Sustainable Low-Volume Analysis of Environmental Samples by Semi-Automated Prioritization of Extracts for Natural Product Research (SeaPEPR)
Abstract
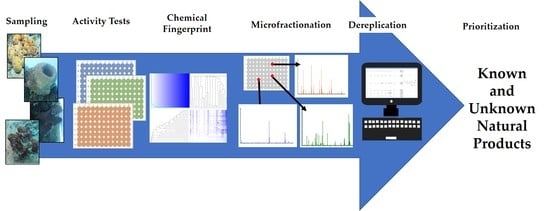
1. Introduction
2. Results
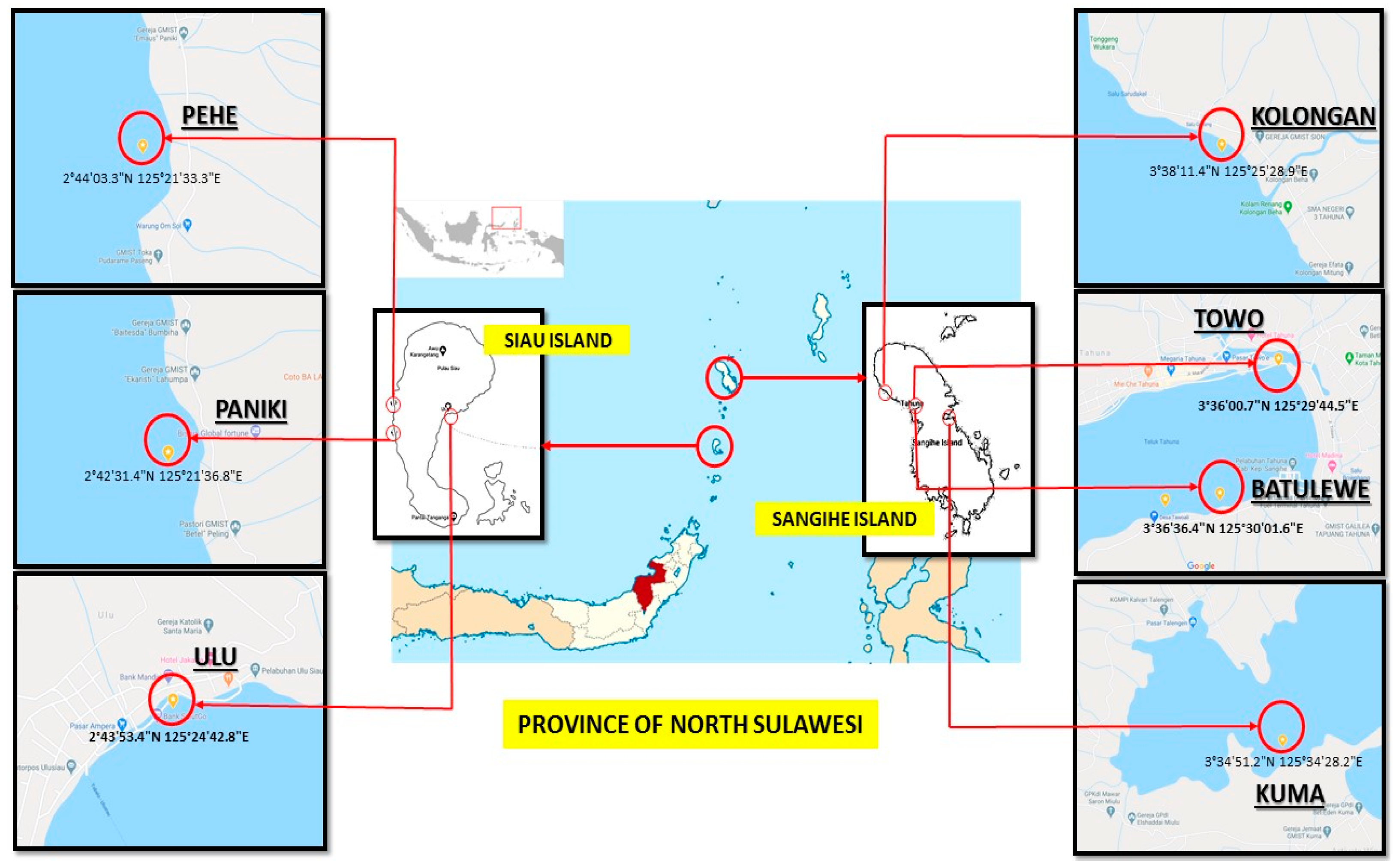
2.1. Sample Collection and Extract Generation
2.2. Bioactivity Assessment—Microbroth Dilution Assays
2.3. Prioritization—Metabolic Fingerprinting
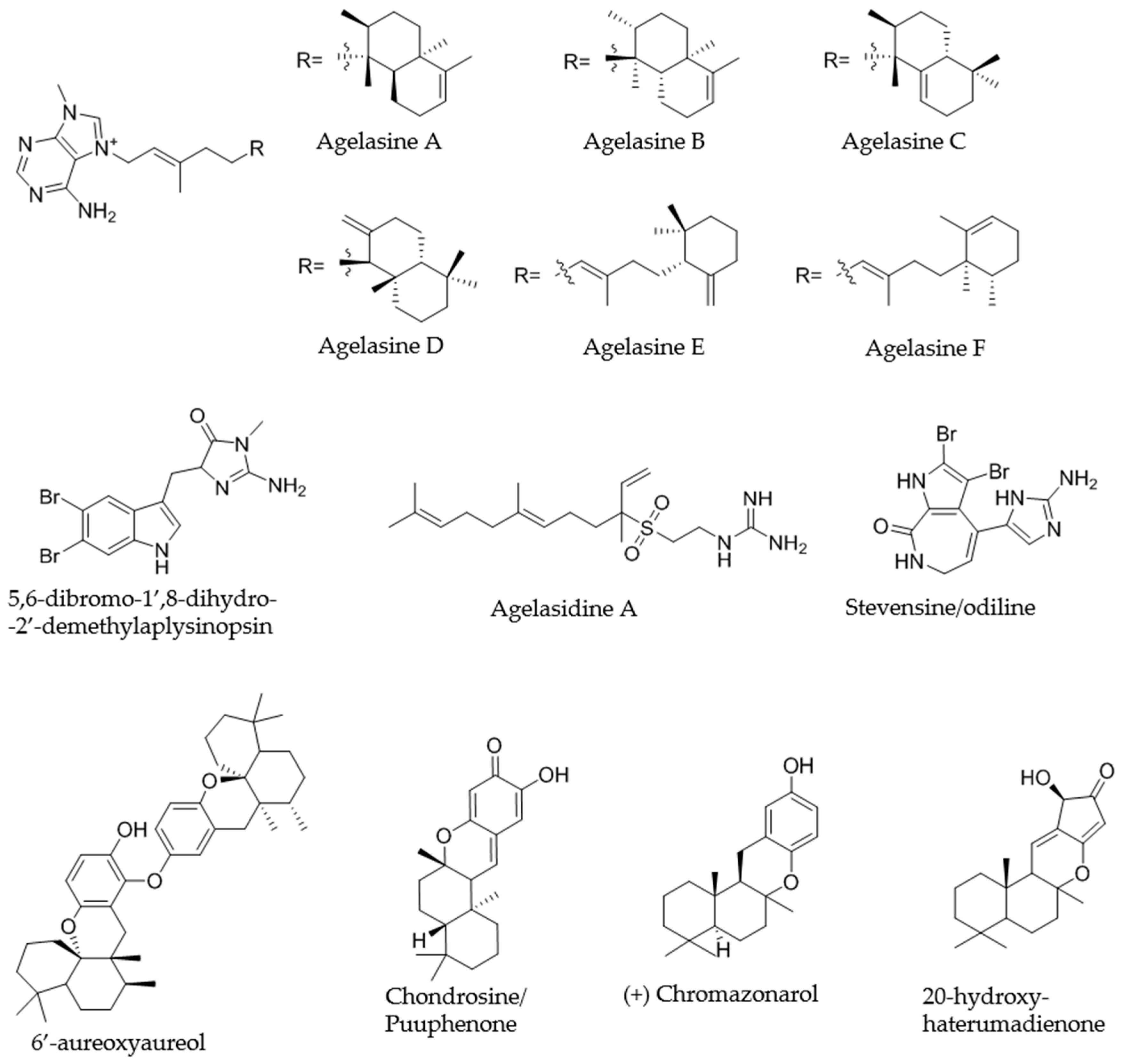
2.4. Dereplication of Bioactive Compounds—Microfractionation
2.4.1. KOL_18 (TSRR0002_D-07) Agelas nakamurai
2.4.2. PEHE_5 (TSRR0002_F-08) Haliclona sp.
2.4.3. ULU_16 (TSRR0002_H-07) Neopetrosia sp.
2.4.4. PANIKI_4 (TSRR0002_D-12) Halichondria sp.
2.4.5. ULU_11 (TSRR0002_H-03)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sponge Collection
4.2. Sample Extraction
4.3. Antimicrobial Bioassays
4.4. UPLC-HRMS/MS and Microfractionation
4.5. Metabolic Fingerprinting
4.6. Dereplication
4.7. Molecular Networking
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.L.; Schneider, T.; Peoples, A.J.; Spoering, A.L.; Engels, I.; Conlon, B.P.; Mueller, A.; Schäberle, T.F.; Hughes, D.E.; Epstein, S.; et al. A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance. Nature 2015, 517, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Meyer, K.J.; Iinishi, A.; Favre-Godal, Q.; Green, R.; Manuse, S.; Caboni, M.; Mori, M.; Niles, S.; Ghiglieri, M.; et al. A new antibiotic selectively kills Gram-negative pathogens. Nature 2019, 576, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meek, R.W.; Vyas, H.; Piddock, L.J.V. Nonmedical uses of antibiotics: Time to restrict their use? PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatz, A.; Bugle, E.; Waksman, S.A. Streptomycin, a substance exhibiting antibiotic activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1944, 55, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, D.; Berrué, F.; Correa, H.; Duncan, K.; Kerr, R.G. Chemical dereplication of marine actinomycetes by liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry profiling and statistical analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 805, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Sanchez, L.M.; Rath, C.M.; Liu, X.; Boudreau, P.D.; Bruns, N.; Glukhov, E.; Wodtke, A.; de Felicio, R.; Fenner, A.; et al. Molecular networking as a dereplication strategy. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Wu, H.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y. Agelasine-A, -B, -C and -D, novel bicyclic diterpenoids with a 9-methyladeninium unit possessing inhibitory effects on Na, K-ATPase from the Okinawa sea sponge Agelas sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 2989–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Wu, H.; Kobayashi, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y. Agelasidines. Novel hypotaurocyamine derivatives from the Okinawan sea sponge Agelas nakamurai Hoshino. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 2494–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, E.P.; Yu, L.C.; Molinski, T.F. Antifungal diterpene alkaloids from the Caribbean sponge Agelas citrina: Unified configurational assignments of agelasidines and agelasines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5131–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialonska, D.; Zjawiony, J.K. Aplysinopsins-marine indole alkaloids: Chemistry, bioactivity and ecological significance. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balansa, W.; Islam, R.; Gilbert, D.F.; Fontaine, F.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.; Piggott, A.M.; Lynch, J.W.; Capon, R.J. Australian marine sponge alkaloids as a new class of glycine-gated chloride channel receptor modulator. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2013, 21, 4420–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, I.; Guella, G.; Zibrowius, H.; Pietra, F. On the origin of quasi-racemic aplysinopsin cycloadducts, (bis)indole alkaloids isolated from scleractinian corals of the family Dendrophylliidae. Involvement of enantiodefective Diels–Alderases or asymmetric induction in artifact processes involving adventitious catalysts? Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 8757–8762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guella, G.; Mancini, I.; Zibrowius, H.; Pietra, F. Aplysinopsin-type alkaloids from Dendrophyllia sp., a scleractinian coral of the family Dendrophylliidae of the philippines, facile photochemical (Z/E) photoisomerization and thermal reversal. Helv. Chim. Acta 1989, 72, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Miyagawa-Kohshima, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Naya, Y. Characterization of compounds that induce symbiosis between sea anemone and anemone fish. Science 1986, 234, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; De Stefano, S.; Minale, L. ent-Chromazonarol, a chroman-sesquiterpenoid from the sponge Disidea pallescens. Experientia 1975, 31, 1117–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordaliza, M. Cytotoxic terpene quinones from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2849–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawat, H.; Mahidol, C.; Kaweetripob, W.; Wittayalai, S.; Ruchirawat, S. Iodo–sesquiterpene hydroquinone and brominated indole alkaloids from the Thai sponge Smenospongia sp. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 6881–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, B.N.; Perzanowski, H.P.; Ross, R.A.; Erdman, T.R.; Scheuer, P.J.; Finer, J.; Clardy, J. Recent research in marine natural products: The puupehenones. Pure Appl. Chem. 1979, 51, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albizati, K.F.; Faulkner, D.J. Stevensine, a novel alkaloid of an unidentified marine sponge. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 4163–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuhiro, U.; Takayuki, O.; Atsushi, S. Cytotoxic haterumadienone congeners from the Okinawan marine sponge Dysidea sp. Heterocycles 2007, 72, 655–663. [Google Scholar]
- Noyer, C.; Thomas, O.P.; Becerro, M.A. Patterns of chemical diversity in the Mediterranean sponge Spongia lamella. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Demerdash, A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Horbanczuk, O.K.; Tammam, M.A.; Abdel-Mogib, M.; Hooper, J.N.; Sekeroglu, N.; Al-Mourabit, A.; Kijjoa, A. Chemical diversity and biological activities of marine sponges of the genus Suberea: A systematic review. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopmans, M.; Martens, D.; Wijffels, R.H. Towards commercial production of sponge medicines. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malve, H. Exploring the ocean for new drug developments: Marine pharmacology. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2016, 8, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohni, N.; Cordero-Maldonado, M.L.; Maes, J.; Siverio-Mota, D.; Marcourt, L.; Munck, S.; Kamuhabwa, A.R.; Moshi, M.J.; Esguerra, C.V.; de Witte, P.A.M.; et al. Integration of microfractionation, qNMR and zebrafish screening for the in vivo bioassay-guided isolation and quantitative bioactivity analysis of natural products. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohotti, S.; Rajendran, S.; Muhammad, T.; Strömstedt, A.A.; Adhikari, A.; Burman, R.; de Silva, E.D.; Göransson, U.; Hettiarachchi, C.M.; Gunasekera, S. Screening for bioactive secondary metabolites in Sri Lankan medicinal plants by microfractionation and targeted isolation of antimicrobial flavonoids from Derris scandens. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothias, L.-F.; Nothias-Esposito, M.; da Silva, R.; Wang, M.; Protsyuk, I.; Zhang, Z.; Sarvepalli, A.; Leyssen, P.; Touboul, D.; Costa, J.; et al. Bioactivity-based molecular networking for the discovery of drug leads in natural product bioassay-guided fractionation. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggen, H.; Gundersen, L.-L. Synthetic studies directed towards agelasine analogs—Synthesis, tautomerism, and alkylation of 2-substituted N-methoxy-9-methyl-9H-purin-6-amines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 2008, 5099–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggen, H.; Charnock, C.; Burman, R.; Felth, J.; Larsson, R.; Bohlin, L.; Gundersen, L.-L. Antimicrobial and antineoplastic activities of agelasine analogs modified in the purine 2-position. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2011, 344, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balansa, W.; Wodi, S.I.M.; Rieuwpassa, F.J.; Ijong, F.G. Agelasines B, D and antimicrobial extract of a marine sponge Agelas sp. from Tahuna Bay, Sangihe Islands, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 2020, 21, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordaliza, M. Terpenyl-purines from the sea. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.M.; Puyana, M.; Fenical, W.; Pawlik, J.R. Chemical defense of the Caribbean reef sponge Axinella corrugata against predatory fishes. J. Chem. Ecol. 1999, 25, 2811–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbold, R.W.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.; Pawlik, J.R. Antimicrobial activity of Caribbean sponge extracts. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 19, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuhiro, U.; Tomoyuki, U.; Oktavianus, S.E.R.; Masaki, K.; Daisuke, U. Haterumadienone: A new puupehenone congener from an Okinawan marine sponge, Dysidea sp. Chem. Lett. 2005, 34, 1530–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.J.; Hoobler, E.K.; Riener, M.; Loveridge, S.T.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Holman, T.R.; Crews, P. Using enzyme assays to evaluate the structure and bioactivity of sponge-derived meroterpenes. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1857–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marner, M.; Patras, M.A.; Kurz, M.; Zubeil, F.; Förster, F.; Schuler, S.; Bauer, A.; Hammann, P.; Vilcinskas, A.; Schäberle, T.F.; et al. Molecular networking-guided discovery and characterization of stechlisins, a group of cyclic lipopeptides from a Pseudomonas sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salek, R.M.; Steinbeck, C.; Viant, M.R.; Goodacre, R.; Dunn, W.B. The role of reporting standards for metabolite annotation and identification in metabolomic studies. GigaScience 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creek, D.J.; Dunn, W.B.; Fiehn, O.; Griffin, J.L.; Hall, R.D.; Lei, Z.; Mistrik, R.; Neumann, S.; Schymanski, E.L.; Sumner, L.W. Metabolite identification: Are you sure? And how do your peers gauge your confidence? Metabolomics 2014, 10, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torriani, S.F.F.; Melichar, J.P.E.; Mills, C.; Pain, N.; Sierotzki, H.; Courbot, M. Zymoseptoria tritici: A major threat to wheat production, integrated approaches to control. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 79, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, J.N.A.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Systema Porifera. A Guide to the Classification of Sponges. In Systema Porifera a Guide to the Classification of Sponges; Hooper, J.N.A., Van Soest, R.W.M., Willenz, P., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 1–7. ISBN 978-0-306-47260-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, J. Sponguide: Guide to Sponge Collection and Identification. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242495363_Sponguide_Guide_to_Sponge_Collection_and_Identification (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- R Core Team. The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Wickham, H.; Hester, J.; Francois, R. readr: Read Rectangular Text Data. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=readr (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Schmidt, D.; Heckendorf, C. coop: Co-Operation: Fast Covariance, Correlation, and Cosine Similarity Operations. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=coop (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Warnes, G.R.; Bolker, B.; Bonebakker, L.; Gentleman, R.; Huber, W.; Liaw, A.; Lumley, T.; Maechler, M.; Magnusson, A.; Moeller, S.; et al. Gplots: Various R Programming Tools for Plotting Data. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gplots (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Dowle, M.; Srinivasan, A.; Gorecki, J.; Chirico, M.; Stetsenko, P.; Short, T.; Lianoglou, S.; Antonyan, E.; Bonsch, M.; Parsonage, H.; et al. Data.Table: Extension of “Data.Frame”. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=data.table (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Eckert, A.; Godoy, L.; KS, S. parallelDist: Parallel Distance Matrix Computation using Multiple Threads. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=parallelDist (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Wickham, H.; Hester, J.; Chang, W.; RStudio, R. Core team devtools: Tools to Make Developing R Packages Easier. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=devtools (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Griffith, O. L Heatmap.3.R. GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/obigriffith/biostar-tutorials (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Laatsch, H. AntiBase: The Natural Compound Identifier; Wiley-Vch: Weinheim, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-527-34359-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dictionary of Natural Products 29.1 Chemical Search. Available online: http://dnp.chemnetbase.com/faces/chemical/ChemicalSearch.xhtml;jsessionid=DB01289ACAA79C222859E1CD8A98A894 (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- SciFinder. Redistributed with Permission. Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society (ACS). All rights reserved.
- Allard, P.-M.; Péresse, T.; Bisson, J.; Gindro, K.; Marcourt, L.; Pham, V.C.; Roussi, F.; Litaudon, M.; Wolfender, J.-L. Integration of molecular networking and in-silico MS/MS fragmentation for natural products dereplication. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3317–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riyanti; Marner, M.; Hartwig, C.; Patras, M.A.; Wodi, S.I.M.; Rieuwpassa, F.J.; Ijong, F.G.; Balansa, W.; Schäberle, T.F. Sustainable Low-Volume Analysis of Environmental Samples by Semi-Automated Prioritization of Extracts for Natural Product Research (SeaPEPR). Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120649
Riyanti, Marner M, Hartwig C, Patras MA, Wodi SIM, Rieuwpassa FJ, Ijong FG, Balansa W, Schäberle TF. Sustainable Low-Volume Analysis of Environmental Samples by Semi-Automated Prioritization of Extracts for Natural Product Research (SeaPEPR). Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(12):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120649
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiyanti, Michael Marner, Christoph Hartwig, Maria A. Patras, Stevy I. M. Wodi, Frets J. Rieuwpassa, Frans G. Ijong, Walter Balansa, and Till F. Schäberle. 2020. "Sustainable Low-Volume Analysis of Environmental Samples by Semi-Automated Prioritization of Extracts for Natural Product Research (SeaPEPR)" Marine Drugs 18, no. 12: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120649
APA StyleRiyanti, Marner, M., Hartwig, C., Patras, M. A., Wodi, S. I. M., Rieuwpassa, F. J., Ijong, F. G., Balansa, W., & Schäberle, T. F. (2020). Sustainable Low-Volume Analysis of Environmental Samples by Semi-Automated Prioritization of Extracts for Natural Product Research (SeaPEPR). Marine Drugs, 18(12), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120649