Bioactive Compounds from Marine Sponges: Fundamentals and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
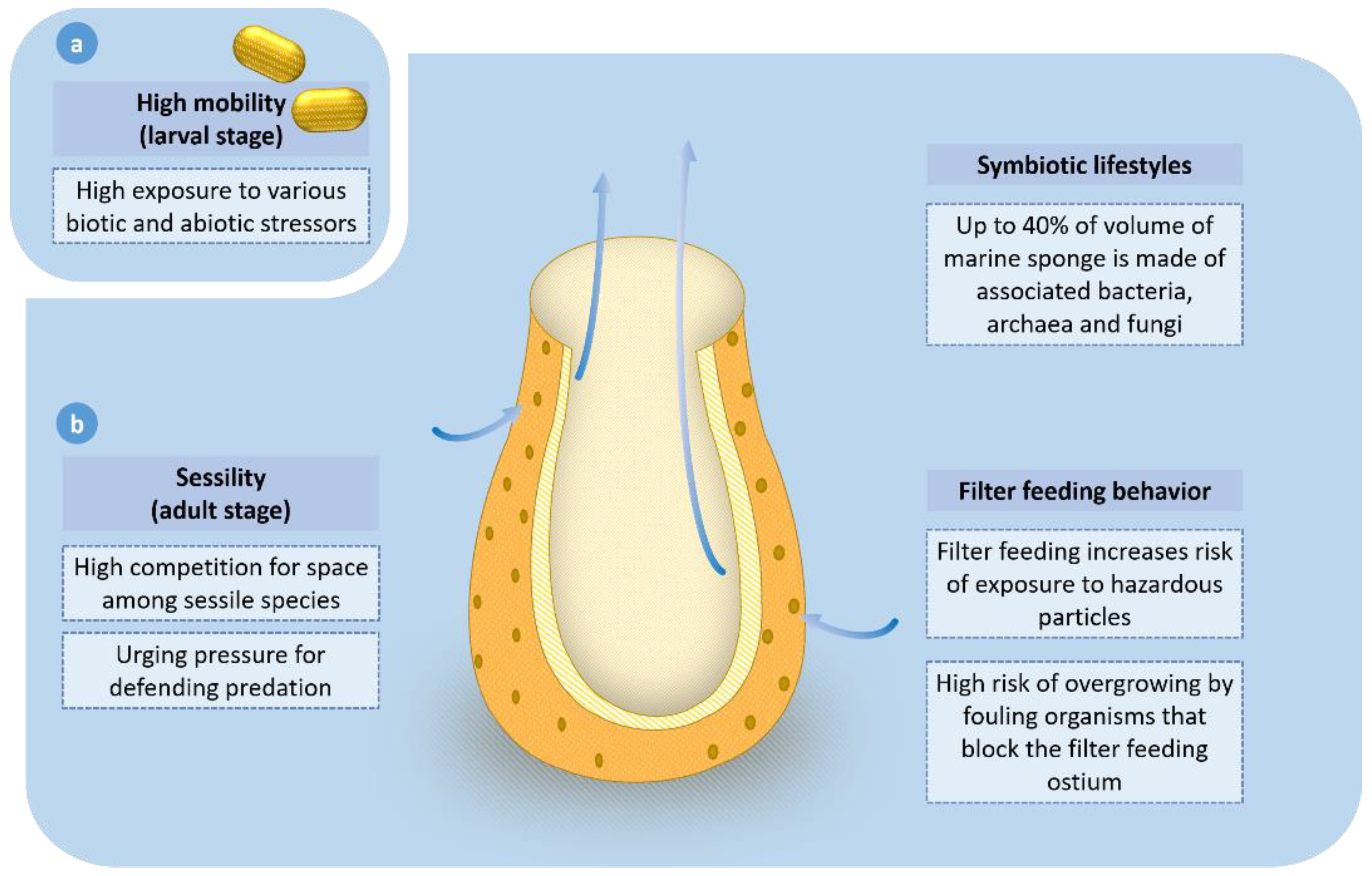
2. Ecological and Biological Factors Driving the High Abundance of Bioactive Compounds from Marine Sponges
3. Chemistry of Compounds from Marine Sponges
3.1. Extraction Process
3.1.1. Traditional Extraction Method
3.1.2. Emerging Technology
3.1.3. Factors Affecting the Extraction
3.2. Classification of Compounds
3.2.1. Terpenes
3.2.2. Alkaloids
3.2.3. Peptides
4. Bioactivities of Marine Sponges With Regard to Human Diseases
4.1. Antibacterial Activity
4.2. Antiviral Activity
4.3. Antifungal Activity
4.4. Antiparasite Activity
5. Applications in Aquaculture
5.1. Antimicrobial Activity Against Fish Pathogens
5.1.1. Antibacterial
5.1.2. Antifungal and Antiviral
5.2. Antifouling Activity
6. Applications in Veterinary Commodities
7. New Compounds from Marine Sponges and Associates
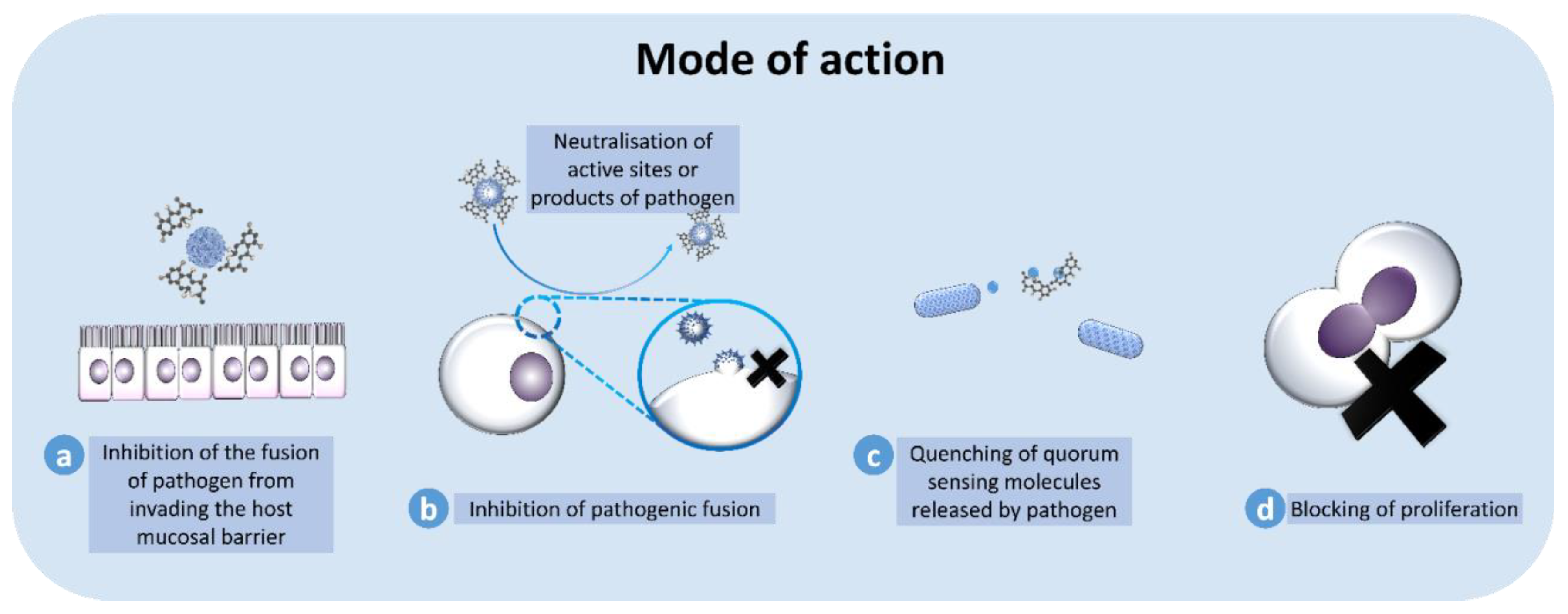
8. Mode of Action
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sutton, T.T.; Clark, M.R.; Dunn, D.C.; Halpin, P.N.; Rogers, A.D.; Guinotte, J.; Bograd, S.J.; Angel, M.V.; Perez, J.A.A.; Wishner, K.; et al. A global biogeographic classification of the mesopelagic zone. Deep. Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2017, 126, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzkar, N.; Jahromi, S.T.; Poorsaheli, H.B.; Vianello, F. Metabolites from marine microorganisms, micro, and macroalgae: Immense scope for pharmacology. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; Proksch, P. The chemistry of marine sponges. In Handbook of Marine Natural Products; Fattorusso, E., Gerwick, W.H., Taglialatela-Scafati, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 191–293. ISBN 9789048138340. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, L.-E.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Schupp, P.J. Secondary metabolites of marine microbes: From natural products chemistry to chemical ecology. In YOUMARES 9—The Oceans: Our Research, Our Future; Jungblut, S., Liebich, V., Bode-Dalby, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 159–180. ISBN 9783030203894. [Google Scholar]
- Carte, B.K. Marine natural products as a source of novel pharmacological agents. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1993, 4, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, K.; Kim, S.K. Marine invertebrate natural products for anti-inflammatory and chronic diseases. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, R.K.; Zi-rong, X. Biomedical compounds from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, M.A.; Clarke, S.A. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Organisms: Potential for Bone Growth and Healing. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiuru, P.; D’Auria, M.V.; Muller, C.D.; Tammela, P.; Vuorela, H.; Yil-Kauhaluoma, J. Exploring Marine Resources for Bioactive Compounds. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A. Pharmacological Significance of Marine Microbial Bioactive Compounds. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laport, M.; Santos, O.; Muricy, G. Marine Sponges: Potential sources of new antimicrobial drugs. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.J. The functional roles of marine sponges. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.G.M.; Dasari, R.; Chandra, S.; Kiss, R.; Kornienko, A. Marine invertebrate metabolites with anticancer activities: Solutions to the “supply problem”. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Sponges and Their Role in the Marine Environment; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Mar. Nat. Prod. 2004, 21, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Othman, E.M.; Reimer, A.; Grüne, M.; Kozjak-Pavlovic, V.; Stopper, H.; Hentschel, U.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Ageloline A, New Antioxidant and Antichlamydial Quinolone from the Marine Sponge-Derived Bacterium Streptomyces sp. SBT345. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 2786–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.M.; Tang, X.L.; Sun, Y.T.; Song, D.Y.; Cheng, Y.J.; Liu, H.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Biological and chemical diversity of marine sponge-derived microorganisms over the last two decades from 1998 to 2017. Molecules 2020, 25, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loya, S.; Hizi, A. The Inhibition of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Reverse Transcriptase by Avarol and Avarone Derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1990, 269, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipkema, D.; Franssen, M.C.R.; Osinga, R.; Tramper, J.; Wijffels, R.H. Marine Sponges as Pharmacy. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, K.D.; Cambie, R.C.; Rutledge, P.S.; Bergquist, P.R. Chemistry of sponges. 19. Novel bioactive metabolites from Hamigera tarangaensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.; Kaur, M.; Minneman, K.P. Antiviral Lead Compounds from Marine Sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2619–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quévrain, E.; Domart-Coulon, I.; Pernice, M.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L. Novel Natural Parabens produced by a Microbulbifer Bacterium in its Calcareous Sponge Host Leuconia nivea. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, G.; Stauffer, C.H.; Aas-Valleriani, N.; Borchert, E.; Bhushan, A.; Campbell, A.; De Mares, M.C.; Costa, M.; Gutleben, J.; Knobloch, S.; et al. BluePharmTrain: Biology and Biotechnology of Marine Sponges; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9783319690759. [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel, U.; Piel, J.; Degnan, S.M.; Taylor, M.W. Genomic insights into the marine sponge microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrl, M.; Steinert, M.; Hentschel, U. Bacterial uptake by the marine sponge Aplysina aerophoba. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 53, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.W.; Hill, R.T.; Hentschel, U. Meeting Report: 1st International Symposium on Sponge Microbiology. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.R. Microbial associations in sponges. I. Ecology, physiology and microbial populations of coral reef sponges. Mar. Biol. 1978, 49, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.R. Microbial associations in sponges. II. Numerical analysis of sponge and water bacterial populations. Mar. Biol. 1978, 49, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, U.; Usher, K.M.; Taylor, M.W. Marine sponges as microbial fermenters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 55, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdicaris, S.; Vlachogianni, T.; Valavanidis, A. Bioactive natural substances from marine sponges: New developments and prospects for future pharmaceuticals. Nat. Prod. Chem. Res. 2013, 1, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.E.; Walker, R.P.; Faulkner, D.J. Screening and bioassays for biologically-active substances from forty marine sponge species from San Diego, California, USA. Mar. Biol. 1985, 88, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowe, S.D.; Richards, J.J.; Tucker, A.T.; Thompson, R.; Melander, C.; Cavanagh, J. Anti-biofilm compounds derived from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2010–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unson, M.D.; Holland, N.D.; Faulkner, D.J. A brominated secondary metabolite synthesized by the cyanobacterial symbiont of a marine sponge and accumulation of the crystalline metabolite in the sponge tissue. Mar. Biol. 1994, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, J.; Hui, D.; Wen, G.; Butzke, D.; Platzer, M.; Fusetani, N.; Matsunaga, S. Antitumor polyketide biosynthesis by an uncultivated bacterial symbiont of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16222–16227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unson, M.D.; Faulkner, D.J. Cyanobacterial symbiont biosynthesis of chlorinated metabolites from Dysidea herbacea (Porifera). Experientia 1993, 49, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, P.; Willoughby, R.; Pomponi, S.A.; Kerr, R.G. Biosynthetic studies of the alkaloid, stevensine, in a cell culture of the marine sponge Teichaxinella morchella. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 4775–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon, X.; Becerro, M.A.; Uriz, M.J. Distribution of brominated compounds within the sponge Aplysina aerophoba: Coupling of X-ray microanalysis with cryofixation techniques. Cell Tissue Res. 2000, 301, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriz, M.J.; Turon, X.; Galera, J.; Tur, J.M. New light on the cell location of avarol within the sponge Dysidea avara (Dendroceratida). Cell Tissue Res. 1996, 285, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reintamm, T.; Lopp, A.; Kuusksalu, A.; Pehk, T.; Kelve, M. ATP N-glycosidase: A novel ATP-converting activity from a marine sponge Axinella polypoides. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 4122–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwack, G. Nucleic Acids and Molecular Genetics. In Human Biochemistry; Academic Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 257–317. ISBN 9780123838643. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Miao, S.; Ni, N.; Man, Y.; Gong, K. A Review of the Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponges of the Genus Aaptos. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, P. Defensive Roles for Secondary Metabolites from Marine Sponges and Sponge-feeding Nudibranchs. Toxicon 1994, 32, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, S. Novel Secondary Metabolites from Marie Sponges and Sponge-associated Fungi; University of California: Santa Cruz, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P. Chemical Constituents of Haliclona: An Overview. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 823–827. [Google Scholar]
- Forenza, S.; Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Fattorusso, E. New Bromo-Pyrrole Derivatives from the Sponge Agelas oroides. J. Chem. Soc. D Chem. Commun. 1971, 285, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, Y.; Kuo, J.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Kelly, M.; Scheuer, P.J. More Kapakahines from the Marine Sponge Cribrochalina olemda. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 1387–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Y.; Meng, Y.H.; Zeng, L.M. Stellettin A, A New Triterpenoid Pigment from the MArine Sponge Stelletta tenuis. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1450–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, J.E.; Whitehead, R.C. On the Biosynthesis of Manzamines. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 2059–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, G.L.; Turner, H. Kinases and Kinase Inhibitors. In Antimalarial Agents; Patrick, G.L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 459–494. ISBN 9780081012109. [Google Scholar]
- de Silva, E.D.; Scheuer, P.J. Monoalide, an Antibiotic Sesterterpenoid from the MArine Sponge Luffariella variabilis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21, 1611–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Lin, L.G.; Ye, W.C. Techniques for Extraction and Isolation of Natural Products: A Comprehensive Review. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getachew, A.T.; Jacobsen, C.; Holdt, S.L. Emerging Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Phenolics: Opportunities and Challenges. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayona, L.M.; Videnova, M.; Choi, Y.H. Increasing Metabolic Diversity in Marine Sponges Extracts by Controlling Extraction Parameters. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nn, A. A Review on the Extraction Methods Use in Medicinal Plants, Principle, Strength and Limitation. Med. Aromat. Plants 2015, 04, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Abubakar, A.R.; Haque, M. Preparation of Medicinal Plants: Basic Extraction and Fractionation Procedures for Experimental Purposes. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2020, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, C.; Valentão, P.; Ferreres, F.; Andrade, P.B. Alternative and Efficient Extraction Methods for Marine-derived Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3182–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantidos, N.; Boath, A.; Lund, V.; Conner, S.; McDougall, G.J. Phenolic-rich Extracts from the Edible Seaweed, Ascophyllum nodosum, Inhibit α-amylase and α-glucosidase: Potential Anti-hyperglycemic Effects. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, G.; Sousa, C.; Silva, L.R.; Pinto, E.; Andrade, P.B.; Bernado, J.; Mouga, T.; Valentäo, P. Can Phlorotannins Purified Extracts Constitute a Novel Pharmacologicaal Alternative for Microbial Infections with Associated Inflammatory Conditions? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Mateus, N.; Cardoso, S.M. Optimization of Phlorotannins Extraction from Fucus vesiculosus and Evaluation of their Potential to Prevent Metabolic Disorders. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parys, S.; Kehraus, S.; Krick, A.; Glombitza, K.W.; Carmeli, S.; Klimo, K.; Gerhäuser, C.; König, G.M. In vitro Chemopreventive Potential of Fucophlorethols from the Brown Alga Fucus vesiculosus L. by Anti-oxidant Activity and Inhibition of Selected Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostagno, M.A.; Villares, A.; Guillamón, E.; García-Lafuente, A.; Martínez, J.A. Sample Preparation for the Analysis of Isoflavones from Soybeans and Soy Foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, P.; Kaufmann, B. Recent Extraction Techniques for Natural Products: Microwave-assisted Extraction and Pressurised Solvent Extraction. Phytochem. Anal. 2002, 113, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Luque-García, J.L.; Luque De Castro, M.D. Ultrasound: A Powerful Tool for Leaching. Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 22, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Khan, M.K. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry Applications of ultrasound in food technology: Processing, preservation and extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.B.; Jia, Q.; Li, H.W.; Wang, C.X.; Wu, H.F. Response Surface Methodology for Ultrasound-assisted Extraction of Astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picó, Y. Ultrasound-assisted Extraction for Food and Environmental Samples. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardanega, R.; Santos, D.T.; De Almeida, M.A. Intensification of Bioactive Compounds Extraction from Medicinal Plants using Ultrasonic Irradiation. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2014, 8, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L. Advances in Extraction of Plant Products in Nutraceutical Processing. In Handbook of Nutraceuticals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 15–52. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero, M.; Castro-Puyana, M.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibañez, E. Compressed Fluids for the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.U.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’Donnell, C.P. Application of Novel Extraction Technologies for Bioactives from Marine Algae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4667–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riguera, R. Isolating bioactive compounds from marine organisms. J. Mar. Biotechnol. 1997, 5, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ebada, S.S.; Edrada, R.A.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Methods for Isolation, Purification and Structural Elucidation of Bioactive Secondary Metabolites from Marine Invertebrates. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1820–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutagalung, R.A.; Victor; Karjadidjaja, M.; Prasasty, V.D.; Mulyono, N. Extraction and Characterization of Bioactive Compounds from Cultured and Natural Sponge, Haliclona molitba and Stylotella aurantium Origin of Indonesia. Int. J. Biosci. Biochem. Bioinform. 2014, 4, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varijakzhan, D.; Yang, S.-K.; Chong, C.M.; Akseer, R.; Alhosani, M.S.; Thomas, W.; Lai, K.S.; Lim, S.H.E. Essential oils as potential antimicrobial agents. In Mitigation of Antimicrobial Resistance; Panwar, H., Sharma, C., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 3975–3988. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Kempinski, C.; Chappell, J. Extraction and Analysis of Oxysterols. Curr. Protoc. Plant Biol. 2016, 1, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, J.; Lipton, A.P. Biopotentials of Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Marine Sponges. Hydrobiologia 2004, 513, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.R.; Pisabarro, M.T.; Gago, F. Molecular Model of the Interaction of Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 with Manoalide. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 1866–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, P.B.; Marshall, L.A.; Sung, A.; Jacobs, R.S. Inactivation of Human Synovial Fluid Phospholipase a2 by the Marine Natural Product, Manoalide. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1990, 39, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, T.; Clardy, J.; Minale, L.; Pizza, C.; Zollo, F.; Riccio, R. A triterpenoid Pigment with the Isomalabaricane Skeleton from the Marine Sponge Stelletta sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 3307–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, B.N.; Wells, R.J.; Croft, K.D. Malabaricane Triterpenes from a Fijian Collection of the Sponge Jaspis stellifera. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 1998–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.K.H.; Holmes, M.J.; Higa, T.; Hamann, M.T.; Kara, U.A.K. In Vivo Antimalarial Activity of the Beta-Carboline Alkaloid Manzamine, A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1645–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, R.; Higa, T.; Jefford, C.W.; Bernardinelli, G. Manzamine A, a Novel Antitumor Alkaloid from a Sponge. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 6404–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, Y.; Yeung, B.K.S.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-borges, M. Kapakahine B: A Cyclic Hexapeptide with an α-Carboline Ring ystem from the Marine Sponge Cribrochalina olemda. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8271–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, B.K.S.; Nakao, Y.; Kinnel, R.B.; Carney, J.R.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. The Kapakahines, Cyclic Peptides from the Marine Sponge Cribrochalina olemda. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 7168–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Characterization, Preparation, and Purification of Marine Bioactive Peptides. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, A. Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Marine Sponges. Am. J. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2018, 1, 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N.; Konosu, S. Bioactive Marine Metabolites, IV. Isolation and the Amino Acid Composition of Discodermin A, an Antimicrobial Peptide, from the Marine Sponge Discodermia kiiensis. J. Nat. Prod. 1985, 48, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N.; Konosu, S. Bioactive Marine Metabolites VI. Structure Elucidation of Discodermin A, an Antimicrobial Peptide from the Marine Sponge Discodermia kiiensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 5165–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, B.; Kumar, D.; Rawat, D.S. Marine Peptides as Anticancer Agents: A Remedy To Mankind By Nature. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Morinaka, B.I.; Molinski, T.F. Structures and Solution Conformational Dynamics of Stylissamides G and H from the Bahamian Sponge Stylissa caribica. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance Julian. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varijakzhan, D.; Chong, C.M.; Abushelaibi, A.; Lai, K.S.; Lim, S.H.E. Middle eastern plant extracts: An alternative to modern medicine problems. Molecules 2020, 25, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graça, A.P.; Viana, F.; Bondoso, J.; Correia, M.I.; Gomes, L.; Humanes, M.; Reis, A.; Xavier, J.R.; Gaspar, H.; Lage, O.M. The antimicrobial activity of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from the marine sponge Erylus deficiens (Astrophorida, Geodiidae). Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadanandan, R.; Rauf, A.A. Antibacterial activity of a lectin isolated from marine sponge Axinella donnani. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2018, 6, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Sharma, U.; Schulz, T.C.; McLean, A.B.; Robins, A.J.; West, L.M. Bicyclic C21 terpenoids from the marine sponge Clathria compressa. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keffer, J.L.; Plaza, A.; Bewley, C.A. Motualevic Acids A-F, Antimicrobial Acids from the Sponge Siliquariaspongia sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.B.; Yang, F.; Sun, F.; Li, J.; Jiao, W.H.; Gan, J.H.; Hu, W.Z.; Lin, H.W. Aaptamine Derivatives with Antifungal and Anti-HIV-1 Activities from the South China Sea Sponge Aaptos aaptos. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6003–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.; Tamaki, M.; Kasai, H.; Tanaka, T.; Otoguro, T.; Ryo, A.; Maekawa, S.; Enomoto, N.; De Voogd, N.J.; Tanaka, J.; et al. Inhibitory Effects of Metachromin A on Hepatitis B Virus Production via Impairment of the Viral Promoter Activity. Antivir. Res. 2017, 145, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Lin, X.; Lu, X.; Wan, J.; Zhou, X.; Liao, S.; Tu, Z. Sesquiterpenoids and Xanthones Derivatives Produced by Sponge-Derived Fungus Stachybotry sp. HH1. J. Antibiot. 2014, 68, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Subramani, R.; Aalbersberg, W. Three Bioactive Sesquiterpene Quinones from the Fijian Marine Sponge of the Genus Hippospongia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1488–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpiński, T.M. Marine drugs Marine Macrolides with Antibacterial and/or antifungal activity. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desoubzdanne, D.; Marcourt, L.; Raux, R.; Chevalley, S.; Dorin, D.; Doerig, C.; Valentin, A.; Ausseil, F.; Debitus, C. Alisiaquinones and Alisiaquinol, dual inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum enzyme targets from a new caledonian deep water sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeano, E.; Thomas, O.P.; Robledo, S.; Munoz, D.; Martinez, A. Antiparasitic Bromotyrosine Derivatives from the Marine Sponge Verongula rigida. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1902–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; De Martino, L.; Coppola, R.; De Feo, V. Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo, C.-L.; Yang, S.-K.; Yusoff, K.; Ajat, M.; Thomas, W.; Abushelaibi, A.; Lim, S.-H.-E.; Lai, K.-S. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and alternative approaches to overcome AMR. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2019, 16, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljaafari, M.; Alhosani, M.S.; Abushelaibi, A.; Kok-Song, L.; Swee-Hua, E.L. Essential Oils: Partnering with antibiotics. In Essential Oils-Oils of Nature; El-Shemy, H., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2019; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaid, C.; Belmadani, A.; Djeribi, R.; Rouabhia, M. The effects of mentha × piperita essential oil on C. Albicans growth, transition, biofilm formation, and the expression of secreted aspartyl proteinases genes. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-K.; Yusoff, K.; Ajat, M.; Thomas, W.; Abushelaibi, A.; Akseer, R.; Lim, S.-H.E.; Lai, K.-S. Disruption of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae membrane via induction of oxidative stress by cinnamon bark (Cinnamomum verum J. Presl) essential oil. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shushizadeh, M.R.; Behroozi, S.; Behfar, A.A.; Nazemi, M. Antibacterial activity and Gc-Mass analysis of organic extract From Persian Gulf Haliclona sp. Pharmacophore 2018, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Nagahamide A, an Antibacterial Depsipeptide from the Marine Sponge Theonella swinhoei. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3039–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, A.; Kubota, T.; Aoyama, K.; Mikami, Y.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Nagelamides Q and R, Novel Dimeric Bromopyrrole Alkaloids from Sponges Agelas sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana, R.; Favi, G.; Baffone, W.; Lucarini, S. Marine alkaloid 2,2-bis(6-bromo-3-indolyl) Ethylamine and its Synthetic Derivatives Inhibit Microbial Biofilms Formation and Disaggregate Developed Biofilms. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderblom, H.R. Structure and classification of viruses. In Medical Microbiology; Baron, S., Ed.; The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Drexler, M. What You Need to Know About Infectious Disease; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780309161398. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, A.; Fujimoto, Y.; Tamaki, M.; Setiawan, A.; Tanaka, T.; Okuyama-dobashi, K.; Kasai, H.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T.; Toyama, M.; et al. Identification of Antiviral Agents Targeting Hepatitis B Virus Promoter from Extracts of Indonesian Marine Organisms by a Novel Cell-based Screening Assay. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6759–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, K.A.; Furuta, A.; Noda, N.; Tsuneda, S.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Tanaka, J.; Akimitsu, N. Inhibition of Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Helicase by Manoalide. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, K.A.; Akimitsu, N. Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Inhibitors: Current and Future Perspectives. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, K.A.; Furuta, A.; Noda, N.; Tsuneda, S.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Moriishi, K.; Nakakoshi, M.; Tsubuki, M.; Tani, H.; et al. Psammaplin A Inhibits Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Helicase. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 67, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Kurimoto, S.I.; Kobayashi, J. The Manzamine Alkaloids. In Alkaloids: Chemistry and Biology; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 84, pp. 1–124. ISBN 9780128209820. [Google Scholar]
- El Sayed, K.A.; Kelly, M.; Kara, U.A.K.; Ang, K.K.H.; Katsuyama, I.; Dunbar, D.C.; Khan, A.A.; Hamann, M.T. New Manzamine Alkaloids with Potent Activity against Infectious Diseases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palem, J.R.; Bedadala, G.R.; El Sayed, K.A.; Hsia, S.C.V. Manzamine A as a Novel Inhibitor of Herpes Simplex Virus type-1 Replication in Cultured Corneal Cells. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Li, Z.; Shen, S.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, M.; Bruhn, T.; Bruhn, H.; Morschhäuser, J.; Bringmann, G.; et al. Baculiferins A–O, O-sulfated Pyrrole Alkaloids with Anti-HIV-1 Activity, from the Chinese Marine Sponge Iotrochota baculifera. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5466–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Rashid, M.A.; Cartner, L.K.; Bokesch, H.R.; Wilson, J.A.; McMahon, J.B.; Gustafson, K.R. Stellettapeptins A and B, HIV-Inhibitory Cyclic Depsipeptides from the Marine Sponge Stelletta sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 4215–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janbon, G.; Quintin, J.; Lanternier, F.; d’Enfert, C. Studying fungal pathogens of humans and fungal infections: Fungal diversity and diversity of approaches. Genes Immun. 2019, 20, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rubio, R.; de Oliveira, H.C.; Rivera, J.; Trevijano-Contador, N. The Fungal Cell Wall: Candida, Cryptococcus, and Aspergillus Species. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanadilok, R.; Sonchaeng, P.; Kijjoa, A.; Damas, A.M.; Gales, L.; Silva, A.M.S.; Herz, W. Tetillapyrone and Nortetillapyrone, Two Unusual Hydroxypyran-2-ones from the Marine Sponge Tetilla japonica. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1056–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanadilok, R.; Sawangwong, P.; Rodrigues, C.; Cidade, H.; Pinto, M.; Pinto, E.; Silva, A.; Kijjoa, A. Antifungal Activity Evaluation of the Constituents of Haliclone baeri and Haliclona cymaeformis, Collected from the Gulf of Thailand. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.B.; Liu, X.F.; Xu, Y.; Gan, J.H.; Jiao, W.H.; Shen, Y.; Lin, H.W. Woodylides A–C, New Cytotoxic Linear Polyketides from the South China Sea Sponge Plakortis simplex. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Shaala, L.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Badr, J.M.; Bamanie, F.H.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Theonellamide G, a Potent Antifungal and Cytotoxic Bicyclic Glycopeptide from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Mooberry, S.L. Hurghadolide A and Swinholide I, Potent Actin-Microfilament Disrupters from the Red Sea Sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angawi, R.F.; Bavestrello, G.; Calcinai, B.; Dien, H.A.; Donnarumma, G.; Tufano, M.A.; Paoletti, I.; Grimaldi, E.; Chianese, G.; Fattorusso, E.; et al. Aurantoside J: A New Tetramic Acid Glycoside from Theonella swinhoei. Insights into the Antifungal Potential of Aurantosides. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, E.; Latif, A.; Kong, C.S.; Seo, Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Dalal, S.R.; Cassera, M.B.; Kingston, D.G.I. Antimalarial Activity of the Isolates from the Marine Sponge Hyrtios erectus against the Chloroquine-resistant Dd2 Strain of Plasmodium falciparum. Z. Naturforsch. Sect. C J. Biosci. 2018, 73, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faruk, M.A.R.; Sarker, M.M.R.; Alam, M.J.; Kabir, M.B. Economic Loss from Fish Diseases on Rural Freshwater Aquaculture of Bangladesh. Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 2004, 7, 2086–2091. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Das, R.; Swain, P. Status of Fish Diseases in Aquaculture and Assessment of Economic Loss due to Disease. In Contemporary Trends in Fisheries and Aquaculture; Rao, P., Pandey, B., Pandey, P., Joshi, B.D., Eds.; Today and Tomorrow’s Printers and Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, N.E.D.A.; Atta, N.S.; Aziz, A.E.; Ahmed, M. Oral Vaccination of Nile Tilapia (Orechromis niloticus) against Motile Aeromonas Septicaemia. Nat. Sci. 2010, 8, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo, A.E.; Magariños, B.; Romalde, J.L. A review of the main bacterial fish diseases in mariculture systems. Aquaculture 2005, 246, 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonia, G.A.S.; Lipton, A.P.; Raj, R.P. Antibacterial activty of marine sponge extracts towards fish pathogenic bacteria. ISR J. Aquac. 2008, 60, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.K.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, H.K. Microbial Symbiosis in Marine Sponges. J. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 254–264. [Google Scholar]
- Wahyudi, A.T.; Priyanto, J.A.; Maharsiwi, W.; Astuti, R.I. Screening and characterization of sponge-associated bacteria producing bioactive compounds anti-vibrio sp. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mora-Cristancho, J.A.; Arévalo-Ferro, C.; Ramos, F.A.; Tello, E.; Duque, C.; Lhullier, C.; Falkenberg, M.; Schenkelc, E.P. Antifouling activities against colonizer marine bacteria of extracts from marine invertebrates collected in the Colombian Caribbean sea and on the Brazilian coast (Santa Catarina). Z. Naturforsch. Sect. C J. Biosci. 2011, 66C, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.D.; McCluskey, A.; Robertson, M.J.; MacGregor, K.A.; Gordon, C.P.; Guenther, J. Anti-malarial, Anti-algal, Anti-tubercular, Anti-bacterial, Anti-photosynthetic, and Anti-fouling Activity of Diterpene and Diterpene Isonitriles from the Tropical Marine sponge Cymbastela hooperi. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mol, R.R.; Lipton, A.; Thankamani, V. Antibacterial and Antifouling Activity of the Marine Sponge Callyspongia diffusa Collected from South-west Coast of India. Int. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 12, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Novel Bromotyrosine Derivatives That Inhibit Growth of the Fish Pathogenic Bacterium Aeromonas hydrophila, from a Marine Sponge Hexadella sp. 1 Hexadella sp. collected in southern Japan exhibited Aeromonas hydrophila, which causes hemorrhagic septio. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 1893–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kong, F.; Zhou, S.; Huang, D.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, W. Streptomyces tirandamycinicus sp. Nov., a Novel Marine Sponge-derived Actinobacterium with Antibacterial Potential against Streptococcus agalactiae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Ravichandran, S.; Ribeiro, M.; Ciavatta, M. Antifungal Potential of Marine Sponge Extract against Plant and Fish Pathogenic Fungi. Oceanogr. Open Access 2013, 01, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kurnianda, V.; Khairunnisa; Winanda, A.; Mauliza, A.; Ulfah, M.; Nurfadillah; Ishida, R.; Kobayashi, M. Polyhydroxy Isocopalane from Indonesian’s Marine Sponge Callyspongia Sp. as Anti–White Spot Syndrome Virus from Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Pharmacogn. Nat. Prod. 2017, 3, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, N.; Jiao, W.H.; Wang, R.P.; Peng, Y.; Qi, S.H.; Song, S.J.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, H.W. Antifouling and Cytotoxic Constituents from the South China Sea Sponge Acanthella cavernosa. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 2876–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjögren, M.; Dahlström, M.; Hedner, E.; Jonsson, P.R.; Vik, A.; Gundersen, L.L.; Bohlin, L. Antifouling Activity of the Sponge Metabolite Agelasine D and Synthesised Analogs on Balanus improvisus. Biofouling 2008, 24, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blihoghe, D.; Manzo, E.; Villela, A.; Cutignano, A.; Picariello, G.; Faimali, M.; Fontana, A. Evaluation of the Antifouling Properties of 3-alyklpyridine Compounds. Biofouling 2011, 27, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukatou, M.; Hellio, C.; Vagias, C.; Harvala, C.; Roussis, V. Chemical Defense and Antifouling Activity of Three Mediterranean Sponges of the Genus Ircinia. Z. Naturforsch. Sect. C J. Biosci. 2002, 57, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.C.; Longeon, A.; Pham, V.C.; Urvois, F.; Bressy, C.; Van Trinh, T.T.; Nguyen, H.N.; Phan, V.K.; Chau, V.M.; Briand, J.F.; et al. Antifouling 26,27-cyclosterols from the Vietnamese Marine Sponge Xestospongia testudinaria. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.-Y.; Yao, J.-C.; Tang, S.-K.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.-W.; Li, W.-J. The Futalosine Pathway Played an Important Role in Menaquinone Biosynthesis during Early Prokaryote Evolution. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, Y.; Kondo, K.; Ikeda, A.; Harada, R.; Dairi, T. Identification of Tirandamycins as Specific Inhibitors of the Futalosine Pathway. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, G.S.; Lipton, A.N.; Priyadharshini, S.; Anitha, K.; Suárez, L.E.C.; Arasu, M.V.; Choi, K.C.; Selvin, J.; Al-Dhabi, N.A. Antiadhesive Activity of Poly-hydroxy Butyrate Biopolymer from a Marine Brevibacterium casei MSI04 against Shrimp Pathogenic Vibrios. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Ding, L.; Wei, J.; Li, Q.; Gui, M.; He, X.; Su, D.; He, S.; Jin, H. A New Aquatic Pathogen Inhibitor Produced by the Marine Fungus Aspergillus sp. LS116. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, E.; Shpigel, M.; Ilan, M. Sea Ranching of the Marine Sponge Negombata magnifica (Demospongiae, Latrunculiidae) as a First Step for Latrunculin B Mass Production. Aquaculture 2005, 244, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Twan, W.H.; Tseng, L.C.; Peng, S.H.; Hwang, J.S. First Detection of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in the Mud Shrimp Austinogebia edulis in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannister, J.; Sievers, M.; Bush, F.; Bloecher, N. Biofouling in Marine Aquaculture: A Review of Recent Research and Developments. Biofouling 2019, 35, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedner, E.; Sjögren, M.; Hodzic, S.; Andersson, R.; Göransson, U.; Jonsson, P.R.; Bohlin, L. Antifouling Activity of a Dibrominated Cyclopeptide from the Marine Sponge Geodia barretti. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Hertiani, T.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A.; Ortlepp, S.; van Soest, R.W.M.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Hentschel, U.; Kozytska, S.; Müller, W.E.G.; Proksch, P. From Anti-fouling to Biofilm Inhibition: New Cytotoxic Secondary Metabolites from Two Indonesian Agelas Sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoukatou, M.; Maréchal, J.P.; Hellio, C.; Novaković, I.; Tufegdzic, S.; Sladić, D.; Gašić, M.J.; Clare, A.S.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Evaluation of the Activity of the Sponge Metabolites Avarol and Avarone and their Synthetic Derivatives against Fouling Micro-and Macroorganisms. Molecules 2007, 12, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.; Depree, C.; Thompson, K.J. Natural Product Communications Antifouling Sesterterpenes from the New Zealand Marine Sponge Semitaspongia bactriana. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Hellio, C.; Tsoukatou, M.; Maréchal, J.-P.; Aldred, N.; Beaupoil, C.; Clare, A.S.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Inhibitory Effects of Mediterranean Sponge Extracts and Metabolites on Larval Settlement of the Barnacle Balanus amphitrite. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Cross, S.S. Fistularin 3 and 11-ketofistularin 3. Feline leukemia virus active bromotyrosine metabolites from the marine sponge Aplysina archeri. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luduena, R.F.; Roach, M.C.; Prasad, V.; Pettit, G.R. Interaction of Halichondrin B and Homohalichondrin B with Bovine Brain Tubulin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993, 45, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laport, M.S.; Marinho, P.R.; da Silva Santos, O.C.; de Almeida, P.; Romanos, M.T.V.; Muricy, G.; Brito, M.A.V.P.; Giambiagi-deMarval, M. Antimicrobial activity of marine sponges against coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 155, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, L.K.; Porto, P.; Bianchi, B.; Santos, M.; Berlinck, R.; Arns, C. NOR-Batzelladine L from the sponge Monanchora sp. displays antiviral activity against Herpes simplex virus type 1. Planta Med. 2012, 78, CL27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Demerdash, A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Bishayee, A.; Abdel-Mogib, M.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Al-Mourabit, A. Batzella, Crambe and Monanchora: Highly prolific marine sponge genera yielding compounds with potential applications for cancer and other therapeutic areas. Nutrients 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, M.; Trotter, N.; Vijayasarathy, S.; Salim, A.A.; Khalil, Z.G.; Lacey, E.; Capon, R.J. Isolation and Synthesis of N-acyladenine and Adenosine Alkaloids from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Phoriospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 5902–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.D.; Freyer, A.J.; Carte, B.; Johnson, R.K.; Lahouratate, P. Plakortides, Novel Cyclic Peroxides from the Sponge Plakortis halichondrioides. Activators of Cardiac SR-Ca2+ Pumping ATPase. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhu, S.; Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; She, R.; Hu, F.; Quan, R.; Liu, J.; et al. Avian Metapneumovirus subgroup C infection in chickens, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1092–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Sid, H.; Rautenschlein, S. Avian metapneumovirus infection of chicken and turkey tracheal organ cultures: Comparison of virus–host interactions. Avian Pathol. 2015, 44, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyörälä, S.; Taponen, S. Coagulase-negative staphylococci-Emerging mastitis pathogens. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bande, F.; Arshad, S.S.; Hassan, L.; Zakaria, Z. Molecular detection, phylogenetic analysis, and identification of transcription motifs in feline leukemia virus from naturally infected cats in Malaysia. Vet. Med. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, S.; Bienzle, D.; Carioto, L.; Chisholm, H.; Brien, E.O.; Scherk, M. Feline leukemia virus and feline immunodeficiency virus in Canada: Recommendations for testing and management. Can. Vet. J. 2011, 52, 849–855. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, K.P.; Bienzle, D.; Mcdonnell, J.J. Feline Leukemia Virus-associated Myelopathy in Cats. Vet. Pathol. 2002, 39, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Mai, L.H.; Longeon, A.; Mangoni, A.; Durieu, E.; Meijer, L.; Van Soest, R.; Costantino, V.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L. A collection of bioactive nitrogen-containing molecules from the marine sponge acanthostrongylophora ingens. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Liao, X.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Feng, P.; Zhao, B.X.; Xu, S. Isolation and Synthesis of Misszrtine A: A Novel Indole Alkaloid from Marine Sponge-Associated Aspergillus sp. SCSIO XWS03F03. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taufa, T.; Singh, A.J.; Harland, C.R.; Patel, V.; Jones, B.; Halafihi, T.; Miller, J.H.; Keyzers, R.A.; Northcote, P.T. Zampanolides B-E from the Marine Sponge Cacospongia mycofijiensis: Potent Cytotoxic Macrolides with Microtubule-Stabilizing Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2539–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balansa, W.; Mettal, U.; Wuisan, Z.G.; Plubrukarn, A.; Ijong, F.G.; Liu, Y.; Schäberle, T.F. A New Sesquiterpenoid Aminoquinone from an Indonesian Marine Sponge. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.B.; Yin, Z.F.; Gu, B.B.; Zhang, J.P.; Wang, S.P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.W. Cytotoxic Meroterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Dactylospongia elegans. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubina, L.K.; Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Popov, R.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Grebnev, B.B.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; von Amsberg, G.; Stonik, V.A. Gracilosulfates A–G, Monosulfated Polyoxygenated Steroids from the Marine Sponge Haliclona gracilis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.; Pichon, E.; Moriou, C.; Clerc, P.; Tr, R.; Frederich, M.; De Voogd, N.; Hellio, C.; Gauvin-bialecki, A.; Al-mourabit, A. New Antimalarial and Antimicrobial Tryptamine Derivatives from the Marine Sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.E.; Herbette, G.; Chendo, C.; Clerc, P.; Tintillier, F.; Voogd, N.J.D.; Papanagnou, E.D.; Trougakos, I.P.; Jerabek, M.; Bignon, J.; et al. Osirisynes G–I, New Long-Chain Highly Oxygenated Polyacetylenes from the Mayotte Marine Sponge Haliclona sp. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagabhishek, S.N.; Madankumar, A. A Novel Apoptosis-Inducing Metabolite Isolated from Marine Sponge Symbiont: Monascus sp. NMK7 Attenuates Cell Proliferation, Migration and ROS Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5878–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Panek, J.S. Total synthesis of (−)-mycalolide A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 1235–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi-Takanaka, Y.; Kina, Y.; Nakamura, F.; Yamazaki, S.; Harata, M.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Kimura, H.; Nakao, Y. Effect of Mycalolides Isolated from a Marine Sponge Mycale aff. nullarosette on Actin in Living Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Lin, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Spiro-Phthalides and Isocoumarins Isolated from the Marine-Sponge-Derived Fungus Setosphaeria sp. SCSIO41009. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashari, M.H.; Huda, F.; Tartila, T.S.; Shabrina, S.; Putri, T.; Qomarilla, N.; Atmaja, H.; Subhan, B.; Sudji, I.R.; Meiyanto, E. Bioactive Compounds in the Ethanol Extract of Marine Sponge Stylissa carteri Demonstrates Potential Anti-Cancer Activity in Breast Cancer Cells. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Ni, J.; Chang, F.; Liu, S.; Xu, N.; Sun, W.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. Bio-Source of di-n-butyl Phthalate Production by Filamentous Fungi. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, K.M.; Beltagy, E.A. Bioactive Phthalate from Marine Streptomyces ruber EKH2 against Virulent Fish Pathogens. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 41, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinovskaya, N.I.; Romanenko, L.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I. Antibacterial Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds Produced by the Marine Bacterium Rheinheimera japonica KMM 9513T. Antonie Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 110, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, V.L.T.; Li, Y.; Kim, S.K. Cathepsin B Inhibitory Activities of Phthalates Isolated from a Marine Pseudomonas strain. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.; Tsai, C.; Hsu, C.; Kuo, P.; Lee, J.; Chai, C.; Wang, S.; Tsai, E. Phthalates Induce Proliferation and Invasiveness of Estrogen Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer through the AhR/HDAC6/c-Myc Signaling Pathway. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirpu Natesh, N.; Arumugam, M.; Karanam, G. Apoptotic Role of Marine Sponge Symbiont Bacillus subtilis NMK17 through the Activation of Caspase-3 in Human Breast Cancer Cell Line. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 2641–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliara, P.; Barca, A.; Verri, T.; Caroppo, C. The Marine Sponge Petrosia ficiformis Harbors Different Cyanobacteria Strains with Potential Biotechnological Application. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, G.S.; Hassan, S.; Sajayan, A.; Selvin, J. Quorum quenching compounds from natural sources. In Bioresources and Bioprocess in Biotechnology; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2017; pp. 351–363. ISBN 9789811042843. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.; Zhang, X.H. Quorum quenching agents: Resources for antivirulence therapy. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3245–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uroz, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Oger, P. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching: The Yin and Yang of bacterial communication. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbetter, J.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Metabolism of acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals by Variovorax paradoxus. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 6921–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Gustchina, E.; Baker, H.L.; Kelly, M.; Bewley, C.A. Mirabamides A–D, depsipeptides from the sponge Siliquariaspongia mirabilis that inhibit HIV-1 fusion. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerata, M.S.; D’Souza, S.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Dube, A.; Meyer, M.; Samaai, T.; Antunes, E.M.; Beukes, D.R. Encapsulation of variabilin in stearic acid solid lipid nanoparticles enhances its anticancer activity in vitro. Molecules 2020, 25, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Lim, H.K.; Oh, S.R.; Chung, W.H.; Jung, J. Anticancer Effects of the Marine Sponge Lipastrotethya sp. Extract on Wild-Type and p53 Knockout HCT116 Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcabrini, C.; Catanzaro, E.; Bishayee, A.; Turrini, E.; Fimognari, C. Marine sponge natural products with anticancer potential: An updated review. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
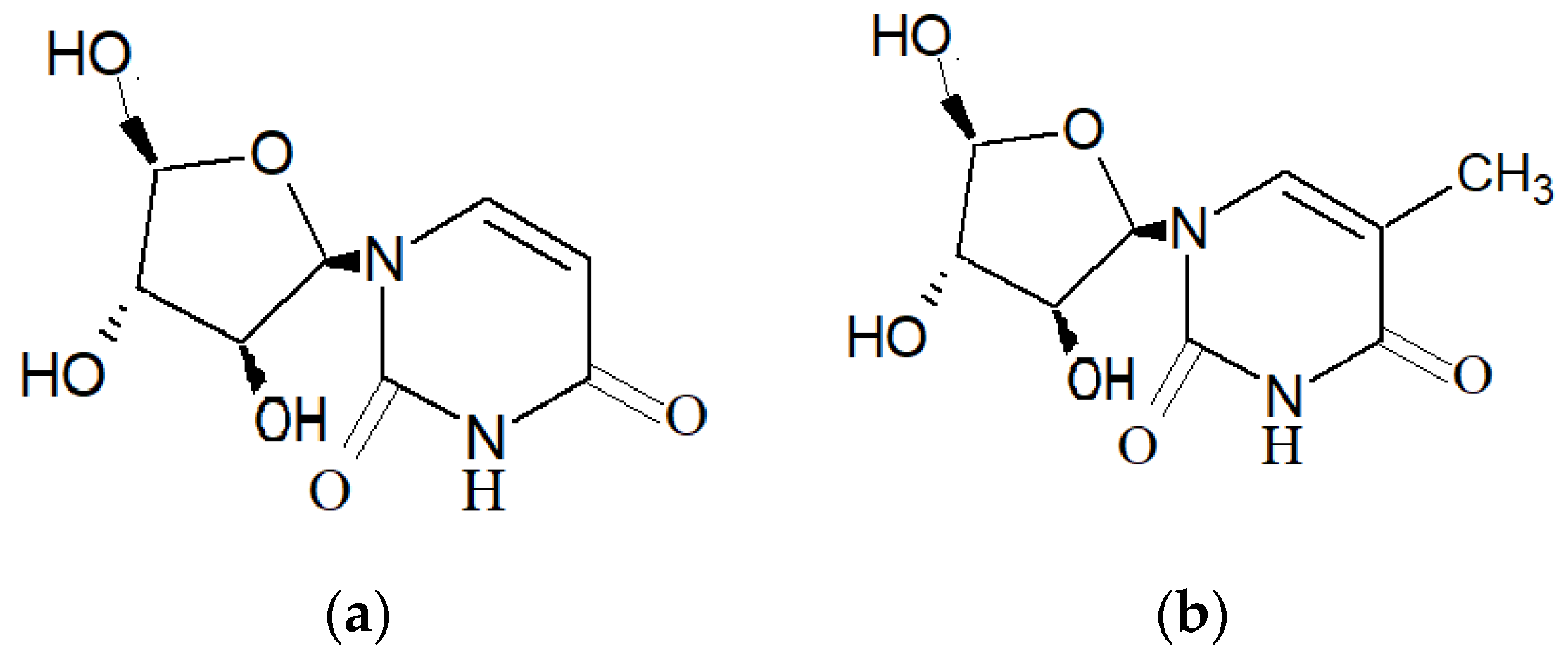
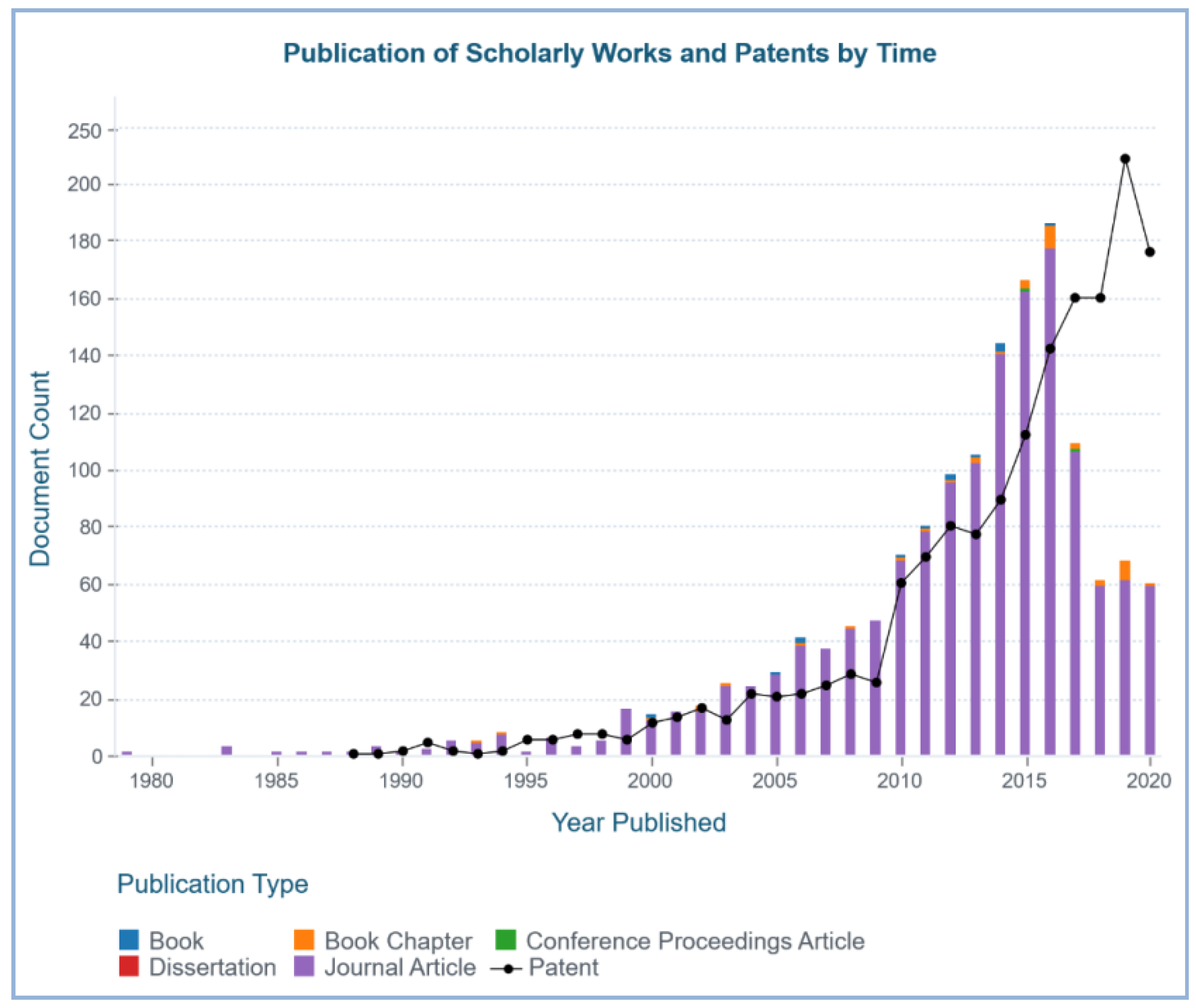
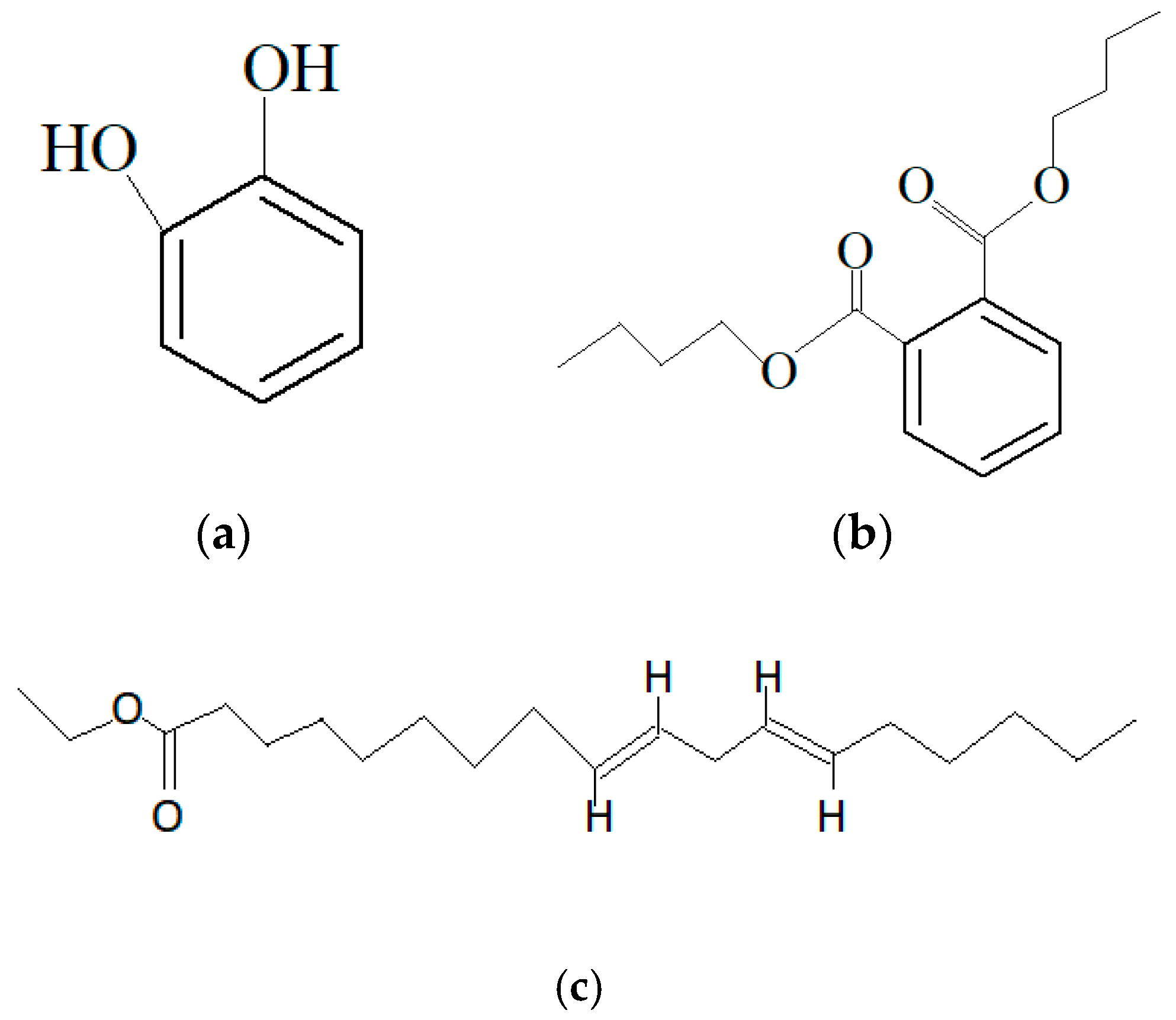
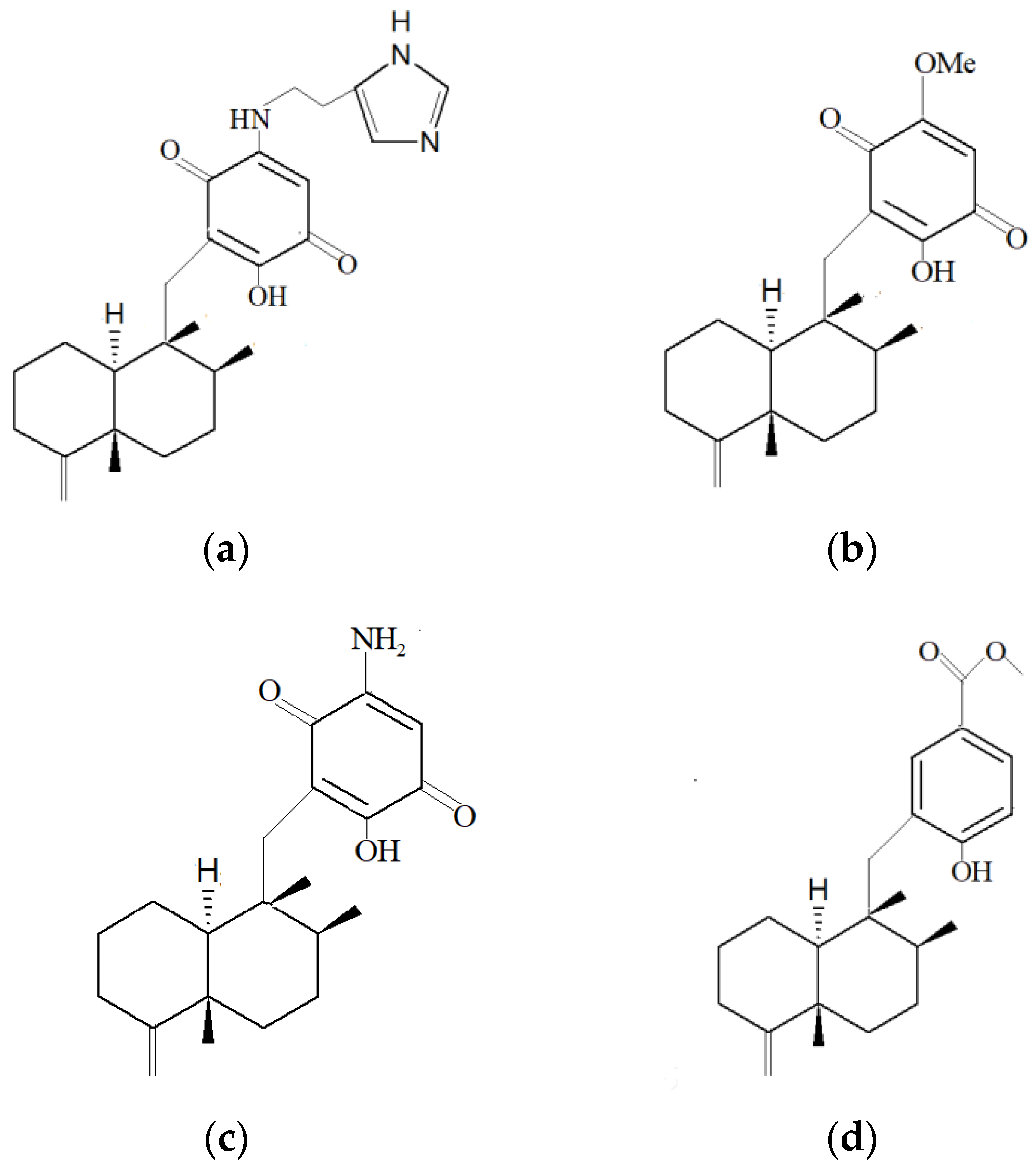
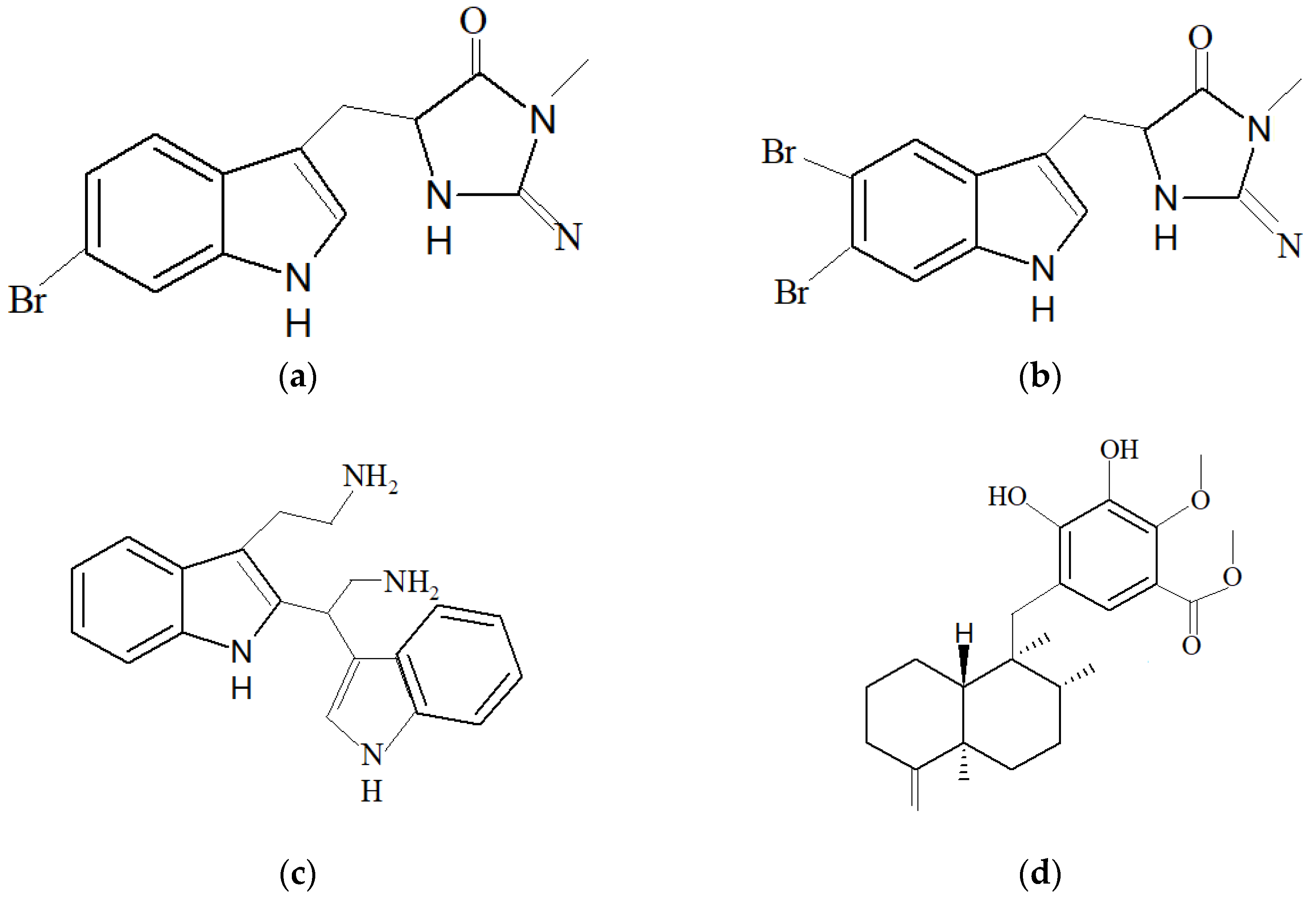
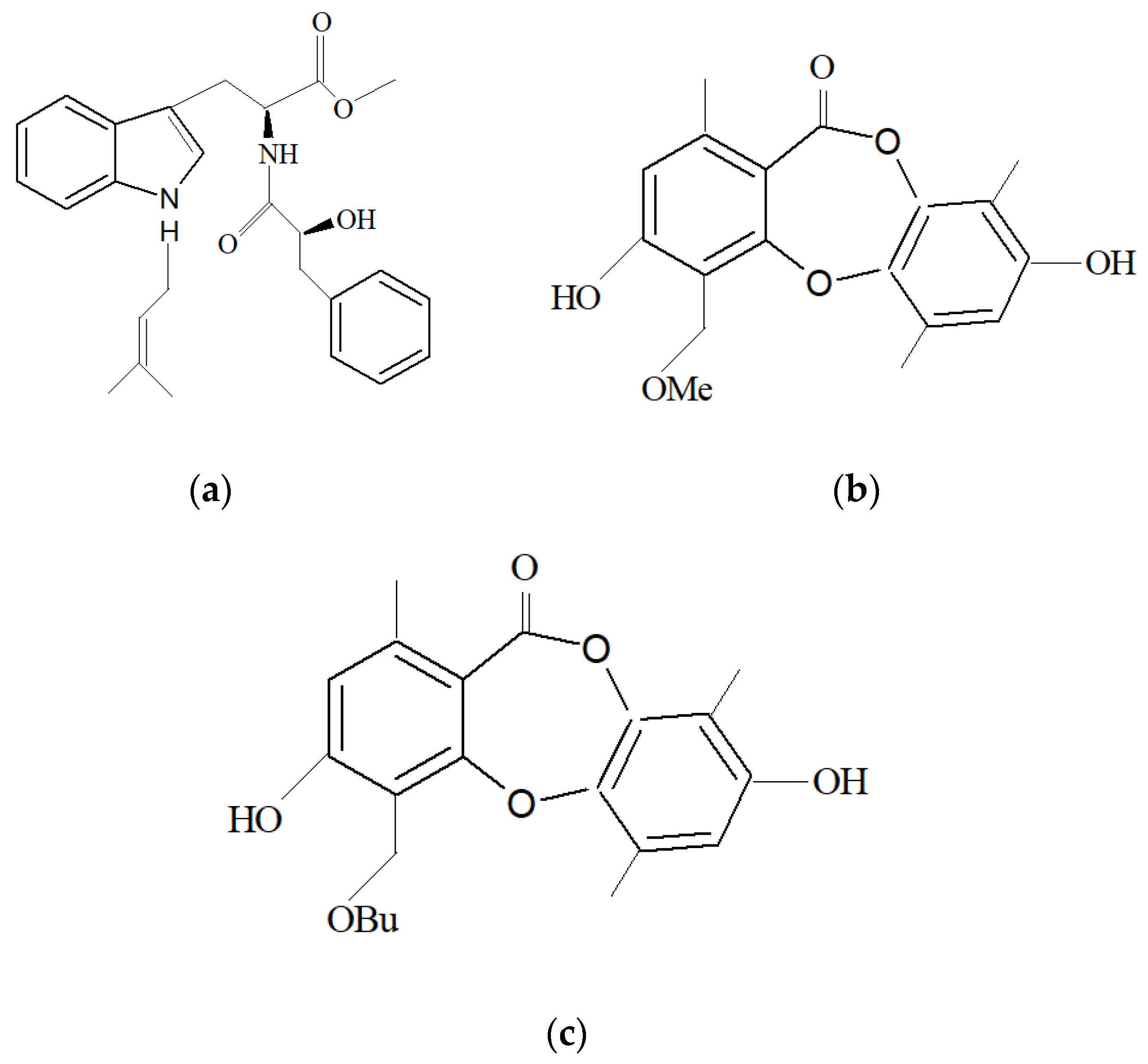
| Marine Sponge | Compound | Bioactivity | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agelas oroides (Schmidt, 1864) associated with Streptomyces sp. SBT345 | 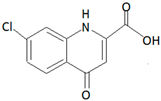 Compound quinolone ageloline A |
| [16,17] |
| Dysidea avara (Schmidt, 1862) | 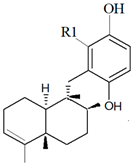 6′-Hydroxy avarol (R1: OH) 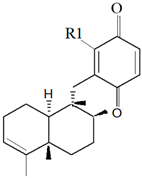 3′-hydroxy avarone (R1: OH) |
| [18,19] |
| Hamigera tarangaensis (Bergquist and Fromont, 1988) | 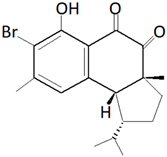 Compound Hamigeran B |
| [20,21] |
| Leuconia nivea (Grant, 1826) Synthesized by the symbiont bacteria Microbulbifer sp. |  Natural paraben (R:-(CH2)9 –(CH3) |
| [17,22] |
| Marine Sponge | Classification | Compound | Chemical Structure | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agelas oroides (Schmidt, 1864) | Bromopyrrole alkaloid | Oroidin | 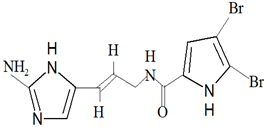 | [3,45] |
| Discodermia kiiensis (Hoshino, 1977) | Peptide | Discodermin A |  | [46] |
| Jaspis stellifera (Carter, 1879) Stelleta tenuis (Lindgren, 1897) | Triterpene | Stelletin A | 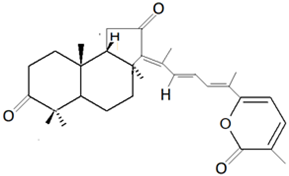 | [47] |
| Haliclona sp. | Polycyclic, β-carboline-derived alkaloid | Manzamine A | 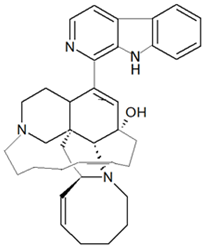 | [48,49] |
| Luffariella variabilis (Polejaeff, 1884) | Sesterterpene | Manoalide |  | [50] |
| Bioactivity | Marine Sponge | Compound | Properties | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial | Axinella donnani (Bowerbank, 1873) |
|
| [95] |
| Clathria compressa (Schmidt, 1862) |
|
| [96] | |
| Siliquariaspongia sp. (Hoshino, 1981) |
|
| [97] | |
| Antiviral | Aaptos aaptos (Schmidt, 1864) |
|
| [98] |
| Dactylospongia metachromia (de Laubenfels, 1954) |
|
| [99] | |
| Stachybotri sp. HH1 ZSDS1F1-2 fungal strain from unknown marine sponge |
|
| [100] | |
| Antifungal | A. aaptos |
|
| [98] |
| Hippospongia sp. (Schulze, 1879) |
|
| [101] | |
| Xestospongia exigua (Kirkpatrick, 1900) |
|
| [102] | |
| Anti-parasite | New Caledonian deep sea sponge Verongula rigida (Esper, 1794) |
|
| [103,104] |
| Bioactivity | Marine Sponge | Compound | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial | Acanthella kletra (Pulitzer-Finali, 1982) |
|
| [142] |
| Callyspongia diffusa (Ridley, 1884) |
|
| [143] | |
| Hexadella sp. (Topsent, 1896) |
|
| [144] | |
| Streptomyces tirandamycinicus from unknown sponge, coast of Wenchang City, Hainan Province of China |
|
| [145] | |
| Antifungal | Negombota magnifica (Keller, 1889) |
|
| [146] |
| Antiviral | Callyspongia sp. |
|
| [147] |
| Antifouling | Acanthella cavernosa (Dendy, 1922) |
|
| [148] |
| Agelas sp. (Duchassaing and Michelotti, 1864) |
|
| [149] | |
| Cymbastela hooperi van Soest (Desqueyroux-Faùndez, Wright and König, 1996) |
|
| [142] | |
| Haliclona sp. |
|
| [150] | |
| Ircinia oros (Schmidt, 1864) |
|
| [151] | |
| Ircinia spinosula (Schmidt, 1862) |
|
| [151] | |
| Ircinia variabilis (Schmidt, 1862) |
|
| [151] | |
| Xestospongia testudinaria (Lamarck, 1815) |
|
| [152] |
| Marine Sponge | Compound | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aplysina thiona (Laubenfels, 1930) |
|
| [165] |
| Axinella sp. (Schmidt, 1862) |
|
| [166] |
| Cinachyrella sp. (Wilson, 1925), Haliclona sp., and Petromica citrine (Muricy, Hajdu, Minervino, Madeira and Peixinho, 2001) |
|
| [167] |
| Monanchora sp. (Carter, 1883) |
|
| [168,169] |
| Phoriospongia sp. (Marshall, 1880) |
|
| [170] |
| Plakortis halichondrioides (Wilson, 1902) |
|
| [171] |
| Marine Sponge and Associates | Location | Compound | Classification | Bioactivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acanthostrongylophora ingens (Thiele, 1899) | South Sulawesi, Indonesia | epi-tetradehydrohalicyclamine B and tetradehydrohalicyclamine B, acanthocycloamine A, halicyclamine B chloromethylhalicyclamine B and diketopiperazines. | Alkaloids | Antibacterial activity, reduce the production of amyloid β-42, and antikinase activity. | [178] |
| Aspergillus sp., a marine fungus associated with marine sponge (not specified) | Xuwen County, China | Misszrtine A | Alkaloids | Anti-cancer activity against HL-60 and LNCap cells. | [179] |
| Cacospongia mycofijiensis (Kakou, Crews and Bakus, 1987) | ‘Eua, Kingdom of Tonga | Zampanolides B, C and D | Macrolide | Anti-proliferative and anti-mitotoic activities with microtubule stabilizing activity. | [180] |
| Dactylspongia elegans T3 (Thiele, 1899 | North Sulawesi, Indonesia | Nakijiquinone V, illimaquinone, smenospongine and dyctioceratine C. | Sesquiterpene aminoquinone, sesquiterpene quinones and sesquiterpene hydroquinone. | Antibacterial activity. | [181] |
| Dactylspongia elegans T3 (Thiele, 1899 | Yongxing Island in the South China Sea | 19-methoxy-dictyoceratin-A | Sesquiterpene quinones | Anti-cancer activity against the human cancer cell lines DU145, SW1990, Huh7, and PANC-1 | [182] |
| Haliclona gracilis (Miklucho-Maclay, 1870) | Shikotan Island | Gracilosulfates A, B, C, D, E, F and G | Steroid | Anti-tumor activity against human prostate cancer. | [183] |
| Fascaplysinopsis reticulata (Hentschel, 1912) | Passe Bateau, Mayotte | 6-bromo-8,1′ -dihydro-isoplysin A and 5,6-dibromo-8,1′ -dihydro-isoplysin A | Tryptophan derived alkaloids | Antibacterial activity against Vibrio sp. | [184] |
| Haliclona sp. (Grant, 1836) | Mayotte | Osirisynes G, H and I | Long-chain highly oxygenated polyacetylenes | Enzyme-inhibitory activity against proteasome kinase. | [185] |
| Monascus sp. (Tiegh, 1884), a marine fungus associated with the marine sponge Clathria frondifera (Bowerbank, 1875) | Gulf of Mannar | Monacolin X | Polyketide | Anti-proliferative and anti-migratory activities against human breast cancer cell lines. | [186] |
| Mycale aff. nularosette (Hoshino, 1981) | Miyagi, Japan | Mycalolide A, mycalolide B and 38-hydroxymycalolide B | Macrolide | Actin depolymerization resulting in incomplete cytokinesis. | [187,188] |
| Setosphaeria sp. (Leonard and Suggs, 1974), marine fungus associated with the marine sponge Callyspongia sp. (Duchassaing and Michelotti, 1864) | Xuwen County, China | Botryorhodines I and J | Depsidones | Moderate antifungal activities against the phytopathogenic fungi Colletotrichum asianum and Colletotrichum acutatum. | [189] |
| Stylissa carteri (Dendy, 1889) | Indonesia | Flavonoid, triterpenoid and steroid | Anti-cancer activity against breast cancer MDA MB 231 cell line. | [190] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varijakzhan, D.; Loh, J.-Y.; Yap, W.-S.; Yusoff, K.; Seboussi, R.; Lim, S.-H.E.; Lai, K.-S.; Chong, C.-M. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Sponges: Fundamentals and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050246
Varijakzhan D, Loh J-Y, Yap W-S, Yusoff K, Seboussi R, Lim S-HE, Lai K-S, Chong C-M. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Sponges: Fundamentals and Applications. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(5):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050246
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarijakzhan, Disha, Jiun-Yan Loh, Wai-Sum Yap, Khatijah Yusoff, Rabiha Seboussi, Swee-Hua Erin Lim, Kok-Song Lai, and Chou-Min Chong. 2021. "Bioactive Compounds from Marine Sponges: Fundamentals and Applications" Marine Drugs 19, no. 5: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050246
APA StyleVarijakzhan, D., Loh, J.-Y., Yap, W.-S., Yusoff, K., Seboussi, R., Lim, S.-H. E., Lai, K.-S., & Chong, C.-M. (2021). Bioactive Compounds from Marine Sponges: Fundamentals and Applications. Marine Drugs, 19(5), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050246





