Update on Monoterpenes from Red Macroalgae: Isolation, Analysis, and Bioactivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biosynthesis of Monoterpenes in Macroalgae
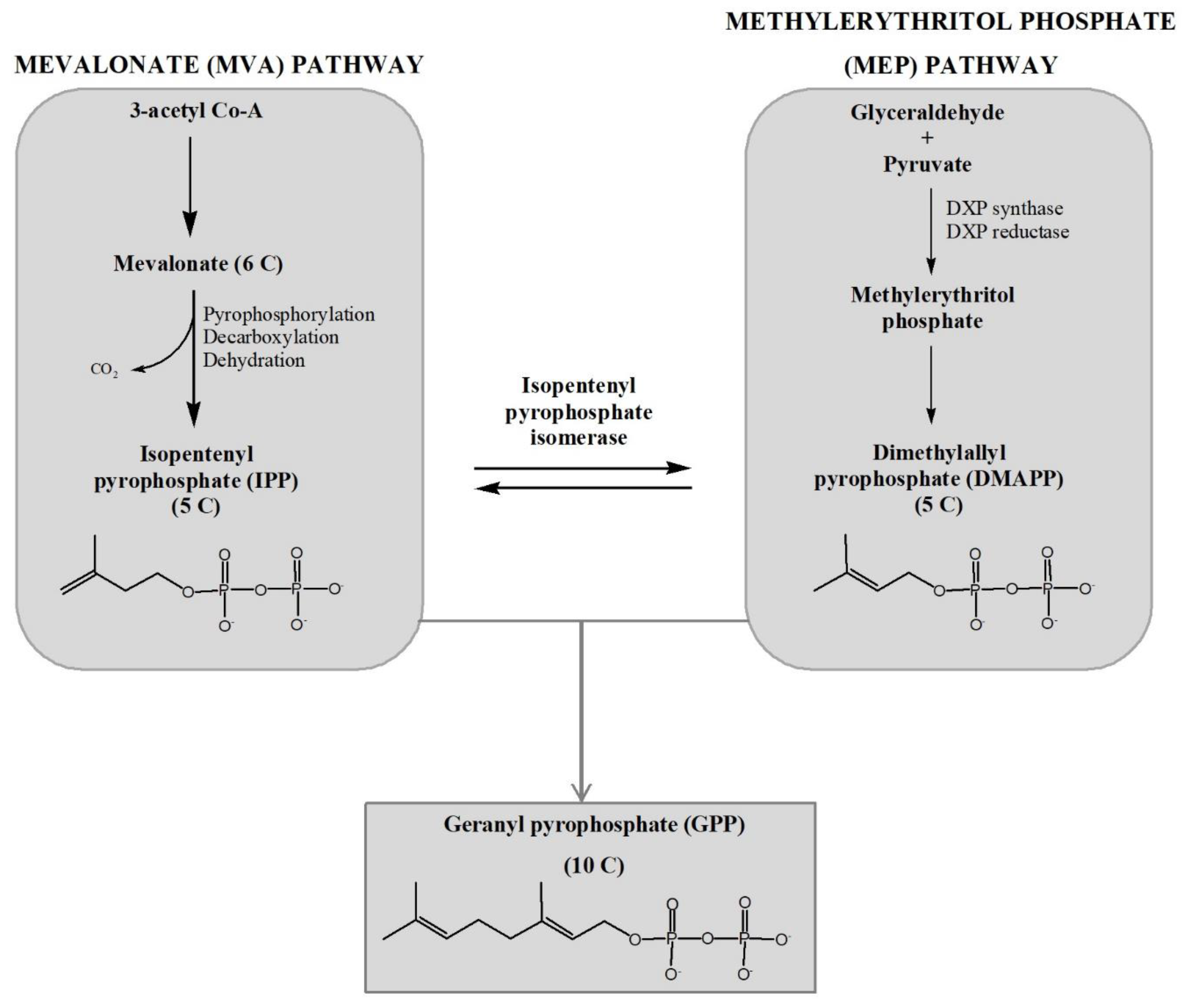
2.1. Mevalonate (MVA) Pathway and Methylerithritol Phosphate (MEP) Pathway
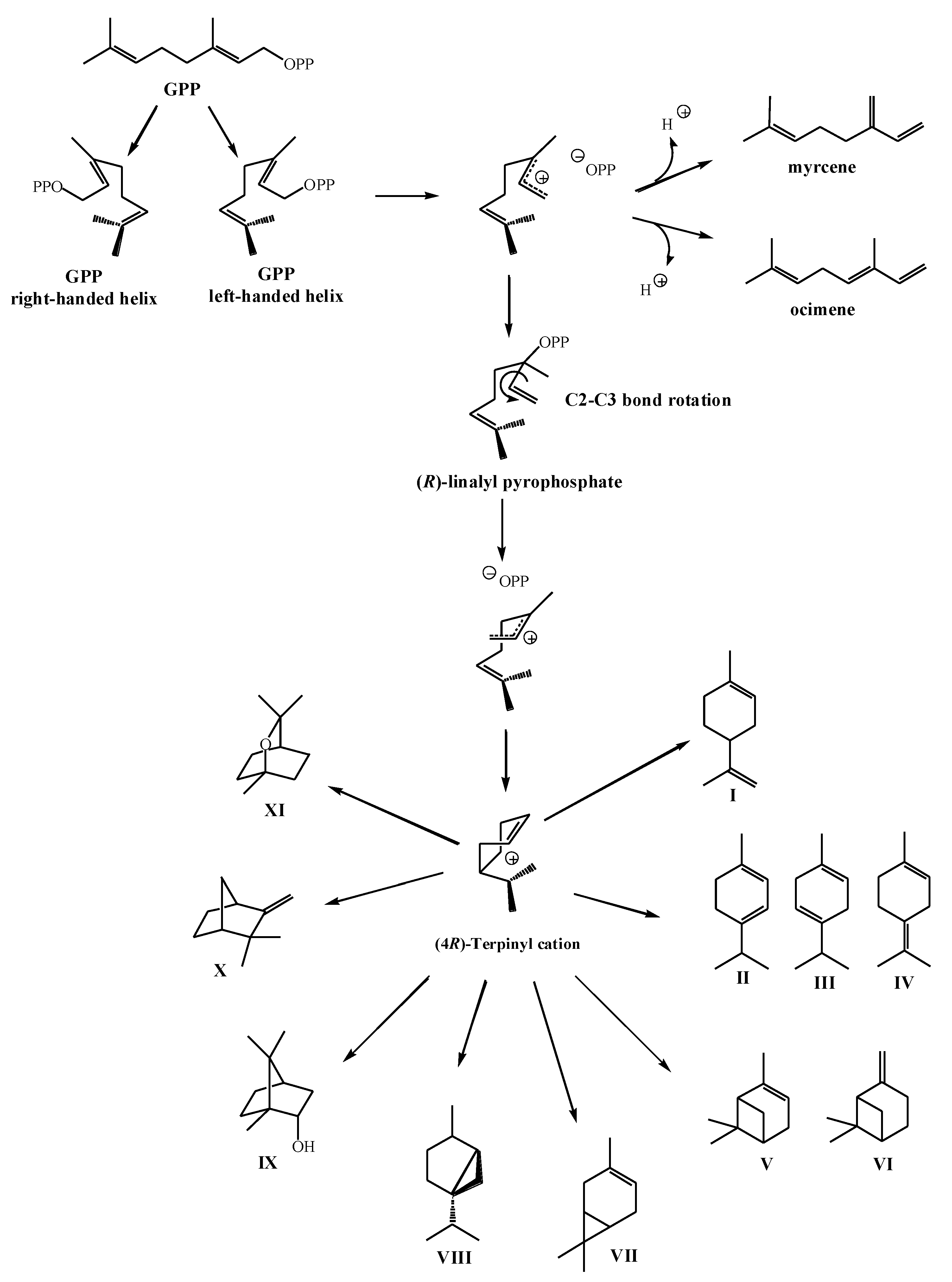
2.2. Biosynthesis of Cyclic Monoterpenes in Macroalgae
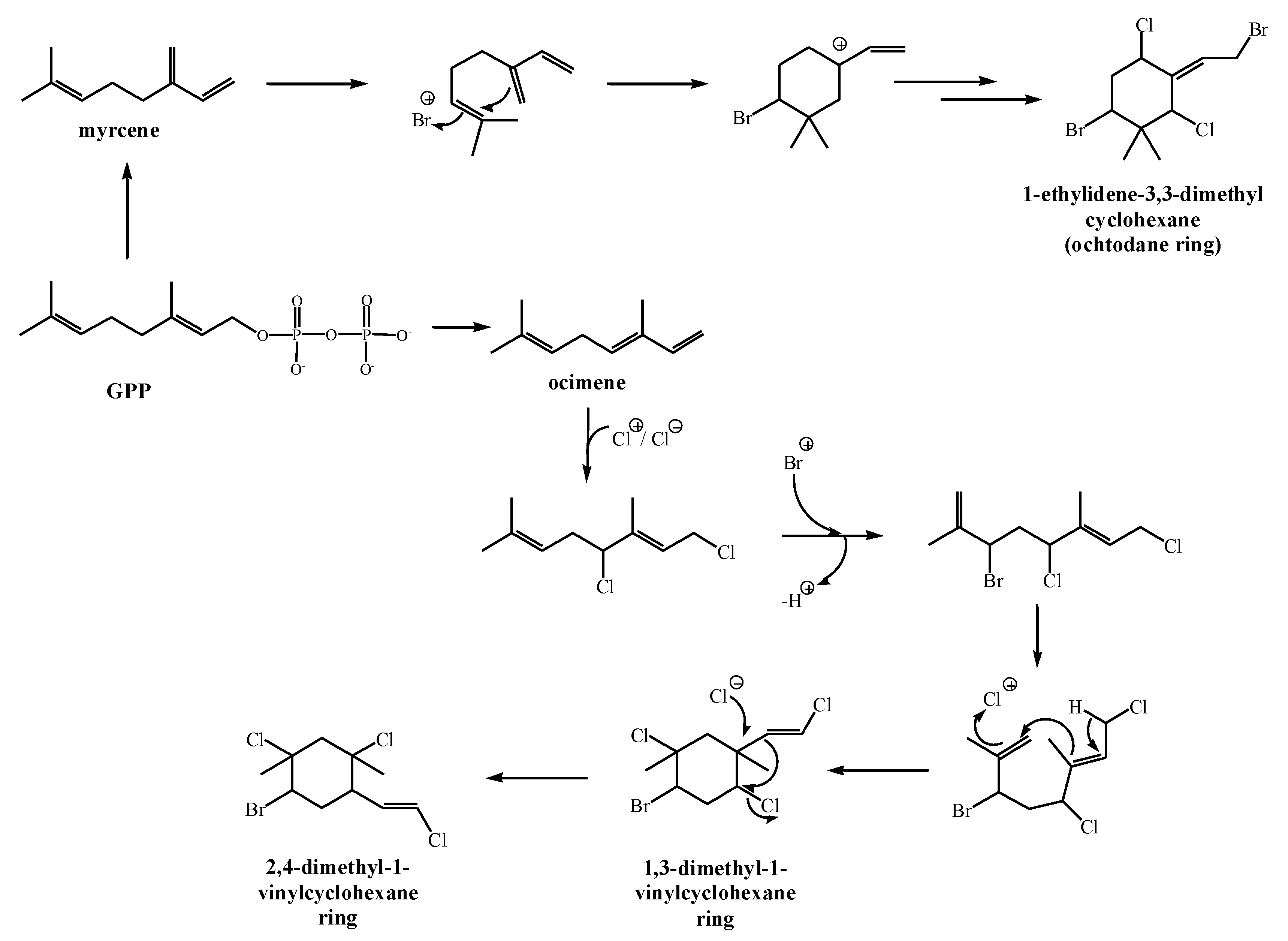
2.3. Biosynthesis of Halogenated Monoterpenes in Macroalgae
3. Isolation and Biodiversity of Monoterpenes from Macroalgae
3.1. Comparison of Different Extraction Methods for the Isolation of Monoterpenes
3.2. Monoterpenes Isolated from Different Macroalgae Species
4. Bioactivity of Monoterpenes in Macroalgae
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, J. Natural products in cancer chemotherapy: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, T.L.; Andrianasolo, E.; McPhail, K.; Flatt, P.; Gerwick, W.H. Marine natural products as anticancer drugs. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramawat, K.G.; Goyal, S. Chapter 10—Natural Products in Cancer Chemoprevention and Chemotherapy. In Herbal Drugs: Ethnomedicine to Modern Medicine; Ramawat, K.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 153–171. ISBN 978-3-540-79116-4. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, M.J.; Falque, E.; Dominguez, H. Antimicrobial Action of Compounds from Marine Seaweed. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S. Secondary metabolites from marine microorganisms and therapeutic efficacy: A mini review. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2016, 45, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai, V.K. Antimicrobial bioactive compounds from marine algae: A mini review. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2016, 45, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar]
- El Gamal, A.A. Biological importance of marine algae. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.S.; Kim, J.A.; Yoon, N.Y.; Kim, S.K. Induction of apoptosis by phloroglucinol derivative from Ecklonia cava in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.A.E.; Passalacqua, T.G.; Velásquez, A.M.A.; De Souza, R.A.; Colepicolo, P.; Graminha, M.A.S. New drugs with antiprotozoal activity from marine algae: A review. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2014, 24, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini-Costa, T.S.; Vieira, R.F.; Bizzo, H.R.; Silveira, D.; Gimenes, M.A. Chapter 8—Secondary metabolites. In Chromatography and Its Applications; Dhanarasu, S., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2012; pp. 131–164. ISBN 978-953-51-0357-8. [Google Scholar]
- El Shoubaky, G.A.; Salem, E.S. Terpenes and Sterols Composition of Marine Brown Algae Padina pavonica (Dictyotales) and Hormophysa triquetra (Fucales). Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2014, 6, 894–900. [Google Scholar]
- Katayama, T. The Volatile Constituents of Seaweed. III. The Terpenes of Volatile Constituents of Ulva pertusa. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fisheries 1955, 21, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, D.J.; Stallard, M.O. 7-Chloro-3,7-dimethyl-1,4,6-tri-bromo-1-octen-3-ol, A Novel Monoterpene Alcohol from Aplysia californica. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 14, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, D.J.; Stallard, M.O.; Fayos, J.; Clardy, J. (3R, 4S, 7S)-trans,trans-3,7-dimethyl-1,8,8-tribromo-3,4,7-trichloro-1,5-octadiene, a Novel Monoterpene from the Sea Hare, Aplysia californica. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 3413–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.J.; Hay, M.E.; Duffy, E.; Fenical, W.; Gustafson, K. Chemical defense in the seaweed Ochtodes secundiramea (Montagne) Howe (Rhodophyta): Effects of its monoterpenoid components upon diverse coral-reef herbivores. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1987, 114, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Linden, A. Plocamium hamatum and its monoterpenes: Chemical and biological investigations of the tropical marine red alga. Phytochemistry 1999, 52, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, M.G.; Mkwananzi, H.; Arendse, C.E.; Hendricks, D.T.; Bolton, J.J.; Beukes, D.R. Plocoralides A–C, polyhalogenated monoterpenes from the marine alga Plocamium corallorhiza. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, M.G.A.; Mkwananzi, H.B.; Antunes, E.M.; Whibley, C.E.; Hendricks, D.T.; Bolton, J.J.; Beukes, D.R. Halogenated Monoterpene Aldehydes from the South African Marine Alga Plocamium corallorhiza. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mayo, P. Mono- and Sesquiterpenoids. In The Chemistry of Natural Products; Bratley, K.W., Ed.; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1959; pp. 1–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ružička, L. History of the Isoprene Rule. Proc. Chem. Soc. 1959, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devon, T.K.; Scott, A.I. Handbook of Naturally Occurring Compounds; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; p. 576. [Google Scholar]
- Cavill, G.W.K. Insect Terpenoids and Nepetalactone. In Cyclopentanoid Terpene Derivatives; Taylor, W.I., Battersby, A.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 203–235. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, M.J.O. Monoterpene Biosynthesis. In Aspects of Terpenoid Chemistry and Biochemistry; Goodwin, T.W., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Poulter, C.D.; Rilling, H.C. The Prenyl Transfer Reaction. Enzymatic and Mechanistic Studies of the 1-4 Coupling Reaction in the Terpene Biosynthetic Pathway. Acc. Chem. Res. 1978, 11, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, W.D. Biosynthesis and Metabolism of Monoterpenes. In Terpenoids in Plants; Pridham, J.B., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1967; pp. 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, D. The Monoterpenes. In Chemistry of Terpenes and Terpenoids; Newman, A.A., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 11–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kladi, M.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Volatile halogenated metabolites from marine red algae. Phytochem. Rev. 2004, 3, 337–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrita, M.T.; Vale, C.; Rauter, A.P. Halogenated compounds from marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2301–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.P.; Zhou, X.F.; Yang, X.W.; Liu, Y. Chapter 5—Chemical composition of seaweeds. In Seaweed Sustainability. Food and Non-Food Applications; Tiwari, B.K., Troy, D.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 79–113. ISBN 978-0-12-418697-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.; Salman, M.; Kamal, S.; Rehman, S.; Razzaq, A.; Akash, S.H. Chapter 6—Algae- Based Biologically Active Compounds. In Algae Based Polymers, Blends and Composites; Zia, K.M., Zuber, M., Ali, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 155–271. ISBN 978-0-12-812360-7. [Google Scholar]
- Zatelli, G.A.; Philippus, A.C.; Falkenberg, M. An overview of odoriferous marine seaweeds of the Dictyopteris genus: Insights into their chemical diversity, biological potential and ecological roles. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2018, 28, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.J.; McConnell, O.J.; Fenical, W. Cyclic Monoterpenoid Feeding Deterrents from the Red Marine Alga Ochtodes crockeri. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 3401–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.; Walker, J.V. Marine Haloperoxidases. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahona, L.F.; Rorrer, G.L. Isolation of Halogenated Monoterpenes from Bioreactor—Cultured Microplantlets of the Macrophytic Red Algae Ochtodes secundiramea and Portieria hornemannii. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, S.; Hanke, F.J.; Manes, L.V.; Crews, P. Chemical and Biological Aspects of Marine Monoterpenes. Fortschr. Chem. Org. Naturst. 1983, 44, 189–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, M.; Schwender, J.; Polle, J.E.W. Isoprenoid biosynthesis in eukaryotic phototrophs: A spotlight on algae. Plant. Sci. 2012, 185, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidnia, S.; Gohari, A.R. Chapter 6—Trypanocidal Monoterpenes: Lead Compounds to Design Future Trypanocidal Drugs. In Studies in Natural Product Chemistry; Rahman, A.U., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 173–190. ISBN 978-0-444-59514-0. [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko, H.M. Enzymes of the mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 505, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, J.; Moreira, D. Origins and Early Evolution of the Mevalonate Pathway of Isoprenoid Biosynthesis in the Three Domains of Life. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polzin, J.; Rorrer, G.L. Selective production of the acyclic monoterpene β-myrcene by microplantlet suspension cultures of the macrophytic marine red alga Ochtodes secundiramea under nutrient perfusion cultivation with bromide-free medium. Algal Res. 2018, 36, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, M.J.; Rorrer, G.L.; Polzin, J.J.; Croteau, R. Biosynthesis of Marine Natural Products: Isolation and Characterization of a Myrcene Synthase from Cultured Tissues of the Marine Red Alga Ochtodes secundiramea. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 400, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, M.J. Monoterpene biosynthesis in marine algae. Phycologia 2003, 42, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, W.D.; Hager, L.P. Bromoperoxidases and halogenated lipids in marine algae. J. Phycol. 1980, 16, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenical, W. Natural products chemistry in the marine environment. Science 1982, 215, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Ichinose, J.; Kamoshida, A.; Kitahara, Y. Cyclization of polyenes. Biogenetic-type synthesis of snyderols. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Comm. 1976, 13, 518–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Hirose, Y. The derivation of a brominated algal component from myrcene. B. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1978, 51, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Sakuma, K.; Kaji, K. New ochtodane syntheses from myrcene. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliakal, S.; Cheney, D.P.; Rorrer, G.L. Halogenated monoterpene production in regenerated plantlet cultures of Ochtodes secundiramea (Rhodophyta, Cryptonemiales). J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polzin, J.J.; Rorrer, G.L.; Cheney, D.P. Metabolic flux analysis of halogenated monoterpene biosynthesis in microplantlets of the macrophytic red alga Ochtodes secundiramea. Biomol. Eng. 2003, 20, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenical, W. Halogenation in the Rhodophyta. A review. J. Phycol. 1975, 11, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Okuda, R. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Halogenated Monoterpenes from the Red Alga Plocamium cartilagineum. J. AOAC Int. 2001, 84, 1313–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Kempinski, C.; Chappell, J. Extraction and analysis of terpenes/terpenoids. Curr. Protoc. Plant. Biol. 2016, 1, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, K.C.; Sezik, E.; Kaleagasiougl, F.; Erdugan, H.; Coban, B.; Karakas, E. Vlatile Oils from Marine Macroalgae. In Natural Products; Ramawat, K.G., Merillom, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 2883–2912. [Google Scholar]
- Koziol, A.; Stryjewska, A.; Librowski, T.; Salat, K.; Gawel, M.; Moniczewski, A.; Lochynski, S. An Overview of the Pharmacological Properties and Potential Applications of Natural Monoterpenes. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerković, I.; Marijanović, Z.; Roje, M.; Kus, P.M.; Jokić, S.; Čož-Rakovac, R. Phytochemical study of the headspace volatile organic compounds of fresh algae and seagrass from the Adriatic Sea (single point collection). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmulla, R.; Harder, J. Microbial monoterpene transformations–A review. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Martin, A.; Negrete, R.; Rovirosa, J. Insecticide and acaricide activities of polyhalogenated monoterpenes from Chilean Plocamium cartilagineum. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2165–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darias, J.; Rovirosa, J.; San Martin, A.; Diaz, A.R.; Dorta, E.; Cueto, M. Furoplocamioids A-C, Novel Polyhalogenated Furanoid Monoterpenes from Plocamium cartilagineum. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Marrero, A.R.; Cueto, M.; Dorta, E.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martin, A.; Darias, J. New halogenated monoterpenes from the red alga Plocamium cartilagineum. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 8539–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.G.; Darias, V.; Estevez, E. Chemotherapeutic Activity of Polhalogenated Terpenes from Spanish Algae. J. Med. Plant. Res. 1982, 44, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Sticher, O. A new polyhalogented monoterpene from the red alga Plocamium cartilagineum. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 1615–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierle, D.B.; Sims, J.J. Polyhalogenated cyclic monoterpenes from the red alga Plocamium cartilagineum of Antartica. Tetrahedron 1979, 35, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilling, A.J.; von Salm, J.L.; Sanchez, A.R.; Kee, Y.; Amsler, C.D.; McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. Anverenes B–E, New Polyhalogenated Monoterpenes from the Antarctic Red Alga Plocamium cartilagineum. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, M.G.; de la Mare, J.A.; Edkins, A.L.; Zhang, A.; Stillman, M.J.; Bolton, J.J.; Antunes, E.M.; Beukes, D.R. Plaxenone A and B: Cytotoxic halogenated monoterpenes from the South African red seaweed Plocamium maxillosum. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 29, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracegirdle, J.; Sohail, Z.; Fairhurst, M.J.; Gerth, M.L.; Zuccarello, G.C.; Hasmi, M.A.; Keyzers, R.A. Costatone C – A new halogenated mnonoterpene from the New Zealand red alga Plocamium angustum. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierle, D.B.; Wing, R.M.; Sims, J.J. Marine Natural Products XI costatone and costatolide, new halogenated monoterpenes from the red seaweed, Plocamium costatum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1976, 49, 4455–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motti, C.A.; Thomas-Hall, P.; Hagiwara, K.A.; Simmons, C.J.; Willis, R.; Wright, A.D. Accelerated Identification of Halogenated Monoterpenes from Australian Specimens of the Red Algae Plocamium hamatum and Plocamium costatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.; Urban, S. Phytochemical Analysis of the Southern Australian Marine Alga, Plocamium mertensii using HPLC-NMR. Phytochem. Anal. 2008, 19, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, M.A.; Dias, D.A.; Urban, S. Application of HPLC-NMR in the Identification of Plocamenone and Isoplocamenone from the Marine Red Alga Plocamium angustum. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2089–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.D.; König, G.M.; Sticher, O. Five new monoterpenes from the marine red alga Portieria hornemannii. Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 5717–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunatilaka, A.A.L.; Paul, V.J.; Park, P.U.; Puglisi, M.P.; Gitler, A.D.; Eggleston, D.S.; Haltiwanger, R.C.; Kingston, D.G.I. Apakaochtodenes A and B: Two Tetrahalogenated Monoterpenes from the Red Marine Alga Portieria hornemannii. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1376–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, P.; Ng, P.; Kho-Wiseman, E.; Pace, C. Halogenated monoterpenes of the red alga Microcladia. Phytochemistry 1976, 15, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, P.; Kho, E.; Plocamene, B. New cyclic monoterpene skeleton from a red marine alga. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 2568–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, E.M.; Afolayan, A.F.; Chiwakata, M.T.; Fakee, J.; Knott, M.G.; Whibley, C.E.; Hendricks, D.T.; Bolton, J.J.; Beukes, D.R. Identification and in vitro anti-esophageal cancer activity of a series of halogenated monoterpenes isolated from the South African seaweeds Plocamium suhrii and Plocamium cornutum. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R.W.; Cardellina, J.H.; Kato, Y.; Brinen, L.S.; Clardy, J.; Snader, K.M.; Boyd, M.R. A Pentahalogenated Monoterpene from the Red Alga Portieria hornemannii Produces a Novel Cytotoxicity Profile against a Diverse Panel of Human Tumor Cell Lines. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 3007–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ines, C.; Argandona, V.H.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martin, A.; Diaz-Marrero, A.R.; Cueto, M.; Gonzalez-Coloma, A. Cytotoxic Activity of Halogenated Monoterpenes from Plocamium cartilagineum. Z. Naturforsch. 2004, 59, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Mare, J.A.; Lawson, J.C.; Chiwakata, M.T.; Beukes, D.R.; Edkins, A.L.; Blatch, G.L. Quinones and halogenated monoterpenes of algal origin show anti-proliferative effects against breast cancer cells in vitro. Invest. New Drugs 2012, 30, 2187–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R.W.; Cardellina, J.H.; Jurek, J.; Scheuer, P.J.; Alvarado-Lindner, B.; McGuire, M.; Gray, G.N.; Rios Steiner, J.; Clardy, J.; Menez, E.; et al. Isolation and Structure/Activity Features of Halomon-Related Antitumor Monoterpenes from the Red Alga Portieria hornemannii. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 4407–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, O.M.M.; Goeger, D.E.; Valeriote, F.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Cytotoxic halogenated monoterpenes from Plocamium cartilagineum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 31, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianasolo, E.H.; France, D.; Cornell-Kennon, S.; Gerwick, W.H. DNA Methyl Transferase Inhibiting Halogenated Monoterpenes from the Madagascar Red Marine Alga Portieria hornemannii. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, A.F.; Mann, M.G.A.; Lategan, C.A.; Smith, P.J.; Bolton, J.J.; Beukes, D.R. Antiplasmodial halogenated monoterpenes from the marine red alga Plocamium cornutum. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argandona, V.H.; Rovirosa, J.; San-Martin, A.; Riquelme, A.; Diaz-Marrero, A.R.; Cueto, M.; Daria, J.; Santana, O.; Guadano, A.; Gonzalez-Coloma, A. Antifeedant Effects of Marine Halogenated Monoterpenes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7029–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Umeda, K.; Kurita, Y.; Takayama, C.; Miyakado, M. Two Insecticidal Monoterpenes, Telfairine and Aplysiaterpenoid A, from the Red Alga Plocamium telfairiae: Structure Elucidation, Biological Activity, and Molecular Topographical Consideration by a Semiempirical Molecular Orbital Study. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 1990, 37, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovirosa, J.; Soler, A.; Blanc, V.; Leon, R.; San-Martin, A. Bioactive monoterpenes from Antartic Plocamium cartilagineum. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2013, 58, 2025–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, L.P.; Carvalho, L.R.; Young, M.C.M.; Cardoso-Lopes, E.M.; Centeno, D.C.; Zambotti-Villela, L.; Colepicolo, P.; Yokoya, N.S. Evaluation of acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of Brazilian red macroalgae organic extracts. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2015, 25, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
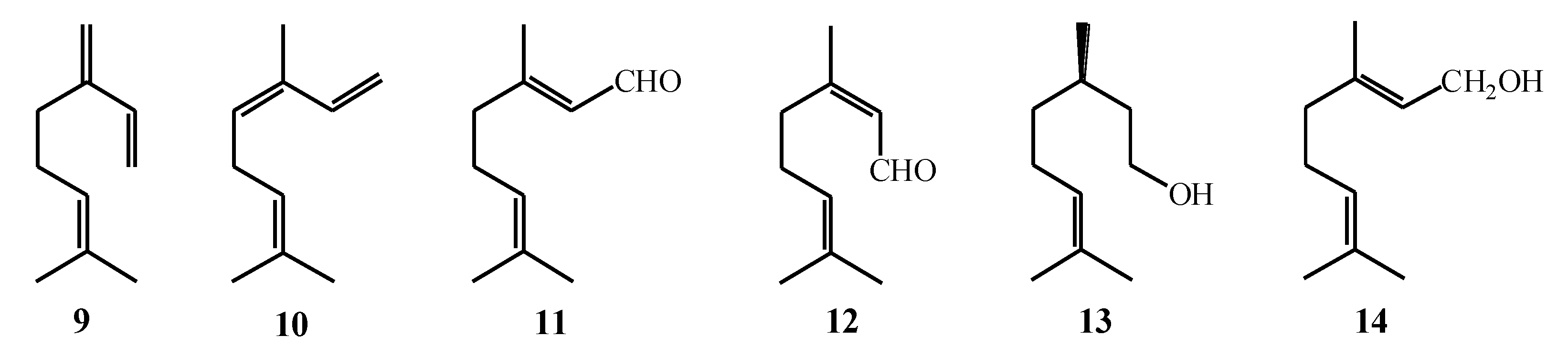
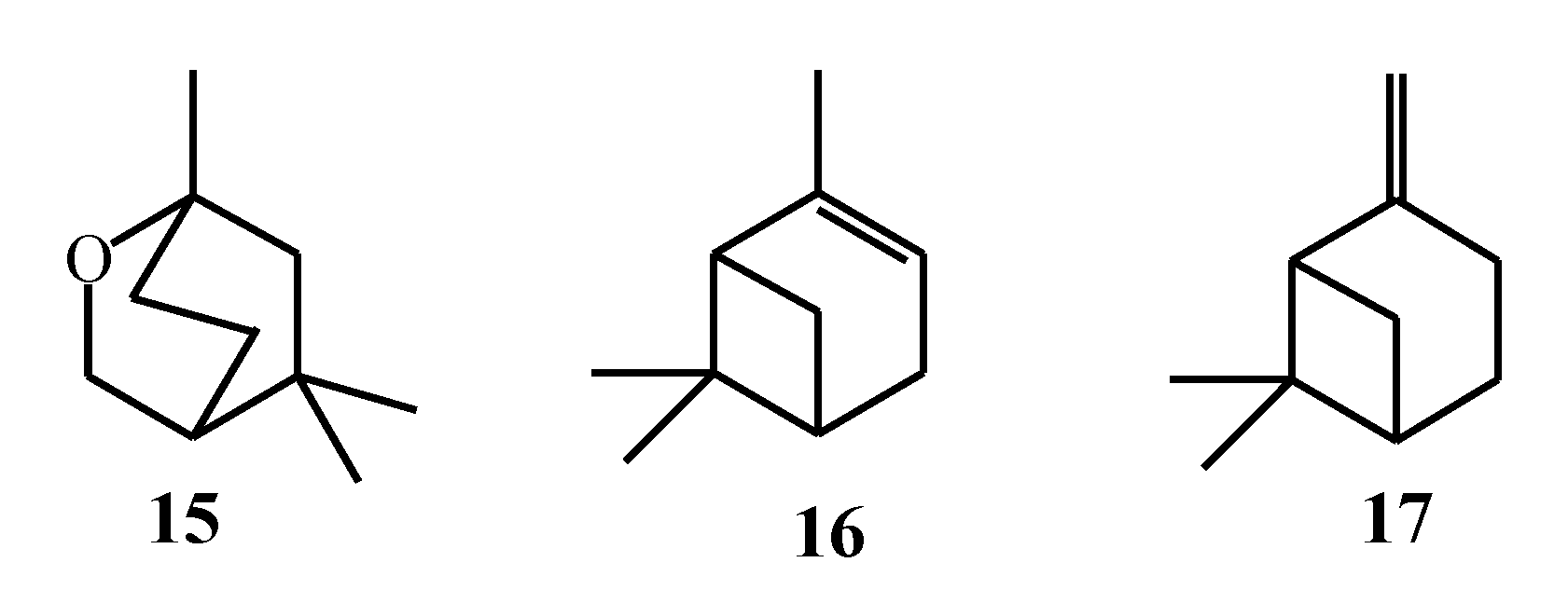
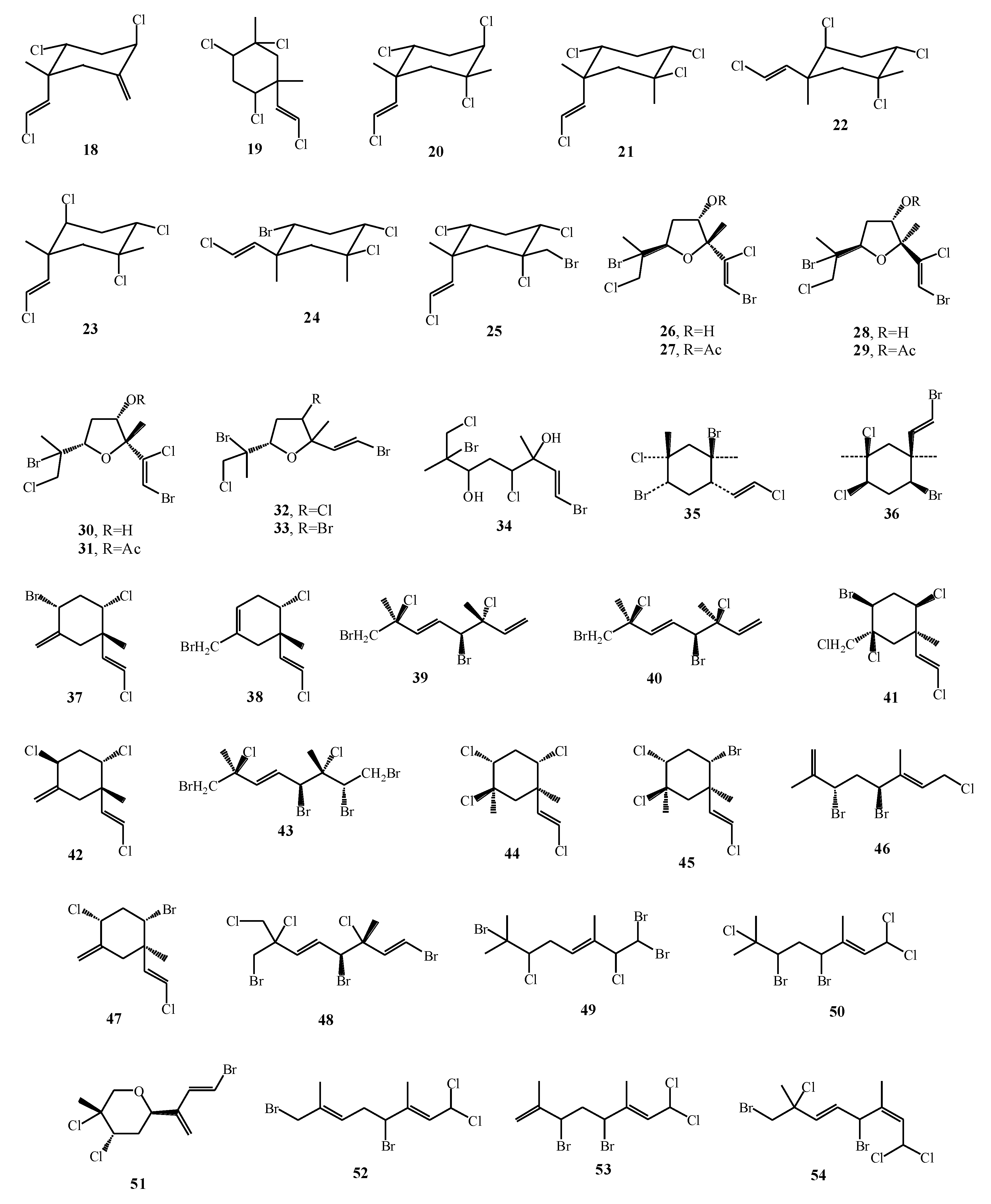
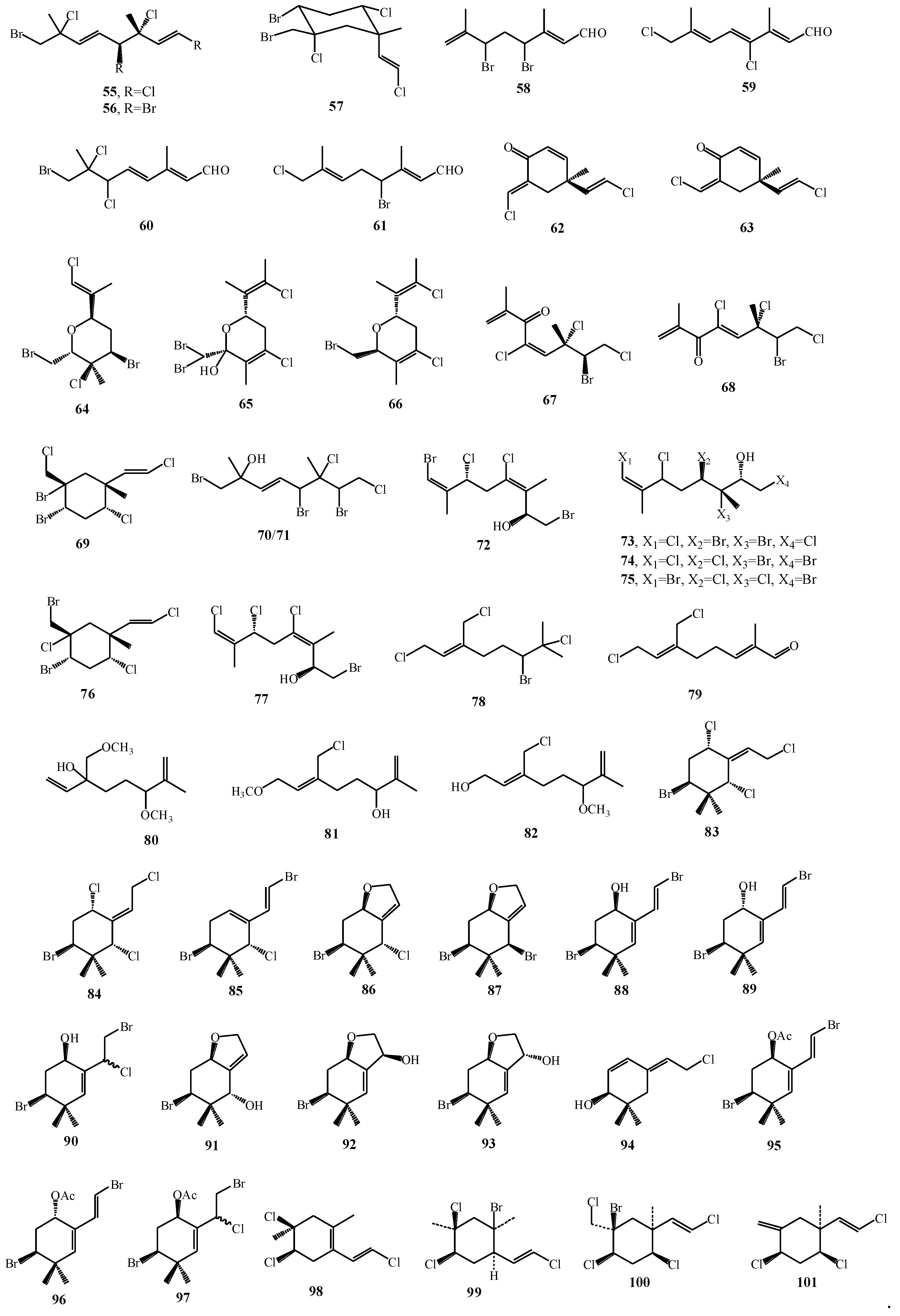
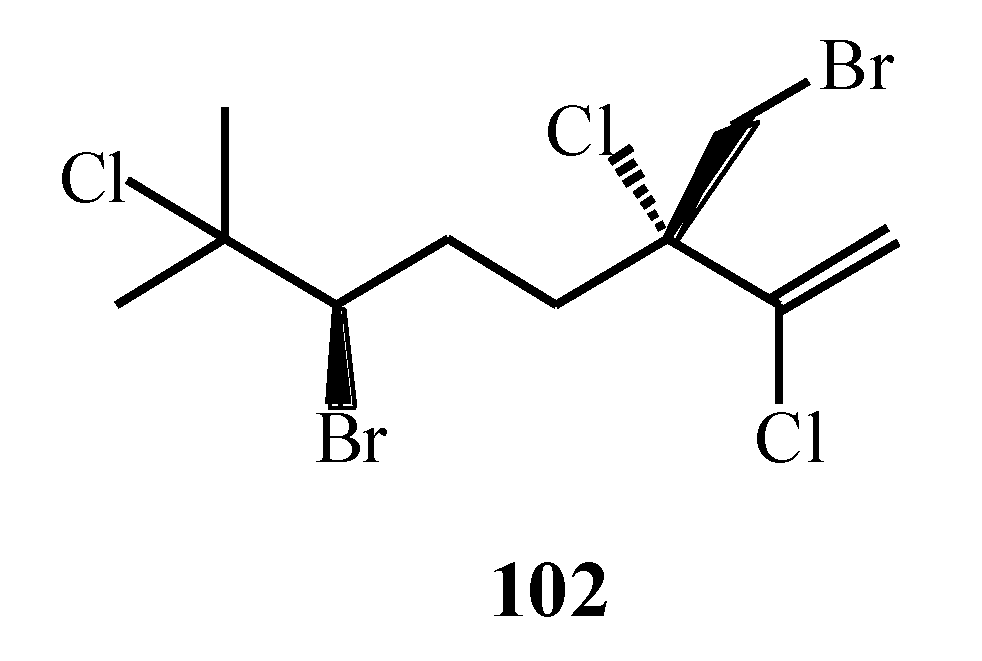
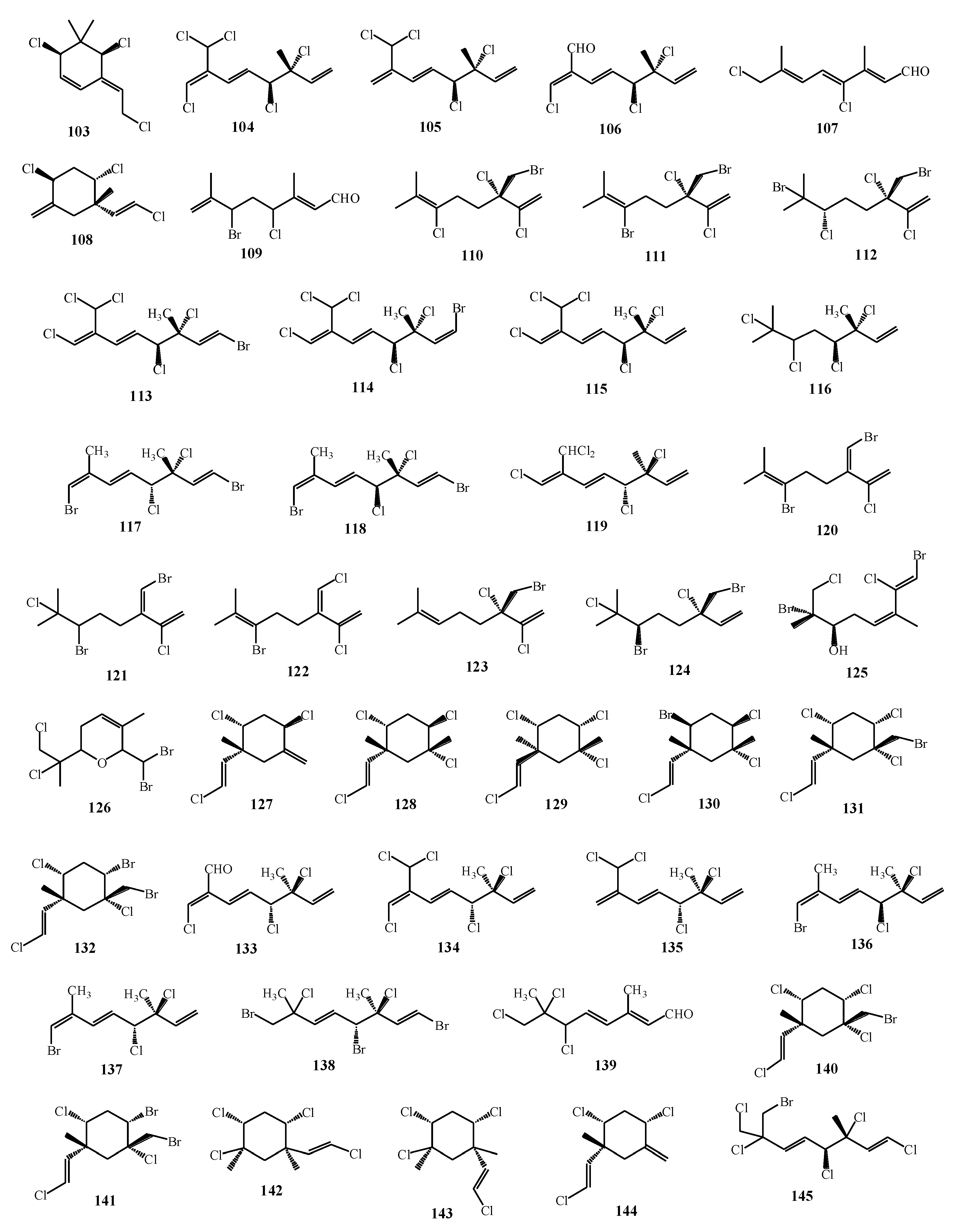
| Macroalgae Species | Isolated Monoterpenes | Extraction Solvent | Analytical Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus Plocamium | ||||
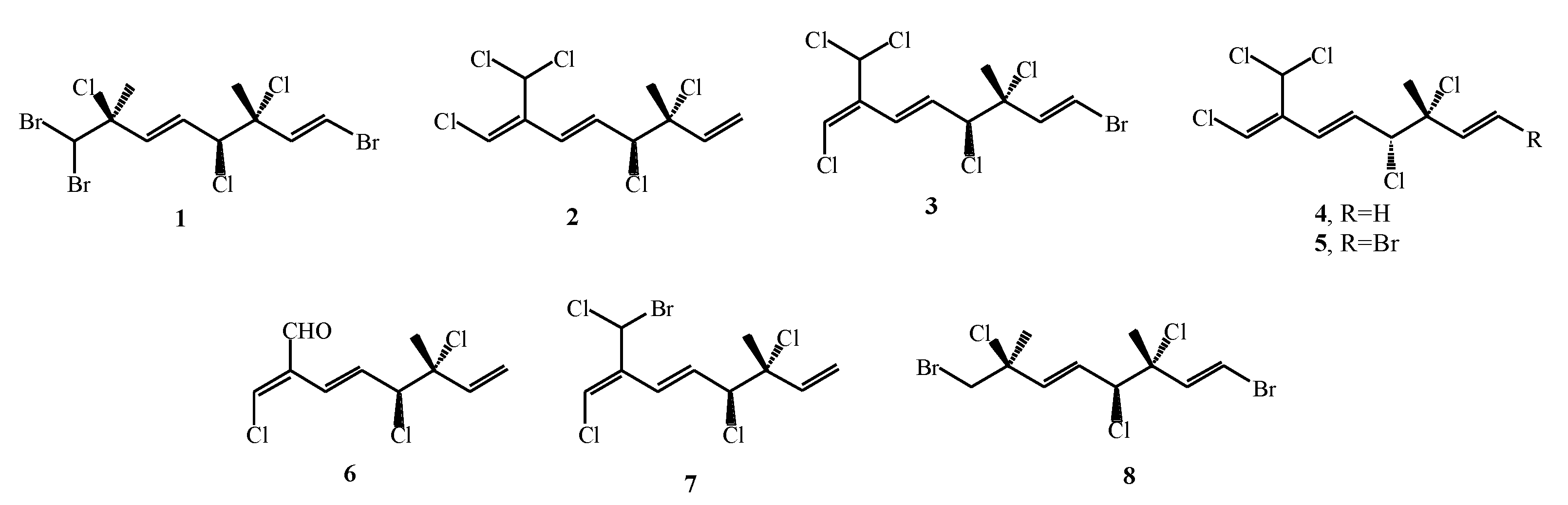
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 1–8 | Conventional extraction with MeOH and EtOAc; SC–CO2 extraction (pure CO2 and with 10 % MeOH as co-solvent) | GC–MS, NMR | [51] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 18–25 | CHCl3 and EtOH | NMR | [57] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 26–31 | EtOAc–CH2Cl2-hexane | HPLC, NMR | [58] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 32–34 | hexane/EtOAc/CH2Cl2/MeOH | HPLC, NMR | [59] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 35, 36 | Et2O | NMR | [60] |
| Plocamium hamatum | 37–47 | CH2Cl2 | NMR | [16] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 48–51 | CH2Cl2/H2O | GC–MS, HPLC, NMR | [63] |
| Plocamium corallorhiza | 52–57 | MeOH and CH2Cl2 | NMR | [17] |
| Plocamium corallorhiza | 58–61 | CH2Cl2–MeOH | NMR | [18] |
| Plocamium maxillosum | 62, 63 | CH2Cl2–MeOH | NMR | [64] |
| Plocamium angustum | 64 | MeOH | NMR, HPLC | [65] |
| Plocamium costatum | 65 | Hexane | NMR | [66] |
| Plocamium angustum | 67, 68 | CH2Cl2–MeOH | HPLC–NMR | [69] |
| Plocamium hamatum, Plocamium costatum | 66, 69–77 | CH2Cl2–MeOH | HPLC–UV–MS–SPE–NMR | [67] |
| Genus Portieria | ||||
| Portieria hornemannii | 78–82 | MeOH:CH2Cl2 | NMR | [70] |
| Portieria hornemannii | 83, 84 | CH2Cl2/MeOH | HPLC, NMR | [71] |
| Genera Ochtodes and Microcladia | ||||
| Ochtodes crockeri | 85–97 | CHCl3:MeOH | HPLC | [32] |
| Microcladia coulteri, M. borealis, M. californica | 98–101 | CHCI3, CH2Cl2 and EtOH, CHCl3 and EtOH | GC–MS, NMR | [72] |
| Macroalgae Species | Isolated Monoterpenes | References |
|---|---|---|
| Anticancer activity | ||
| Portieria hornemannii | 102, 103 | [75] |
| Plocamium corallorhiza, Plocamium cornutum | 54, 55, 58, 60, 104–109 | [77] |
| Portieria hornemannii | 110–112 | [78] |
| Polcamium suhrii, Plocamium cornutum | 5, 113–118 | [74] |
| Plocamium corallorhiza | 52–57 | [17] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 119 | [79] |
| Portieria hornemannii | 102, 120–124 | [80] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 30, 125, 126, 127–132 | [76] |
| Plocamium maxillosum | 62, 63 | [64] |
| Antiplasmodial (antimalarial) activity | ||
| Plocamium cornutum | 53, 58, 133–139 | [81] |
| Insecticidal activity | ||
| Plocamium cartilagineum, Pantineura plocamioides | 26, 27, 30, 31, 140, 141 | [82] |
| Plocamium telfairiae | 142, 143 | [83] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 18–25 | [16] |
| Plocamium cartilagineum | 144, 145 | [84] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cikoš, A.-M.; Jurin, M.; Čož-Rakovac, R.; Jokić, S.; Jerković, I. Update on Monoterpenes from Red Macroalgae: Isolation, Analysis, and Bioactivity. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090537
Cikoš A-M, Jurin M, Čož-Rakovac R, Jokić S, Jerković I. Update on Monoterpenes from Red Macroalgae: Isolation, Analysis, and Bioactivity. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(9):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090537
Chicago/Turabian StyleCikoš, Ana-Marija, Mladenka Jurin, Rozelindra Čož-Rakovac, Stela Jokić, and Igor Jerković. 2019. "Update on Monoterpenes from Red Macroalgae: Isolation, Analysis, and Bioactivity" Marine Drugs 17, no. 9: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090537
APA StyleCikoš, A.-M., Jurin, M., Čož-Rakovac, R., Jokić, S., & Jerković, I. (2019). Update on Monoterpenes from Red Macroalgae: Isolation, Analysis, and Bioactivity. Marine Drugs, 17(9), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090537








