Cytoprotective Role of Edible Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis)-Derived Peptides in H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purification and Identification of BAPs from Edible Seahorse Hydrolysates by Alcalase®
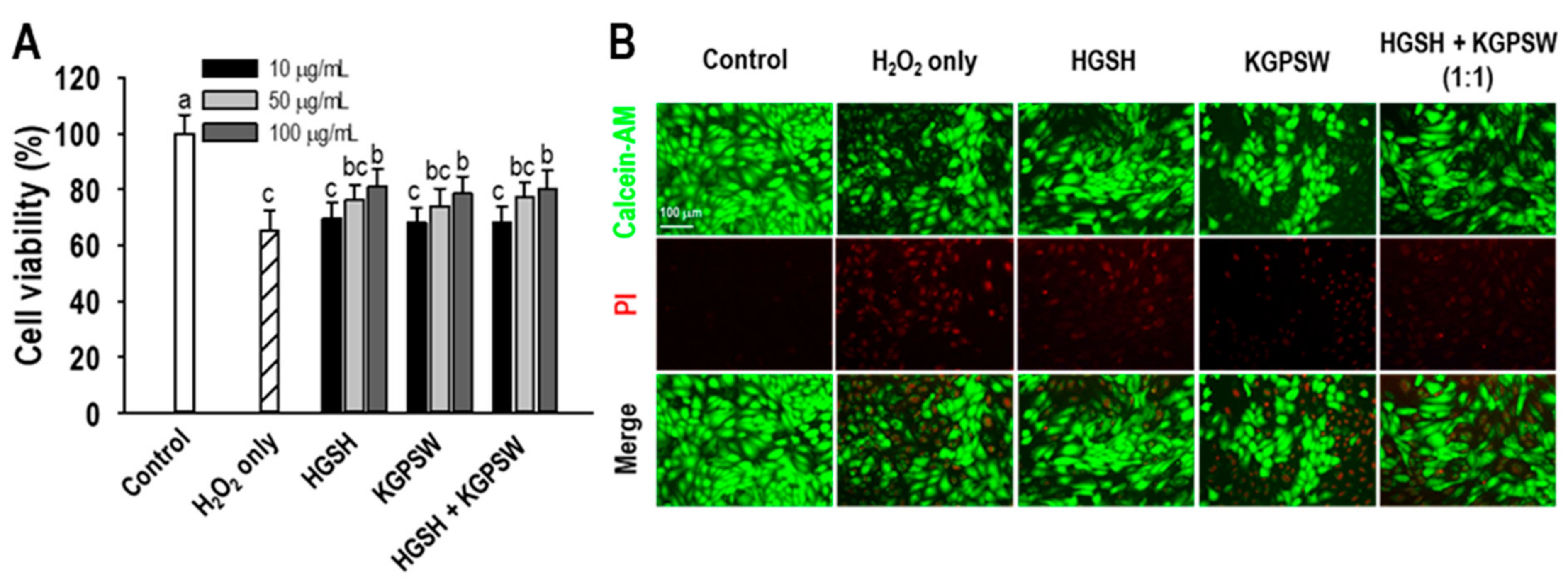
2.2. Two BAPs Protect H2O2-Induced HUVECs Damage
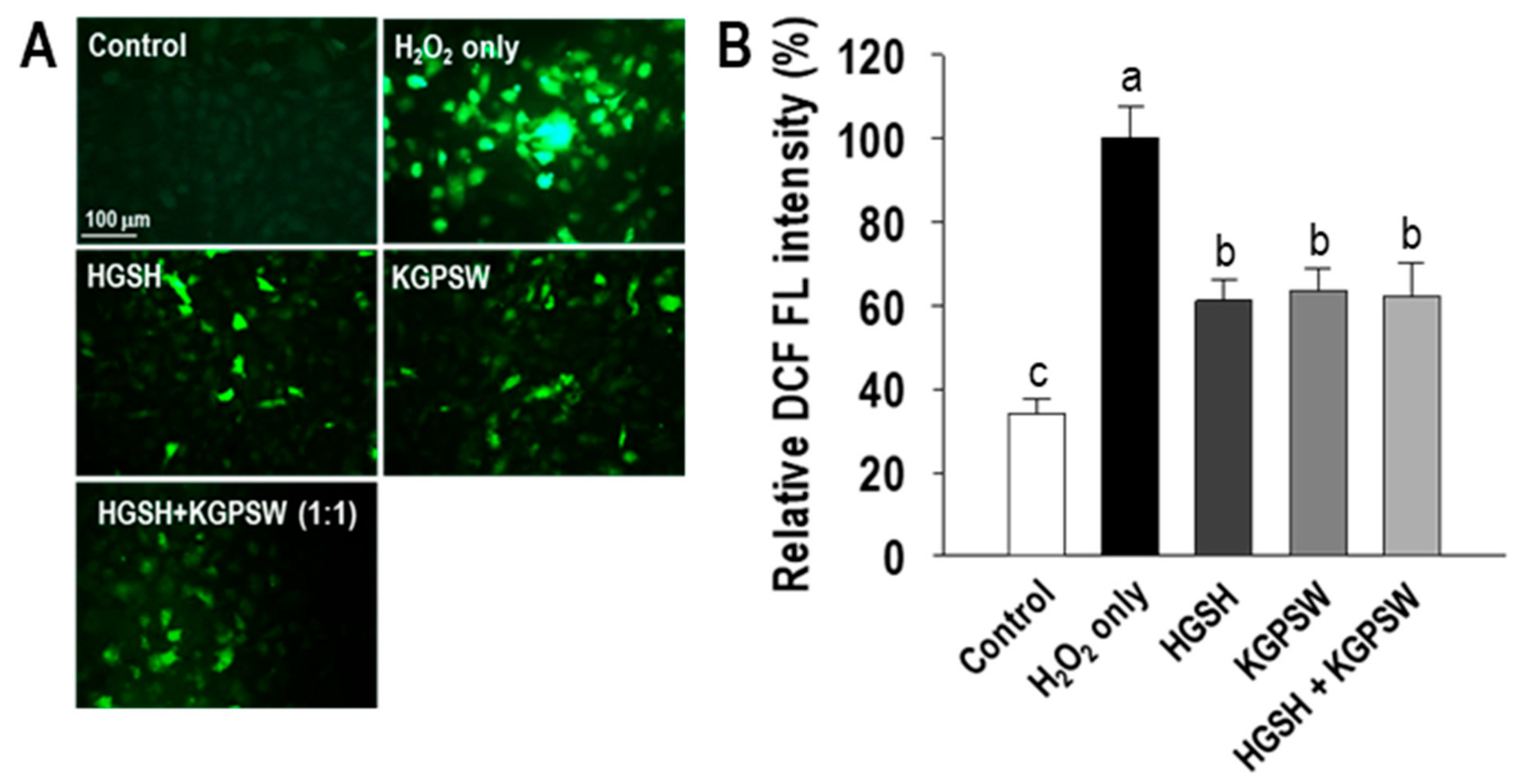
2.3. Two BAPs Inhibit Intracellular ROS Generation and Activate HO-1/Nrf2 Pathway
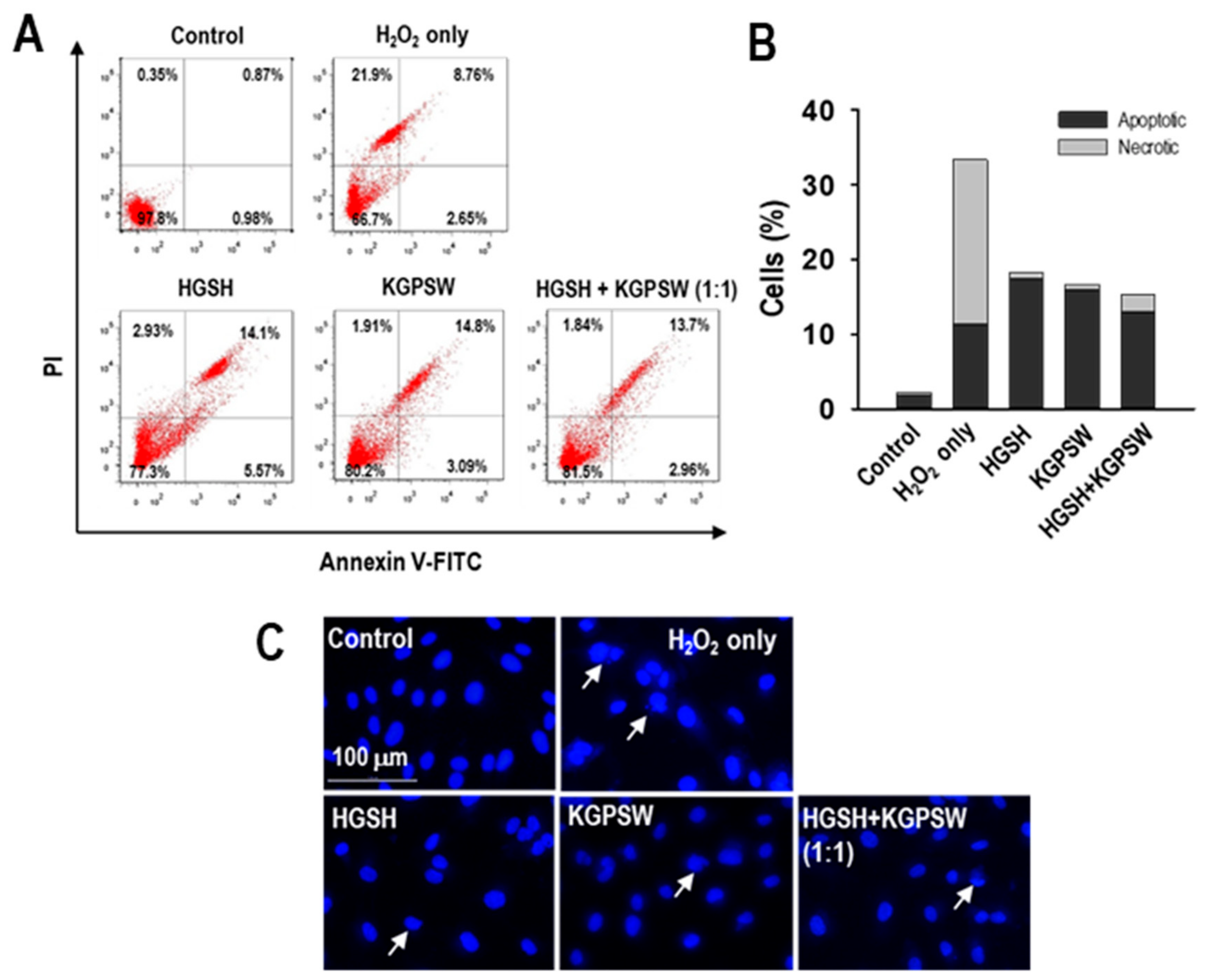
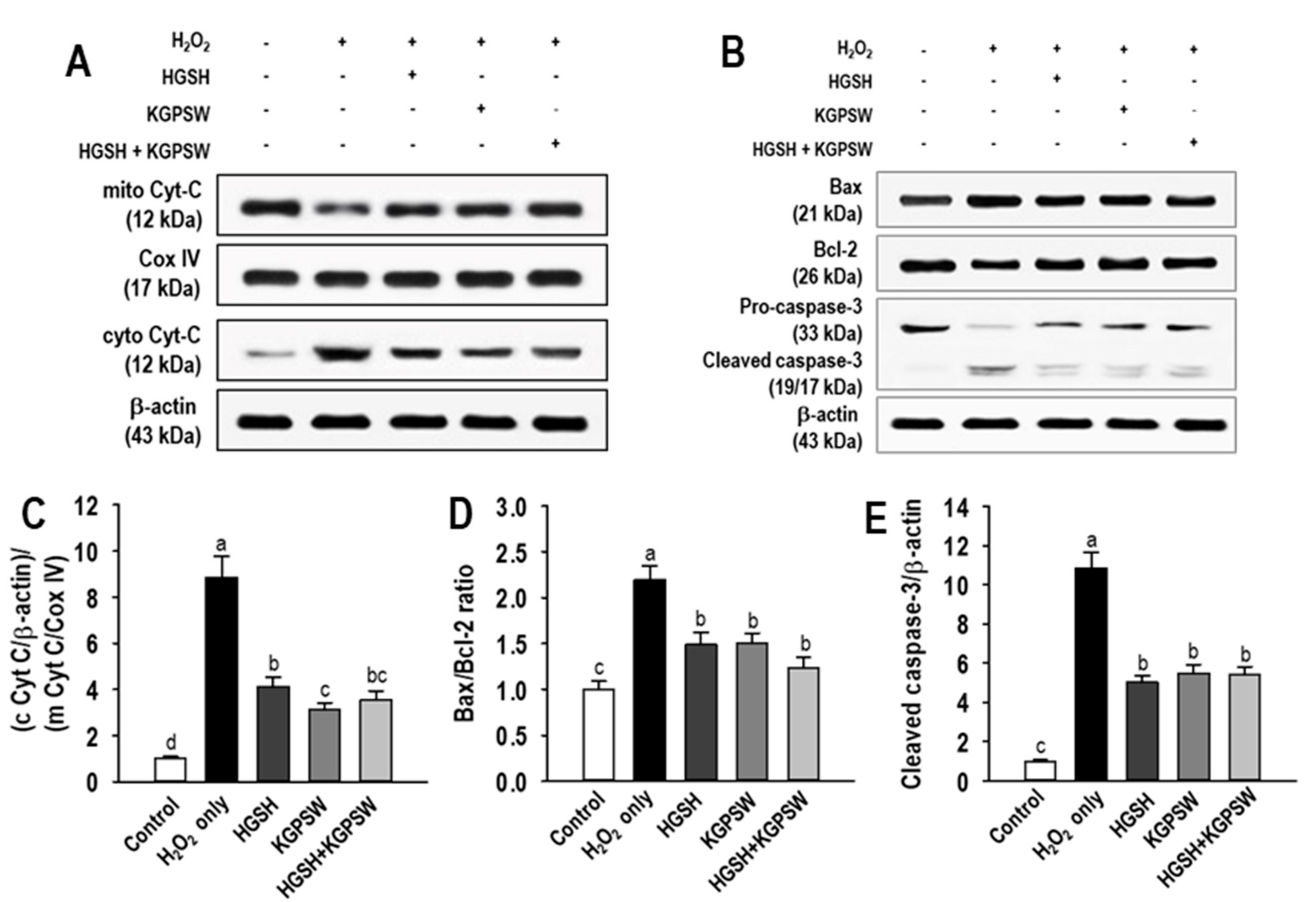
2.4. Antiapoptotic Action of Two BAPs and Their Combination in H2O2-Induced HUVECs Damage
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Edible Seahorse Hydrolysates by Alcalase
4.3. Purification and Identification of Cytoprotective Peptides from Edible Seahorse Hydrolysates
4.4. Peptide Synthesis
4.5. Cell Culture and Peptide Treatment
4.6. Cell Viability Assessment
4.7. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
4.8. Intracellular ROS Determination
4.9. Annexin V-FITC/PI Double Staining
4.10. Hoechst 33342 Staining Analysis
4.11. Western Blot Analysis
4.12. Immunofluorescence Staining of Nrf2 Nuclear Translocation
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, G.-B.; Qin, M.; Ye, J.-X.; Meng, X.-B.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Wang, H.-W.; Sun, X.-B. Inhibitory effects of myricitrin on oxidative stress-induced endothelial damage and early atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 271, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.-L.; Chen, L.-K.; Chang, Y.-L.; Yung, M.-C.; Hsu, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lo, W.-L.; Chen, S.-J.; Ku, H.-H.; Hwang, S.-J. Resveratrol protects human endothelium from H2O2-induced oxidative stress and senescence via SirT1 activation. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010, 17, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davignon, J.; Ganz, P. Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004, 109 (Suppl. 1), III-27–III-32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, Y.; Maruhashi, T.; Noma, K.; Kihara, Y. Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction: Clinical evidence and therapeutic implications. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 24, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.-F.; Huang, G.-D.; Luo, T.; Deng, Z.-Y.; Hu, J.-N. Protective effect of rhein against oxidative stress-related endothelial cell injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Madamanchi, N.R.; Runge, M.S. Mitochondrial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.; Qian, Z.-J.; Kim, S.-K. SHP-1, a novel peptide isolated from seahorse inhibits collagen release through the suppression of collagenases 1 and 3, nitric oxide products regulated by NF-κB/p38 kinase. Peptides 2010, 31, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xu, S. The extract from Hippocampus trimaculatus Leach: Its effect of antithrombosis on rats and ingredients analysis. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 1997, 61, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, B.; Qian, Z.-J.; Kim, S.-K. Purification of a peptide from seahorse, that inhibits TPA-induced MMP, iNOS and COX-2 expression through MAPK and NF-κB activation, and induces human osteoblastic and chondrocytic differentiation. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2010, 184, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himaya, S.; Ryu, B.; Qian, Z.-J.; Kim, S.-K. Paeonol from Hippocampus kuda Bleeler suppressed the neuro-inflammatory responses in vitro via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ryu, B.; Cui, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Lee, B.; Qian, Z.-J. A peptide isolated from Hippocampus abdominalis improves exercise performance and exerts anti-fatigue effects via AMPK/PGC-1α pathway in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 61, 103489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.-G.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, H.-G.; Oh, J.-Y.; Lu, Y.A.; Wang, L.; Rho, S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Low-molecular weight peptides isolated from seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis) improve vasodilation via inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme in vivo and in vitro. Process Biochem. 2020, 95, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, K.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Cho, M. Bigbelly seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis)-derived peptides enhance skeletal muscle differentiation and endurance performance via activated P38MAPK/AKT signalling pathway: An in vitro and in vivo analysis. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Shin, B.-O.; Kim, S.-Y.; Wang, L.; Lee, W.; Kim, Y.T.; Rho, S.; Cho, M.; Jeon, Y.-J. Antioxidant activity of pepsin hydrolysate derived from edible Hippocampus abdominalis in vitro and in Zebrafish models. Korean J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2016, 49, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, Y.; Ahn, C.-B.; Yoon, N.Y.; Nam, K.H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Je, J.-Y. Protective effect of enzymatic hydrolysates from seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis) against H2O2-mediated human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleria, H.A.R.; Gobe, G.; Masci, P.; Osborne, S.A. Marine bioactive compounds and health promoting perspectives; innovation pathways for drug discovery. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.B.; Je, J.Y. Bone health-promoting bioactive peptides. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-R.; Qiu, Y.-T.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptides derived from protein hydrolysate of the marine bivalve mollusk Tergillarca granosa. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Ahn, C.-B.; Moon, S.W.; Je, J.-Y. Purification and antioxidant activities of peptides from sea squirt (Halocynthia roretzi) protein hydrolysates using pepsin hydrolysis. Food Biosci. 2018, 25, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-E.; Ahn, C.-B.; Je, J.-Y. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from enzymatically hydrolyzed ark shell (Scapharca subcrenata). Process Biochem. 2018, 72, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Je, J.-Y.; Kang, N.; Han, E.J.; Um, J.H.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Ahn, G.; Ahn, C.-B. Antihypertensive effects of Ile–Pro–Ile–Lys from krill (Euphausia superba) protein hydrolysates: Purification, identification and in vivo evaluation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Ahn, C.-B.; Je, J.-Y. Partial purification and identification of three antioxidant peptides with hepatoprotective effects from blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) hydrolysate by peptic hydrolysis. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, N.; Chisci, E.; Giovannoni, R. The Role of Hydrogen Peroxide in Redox-Dependent Signaling: Homeostatic and Pathological Responses in Mammalian Cells. Cells 2018, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasanaro, P.; Magenta, A.; Zaccagnini, G.; Cicchillitti, L.; Fucile, S.; Eusebi, F.; Biglioli, P.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Martelli, F. Cyclin D1 degradation enhances endothelial cell survival upon oxidative stress. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1242–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-T.; He, J.-L.; Li, W.-M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.-X.; Bai, X.-F.; Yu, C.; Du, Y.-G. Chitosan oligosaccharides protect human umbilical vein endothelial cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Ahn, C.B.; Nam, K.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Yoon, N.Y.; Je, J.Y. Amino Acid Composition, Antioxidant, and Cytoprotective Effect of Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Hydrolysate through the Inhibition of Caspase-3 Activation in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Endothelial Cell Injury. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.; Francis, N.; Blanchard, C.L.; Schwarz, L.J.; Santhakumar, A.B. Rice Bran Phenolic Compounds Regulate Genes Associated with Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells with Induced Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, G.S.; Baum, J.; Greenberg, M.; Lewis, D.; Abraham, N.G. HO-1 overexpression and underexpression: Clinical implications. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 673, 108073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.K.; Chen, S.E.; Chang, L.C. A Dual Role of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Kim, S.; Izumi, Y.; Izumiya, Y.; Nakao, T.; Miyazaki, H.; Iwao, H. Role of JNK, p38, and ERK in platelet-derived growth factor-induced vascular proliferation, migration, and gene expression. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo Choi, R.; Cheng, M.S.; Shik Kim, Y. Desoxyrhapontigenin up-regulates Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression in macrophages and inflammatory lung injury. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zeng, Y.; He, K.; Luo, Y.; Yu, F. Antioxidant peptides from Mytilus Coruscus on H2O2-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell stress. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 100762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.-Y.; Lee, D.-B. Nelumbo nucifera leaves protect hydrogen peroxide-induced hepatic damage via antioxidant enzymes and HO-1/Nrf2 activation. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritani, C.; Kawakami, K.; Shimoda, H.; Hatanak, T.; Suzaki, E.; Tsuboi, S. Protective effects of rice peptide Oryza Peptide-P60 against oxidative injury through activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13096–13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Fang, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Li, M.; Min, W. Peptides from walnut (Juglans mandshurica Maxim.) protect hepatic HepG2 cells from high glucose-induced insulin resistance and oxidative stress. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8112–8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.-M.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Cytoprotective effect of antioxidant pentapeptides from the protein hydrolysate of swim bladders of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) against H2O2-mediated human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Huang, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J. Rice bioactive peptide binding with TLR4 to overcome H2O2-induced injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through NF-κB signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.-B.; Shin, T.-S.; Seo, H.K.; Je, J.-Y. Phenolic composition and antioxidant effect of aqueous extract of Arisaema cum Bile, the oriental herb medicine, in human fibroblast cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 34, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.; Ahn, C.-B.; Je, J.-Y. Cytoprotective Role of Edible Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis)-Derived Peptides in H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020086
Oh Y, Ahn C-B, Je J-Y. Cytoprotective Role of Edible Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis)-Derived Peptides in H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(2):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020086
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Yunok, Chang-Bum Ahn, and Jae-Young Je. 2021. "Cytoprotective Role of Edible Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis)-Derived Peptides in H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells" Marine Drugs 19, no. 2: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020086
APA StyleOh, Y., Ahn, C.-B., & Je, J.-Y. (2021). Cytoprotective Role of Edible Seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis)-Derived Peptides in H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Marine Drugs, 19(2), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020086





