Y.; Kang, D.J.; Chen, Z.B.; Hay, A.G.; et al. Effects of environmental and spatial variables on bacteria in Zhanjiang mangrove sediments. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Campo, J.T.F.; Olvera-Vargas, M.; Silla-Cortés, F.; Figueroa-Rangel, B.L.; Iñiguez-Dávalos, L.I. Composition and structure of vegetation and tide regulate the occurrence of Oryzomys couesi and Hodomys alleni in mangrove forests of Laguna de Cuyutlán, West-Central Mexico. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 30, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Du, J.; Su, F.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, S.; Feng, P. Reclamation and ecological service value evaluation of coastal wetlands using multispectral satellite imagery. Wetlands 2022, 42, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.K.; Singh, R.; Ojha, A. Dynamical study of harmful algal bloom in Sundarban mangrove wetland with spatial interaction and competing effects. Model Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 555–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lai, Q.; Chen, X.; Dong, C.; Huang, X. Oceanobacter mangrovi sp. Nov., a Novel Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate accumulating bacterium isolated from mangrove sediment. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y.; Li, H.; Zhong, Y.H.; Shen, Z.J.; Ma, D.N.; Gao, C.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; You, Y.P.; et al. Transcriptomic analyses reveal the effect of nitric oxide on the lateral root development and growth of mangrove plant Kandelia obovata. Plant Soil. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadatha, B.; Jones, E.B.G.; Pang, K.L.; Abdel-Wahab, M.A.; Hyde, K.D.; Sakayaroj, J.; Bahkali, A.H.; Calabon, M.S.; Sarma, V.V.; Sutreong, S.; et al. Occurrence and geographical distribution of mangrove fungi. Fungal Divers. 2021, 106, 137–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, D.P.; Isnansetyo, A.; Istiqomah, I.; Jumina, J. New report: Genome mining untaps the antibiotics biosynthetic gene cluster of Pseudoalteromonas xiamenensis STKMTI.2 from a mangrove soil sediment. Mar. Biotechnol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.J.; Wu, M.-D.; Khamthong, N.; Tseng, M. Polar metabolites from the Actinobacterium Isoptericola chiayiensis isolated from mangrove soil. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2021, 57, 1134–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Bhattarcharya, D.; Saha, M.; Mukherjee, J.; Karmakar, S. Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of the extract of Streptomyces euryhalinus isolated from the Indian Sundarbans. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.L.Y.; Huang, D.; Quek, Z.B.R.; Lee, J.N.; Wainwright, B.J. Distinct fungal communities associated with different organs of the mangrove Sonneratia alba in the Malay Peninsula. IMA Fungus 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, L.M.d.S.; Caria, C.R.e.P.; Santos, P.S.; Ruy, C.C.; Da Silva Lima, N.; Moreira, D.K.T.; da Rocha, C.Q.; Murador, D.C.; de Rosso, V.V.; Gambero, A.; et al. Modulatory effect of polyphenolic compounds from the mangrove tree rhizophora mangle L. on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance in high-fat diet obese mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Quispe, C.; Hossain, R.; Jain, D.; Ahmed Khan, R.; Janmeda, P.; Islam, M.T.; Suleria, A.R.H.; Martorell, M.; Daştan, S.D.; et al. Ethnomedicinal use, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Xylocarpus granatum J. Koenig. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 8922196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; Samantaray, D.; Mahapatra, A.; Pal, N.; Munda, R.; Thatoi, H. Pharmacological activities of leaf and bark extracts of a medicinal mangrove plant Avicennia officinalis L. Clin. Phytosci. 2018, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, N.W.; Clements, C.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A. Targeted isolation of anti-trypanosomal naphthofuran-quinone compounds from the mangrove plant Avicennia lanata. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.C.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Lin, Y.M.; Ding, Z.H.; Chai, W.M.; Wei, S.D. Relationships between degree of polymerization and antioxidant activities: A study on proanthocyanidins from the leaves of a medicinal mangrove plant Ceriops tagal. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, S.N.; Fawzi, M.M.; Gokhan, Z.; Rajesh, J.; Nadeem, N.; Kannan, R.R.R.; Albuquerque, R.D.D.G.; Pandian, S.K. Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and global distribution of mangroves-a comprehensive review. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawar, M.K.; Basyuni, M.; Hanum, C.; Siregar, E.S. Bioprospecting opportunities of mangrove fruits for the coastal community in lubuk kertang and pulau sembilan, north sumatra, indonesia. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2022, 21, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, M.; Eid, E.M.; Hasan, M. Mangrove health along the hyper-arid southern Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; El-Askary, H.; Qurban, M.A.; Li, J.; ManiKandan, K.P.; Piechota, T. Using multi-indices approach to quantify mangrove changes over the Western Arabian Gulf along Saudi Arabia coast. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahasheer, H. Spatial coverage of mangrove communities in the Arabian Gulf. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonggo, D.; Berhimpon, S.; Kurnia, D.; Dotulong, V. Antioxidant activities of mangrove fruit (Sonneratia alba) taken from Wori Village, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2017, 10, 284–290. [Google Scholar]
- Riyadi, P.H.; Tanod, W.A.; Dewanto, D.K.; Herawati, V.E.; Susanto, E.; Aisiah, S. Chemical profiles and antioxidant properties of Bruguiera gymnorrhiza fruit extracts from central sulawesi, indonesia. Food Res. 2021, 5, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, F.I.; Abu Bakar, M.F.; Hassan, S.H.A.; Sanusi, S.B.; Kormin, F.; Sabran, S.F.; Fuzi, F.Z.M. Comparison of phytochemicals, antioxidant and anti-cholinesterase activity of unripe and ripe fruit of Sonneratia caseolaris. Food Res. 2020, 4, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.J.; Basar, M.H.; Rokeya, B.; Arif, K.M.T.; Sultana, M.S.; Rahman, M.H. Evaluation of antioxidant, antidiabetic and antibacterial activities of the fruit of Sonneratia apetala (Buch.-Ham.). Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2013, 13, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basyuni, M.; Yusraini, E.; Susilowati, A.; Hayati, R.; Siregar, E.S.; Desrita; Susetya, I.E.; Kajita, T. Bioprospecting of selected mangrove fruits based-nutritional, antioxidant, and element properties to support functional food materials for Pulau Sembilan coastal communities, Indonesia. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2021, 11, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Banerjee, A.; Mullick, J.; Jana, T.K. Nutritional composition of some selected wild mangrove fruits of Sundarbans. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2015, 44, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Sudirman, S.; Nurjanah; Jacoeb, A.M. Proximate compositions, bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity from large-leafed mangrove (Bruguiera gymnorrhiza) fruit. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 2387–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, S.; Paul, G.K.; Afroze, M.; Islam, S.; Gupt, S.B.R.; Razu, M.H.; Biswas, S.; Zaman, S.; Uddin, M.S.; Khan, M.; et al. Efficacy of phytochemicals derived from Avicennia officinalis for the management of covid-19: A combined in silico and biochemical study. Molecules 2021, 26, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahyadi, J.; Satriani, G.I.; Gusman, E.; Weliyadi, E. Inhibiting vibrio harveyi infection in Penaeus monodon using enriched Artemia salina with mangrove fruit Sonneratia alba extract. AACL Bioflux 2020, 13, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, L.; Sleiman, A.; Abdel-Massih, R.M. Antimicrobial activity of polyphenols and alkaloids in middle eastern plants. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharief, M.N.; Srinivasulu, A.; Veni, P.S.; Rao, V.U.M. Quantification of phytochemicals and antibacterial activity of fruit extract of Avicennia officinalis. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2014, 7, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Pagarra, H.; Hartati; Rachmawaty; Hala, Y.; Rahman, R.A. Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial activity from Sonneratia caseolaris fruit extract. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2019, 967, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Ambarwati, N.S.S.; Lukman, A.; Masruhim, M.A.; Rijai, L.; Mun’Im, A. In vitro antimicrobial activity evaluation of mangrove fruit (Sonneratia caseolaris L.) extract. Pharmacogn. J. 2018, 10, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeer, N.B.; Rocchetti, G.; Senizza, B.; Montesano, D.; Zengin, G.; Uysal, A.; Jeewon, R.; Lucini, L.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Untargeted metabolomic profiling, multivariate analysis and biological evaluation of the true mangrove (Rhizophora mucronata lam.). Antioxidants 2019, 8, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeer, N.B.; Haddad, J.G.; Ezzat, M.O.; Desprès, P.; Abdallah, H.H.; Zengin, G.; Uysal, A.; El Kalamouni, C.; Gallo, M.; Montesano, D.; et al. Bruguiera gymnorhiza (L.) lam. at the forefront of pharma to confront zika virus and microbial infections—an in vitro and in silico perspective. Molecules 2021, 26, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, M.; Bailey, M.A.; Thiagarajan, T.R.; Troyer, T.L.; Huggins, L.G. Antibacterial and cytotoxic effects of red mangrove (Rhizophora mangle L.Rhizophoraceae) fruit extract. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2011, 63, 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Wetwitayaklung, P.; Limmatvapirat, C.; Phaechamud, T. Antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities in various parts of Sonneratia caseolaris (L.). Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sulmartiwi, L.; Pujiastuti, D.Y.; Tjahjaningsih, W.; Jariyah. Potential of mangrove Avicennia rumphiana extract as an antioxidant agent using multilevel extraction. In Proceedings of the ASEAN-Fen International Fisheries Symposium, Batu, East Java, Indonesia, 7–9 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Liao, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Zhong, H.; Zhou, Q.; Qing, Z. Acaricidal activity against Panonychus citri and active ingredient of the mangrove plant Cerbera manghas. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthiban, A.; Sivasankar, R.; Sachithanandam, V.; Khan, S.A.; Jayshree, A.; Murugan, K.; Sridhar, R. An integrative review on bioactive compounds from Indian mangroves for future drug discovery. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masdar, H.; Hamidy, M.Y.; Darmawi; Trihardi, R.; Perwira, A.; Utari, D. Anti-atherosclerotic effects of Sonneratia Alba fruit extract in atherosclerotic-induced rats. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2020, 12, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okla, M.K.; Alatar, A.A.; Al-Amri, S.S.; Soufan, W.H.; Ahmad, A.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.A. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of the extracts of different parts of Avicennia marina (Forssk.) vierh. Plants 2021, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Tiwari, P.; Srivastava, S.P.; Srivastava, R.; Mishra, A.; Rahuja, N.; Pandeti, S.; Tamrakar, A.K.; Narender, T.; Srivastava, M.N.; et al. Antihyperglycaemic and antidyslipidemic activities in ethyl acetate fraction of fruits of marine mangrove Xylocarpus Moluccensis. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 809–826. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Luo, D.; Wu, Y.; Gao, C.; Lin, G.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, J.; Su, Z. The protective effect of Sonneratia apetala fruit extract on acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 6919834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, S.; Venditti, P. Evolution of the knowledge of free radicals and other oxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 9829176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yompakdee, C.; Thunyaharn, S.; Phaechamud, T. Bactericidal activity of methanol extracts of crabapple mangrove tree (Sonneratia caseolaris Linn.) against multi-drug resistant pathogens. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 74, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hosen, M.Z.; Biswas, A.; Islam, M.R.; Hossain, S.J. Anti-bacterial, anti-diarrheal, and cytotoxic activities of edible fruits in the Sundarbans mangrove forest of Bangladesh. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 26, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidy, M.Y.; Masdar, H.; Darmawi. Effect of mangrove (Rhizophora sp.) fruit extract on foam cell formation at the initiation stage of atherosclerosis. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2020, 13, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatana, C.; Saini, N.K.; Chakrabarti, S.; Saini, V.; Sharma, A.; Saini, R.V.; Saini, A.K. Mechanistic insights into the oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced atherosclerosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 5245308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Song, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Long non-coding RNAs link oxidized low-density lipoprotein with the inflammatory response of macrophages in atherogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Friedman, A. The LDL-HDL profile determines the risk of atherosclerosis: A mathematical model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulholland, D.A.; Parel, B.; Coombes, P.H. The chemistry of the Meliaceae and Ptaeroxylaceae of Southern and Eastern Africa and Madagascar. Curr. Org. Chem. 2000, 4, 1011–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wu, J.; Deng, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Xylocarpins A-I, limonoids from the Chinese mangrove plant Xylocarpus granatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, R.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Shukla, V.N.; Yadav, P.; Hasanain, M.; Sarkar, J.; Narender, T.; Mitra, K. Gedunin isolated from the mangrove plant Xylocarpus granatum exerts its anti-proliferative activity in ovarian cancer cells through G2/M-phase arrest and oxidative stress-mediated intrinsic apoptosis. Apoptosis 2020, 25, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, C.; Ding, H.; Li, Q. Complete assignments of 1H and 13C NMR data for two 3β,8β-epoxymexicanolides from the fruit of a Chinese mangrove Xylocarpus granatum. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2006, 44, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Song, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Q. Two new mexicanolides from the fruit of a Chinese mangrove Xylocarpus granatum. Z. Nat. B, Chem. Sci. 2005, 60b, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Zou, K. Xyloccensins X1 and X2, two new mexicanolides from the fruit of a Chinese mangrove Xylocarpus granatum. Z. Nat. B, Chem. Sci. 2005, 61b, 626–628. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, F.; Wu, J.; Zou, K. Polyhydroxylated phragmalins from the fruit of a Chinese Mangrove, Xylocarpus granatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Q. Xylogranatins A-D, new mexicanolides from the fruit of a Chinese mangrove Xylocarpus granatum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 1582–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ding, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, S. Xylogranatin E, a new phragmalin with a rare oxygen bridge between C 1 and C29, from the fruit of a Chinese mangrove Xylocarpus granatum. Z. Nat. Sect. B J. Chem. Sci. 2007, 62b, 569–572. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Zou, K. Xylogranatinin, a new pyrido[1, 2-a]pyrazine alkaloid from the fruit of a Chinese mangrove Xylocarpus granatum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2007, 43, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Deng, Z.; Xu, M.; Proksch, P.; Li, Q.; Lin, W. Protolimonoids and limonoids from the chinese mangrove plant Xylocarpus granatum. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, M.; Xiao, Z.; Zhou, Y. Butyrospermol fatty acid esters from the fruit of a Chinese mangrove Xylocarpus granatum. Z. Nat. Sect. B J. Chem. Sci. 2006, 61, 1447–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.M.; Gao, C.H.; Yi, X.X.; Xie, W.P.; Xu, M.B.; Huang, R.M. Two new secondary metabolites from the fruits of mangrove Avicennia marina. Z. Nat. 2015, 70, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.X.; Chen, Y.; Xie, W.P.; Xu, M.B.; Chen, Y.N.; Gao, C.H.; Huang, R.M. Four new jacaranone analogs from the fruits of a Beibu Gulf mangrove Avicennia marina. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.H.; Yi, X.X.; Xie, W.P.; Chen, Y.N.; Xu, M.B.; Su, Z.W.; Yu, L.; Huang, R.M. New antioxidative secondary metabolites from the fruits of a beibu gulf mangrove, Avicennia marina. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4353–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Ouyang, J.; Deng, Z.; Lin, W. Structure elucidation of an unprecedented alkaloid and a new limonoid from Xylocarpus granatum. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2008, 46, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakhathirathien, C.; Karalai, C.; Ponglimanont, C.; Subhadhirasakul, S.; Chantrapromma, K. Dammarane triterpenes from the hypocotyls and fruits of Ceriops tagal. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Jiang, S.; Qin, M.; Liu, K.; Cao, P.; Chen, S.; Deng, J.; Gao, C. Compounds from the fruits of mangrove Sonneratia apetala: Isolation, molecular docking and antiaging effects using a Caenorhabditis elegans model. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, T.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Sun, M.; Shi, Q.; Huo, C.; Wang, Q.; Gu, Y. A chemometric-assisted LC–MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of 17 limonoids from different parts of Xylocarpus granatum fruit. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4669–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narender, T.; Khaliq, T.; Shweta; Reddy, K.P.; Sharma, R.K. Occurrence, biosynthesis, biological activity and NMR spectroscopy of D and B, D ring seco-limonoid of Meliaceae family. Natural Product Commun. 2007, 2, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Long, L. Xyloccensin M and N, Two New B, D-seco limonoids from Xylocarpus granatum. Z. Nat. Sect. B J. Chem. Sci. 2003, 58b, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, K.A.; Crews, P.; Aalbersberf, B.; Prasa, R. Limonoids from the Fijian medicinal plant dabi (Xylocarpus). Tetrahedron 1991, 41, 8943–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, M.Y.; Feng, G.; Xiao, Q.; Sinkkonen, J.; Satyanandamurty, T.; Wu, J. Limonoids from the seeds of a Godavari mangrove, Xylocarpus moluccensis. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Q. Two new limonoids with a 3-0-β-tigloyl group from the seeds of the Chinese mangrove Xylocarpus granatum. Z. Nat. Sect. B J. Chem. Sci. 2007, 62, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.L.; Zou, X.P.; Li, W.S.; Shen, L.; Wu, J. Limonoids containing a C1-O-C29 Moiety: Isolation, structural modification, and antiviral activity. Mar. Drugs. 2018, 16, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.R.; Yin, B.W.; Zhang, M.L.; Shi, Q.W.; Huo, C.H.; Dong, M.; Cong, B.; Guo, D.; Kiyota, H.; Suzuki, N. Xylomexicanins A and B, new Δ14,15-Mexicanolides from seeds of the Chinese mangrove Xylocarpus granatum. Z. Nat. Sect. C J. Biosci. 2009, 64, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, M.Y.; Feng, G.; Zhang, J.; Karonen, M.; Sinkkonen, J.; Satyanandamurty, T.; Wu, J. Moluccensins R-Y, Limonoids from the Seeds of a Mangrove, Xylocarpus moluccensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Satyanandamurty, T.; Shen, L.; Wu, J. Krishnolides A–D: New 2-ketokhayanolides from the Krishna mangrove, Xylocarpus moluccensis. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Dai, Y.; Shen, L.; Wu, J. Twenty-nine new limonoids with skeletal diversity from the mangrove plant, Xylocarpus moluccensis. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.G.; Li, W.S.; Pedpradab, P.; Liu, J.J.; Wu, J.; Shen, L. Thaixylomolins O-R: Four new limonoids from the Trang mangrove, Xylocarpus moluccensis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85978–85984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.X.; Liao, Q.; Shen, L.; Wu, J. Krishnagranatins A–I: New limonoids from the mangrove, Xylocarpus granatum, and NF-κB inhibitory activity. Fitoterapia 2018, 131, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.G.; Wu, J.; Padmakumar, K.P.; Shen, L. Sundarbanxylogranins A–E, five new limonoids from the Sundarban Mangrove, Xylocarpus granatum. Fitoterapia 2017, 122, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Wang, X.-N.; Fan, C.-Q.; Lin, L.-P.; Ding, J.; Yue, J.-M. Limonoids from the seeds of the marine mangrove, Xylocarpus granatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Pedpradab, P.; Wu, J. Thaixylogranins A–H: Eight new limonoids from the Thai mangrove, Xylocarpus granatum. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 19, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shen, L.; Bruhn, T.; Pedpradab, P.; Wu, J.; Bringmann, G. Trangmolins A–F with an unprecedented structural plasticity of the rings A and B: New insight into limonoid biosynthesis. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 11719–11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Jiang, Z.; Shen, L.; Pedpradab, P.; Bruhn, T.; Wu, J.; Bringmann, G. Antiviral limonoids including khayanolides from the trang mangrove plant Xylocarpus moluccensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarigaputi, C.; Sommit, D.; Teerawatananond, T.; Pudhom, K. Weakly anti-inflammatory limonoids from the seeds of Xylocarpus rumphii. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Xiao, Q.; Satyanandamurty, T.; Wu, J. Limonoids with an oxygen bridge between C(1) and C(29) from the seeds of a Krishna Mangrove, Xylocarpus granatum. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Cui, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; She, Z. Peniisocoumarins A-J: Isocoumarins from Penicillium commune QQF-3, an Endophytic Fungus of the Mangrove Plant Kandelia candel. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhai, R.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; She, Z. Altenusin derivatives from mangrove endophytic fungus: Alternaria sp. SK6YW3L. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 72127–72132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Huang, C.; Guo, H.; Zheng, S.; He, J.; Lin, J.; Long, Y. Isobenzofuranone monomer and dimer derivatives from the mangrove endophytic fungus Epicoccum nigrum SCNU-F0002 possess α-glucosidase inhibitory and antioxidant activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsbaey, M.; Tanaka, C.; Miyamoto, T. Allantopyrone E, a rare α-pyrone metabolite from the mangrove derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Lin, X.; Lu, X.; Tu, Z.; Wang, J.; Kaliyaperumal, K.; Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y. Botryoisocoumarin A, a new COX-2 inhibitor from the mangrove Kandelia candel endophytic fungus Botryosphaeria sp. KcF6. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, C.; Li, C.; You, T.; She, Z. Naphthoquinone derivatives with anti-inflammatory activity from mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Talaromyces sp. SK-S009. Molecules 2020, 25, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cai, R.; Chen, G.; She, Z. Secondary metabolites with α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity from the mangrove fungus mycosphaerella sp. SYSU-DZG01. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Su, X.; Yan, W.; Wu, M.; Wu, Y.; Lu, J.; He, X.; Ding, X.; Xue, Y. Acorenone C: A New spiro-sesquiterpene from a mangrove-associated fungus, Pseudofusicoccum sp. J003. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Pan, J.H.; Chen, B.; Yu, M.; Huang, H.B.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Y.J.; She, Z.G.; Lin, Y.C. Three bianthraquinone derivatives from the mangrove endophytic fungus Alternaria sp. ZJ9-6B from the South China Sea. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-K.; Seok, S.-J.; Kim, W.-G.; Yun, B.-S. Diaporthin and orthosporin from the fruiting body of Daldinia concentrica. Mycobiology 2006, 34, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Larsen, T.O.; Breinholt, J. Dichlorodiaportin, diaportinol, and diaportinic acid: Three novel isocoumarins from Penicillium nalgiovense. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1182–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, M.; Nishida, M.; Kuramochi, K.; Sugawara, F.; Yoshida, H.; Mizushina, Y. 1-Deoxyrubralactone, a novel specific inhibitor of families X and Y of eukaryotic DNA polymerases from a fungal strain derived from sea algae. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Yoshinari, T.; Koshino, H.; Fujioka, S.; Okada, K.; Shimada, A. Rubralactone, rubralides A, B and C, and rubramin produced by Penicillium rubrum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Podlech, J.; Pfeiffer, E.; Metzler, M. Total synthesis of alternariol. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 3275–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Krohn, K.; Draeger, S.; Schulz, B. Bioactive isocoumarins isolated from the endophytic fungus Microdochium bolleyi. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurunnabi, T.R.; Sabrin, F.; Sharif, D.I.; Nahar, L.; Sohrab, M.H.; Sarker, S.D.; Rahman, S.M.M.; Billah, M.M. Antimicrobial activity of endophytic fungi isolated from the mangrove plant Sonneratia apetala (Buch.-Ham) from the Sundarbans mangrove forest. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2020, 20, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanate, A.S.; Annapure, U.S. Effect of physicochemical and rheological properties of flour from different local wheat varieties on the quality of varanphal: An Indian traditional product. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3033–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoza, M.; Kayitesi, E.; Dlamini, B.C. Physicochemical characteristics, microstructure and health promoting properties of green banana flour. Foods 2021, 10, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangestuti, R.; Getachew, A.T.; Siahaan, E.A.; Chun, B.S. Characteristics of functional materials recovered from Indonesian mangroves (Sonneratia alba and Rhizhophora mucronata) using subcritical water extraction. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, the 3rd International Symposium on Marine and Fisheries Research, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 8–9 July 2020; p. 030313. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Zhu, J.; Dong, W.; Sun, Y.; Lv, C.; Guo, B.; Xu, R. Comparison of pasting properties measured from the whole grain flour and extracted starch in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Gallo, R.; Durán, R.; García-Camargo, J.; Morales, O.; Acevedo, D.; Tirado, D.F. Pasting and dough rheological properties of ackee (Blighia sapida) aril flour: A contribution to the search for wheat flour substitutes. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 5526912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adefegha, S.A.; Olasehinde, T.A.; Oboh, G. Pasting alters glycemic index, antioxidant activities, and starch-hydrolyzing enzyme inhibitory properties of whole wheat flour. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.N.G.; Pebruwantoro, D.; Pralebda, S.A.; Hasan, M.N.; Zakariya; Subekti, S.; Pramono, H.; Alamsjah, M.A. Functional and rheological properties of mixed flour from mangrove fruit of Bruguiera gymnorrhiza flour and wheat flour. Food Res. 2021, 5, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, M.; Handa, S.D.M.; Singh, R.K. Physicochemical, functional and rheological properties of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) flour as influenced by particle size. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awolu, O.O.; Sudha, L.M.; Manohar, B. Influence of defatted mango kernel seed flour addition on the rheological characteristics and cookie making quality of wheat flour. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Espinoza, C.; Carvajal-Millán, E.; Balandrán-Quintana, R.; López-Franco, Y.; Rascón-Chu, A. Pectin and pectin-based composite materials: Beyond food texture. Molecules 2018, 23, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tang, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Physicochemical properties and microstructure of corn flour–cellulose fiber extrudates. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.T.; Kim, H.R.; Moon, T.W.; Choi, S.J. Isothermal and temperature-cycling retrogradation of high-amylose corn starch: Impact of sonication on its structural and retrogradation properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Niu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Hu, X.; Bu, Y. The effect of retrogradation time and ambient relative humidity on the quality of extruded oat noodles. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2940–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stribiţcaia, E.; Evans, C.E.L.; Gibbons, C.; Blundell, J.; Sarkar, A. Food texture influences on satiety: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jariyah; Widjanarko, S.B.; Yunianta; Estiasih, T.; Sopade, P.A. Pasting properties mixtures of mangrove fruit flour (Sonneratia caseolaris) and starches. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 2161–2167. [Google Scholar]
- Le Cosquer, G.; Buscail, E.; Gilletta, C.; Deraison, C.; Duffas, J.-P.; Bournet, B.; Tuyeras, G.; Vergnolle, N.; Buscail, L. Incidence and risk factors of cancer in the anal transitional zone and ileal pouch following surgery for ulcerative colitis and familial adenomatous polyposis. Cancers 2022, 14, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, H.; Malmquist, M.; Barkman, C.; Östman, S.; Gjertsson, I.; Saalman, R.; Wold, A.E. Distinct patterns of naive, activated and memory T and B cells in blood of patients with ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 197, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Saw, C.L.L.; Yu, R.; Kong, A.N.T. Regulation of NF-E2-related factor 2 signaling for cancer chemoprevention: Antioxidant coupled with antiinflammatory. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1679–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Tsao, R.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, H. Green pea (Pisum sativum L.) hull polyphenol extracts ameliorate dss-induced colitis through keap1/nrf2 pathway and gut microbiota modulation. Foods 2021, 10, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chen, J.; Luo, D.; Xie, J.; Su, Z.; Huang, X.; Yi, X.; Wei, L.; Cai, J.; et al. Protective effect of Bruguiera gymnorrhiza (L.) lam. fruit on dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice: Role of Keap1/Nrf2 pathway and gut microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardoko; Suprayitno, E.; Puspitasari, Y.E.; Amalia, R. Study of ripe Rhizophora mucronata fruit flour as functional food for antidiabetic. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 953–959. [Google Scholar]
- Livesey, G.; Taylor, R.; Livesey, H.F.; Buyken, A.E.; Jenkins, D.J.A.; Augustin, L.S.A.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Barclay, A.W.; Liu, S.; Wolever, T.M.S.; et al. Dietary glycemic index and load and the risk of type 2 diabetes: Assessment of causal relations. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livesey, G.; Taylor, R.; Livesey, H.F.; Buyken, A.E.; Jenkins, D.J.A.; Augustin, L.S.A.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Barclay, A.W.; Liu, S.; Wolever, T.M.S.; et al. Dietary glycemic index and load and the risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and updated meta-analyses of prospective cohort studies. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jariyah; Susiloningsih, E.K.B.; Nilasari, K. Glycemic index biscuits formulation of pedada flour (Sonneratia caseolaris) with Tubers Starch. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Joint Conference on Science and Technology, Bali, Indonesia, 27–28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, R.; Nomura, T.; Yamada, K.; Mochida, K.; Suzuki, K. Genetic engineering strategies for Euglena gracilis and its industrial contribution to sustainable development goals: A review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanxin, L. Avicennia marina Chocolate and Making Process Thereof. CN103141648A, 12 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Q.; Yejun, C. Mangrove Fruit Flavor Food. CN103750209A, 30 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shaozhong, S. Flavoring Sauce with Avicennia marina Fruit and Production Method Thereof. CN104323217A, 9 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Mai, R.; Long, W.; Ma, C. Mangrove Fruit Wine and Its Preparation Method. CN107557227A, 9 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Mai, R.; Long, W.; Ma, C. A Kind of Method for Preparing Mangrove Fruit Tea Bag. CN107593976A, 19 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Mai, R.; Long, W.; Ma, C. A Kind of Method for Preparing Mangrove Fruit Alcohol for Promoting Blood Circulation and Removing Blood Statis. CN107574079A, 12 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S. Method for Preparing Synthetic Rice from Mangrove Fruit Starch. CN10516628A, 23 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yanxin, L. Processing Technique of Avicennia marina Fruit. CN103141781A, 25 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huichuan, L. Method for Processing Avicennia marina Fruits. CN104605431A, 18 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, T. An Antitumor Mangrove Fruit Particle. CN106107961A, 16 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, L.; Rigui, M.; Wanshen, L.; Chunyan, M. Mangrove Fruit Blood-Pressure Decreasing Tea and Preparation Method Thereof. CN107549412A, 9 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Wendong, S.; Fuyong, F.; Weidong, H.; Suhua, O. Method for Making Chocolate with Avicennia Marina. CN101496549A, 5 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Weidong, H.; Xiujuan, L. Technique for Processing Fruit of Avicennia Marina. CN101268796A, 24 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Erokhin, V.; Gao, T. Impacts of COVID-19 on trade and economic aspects of food security: Evidence from 45 developing countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, N.P. Investigation of mangrove apple (Sonneratia caseolaris) juice production. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019, 11, 809–812. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, S.J.; Pervin, T.; Suma, S.A. Effects of cooking methods at different time durations on total phenolics and antioxidant activities of fresh and dried-stored fruits of Sonneratia apetala (Buch.-Ham.). Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 556–563. [Google Scholar]
- Basyuni, M.; Siagian, Y.S.; Wati, R.; Putri, L.A.P.; Yusraini, E.; Lesmana, I. Fruit nutrition content, hedonic test, and processed products of pidada (Sonneratia caseolaris). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 251, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayatissa, L.P.; Hettiarachi, S.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F. An attempt to recover economic losses from decadal changes in two lagoon systems of Sri Lanka through a newly patented mangrove product. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 8, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Afifah, D.N.; Alamsyah, A.A.M.; Huwaida, A.; Nissa, C.; Wijayanti, H.S.; Purwanti, R.; Hastuti, V.N.; Sugianto, D.N. Cookies made from mangrove (Bruquiera gymnorrhiza) fruit and soybean (Glycine max) flour. Food Res. 2021, 5, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranti, D.I.; Ichiura, H.; Ohtani, Y. The bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of food products of Rhizophora stylosa fruit (coffee and tea mangrove). Int. J. For. Res. 2018, 2018, 2315329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basyuni, M.; Prabuanisa, A.N.; Hamiuddin; Guntur; Kusuma, I.K.T.W.; Oku, H. Distribution of polyprenols and dolichols from fruits and rinds of Barringtonia racemosa, Thespesia populnea, and Xylocarpus granatum. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Seminar on Chemistry: Greeen Chemistry and its Role for Sustainability, Surabaya, Indonesia, 18–19 July 2018; pp. 020075-1–020075-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jariyah, J.; Widjanarko, S.B.; Yunianta; Estiasih, T. Quality Evaluation of Wheat-Pedada Fruit Flour (PFF) Biscuit with Different Emulsifiers. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 9, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jariyah; Yektiningsih, E.; Sarofa, U. Evaluation of antidiabetic and anticholesterol properties of biscuit product with mangrove fruit flour (MFF) substitution. Carpathian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 11, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Fatmah, F.; Utomo, S.W.; Lestari, F. Broccoli-soybean-mangrove food bar as an emergency food for older people during natural disaster. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolak, H.; Piechota, D.; Kucharska, A. Kombucha tea—A double power of bioactive compounds from tea and symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeasts (SCOBY). Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Zarei, M.; Gholami, A.; Lai, C.W.; Chiang, W.H.; Omidifar, N.; Bahrani, S.; Mazraedoost, S. Recent progress in chemical composition, production, and pharmaceutical effects of kombucha beverage: A complementary and alternative medicine. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 4397543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.D.; Saimaiti, A.; Luo, M.; Huang, S.Y.; Xiong, R.G.; Shang, A.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Fermentation with tea residues enhances antioxidant activities and polyphenol contents in kombucha beverages. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewkod, T.; Bovonsombut, S.; Tragoolpua, Y. Efficacy of kombucha obtained from green, oolongand black teas on inhibition of pathogenic bacteria, antioxidation, and toxicity on colorectal cancer cell line. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardoko; Harisman, E.K.; Puspitasari, Y.E. The kombucha from Rhizophora mucronata Lam. herbal tea: Characteristics and the potential as an antidiabetic beverage. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2020, 8, 410–421. [Google Scholar]
- Yoong, M.H.; Rozaina, T.M.T. Effects of mangrove apple (Sonneratia caseolaris) fruit extract on oxidative stability of palm olein under accelerated storage. Food Res. 2021, 5, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Ghosh, D.; Ramakrishna, K. A complete profile on blind-your-eye mangrove Excoecaria agallocha L. (Euphorbiaceae): Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacological aspects. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2016, 10, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, I.; Islam, M.K.; Saha, S.; Barman, A.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Anisuzzman, M.; Rahman, T.; Al-Nahain, A.; Jahan, R.; Rahmatullah, M. Pharmacological and ethnomedicinal overview of Heritiera fomes: Future prospects. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 938543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.C.; Lin, Y.M.; Feng, D.Q.; Ke, C.H.; Peng, L.; Yan, C.L.; Chen, J.D. A new atisane-type diterpene from the bark of the mangrove plant Excoecaria agallocha. Molecules 2009, 14, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.P.; Luan, Z.L.; Liu, R.X.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, X.C.; Shen, L.; Wu, J. Mangrove tirucallane- and apotirucallane-type triterpenoids: Structure diversity of the C-17 side-chain and natural agonists of human farnesoid/Pregnane–X–Receptor. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthi, S.; Uthirarajan, K.; Manohar, V.; Venkatesan, M.; Chinnaperumal, K.; Vasantha-Srinivasan, P.; Krutmuang, P. Larvicidal enzyme inhibition and repellent activity of red mangrove Rhizophora mucronata (Lam.) leaf extracts and their biomolecules against three medically challenging aarthropod vectors. Molecules 2020, 25, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.; Baalkhuyur, F.; Valluzzi, L.; Saderne, V.; Cusack, M.; Almahasheer, H.; Krishnakumar, P.K.; Rabaoui, L.; Qurban, M.A.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; et al. Exponential increase of plastic burial in mangrove sediments as a major plastic sink. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Analuddin, K.; Sharma, S.; Jamili; Septiana, A.; Sahidin, I.; Rianse, U.; Nadaoka, K. Heavy metal bioaccumulation in mangrove ecosystem at the coral triangle ecoregion, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Lin, J.; Liang, K.; Xia, Z. Selected trace metals (As, Cd and Hg) distribution and contamination in the coastal wetland sediment of the northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 66, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.; Shen, X.; Li, R.; Qiu, G. The risk assessment of heavy metals in Futian mangrove forest sediment in Shenzhen Bay (South China) based on SEM–AVS analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi-nozar, S.L.; Pauzi, M.; Ruslan, W. Total petroleum hydrocarbons in sediments from the coastline and mangroves of the northern Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, P.; Nath, B.; Birch, G. Accumulation of trace metals in grey mangrove Avicennia marina fine nutritive roots: The role of rhizosphere processes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.L.; Reynolds, C.J. The value of a mangrove area in Sarawak. Biodivers. Conserv. 1993, 2, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Smith, T.J.; Possley, J.; Collins, T.M.; Lee, D.; Namoff, S. Are mangroves in the tropical Atlantic ripe for invasion? Exotic mangrove trees in the forests of South Florida. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 2509–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecep, K. Integrated sustainable mangrove forest management. J. Nat. Resour. Environ. Manag. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udoh, J.P. Sustainable nondestructive mangrove-friendly aquaculture in Nigeria II: Models, best practices and policy frame work. AACL Bioflux 2016, 9, 151–173. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, A.M.; Felson, A.J.; Friess, D.A. Mangrove rehabilitation and restoration as experimental adaptive management. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Thompson, S.; Glaser, M. Integrated mangrove-shrimp cultivation: Potential for blue carbon sequestration. Ambio 2018, 47, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitra, J.; Yacoob, S.A.M.; Kumar, S.S.; Venkataraman, A.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Nagarajan, Y. HPLC characterization, acute and sub-acute toxicity evaluation of bark extract of Rhizophora mucronata in Swiss Albino mice. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.S. Mangrove forests of the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. In Threat to Mangrove Forests., 1st ed.; Makowski, C., Finkl, C.W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 53–75. [Google Scholar]
- Rasul, N.M.A.; Stewart, I.C.F.; Nawab, Z.A. Introduction to the Red Sea: Its origin, structure, and environment. In The Red Sea: The Formation, Morphology, Oceanography and Environment of a Young Ocean Basin, 1st ed.; Rasul, N.M.A., Stewart, I.C.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- El-Juhany, L.I. Present status and degradation trends of mangrove forests on the Southern Red Sea Coast of Saudi Arabia. Am. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2009, 6, 328–340. [Google Scholar]
- Almahasheer, H.; Aljowair, A.; Duarte, C.M.; Irigoien, X. Decadal stability of Red Sea mangroves. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2016, 169, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithambaran, S. Restoration of mangrove vegetation at Red Sea coast, Saudi Arabia. Indian J. Geo-Marine Sci. 2019, 48, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, A.; Almahasheer, H.; Delgado, A.; Garcias-Bonet, N.; Carrillo-de-Albornoz, P.; Marbà, N.; Hendriks, I.E.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Saderne, V.; Baldry, K.; et al. Stunted mangrove trees in the oligotrophic central red sea relate to nitrogen limitation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abohassan, R.A.A.; Okia, C.A.; Agea, J.G.; Kimondo, J.M.; McDonald, M.M. Perennial biomass production in arid mangrove systems on the Red Sea Coast of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Res. J. 2012, 6, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Almahasheer, H.; Duarte, C.M.; Irigoien, X. Phenology and growth dynamics of Avicennia marina in the Central Red Sea. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almahasheer, H.; Serrano, O.; Duarte, C.M.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Masque, P.; Irigoien, X. Low Carbon sink capacity of Red Sea mangroves. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Guwaiz, S.M.; Alatar, A.A.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Al-Gehni, G.A.; Faisal, M.; Qahtan, A.A.; Abdel-Salam, E.M. Role of mangrove rehabilitation and protection plans on carbon storage in Yanbu industrial city, Saudi Arabia: A case study. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, A.; Dubovyk, O.; El-Magd, I.A.; Menz, G. Mapping mangroves extents on the Red Sea coastline in Egypt using polarimetric SAR and high resolution optical remote sensing data. Sustainability 2018, 10, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gab-Alla, A.A.; Ishrak, K.K.; Waleed, M.M.; Fouda, M.M. Ecology of Avicennia marina mangals along Gulf of Aqaba, South Sinai, Red Sea. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2010, 14, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afefe, A.A.; Khedr, A.H.A.; Abbas, M.S.; Soliman, A.S. Responses and tolerance mechanisms of mangrove trees to the ambient salinity along the Egyptian Red Sea Coast. Limnol. Rev. 2021, 21, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afefe, A.A.; Abbas, M.S.; Soliman, A.S.; Khedr, A.H.A.; Hatab, E.B.E. Physical and chemical characteristics of mangrove soil under marine influence. A case study on the Mangrove Forests at Egyptian-African Red Sea Coast. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019, 23, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Khan, M.A.; Muqtadir, A. Distribution of mangroves along the Red Sea Coast of the Arabian Peninsula: Part-3: Coast of Yemen. Earth Sci. India 2010, 3, 28–42. [Google Scholar]
- Alshawafi, A.; Analla, M.; Aksissou, M.; Triplet, P. Physicochemical properties of water, soil, and morphological characteristics of mangrove forests in the Island of Kamaran, Al Hodaidah, Yemen. J. Ecosyst. Ecography 2016, 06, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahasheer, H. Internodal analysis of Avicennia marina in the Western Arabian Gulf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 698596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khayat, J.; Balakrishnan, P. Avicennia marina around Qatar: Tree, seedling and pneumatophore densities in natural and planted mangroves using remote sensing. Int. J. Sci. 2014, 3, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Al Jufaili, S.M.; Jawad, L.A.; Park, J.M.; Al Sariri, T.S.; Al Balushi, B.Y. Fish diversity of mangrove ecosystems in Sultanate of Oman. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2021, 62, 235–249. [Google Scholar]
- Samara, F.; Solovieva, N.; Ghalayini, T.; Nasrallah, Z.A.; Saburova, M. Assessment of the environmental status of the mangrove ecosystem in the United Arab Emirates. Water 2020, 12, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.A.H.; Abdel-Latif, H.H.; Zaghloul, E.H. Phytochemical composition of Avicennia marina leaf extract, its antioxidant, antimicrobial potentials and inhibitory properties on Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilm. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2022, 48, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Odeh, A.M.; Talib, W.H. Middle East medicinal plants in the treatment of diabetes: A review. Molecules 2021, 26, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounekti, T.; Mahdhi, M.; Khemira, H. Ethnobotanical study of indigenous medicinal plants of Jazan region, Saudi Arabia. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 3190670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Elela, G.M.; El-Sersy, M.A.; El-Shenawy, M.A.; Abd-Elnabi, H.; Ibrahim, H.A.H. Bio-control of Vibrio fluvialis in aquaculture by mangrove (Avicennia marina) seeds extracts. Res. J. Microbiol. 2009, 4, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, M.M.; Abdrabo, M.A.A.; Fahmy, N.M.; Abdelfattah, L.S.; Kelany, M.S.; Abd-El Latif, H.H.; Abou-Elela, G.M.; Abd-Elnaby, H.M.; Hassan, S.W.M. Distribution and characterization of actinomycetes in mangrove habitats (Red Sea, Egypt) with special emphasis on Streptomyces mutabilis M3MT483919. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodhod, M.S.E.D.; Gaafar, A.R.Z.; Alshameri, A.; Qahtan, A.A.; Noor, A.; Abdel-Wahab, M. Molecular characterization and bioactive potential of newly identified strains of the extremophilic black yeast Hortaea werneckii isolated from Red Sea mangrove. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2020, 34, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).