Hemimycalins C–E; Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Alkaloids with Hydantoin and 2-Iminoimidazolidin-4-one Backbones from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Materials
3.3. Purification of Compounds 1–3
3.4. Spectral Data of the Compounds
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- Hemimycalin E (3) Yellow powder; IR γmax (film) 3375, 1723, 1647, 1595 cm−1; NMR data: see Table 5; HRESIMS m/z 311.1118 (calculated for C14H16N4O3Na [M + Na]+, 311.1114).
3.5. Biological Evaluation of the Compounds
3.5.1. Cytotoxicity of the Compounds
Culture of Cell Lines
Evaluation of Antiproliferative Activity
3.5.2. Disk Diffusion Assay
3.5.3. Evaluation of the MIC Values
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 362–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine natural products and related compounds in clinical and advanced preclinical trials. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1216–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, B.; Liu, N.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Lyu, C.; Chen, T. CMNPD: A comprehensive marine natural products database towards facilitating drug discovery from the ocean. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D509–D515. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Almagthali, H.; Shaala, L.A.; Schmidt, E.W. Secondary metabolites of the genus Didemnum: A comprehensive review of chemical diversity and pharmacological properties. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laport, M.S.; Santos, O.C.S.; Muricy, G. Marine sponges: Potential sources of new antimicrobial drugs. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little, R.D.; McIntosh, J.M.; Newman, D.J.; Potts, B.C.; Shuster, D.E. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.midwestern.edu/departments/marinepharmacology/clinical-pipeline (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Ohtani, I.; Kusumi, T.; Kakisawa, H.; Kashman, Y.; Hirsh, S. Structure and chemical properties of ptilomycalin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 8472–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashman, Y.; Hirsh, S.; McConnell, O.J.; Ohtani, I.; Kusumi, T.; Kakisawa, H. Ptilomycalin A: A novel polycyclic guanidine alkaloid of marine origin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 8925–8926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Shaala, L.A.; Alshali, K.Z. Bioactive hydantoin alkaloids from the Red Sea marine sponge Hemimycale arabica. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6609–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.A.; Lemke, T.L. (Eds.) Foye’s Principles of Medicinal Chemistry, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Malawska, B. New anticonvulsant agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrtus, H.; Obniska, J.; Czopek, A.; Kaminski, K.; Pawlowski, M. Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of new N-Mannich bases derived from 5-cyclopropyl-5-phenyl- and 5-cyclopropyl-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-imidazolidine-2,4-diones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6149–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiallo, M.M.L.; Kozlowski, H.; Garnier-Suillerot, A. Mitomycin antitumor compounds. Part 1. CD studies on their molecular structure. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoriou, M.; Noble, M.E.M.; Watson, K.A.; Garman, E.F.; Krulle, T.M.; Delafuente, C.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Oikonomakos, N.G.; Johnson, L.N. The structure of a glycogen phosphorylase glucopyranose spirohydantoin complex at 1.8 angstrom resolution and 100 k—The role of the water structure and its contribution to binding. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiozaki, M. Syntheses of hydantocidin and C-2 thioxohydantocidin. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.A.; Hill, R.A.; Kaddoumi, A.; El Sayed, K.A. Discovery of novel GSK-3 beta inhibitors with potent in vitro and in vivo activities and excellent brain permeability using combined ligand- and structure-based virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8534–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudit, M.; Khanfar, M.A.; Muralidharan, A.; Thomas, S.; Shah, G.V.; van Soest, R.W.; El Sayed, K.A. Discovery, design, and synthesis of anti-metastatic lead phenylmethylene hydantoins inspired by marine natural products. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaala, L.A.; Alzughaibi, T.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Youssef, D.T.A. Fusaripyridines A and B; highly oxygenated antimicrobial alkaloid dimers featuring an unprecedented 1,4-Bbs(2-hydroxy-1,2-dihydropyridin-2-yl)butane-2,3-dione core from the marine fungus Fusarium sp. LY019. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Shaala, L.A. Psammaceratin A: A cytotoxic psammaplysin dimer featuring an unprecedented (2Z,3Z)-2,3-Bis(aminomethylene)succinamide backbone from the Red Sea sponge Pseudoceratina arabica. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Asfour, H.Z.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Shaala, L.A. Magnificines A and B, antimicrobial marine alkaloids featuring a tetrahydrooxazolo[3,2-a]azepine-2,5(3H,6H)-dione backbone from the Red Sea sponge Negombata magnifica. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A. Pseudoceratonic acid and moloka’iamine derivatives from the Red Sea Verongiid sponge Pseudoceratina arabica. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, X.C.A.; Longeon, K.A.; Le, M.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Chau, V.M.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M. Antioxidant benzylidene 2-aminoimidazolones from the Mediterranean sponge Phorbas topsenti. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9256–9259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Aalbersberg, W.; Meo, S.; Moreira da Rocha, R.; Ireland, C.M. The isolation and synthesis of polyandrocarpamines A and B. Two new 2-aminoimidazolone compounds from the Fijian ascidian, Polyandrocarpa sp. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 3263–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guella, G.; Mancini, I.; Zibrowius, H.; Pietra, F. Novel aplysinopsin-type alkaloids from Scleractinian corals of the family Dendrophylliidae of the Mediterranean and the Philippines. Configurational-assignment criteria, stereospecific synthesis, and photoisomerization. Helv. Chim. Acta 1988, 7, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A. Cytotoxic psammaplysin analogues from the Verongid Red Sea sponge Aplysinella species. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Mooberry, S.L. Hurghadolide A and swinholide I, potent actin-microfilament disrupters from the Red Sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, J.F. The Disc Susceptibility Test. In Antibiotics in Laboratory Medicine; Lorian, V., Ed.; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1980; pp. 24–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kiehlbauch, J.A.; Hannett, G.E.; Salfinger, M.; Archinal, W.; Monserrat, C.; Carlyn, C. Use of the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards Guidelines for Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Testing in New York State Laboratories. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Alzughaibi, T.A.; Elhady, S.S. Antimicrobial chlorinated 3-phenylpropanoic acid derivatives from the Red Sea marine actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor LY001. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. CLSI Documents M07-A9. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 9th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
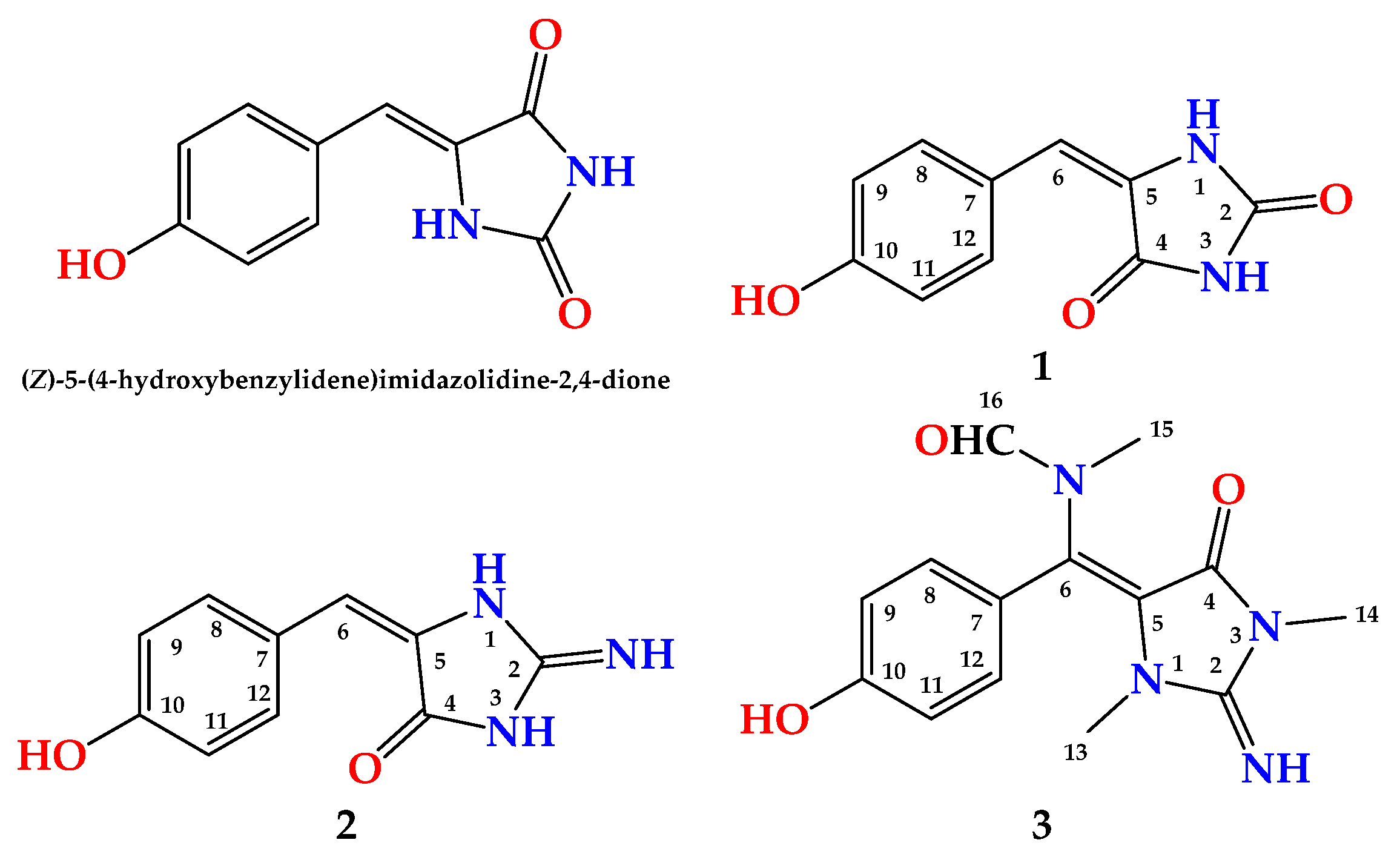
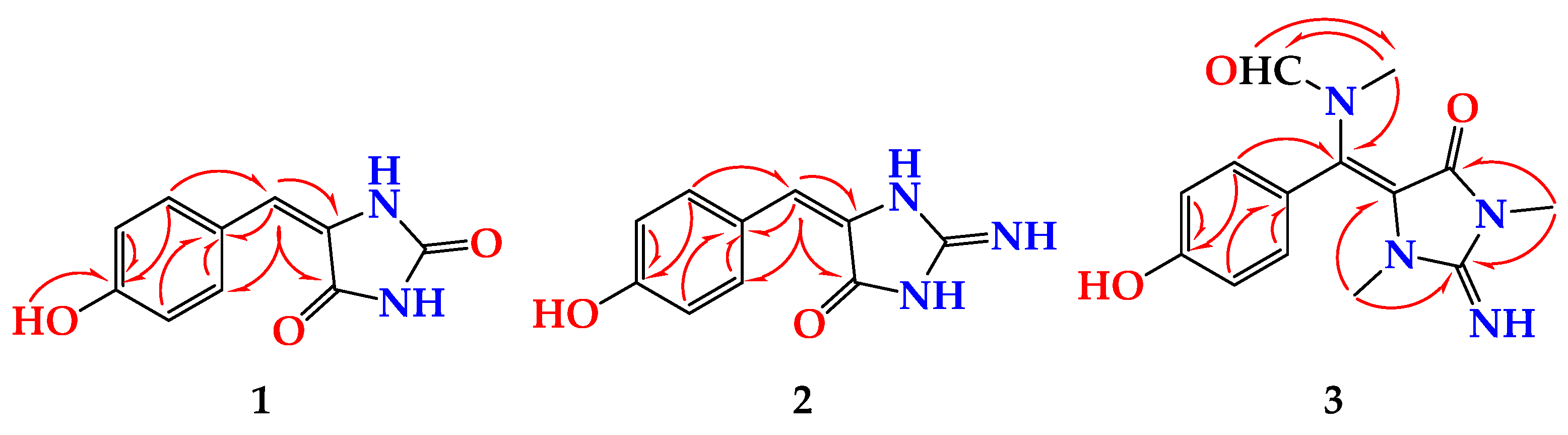
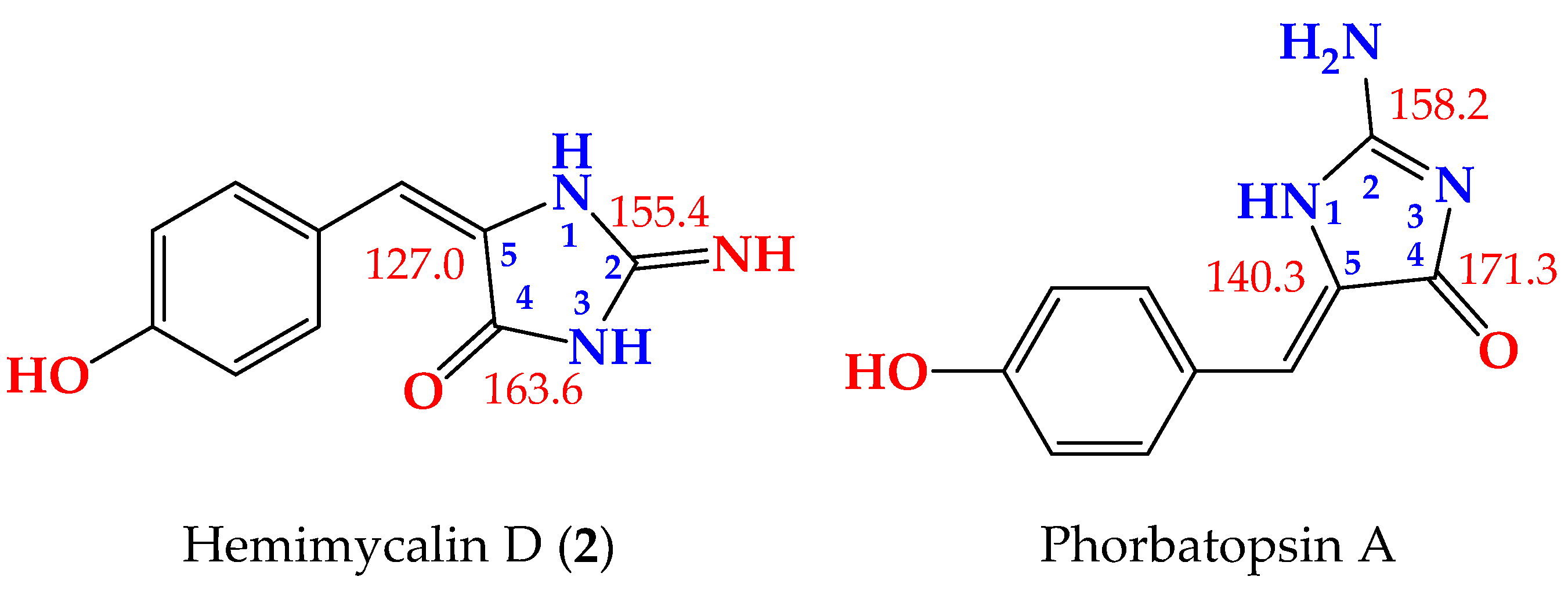
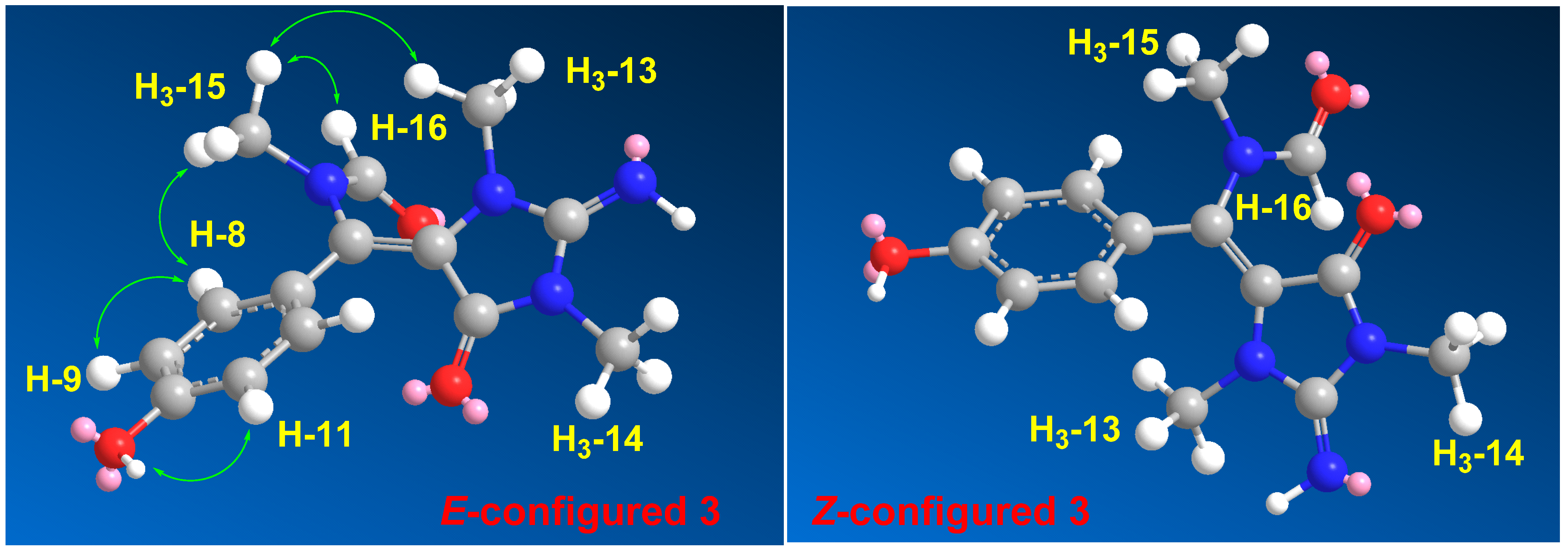

| Position | δC, Type | δH (Mult., J in Hz) | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 153.6, C | ||
| 4 | 163.6, C | ||
| 5 | 127.0, C | ||
| 6 | 116.8, CH | 6.23 (s) | C-4, C-8, C-12 |
| 7 | 124.1, C | ||
| 8 | 131.8, CH | 7.82 (d, 9.0) | C-6, C-7, C-10, C-12 |
| 9 | 115.0, CH | 6.72 (d, 9.0) | C-7, C-10, C-11 |
| 10 | 158.0, C | ||
| 11 | 115.0, CH | 6.72 (d, 9.0) | C-7, C-10, C-9 |
| 12 | 131.8, CH | 7.82 (d, 9.0) | C-6, C-7, C-10, C-8 |
| NH, OH | 10.50 (br hump) |
| Position | (E)-1 | (Z)-1 a | Δδ (E−Z) in ppm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH, (Mult., J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH, (Mult., J in Hz) | ΔδC(E−Z) | ΔδH(E−Z) | |
| 2 | 153.6, C | 155.7, C | −2.1 | |||
| 4 | 163.6, C | 165.7, C | −2.1 | |||
| 5 | 127.0, C | 125.3, C | +1.7 | |||
| 6 | 116.8, CH | 6.23 (s) | 109.2, CH | 6.33 (s) | +7.6 | −0.10 |
| 7 | 124.1, C | 123.8, C | +0.3 | |||
| 8 | 131.8, CH | 7.82 (d, 9.0) | 131.2, CH | 7.46 (d, 9.0) | +0.6 | +0.36 |
| 9 | 115.0, CH | 6.72 (d, 9.0) | 115.6, CH | 6.76 (d, 9.0) | −0.6 | −0.04 |
| 10 | 158.0, C | 158.0, C | 0.0 | |||
| 11 | 115.0, CH | 6.72 (d, 9.0) | 115.6, CH | 6.76 (d, 9.0) | −0.6 | −0.04 |
| 12 | 131.8, CH | 7.82 (d, 9.0) | 131.2, CH | 7.46 (d, 9.0) | +0.6 | +0.36 |
| Position | δC, Type | δH (Mult., J in Hz) | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 155.4, C | ||
| 4 | 163.2, C | ||
| 5 | 126.5, C | ||
| 6 | 116.5, CH | 6.23 (s) | C-4, C-8, C-12 |
| 7 | 123.5, C | ||
| 8 | 131.6, CH | 7.43 (d, 9.0) | C-6, C-7, C-10, C-12 |
| 9 | 114.8, CH | 6.72 (d, 9.0) | C-7, C-10, C-11 |
| 10 | 157.9, C | ||
| 11 | 114.8, CH | 6.72 (d, 9.0) | C-7, C-10, C-9 |
| 12 | 131.6, CH | 7.43 (d, 9.0) | C-6, C-7, C-10, C-8 |
| NH, OH | 10.50 (br hump) |
| Position | δC, Type | δH (Mult., J in Hz) | HMBC | NOESY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 153.6, C | |||
| 4 | 149.7, C | |||
| 5 | 93.9, C | |||
| 6 | 126.1, C | |||
| 7 | 124.5, C | |||
| 8 | 131.3, CH | 7.48 (d, 8.4) | C-6, C-7, C-10 | H-9, OH, H3-15 |
| 9 | 115.2, CH | 6.73 (d, 8.4) | C-7, C-10 | H-8 |
| 10 | 159.8, C | |||
| OH | 10.78 (brs) | C-10 | H-9, H-11 | |
| 11 | 115.2, CH | 6.73 (d, 8.4) | C-7, C-10 | H-12, OH |
| 12 | 131.3, CH | 7.48 (d, 8.4) | C-6, C-7, C-10 | H-11, H3-15 |
| 13 | 31.1, CH3 | 2.79 (s) | C-2, C-5 | H3-15 |
| 14 | 29.4, CH3 | 3.21 (s) | C-2, C-4 | |
| 15 | 33.6, CH3 | 2.83 (s) | C-6, C-16 | H-8, H-12, H-16, H3-13 |
| 16 | 166.3, CH | 7.91 (s) | C-15 | H3-15 |
| Compound | IC50 (μM) (Mean + SEM) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | HeLa | HCT 116 | |
| 1 | 28.5 ± 0.21 | ≥25.0 | 18.6 ± 0.12 |
| 2 | 31.7 ± 0.25 | ≥25.0 | 17.1 ± 0.09 |
| 3 | 21.5 ± 0.18 | ≥25.0 | 8.6 ± 0.06 |
| 5-FU b | 13.0 ± 0.30 | 12.3 ± 0.25 | 4.6 ± 0.23 |
| Compound | Inhibition Zones (mm) and MIC Values (µM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans | MIC (µM) | E. coli | MIC (µM) | S. aureus | |
| 1 | 22 | 8 | 17 | 8 | NI |
| 2 | 20 | 8 | 18 | 8 | NI |
| 3 | 20 | 8 | 17 | 8 | NI |
| Ciprofloxacin a | NT | 30 | 0.08 | 22 | |
| Ketoconazole b | 30 | 0.26 | NT | NT | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A. Hemimycalins C–E; Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Alkaloids with Hydantoin and 2-Iminoimidazolidin-4-one Backbones from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale sp. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120691
Shaala LA, Youssef DTA. Hemimycalins C–E; Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Alkaloids with Hydantoin and 2-Iminoimidazolidin-4-one Backbones from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale sp. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(12):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120691
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaala, Lamiaa A., and Diaa T. A. Youssef. 2021. "Hemimycalins C–E; Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Alkaloids with Hydantoin and 2-Iminoimidazolidin-4-one Backbones from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale sp." Marine Drugs 19, no. 12: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120691
APA StyleShaala, L. A., & Youssef, D. T. A. (2021). Hemimycalins C–E; Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Alkaloids with Hydantoin and 2-Iminoimidazolidin-4-one Backbones from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale sp. Marine Drugs, 19(12), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120691







