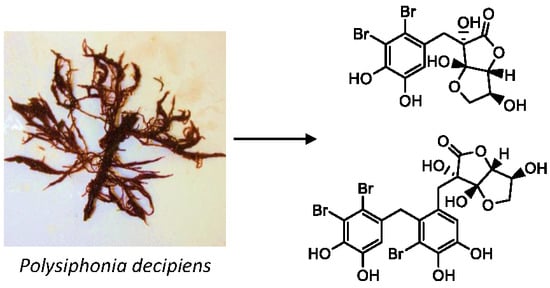
Bromophenolics from the Red Alga Polysiphonia decipiens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
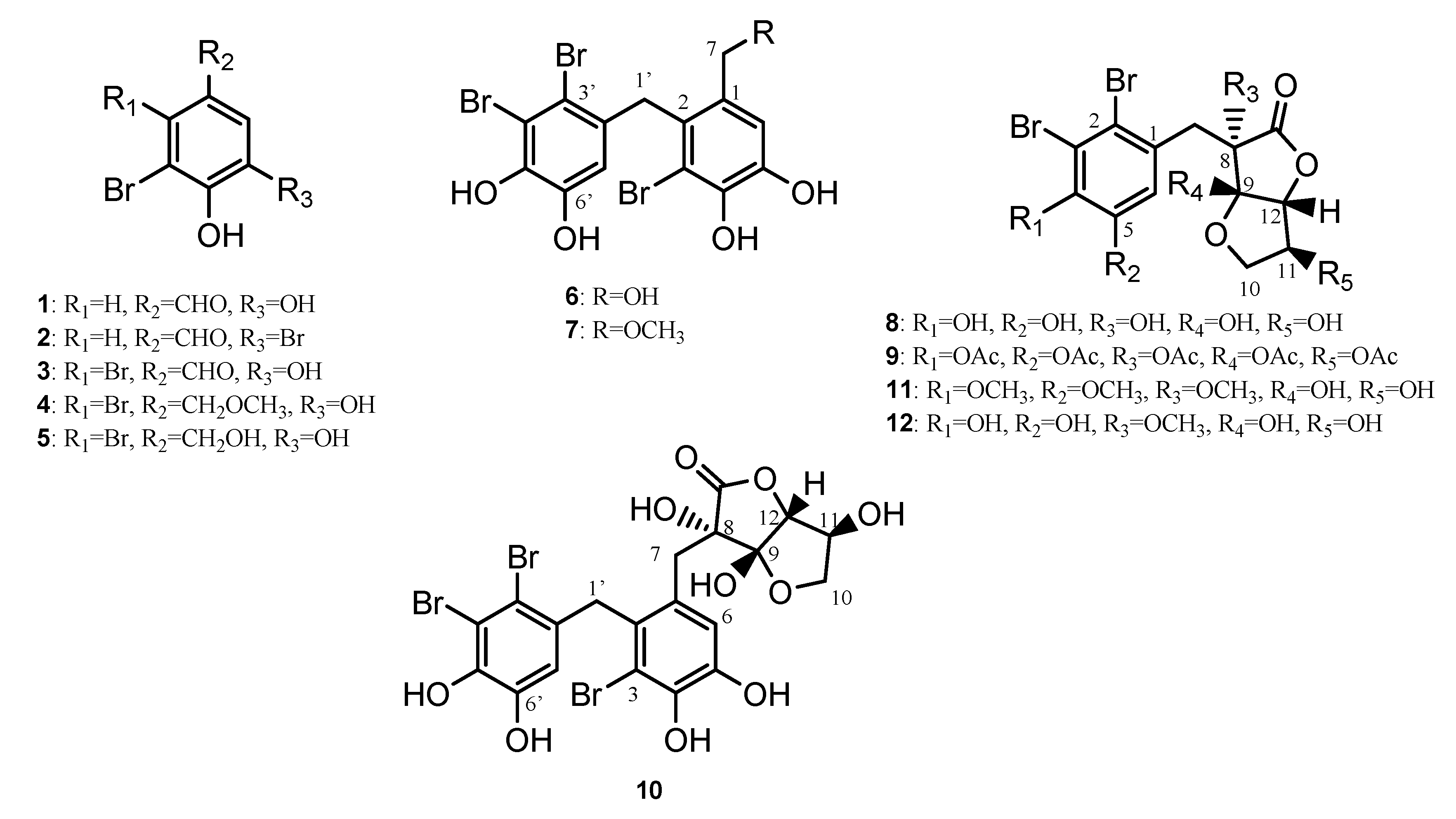
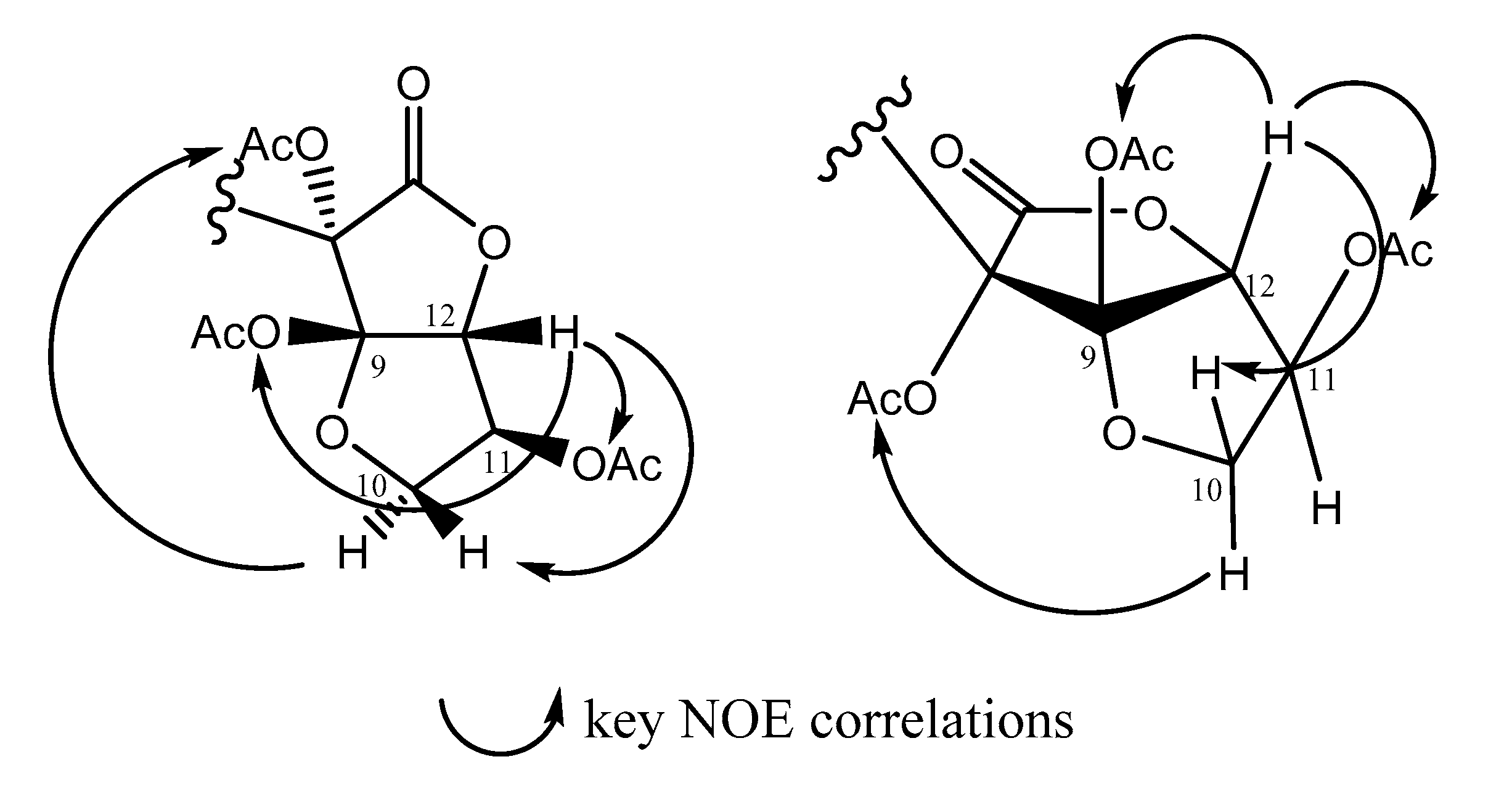
2.1. Structural Elucidation
2.2. Biological Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental
3.2. Biological Activity
3.3. Collection Details
3.4. Extraction and Isolation
3.5. Compound Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Algae Base. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org/search/species/detail/?species_id=12081 (accessed on 23 March 2019).
- Hodgkin, J.H.; Craigie, J.S.; McInnes, A.G. The occurence of 2,3-dibromobenzyl alcohol 4,5-disulfate, dipotassium salt, in Polysiphonia lanosa. Can. J. Chem. 1966, 44, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, K.W.; Sukopp, I.; Wiedenfeld, H. Antibiotics from Algae XXXVII. Rhodomelol and Methylrhodomelol from Polysiphonia lanosa. Planta Med. 1985, 51, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aknin, M.; Samb, A.; Mirailles, J.; Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A. Polysiphenol, a new brominated 9, 10-dihydrophenanthrene from the Senegalese red alga Polysiphonia ferulacea. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flodin, C.; Whitfield, F.B. Brominated anisoles and cresols in the red alga Polysiphonia sphaerocarpa. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.W.; Tan, C.H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.J.; Han, L.J.; Fan, X.; Zhu, D.Y. Urceolatol, a tetracyclic bromobenzaldehyde dimer from Polysiphonia urceolata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, X.M.; Ji, N.Y.; Wang, B.G. Natural bromophenols from the marine red alga Polysiphonia urceolata (Rhodomelaceae): Structural elucidation and DPPH radical-scavenging activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6627–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, X.M.; Ji, N.Y.; Gloer, J.B.; Wang, B.G. Urceolatin, a structurally unique bromophenol from Polysiphonia urceolata. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1429–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, X.M.; Ji, N.Y.; Wang, B.G. Bromophenols from the Marine Red Alga Polysiphonia urceolata with DPPH Radiacal Scavenging Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.W.; Qiao, Q.A.; Zhang, T.; Sun, L.X.; Wang, M.S. The structure elucidation of a new bromophenol metabolite from Polysiphonia urceolata by experimental and DFT theoretical methods. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 929, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.K.; Ye, B.R.; Kim, E.A.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, W.W.; Ahn, G.N.; Kang, N.; Jung, W.K.; Heo, S.J. Bis (3-bromo-4,5-dihydroxybenzyl) ether, a novel bromophenol from the marine red alga Polysiphonia morrowii that suppresses LPS-induced inflammatory response by inhibiting ROS-mediated ERK signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsui, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Kitamura, S.; Irie, T. 5, 6-dibromoprotocatechualdehyde and 2, 3-dibromo-4, 5-dihydroxybenzyl methyl ether. Tetrahedron 1967, 23, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, K.K.; Taniguchii, K.; Takashima, K.; Hayashi, I.; Suzuki, M. Feeding deterrent bromophenols from Odonthalia corymbifera. Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MarinLit Database. Available online: http://pubs.rsc.org/marinlit/ (accessed on 18 February 1991).
- Weinstein, B.; Rold, T.L.; Harrell, C.E.; Burns, M.W.; Waaland, J.R. Reexamination of the Bromophenols in the red alga Rhodomela larix. Phytochemistry 1975, 14, 2667–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, K.; Amiya, T. Two new bromophenols from the red alga, Rhodomela larix. Chem. Lett. 1977, 6, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, H.; Mitani, T.; Kawabata, J.; Takashi, K. Two new bromophenols from the red alga Odonthalia corymbifera. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 882–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xu, N.J.; Shi, J.G. Bromophenols from the red alga Rhodomela confervoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popplewell, W.L.; Northcote, P.T. Colensolide A: A new nitrogenous bromophenol from the New Zealand marine red alga Osmundaria colensoi. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 6814–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poss, A.J.; Belter, R.K. Vitamin C in organic synthesis: Reaction with p-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.D.; Wu, Y.N.; Xu, J.; He, J.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.R.; Xia, C.F.; Zhao, Q.S. Synthesis of l-Ascorbic Acid Lactone Derivatives. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2014, 4, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oh, K.B.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, S.C.; Shin, J.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, H.S. Antimicrobial activities of the bromophenols from the red alga Odonthalia corymbifera and some synthetic derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Fan, X.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Niu, R.; Tseng, C.K. Antibacterial bromophenols from the marine red alga Rhodomela confervoides. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, H.; Mitani, T.; Kawabata, J.; Takashi, K. Inhibitory potencies of bromophenols from the Rhodomelaceae algae against alpha-Glucosidase activity. Fisheries Sci. 1999, 65, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, D.; Kurihara, H.; Ono, M.; Kim, S.M.; Takahashi, K. Inhibition of algal bromophenols and their related phenols against glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Fitoterapia 2016, 108, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaskovich, M.A.; Zuegg, J.; Elliot, A.G.; Cooper, M.A. Helping Chemists Discover New Antibiotics. ACS Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Position | Carbon, Type a | Proton, Mult. (J in Hz) | gHMBCAD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 125.9, C b | ||
| 2 | 129.4, C b | ||
| 3 | 114.7, C c | ||
| 4 | 142.4, C d | ||
| 5 | 143.8, C d | ||
| 6 | 117.5, CH | 6.92, s | 2, 4, 5, 7 |
| 7a | 36.9, CH2 | 2.93, d (15.0) | 1, 2, 6, 8, 9, 13 W |
| 7b | 2.78, d (15.0) | 1, 2, 6, 8, 9 | |
| 8 | 79.1, C | ||
| 9 | 107.4, C | ||
| 10a | 74.9, CH2 | 4.19, dd (5.5, 9.5) | 9, 12, 11 W |
| 10b | 4.03, dd (3.0, 9.5) | 11 W | |
| 11 | 74.2, CH | 4.36, bs | 10 |
| 12 | 86.8, CH | 4.36, bs | 10, 13 |
| 13 | 175.6, C | ||
| 1a’ | 39.3, CH2 | 4.24, d (17.5) | 1 W, 2, 2′ W, 7′ W |
| 1b’ | 4.08, d (17.5) | 1, 2, 2′, 3′, 7′ | |
| 2′ | 131.3, C | ||
| 3′ | 114.7, C c | ||
| 4′ | 114.7, C c | ||
| 5′ | 142.5, C e | ||
| 6′ | 144.9, C e | ||
| 7′ | 113.8, CH | 5.97, s | 3′ W, 5′, 6′ |
| 4-OH | ND | ||
| 5-OH | ND | ||
| 8-OH | ND | ||
| 9-OH | ND | ||
| 11-OH | ND | ||
| 5′-OH | ND | ||
| 6′-OH | ND |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lever, J.; Curtis, G.; Brkljača, R.; Urban, S. Bromophenolics from the Red Alga Polysiphonia decipiens. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090497
Lever J, Curtis G, Brkljača R, Urban S. Bromophenolics from the Red Alga Polysiphonia decipiens. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(9):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090497
Chicago/Turabian StyleLever, James, Grace Curtis, Robert Brkljača, and Sylvia Urban. 2019. "Bromophenolics from the Red Alga Polysiphonia decipiens" Marine Drugs 17, no. 9: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090497
APA StyleLever, J., Curtis, G., Brkljača, R., & Urban, S. (2019). Bromophenolics from the Red Alga Polysiphonia decipiens. Marine Drugs, 17(9), 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090497