Echinochrome A Protects against Ultraviolet B-induced Photoaging by Lowering Collagen Degradation and Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in Hairless Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
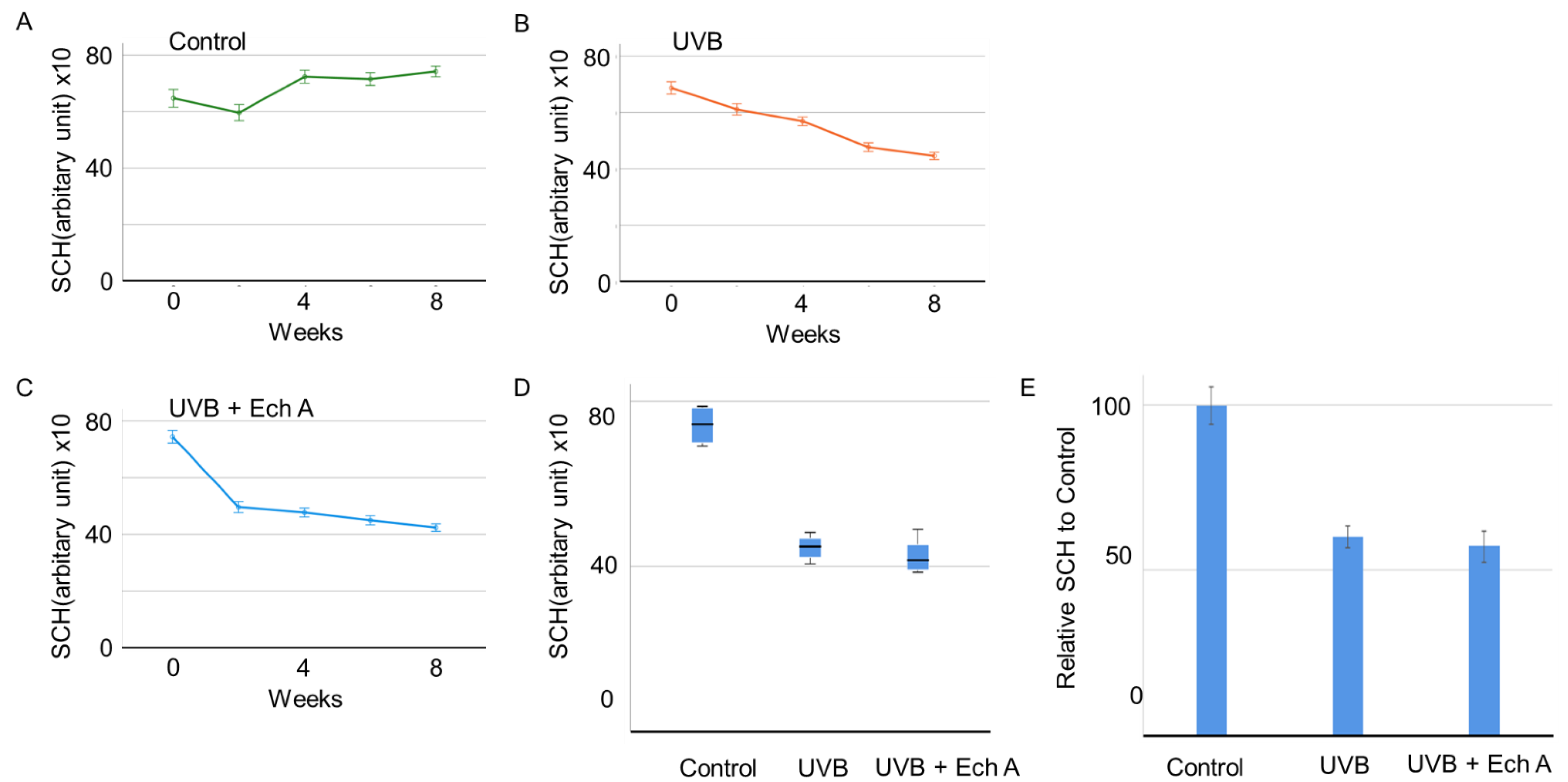
2.1. Effects of Ech A on the Skin Physiological Function
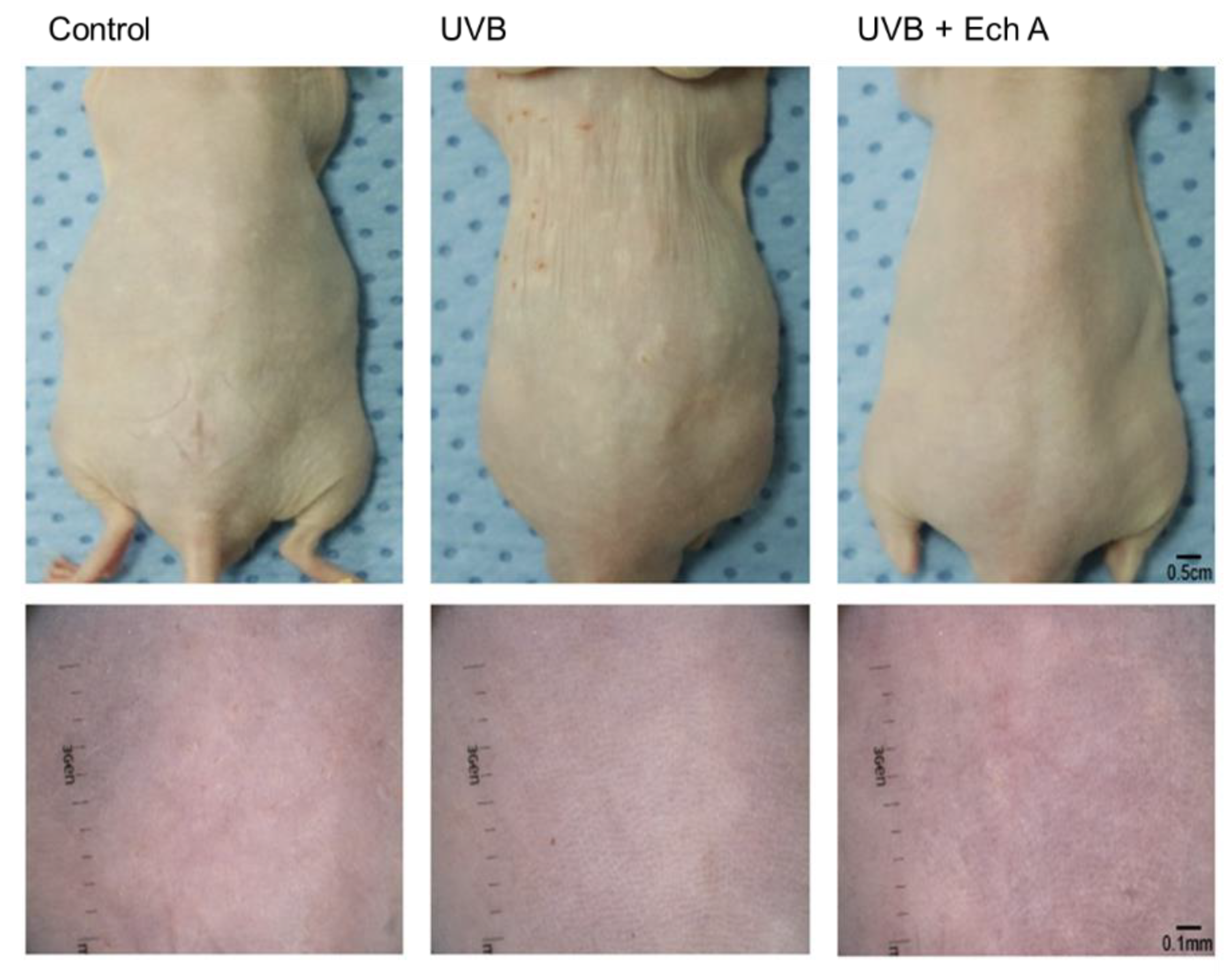
2.2. Effects of Ech A on the Macroscopic Appearance of the Mouse Skin
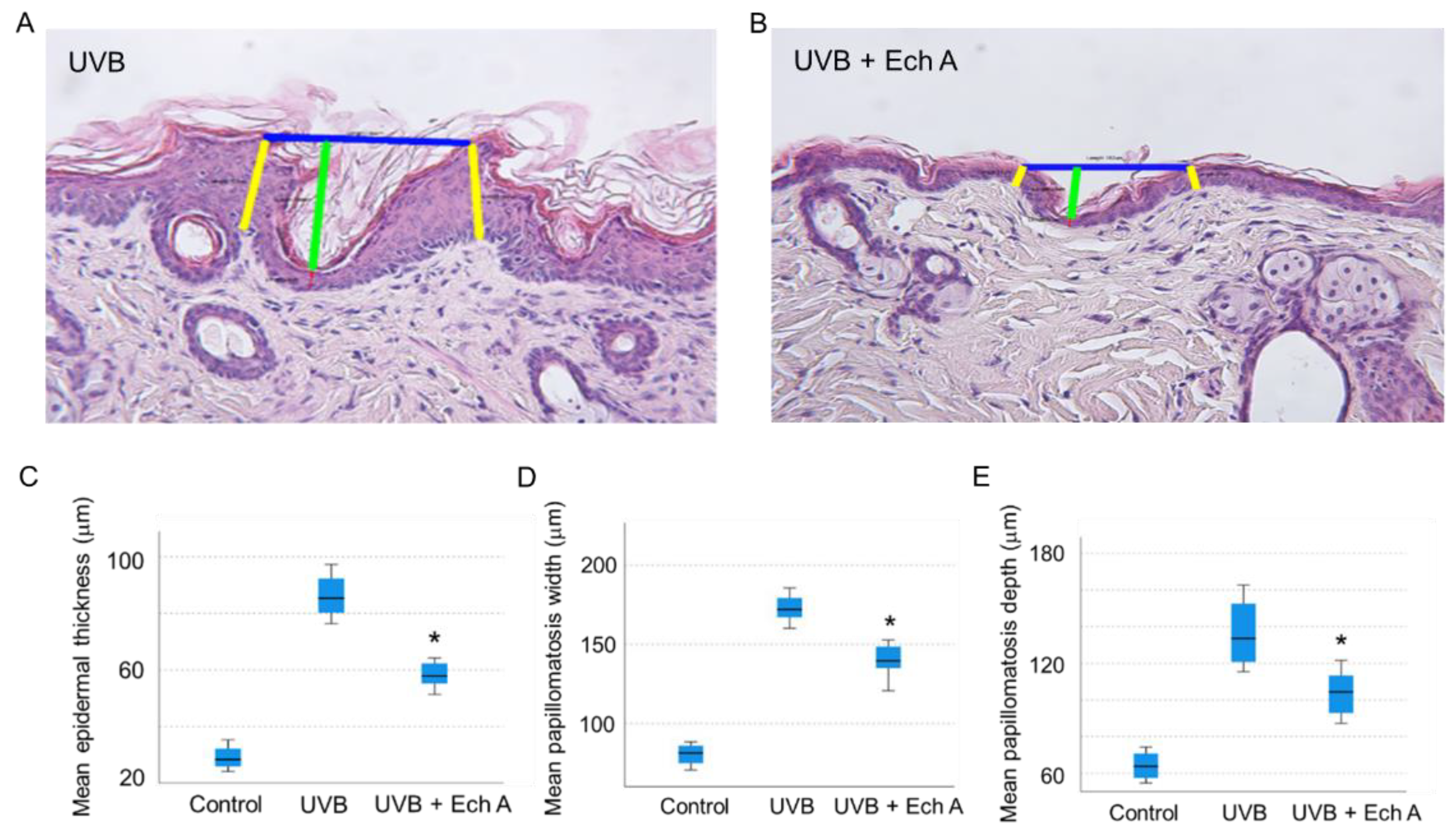
2.3. Effects of Ech A on the Histopathologic Features of the Mouse Skin
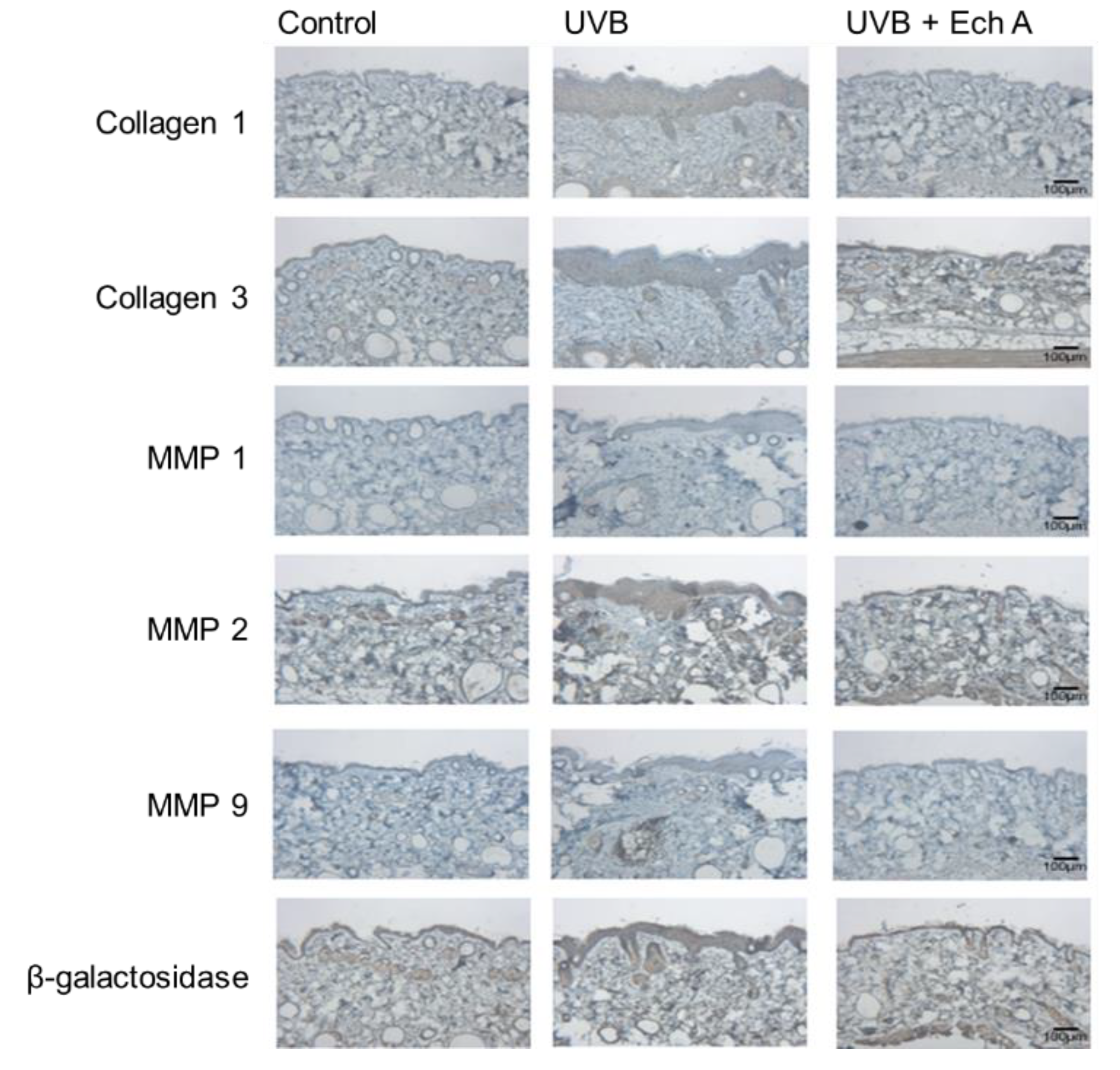
2.4. Effects of Ech A on the Immunohistochemical Expression Levels of Collagen 1,3, MMP 1,2,9 and Beta-Galactosidase of the Mouse Skin
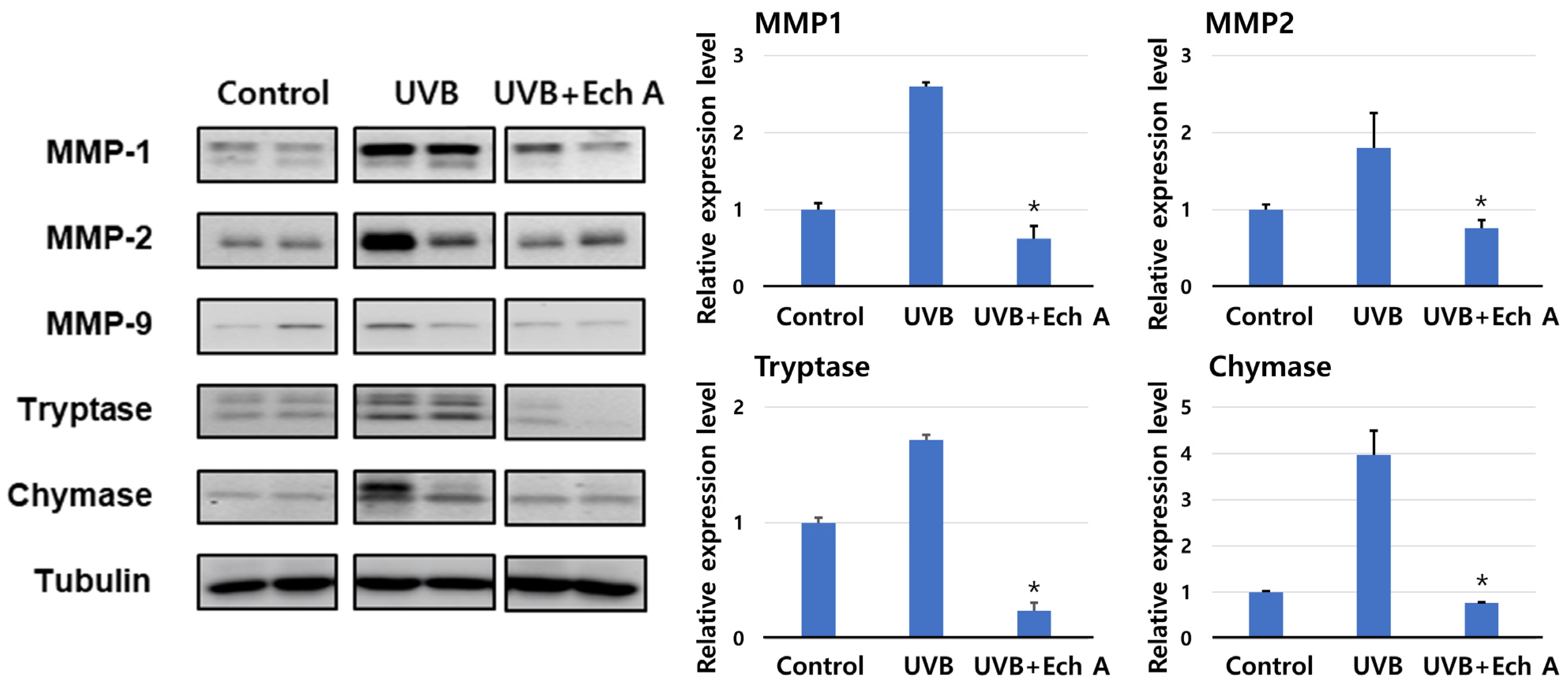
2.5. Effects of Ech A on the Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase, Tryptase, and Chymase of the Mouse Skin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Ech A
4.2. Care and Use of Animals
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. UV Irradiation
4.5. Setting 1 MED
4.6. Intraperitoneal Injection
4.7. Clinical Observation of skin Condition
4.8. Measurement of Transepidermal Water Loss, Stratum Corneum Hydration
4.9. Histological Analysis
4.10. Western Blot
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shikov, A.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.; Krishtopina, A.S.; Makarov, V.G. Naphthoquinone pigments from sea urchins: Chemistry and pharmacology. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 509–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.V.; Ivanova, M.V.; Levitsky, D.O. Echinochrome, a naturally occurring iron chelator and free radical scavenger in artificial and natural membrane systems. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buĭmov, G.A.; Maksimov, I.V.; Perchatkin, V.A.; Repin, A.N.; Afanas’ev, S.A.; Markov, V.A.; Karpov, R.S. Vliianie bioantioksidanta gistrokhroma na povrezhdenie miokarda pri reperfuzionnoĭ terapii u bol’nykh infarktom miokardom [Effect of the bioan-tioxidant histochrome on myocardial injury in reperfusion therapy on patients with myocardial infarction]. Ter Arkh. 2002, 74, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Egorov, E.A.; Alekhina, V.A.; Volobueva, T.M.; Fedoreev, S.A.; Mishchenko, N.P.; Kol’tsova, E.A. Novyĭ bioantioksidant "Gistokhrom" v klinike glaznykh bolezneĭ [Histochrome, a new antioxidant, in the treatment of ocular diseases]. Vestn. -talmol. 1999, 115, 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Prokopov, I.A.; Kovaleva, E.L.; Minaeva, E.D.; Pryakhina, E.A.; Savin, E.V.; Gamayunova, A.V.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Makarov, V.G.; Shikov, A.N. Animal-derived medicinal prod-ucts in Russia: Current nomenclature and specific aspects of quality control. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 240, 111933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.K.; Song, I.S.; Lee, S.J.; Ko, K.S.; Rhee, B.D.; Kim, N.; Mishchenko, N.P.; Fedoryev, S.A.; Stonik, V.A.; et al. Echino-chrome A protects mitochondrial function in cardiomyocytes against cardiotoxic drugs. Mar. Drugs. 2014, 12, 2922–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayed, D.A.; Soliman, A.M.; Fahmy, S.R. Echinochrome pigment as novel therapeutic agent against experimentally—Induced gastric ulcer in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennikov, A.; Kitaichi, N.; Noda, K.; Mizuuchi, K.; Ando, R.; Dong, Z.; Fukuhara, J.; Kinoshita, S.; Namba, K.; Ohno, S.; et al. Ame-lioration of endotoxin-induced uveitis treated with the sea urchin pigment echinochrome in rats. Mol. Vis. 2014, 20, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.-J.; Seo, Y.; Ahn, J.-S.; Shin, Y.Y.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, H.K.; Han, J.; Mishchenko, N.P.; Fedoreyev, S.A.; Stonik, V.A.; et al. Echinochrome A Reduces Colitis in Mice and Induces In Vitro Generation of Regulatory Immune Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Vasileva, E.; Mishchenko, N.; Fedoreyev, S.; Han, J. Multifaceted Clinical Effects of Echinochrome. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittié, L.; Fisher, G.J. UV-light-induced signal cascades and skin aging. Ageing. Res. Rev. 2002, 1, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Datta, S.C.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultravi-olet light. N Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, H. Role of antioxidants in the skin: Anti-aging effects. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 58, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, Z.A.M.; Ibrahim, F.; Rashid, N.N.; Razif, M.F.M.; Yusof, R. The Importance of Some Plant Extracts as Skin Anti-aging Re-sources: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 18, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavker, R.M.; Gerberick, G.; Veres, D.; Irwin, C.J.; Kaidbey, K.H. Cumulative effects from repeated exposures to suberythemal doses of UVB and UVA in human skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1995, 32, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruk, G.; Del Giudice, R.; Rigano, M.M.; Monti, D.M. Antioxidants from Plants Protect against Skin Photoaging. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sotiropoulou, G.; Zingkou, E.; Pampalakis, G. Redirecting drug repositioning to discover innovative cosmeceuticals. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, W.-G.; Park, W.-S.; Sim, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-J. Protective effects of dietary soy isoflavones against UV-induced skin-aging in hairless mouse model. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.S.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, S.I.; Lee, H.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Jang, M.J.; Son, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, C.H.; Kim, B.H.; et al. UV radia-tion-induced skin aging in hairless mice is effectively prevented by oral intake of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) fruit blend for 6 weeks through MMP suppression and increase of SOD activity. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davinelli, S.; Bertoglio, J.C.; Polimeni, A.; Scapagnini, G. Cytoprotective Polyphenols Against Chronological Skin Aging and Cutaneous Photodamage. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, M.K.; Han, M.D. Inhibitory effect of Hyaluronidase and DPPH radical scavenging activity using extraction of Equisetum arvens. Europ. J. Adv. Res. Biologic. Life Sci. 2015, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Song, E.; Chung, H.; Shim, E.; Jeong, J.K.; Han, B.K.; Choi, H.J.; Hwang, J. Gastrodia elata Blume Extract Modulates Antioxidant Ac-tivity and Ultraviolet A-Irradiated Skin Aging in Human Dermal Fibroblast Cells. J. Med. Food. 2016, 19, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.; Sim, Y.; Lee, W.; Sung, S.H.; Oh, M.S. Protection on Skin Aging Mediated by Antiapoptosis Effects of the Water Lily (Nymphaea Tetragona Georgi) via Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging in Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. Pharmacology 2016, 97, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbossa, W.A.C.; Campos, P.M.B.G.M. Euterpe oleracea, Matricaria chamomilla, and Camellia sinensis as promising ingredi-ents for development of skin care formulations. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2016, 83, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.; Heo, S.-J.; Dias, M.; Madusanka, D.; Han, E.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Sanjeewa, K.; Lee, K.; Ahn, G. (−)-Loliolide Isolated from Sargassum horneri Abate UVB-Induced Oxidative Damage in Human Dermal Fibroblasts and Subside ECM Degradation. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Park, C.W.; Kim, B.; Sim, H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, J.C.; Yang, G.E.; Her, Y. Laminarin Attenuates Ultraviolet-Induced Skin Damage by Re-ducing Superoxide Anion Levels and Increasing Endogenous Antioxidants in the Dorsal Skin of Mice. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-I.; Oh, W.-S.; Song, P.H.; Yun, S.; Kwon, Y.-S.; Lee, Y.J.; Ku, S.-K.; Song, C.-H.; Oh, T.-H. Anti-Photoaging Effects of Low Molecular-Weight Fucoidan on Ultraviolet B-Irradiated Mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Shilnikova, K.; Park, J.E.; Hyun, Y.J.; Zhen, A.X.; Kang, H.K.; Koh, Y.S.; Ahn, M.J.; et al. The Red Algae Compound 3-Bromo-4,5-dihydroxybenzaldehyde Protects Human Keratinocytes on Oxidative Stress-Related Molecules and Pathways Activated by UVB Irradiation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Kim, E.-A.; Son, K.-T.; Jeon, Y.-J. Bioactive properties and potentials cosmeceutical applications of phlorotannins isolated from brown seaweeds: A review. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 162, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutmann, J.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Pan, X.; Crawford, M.; Sore, G.; Seite, S. Pollution and skin: From epidemiological and mechanistic studies to clinical implications. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 76, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, T.L.; Van Lonkhuyzen, D.R.; Dawson, R.A.; Kimlin, M.; Upton, Z. Characterization of a Human Skin Equivalent Model to Study the Effects of Ultraviolet B Radiation on Keratinocytes. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2014, 20, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amano, S. Possible Involvement of Basement Membrane Damage in Skin Photoaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takema, Y.; Hattori, M.; Aizawa, K. The relationship between quantitative changes in collagen and formation of wrinkles on hairless mouse skin after chronic UV irradiation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1996, 12, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissett, D.; Hannonand, D.; Orr, T. An animal model of solar-aged skin: Histological, physical, and visible changes in uv-irradiated hairless mouse skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 1987, 46, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, H.; Brown, S.; Danby, S.; Flohr, C. Research Techniques Made Simple: Transepidermal Water Loss Measurement as a Research Tool. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2295–2300.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, C.-H.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, J.-P.; Yoo, I.D.; Chung, J.H. Prevention of UV Radiation–Induced Premature Skin Aging in Hairless Mice by the Novel Compound Melanocin A. Photochem. Photobiol. 2006, 82, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, S.J.; Edmonds, S.H.; Giddens, L.D.; Learn, D.B. The hairless mouse model of photoaging: Evaluation of the relationship between dermal elastin, collagen, skin thickness and wrinkles. Photochem. Photobiol. 1992, 56, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosline, J.; Lillie, M.; Carrington, E.; Guerette, P.; Ortlepp, C.; Savage, K. Elastic proteins: Biological roles and mechanical proper-ties. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 357, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyachi, Y. Photoaging from an oxidative standpoint. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1995, 9, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.X.; Hong, X.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liao, K.H. Tempol, one of nitroxides, is a novel ultraviolet-A1 radiation protector for human der-mal fibroblasts. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2005, 37, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, M.E.; Girard, M.T.; Matsubara, M. Collagenolytic/gelatinolytic enzymes in corneal wound healing. Acta Ophthalmol. Suppl. 1992, 70, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azar, D.T.; Hahn, T.W.; Jain, S.; Yeh, Y.C.; Stetler-Stevensen, W.G. Matrix metalloproteinases are expressed during wound healing after excimer laser keratectomy. Cornea 1996, 15, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortino, V.; Maioli, E.; Torricelli, C.; Davis, P.; Valacchi, G. Cutaneous MMPs are differently modulated by environmental stressors in old and young mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 173, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenneisen, P.; Wenk, J.; Wlaschek, M.; Krieg, T.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Activation of p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase is an essential step in the DNA damage-dependent signaling pathway responsible for the ultraviolet B-mediated increase in in-terstitial collagenase (MMP-1) and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) protein levels in human dermal fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4336–4344. [Google Scholar]
- Visse, R.; Nagase, H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Structure, function, and bio-chemistry. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, N.C.; Hu, M.L. The limitations and validities of senescence associated-beta-galactosidase activity as an aging marker for human foreskin fibroblast Hs68 cells. Exp Gerontol. 2005, 40, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seol, J.E.; Ahn, S.W.; Seol, B.; Yun, H.R.; Park, N.; Kim, H.K.; Vasileva, E.A.; Mishchenko, N.P.; Fedoreyev, S.A.; Stonik, V.A.; et al. Echinochrome A Protects against Ultraviolet B-induced Photoaging by Lowering Collagen Degradation and Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in Hairless Mice. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19100550
Seol JE, Ahn SW, Seol B, Yun HR, Park N, Kim HK, Vasileva EA, Mishchenko NP, Fedoreyev SA, Stonik VA, et al. Echinochrome A Protects against Ultraviolet B-induced Photoaging by Lowering Collagen Degradation and Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in Hairless Mice. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(10):550. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19100550
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeol, Jung Eun, Sang Woo Ahn, Bomin Seol, Hyeong Rok Yun, Nammi Park, Hyoung Kyu Kim, Elena A. Vasileva, Natalia P. Mishchenko, Sergey A. Fedoreyev, Valentin A. Stonik, and et al. 2021. "Echinochrome A Protects against Ultraviolet B-induced Photoaging by Lowering Collagen Degradation and Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in Hairless Mice" Marine Drugs 19, no. 10: 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19100550
APA StyleSeol, J. E., Ahn, S. W., Seol, B., Yun, H. R., Park, N., Kim, H. K., Vasileva, E. A., Mishchenko, N. P., Fedoreyev, S. A., Stonik, V. A., & Han, J. (2021). Echinochrome A Protects against Ultraviolet B-induced Photoaging by Lowering Collagen Degradation and Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in Hairless Mice. Marine Drugs, 19(10), 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19100550







