Marine Antithrombotics
Abstract
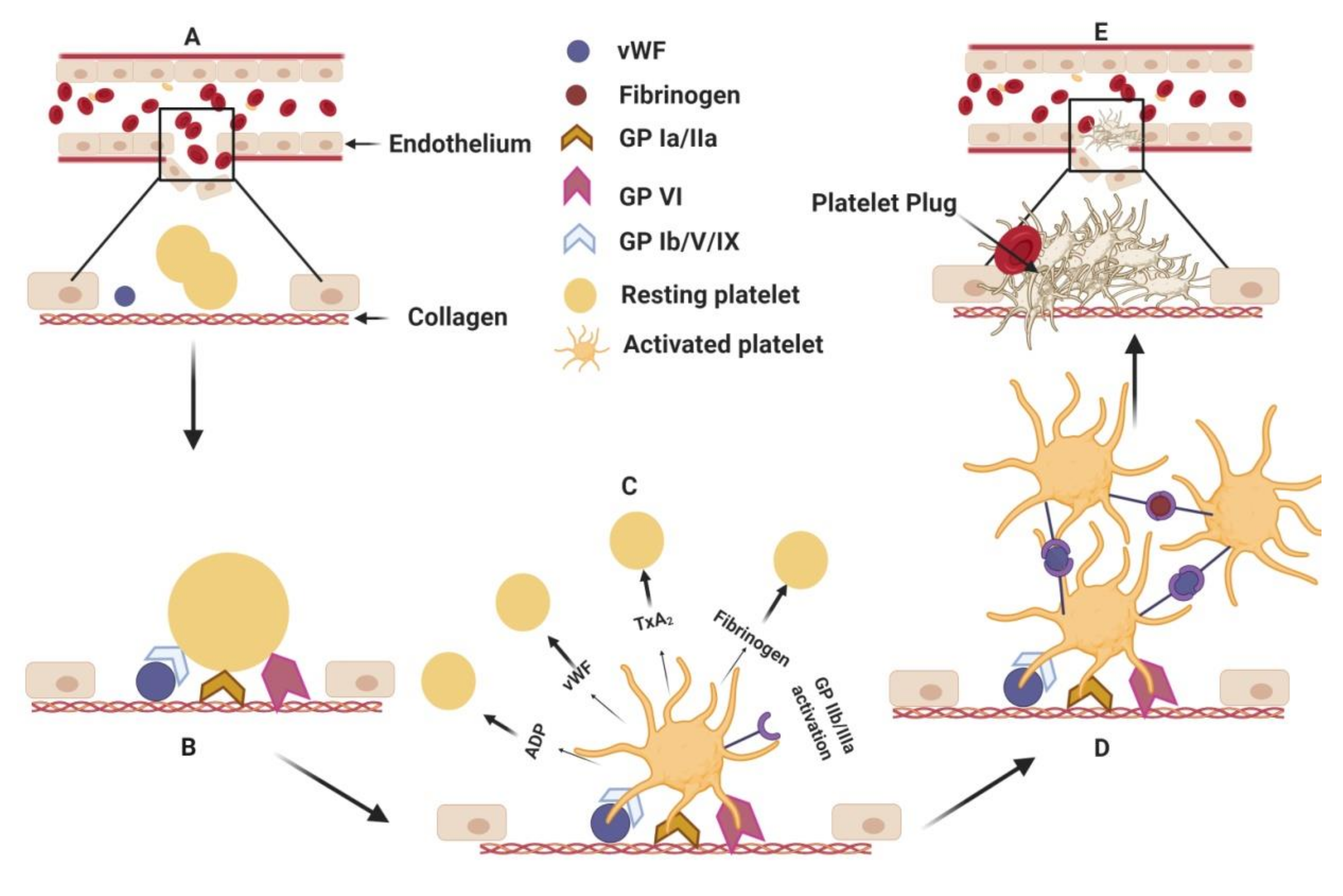
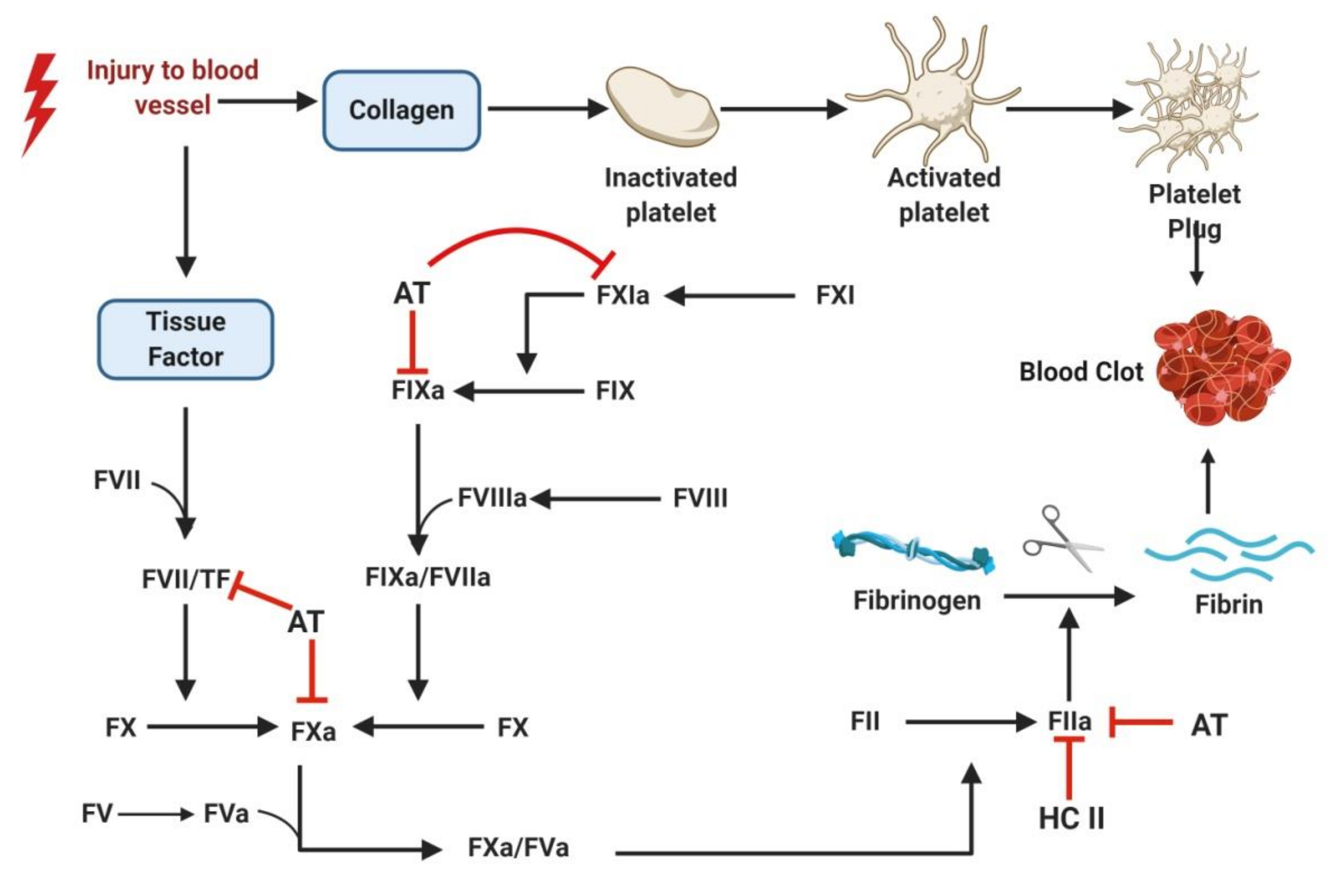
1. Introduction
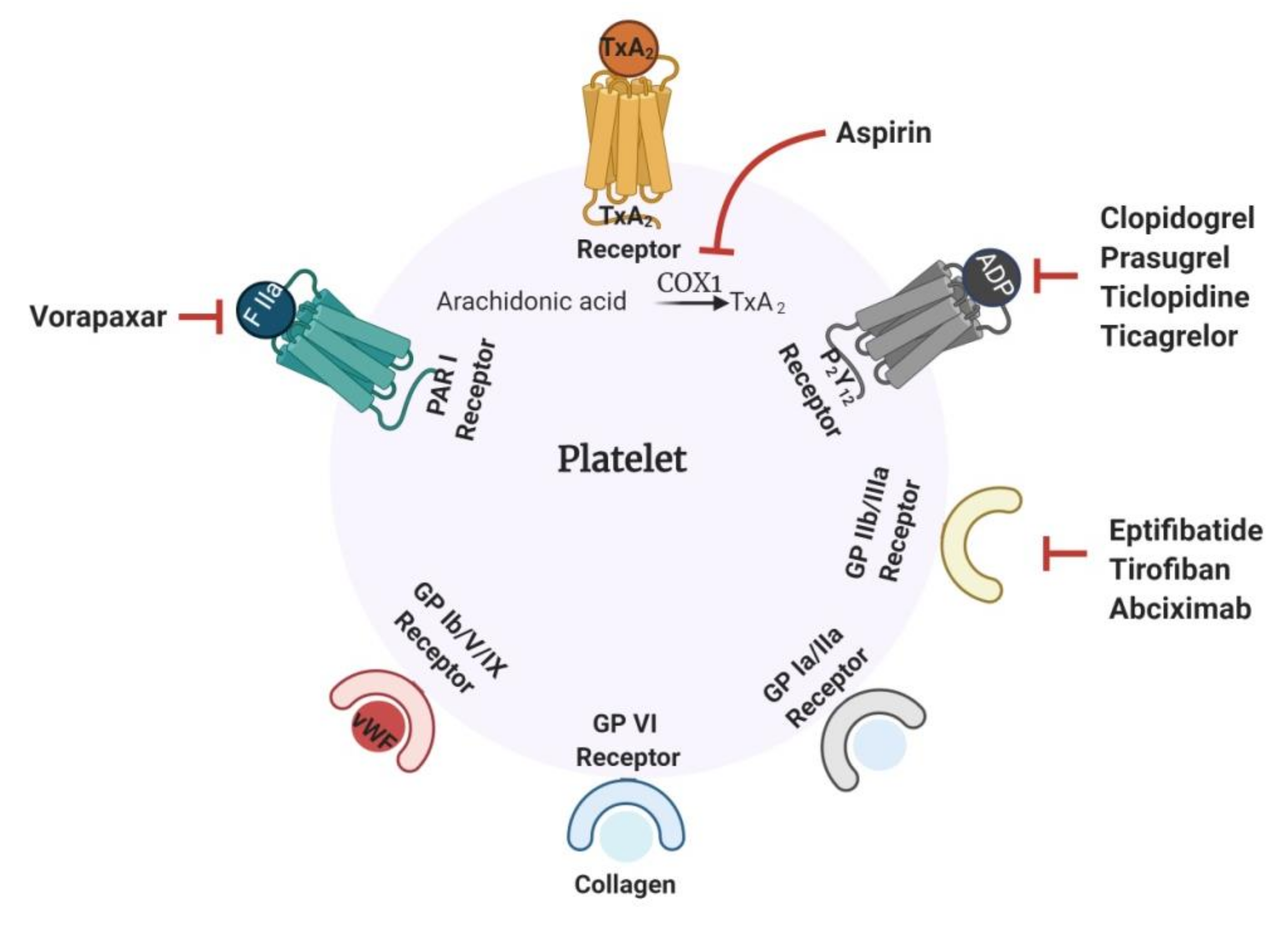
1.1. Current Antithrombotics
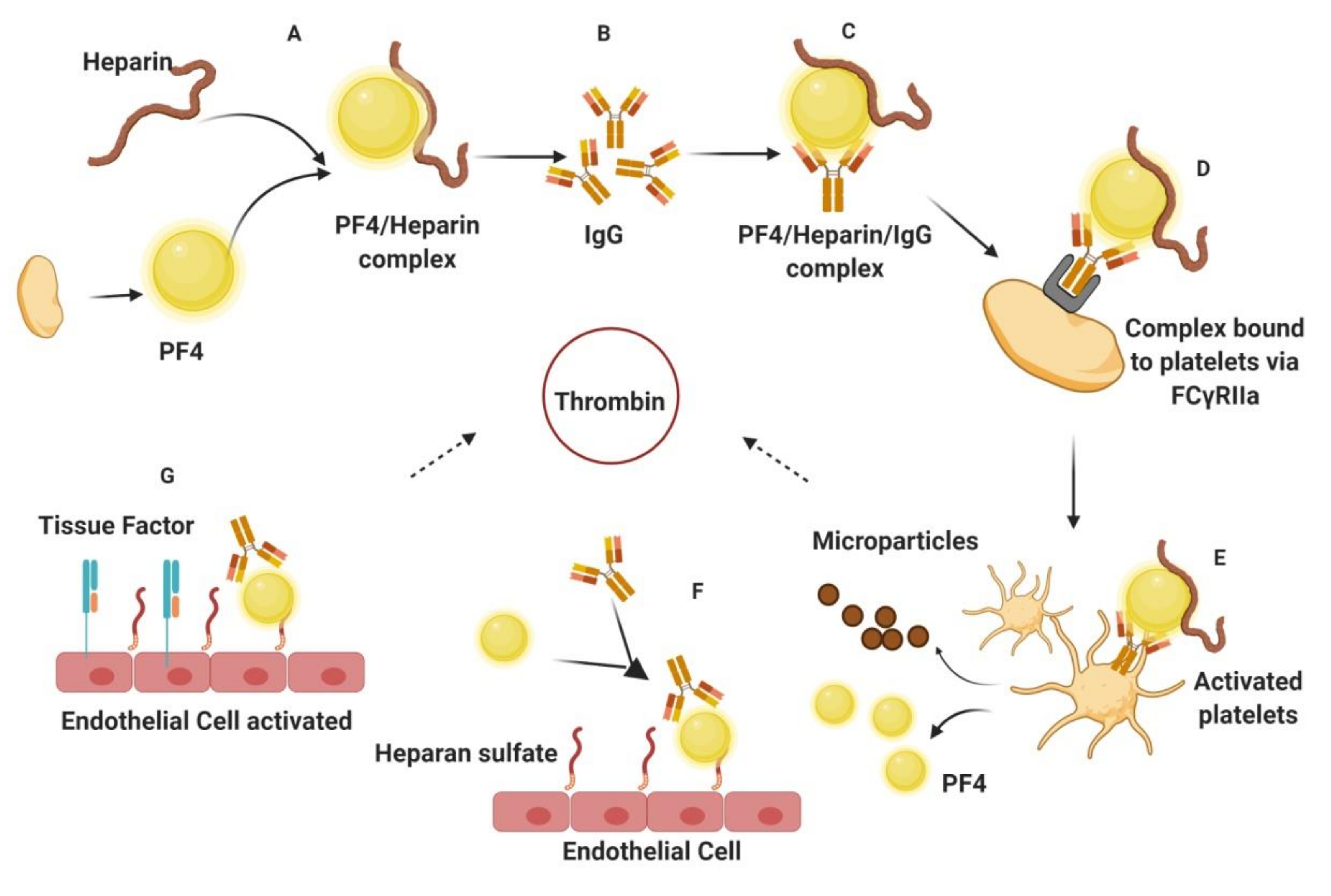
1.2. Challenges Associated with Current Antithrombotics
2. Marine Antithrombotics
2.1. Organic Small Molecules
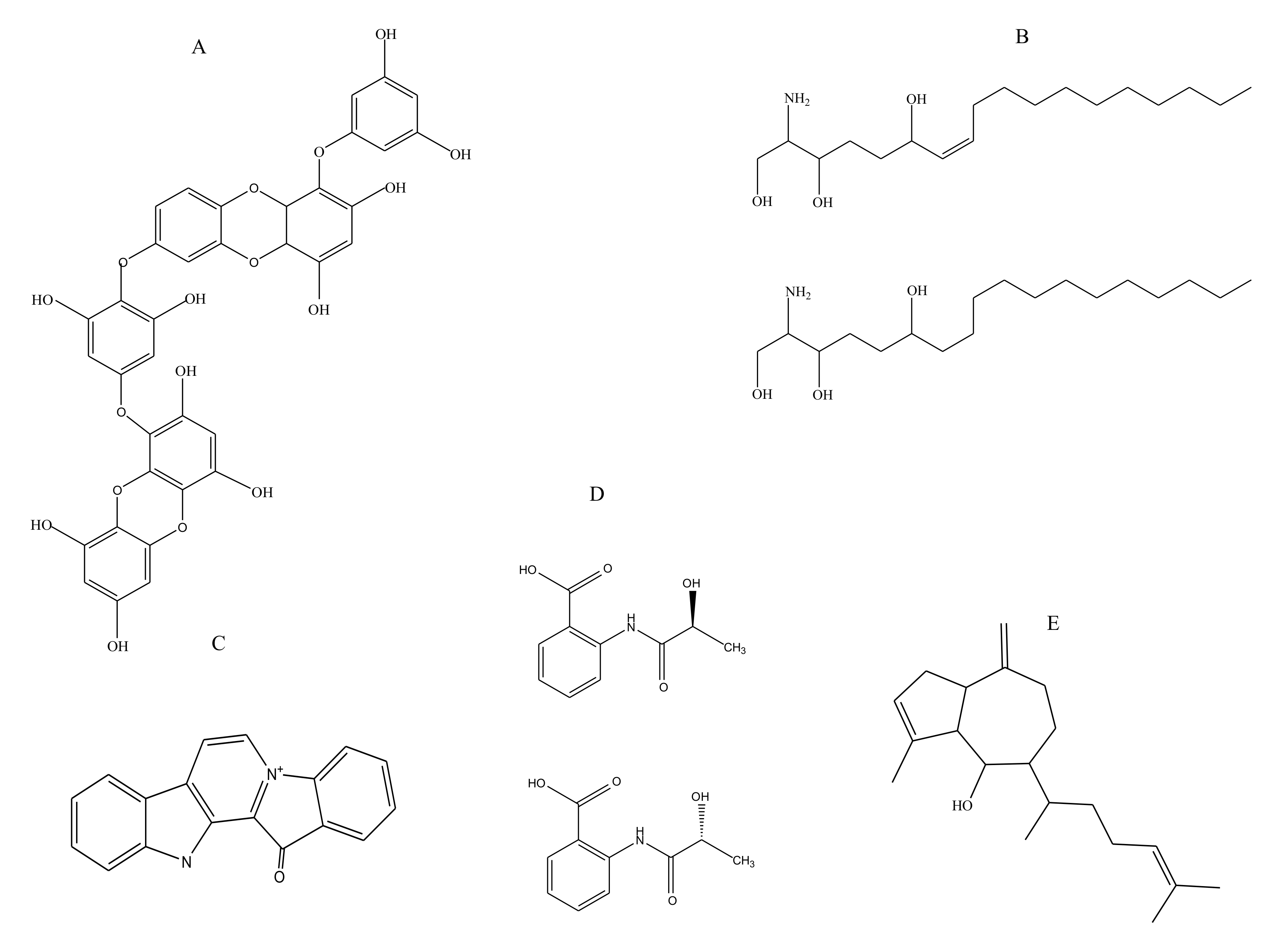
2.1.1. Polyphenols
2.1.2. Sphingosines
2.1.3. Terpenes
2.1.4. Benzoic Acid Derivative
2.1.5. Alkaloids
2.2. Biomacromolecules
2.2.1. Lipids
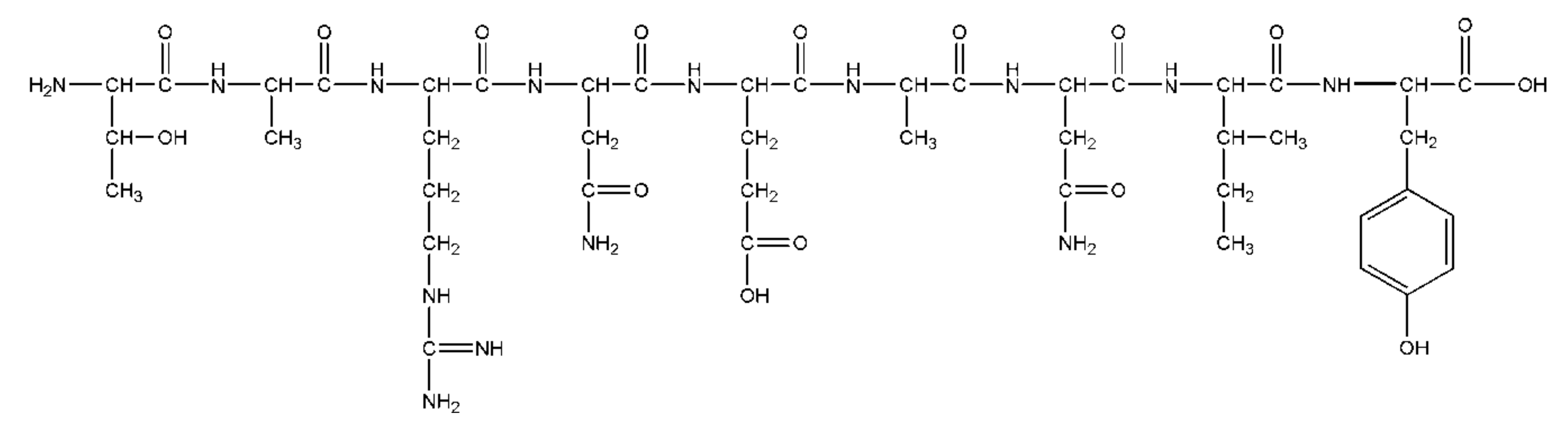
2.2.2. Peptides
2.2.3. Proteins
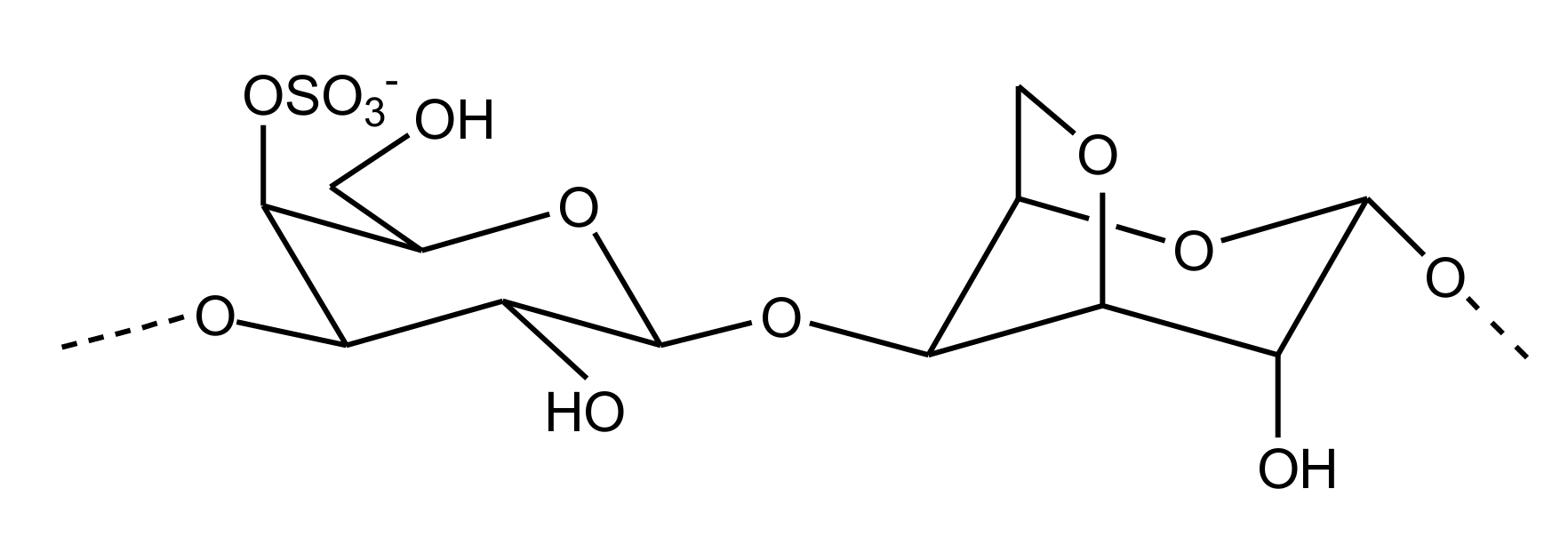
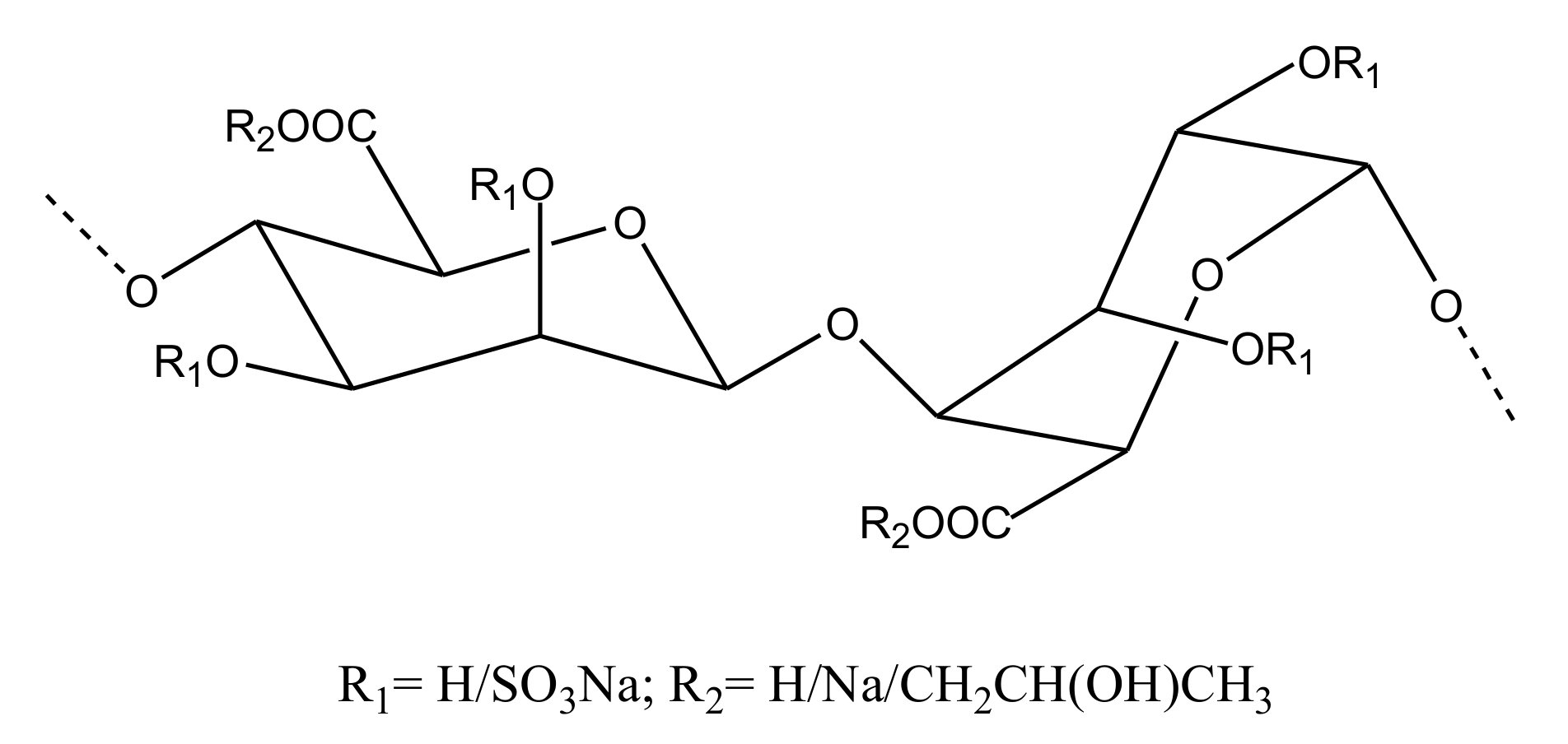
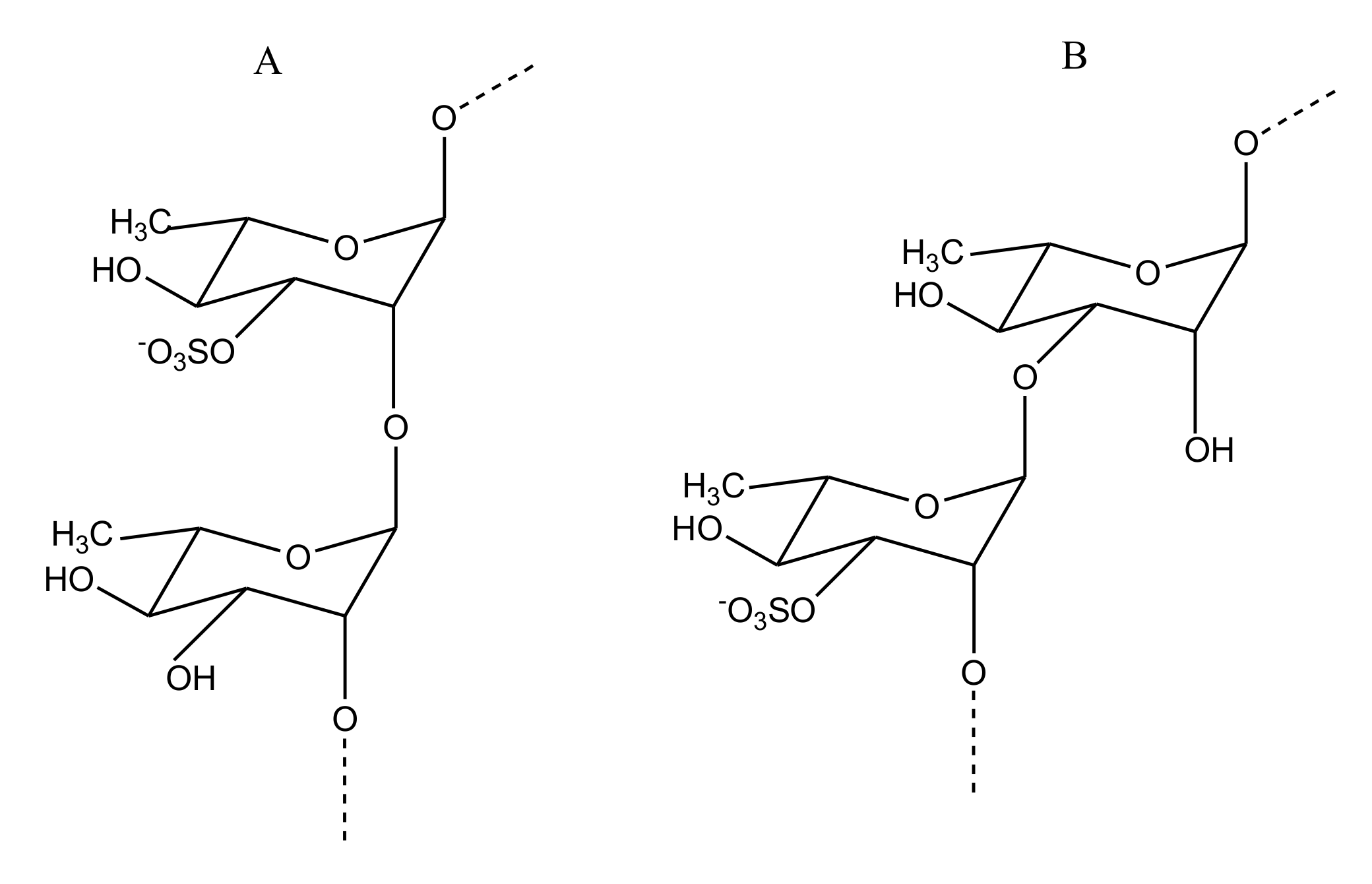
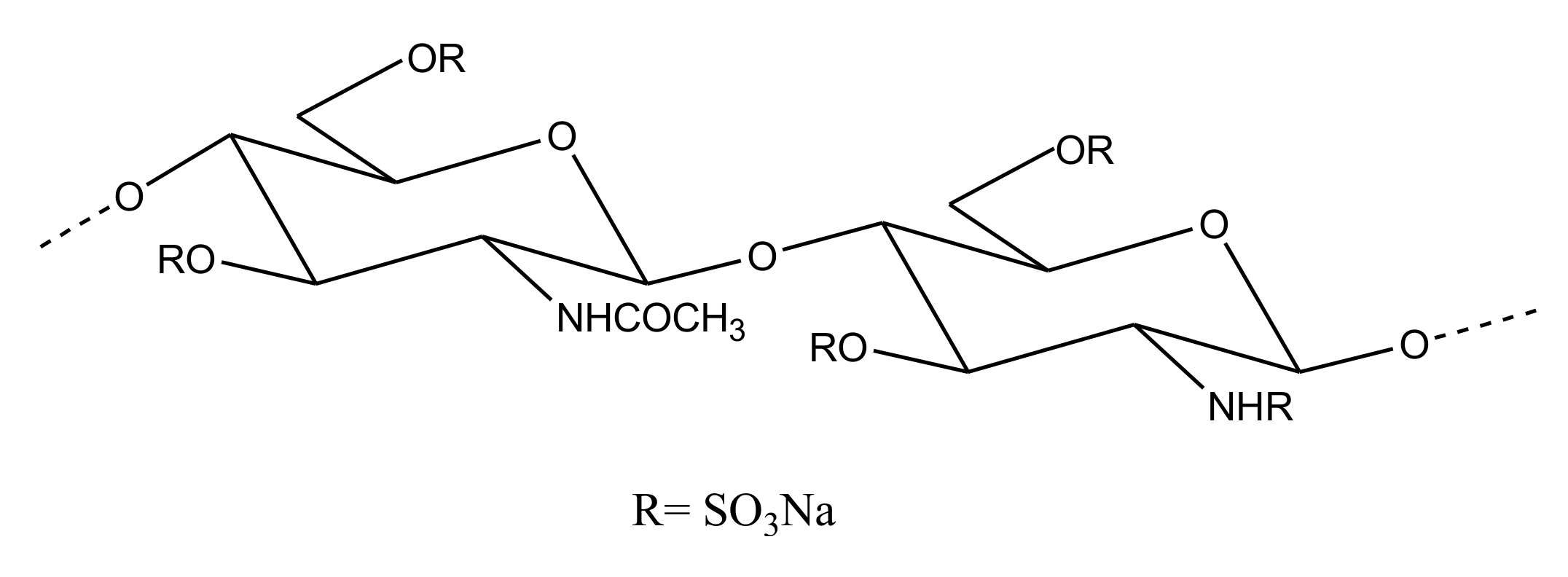
2.2.4. Sulfated Glycans
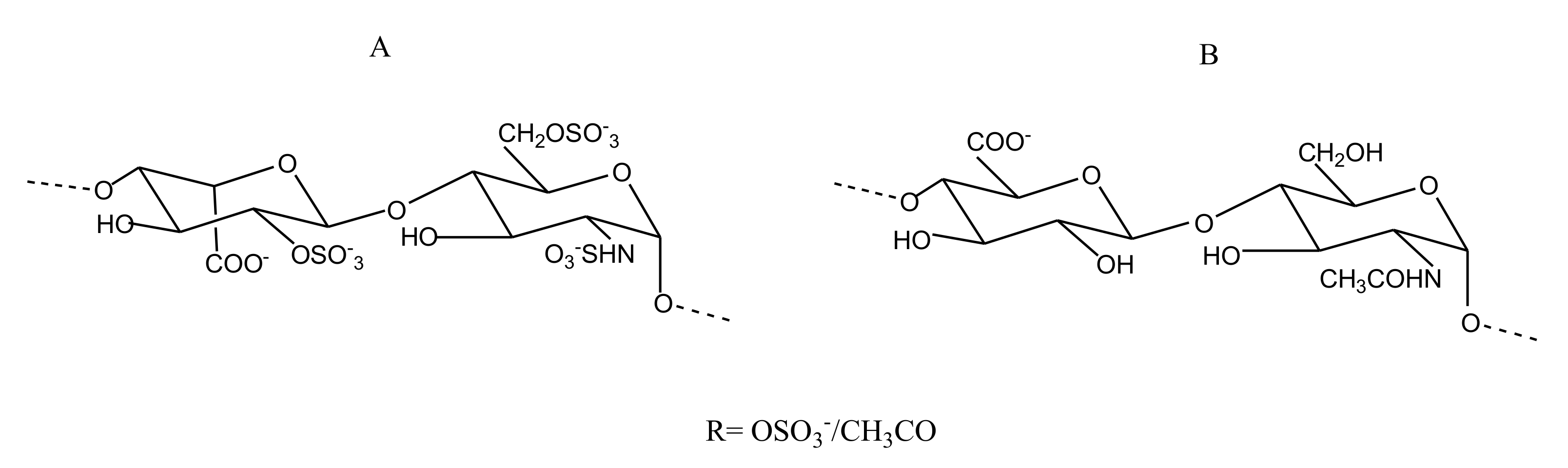
CS/DS
Heparin/HS
FucCS
| Sea Cucumber Spp. | aPTT | TT | PT | Anti FXase | Anti FIIa/Plasma | Anti FXa/AT | Anti FXa/HCII | Anti FIIa/AT | Anti FIIa/HCII | Mol. Wt | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/ml | IC 50 (ng/mL) | kDa | |||||||||
| Apostichopus japonicas | 3.06 | - | - | 9.20 | - | - | - | - | - | 76.4 | [66] |
| Bohadschia argus | 4.13 | - | 1280 | 14.83 | - | 3341 | - | 530.8 | - | 70.3 | [73] |
| Cucumaria frondosa | - | - | - | - | - | 1000 | - | 500 | 1000 | 58 | [72] |
| Cucumaria japonica | 2.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | [75] |
| Holothuria coluber | 4.94 | 10.32 | 1280 | 14.73 | - | - | - | - | - | 49.48 | [64] |
| Holothuria coluber | 3.31 | 7.68 | 26.4 | - | 10000 | - | 1260 | - | 54.9 | [65] | |
| Holothuria fuscopunctata | 3.45 | 6.46 | 1280 | 41.9 | - | 10000 | - | 448 | 589 | 42.6 | [76] |
| Holothuria lentiginosa | 30 IU/mg | - | - | - | 10.2 | 5.5 | - | 0.7 | - | 50.8 | [77] |
| Holothuria mexicana | 100 | 150 | - | - | - | 1000 | - | 100 | - | - | [67] |
| Holothuria pollii | 220 IU/mg | - | - | - | - | - | - | 125 | 35 | 45.8 | [70] |
| Holothuria scabra | 20 | 60 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 69.1 | [74] |
| Massinium magnum | 2.8 | 6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 27 | [71] |
| Patallus mollis | 3.5 | 10.7 | - | 13.7 | - | - | - | - | - | 60.3 | [63] |
| Pearsonothuriagraffei | 20.9 | 9.84 | - | 330 | - | 5490 | - | 5080 | - | 73 | [78] |
| Thelenota ananas | - | - | - | - | - | 1000 | - | 500 | 1000 | 63 | [72] |
GAG-Like Molecules
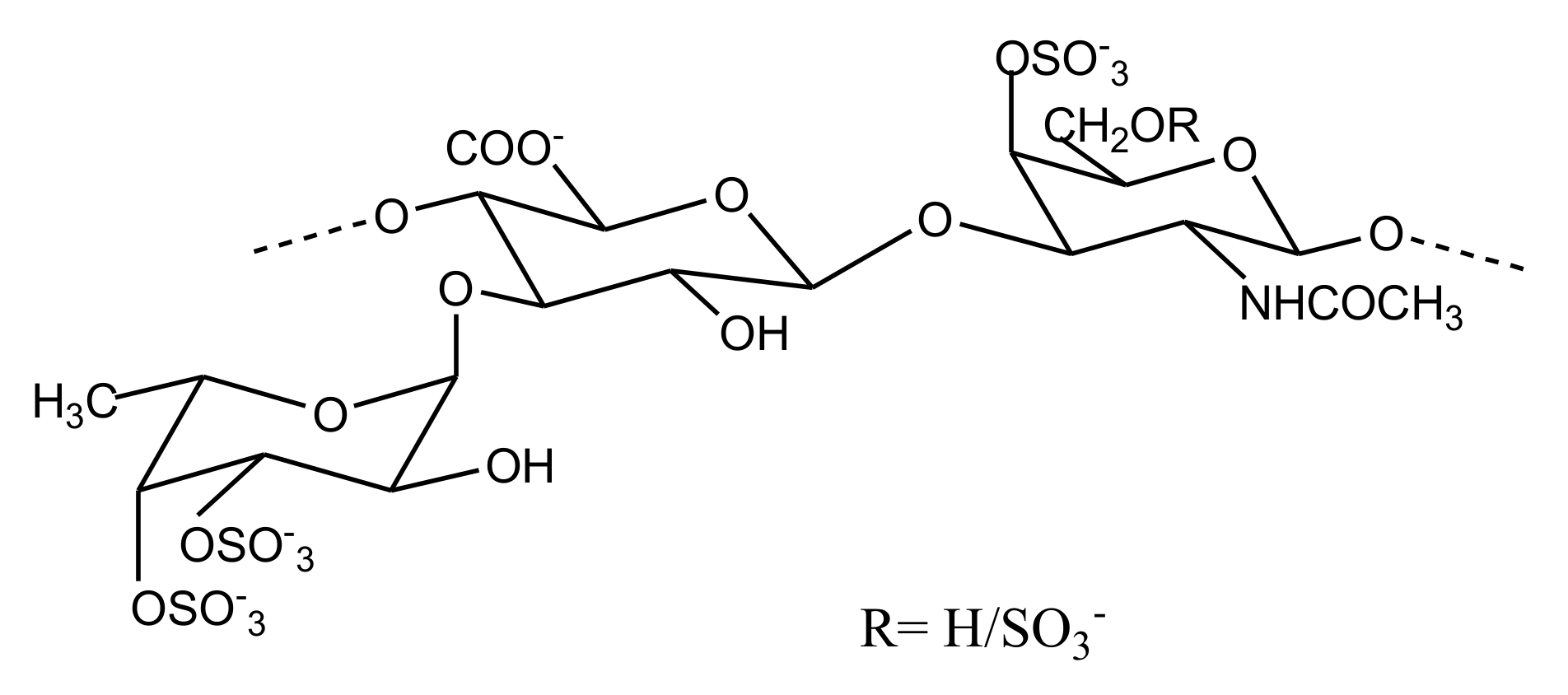
Sulfated Galactans
Sulfated Fucans
| Source | Species | aPTT | TT | PT | Anti FXase | Anti FXa/AT | Anti FIIa/AT | Anti FIIa/HCII | Mol. Wt | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/ml | IC 50 (ng/mL) | kDa | ||||||||
| Green alga | Udotea flabellum | 3 | - | - | 9.20 | - | 500 | - | 76.4 | [82] |
| Brown alga | Punctaria plantaginea | >100 | >100 | 1280 | 14.83 | no | no | - | 70.3 | [84] |
| Sea cucumber | Holothuria albiventer | 25.79 | 115.47 | >1280 | 71.99 | - | - | - | >2000 | [86] |
| Holothuria coluber | 78.92 | >1280 | >1280 | 244 | - | - | - | 64.55 | [64] | |
| Holothuria fuscopunctata | 11.3 IU/mg | - | - | 92.8 | 1780 | 882 | 2947 | 36.8 | [87] | |
| Holothuria pollii | 2.5 | 2 | - | - | 125 | 35 | 45.8 | [88] | ||
| Patallus mollis | 24.3 | - | - | 74 | - | 0.5 | 0.16 | 6.12 | [63] | |
| Stichopus horrens | 19.6 IU/mg | - | - | 51.2 | 53256 | 3758 | - | 487.9 | [87] | |
| Thelenota ananas | 10.4 IU/mg | - | - | 196.7 | 1150 | 1176 | 292.6 | 61.2 | [87] | |
| Sea Urchin | Lytechinus variegatus | - | - | - | - | 0.29 IU/mg | 0.44 IU/mg | - | - | |
| Strongylocentrotus franciscanus | - | - | - | - | 0.05 IU/mg | 0.02 IU/mg | - | - | [89] | |
| Echinometra lucunter | - | - | - | - | 0.27 IU/mg | 0.56 IU/mg | - | - | ||
Other Sulfated Polysaccharides
- Alginate
Sulfated Rhamnan
Sulfated Chitosan
3. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raskob, G.E.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blanco, A.N.; Buller, H.; Gallus, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Hylek, E.M.; Kakkar, A.; Konstantinides, S.V.; McCumber, M.; et al. Thrombosis: A major contributor to global disease burden. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendelboe, A.M.; Raskob, G.E. Global Burden of Thrombosis: Epidemiologic Aspects. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, N.C.; Weitz, J.I. Antithrombotic Agents. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.; Hangge, P.; Albadawi, H.; Wallace, A.; Shamoun, F.; Knuttien, M.G.; Naidu, S.; Oklu, R. Deep vein thrombosis: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and medical management. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 7, S276–S284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Franchini, M.; Targher, G. Arterial thrombus formation in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previtali, E.; Bucciarelli, P.; Passamonti, S.M.; Martinelli, I. Risk factors for venous and arterial thrombosis. Blood Transfus. 2011, 9, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voetsch, B.; Loscalzo, J. Genetic Determinants of Arterial Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackman, N. Triggers, targets and treatments for thrombosis. Nature 2008, 451, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, M.Z.; Mendolicchio, G.L. Adhesion Mechanisms in Platelet Function. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.K.; López, J.A.; Berndt, M.C. Molecular mechanisms of platelet adhesion and activation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meijden, P.E.J.; Heemskerk, J.W.M. Platelet biology and functions: New concepts and clinical perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.A.; Travers, R.J.; Morrissey, J.H. How it all starts: Initiation of the clotting cascade. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 50, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palta, S.; Saroa, R.; Palta, A. Overview of the coagulation system. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, J.A.; Chen, J. Pathophysiology of venous thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2009, 123, S30–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, J.I.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Samama, M.M. New antithrombotic drugs: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012, 141, e120S–e151S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harter, K.; Levine, M.; Henderson, S.O. Anticoagulation Drug Therapy: A Review. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 16, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyen, J.D.; Schaff, M.; Peter, K. Current and future antiplatelet therapies: Emphasis on preserving haemostasis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, N.S.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Inselman, J.; Herrin, J.; Yao, X.; Sangaralingham, L.R.; Cornish, G.; Ngufor, C. Risk of Gastrointestinal Bleeding Increases with Combinations of Antithrombotic Agents and Patient Age. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 337–346.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, R.; Olesen, J.B.; Charlot, M.; Gislason, G.H. Risk of bleeding related to antithrombotic treatment in cardiovascular disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 5362–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Majeed, A.; Powell, R. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia: Diagnosis and management update. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, N.; Feo, M.D.; Santo, L.S.D.; Pollice, A.; Tedesco, N.; Cotrufo, M. Dose-Dependent Fetal Complications of Warfarin in Pregnant Women with Mechanical Heart Valves. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999, 33, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, J.I.; Chan, N.C. Advances in Antithrombotic Therapy. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Selleng, K. Reversal of anticoagulants: An overview of current developments. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdoes, G.; Reid, C.; Koster, A. Oral Anticoagulants in Cardiovascular Surgery: Between Nightmare Tour and Safe Cruise. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2019, 33, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.Y.; Vaidya, V.R.; Asirvatham, S.J. Reversing anticoagulant effects of novel oral anticoagulants: Role of ciraparantag, andexanet alfa, and idarucizumab. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.B.; Pahade, A.; Chawla, R. Novel reversal agents and laboratory evaluation for direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOAC): An update. Indian J. Anaesth. 2019, 63, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadyen, J.D.; Peter, K. Novel Antithrombotic Drugs on the Horizon: The Ultimate Promise to Prevent Clotting While Avoiding Bleeding. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 1133–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalhal, F.; Cristelo, R.R.; Resende, D.I.S.P.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Sousa, E.; Correia-da-Silva, M. Antithrombotics from the Sea: Polysaccharides and Beyond. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, R.; Luesch, H. Marine natural products: A new wave of drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donia, M.; Hamann, M.T. Marine natural products and their potential applications as anti-infective agents. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pinteus, S.; Gaspar, H.; Alpoim, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Pedrosa, R. From Marine Origin to Therapeutics: The Antitumor Potential of Marine Algae-Derived Compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malve, H. Exploring the ocean for new drug developments: Marine pharmacology. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2016, 8, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Gálvez, J. Potential Role of Seaweed Polyphenols in Cardiovascular-Associated Disorders. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Kwon, T.-H.; Yun, B.-S.; Park, N.-H.; Rhee, M.H. Eisenia bicyclis (brown alga) modulates platelet function and inhibits thrombus formation via impaired P2Y12 receptor signaling pathway. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2018, 40, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegelmeyer, R.; Schröder, R.; Rambo, D.F.; Dresch, R.R.; Carraro, J.L.F.; Mothes, B.; Moreira, J.C.F.; da Frota Junior, M.L.C.; Henriques, A.T. Sphingosines Derived from Marine Sponge as Potential Multi-Target Drug Related to Disorders in Cancer Development. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5552–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, H.; König, G.M. Terpenoids from Marine Organisms: Unique Structures and their Pharmacological Potential. Phytochem. Rev. 2006, 5, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, L.; de, A.; Marqui de Almeida, A.C.; Francielle Souza Domingos, T.; Ortiz-Ramirez, F.; Negrão Cavalcanti, D.; Laneuville Teixeira, V.; Lopes Fuly, A. Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Effects of Diterpenes Isolated from the Marine Alga, Dictyota menstrualis. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2471–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.C.C.; Lourenço, A.L.; Terra, L.; Abreu, P.A.; Laneuville Teixeira, V.; Castro, H.C. Marine Diterpenes: Molecular Modeling of Thrombin Inhibitors with Potential Biotechnological Application as an Antithrombotic. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampofo, E.; Später, T.; Nalbach, L.; Menger, M.D.; Laschke, M.W. The Marine-Derived Triterpenoid Frondoside A Inhibits Thrombus Formation. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z. Studies on New Activities of Enantiomers of 2-(2-Hydroxypropanamido) Benzoic Acid: Antiplatelet Aggregation and Antithrombosis. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0170334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Güven, K.C.; Percot, A.; Sezik, E. Alkaloids in Marine Algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampofo, E.; Später, T.; Müller, I.; Eichler, H.; Menger, M.D.; Laschke, M.W. The Marine-Derived Kinase Inhibitor Fascaplysin Exerts Anti-Thrombotic Activity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6774–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burri, L.; Hoem, N.; Banni, S.; Berge, K. Marine Omega-3 Phospholipids: Metabolism and Biological Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15401–15419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Demuru, M.; Shiels, K.; Saha, S.K.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. Structural Elucidation of Irish Organic Farmed Salmon (Salmo salar) Polar Lipids with Antithrombotic Activities. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Shiels, K.; Saha, S.K.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. In Vitro Antithrombotic Properties of Salmon (Salmo salar) Phospholipids in a Novel Food-Grade Extract. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; O’Keeffe, E.; Lordan, R.; Redfern, S.; Zabetakis, I. Bioprospecting for Antithrombotic Polar Lipids from Salmon, Herring, and Boarfish By-Products. Foods 2019, 8, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2003-4: Marine Compounds with Anthelmintic, Antibacterial, Anticoagulant, Antifungal, Anti-inflammatory, Antimalarial, Antiplatelet, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, and Antiviral Activities; affecting the Cardiovascular, Immune and Nervous Systems, and other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2007, 145, 553–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indumathi, P.; Mehta, A. A novel anticoagulant peptide from the Nori hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, S.; Fan, F.; Tu, M.; Xu, Z.; Du, M. Identification and molecular mechanism of antithrombotic peptides from oyster proteins released in simulated gastro-intestinal digestion. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5426–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Tu, M.; Chen, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, B.; Du, M. Identification and inhibitory activity against α-thrombin of a novel anticoagulant peptide derived from oyster (Crassostrea gigas) protein. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 6391–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Tu, M.; Wang, Z.; Mao, F.; Chen, H.; Qin, L.; Du, M. Identification and Antithrombotic Activity of Peptides from Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Tu, M.; Chen, H.; Mao, F.; Yu, C.; Du, M. Identification and In Silico Prediction of Anticoagulant Peptides from the Enzymatic Hydrolysates of Mytilus edulis Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Huang, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Wu, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, W. The inhibitory effect of tachyplesin I on thrombosis and its mechanisms. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 94, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harish, B.S.; Uppuluri, K.B. Potential Anticoagulant Activity of Trypsin Inhibitor Purified from an Isolated Marine Bacterium Oceanimonas Sp. BPMS22 and its Kinetics. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Zhou, G.-S.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.-P.; Liu, R.; Liu, P.; Li, N.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. A Novel Antithrombotic Protease from Marine Worm Sipunculus nudus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, H.; Krichen, F.; Capitani, F.; Ben, I.; Gargouri, J.; Maccari, F.; Mantovani, V.; Galeotti, F.; Volpi, N.; Bougatef, A.; et al. Purification, compositional analysis, and anticoagulant capacity of chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate from bone of corb ( Sciaena umbra ). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, H.; Krichen, F.; Capitani, F.; Amor, I.B.; Maccari, F.; Mantovani, V.; Galeotti, F.; Volpi, N.; Bougatef, A.; Sila, A. Chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate from corb (Sciaena umbra) skin: Purification, structural analysis and anticoagulant effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, H.; Ghlissi, Z.; Kallel, R.; Amor, I.B.; Boudawara, T.; Gargouri, J.; Sahnoun, Z.; Volpi, N.; Sila, A.; Bougatef, A. Chondroitin/dermatan sulfate purified from corb (Sciaena umbra) skin and bone: In vivo assessment of anticoagulant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.S.; Cavalcante, R.S.; Palhares, L.C.G.F.; Hughes, A.J.; Andrade, G.P.V.; Yates, E.A.; Nader, H.B.; Lima, M.A.; Chavante, S.F. A non-hemorrhagic hybrid heparin/heparan sulfate with anticoagulant potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.S.; Cavalcante, R.S.; Cavalheiro, R.P.; Palhares, L.C.G.F.; Nobre, L.T.D.B.; Andrade, G.P.V.; Nader, H.B.; Lima, M.A.; Chavante, S.F. Anti-IIa activity and antitumor properties of a hybrid heparin/heparan sulfate-like compound from Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seedevi, P.; Moovendhan, M.; Vairamani, S. Mucopolysaccharide from cuttlefish: Purification, chemical characterization and bioactive potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.P.; Mourao, P.A.S. Occurrence of a Unique Fucose branched Chondroitin Sulfate in the Body Wall of a Sea Cucumber. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 18176–18183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhou, L.; Lin, L.; Cai, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhao, L.; Gao, N.; Yin, R.; Zhao, J. Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of the Polysaccharides from Sea Cucumber Pattalus mollis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cai, Y.; Yin, R.; Lin, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J. Structural analysis and anticoagulant activities of two sulfated polysaccharides from the sea cucumber Holothuria coluber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Chen, D.; He, Z.; Zhou, L.; Cai, Y.; Mao, H.; Gao, N.; Zuo, Z.; Yin, R.; Zhao, J. NMR characterization and anticoagulant activity of the oligosaccharides from the fucosylated glycosaminoglycan isolated from Holothuria coluber. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Yuan, Q.; Gao, N.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, J. Precise Structure and Anticoagulant Activity of Fucosylated Glycosaminoglycan from Apostichopus japonicus: Analysis of Its Depolymerized Fragments. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Cai, C.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Xue, C.; Li, G.; Yu, G. A novel structural fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from Holothuria Mexicana and its effects on growth factors binding and anticoagulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, J.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Yang, J. Purification, structural characterization and anticoagulant properties of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate isolated from Holothuria mexicana. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, L.; Cai, Y.; Yang, W.; Lin, L.; Li, Z.; Gao, N.; Purcell, S.W.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J. Structural Elucidation and Biological Activity of a Highly Regular Fucosylated Glycosaminoglycan from the Edible Sea Cucumber Stichopus herrmanni. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9315–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mansour, M.; Balti, R.; Ollivier, V.; Ben Jannet, H.; Chaubet, F.; Maaroufi, R.M. Characterization and anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate with unusually procoagulant effect from sea cucumber. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Borodina, E.Y.; Stonik, V.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. A highly regular fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Massinium magnum: Structure and effects on coagulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hao, J.; Shan, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Cai, C.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Antithrombotic activities of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates and their depolymerized fragments from two sea cucumbers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Zhou, L.; Gao, N.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Shang, F.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J. Oligosaccharides from depolymerized fucosylated glycosaminoglycan: Structures and minimum size for intrinsic factor Xase complex inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14089–14099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Lv, Z. Separation, purification, structures and anticoagulant activities of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from Holothuria scabra. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kusaykin, M.I.; Stonik, V.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Structure and biological activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Cucumaria japonica. Glycobiology 2016, 26, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Gao, N.; Sun, H.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Lin, L.; Yin, R.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ji, X.; et al. Effects of Native Fucosylated Glycosaminoglycan, Its Depolymerized Derivatives on Intrinsic Factor Xase, Coagulation, Thrombosis, and Hemorrhagic Risk. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.A.G.; Ribeiro, K.A.; Valente, A.P.; Capillé, N.V.; Oliveira, S.-N.M.C.G.; Tovar, A.M.F.; Pereira, M.S.; Vilanova, E.; Mourão, P.A.S. A unique fucosylated chondroitin sulfate type II with strikingly homogeneous and neatly distributed α-fucose branches. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wang, D.; Zhu, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ye, X.; Linhardt, R.J.; Chen, S. Highly purified fucosylated chondroitin sulfate oligomers with selective intrinsic factor Xase complex inhibition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Ding, T.; Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Linhardt, R.J.; Chen, S. Molecular size is important for the safety and selective inhibition of intrinsic factor Xase for fucosylated chondroitin sulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 178, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo-espinosa, D.C.; Román, Y.; Colorado-ríos, J.; Santana-filho, A.P.D.; Lanzi, G.; Cipriani, T.R. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Structural analysis of a sulfated galactan from the tunic of the ascidian Microcosmus exasperatus and its inhibitory effect of the intrinsic coagulation pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, D.A.; Cordeiro, S.L.; Ferreira Silva, C.H.; Cunha Farias, E.H.; Sassaki, G.L.; Nader, H.B.; Oliveira Rocha, H.A. Pharmacological prospection and structural characterization of two purified sulfated and pyruvylated homogalactans from green algae Codium isthmocladum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes Marques, M.L.; Presa, F.B.; Viana, R.L.S.; Costa, M.S.S.P.; Amorim, M.O.R.; Bellan, D.L.; Alves, M.G.C.F.; Costa, L.S.; Trindade, E.S.; Rocha, H.A.O. Anti-Thrombin, Anti-Adhesive, Anti-Migratory, and Anti-Proliferative Activities of Sulfated Galactans from the Tropical Green Seaweed, Udotea flabellum. Mar. Drugs 2018, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudharsan, S.; Giji, S.; Seedevi, P.; Vairamani, S.; Shanmugam, A. Isolation, characterization and bioactive potential of sulfated galactans from Spyridia hypnoides (Bory) Papenfuss. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Gerbst, A.G.; Ushakova, N.A.; Tsvetkova, E.A.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Usov, A.I.; Nifantiev, N.E. Anticoagulant and antithrombotic activities of modified xylofucan sulfate from the brown alga Punctaria plantaginea. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, K.; Tai, W.; Shan, X.; Hao, J.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Structural characterization and anti-thrombotic properties of fucoidan from Nemacystus decipiens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, W.; Yin, R.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J. An anticoagulant fucan sulfate with hexasaccharide repeating units from the sea cucumber Holothuria albiventer. Carbohydr. Res. 2018, 464, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Mou, R.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, N.; Lin, L.; Li, Z. Structural analysis and anticoagulant activities of three highly regular fucan sulfates as novel intrinsic factor Xase inhibitors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Niu, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Cai, C.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Fucoidan from sea cucumber Holothuria polii: Structural elucidation and stimulation of hematopoietic activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, A.A.; Sucupira, I.D.; Guedes, A.L.; Queiroz, I.N.; Frattani, F.S.; Fonseca, R.J.; Pomin, V.H. Anticoagulant and Antithrombotic Properties of Three Structurally Correlated Sea Urchin Sulfated Glycans and Their Low-Molecular-Weight Derivatives. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Borodina, E.Y.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. A highly regular fucan sulfate from the sea cucumber Stichopus horrens. Carbohydr. Res. 2018, 456, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X. Anticoagulant and FGF / FGFR signal activating activities of the heparinoid propylene glycol alginate sodium sulfate and its oligosaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; He, X.; Qin, L.; He, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Mao, W. Anticoagulant and Antithrombotic Properties in Vitro and in Vivo of a Novel Sulfated Polysaccharide from Marine Green Alga Monostroma nitidum. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.C.R.; Duarte, M.E.R.; Noseda, M.D.; Ferreira, L.G.; Cassolato, J.E.F.; Sanchez, E.F.; Fuly, A.L. Potential Utilization of a Polysaccharide from the Marine Algae Gayralia oxysperma, as an Antivenom for Viperidae Snakebites. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, X.; He, X.; Wang, S.; Cao, S.; Xia, Z.; Xian, H.; Qin, L.; Mao, W. Structure and anticoagulant property of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the green seaweed Monostroma angicava. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 159, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, P.; Subhapradha, N.; Thinesh, T.; Selvin, J.; Selvan, K.M.; Shanmugam, V.; Shanmugam, A. Characterization of bioactive chitosan and sulfated chitosan from Doryteuthis singhalensis (Ortmann, 1891). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, R.; Manigandan, V.; Saravanan, R.; Rajesh, R.P.; Chandrika, B. Structural characterization and in vitro biomedical activities of sulfated chitosan from Sepia pharaonis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 84, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seedevi, P.; Moovendhan, M.; Vairamani, S. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Evaluation of antioxidant activities and chemical analysis of sulfated chitosan from Sepia prashadi. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | Dose (mg/kg) | Bleeding Time (min) a | Clotting Time (sec) a | Thrombus b Weight (mg) | Recovery c Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-HPABA | 100 | 11.04 ± 0.76 | 247 ± 26.1 | 1.90 ± 0.10 | 6 |
| S-HPABA | 100 | 9.50 ± 0.60 | 230 ± 24.4 | 2.14 ± 0.18 | 3 |
| Aspirin | 100 | 10.1 ± 0.35 | 244 ± 24.7 | 2.05 ± 0.17 | 4 |
| Total Polar Lipids (Salamon salar) | PAF Inhibition IC50 (μg) | Thrombin Inhibition IC50 (μg) |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional extraction | 45 ± 22 | 382 ± 39 |
| Food grade extraction | 86 ± 18 | 102 ± 29 |
| Activity (sec) | Concentration (mg/mL) | Native Control | Trypsin | Papain | Neutrase | Pepsin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aPTT | 50 | 41.7 ± 0.53 | 46.1 ± 1.04 | 41.6 ± 0.42 | 60.4 ± 1.87 | 183.8 ± 10.26 |
| TT | 50 | 9.9 ± 0.12 | 21.4 ± 0.29 | 14.7 ± 0.35 | 33.8 ± 2.56 | 31.8 ± 0.56 |
| Dose (μg/mL) | Hp/HS | Heparin | Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 40,000 | 40,000 | 15,000 |
| 50 | 35,000 | - | - |
| 25 | 30,000 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dwivedi, R.; Pomin, V.H. Marine Antithrombotics. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18100514
Dwivedi R, Pomin VH. Marine Antithrombotics. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(10):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18100514
Chicago/Turabian StyleDwivedi, Rohini, and Vitor H. Pomin. 2020. "Marine Antithrombotics" Marine Drugs 18, no. 10: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18100514
APA StyleDwivedi, R., & Pomin, V. H. (2020). Marine Antithrombotics. Marine Drugs, 18(10), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18100514





