Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites from Soft Coral Genus Sinularia since 2013
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemistry and Bioactivity of Secondary Metabolites from Genus Sinularia
2.1. Terpenoids
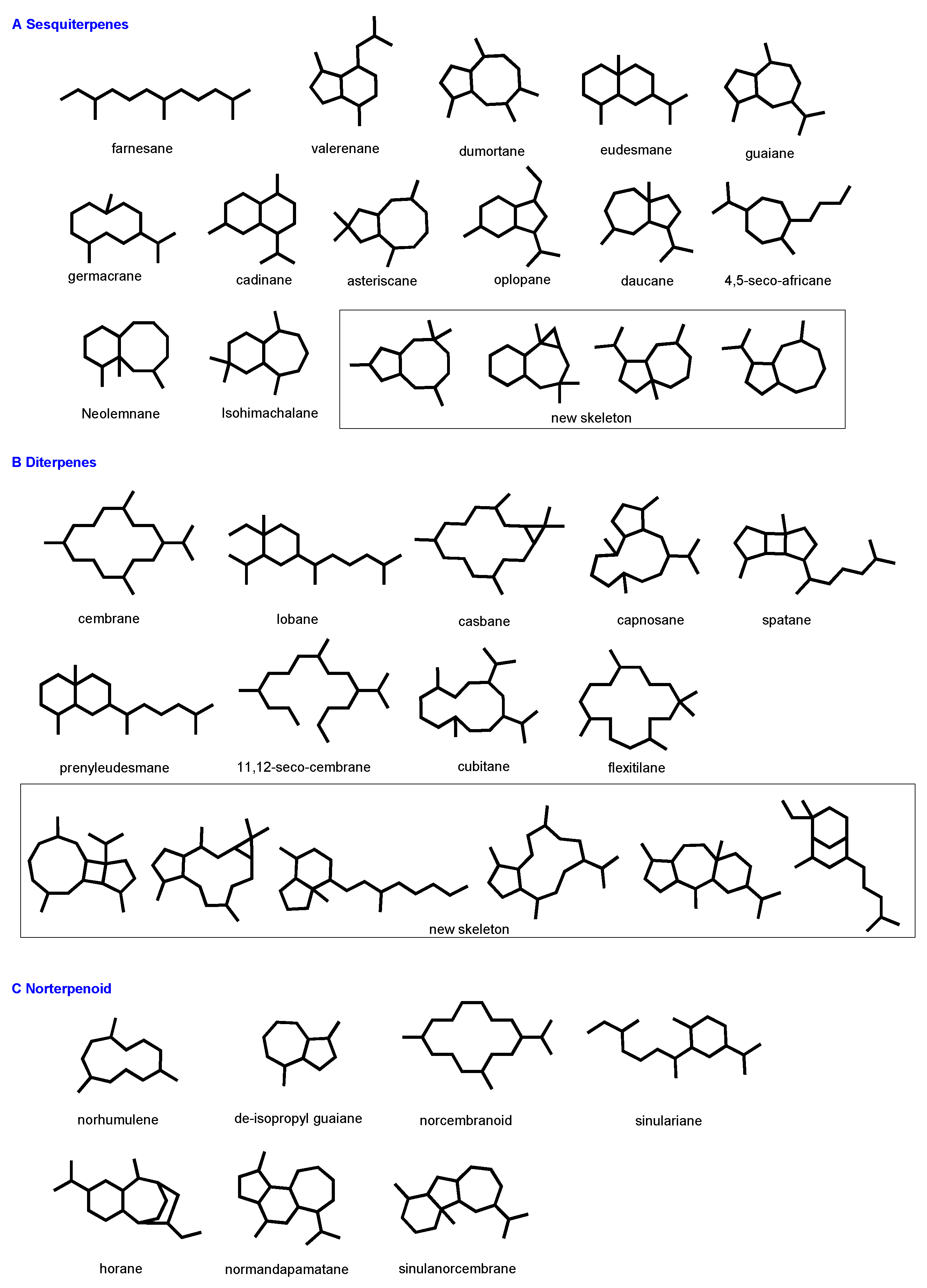
2.1.1. Sesquiterpenes and Bioactivities
2.1.2. Diterpenes
2.1.3. Norterpenoid
2.2. Steroids/Steroidal Glycosides
2.3. Other Types
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.-T.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.-W. Terpenoids of Sinularia soft corals: Chemistry and bioactivity. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2012, 2, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Miao, Z.-H.; Wu, X.; Gu, Y.-C.; Yao, L.-G.; Huan, X.-J.; Luo, H.; Guo, Y.-W. Erectsterates A and B, a pair of novel highly degraded steroid derivatives from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia erecta. Steroids 2020, 161, 108681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-J.; Chokkalingam, U.; Hwang, T.-L.; Hsu, C.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Sung, P.-J.; Sheu, J.-H. Bioactive isoprenoid-derived natural products from a Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sinularia erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.-L.; Li, W.-S.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Yao, L.-G.; Luo, H.; Guo, Y.-W.; Li, X.-W. Uncommon Diterpenoids from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia humilis and Their Stereochemistry. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cui, W.-X.; Li, H.; Tang, W.; Li, S.-W.; Yao, L.-G.; Mudianta, I.W.; Guo, Y.-W. Sinulasterols A-C, three new bioactive oxygenated steroids from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia depressa. Steroids 2020, 157, 108598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammam, M.A.; Rarova, L.; Kvasnicova, M.; Emam, A.M.; Gonzalez, G.; Mahdy, A.; Strand, M.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V. Bioactive Steroids from the Red Sea Soft Coral Sinularia polydactyla. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Wu, M.-J.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.-R.; Gu, Y.-C.; Wang, H.; Li, X.-W.; Guo, Y.-W. Sinueretone A, a diterpenoid with unprecedented tricyclo[12.1.0.0(5,9)]pentadecane carbon scaffold from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia erecta. J. Org. Chem. 2020. Ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-S.; Cui, W.-X.; Tang, W.; Guo, Y.-W. Uncommon terpenoids with anti-inflammatory activity from the Hainan soft coral Sinularia tumulosa. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 104, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-S.; Ru, T.; Huan, X.-J.; Miao, Z.-H.; Guo, Y.-W. New cytotoxic ergostane-type sterols from the Chinese soft coral Sinularia sp. Steroids 2019, 149, 108425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.-F.; Tang, X.-L.; Sun, Y.-T.; Luo, X.-C.; Zhang, J.; Ofwegen, L.V.; Sung, P.-J.; Li, P.-L.; Li, G.-Q. Terpenoids from the Soft Coral Sinularia sp. Collected in Yongxing Island. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-W.; Chen, W.-T.; Yao, L.-G.; Guo, Y.-W. Two new cytotoxic steroids from the Chinese soft coral Sinularia sp. Steroids 2018, 136, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Su, J.-H.; Liaw, C.-C.; Sung, P.-J.; Chiang, P.-L.; Hwang, T.-L.; Dai, C.-F.; Sheu, J.-H. Bioactive Steroids with Methyl Ester Group in the Side Chain from a Reef Soft Coral Sinularia brassica Cultured in a Tank. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.P.; Nam, N.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Quang, T.H.; Tung, P.T.; Dat, L.D.; Chae, D.; Kim, S.; Koh, Y.-S.; Van Kiem, P.; et al. Anti-inflammatory norditerpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia maxima. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, D.; Geng, Z.; Deng, Z.; Van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Sinularia rigida with Antifouling Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.-F.; Li, Y.-F.; Liu, H.-L.; Guo, Y.-W. Research advance on the chemistry and bioactivity of secondary metabolites from the soft corals of the genus Sinularia. Guoji Yaoxue Yanjiu Zazhi 2013, 40, 643–669. [Google Scholar]
- Sheu, J.-H.; Peng, B.-R.; Fang, L.-S.; Hwang, T.-L.; Su, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. Hydroperoxyditerpenoids from Octocorals. Isr. J. Chem. 2019, 59, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V.; Kumar, R. Metabolites from Sinularia species. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 801–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, I.G.; Miguel, M.G.; Mnif, W. A brief review on new naturally occurring cembranoid diterpene derivatives from the soft corals of the Genera Sarcophyton, Sinularia, and Lobophytum since 2016. Molecules 2019, 24, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, P.P.; Yegdaneh, A.; Aghaei, M.; Ali, Z.; Khan, I.A.; Ghanadian, M. Novel 16,17-epoxy-23-methylergostane derivative from Sinularia variabilis, a soft coral from the Persian Gulf, with apoptotic activities against breast cancer cell lines. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.-H.; Lin, J.-J.; Wu, Y.-J.; Su, J.-H.; El-Shazly, M. Quinone Derivatives from the Soft Coral Sinularia scabra. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2021, 57, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Chen, Z.-H.; Gu, Y.-C.; Guo, Y.-W.; Li, X.-W. New lobane-type diterpenoids from the Xisha soft coral Sinularia polydactyla. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 839–843. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Liang, L.-F.; Li, H.; Tang, W.; Guo, Y.-W. A new 5α,8α-epidioxysterol with immunosuppressive activity from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Huan, X.-J.; Wu, M.-J.; Chen, Z.-H.; Chen, B.; Miao, Z.-H.; Guo, Y.-W.; Li, X.-W. Chemical constituents from the South China sea soft coral Sinularia humilis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.-X.; Yang, M.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Tang, W.; Li, S.-W.; Yao, L.-G.; Wang, C.-H.; Liang, L.-F.; Guo, Y.-W. Polycyclic furanobutenolide-derived norditerpenoids from the South China Sea soft corals Sinularia scabra and Sinularia polydactyla with immunosuppressive activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, 103350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Lai, K.-H.; Kumar, S.; Chen, P.-J.; Wu, Y.-H.; Lai, C.-L.; Hsieh, H.-L.; Sung, P.-J.; Hwang, T.-L. NMR H1-based isolation of anti-inflammatory 9,11-secosteroids from the octocoral Sinularia leptoclados. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.-H.; Chen, K.-X.; Guo, Y.-W.; Li, X.-W.; Tang, W. Highly diverse cembranoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia scabra as a new class of potential immunosuppressive agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3469–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Li, X.-W.; Li, H.; Yao, L.-G.; Tang, W.; Miao, Z.-H.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.-W. Bioactive polyoxygenated cembranoids from a novel Hainan chemotype of the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, P.-L.; Luo, X.-C.; Wang, Q.; Ofwegen, L.V.; Tang, X.L.; Li, G.-Q. Terpenoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia multiflora. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, C.-S.; Yee, C.-S.; Vairappan, C.S.; Ishii, T.; Kamada, T. Sinulaflexiolide P, A Cembrane-Type Diterpenoid from Bornean Soft Coral Sinularia flexibilis. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2019, 55, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-Q.; Li, X.-W.; Li, S.-W.; Cui, Z.; Guo, Y.-W.; Han, G.-Y. Sinuhirtins A and B, two uncommon norhumulene-type terpenoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia hirta. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 151308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Zou, G.; Liao, X.-J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.-X.; Xu, S.-H.; Qin, S.-Y.; Chen, G.-D. Sinulaspirolactam A, a novel aza-spirocyclic valerenane sesquiterpenoid from soft coral Sinularia sp. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 21, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.-S.; Ru, T.; Yao, L.-G.; Miao, Z.-H.; Guo, Y.-W. Four new cembranoids from the Chinese soft coral Sinularia sp. and their anti-Aβ aggregation activities. Fitoterapia 2019, 136, 104176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huong, N.T.; Ngoc, N.T.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Quang, T.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Van Minh, C. Chemical constituents from the soft coral Sinularia digitata. Vietnam. J. Chem. 2019, 57, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhu, Z.-D.; Gu, Y.C.; Li, J.; Zhu, W.-L.; Guo, Y.-W. Further New Diterpenoids as PTP1B Inhibitors from the Xisha Soft Coral Sinularia polydactyla. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Chao, C.-H.; Huang, T.-Z.; Huang, C.-Y.; Hwang, T.-L.; Dai, C.-F.; Sheu, J.-H. Cembranoid-Related Metabolites and Biological Activities from the Soft Coral Sinularia flexibilis. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, T.; Phan, C.-S.; Zanil, I.I.; Vairappan, C.S.; Kang, M.-C.; Jeon, Y.-J. Bioactive cembranoids from the soft coral Genus Sinularia sp. in Borneo. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, T.; Phan, C.-S.; Hamada, T.; Hatai, K.; Vairappan, C.S. Cytotoxic and Antifungal Terpenoids from Bornean Soft Coral, Sinularia flexibilis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.; Ngoc, N.T.; Thanh, N.V.; Dang, N.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V.; Cuong, N.X.; Thung, D.C.; et al. Eudesmane and aromadendrane sesquiterpenoids from the Vietnamese soft coral Sinularia erecta. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1798–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.-Y.; Duh, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-K. Xeniaphyllane-Derived Terpenoids from Soft Coral Sinularia nanolobata. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.-J.; Tang, X.-L.; Han, X.; Li, T.; Luo, X.-C.; Jiang, M.-M.; Van Ofwegen, L.; Luo, L.-Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, P.-L.; et al. Metabolites from the Paracel Islands Soft Coral Sinularia cf. molesta. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhu, Z.-D.; Chen, J.-S.; Li, J.; Gu, Y.-C.; Zhu, W.-L.; Li, X.-W.; Guo, Y.-W. Xishacorenes A–C, Diterpenes with Bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane Nucleus from the Xisha Soft Coral Sinularia polydactyla. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4183–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, P.; Gu, Q.; Li, W.D.; Guo, J.L.; Qiao, W.; Feng, D.Q.; Tang, S.A. Antifouling activity against bryozoan and barnacle by cembrane diterpenes from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 120, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, N.T.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Nguyen, V.T.; Thao, D.T.; Cuong, N.X.; Nguyen, H.N.; Thung, D.C.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V. Cytotoxic steroid derivatives from the Vietnamese soft coral Sinularia brassica. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoc, N.T.; Huong, P.T.M.; Thanh, N.V.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Thung, D.C.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V. Sesquiterpene constituents from the soft coral Sinularia nanolobata. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, N.T.; Huong, P.T.M.; Thanh, N.V.; Chi, N.T.P.; Dang, N.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Thung, D.C.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V. Cytotoxic Steroids from the Vietnamese Soft Coral Sinularia conferta. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, N.T.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Thanh, N.V.; Thao, D.T.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Thung, D.C.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V. Cytotoxic steroids from the Vietnamese soft coral Sinularia leptoclados. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, R.; Radwan, M.M.; Ma, G.; Mohamed, T.A.; Seliem, M.A.; Thabet, M.; ElSohly, M.A. Bioactive sterols and sesquiterpenes from the Red Sea soft coral Sinularia terspilli. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Ahmed, A.F.; Su, J.-H.; Sung, P.-J.; Hwang, T.-L.; Chiang, P.-L.; Dai, C.-F.; Liaw, C.-C.; Sheu, J.-H. Bioactive new withanolides from the cultured soft coral Sinularia brassica. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3267–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Cheng, S.; Fu, W.; Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Cai, Y.; Dong, J.; Huang, K.; Gustafson, K.R.; Yan, P. Structurally diverse metabolites from the soft coral Sinularia verruca collected in the South China Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, F.; Feng, M.-R.; Peng, Q.; Liao, X.-J.; Liu, T.-T.; Xu, S.-H.; Zhang, J. Isolation of a new cytotoxic polyhydroxysterol from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.K.; Ashimine, R.; Ueda, K.; Miyazato, H.; Taira, J. Endoperoxy and hydroperoxy cadinane-type sesquiterpenoids from an Okinawan soft coral, Sinularia sp. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2016, 39, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahelivao, M.P.; Gruner, M.; Lübken, T.; Islamov, D.; Kataeva, O.; Andriamanantoanina, H.; Bauer, I.; Knölker, H.-J. Chemical constituents of the soft corals Sinularia vanderlandi and Sinularia gravis from the coast of Madagascar. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, C.-S.; Ng, S.Y.; Kamada, T.; Vairappan, C.S. Two New Lobane Diterpenes from a Bornean Soft Coral Sinularia sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 899–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Ngoc, N.T.; Anh, H.L.T.; Thung, D.C.; Thao, D.T.; Nguyen, X.C.; Nguyen, H.N.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V. Steroid constituents from the soft coral Sinularia microspiculata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 938–944. [Google Scholar]
- Ngoc, N.T.; Huong, P.T.M.; Thanh, N.V.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Thung, D.C.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V. Steroid Constituents from the Soft Coral Sinularia nanolobata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 1417–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Su, J.-H.; Lo, C.-L.; Huang, C.-Y.; Sheu, J.-H. Isobicyclogermacrene-type Sesquiterpenoids from the Soft Coral Sinularia lochmodes. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; ElShamy, A.I.; Al-Hammady, M.A.; Ohta, S.; Paré, P.W. Casbane Diterpenes from Red Sea Coral Sinularia polydactyla. Molecules 2016, 21, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitturi, B.R.; Tatipamula, V.B.; Dokuburra, C.B.; Mangamuri, U.K.; Tuniki, V.R.; Kalivendi, S.V.; Bunce, R.A.; Yenamandra, V. Pambanolides A–C from the South Indian soft coral Sinularia inelegans. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.-H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y.; Wang, H.-C.; Dai, C.-F.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sheu, J.-H. Cubitanoids and Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Sinularia nanolobata. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.-X.; Tang, X.-L.; van Ofwegen, L.; Xue, L.; Song, W.-J.; Li, P.-L.; Li, G.-Q. Cyclopentenone derivatives and polyhydroxylated steroids from the soft coral Sinularia acuta. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.-T.; Wen, Z.-H.; Lan, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. New Anti-inflammatory Norcembranoids from the Soft Coral Sinularia numerosa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Lin, X.; Liao, S.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. New Casbane Diterpenoids from the Hainan Soft Coral Sinularia Species. Helv. Chim. Acta 2015, 98, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Sheu, J.-H.; Chiang, M.Y.; Wen, Z.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Su, J.-H. Structural Elucidation and Structure–Anti-inflammatory Activity Relationships of Cembranoids from Cultured Soft Corals Sinularia sandensis and Sinularia flexibilis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7211–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-J.; Wu, T.-Y.; Su, T.-R.; Wen, Z.-H.; Chen, J.-J.; Fang, L.-S.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. Terpenoids from the octocoral Sinularia gaweli. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19508–19517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-T.; Li, J.; Wang, J.-R.; Li, X.-W.; Guo, Y.-W. Structural diversity of terpenoids in the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis, evidenced by a collection from the South China Sea. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 23973–23980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-F.; Yin, C.-T.; Cheng, C.-H.; Lu, M.-C.; Fang, L.-S.; Wang, W.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Chen, J.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. Norcembranoidal Diterpenes from the Cultured-Type Octocoral Sinularia numerosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3298–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.-H.; Huang, T.-Z.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chen, B.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Hwang, T.-L.; Dai, C.-F.; Sheu, J.-H. Steroidal and α-tocopherylhydroquinone glycosides from two soft corals Cladiella hirsuta and Sinularia nanolobata. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74256–74262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Liao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, L. Sinulolides A-H, new cyclopentenone and butenolide derivatives from soft coral Sinularia sp. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5316–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-H.; Chen, K.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Hwang, T.-L.; Wang, W.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. New Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Sinularia arborea. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, S.; Ramesh, D.; Ramulu, U.; Anjum, M.; Kumar, P.; Murthy, U.S.N.; Hussain, M.A.; Sastry, G.N.; Venkateswarlu, Y. Chemical examination of the soft coral Sinularia kavarattiensis and evaluation of anti-microbial activity. Indian J. Chem. Sect. B Org. Chem. Incl. Med. Chem. 2014, 53B, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Lillsunde, K.-E.; Festa, C.; Adel, H.; De Marino, S.; Lombardi, V.; Tilvi, S.; Nawrot, D.A.; Zampella, A.; D’Souza, L.; D’Auria, M.V.; et al. Bioactive Cembrane Derivatives from the Indian Ocean Soft Coral, Sinularia kavarattiensis. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4045–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.-F.; Chen, M.-F.; Wang, T.; He, X.-X.; Liu, B.-X.; Deng, Y.; Chen, X.-J.; Li, Y.-T.; Guan, S.-Y.; Yao, J.-H.; et al. Novel cytotoxic nine-membered macrocyclic polysulfur cembranoid lactones from the soft coral Sinularia sp. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 6851–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-S.; Li, Y.; Han, G.-Y.; Guo, Y.-W. Further casbane-type diterpenes from the soft coral Sinularia depressa. Zhongguo Tianran Yaowu 2014, 12, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-T.; Liu, H.-L.; Yao, L.-G.; Guo, Y.-W. 9,11-Secosteroids and polyhydroxylated steroids from two South China Sea soft corals Sarcophyton trocheliophorum and Sinularia flexibilis. Steroids 2014, 92, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Hwang, T.-L.; Chen, C.-Y.; Li, J.-J.; Chen, J.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sheu, J.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; Sung, P.-J. Discovery of novel diterpenoids from Sinularia arborea. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cheng, W.; Liu, D.; Van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Capillosananes S–Z, new sesquiterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia capillosa. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3077–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhao, M.; Ma, M.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Dong, J.; Lei, X.; Huang, K.; Yan, P. New Casbane Diterpenoids from a South China Sea Soft Coral, Sinularia sp. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Liao, S.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. New Sinularianin sesquiterpenes from soft coral Sinularia sp. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4741–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-C.; Wu, Y.-J.; Su, J.-H.; Lin, W.-T.; Lin, Y.-S. A new spatane diterpenoid from the cultured soft coral Sinularia leptoclados. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, M.; Shaaban, K.A.; Ghani, M.A. Hurgadacin: A new steroid from Sinularia polydactyla. Steroids 2013, 78, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram, S.; Ramulu, U.; Ramesh, D.; Srikanth, D.; Bhattacharya, P.; Prabhakar, P.; Kalivendi, S.V.; Babu, K.S.; Venkateswarlu, Y.; Navath, S. Anti-cancer evaluation of carboxamides of furano-sesquiterpene carboxylic acids from the soft coral Sinularia kavarattiensis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 6234–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Nguyen, H.N.; Nguyen, X.C.; Tai, B.H.; Quang, T.H.; Nguyen, T.T.N.; Luyen, B.T.T.; Yang, S.Y.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, S.; et al. Steroidal constituents from the soft coral Sinularia dissecta and their inhibitory effects on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.-F.; Wang, X.-J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Liu, H.-L.; Li, J.; Lan, L.-F.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.-W. Bioactive polyhydroxylated steroids from the Hainan soft coral Sinularia depressa Tixier-Durivault. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Liaw, C.-C.; Chen, B.-W.; Chen, P.-C.; Su, J.-H.; Sung, P.-J.; Dai, C.-F.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.-H. Withanolide-Based Steroids from the Cultured Soft Coral Sinularia brassica. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.-C.; Yen, W.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Chiang, M.Y.-N.; Wen, Z.-H.; Chen, W.-F.; Lu, T.-J.; Chang, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; et al. Cembrane Derivatives from the Soft Corals, Sinularia gaweli and Sinularia flexibilis. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2154–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Arafa, A.S. Anti-H5N1 virus metabolites from the Red Sea soft coral, Sinularia candidula. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 2377–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboutabl, E.-S.A.; Azzam, S.M.; Michel, C.G.; Selim, N.M.; Hegazy, M.F.; Ali, A.-H.A.M.; Hussein, A.A. Bioactive terpenoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sinularia polydactyla. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 2224–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, C.-S.; Guo, Y.-W. New cembrane-type diterpenoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia crassa and their α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 104, 104281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushi, S.; Salim, A.A.; Elbanna, A.H.; Nahar, L.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Capon, R.J. Dysidealactams and dysidealactones: Sesquiterpene glycinyl-lactams, imides, and lactones from a Dysidea sp. marine sponge collected in southern Australia. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperatore, C.; Gimmelli, R.; Persico, M.; Casertano, M.; Guidi, A.; Saccoccia, F.; Ruberti, G.; Luciano, P.; Aiello, A.; Parapini, S.; et al. Investigating the Antiparasitic Potential of the Marine Sesquiterpene Avarone, Its Reduced Form Avarol, and the Novel Semisynthetic Thiazinoquinone Analogue Thiazoavarone. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, S.D.; Iodice, C.; Khalaghdoust, M.; Oryan, S.; Rustaiyan, A. Spatane diterpenoids from the brown alga Stoechospermum marginatum (Dictyotaceae). Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-F.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Wen, Z.-H.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Wang, W.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Sheu, J.-H.; Sung, P.-J. Flexibilisquinone, a new anti-inflammatory quinone from the cultured soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Molecules 2013, 18, 8160–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursch, B.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Herin, M.; Karlsson, R.; Losman, D. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XI. Sinulariolide, a new cembranolide diterpene from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Tetrahedron 1975, 31, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casertano, M.; Menna, M.; Imperatore, C. The Ascidian-Derived Metabolites with Antimicrobial Properties. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tao, H.; Lei, X.-X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, B. Arthriniumsteroids A–D, four new steroids from the soft coral-derived fungus Simplicillium lanosoniveum SCSIO41212. Steroids 2021, 171, 108831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.-F.; Chao, R.; Hai, Y.; Guo, Y.-Y.; Wei, M.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Shao, C.-L. 17-Hydroxybrevianamide N and Its N1-Methyl Derivative, Quinazolinones from a Soft-Coral-Derived Aspergillus sp. Fungus: 13S Enantiomers as the True Natural Products. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.M.; Wiese, J.; Wenzel-Storjohann, A.; Imhoff, J.F. Diversity and antimicrobial potential of bacterial isolates associated with the soft coral Alcyonium digitatum from the Baltic Sea. Anton. Leeuw. 2016, 109, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Sun, W.; Tang, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z. Phylogenetic diversity of actinobacteria associated with soft coral Alcyonium gracllimum and stony coral Tubastraea coccinea in the East China Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Species | Sampling Locations | Authors | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. humilis | Ximao Island, Hainan Province, China | Li-Li Sun; Xu-Wen Li * | [4] |
| S. variabilis | the Persian Gulf | Pardis Mohammadi Pour; Mustafa Ghanadian * | [19] |
| S. scabra | Pingtung, southern Taiwan | Yu-Hung Lu; Mohamed El-Shazly * | [20] |
| S. polydactyla | Xisha Islands, Hainan Province, China | Fei Ye; Xu-wen Li * | [21] |
| S. sp. | Yalong bay, Sanya, China | Min Yang; Yue-Wei Guo * | [22] |
| S. depressa | Ximao Island, Hainan Province, China | Min Yang; Yue-Wei Guo * | [5] |
| S. polydactyla | Hurghada, Egypt | Mohamed A. Tammam; Vassilios Roussis * | [6] |
| S. erecta | Ximao Island, Hainan Province, China | Jiao Liu; Yue-Wei Guo * | [2] |
| S. erecta | Ximao Island, Hainan Province, China | Jiao Liu; Yue-Wei Guo * | [7] |
| S. humilis | Ximao Island, Hainan Province, China | Jie Li; Xu-wen Li * | [23] |
| S. scabra | Xigu Island, Hainan Province, China | Wan-Xiang Cui; Yue-Wei Guo * | [24] |
| S. polydactyla | Ximao Island, Hainan Province, China | Wan-Xiang Cui; Yue-Wei Guo * | [24] |
| S. leptoclados | Pingtung, Taiwan | Yu-Chia Chang; Tsong-Long Hwang * | [25] |
| S. tumulosa | Ximao Island, Hainan Province, China | You-Sheng Cai; Yue-Wei Guo * | [8] |
| S. scabra | Grand Island, NY, USA | Min Yang; Xu-wen Li * | [26] |
| S. flexibilis | Xidao Island, Hainan | Qihao Wu; Yue-Wei Guo * | [27] |
| S. multiflora | Xisha Islands of the South China Sea | Zheng Wang; Guo-Qiang Li * | [28] |
| S. flexibilis | Mantanani Island, Sabah, Malaysia | Chin-Soon Phan; Takashi Kamada * | [29] |
| S. hirta | Yalong Bay, Hainan, China | Si-Qi Lu; Guan-Ying Han * | [30] |
| S. sp. | Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province, China | Wei Lai; Shi-Hai Xu * | [31] |
| S. sp. | Xisha Island, South China Sea, China | Cheng-Shi Jiang; Yue-Wei Guo * | [32] |
| S. sp. | Xisha Island, South China Sea, China | Cheng-Shi Jiang; Yue-Wei Guo * | [9] |
| S. digitata | Tho Chu island, Phu Quoc, Kien Giang, Vietnam | Nguyen Thi Huong; Nguyen Hoai Nam * | [33] |
| S. polydactyla | Xisha Island, South China Sea, China | Fei Ye; Yue-Wei Guo * | [34] |
| S. flexibilis | Liuqiu, Taiwan | Chia-Hua Wu; Jyh-Horng Sheu * | [35] |
| S. sp. | Yongxing Island, Xisha Islands, the South China Sea | Guo-Fei Qin; Guo-Qiang Li * | [10] |
| S. sp. | Ximao Island, Hainan Province, China | Song-Wei Li; Yue-Wei Guo * | [11] |
| S. sp. | Mantanani Island, Sabah | Takashi Kamada; Charles S. Vairappan * | [36] |
| S. flexibilis | Mengalum Island, Sabah | Takashi Kamada; Charles S. Vairappan * | [37] |
| S. erecta | Cu Lao Cham island, Quang Nam, Vietnam | Nguyen Thi Huong; Chau Van Minh * | [38] |
| S. nanolobata | San-Shin-Tai, Taitong County, Taiwan | Fu-Yun Hsu; Chang-Yih Duh * | [39] |
| S. cf. molesta | the Paracel Islands, the South China Sea | Mei-Jun Chu; Guo-Qiang Li * | [40] |
| S. polydactyla | Xisha Island, the South China Sea | Fei Ye; Yue-Wei Guo * | [41] |
| S. flexibilis | Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China | Jia Wang; Sheng An Tang * | [42] |
| S. brassica | Con Co Island, Quangtri province, Vietnam | Hong Hanh Thi Tran; Chau Van Minh * | [43] |
| S. nanolobata | Lang Co, Hue, Vietnam | Ninh Thi Ngoc; Chau Van Minh * | [44] |
| S. conferta | Con Co island, Quangtri, Vietnam | Ninh Thi Ngoc; Chau Van Minh * | [45] |
| S. leptoclados | Con Co island, Quangtri, Vietnam | Ninh Thi Ngoc; Chau Van Minh * | [46] |
| S. terspilli | Hurghada, Egypt | Rabab Mohammed; Mahmoud A. ElSohly * | [47] |
| S. brassica | Cultured, Taiwan | Chiung-Yao Huang; Jyh-Horng Sheu * | [12] |
| S. brassica | Cultured, Taiwan | Chiung-Yao Huang; Jyh-Horng Sheu * | [48] |
| S. verruca | Ximao Island, Hainan Province, China | Weiping Yuan; Pengcheng Yan * | [49] |
| S. sp. | Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province, China | Huan Sun; Shi-Hai Xu * | [50] |
| S. sp. | Irabu Island, Okinawa, Japan | Prodip K. Roy; Katsuhiro Ueda * | [51] |
| S. vanderlandi | Madagascan | Rahelivao M.; Hans-Joachim Knölker * | [52] |
| S. sp. | Mantanani Island, Sabah, Malaysia | Chin-Soon Phan; Charles S. Vairappan * | [53] |
| S. microspiculata | Da Den, Quangninh, Vietnam, | Nguyen Van Thanh; Chau Van Minh * | [54] |
| S. nanolobata | Lang Co., Hue, Vietnam | Ninh Thi Ngoc; Chau Van Minh * | [55] |
| S. lochmodes | Northeast corner of Taiwan | Yun-Sheng Lin; Jyh-Horng Sheu * | [56] |
| S. erecta | Dongsha Atoll | Chiung-Yao Huang; Jyh-Horng Sheu * | [3] |
| S. polydactyla | Red Sea, Hurghada, Egyptian | Mohamed-Elamir F. Hegazy; Paul W. Paré * | [57] |
| S. inelegans | Mandapam, the Gulfof Mannar, India | Bhujanga Rao Chitturi * | [58] |
| S. nanolobata | Jihui Fishing Port, Taitung County, Taiwan | Chih-Hua Chao; Jyh-Horng Sheu * | [59] |
| S. acuta | Weizhou Island, Guangxi Province, China | Nai-Xia Zhang; Guo-Qiang Li * | [60] |
| S. numerosa | Cultured, Taiwan | Chen-Ting Yin; Ping-Jyun Sung * | [61] |
| S. sp. | Dongluo Island, Hainan Province, China | Bin Yang; Yonghong Liu * | [62] |
| S. flexibilis | Cultured, Taiwan | Tsung-Chang Tsai; Jui-Hsin Su * | [63] |
| S. gaweli | Sansiantai, Taitung County, Taiwan | Wun-Jie Lin; Ping-Jyun Sung * | [64] |
| S. flexibilis | Yalong Bay, Hainan Province, China, | Wen-Ting Chen; Yue-Wei Guo * | [65] |
| S. numerosa | Cultured, Taiwan | Wu-Fu Chen; Ping-Jyun Sung * | [66] |
| S. nanolobata | Sianglu Islet, Penghu Islands, Taiwan | Chih-Hua Chao; Jyh-Horng Sheu * | [67] |
| S. sp. | Dongluo Island, Hainan Province, China | Bin Yang; Yonghong Liu * | [68] |
| S. arborea | Taiwan | Li-Hsueh Wang; Ping-Jyun Sung * | [69] |
| S. kavarattiensis | Mandapam, Tamil Nadu, India | S Rajaram; Y Venkateswarlu * | [70] |
| S. kavarattiensis | Rameshwaram, Tamil Nadu, India | Katja-Emilia Lillsunde; Päivi Tammela * | [71] |
| S. sp. | Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China | Ling-Fang Lei; Cui-Xian Zhang * | [72] |
| S. depressa | Lingshui Bay, Hainan Province, China | Cheng-shi Jiang; Yue-Wei Guo * | [73] |
| S. flexibilis | Yalong Bay, Hainan Province, China | Wen-Ting Chen; Yue-Wei Guo * | [74] |
| S. arborea | Taiwan | Kuan-Hua Chen; Ping-Jyun Sung * | [75] |
| S. capillosa | Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China | Dawei Chen; Wenhan Lin * | [76] |
| S. sp. | Ximao island, Hainan Province, China | Jian Yin; Pengcheng Yan * | [77] |
| S. sp. | Dongluo Island, Hainan province, China | Bin Yang; Yonghong Liu * | [78] |
| S. leptoclados | Cultured, Taiwan | Tsung-Chang Tsai; Yun-Sheng Lin * | [79] |
| S. maxima | Nha Trang Bay, Vietnam | Nguyen Phuong Thao; Young Ho Kim * | [13] |
| S. polydactyla | Red Sea, Hurghada, Egyptian | Mohamed Shaaban * | [80] |
| S. kavarattiensis | Mandapam, Tamilnadu, India | Singanaboina Rajaram; Suryakiran Navath * | [81] |
| S. dissecta | Hai Van-Son Cha, Hue, Vietnam | Nguyen Phuong Thao; Young Ho Kim * | [82] |
| S. depressa | Lingshui Bay, Hainan, China | Lin-Fu Liang; Yue-Wei Guo * | [83] |
| S. rigida | Sanya Bay, Hainan Island of China | Daowan Lai; Wenhan Lin * | [14] |
| S. brassica | Cultured, Taiwan | Chiung-Yao Huang; Jyh-Horng Sheu * | [84] |
| S. flexibilis | Sansiantai, Taitung County, Taiwan | Li-Chung Hu; Ping-Jyun Sung * | [85] |
| S. candidula | Egyptian Red Sea | Safwat Ahmed * | [86] |
| S. polydactyla | the Red Sea | El-Sayed A. Aboutabl; Ahmed A. Hussein * | [87] |
| S. crassa | West Island, the South China Sea | Meng-Jun Wu; Yue-Wei Guo * | [88] |
| Drug Class | Compounds | Pharmacology | Activities | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory | sinularianins C–F (1–4) | NF-κB inhibition | inhibition rate: 24.3–43.0%, 10 µg/mL | [78] |
| capillosananes W (9) | TNF-α inhibition | inhibition rate: 34%, 10 µM | [76] | |
| sinulatumolin A (32) | TNF-α inhibition | IC50: 7.5 μM | [8] | |
| sinulatumolin C (33) | TNF-α inhibition | IC50: 2.6 μM | [8] | |
| sinulatumolin D (34) | TNF-α inhibition | IC50: 3.6 μM | [8] | |
| Antibacterial | 13 | against Staphylococcus aureus | MIC: 18.75 µg/mL | [70] |
| 16–18 | against Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella enteric | <12 mm a, 25 µg/disc | [51] | |
| 17, 18 | against Serratia marcescens | <14 mm a, 26 µg/disc | [51] | |
| Cytotoxicity | 16–18 | against HCT 116 | IC50: 43.6–75.34 μM | [51] |
| 27 | against A549 | IC50: 14.79 ± 0.91 μM | [38] | |
| sinuketal (28) | against Jurkat, MDA-MB-231, U2OS | IC50: 24.9, 32.3, 41.7 µM | [10] | |
| Antimalarial | sinuketal (28) | against Plasmodium falciparum 3D7 | IC50: 80 µM | [10] |
| Antidiabetic | molestin C (26) | PTP1B inhibition | IC50: 218 µM | [40] |
| Drug Class | Compounds | Pharmacology | Activities | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory | sinularcasbane B (51) | inhibit NO production | IC50: 8.3 μM | [77] |
| sinularcasbane E (54) | inhibit NO production | IC50: 5.4 μM | [77] | |
| nanoculone B (86) | inhibit NO production | inhibition rate: 8%, 10 μM | [59] | |
| sinularolide F (104) | inhibit NO production | IC50 < 6.25 µg/mL | [36] | |
| humilisin F (139) | inhibit NO production | inhibition rate: 83.96%, 10 μM; 65.70%, 20 μM | [4] | |
| arbolide C (63) | inhibit release of elastase | IC50: 5.13 μg/mL | [69] | |
| sinulerectol C (96) | inhibit release of elastase | inhibition rate: 33%, 10 μM | [3] | |
| sinularbol B (57) | inhibit superoxide anion generation | inhibition rate 23.94%, 10 μg/mL | [75] | |
| flexibilin D (36) | iNOS and COX-2 inhibition | inhibition rate: 19.27% and 30.08%, 20 μM | [85] | |
| isosinulaflexiolide K (78) | iNOS and COX-2 inhibition | inhibition rate: 30.9% and 47.1%, 10 μM | [63] | |
| sinulacembranolide A (73) | iNOS inhibition | inhibition rate: 8.55%, 10 μM | [64] | |
| xidaosinularide A (118) | TNF-α inhibition | IC50: 38.9 μM | [27] | |
| sinueretone A (128) | TNF-α inhibition | inhibition rate: 21.9%, 20 μM | [7] | |
| sinuereperoxide A (129) | TNF-α inhibition | inhibition rate: 56.2%, 20 μM, IC50: 10.6 μM | [7] | |
| Cytotoxicity | leptoclalin A (49) | against T-47D and K-562 | IC50: 15.4 and 12.8 μg/mL | [79] |
| sinulariaoid A (59) | against HepG2, HepG2/ADM, MCF-7, and MCF-7/ADM | IC50: 15.35, 9.70, 18.41 and 16.95 μM | [72] | |
| sinulerectol C (96) | against K-562 | IC50: 9.2 μM | [3] | |
| pambanolides B–C (91 and 92) | against DU145 and A549 | IC50: 63–55 mM | [58] | |
| xishacorenes A−C (99–101) | promote the ConA-induced T lymphocytes proliferation | dose-dependency (10–40 μM) | [41] | |
| molestin E (102) | against HeLa and HCT-116 | IC50: 5.26 and 8.37 μM | [40] | |
| ent-sinuflexibilin D (103) | against S1T | IC50: 5.27 μg/mL | [37] | |
| sinularolide F (104) | against HL-60 | cell viability: <30%, 25.0 µg/mL | [36] | |
| Antimalarial | sinulariol Z5 (48) | against barnacle Ba. amphitrite | EC50: 4.57 μg/mL | [14] |
| against Bu. neritina | EC50: 13.48 μg/mL | [14] | ||
| multifloralin (144) | barnacle Balanus albicostatus | adhesive rate: 0%; lethal rate: 58.11%, at 25 ppm | [28] | |
| Antidiabetic | sinupol (111) | PTP1B inhibition | IC50: 63.9 µM | [34] |
| sinulacetate (112) | PTP1B inhibition | IC50: 51.8 µM | [34] | |
| sinulacrassin (141) | α-glucosidase inhibitor | IC50: 10.65 µM | [88] | |
| Antibacterial | prenyl-α-elemenone (97) | against S. aureus | MBC: 50 µg mL−1; MIC: 20 µg mL−1 | [53] |
| Antifungal | sinulaflexiolide P (117) | against H. milfordensis | MIC: 25 μg/mL | [29] |
| Anti-AD | 113 and 115 | inhibit Aβ42 aggregation | inhibition rate: 20.6% and 37.2%, respectively, 10 μM | [32] |
| Immunosuppression | xiguscabrate B (122) | inhibit Con A-induced T lymphocyte cells proliferation | IC50: 8.4 μM | [26] |
| xiguscabrol A (124) | inhibit Con A-induced T lymphocyte cells proliferation | IC50: 5.5 μM | [26] | |
| xiguscabrol B (125) | inhibit Con A-induced T lymphocyte cells proliferation | IC50: 3.9 μM | [26] | |
| 8-epi-xiguscabrol B (126) | inhibit Con A-induced T lymphocyte cells proliferation | IC50: 2.3 μM | [26] |
| Drug Class | Compounds | Pharmacology | Activities | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory | sinumerolide A (149) | inhibit NO production | inhibition rate: 59.82%, 10 µM | [61] |
| 7E-sinumerolide A (150) | inhibit NO production | inhibition rate: 68.40%, 10 µM | [61] | |
| sinulerectol A (151) | inhibit superoxide anion generation and release of elastase | IC50: 2.3, 0.9 μM | [3] | |
| sinulerectol B (152) | inhibit superoxide anion generation and release of elastase | IC50: 8.5, 3.8 μM | [3] | |
| 13-epi-scabrolide C (161) | inhibit IL-12 and IL-6 | IC50: 5.3, 13.12 μM | [13] | |
| Cytotoxicity | 4α-hydroxy-5-episinuleptolide (148) | against CCRF-CEM | IC50: 4.21 μg/mL | [40] |
| sinulerectadione (153) | against K-562 and MOLT-4 | IC50: 8.6, 9.7 μM | [3] | |
| Antidiabetic | molestins D (147) | PTP1B inhibition | IC50: 344 μM | [40] |
| Immunosuppression | xiguscabrolide H (154) | inhibit T and B lymphocyte cells proliferation | IC50: 45.76, 44.14 μM | [3] |
| Antimalarial | sinulariadiolide B (155) | against barnacle B. albicostatus | adhesive rate: 41.55%, at 25 ppm | [24] |
| Drug Class | Compounds | Pharmacology | Activities | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytotoxicity | sinubrasolide B (167) | against P388, MOLT 4 and HT-29 | ED50: 9.1, 4.8, 4.8 μM | [84] |
| sinubrasolide E (171) | against K562 | ED50: 9.9, 7.5 μM | [84] | |
| sinubrasolide A (166) | against MOLT 4 and HT-30 | ED50: 8.7, 7.6 μM | [84] | |
| 177–179 | against K562 and HL-60 | IC50: 36.28–93.43 μM | [74] | |
| 183 | against HeLa | IC50: 44.8 μM | [60] | |
| 184 | against HL-60 and HeLa | IC50: 7.3, 27.1 μM | [60] | |
| 188 | against HL-60, HepG2, SW480 | IC50: 33.53, 64.35, 71.02 μM | [55] | |
| 191 | against HepG2 and HeLa | IC50: 37.30, 19.32 μM | [50] | |
| sinubrasolide H (192) | against P388, MOLT-4, K-562 and HT-29 | IC50: 39.8, 28.6, 29.7, 24.4 μM | [48] | |
| sinubrasolide J (194) | against P388, MOLT-4, K-562 and HT-30 | IC50: 18.7, 17.2, 12.6, 11.2 μM | [48] | |
| sinubrasolide K (195) | against P388, MOLT-4, K-562 and HT-31 | IC50: 18.3, 13.7, 17.4, 20.5 μM | [48] | |
| sinubrasone A (197) | against P388D1, MOLT-4 | IC50: 37.2, 37.8 μM | [48] | |
| sinubrasone B (198) | against P388D1, MOLT-4, K-562, and HT-29 | IC50: 9.7, 6.0, 5.2, 7.6 μM | [12] | |
| sinubrasone C (199) | against P388D1, MOLT-4, K-562, and HT-29 | IC50: 5.7, 5.3, 12.1, 10.4 μM | [12] | |
| sinubrasone D (200) | against P388D1, MOLT-4, K-562, and HT-29 | IC50: 24.4, 31.2, 21.3, 36.5 μM | [12] | |
| leptosteroid (201) | against HepG2 and SW480 | IC50: 21.13, 28.65 μM | [46] | |
| sinubrassione (208) | against PANC-1 | IC50: 15.24 μM | [43] | |
| ximaosteroid E (210) | against HL-60 | IC50: 1.79 μM | [11] | |
| ximaosteroid F (211) | against HL-60 | IC50: 4.03 μM | [11] | |
| 212 | against MDA-MB-436, Hep3B, HT-29, and H157 | IC50: 17.15, 29.28, 30.06, 10.14 μM | [9] | |
| 213 | against MDA-MB-436, A549, Hep3B, HT-29 | IC50: 18.21, 41.71, 19.03, 10.38 μM | [9] | |
| erectsterate (217) | against A549, HT29, SNU-398 and Capan-1 | IC50: 40.55, 32.83, 15.57, 23.51 μM | [2] | |
| 16,17-epoxy-23-methylergostane (225) | against MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 | IC50: 31.44, 25.67 μM | [19] | |
| 223 | inhibit androgen receptors | inhibition rate: >100%, 10 μM | [6] | |
| Anti-inflammatory | dissesterol (175) | IL-12 p40 inhibition | IC50: 4.0 μM | [82] |
| sinubrasolide H (192) | inhibit release of elastase | inhibition rate: 32.4%, 10 μM | [48] | |
| sinubrasolide J (194) | inhibit superoxide anion generation | inhibition rate: 32.1%, 10 μM | [48] | |
| sinubrasolide K (195) | inhibit superoxide anion generation | inhibition rate: 34.3%, 10 μM | [48] | |
| sinubrasolide L (196) | inhibit superoxide anion generation and release of elastase | inhibition rate: 26.3%, 25.0%, 10 μM | [48] | |
| sinubrasone C (199) | inhibit the release of elastase | inhibition rate: 58.8%, 10 μM | [12] | |
| sinubrasone D (200) | inhibit the release of elastase | inhibition rate: 66.3%, 10 μM | [12] | |
| sinleptosterol A (214) | inhibit superoxide anion generation and release of elastase | IC50: 7.07, 7.57 μM | [25] | |
| sinleptosterol B (215) | inhibit superoxide anion generation and release of elastase | IC50: 4.68, 4.29 μM | [25] | |
| sinulasterol A (226) | TNF-α inhibition | IC50: 51.1 μM | [5] | |
| sinulasterol B (227) | TNF-α inhibition | IC50: 22.7 μM | [5] | |
| Antidiabetic | 7α-hydroxy-crassarosterol A (178) | PTP1B inhibition | IC50: 33.05 μM | [74] |
| Immunosuppression | yalongsterol A (224) | inhibit T and B lymphocyte cells proliferation | IC50: 46.0, 56.5 μM | [22] |
| Antiviral | 165 | against H5N1 | inhibition rate: 55.16%, 1 ng/mL | [84] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Leng, X.; Ouyang, H. Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites from Soft Coral Genus Sinularia since 2013. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060335
Yan X, Liu J, Leng X, Ouyang H. Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites from Soft Coral Genus Sinularia since 2013. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(6):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060335
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Xia, Jing Liu, Xue Leng, and Han Ouyang. 2021. "Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites from Soft Coral Genus Sinularia since 2013" Marine Drugs 19, no. 6: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060335
APA StyleYan, X., Liu, J., Leng, X., & Ouyang, H. (2021). Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites from Soft Coral Genus Sinularia since 2013. Marine Drugs, 19(6), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060335





