Characterization of Neoagarooligosaccharide Hydrolase BpGH117 from a Human Gut Bacterium Bacteroides plebeius
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
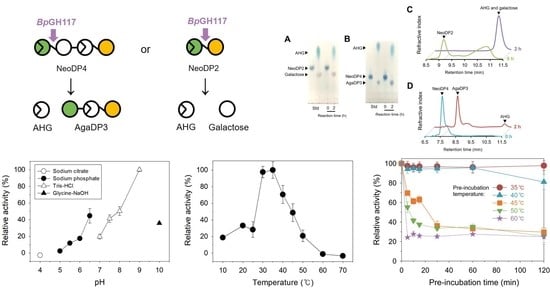
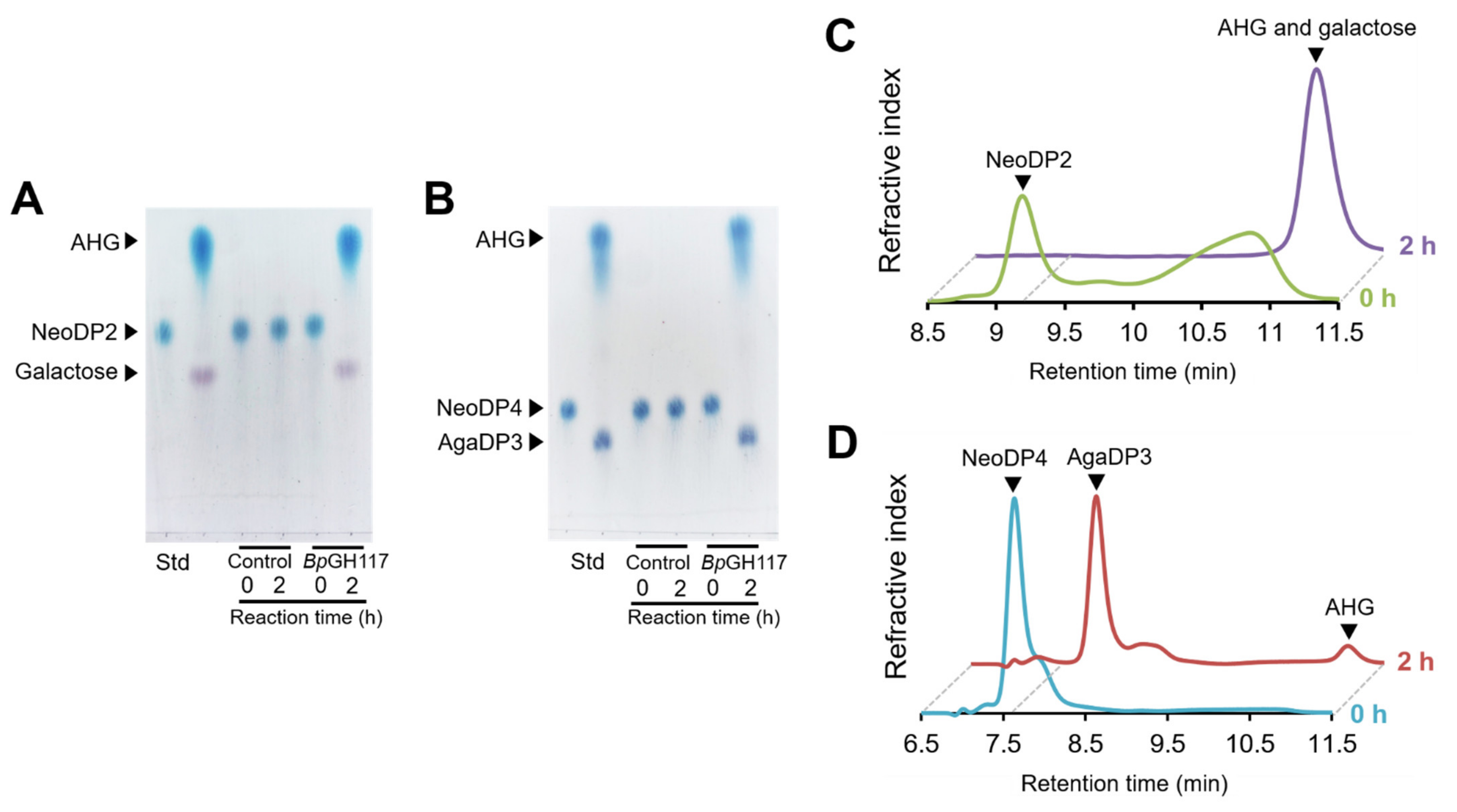
2.1. Analysis of the Enzymatic Reaction Products by Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
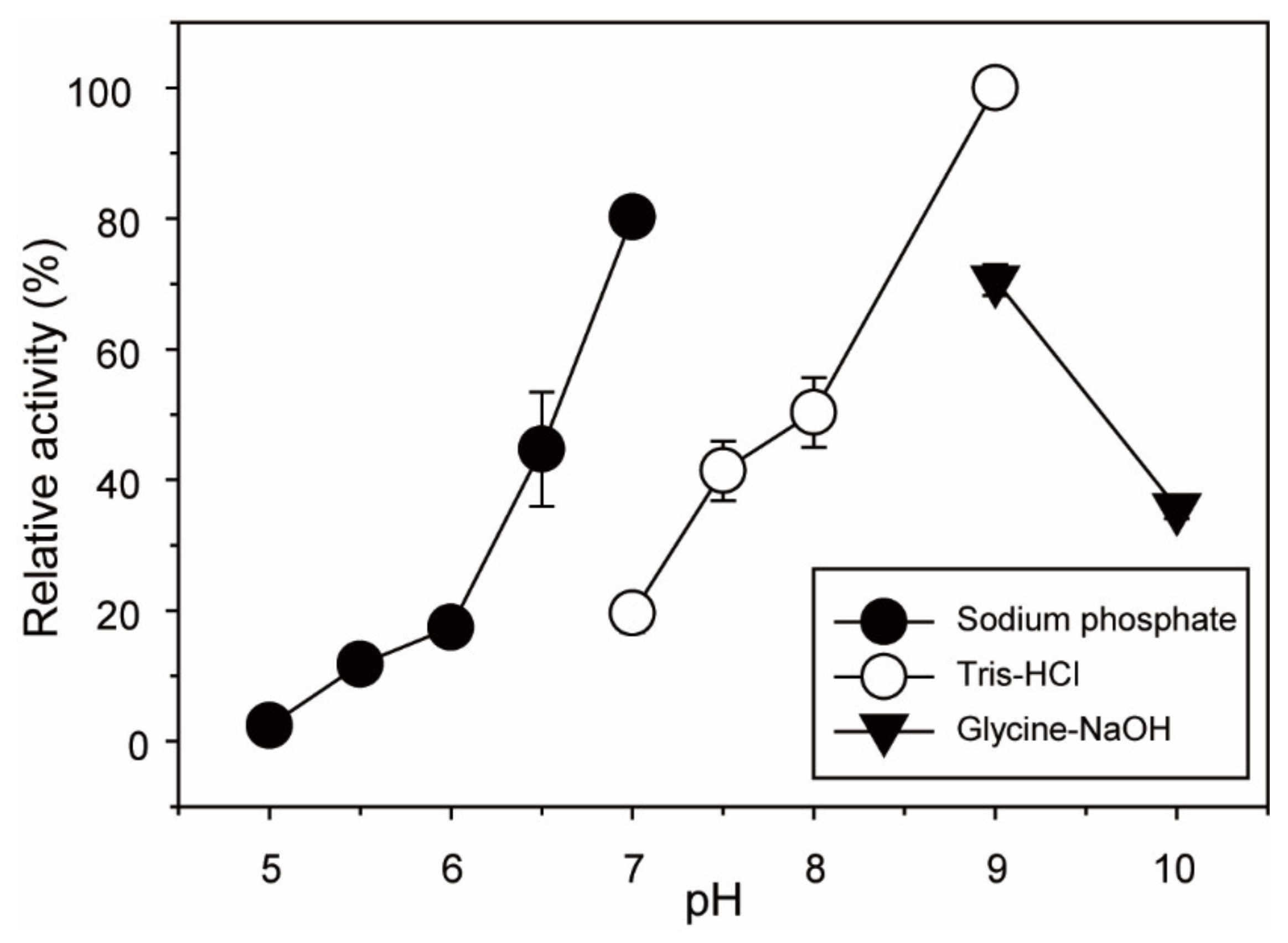
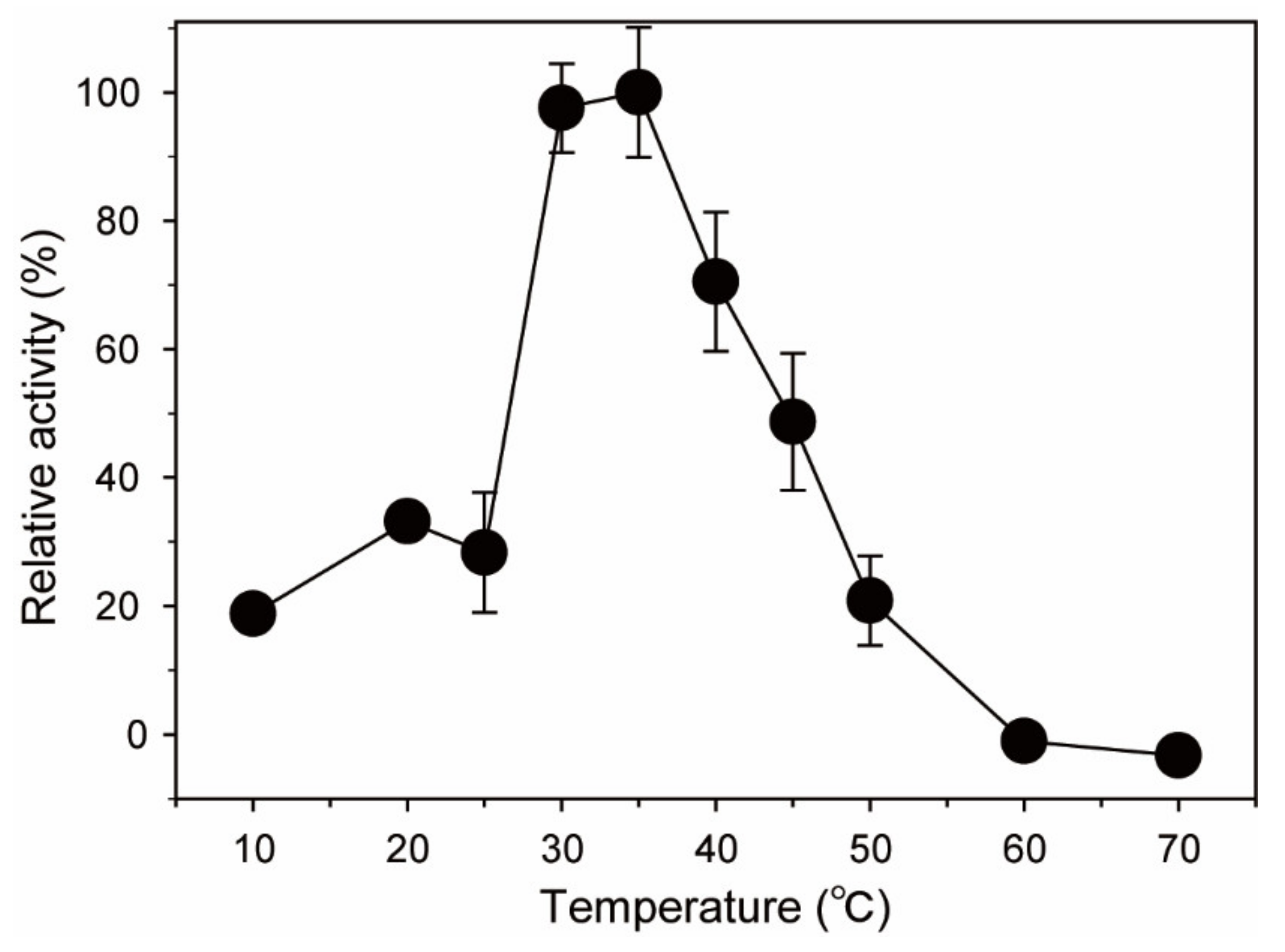
2.2. Optimal pH and Temperature of BpGH117
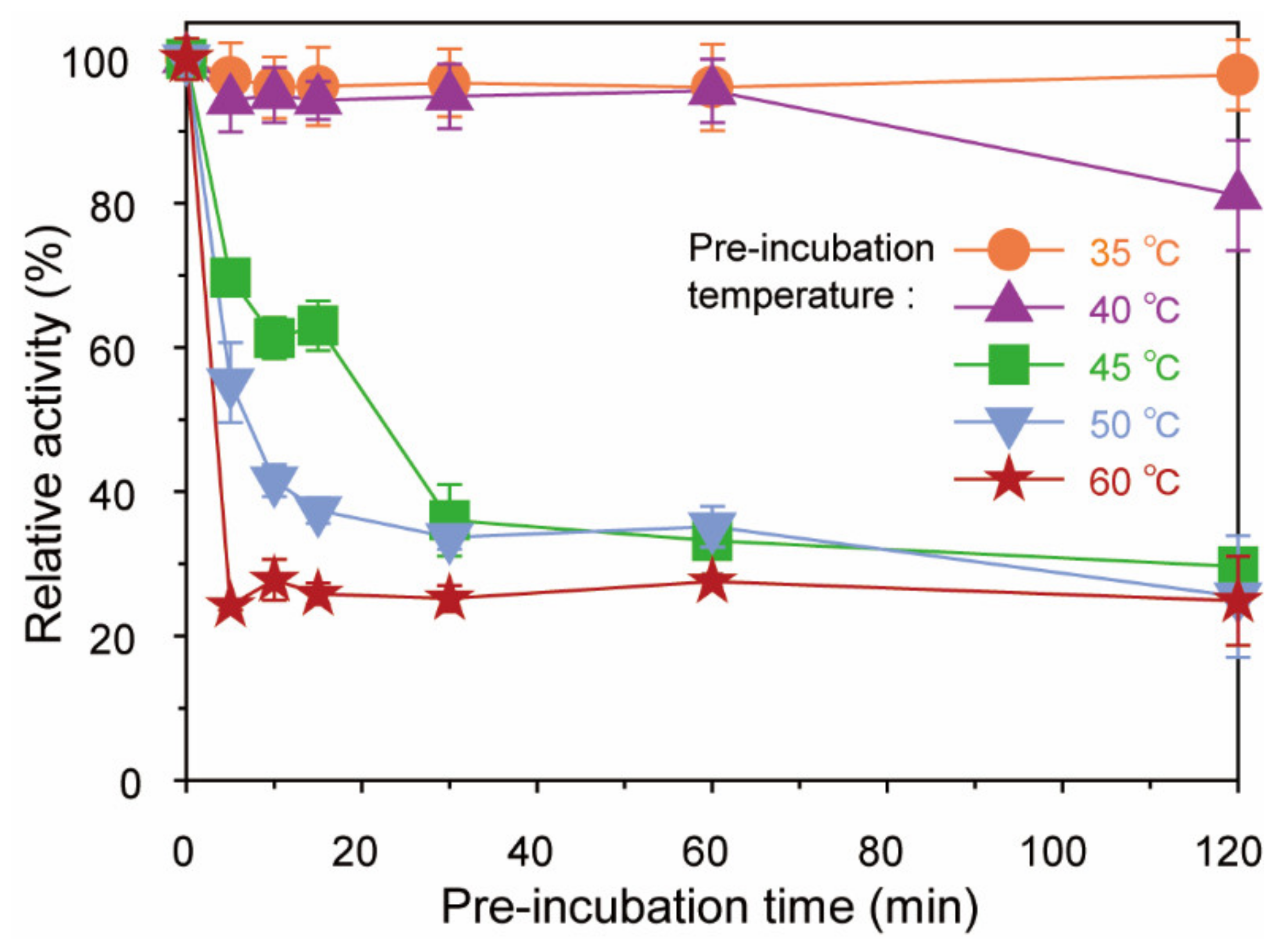
2.3. Thermostability of BpGH117
2.4. Effect of Metal Ions and EDTA on the Activity of BpGH117
2.5. Kinetic Parameters of BpGH117
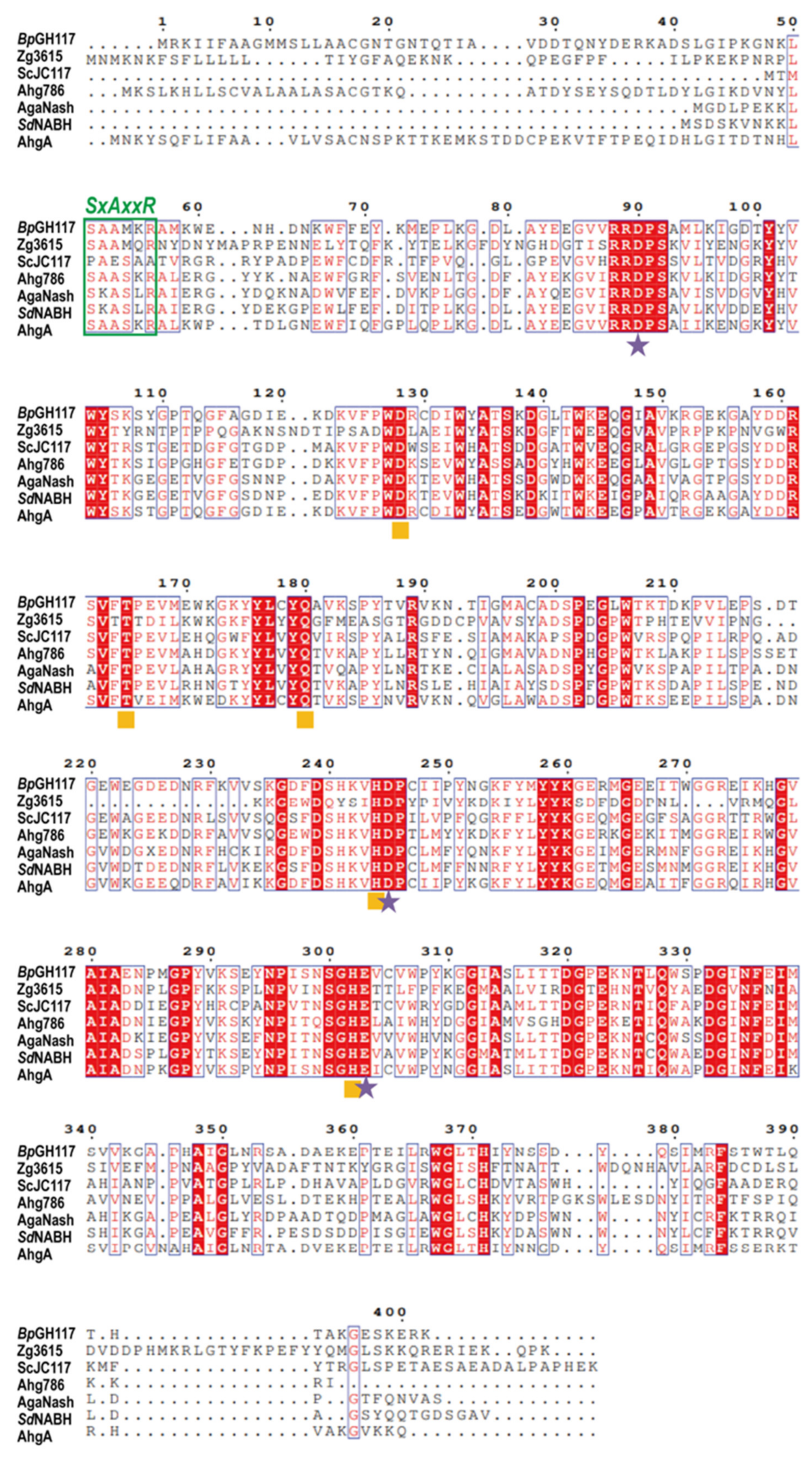
2.6. Amino Acid Sequence Analysis of BpGH117
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
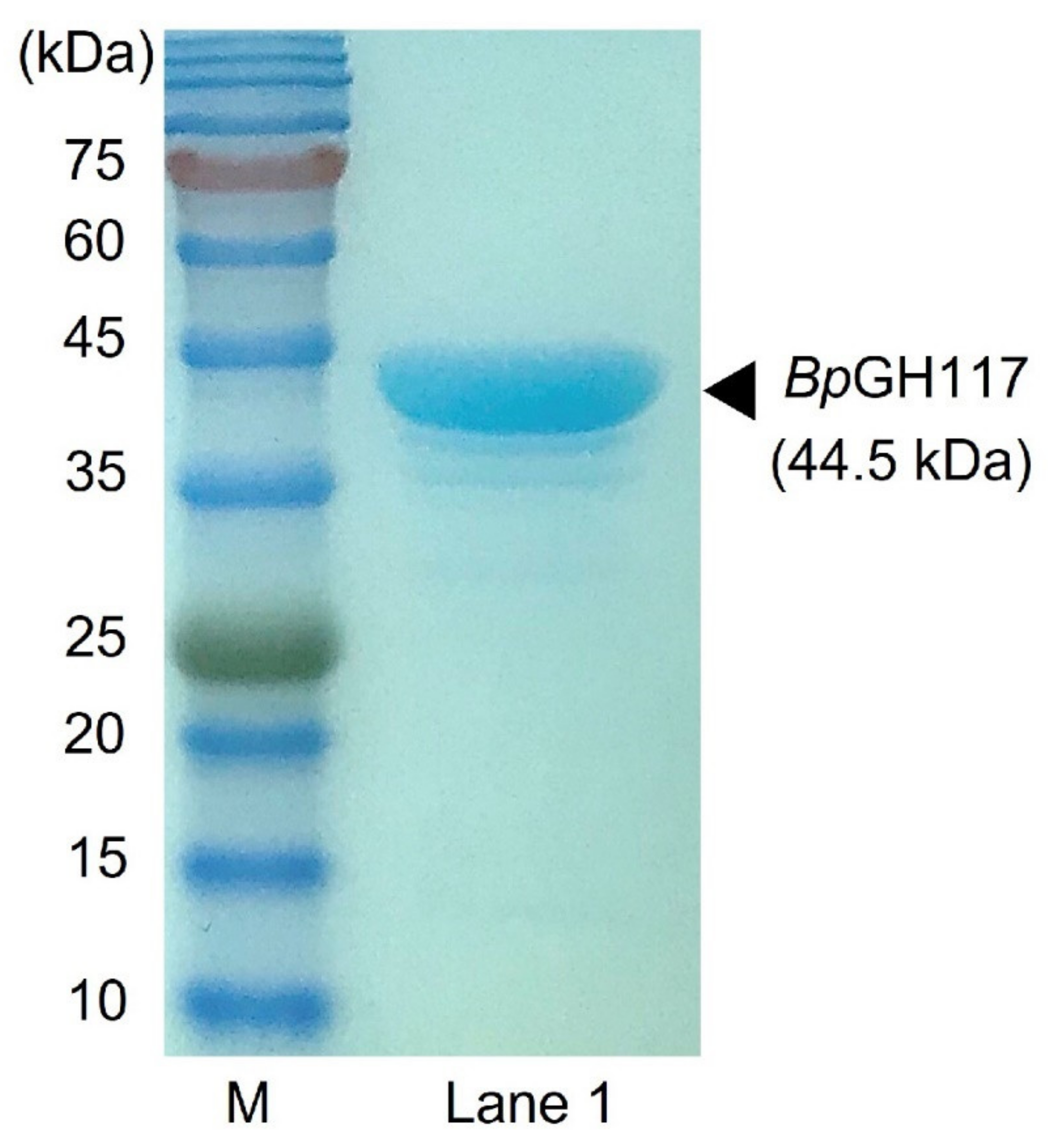
4.1. Overexpression and Purification of Recombinant BpGH117
4.2. Enzyme Activity Measurement Using 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic Acid (DNS) Assay
4.3. TLC and HPLC Analyses of Enzymatic Reaction Products
4.4. Biochemical Characterization of BpGH117
4.5. Determination of the Kinetic Parameters of BpGH117
4.6. Amino Acid Sequence Analysis of BpGH117 for Comparison with other GH117 Enzymes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Faust, K.; Raes, J.; Faith, J.J.; Frank, D.N.; Zaneveld, J.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R. Identifying genomic and metabolic features that can underlie early successional and opportunistic lifestyles of human gut symbionts. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1974–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistollato, F.; Sumalla Cano, S.; Elio, I.; Masias Vergara, M.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. Role of gut microbiota and nutrients in amyloid formation and pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, E.D.; Sonnenburg, J.L. Starving our microbial self: The deleterious consequences of a diet deficient in microbiota-accessible carbohydrates. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehemann, J.-H.; Correc, G.; Thomas, F.; Bernard, T.; Barbeyron, T.; Jam, M.; Helbert, W.; Michel, G.; Czjzek, M. Biochemical and structural characterization of the complex agarolytic enzyme system from the marine bacterium Zobellia galactanivorans. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 30571–30584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, N.; Vallorani, L.; Milanović, N.; Stocchi, V. Evaluation of marine algae wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and kombu (Laminaria digitata japonica) as food supplements. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 42, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Lin, B.K.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, M.; Liu, G.M. Production and purification of agarase from a marine agarolytic bacterium Agarivorans sp. HZ105. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, D.; Ying, J.; Li, X.; Gao, Z.; Wei, G.; Shao, Z. Draft genome sequence of the carrageenan-degrading bacterium Cellulophaga sp. strain KL-A, isolated from decaying marine algae. Genome. Announc. 2014, 2, e00145-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, H.; Fujise, A.; Itabashi, N.; Ohshiro, T. Purification and characterization of a novel alginate lyase from the marine bacterium Cobetia sp. NAP1 isolated from brown algae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 2338–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehemann, J.-H.; Kelly, A.G.; Pudlo, N.A.; Martens, E.C.; Boraston, A.B. Bacteria of the human gut microbiome catabolize red seaweed glycans with carbohydrate-active enzyme updates from extrinsic microbes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19786–19791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, G.; Zhu, L.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiang, C.; Yu, G.; Wang, X. Isolation and characterization of an agaro-oligosaccharide (AO)-hydrolyzing bacterium from the gut microflora of Chinese individuals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shang, Q.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Yu, G. Degradation of marine algae-derived carbohydrates by Bacteroidetes isolated from human gut microbiota. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehemann, J.-H.; Correc, G.; Barbeyron, T.; Helbert, W.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Transfer of carbohydrate-active enzymes from marine bacteria to Japanese gut microbiota. Nature 2010, 464, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correc, G.; Hehemann, J.-H.; Czjzek, M.; Helbert, W. Structural analysis of the degradation products of porphyran digested by Zobellia galactanivorans β-porphyranase A. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, C. Structure of the agarose constituent of agar-agar. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1956, 29, 543–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloareg, B.; Quatrano, R. Structure of the cell walls of marine algae and ecophysiological functions of the matrix polysaccharides. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1988, 26, 259–315. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, E.C.; Koropatkin, N.M.; Smith, T.J.; Gordon, J.I. Complex glycan catabolism by the human gut microbiota: The Bacteroidetes Sus-like paradigm. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24673–24677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, S.; Lee, C.-R.; Park, J.-S.; Chi, W.-J.; Kang, D.-K.; Hong, S.-K. Identification and biochemical characterization of a novel cold-adapted 1, 3-α-3, 6-anhydro-L-galactosidase, Ahg786, from Gayadomonas joobiniege G7. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 8855–8866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehemann, J.-H.; Smyth, L.; Yadav, A.; Vocadlo, D.J.; Boraston, A.B. Analysis of keystone enzyme in agar hydrolysis provides insight into the degradation (of a polysaccharide from) red seaweeds. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13985–13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, E.J.; Yu, S.; Kim, Y.-A.; Liu, J.-J.; Kang, N.J.; Jin, Y.-S.; Kim, K.H. In vitro prebiotic and anti-colon cancer activities of agar-derived sugars from red seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, E.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.B.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, S.H.; Pelton, J.G.; Kang, N.J.; Choi, I.-G.; Kim, K.H. Enzymatic production of 3, 6-anhydro-L-galactose from agarose and its purification and in vitro skin whitening and anti-inflammatory activities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 2961–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, E.J.; Lee, A.R.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, K.M.; Kim, K.H. 3, 6-Anhydro-l-galactose, a rare sugar from agar, a new anticariogenic sugar to replace xylitol. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J.; Mao, X. Characterization of a novel α-neoagarobiose hydrolase capable of preparation of medium- and long-chain agarooligosaccharides. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2020, 7, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, S.; Lee, C.-R.; Chi, W.-J.; Kang, D.-K.; Hong, S.-K. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel cold-adapted alkaline 1, 3-α-3, 6-anhydro-l-galactosidase, Ahg558, from Gayadomonas joobiniege G7. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 1077–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, K.R.M.; Valdehuesa, K.N.G.; Maza, P.A.M.M.; Nisola, G.M.; Lee, W.-K.; Chung, W.-J. Overexpression and characterization of a novel α-neoagarobiose hydrolase and its application in the production of D-galactonate from Gelidium amansii. Process Biochem. 2017, 63, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kashimura, K.; Kirimura, K. Purification, characterization and gene identification of a α-neoagarooligosaccharide hydrolase from an alkaliphilic bacterium Cellvibrio sp. WU-0601. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 133, S328–S336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yang, M.; Mao, X.; Mu, B.; Wei, D. Molecular cloning and expression of a new α-neoagarobiose hydrolase from Agarivorans gilvus WH0801 and enzymatic production of 3, 6-anhydro-l-galactose. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2016, 63, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, O.; Okamoto, N.; Harimoto, N.; Nakasaki, K. Purification and characterization of α-neoagarooligosaccharide hydrolase from Cellvibrio sp. OA-2007. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.C.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.T.; Ko, H.-J.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, I.-G. Crystal structure of a key enzyme in the agarolytic pathway, α-neoagarobiose hydrolase from Saccharophagus degradans 2–40. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuffet, E.; Groisillier, A.; Thompson, A.; Jeudy, A.; Barbeyron, T.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Discovery and structural characterization of a novel glycosidase family of marine origin. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1253–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Sawai, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kawai, K. Purification and characterization of an extracellular α-neoagarooligosaccharide hydrolase from Bacillus sp. MK03. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2002, 93, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, Y.; Kodama, H.; Terada, I.; Yamazaki, Y.; Noma, M. Purification and characterization of a novel enzyme, alpha-neoagarooligosaccharide hydrolase (alpha-NAOS hydrolase), from a marine bacterium, Vibrio sp. strain JT0107. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 6812–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Meulen, H.; Harder, W. Characterization of the neoagarotetra-ase and neoagarobiase of Cytophaga flevensis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1976, 42, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Day, D.; Yaphe, W. Enzymatic hydrolysis of agar: Purification and characterization of neoagarobiose hydrolase and p-nitrophenyl α-galactoside hydrolases. Can. J. Microbiol. 1975, 21, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.J.; Yu, S.; Kim, D.H.; Yun, E.J.; Kim, K.H. Characterization of BpGH16A of Bacteroides plebeius, a key enzyme initiating the depolymerization of agarose in the human gut. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lineweaver, H.; Burk, D. The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouet, P.; Courcelle, E.; Stuart, D.I.; Metoz, F. ESPript: Analysis of multiple sequence alignments in PostScript. Bioinformatics 1999, 15, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Relative Activity (%) | |
|---|---|
| Control | 100.0 ± 4.3 |
| Metal ion in the form of chloride salt | |
| KCl | 92.6 ± 11.6 |
| NaCl | 102.7 ± 8.7 |
| NH4Cl | 98.8 ± 5.6 |
| LiCl | 95.5 ± 12.7 |
| CaCl2 | 80.0 ± 4.2 |
| MgCl2 | 100.3 ± 7.4 |
| RbCl2 | 100.9 ± 7.9 |
| MnCl2 | 98.6 ± 7.9 |
| Chelating agent | |
| EDTA | 98.1 ± 0.7 |
| Strain (Enzyme) | Molar Mass of Subunit (kDa) | Monomer/ Multimer | Location of Protein | Effect of Metal Ion | Optimum | Km (mM) | Vmax (U/mg) | Substrate | Identity (%) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation | Inhibition | Temp. (°C) | pH | |||||||||
| Bacteroides plebeius (BpGH117) | 45.6 | Dimer | Extracellular | n.a. | n.a. | 35 | 9.0 | 30.22 | 54.84 | NeoDP2/4/6 | This study, [19] | |
| Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (ScJC117) | 41 | n.a. | Extracellular | Mg2+ | Ba2+, Ca2+, Co2+, Fe3+, Zn2+, Ni2+ | 30 | 6.0 | 11.57 | n.a. | NeoDP2/4/6 | 51.8 | [23] |
| Gayadomonas joobiniege G7 (Ahg558) | 40.8 | Dimer | n.a. | Mn2+ | Cu2+, Mg2+ | 30 | 9.0 | 8.01 | 133.33 | NeoDP2/4/6 | 59.9 | [24] |
| Gayadomonas joobiniege (Ahg786) | 45.18 | Dimer | Extracellular | Mn2+ | Cu2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Ni2+ | 15 | 7.0 | 4.5 | 1.33 | NeoDP2/4/6 | 56.9 | [18] |
| Cellulophaga sp. W5C (AhgI) | 45 | Octamer | Extracellular | Ca2+ | n.a. | 20–30 | 7.0 | 1.03 | 10.22 | NeoDP2/4/6 | 68.1 | [25] |
| Cellvibrio sp. WU-0601 | 42 | Dimer | Cytosolic | Mn2+, Mg2+ | Ag+, Hg2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ | 25 | 6.0 | 5.8 | 60 | NeoDP2/4/6 | 58.5 | [26] |
| Agarivorans gilvus WH0801 (AgaWH117) | 41 | n.a. | Cytosolic | n.a. | n.a. | 30 | 6.0 | 6.45 | 6.98 | NeoDP2/4 | 59.0 | [27] |
| Cellvibrio sp. OA-2007 | 40 | Dimer | Cytosolic | n.a. | n.a. | 32 | 7.0–7.2 | 6 | 19 | NeoDP2/4/6 | 57.0 | [28] |
| Saccharophagus degradans 2–40T (SdNABH) | 41.6 | Dimer | Cytosolic | n.a. | Zn2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Co2+ | 42 | 6.5 | 3.5 | n.a. | NeoDP2/4/6 | 60.3 | [29] |
| Zobellia galactanivorans (AhgA) | 41 | Dimer | Extracellular | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | NeoDP4/6 | 69.1 | [30] |
| Bacillus sp. MK03 | 42 | Octamer | Extracellular | Mg2+ | Ag+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Hg2+ | 30 | 6.1 | n.a. | 22.2 | NeoDP2/4/6 | n.a. | [31] |
| Vibrio sp. JT0107 | 42 | Dimer | Cytosolic | n.a. | n.a. | 30 | 7.7 | 5.37 | 92 | NeoDP2/4/6 | n.a. | [32] |
| Cytophaga flevensis | n.a. | n.a. | Cytosolic | n.a. | Ag+, Hg2+, Zn2+, Pb2+ | 25 | 6.75 | n.a. | n.a. | NeoDP2 | n.a | [33] |
| Pseudomonas atlantica | 10 | n.a. | Periplasmic | Na+ | n.a. | n.a. | 7.3–8.0 | n.a. | n.a. | NeoDP2 | n.a | [34] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Yu, S.; Kim, D.H.; Yun, E.J.; Kim, K.H. Characterization of Neoagarooligosaccharide Hydrolase BpGH117 from a Human Gut Bacterium Bacteroides plebeius. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050271
Jin Y, Yu S, Kim DH, Yun EJ, Kim KH. Characterization of Neoagarooligosaccharide Hydrolase BpGH117 from a Human Gut Bacterium Bacteroides plebeius. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(5):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050271
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yerin, Sora Yu, Dong Hyun Kim, Eun Ju Yun, and Kyoung Heon Kim. 2021. "Characterization of Neoagarooligosaccharide Hydrolase BpGH117 from a Human Gut Bacterium Bacteroides plebeius" Marine Drugs 19, no. 5: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050271
APA StyleJin, Y., Yu, S., Kim, D. H., Yun, E. J., & Kim, K. H. (2021). Characterization of Neoagarooligosaccharide Hydrolase BpGH117 from a Human Gut Bacterium Bacteroides plebeius. Marine Drugs, 19(5), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050271