Abstract
Shark (Sinica cetorhinus maximum) cartilage was extracted in 1 mol/L Gu- HCl guanidine. Two purified active proteins with apparent molecular weights of 15.2×103 Da and 8.0×103 Da (designated as Sp15 and Sp8, respectively) were obtained through ultrafiltration and Superdex 75 chromatography. The activities of the samples were studied in terms of their potential inhibition of vascular endothelial cell growth in vitro, of angiogenesis both in rabbit cornea and chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay models in vivo, and of growth of transplanted S180 sarcoma in mice in vivo. The results showed that Sp15 expressed a typical lysozymatic activity up to 223,000 U/mg and its N-terminus was highly homologous to lysozymes of various mammalian origins. Sp15 exhibited a strong anti-angiogenic activity only in vitro, whereas Sp8 shared this effect both in vitro and in vivo. Both Sp15 and Sp8 provided an effective anti-tumor activity in mice bearing transplanted S180 sarcoma. These results suggest that Sp15 is a shark cartilage-derived lysozyme that participates in the defense to bacterial invasion to the body, while Sp8 is an angiogenic inhibitor that mediates at least part of the anti-tumor activity associated with shark cartilage probably through the inhibition of tumor-induced angiogenesis.
Introduction
Neovascularization is highly correlated with the rapid growth and metastasis of solid tumors. Various angiogenic inhibitors including angiostatin, endostatin, THP-470, metalloproteinase inhibitors and Bufotanine as the therapeutic intervention for angiogenesis are being tested for the treatment of cancers [1]. Recently, Genentech developed a humanized monoclonal antibody to VEGF (Bevacizumab, Avastin); it is now under Phase III clinical trails for the treatment of colorectal, breast, and non-small cell of the lung cancer [2]. Several studies have indicated that shark cartilage is endowed with effective angiogenic inhibition and anti-tumor activities [3–5], the molecular mechanisms for which remain unclear however. This investigation describes the separation and purification of shark cartilage-derived proteins, and the screening for active molecules via tests for in vitro vascular endothelial cell proliferation-inhibition, in vivo angiogenic inhibition and in vivo anti-tumor activity on mice-bearing transplanted sarcoma 180 (S180).
Results and Discussion
Purification and identification of Sp15 and Sp8
Previous studies on shark cartilage-derived active protein(s) [3–7] indicated that the molecular weights of the main active components seemed to be less than 3.0×104 Da, which prompted us to investigate the composition and activities of lower molecular mass species. Several extraction protocols including ultrafiltration and column chromatography have been attempted to isolate and identify the active fractions from shark cartilage(see the part of Experimenatal), and our data showed that Sp15 was the predominant component in shark cartilage, accounting for approximately more than 50% w/w in extracts, whereas Sp8 accounted for ~20%. Superdex 75 chromatography yielded the highly purified Sp15 and Sp8 in the fractions designated B and D, respectively (Figure 1). A Tricine-SDS-PAGE was used to determine their apparent molecular masses as 1.52×104 Da for Sp15 and 8.3×103 Da for Sp8, respectively (Figure 2).
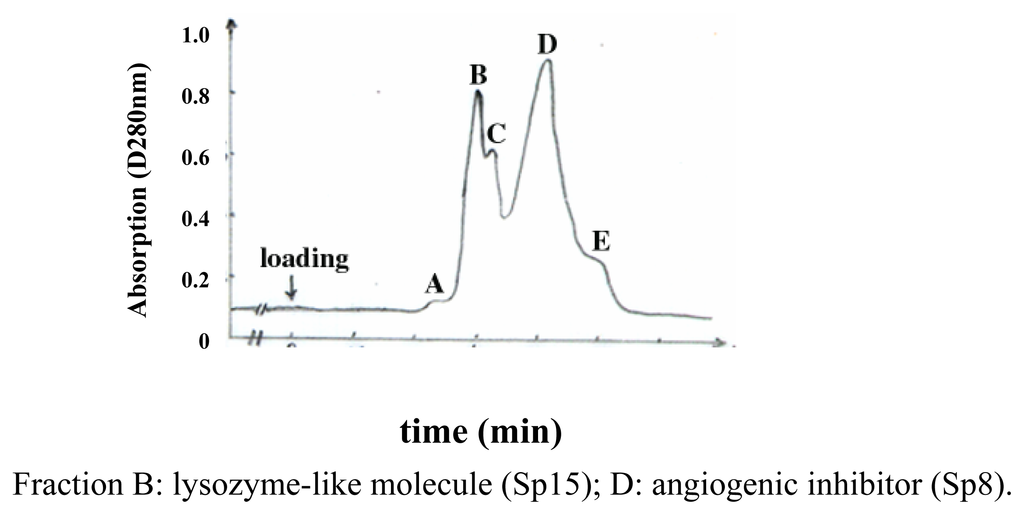
Figure 1.
Superdex 75 column chromatography of proteins derived from shark cartilage time (min)
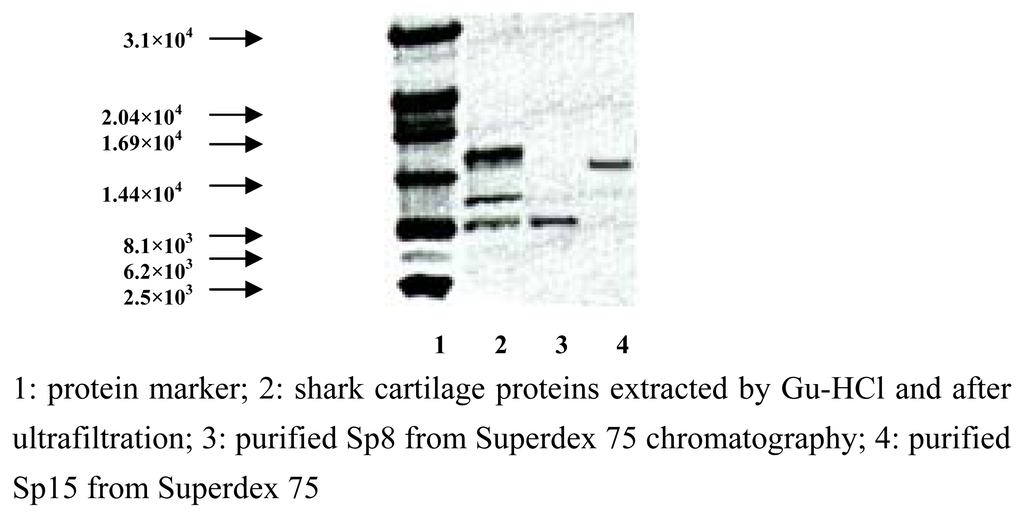
Figure 2.
Tricine-SDS-PAGE of proteins derived from shark cartilage
Determination of the N-terminus and lysozymatic activity of Sp15
The N-terminus of Sp15, as determined by an Edman degradation method, was YTYQKHELARVLQSKGLD(X)QYG (X: unclear). The result showed that Sp15 is a newly identified protein with a high degree of homology to lysozymes derived from human, rat, mouse, dog, cat and rabbit, respectively. The specific lysozymatic activity of Sp15 was determined in a Micrococcus lysodeikticus lytic assay with egg white lysozyme as the control and it was as high as 223,000 U/mg, suggesting that it was a typical lysozyme derived from shark cartilage.
Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation
The inhibition of proliferation by Sp15 and Sp8 on cultivated rat pulmonary capillary and bovine aortic endothelial cells was investigated (data not shown). Results showed that the inhibitory effect of both Sp15 and Sp8 was dose-dependent within the particular range of the concentrations applied. The highest inhibitory rate at 75.0% was reached for Sp15 at 10.0 μg/mL, while it was 20.0% for Sp8 at 40.0 μg/mL (data not shown). Although the inhibition by Sp8 seems to be weaker than that by Sp15, the inhibition by Sp8 was prolonged: it usually took 2–3 d for in vitro cultivated endothelial cells to form a monolayer, but when Sp8 is added to the medium even in a lower concentration (5.0 μg/mL), such a feature could not be seen even after 1 week’s cultivation. In contrast, endothelial cells would grow normally and form monolayers as before when Sp8 was removed from the medium. The results also indicated that both Sp15 and Sp8 display no inhibition of proliferation to cultivated tumor and transformed cell lines, including B16 melanoma and L929 fibroblast.
Inhibition of angiogenesis of Sp8 in vivo
We observed Sp8-mediated angiogenic inhibition on two models, rabbit cornea and chick embryo CAM models, respectively. Both have been used extensively in the angiogenic inhibitor research. The results showed that Sp8 exhibited a strong inhibitory effect up to a rate of 79.0% on the CAM model (Figure 3) and 72.7% on rabbit cornea model (Table 1, Figure 4) at the dose of 40.0 μg, respectively. No obvious dose response relationship has been observed at the range of 20.0~160.0 μg. The results indicate that Sp8 is a potent angiogenic inhibitor present in shark cartilage. In the same test model, Sp15 showed no angiogenic inhibition in vivo.
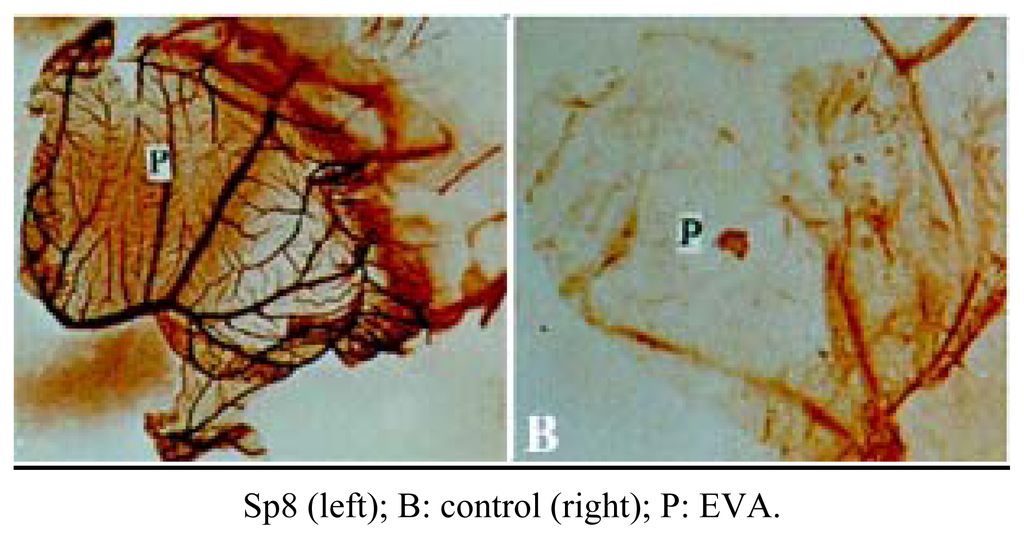
Figure 3.
Sp8 inhibits angiogenesis in CAM

Table 1.
Sp8 inhibits LPS-induced angiogenesis in rabbit cornea model (n=4)
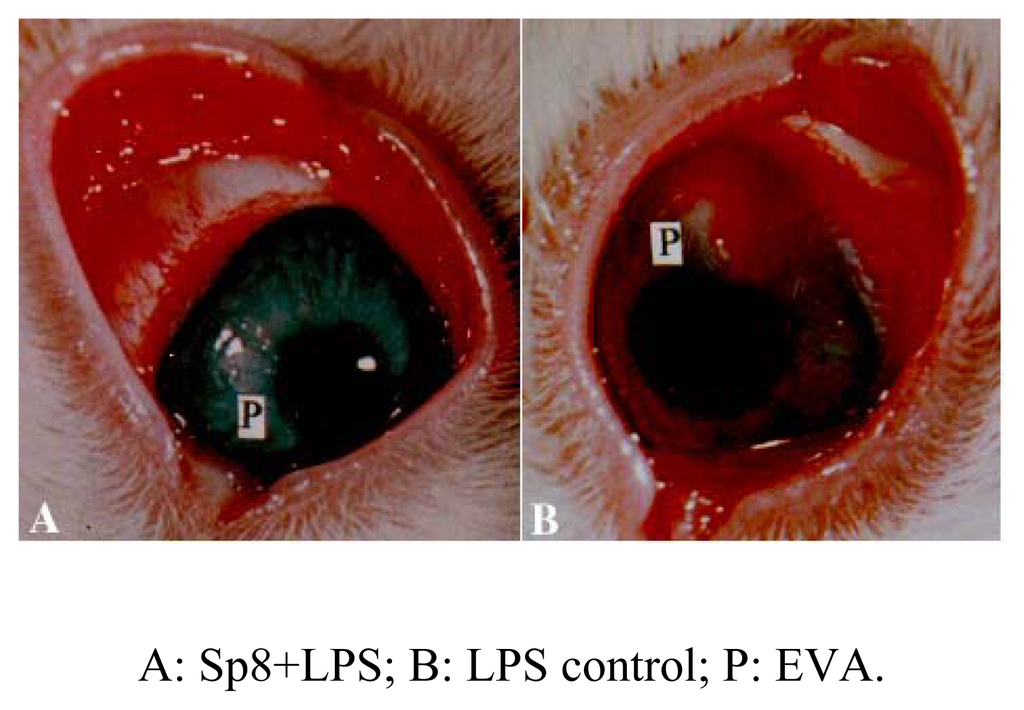
Figure 4.
Sp8 inhibits LPS-induced angiogenesis on rabbit cornea
Anti-tumor activity of Sp15 and Sp8 in vivo
The anti-tumor activities of Sp15 and Sp8 were observed on mice bearing transplanted S180 sarcoma. C57/BL6 mice were transplanted 2×107 S180 cells subcutaneously and different doses of Sp15 and Sp8 in three groups each were given intraperitoneally at day 2, with PBS and cyclophosphamide (CTX) as controls. The result showed that 2.0 mg/kg of Sp15 exhibited no inhibition to tumor growth, while doses of 4.0 and 8.0 mg/kg yielded inhibitory rates of 23.3% (p<0.05) and 33.3% (p<0.01), respectively. Only 10% inhibition was seen in the control group of egg white lysozyme at 20mg/kg (Table 2). Furthermore, mice generally died at day 11 after they were inoculated 5×107 S180 sarcoma cells by peritoneal injection. When these mice bearing S180 ascites were treated with 8 mg/kg of Sp15, their mean life-span was prolonged up to day 17.2 (p<0.01), while those treated with 20 mg/kg of egg white lysozyme died at day 15.2 (data not shown). These data demonstrate that Sp15 has more effective anti-tumor activity in this model than that of egg white one.

Table 2.
Sp15 and Sp8 inhibit the growth of S180 solid sarcoma transplanted in micea
Sp8 also inhibited significantly the rapid growth of the tumor mass at the rate of 21.1, 54.4 and 56.7%, respectively, corresponding to the doses of 5.0, 10.0 and 20.0 μg/kg, respectively (Table 2). Furthermore, the application of Sp8 to this model inhibited nearly 100% of tumor-related skin ulcer formation (data not shown).
No obvious systemic toxicities such as weight loss were observed upon the treatment of Sp15 and Sp8.
Conclusions
Cartilage is one the few tissues containing biological inhibitors of angiogenesis [7]. Various researchers have isolated and characterized several active fractions from shark cartilage while no detailed physico-chemical properties were provided [4–5, 8]. Cartilage-derived angiogenic inhibitors exhibited a significant anti-tumor activity in vivo. Recently, Neovastat, a naturally occurring inhibitor of angiogenesis derived from marine cartilage (dogfish), has been tested in Phase II clinical trails in non-small cell lung cancer and in renal cell carcinoma. It is currently undergoing Phase III clinical trails for the treatment of refractory renal cell carcinoma and nonresectable small cell lung cancer in addition to a Phase II pivotal clinical trails for the treatment of recurrent multiple myeloma. Tumor regressions were seen in some patients and it has been shown highly safe by repeated administration [8–10].
This investigation indicates that shark cartilage contains an active molecule with a weight of 8.3×103 Da (Sp8) which exhibits a stronger inhibition on the proliferation of in vitro cultivated vascular endothelial cells as well as a predominant inhibition of angiogenesis in the rabbit cornea and chick embryo CAM models in vivo. Based on the mechanisms of new capillary formation, the proliferation of the endothelial cells is the most important prerequisite. We are now investigating if Sp8 is involved in the inhibition of other processes of neovascularization including the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase activity and the migration of the endothelial cells. This paper shows also that Sp8 significantly inhibits the growth of S180 tumor mass in mice model and of tumor-related ulcer formation. The anti-tumor activity of Sp8 to other tumor cell lines and its pharmacodynamics and long-term toxicities by repeated injections are also being investigated in our laboratory.
Besides the angiogenic inhibitors, shark cartilage contains also an abundant amount of lysozymelike substance (Sp15). Lysozyme has been studied for its anti-tumor activity for more than forty years (see the review of Sava G, et al [11]). The present study showed that Sp15 expressed a higher inhibitory activity against the growth of S180 sarcoma on tumor-bearing mice, and could also prolong the life-span of the mice. The results indicated that Sp15, a shark cartilage derived lysozyme, may contribute, at least partly, to the anti-tumor activity displayed by shark cartilage.
Experimental
General
Fresh mandibular cartilage was obtained from shark (sinica cetorhinus maximum) captured from the deep sea in Bohai, China. Experimental animals including SD rats, C57/BL6 mice and New Zealand rabbits were provided by Shanghai Laboratory Animals Center. Rat pulmonary capillary endothelial (RCE) and new-born bovine aortic endothelial (BAE) cells were prepared and cultivated according to the methods described by Chen, et al [12] and DeClerck and Lung [13], respectively. Superdex G-75 was purchased from Pharmacia; Gu-HCl (A.R.) from Jassen; MES and Tricine from Amersco; Lower molecular weight marker and non-radioactive cell-proliferation detecting kit from Promega; Ultrafilter and its membrane and PVDF membrane from Millipore.
Extraction and Purification
Sp15 and Sp8 were extracted and purified as follows: 2,000g of cartilage was chopped into pieces before homogenization, and extracted in 10 L of 0.02 mol/L MES, pH 6.0, containing 1 mol/L Gu-HCl for 120 h at room temperature. The extracts were centrifuged at 1.1×104 xg for 1 h at 4°C and filtered through multiple layers of cheesecloth. The filtered extracts, approximately 8 L in volume, were firstly filtered on Millipore membrane PTTK 3.0×104 and then through membrane PLAC 1.0×103. The extracts were subjected to Superdex 75 (1.0×60cm) to obtain the highly purified Sp15 and Sp8.
Analytical
A Tincine-SDS-PAGE technique was applied for the determination of the apparent molecular masses of the active proteins using the procedure of Schagger, et al [14]. Sp15 was run on Tricine- SDS-PAGE and electrically transferred to PVDF membrane at 150mA in CAPS buffer containing 10% methanol at pH 11.0. PVDF membrane was stained with Commassie blue bright R-250. The band corresponding to Sp15 was cut off with a clean blade and rinsed with distilled water. The N- terminal sequence of Sp15 was determined by an automated Edman degradation on Applied Biosystem Model PROCICE protein sequencer.
The lysozymatic activity of Sp15 was determined by a standard Micrococcus lysodeiktikus lytic assay with egg white lysozyme as the control.
A MTT test was used for determining the inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation. Inhibition of angiogenesis on rabbit cornea model was performed according to Langer, et al [15]: lipopolysaccharide (LPS, endotoxin, 140 μg) isolated from Salmonella abortus equi was mixed with Sp8 (40 μg) into ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) to prepare the sustained releasing compound and then transplanted into rabbit cornea; 10 d later, the result of angiogenic inhibition was recorded. Chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) model was also used to assess the inhibition of angiogenic effect of Sp8 according to Taylor, et al [16]: Sp8 was mixed into EVA to prepare the sustained releasing compound and transplanted into the capillary-free area of CAM of chick embryo at 9 d old of age; 3 d later, it was taken out and the result of the inhibition were recorded. In vivo tumor growth inhibition test was performed as the routine procedure.
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
References and Notes
- Hahnfeldt, P.; Panigrahy, D.; Folkman, J.; Hlatky, L. Tumor development under angiogenic signaling: dynamical theory of tumor growth, treatment response, and postvascular dormancy. Cancer Res 1999, 59, 4770–4775. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol 2002, 29 6 Suppl 16, 10–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Jiao, B.; Miao, H. Isolation, purification and physico-chemical characterization of an angiogenetic inhibitor derived from Sinica cetorhinus maximum cartilage. Pharm Biotech 1997, 4, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, R.; Brem, H.; Falterman, K.; Klein, M.; Folkman, J. Isolation of a cartilage factor inhibits tumor neovascularization. Science 1976, 193, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Oikawa, T.; Ashino-Fuse, H.; Shimamura, M.; Koide, U; Lwaguchi, T. A novel angiogenic inhibitor derived from Japanese shark cartilage (I): Extraction and estimation of inhibitory activities toward tumor and embryonic angiogenesis. Cancer Lett 1990, 51, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.H; Wong, K.P. The characterization of angiogenesis inhibitor from shark cartilage. Adv Exp Med Biol 2000, 476, 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Brem, H.; Folkman, J. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis mediated by cartilage. J Exp Med 1975, 141, 427–439. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, E.; Brazeau, P.; Juneau, C. Extracts of shark cartilage having an antiangiogenic activity and an effect on tumor regression; process of making thereof. United States Patent 5618925, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Boivin, D.; Gendron, S.; Beaulieu, E.; Gingras, D.; Beliveau, R. The antiangiogenic agent Neovastat (AE-941) induces endothelial cell apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 2002, 1, 795–802. [Google Scholar]
- Beliveau, R.; Gingras, D.; Kruger, E.; Lamy, S.; Sirois, P.; Simard, B.; Sirois, M.G.; Tranqui, L.; Baffert, F.; Beaulieu, E.; Dimitriadou, V.; Pepin, M.-C.; Courjal, F.; Ricard, I.; Poyet, P.; Falardeau, P.; Figg, W.D; Dupont, E. The antiangiogenic agent neovastat (AE-941) inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated biological effects. Clin Cancer Res 2002, 8, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Sava, G.; Ceschia, V.; Pacor, S. Mechanism of the antineoplastic action of lysozyme: evidence for host mediated effects. Anticancer Res 1989, 9, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.F.; Fei, X.; Li, S.H. A new simple method for the isolation of microvascular endothelial cells. Microvasc. Res 1995, 50, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- DeClerck, Y.A.; Laug, W.E. Inhibition of tumor cell collagenolytic activity bovine endothelial cells. Cancer Res 1986, 46, 3580–3586. [Google Scholar]
- Schagger, H.; von Jagow, G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range 1 to 100 KDa. Anal. Biochem 1987, 166, 368–379. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, R.; Folkman, J. Polymer for sustained release of proteins and other macromolecules. Nature 1976, 263, 797–800. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.; Folkman, J. Protamine is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature 1982, 297, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
© 2004 by MDPI Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.